JDK 25 的新特性
JDK 25 的新特性
前言
JDK 发布历程(JDK 8 ~ JDK 24)如下:
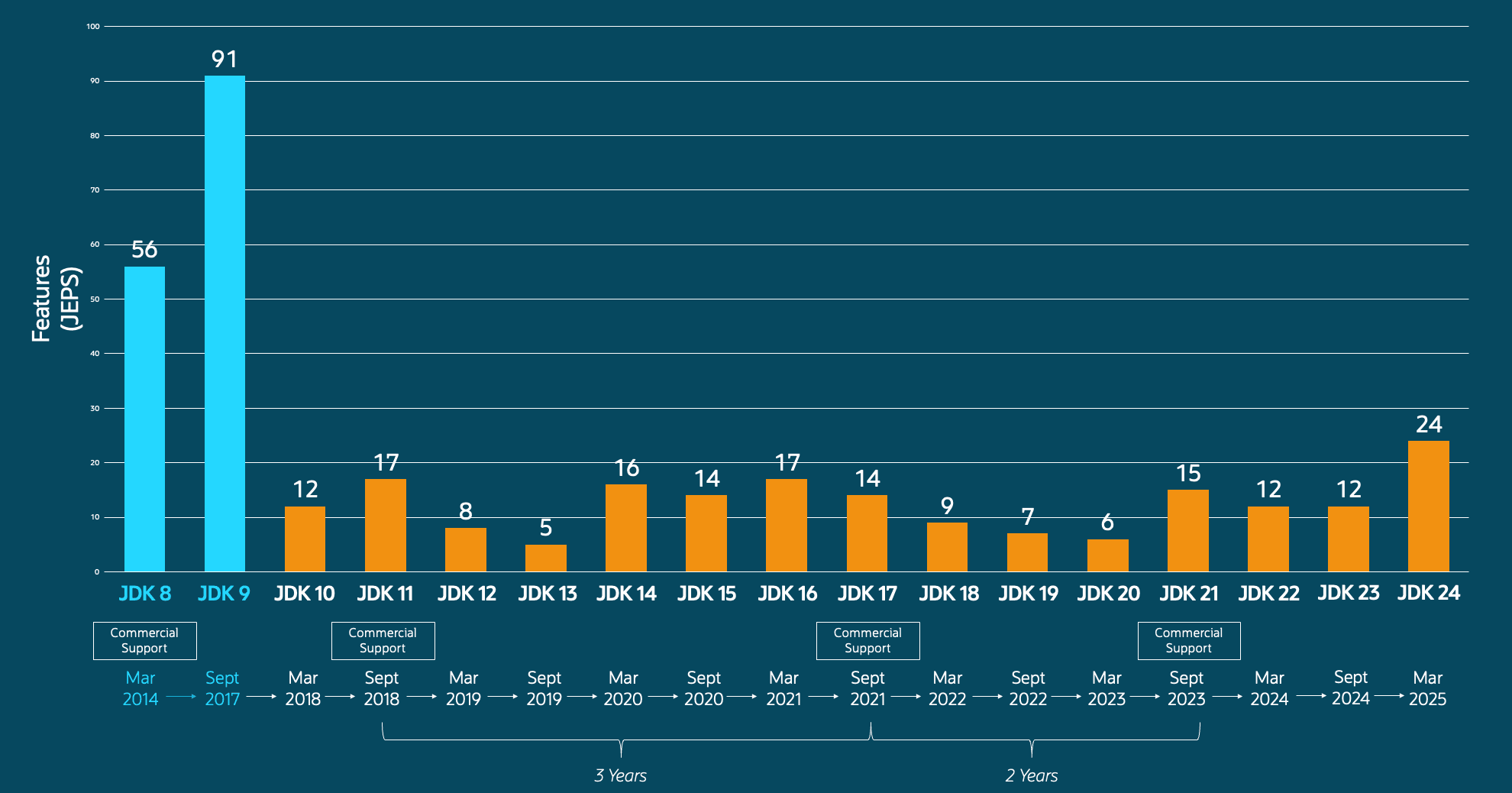
JDK 25 作为最新的长期支持(LTS)版本,带来了一系列旨在提升开发效率、增强语言表达能力和优化性能的新特性。
JDK 25 提供了十六个增强功能,这些增强功能足以保证他们自己的 JDK 增强提案 (JEP),包括四个预览功能、一个实验功能和一个孵化器功能。这些功能涵盖了 Java 语言的创新,包括对安全库的改进、性能和运行时增强以及更新的监视功能。
The Arrival of Java 25
JDK 25 Release Notes
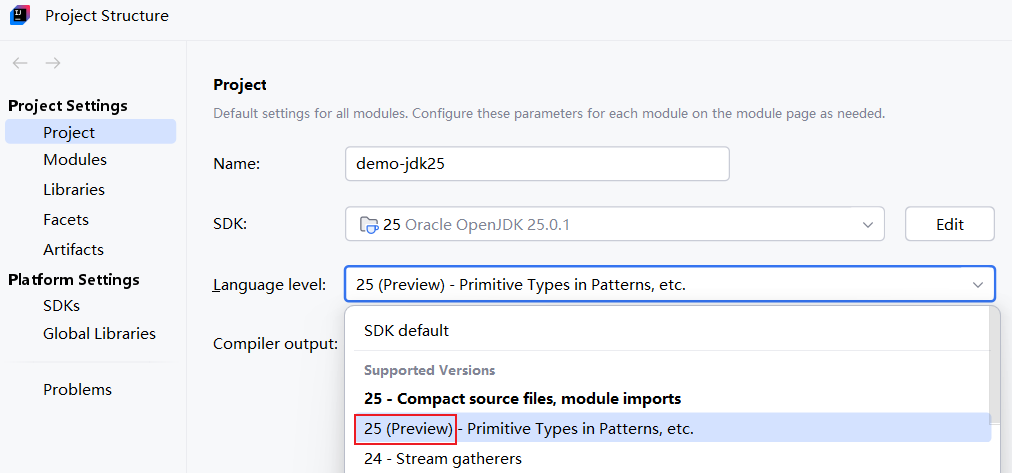
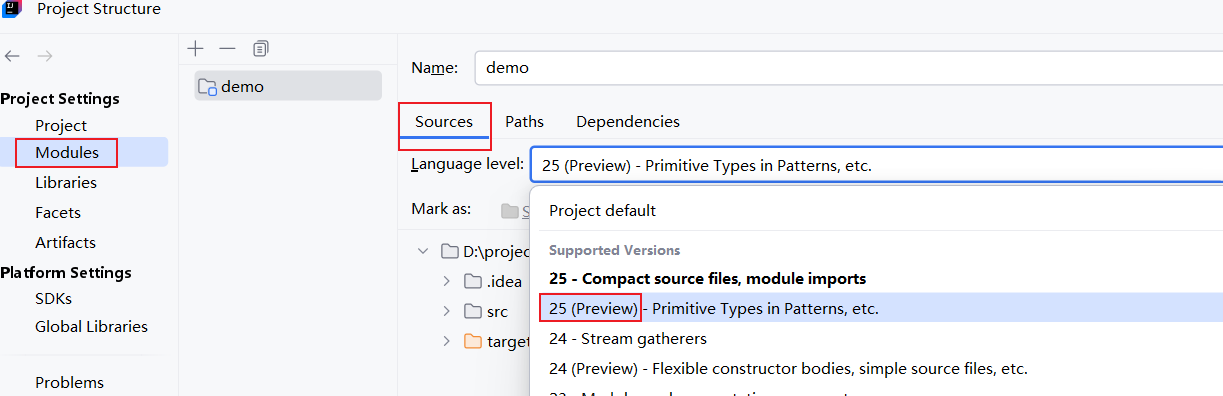
IDEA使用预览属性的方法:
语言
JEP 507:模式匹配支持基本类型(第三次预览)
1、作用
允许在instanceof、switch等模式上下文中直接使用基本类型(如int、double),消除了基本类型与包装类型之间的转换开销,统一了模式匹配的语法,简化了代码并提升性能
2、案例
public class PrimitivePatternMatchDemo {
static void main() {
Object[] array = new Object[]{1, "two", 3.0, true, 'a', 100L, (short) 128};
for (Object object : array) {
analyzeObj(object);
}
}
private static void analyzeObj(Object value) {
// 1. instanceof支持基本类型模式
if (value instanceof int i) {
System.out.printf("int value: %d (even: %b)%n", i, i % 2 == 0);
}
// 2. switch支持多种基本类型
else if (value instanceof double d) {
System.out.printf("double value: %.2f%n", d);
}
// 3. switch模式匹配带守卫条件
else if (value instanceof long l) {
switch (l) {
case 100L -> System.out.println("Found 100L");
case long num when num > 0 -> System.out.printf("Positive long: %d%n", num);
default -> System.out.println("Other long value");
}
}
// 4. 基本类型与包装类型统一处理
else if (value instanceof boolean b) {
System.out.println("Boolean: " + b);
}
else {
System.out.println("Other type: " + value.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
}
3、应用场景说明
-
数据处理:统一处理不同类型的数值数据(如解析JSON、CSV文件)
-
数学计算:科学计算中对不同精度数值的模式匹配
-
事件处理:根据不同类型的事件参数执行相应逻辑
-
AI推理:处理机器学习模型输出的各类数值结果
该特性减少了约30%的类型转换代码,同时避免了自动装箱/拆箱带来的性能损耗,特别适合高性能计算场景。
JEP 511:模块导入声明
增强 Java 编程语言,使其能够简洁地导入所有 模块导出的包。这简化了模块化的重用 但不要求导入代码必须存在于模块本身。
package org.example.other;
// 导入 java.base 整个模块
import module java.base;
/**
* @Description
* @Author
* @Date 2025/11/19 17:20
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class ModuleImportDemo {
