一个简单的spring hello world:
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("src/main/resources/spring.xml");
Person person = ((Person) context.getBean("person"));
person.say();
person.myBook();
Book book = ((Book) context.getBean("book"));
System.out.println(book.toString());
}
}12
1
public class App {2
3
public static void main(String[] args) {4
ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("src/main/resources/spring.xml");5
Person person = ((Person) context.getBean("person"));6
person.say();7
person.myBook();8
Book book = ((Book) context.getBean("book"));9
System.out.println(book.toString());10
}11
12
}首先进入 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 的构造方法,可以看到该构造方法被重载了,可以传递 configLocation 数组,也就是说,可以传递过个配置文件的地址。默认刷新为true,parent 容器为null。
进入另一个构造器:
/**
* Create a new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext with the given parent,
* loading the definitions from the given XML files.
* @param configLocations array of file paths
* @param refresh whether to automatically refresh the context,
* loading all bean definitions and creating all singletons.
* Alternatively, call refresh manually after further configuring the context.
* @param parent the parent context
* @throws BeansException if context creation failed
* @see #refresh()
*/
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}21
1
/**2
* Create a new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext with the given parent,3
* loading the definitions from the given XML files.4
* @param configLocations array of file paths5
* @param refresh whether to automatically refresh the context,6
* loading all bean definitions and creating all singletons.7
* Alternatively, call refresh manually after further configuring the context.8
* @param parent the parent context9
* @throws BeansException if context creation failed10
* @see #refresh()11
*/12
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(13
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)14
throws BeansException {15
16
super(parent);17
setConfigLocations(configLocations);18
if (refresh) {19
refresh();20
}21
}该构造器做了两件事情,一是设置配置文件,二是刷新容器。
其中最重要的就是刷新配置文件refresh(),进入该方法,refresh()方法其实是FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 的父类 AbstractApplicationContext 的refresh()方法。
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 为刷新准备应用上下文
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// 告诉子类刷新内部bean工厂,即在子类中启动refreshBeanFactory()的地方----创建bean工厂,根据配置文件生成bean定义
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 在这个上下文中使用bean工厂
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 设置BeanFactory的后置处理器
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 调用BeanFactory的后处理器,这些后处理器是在Bean定义中向容器注册的
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册Bean的后处理器,在Bean创建过程中调用
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//对上下文的消息源进行初始化
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// 初始化上下文中的事件机制
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 初始化其他的特殊Bean
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// 检查监听Bean并且将这些Bean向容器注册
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// 实例化所有的(non-lazy-init)单件
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 发布容器事件,结束refresh过程
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// 为防止bean资源占用,在异常处理中,销毁已经在前面过程中生成的单件bean
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// 重置“active”标志
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}78
1
2
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {3
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {4
// 为刷新准备应用上下文5
// Prepare this context for refreshing.6
prepareRefresh();7
8
// 告诉子类刷新内部bean工厂,即在子类中启动refreshBeanFactory()的地方----创建bean工厂,根据配置文件生成bean定义9
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.10
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();11
12
// 在这个上下文中使用bean工厂13
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.14
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);15
16
try {17
// 设置BeanFactory的后置处理器18
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.19
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);20
21
// 调用BeanFactory的后处理器,这些后处理器是在Bean定义中向容器注册的22
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.23
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);24
25
// 注册Bean的后处理器,在Bean创建过程中调用26
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.27
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);28
29
//对上下文的消息源进行初始化30
// Initialize message source for this context.31
initMessageSource();32
33
// 初始化上下文中的事件机制34
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.35
initApplicationEventMulticaster();36
37
// 初始化其他的特殊Bean38
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.39
onRefresh();40
41
// 检查监听Bean并且将这些Bean向容器注册42
// Check for listener beans and register them.43
registerListeners();44
45
// 实例化所有的(non-lazy-init)单件46
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.47
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);48
49
// 发布容器事件,结束refresh过程50
// Last step: publish corresponding event.51
finishRefresh();52
}53
54
catch (BeansException ex) {55
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {56
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +57
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);58
}59
60
// 为防止bean资源占用,在异常处理中,销毁已经在前面过程中生成的单件bean61
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.62
destroyBeans();63
64
// 重置“active”标志65
// Reset 'active' flag.66
cancelRefresh(ex);67
68
// Propagate exception to caller.69
throw ex;70
}71
72
finally {73
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we74
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...75
resetCommonCaches();76
}77
}78
}AbstractApplicationContext 的refresh()方法就是整个IOC容器初始化的所有逻辑,该方法大概做了三件事:1、构建BeanFactory 2、构建bean实例并注入相关依赖 3、触发监听
获取BeanFactory
构建BeanFactory就是其中ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();这句代码,也就是AbstractApplicationContext的obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法,从字面上来理解也是获取新的BeanFactory。
AbstractApplicationContext的obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法的第一句代码就是refreshBeanFactory(),refreshBeanFactory()是AbstractApplicationContext的模板方法,进入它的实现AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext里面,其实现代码如下:
/**
* This implementation performs an actual refresh of this context's underlying
* bean factory, shutting down the previous bean factory (if any) and
* initializing a fresh bean factory for the next phase of the context's lifecycle.
