CF734E Anton and Tree
\(\mathtt{CF734E}\)
\(\mathcal{Description}\)
给一棵\(n(n\leq200000)\)个节点的树,每个点为黑色或白色,一次操作可以使一个相同颜色的连通块变成另一种颜色,求使整棵树变成一种颜色的最少操作数。
\(\mathcal{Solution}\)
这棵树中每个点为黑点或白点,然后最后也只要求出最小操作数,对于一个联通块,我们选择其中任何一个节点进行染色的效果是一样的(都会把这个联通块变成同一个颜色),于是我们自然而然的可以想到缩点。然后样例中的树就可以是
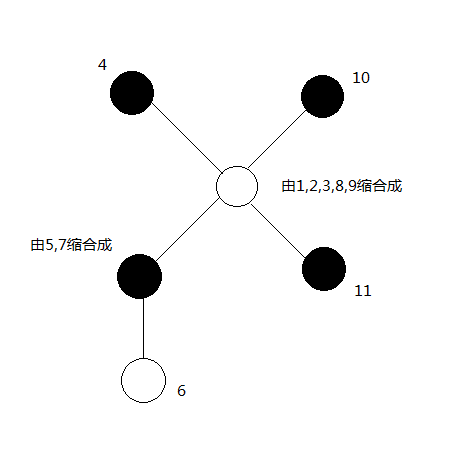
(贺个图\(qwq\))
可以看出我们把这个树从原先的树变成了一棵异层颜色相异(也就是黑白相间)的树,如果当前是一条链,我们要是最后操作数是最小的,我们一定会选择从中间开始染色,所以对于一棵树,我们只需要选择他的直径进行染色,最后的答案就是\((直径+1)/ 2\)。
\(\mathcal{Code}\)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n, color[N];
vector<int> a[N];
inline int read() {
int x = 0, k = 1; char c = getchar();
for (; c < 48 || c > 57; c = getchar()) k ^= (c == '-');
for (; c >= 48 && c <= 57; c = getchar()) x = x * 10 + (c ^ 48);
return k ? x : -x;
}
pair<int, int> dfs(int x, int fa, int depth) {
int sz = a[x].size();
pair<int, int> tmp = make_pair(depth, x);
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
int y = a[x][i];
if (y == fa)
continue;
if(color[y] != color[x])
tmp = std::max(tmp, dfs(y, x, depth + 1));
else
tmp = std::max(tmp, dfs(y, x, depth));
}
return tmp;
}
int main() {
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
color[i] = read();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x = read(), y = read();
a[x].push_back(y), a[y].push_back(x);
}
pair<int, int> tmp = dfs(1, -1, 0);
tmp = dfs(tmp.second, -1, 0);
printf("%d\n", tmp.first + 1 >> 1);
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号