航空货运blog
一.前言
本次题目经历了两次迭代,第一次要求完成一个能实现发件人,收件人,起点,终点,货物信息显示的订单,第二次在第一次的基础上增加了不同的客户类型会有不同的折扣,不同类型的物品会有不同的费率,还需要输出支付方式。两次共同的难点在没有类图,需要完全依靠自己去划分类,还要做到单一职责原则、里氏代换原则、开闭原则以及合成复用原则,这需要我们在做题之前先明确每个类的职责,确定类间关系。判断使用哪个重量作为计费重量时注意计算是一个单独的功能,不能写在商品类或订单类或航班类中,所以应该有单独的一个计算类。还要明确类间关系,尽量降低耦合度,方便下一次迭代程序的扩展。
二.设计与分析
第一次类图:
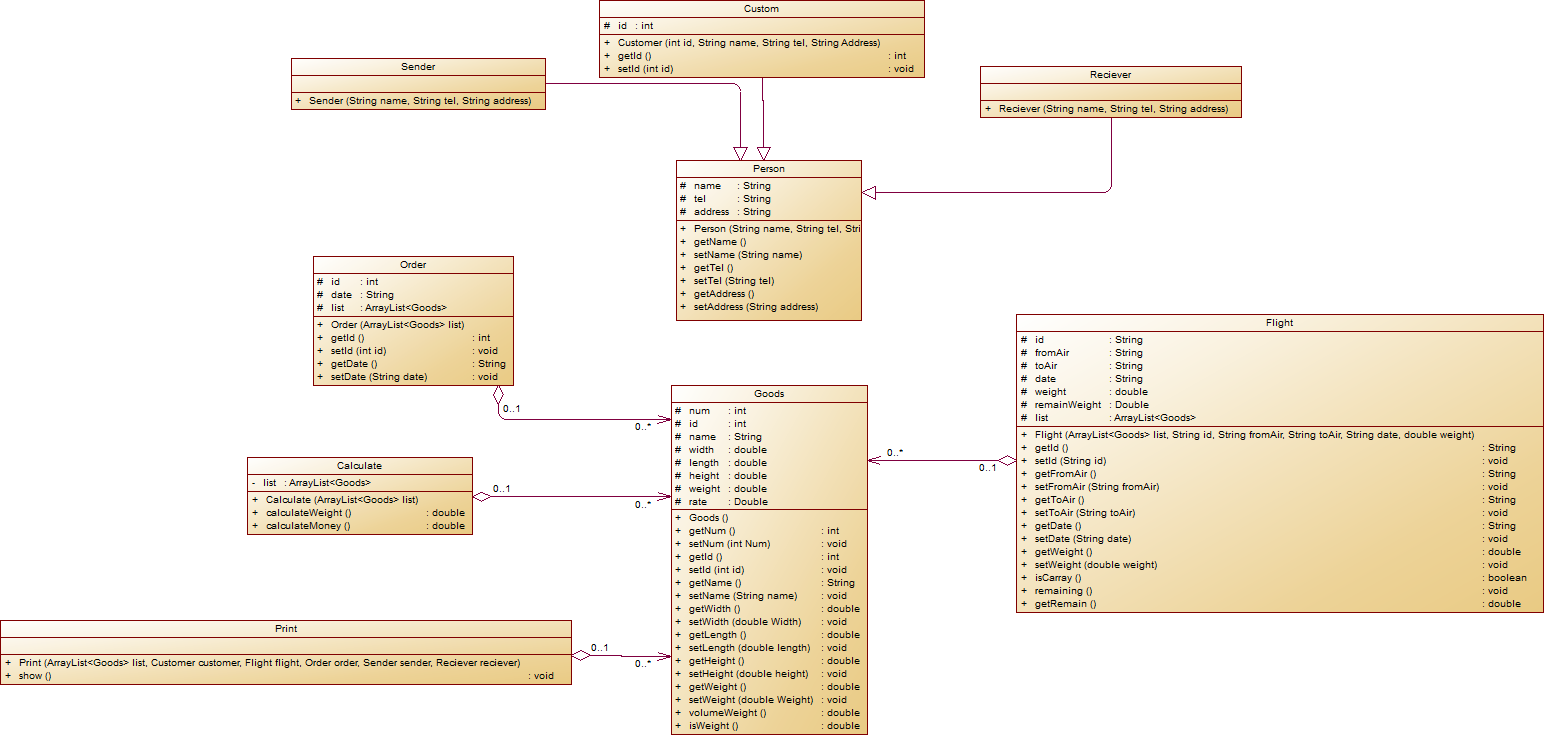
第一次的类图其实有一点问题,依赖关系没有画出来
第二次类图:
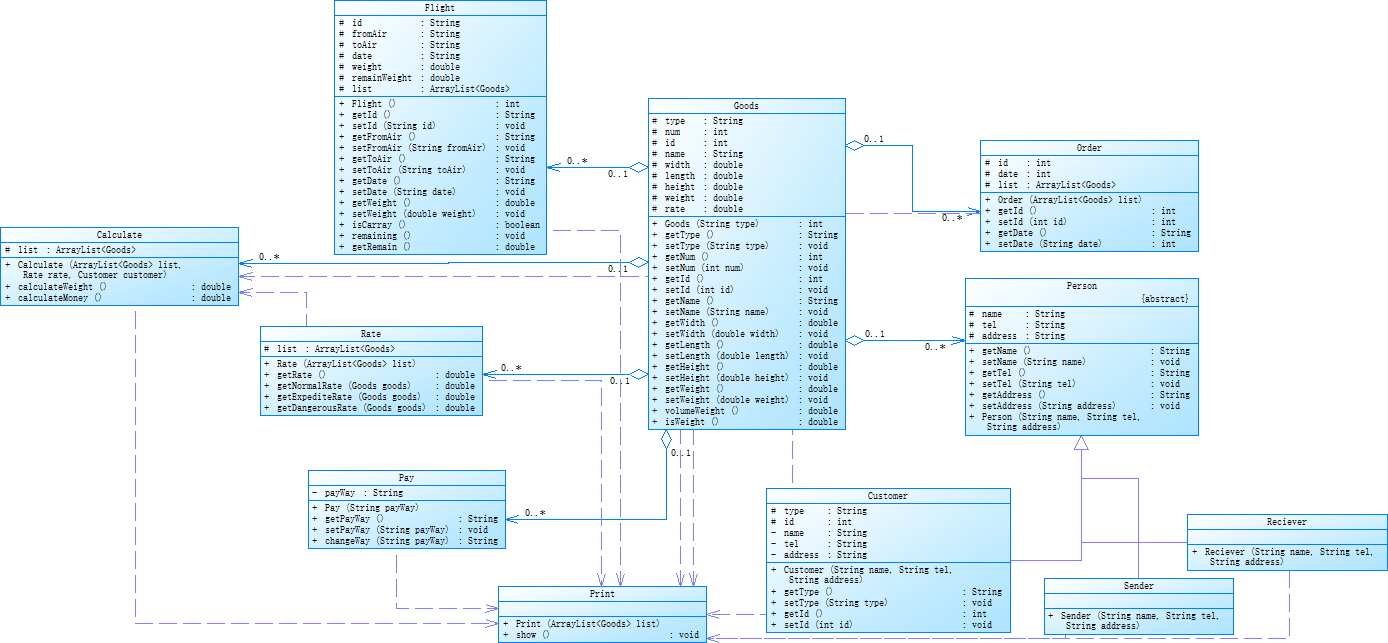
第一次代码分析:
Metrics Summary For Checkpoint 'Baseline'
Parameter Value
========= =====
Project Directory D:\blog代码分析
Project Name 航空1
Checkpoint Name Baseline
Created On 20 May 2025, 17:33:34
Files 1
Lines 339*
Statements 265
Percent Branch Statements 5.3
Method Call Statements 38
Percent Lines with Comments 0.0
Classes and Interfaces 10
Methods per Class 5.60
Average Statements per Method 2.98
Line Number of Most Complex Method {undefined}
Name of Most Complex Method Calculate.getRate()
Maximum Complexity 7
Line Number of Deepest Block {undefined}
Maximum Block Depth 4
Average Block Depth 1.74
Average Complexity 1.29
Most Complex Methods in 10 Class(es): Complexity, Statements, Max Depth, Calls
Calculate.getRate() 7, 11, 2, 0
Customer.setId() 1, 1, 2, 0
Flight.remaining() 2, 2, 3, 0
Goods.isWeight() 3, 4, 2, 3
Main.main() 2, 45, 3, 11
Order.setDate() 1, 1, 2, 0
Person.setAddress() 1, 1, 2, 0
Print.show() 4, 22, 4, 20
Reciever.Reciever() 1, 1, 2, 1
Sender.Sender() 1, 1, 2, 1
Block Depth Statements
0 12
1 86
2 129
3 36
4 2
5 0
6 0
7 0
8 0
9+ 0
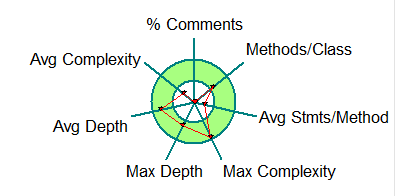
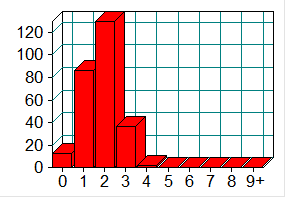
1.最大深度和平均深度都较大,说明if-else语句嵌套过多,结构不够简洁
2.每个类中方法数量较多,说明分类有问题,没有完全做到类的职责单一
3.高复杂度地方的代码量较大,这会导致代码难以理解,调试和修改
第二次代码分析:
Metrics Summary For Checkpoint 'Baseline'
Parameter Value
========= =====
Project Directory D:\blog代码分析\航空货运
Project Name 航空
Checkpoint Name Baseline