*/
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
// 如果存在就销毁
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
// new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory())
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
// 设置序列化
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
// 定制的BeanFactory
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 使用BeanFactory加载bean定义 AbstractXmlApplicationContext
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}29
1
/**2
* This implementation performs an actual refresh of this context's underlying3
* bean factory, shutting down the previous bean factory (if any) and4
* initializing a fresh bean factory for the next phase of the context's lifecycle.5
*/6
7
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {8
if (hasBeanFactory()) {9
// 如果存在就销毁10
destroyBeans();11
closeBeanFactory();12
}13
try {14
// new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory())15
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();16
// 设置序列化17
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());18
// 定制的BeanFactory19
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);20
// 使用BeanFactory加载bean定义 AbstractXmlApplicationContext21
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);22
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {23
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;24
}25
}26
catch (IOException ex) {27
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);28
}29
}这就是刷新BeanFactory的过程,首先判断是否存在了 BeanFactory,如果存在BeanFactory则销毁,调用 createBeanFactory 方法创建BeanFactory,但是该方法创建的是DefaultListableBeanFactory ,那么也就是说,DefaultListableBeanFactory 就是 BeanFactory的默认实现。
在AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的refreshBeanFactory()方法中可以看见一句代码:loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory),该方法的作用是加载 Definitions,Definition 是spring的核心之一,代表着 IOC 中的基本数据结构。该loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory)方法也是个抽象方法,默认实现是 AbstractXmlApplicationContext的loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory),其代码如下:
/**
* Loads the bean definitions via an XmlBeanDefinitionReader.
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader
* @see #initBeanDefinitionReader
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions
*/
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}22
1
/**2
* Loads the bean definitions via an XmlBeanDefinitionReader.3
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader4
* @see #initBeanDefinitionReader5
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions6
*/7
8
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {9
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.10
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);11
12
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's13
// resource loading environment.14
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());15
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);16
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));17
18
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,19
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.20
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);21
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);22
}该方法首先创建一个 XmlBeanDefinitionReader ,用于读取XML中配置,设置了环境、资源加载器,最后初始化,加载。该方法主要是加载BeanDefinition,解析Bean的定义,也就是把xml中定义数据结构转化为 IOC容器中的特定数据结构。
而比较关键的代码则是最后一行的 loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader) 方法。
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader) 方法:
/**
* Load the bean definitions with the given XmlBeanDefinitionReader.
* <p>The lifecycle of the bean factory is handled by the {@link #refreshBeanFactory}
* method; hence this method is just supposed to load and/or register bean definitions.
