Python学习笔记(九)
Python学习笔记(九)—— Python计算生态
一、从数据处理到人工智能
1、流程
![]()


2、Python库的使用
2.1 Python库之数据分析
2.2.1 Numpy
![]()

例子:

2.2.2 Pandas
![]()

2.2.3 SciPy
![]()


2.2 Python库之数据可视化
2.2.1 Matplotlib
![]()

2.2.2 Seaborn
![]()

2.2.3 Mayavi
![]()

2.3 Python库之文本处理
2.3.1 PyPDF2
![]()

2.3.2 NLTK
![]()

2.3.3 Python-docx
![]()

2.4 Python库之机器学习
2.4.1 Scikit-learn
![]()


2.4.2 TensorFlow
![]()

2.4.3 MXNet
![]()

二、实例:霍兰德人格分析雷达图
1、问题分析



2、实例展示
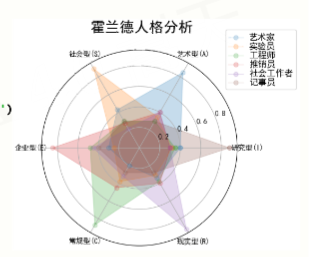
#HollandRadarDraw import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib matplotlib.rcParams['font.family']='SimHei' radar_labels = np.array(['研究型(I)','艺术型(A)','社会型(S)',\ '企业型(E)','常规型(C)','现实型(R)']) #雷达标签 nAttr = 6 data = np.array([[0.40, 0.32, 0.35, 0.30, 0.30, 0.88], [0.85, 0.35, 0.30, 0.40, 0.40, 0.30], [0.43, 0.89, 0.30, 0.28, 0.22, 0.30], [0.30, 0.25, 0.48, 0.85, 0.45, 0.40], [0.20, 0.38, 0.87, 0.45, 0.32, 0.28], [0.34, 0.31, 0.38, 0.40, 0.92, 0.28]]) #数据值 data_labels = ('艺术家', '实验员', '工程师', '推销员', '社会工作者','记事员') angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, nAttr, endpoint=False) data = np.concatenate((data, [data[0]])) angles = np.concatenate((angles, [angles[0]])) fig = plt.figure(facecolor="white") plt.subplot(111, polar=True) plt.plot(angles,data,'o-', linewidth=1, alpha=0.2) plt.fill(angles,data, alpha=0.25) plt.thetagrids(angles*180/np.pi, radar_labels,frac = 1.2) plt.figtext(0.52, 0.95, '霍兰德人格分析', ha='center', size=20) legend = plt.legend(data_labels, loc=(0.94, 0.80), labelspacing=0.1) plt.setp(legend.get_texts(), fontsize='large') plt.grid(True) plt.savefig('holland_radar.jpg') plt.show()
结果:
三、从Web解析到网络空间
1、Python库之网络爬虫
1.1 Requests
![]()

1.2 Scapy
![]()

1.3 pyspider
![]()

2、Python库之Web信息提取
2.1 Beautiful Soup
![]()

2.2 Re
![]()

2.3 Python-Goose
![]()

3、Python库之Web网站开发
3.1 Django
![]()

3.2 Pyramid
![]()

3.3 Flask
![]()

4、Python库之网络应用开发
4.1 WeRoBot
![]()

4.2 aip
![]()

4.3 MyQR
![]()

四、从人机交互到艺术设计
1、Python库之图形用户界面
1.1 PyQt5
![]()

1.2 wxPython
![]()

1.3 PyGObject
![]()

2、Python库之游戏开发
2.1 P有Game
![]()

2.2 Panda3D
![]()

2.3 cocos2d

3、Python库之虚拟现实
3.1 VR Zero

3.2 pyovr

3.3 Vizard

4、Python库之图形艺术
4.1 Quads

4.2 ascii_art

4.3 turtle
![]()
五、实例:玫瑰花绘制
1、问题分析


2、

代码
#RoseDraw.py import turtle as t # 定义一个曲线绘制函数 def DegreeCurve(n, r, d=1): for i in range(n): t.left(d) t.circle(r, abs(d)) # 初始位置设定 s = 0.2 # size t.setup(450*5*s, 750*5*s) t.pencolor("black") t.fillcolor("red") t.speed(100) t.penup() t.goto(0, 900*s) t.pendown() # 绘制花朵形状 t.begin_fill() t.circle(200*s,30) DegreeCurve(60, 50*s) t.circle(200*s,30) DegreeCurve(4, 100*s) t.circle(200*s,50) DegreeCurve(50, 50*s) t.circle(350*s,65) DegreeCurve(40, 70*s) t.circle(150*s,50) DegreeCurve(20, 50*s, -1) t.circle(400*s,60) DegreeCurve(18, 50*s) t.fd(250*s) t.right(150) t.circle(-500*s,12) t.left(140) t.circle(550*s,110) t.left(27) t.circle(650*s,100) t.left(130) t.circle(-300*s,20) t.right(123) t.circle(220*s,57) t.end_fill() # 绘制花枝形状 t.left(120) t.fd(280*s) t.left(115) t.circle(300*s,33) t.left(180) t.circle(-300*s,33) DegreeCurve(70, 225*s, -1) t.circle(350*s,104) t.left(90) t.circle(200*s,105) t.circle(-500*s,63) t.penup() t.goto(170*s,-30*s) t.pendown() t.left(160) DegreeCurve(20, 2500*s) DegreeCurve(220, 250*s, -1) # 绘制一个绿色叶子 t.fillcolor('green') t.penup() t.goto(670*s,-180*s) t.pendown() t.right(140) t.begin_fill() t.circle(300*s,120) t.left(60) t.circle(300*s,120) t.end_fill() t.penup() t.goto(180*s,-550*s) t.pendown() t.right(85) t.circle(600*s,40) # 绘制另一个绿色叶子 t.penup() t.goto(-150*s,-1000*s) t.pendown() t.begin_fill() t.rt(120) t.circle(300*s,115) t.left(75) t.circle(300*s,100) t.end_fill() t.penup() t.goto(430*s,-1070*s) t.pendown() t.right(30) t.circle(-600*s,35) t.done()


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号