Created On 20 May 2025, 10:34:36
Files 1
Lines 438*
Statements 299
Percent Branch Statements 8.4
Method Call Statements 29
Percent Lines with Comments 0.0
Classes and Interfaces 11
Methods per Class 6.18
Average Statements per Method 2.78
Line Number of Most Complex Method {undefined}
Name of Most Complex Method Rate.getExpediteRate()
Maximum Complexity 7
Line Number of Deepest Block {undefined}
Maximum Block Depth 3
Average Block Depth 1.66
Average Complexity 1.45
Most Complex Methods in 11 Class(es): Complexity, Statements, Max Depth, Calls
Calculate.calculateMoney() 4, 7, 3, 4
Customer.setId() 1, 1, 2, 0
Flight.remaining() 2, 2, 3, 0
Goods.isWeight() 3, 4, 2, 3
Main.main() 2, 50, 3, 11
Order.setDate() 1, 1, 2, 0
Pay.setPayWay() 1, 1, 2, 0
Person.setAddress() 1, 1, 2, 0
Rate.getExpediteRate() 7, 11, 2, 0
Reciever.Reciever() 1, 1, 2, 1
Sender.Sender() 1, 1, 2, 1
Block Depth Statements
0 13
1 97
2 168
3 21
4 0
5 0
6 0
7 0
8 0
9+ 0
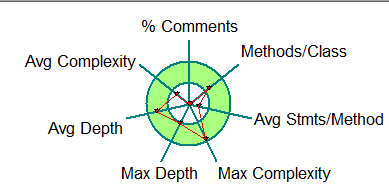
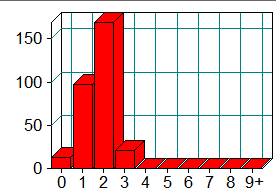
1.最大深度和平均深度都较大,说明存在多层循环嵌套语句,结构不够简洁,难以维护,不容易看出代码的问题
2.每个类中方法数量较多,说明分类有问题,没有完全做到类的职责单一
3.高复杂度地方的代码量较大,这会导致代码难以理解
4.代码耦合度高,复用性差,扩展困难
三.踩坑心得
1.此次作业中变量多,要做到见名只意,否则到后面自己都会看不懂。数据类型要正确,不然运行时会报错,无法识别
int customerId=scanner.nextInt();
String customerName=scanner.next();
String customerTel=scanner.next();
String customerAddress=scanner.next();
int goodsNum=scanner.nextInt();
int goodsId=scanner.nextInt();
String goodsName=scanner.next();
double goodsWidth=scanner.nextDouble();
double goodsLength=scanner.nextDouble();
double goodsHeight=scanner.nextDouble();
double goodsWeight=scanner.nextDouble();
String flightId=scanner.next();
String flightFromAir=scanner.next();
String flightToAir=scanner.next();
String flightDate=scanner.next();
int flightWeight=scanner.nextInt();
int orderId=scanner.nextInt();