* @param reader the XmlBeanDefinitionReader to use
* @throws BeansException in case of bean registration errors
* @throws IOException if the required XML document isn't found
* @see #refreshBeanFactory
* @see #getConfigLocations
* @see #getResources
* @see #getResourcePatternResolver
*/
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
// 加载给定的路径文件
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}23
1
/**2
* Load the bean definitions with the given XmlBeanDefinitionReader.3
* <p>The lifecycle of the bean factory is handled by the {@link #refreshBeanFactory}4
* method; hence this method is just supposed to load and/or register bean definitions.5
* @param reader the XmlBeanDefinitionReader to use6
* @throws BeansException in case of bean registration errors7
* @throws IOException if the required XML document isn't found8
* @see #refreshBeanFactory9
* @see #getConfigLocations10
* @see #getResources11
* @see #getResourcePatternResolver12
*/13
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {14
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();15
if (configResources != null) {16
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);17
}18
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();19
if (configLocations != null) {20
// 加载给定的路径文件21
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);22
}23
}dubug进去看到如图:
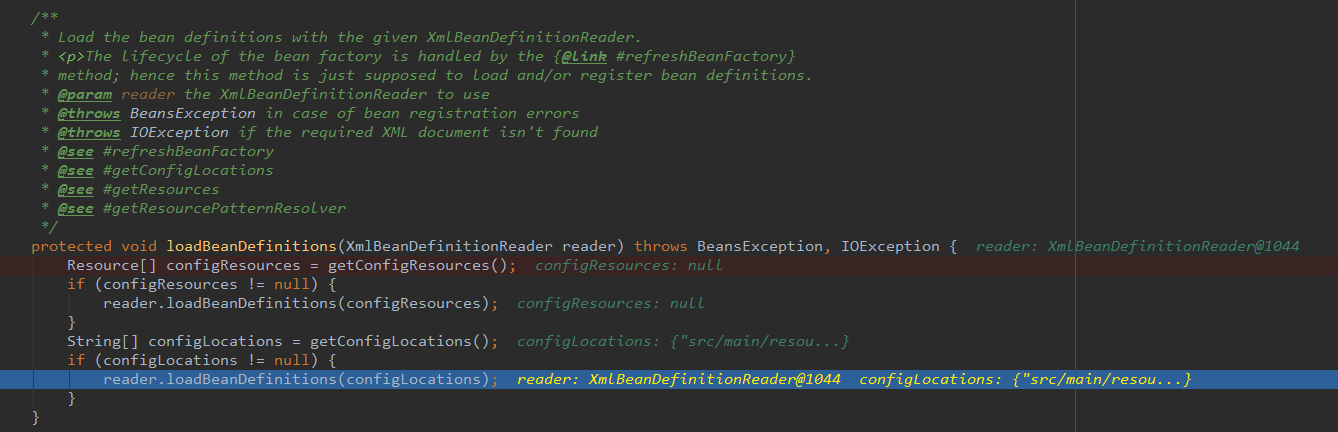
configResources 为 null, 表示不会进入第一个语句块,会进入第二个语句块。
loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) 方法:
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null");
int counter = 0;
for (String location : locations) {
counter += loadBeanDefinitions(location);
}
return counter;
}9
1
2
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {3
Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null");4
int counter = 0;5
for (String location : locations) {6
counter += loadBeanDefinitions(location);7
}8
return counter;9
}该方法的接口介绍:
/**
* 从指定的资源位置加载bean定义。
* Load bean definitions from the specified resource locations.
* @param locations the resource locations, to be loaded with the ResourceLoader
* (or ResourcePatternResolver) of this bean definition reader
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;9
1
/**2
* 从指定的资源位置加载bean定义。3
* Load bean definitions from the specified resource locations.4
* @param locations the resource locations, to be loaded with the ResourceLoader5
* (or ResourcePatternResolver) of this bean definition reader6
* @return the number of bean definitions found7
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors8
*/9
int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;该loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) 方法的核心逻辑是for循环中的 loadBeanDefinitions(location); 该代码最后调用AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources)方法。
loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) 方法 :
/**
* Load bean definitions from the specified resource location.
* <p>The location can also be a location pattern, provided that the
* ResourceLoader of this bean definition reader is a ResourcePatternResolver.
* @param location the resource location, to be loaded with the ResourceLoader
* (or ResourcePatternResolver) of this bean definition reader
* @param actualResources a Set to be filled with the actual Resource objects
* that have been resolved during the loading process. May be {@code null}
* to indicate that the caller is not interested in those Resource objects.
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
* @see #getResourceLoader()
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource)
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource[])
*/
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 获取资源加载器
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
try {
// 获取资源数组
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
// 根据配置文件加载bean definitions
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
for (Resource resource : resources) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return loadCount;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL.