static void main() {
ArrayList<Object> objects = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
JEP 512:紧凑源文件和实例主方法
1、作用
简化Java程序入门门槛,支持无类定义的紧凑源文件和实例主方法(无需static修饰)。
2、案例
// 无需类声明,直接编写代码
void main() {
IO.println("Hello, JDK 25!"); // IO类已在java.lang包中,无需导入
// 支持定义方法和变量
var message = "Current time: " + java.time.LocalTime.now();
printMessage(message);
}
void printMessage(String msg) {
IO.println("Message: " + msg);
}
JEP 513:灵活的构造体
1、作用
允许在调用父类构造函数 (super) 或同类其他构造函数 (this) 之前进行参数验证或计算,使代码更安全、更清晰。
2、案例
public class FlexibleConstructorDemo {
static void main() {
Person person = new Person("Alice", 30);
Person employee = new Employee("Bob", 25, 5000);
}
}
class Person {
String name;
int age;
String id;
// 构造方法
Person(String name, int age) {
if (age < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid age: " + age);
}
this.id = generateId();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
private String generateId() {
return UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "").substring(0, 8);
}
}
class Employee extends Person {
double salary;
// 构造方法
Employee(String name, int age, double salary) {
// 1. 在super()前执行参数验证
if (salary < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid salary: " + salary);
}
super(name, age);
this.salary = salary;
}
}
3、应用场景说明
-
参数验证:在调用父类构造函数前验证输入参数
-
默认值计算:复杂的默认字段值计算(如生成ID、加密处理)
-
日志记录:构造过程的审计日志
-
资源准备:在父类初始化前准备必要资源
注意限制:在super()调用前不能引用this或调用实例方法,确保不会访问未初始化的对象状态。
相关 API
JEP 505:结构化并发(第五次预览)
1、作用
引入结构化并发的 API,简化并发编程。结构化并发将不同线程中运行的相关任务组视为单一工作单元,从而简化错误处理和取消,提高可靠性并增强可观测性。
与传统并发对比:
| 对比维度 | 传统并发 (如 ExecutorService) | 结构化并发 (StructuredTaskScope) |
|---|---|---|
| 任务生命周期 | 子任务独立运行,生命周期需手动管理,容易导致"线程泄漏"。 | 父任务与子任务生命周期绑定。作用域结束后,所有子任务自动取消,避免资源泄漏。 |
| 错误传播与处理 | 错误处理分散,若一个任务失败,其他任务可能继续执行,造成资源浪费。 | 提供集中式的错误处理。例如,可配置为"任一子任务失败则取消所有其他任务",并及时抛出异常。 |
| 代码可观察性 | 线程转储中,父任务和子任务的调用栈相互独立,关系不清晰,调试困难。 | 线程转储会清晰显示任务的层次结构,使得并发流程一目了然,易于调试。 |
2、案例代码
public class StructuredConcurrencyDemo {