String orderDate=scanner.next();
String senderAddress=scanner.next();
String senderName=scanner.next();
String senderTel=scanner.next();
String recieverAddress=scanner.next();
String recieverName=scanner.next();
String recieverTel=scanner.next();
2.有多件货物的情况,要根据实际输入确定,使用循环,每次创建一个货物对象来储存对应属性,并在创建下一个对象前将这些属性加入数组中存储,方便以后使用
int goodsNum=scanner.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<goodsNum;i++){
Goods goods=new Goods();
int goodsId=scanner.nextInt();
goods.setId(goodsId);
String goodsName=scanner.next();
goods.setName(goodsName);
double goodsWidth=scanner.nextDouble();
goods.setWidth(goodsWidth);
double goodsLength=scanner.nextDouble();
goods.setLength(goodsLength);
double goodsHeight=scanner.nextDouble();
goods.setHeight(goodsHeight);
double goodsWeight=scanner.nextDouble();
goods.setWeight(goodsWeight);
list.add(goods);
}
3.使用抽象类可以减少代码重复率,将相同部分只写一次
abstract class Person{
protected String name;
protected String tel;
protected String address;
public Person(String name,String tel,String address){
this.name=name;
this.tel=tel;
this.address=address;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public String getTel(){
return tel;
}
public void setTel(String tel){
this.tel=tel;
}
public String getAddress(){
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address){
this.address=address;
}
}
class Customer extends Person{
protected int id;
public Customer(int id,String name,String tel,String address){
super(name,tel,address);
this.id=id;
}
public int getId(){
return id;
}
public void setId(int id){
this.id=id;
}
}
class Sender extends Person{
public Sender(String name,String tel,String address){
super(name,tel,address);
}
}
class Reciever extends Person{
public Reciever(String name,String tel,String address){
super(name,tel,address);
}
}