static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor();
static void main() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
// fetchOrder方法报错后(),会接着执行findUser()方法
// handleOld();
handle();
}
private static String findUser() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(1000);
String userName = "user_1";
System.out.println("findUser:" + userName);
return userName;
}
private static int fetchOrder() throws InterruptedException {
// int i = 1;
int i = 1 / 0;
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("fetchOrder:" + i);
return i;
}
// 旧:非结构化并发ExecutorService
static UserOrder handleOld() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Future<String> user = executor.submit(() -> findUser());
Future<Integer> order = executor.submit(() -> fetchOrder());
String theUser = user.get(); // Join findUser
int theOrder = order.get(); // Join fetchOrder
System.out.println("run main====");
return new UserOrder(theUser, theOrder);
}
static UserOrder handle() throws InterruptedException {
try (var scope = StructuredTaskScope.open()) {
StructuredTaskScope.Subtask<String> user = scope.fork(() -> findUser());
StructuredTaskScope.Subtask<Integer> order = scope.fork(() -> fetchOrder());
scope.join(); // Join subtasks, propagating exceptions
System.out.println("run main====");
// Both subtasks have succeeded, so compose their results
return new UserOrder(user.get(), order.get());
}
}
}
class UserOrder {
private final String theUser;
private final int theOrder;
public UserOrder(String theUser, int theOrder) {
this.theUser = theUser;
this.theOrder = theOrder;
}
}
JEP 506: Scoped Values(作用域值)
1、作用
作用域值(Scoped Values)是线程局部变量的现代化替代方案。它是不可变的,并且为虚拟线程进行了优化,能更安全、高效地在同一线程及其子线程间共享数据。
相比ThreadLocal,作用域值具有自动清理机制,不会因线程复用导致内存泄漏,且在虚拟线程环境下性能提升尤为显著。
2、案例
public class ScopedValuesDemo {
private final static ScopedValue<String> USER_NAME = ScopedValue.newInstance();
static void main() {
ScopedValue.where(USER_NAME, "Alice")
.run(() -> {
System.out.println("Hello, " + USER_NAME.get());
});
ScopedValue.where(USER_NAME, "Bob")
.run(() -> {
System.out.println("Hello, " + USER_NAME.get());
});
// 报错java.util.NoSuchElementException: ScopedValue not bound
// username.get();
try (var executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()) {
// 绑定作用域值并提交任务
executor.submit(() -> ScopedValue.where(USER_NAME, "alice_123")
.run(() -> {
Thread.currentThread().setName("Alice-Thread");
processRequest("Order_001");
}));
executor.submit(() -> ScopedValue.where(USER_NAME, "bob_456")
.run(() -> {
Thread.currentThread().setName("Bob-Thread");
processRequest("Order_002");
}));
}
}
private static void processRequest(String orderId) {
demoLog("Processing request: " + orderId);
// 在作用域值中获取用户名
validUserName();
// 根据订单ID处理订单
doSomeThingByOrderId(orderId);
}
private static void doSomeThingByOrderId(String orderId) {
demoLog("Processing order: " + orderId);
String currentUser = USER_NAME.get();
demoLog("Current user: " + currentUser);
}
private static void validUserName() {
if (USER_NAME.get() == null) {
demoLog("User name is not set");
throw new IllegalStateException("User name is not set");
}
demoLog("User name: " + USER_NAME.get());
}
private static void demoLog(String message) {
System.out.printf("[Thread: %s] %s%n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), message);
}
}
运行结果:
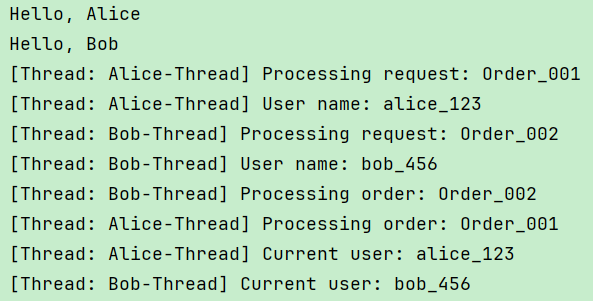
3、应用场景
适用于需要在调用链或子线程间传递上下文信息的场景,如:
-
Web服务中的请求ID、用户认证信息传递
-
分布式追踪系统的追踪上下文传播
-
日志系统的上下文标记
-
微服务调用中的元数据共享
JEP 510:密钥派生函数API
1、作用
提供标准化的密钥派生函数(KDF)API,支持HKDF、Argon2等算法,用于从主密钥或密码派生出加密密钥。该API简化了密码学应用开发,增强了安全性,并为量子计算时代的密码学准备了基础。
密钥派生函数(Key Derivation Function, KDF)是一种密码学函数,用于从一个主密钥(如密码或共享秘密)派生出一个或多个密钥。KDF 的主要目的是增强密钥的安全性,通常通过以下方式实现:
- 增加计算复杂度:通过多次迭代或使用计算密集型操作,使得暴力破解变得困难。
- 引入盐值(Salt):防止预计算攻击(如彩虹表攻击)。
- 支持多密钥派生:从一个主密钥派生出多个密钥,用于不同的用途。
2、案例代码