4.使用foreach循环,既可以引入要使用的Goods类,又可以更简单的使用ArrayList数组,降低遍历时使用索引而导致数组越界的情况
public void remaining(){
for(Goods goods:list){
remainWeight=remainWeight-goods.isWeight();
}
}
5.数据较多,传参时数据类型,变量名称,参数传递顺序都要注意
6.创建实例对象时,要把通过输入获得的值作为参数传入,不然这些变量相当于没有做初始化,都是没有值的,会导致非零返回
Customer customer=new Customer(customerType,customerId,customerName,customerTel,customerAddress);
Goods goods=new Goods(goodsType);
Flight flight=new Flight(list,flightId,flightFromAir,flightToAir,flightDate,flightWeight);
Order order=new Order(list);
Rate rate=new Rate(list);
Calculate calculate=new Calculate(list,rate,customer);
Sender sender=new Sender(senderName,senderTel,senderAddress);
Reciever reciever=new Reciever(recieverName,recieverTel,recieverAddress);
Pay pay=new Pay(payWay);
Print print=new Print(list,customer,flight,order,sender,reciever,calculate,pay,rate);
7.布尔型返回值可以直接给出一个比较式,如果正确这个式子会自动返回true,如果不正确会自动返回false,不用额外添加if-else语句,简化代码,降低复杂度
public boolean isCarray(){
double totalWeight=0;
for(Goods goods:list){
totalWeight=totalWeight+goods.isWeight();
}
return totalWeight<=getRemain();
}
8.支付方式的输入和输出格式不同,需要加一个转换的步骤
public String changeWay(String payWay){
if(payWay.equals("ALiPay"))
payWay="支付宝";
else if(payWay.equals("Wechat"))
payWay="微信";
else if(payWay.equals("Cash"))
payWay="现金";
return payWay;
}
四.改进建议
1.用枚举代替字符串检查,可以简化代码
2.计算费率可以用接口或抽象类,方便在后续如果有增加或者更改时不用改动原代码
3.可以把货物类的相同属性做一个抽象方法,增加代码复用率
4.类的划分可以再做调整,使程序的扩展性更好
五.总结
本次迭代作业难点在类的设计,在开始写代码前应该分好类,保证每个类职责单一,设计好类间关系。遇到这种变量多的题,在最开始定义变量的时候一定要做到见名知意,防止写到后面时自己忘了每个变量对应的名称。在写之前要明确哪个类与其他类连接最紧密,应该用哪种关系去实现,能够使耦合度尽可能的降低,这次这个题的Goods类就与很多类都有关系,需要用到里面的某个参数,但这个类又是每一个货物加进来就要创建一个对象,储存到数组中后就删除这个对象,所以每次调用时不能直接用产生的实例对象去调用,通过foreach循环将Goods类型的数组传进去,就可以使用里面的变量的数值。继承时的子类构造方法中要有传递的参数,super的括号中也要有参数名。学会了foreach循环的用法,类名 实例名:要遍历的数组名,这种循环方法可以不用自己添加索引变量去遍历,不会出现越界的情况。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号