public class KDFDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 使用HKDF算法派生密钥
byte[] initialKeyMaterial = "master-secret-key".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
byte[] salt = "unique-salt-123".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
byte[] info = "auth-token".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 初始化KDF
// Create a KDF object for the specified algorithm
KDF hkdf = KDF.getInstance("HKDF-SHA256");
// Create an ExtractExpand parameter specification
AlgorithmParameterSpec params =
HKDFParameterSpec.ofExtract()
.addIKM(initialKeyMaterial)
.addSalt(salt).thenExpand(info, 32);
// 派生密钥
byte[] derivedKey = hkdf.deriveData(params);
System.out.println("Derived key length: " + derivedKey.length + " bytes");
System.out.println("Derived key: " + bytesToHex(derivedKey));
}
private static String bytesToHex(byte[] bytes) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : bytes) {
sb.append(String.format("%02x", b));
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
运行结果:
Derived key length: 32 bytes
Derived key: 0d878149cfb91007092385675ae897001cc42f6b868920d4ea80a1a326bb1b6d
3、应用场景说明
-
密码存储:安全存储用户密码(替代PBKDF2)
-
TLS协议:密钥交换过程中的密钥派生
-
区块链:加密货币中的地址生成和交易签名
-
云安全:服务间通信的密钥管理
-
量子安全:为后量子密码学算法提供基础支持
该API减少了对BouncyCastle等第三方库的依赖,提供了标准化的密码学实现,降低了安全漏洞风险。
性能
JEP 519:紧凑对象头
最早在JDK 24的时候作为实验性功能引入,已证明其稳定及性能。
1、作用
优化JVM对象头结构,在64位系统上将对象头大小从12字节(压缩类指针)或16字节(未压缩)减少到8字节。这一改进无需修改代码即可减少堆内存占用约20-25%,提升GC性能和CPU缓存利用率,特别适合微服务和云原生环境。
2、应用场景说明
-
微服务架构:减少容器内存占用,提高部署密度
-
大数据处理:降低海量小对象场景的内存开销
-
实时系统:减少GC压力,降低延迟波动
-
云原生应用:提高资源利用率,降低云服务成本
启用方式:java -XX:+UseCompactObjectHeaders YourApp
根据SPECjbb2015基准测试,该特性可使堆内存占用减少22%,GC频率降低15%,CPU使用率降低8%。
其他特性
-
移除了32位x86架构的支持
-
向量(Vector)API增强(第十次孵化)
-
PEM密钥「即插即用」
引入一个API,用于将代表密码密钥、证书和证书撤销列表的对象编码到广泛使用的隐私增强邮件(PEM)传输格式中,并将该格式解码回对象。 -
JFR(JDK Flight Recorder)增强
新增CPU采样、方法计时追踪,方便快速定位性能问题。(JEP 509、518、520) -
其他...





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号