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return loadCount;
}
}58
1
/**2
* Load bean definitions from the specified resource location.3
* <p>The location can also be a location pattern, provided that the4
* ResourceLoader of this bean definition reader is a ResourcePatternResolver.5
* @param location the resource location, to be loaded with the ResourceLoader6
* (or ResourcePatternResolver) of this bean definition reader7
* @param actualResources a Set to be filled with the actual Resource objects8
* that have been resolved during the loading process. May be {@code null}9
* to indicate that the caller is not interested in those Resource objects.10
* @return the number of bean definitions found11
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors12
* @see #getResourceLoader()13
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource)14
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource[])15
*/16
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {17
// 获取资源加载器 18
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();19
if (resourceLoader == null) {20
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(21
"Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");22
}23
24
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {25
// Resource pattern matching available.26
try {27
// 获取资源数组28
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);29
// 根据配置文件加载bean definitions30
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);31
if (actualResources != null) {32
for (Resource resource : resources) {33
actualResources.add(resource);34
}35
}36
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {37
logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");38
}39
return loadCount;40
}41
catch (IOException ex) {42
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(43
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);44
}45
}46
else {47
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL.48
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);49
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);50
if (actualResources != null) {51
actualResources.add(resource);52
}53
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {54
logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");55
}56
return loadCount;57
}58
}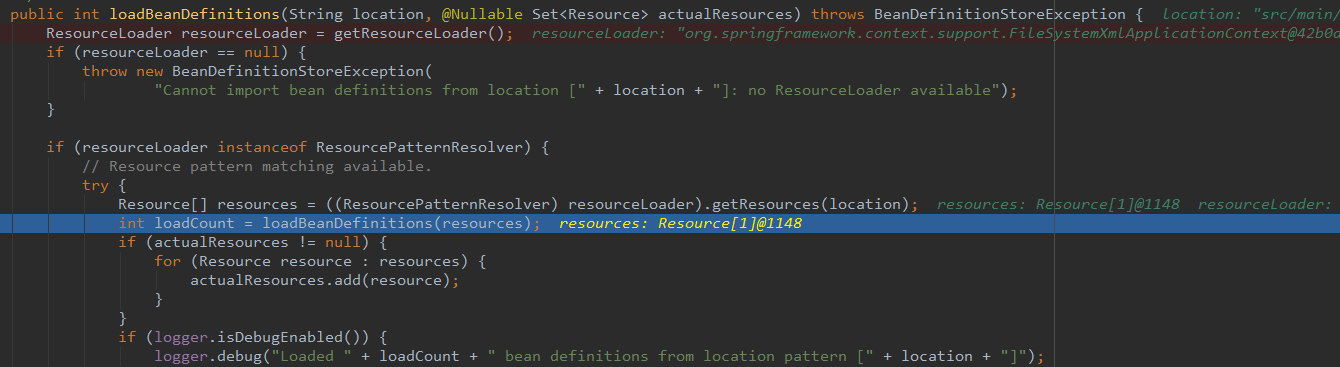
如上图:该方法首先获取资源加载器,然后进入 if 块,获取资源数组,调用 loadBeanDefinitions(resources) ,根据配置文件加载Bean定义。
主要看看 loadBeanDefinitions(resources) 的实现,
loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) 方法 :
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null");
int counter = 0;
for (Resource resource : resources) {
counter += loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
return counter;
}9
1
2
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {3
Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null");4
int counter = 0;5
for (Resource resource : resources) {6
counter += loadBeanDefinitions(resource);7
}8
return counter;9
}该方法主要在循环加载resource 资源数组,看看其加载resource 资源数组的实现 -- int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) 接口, 进入该接口的 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 实现,该实现方法会调用loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource)方法。
该loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource)方法主要调用doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());方法
doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)方法:
/**
* Actually load bean definitions from the specified XML file.
* @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from
* @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
* @see #doLoadDocument
* @see #registerBeanDefinitions
*/
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}39
1
/**2
* Actually load bean definitions from the specified XML file.3
* @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from4
* @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file5
* @return the number of bean definitions found6
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors7
* @see #doLoadDocument8
* @see #registerBeanDefinitions9
*/10
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)11
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {12
try {13
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);14
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);15
}16
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {17
throw ex;18
}19
catch (SAXParseException ex) {20
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),21
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);22
}23
catch (SAXException ex) {24
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),25
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);26
}27
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {28
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),29
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);30
}31
catch (IOException ex) {32
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),33
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);34
}35
catch (Throwable ex) {36
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),37
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);38
}39
}该方法主要做两件事:
1、根据输入流加载 Document 文档对象
2、根据得到的文档对象注册到容器
看看 根据得到的文档对象注册到容器 的实现:
registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource)方法:
/**
* Register the bean definitions contained in the given DOM document.
* Called by {@code loadBeanDefinitions}.
* <p>Creates a new instance of the parser class and invokes
* {@code registerBeanDefinitions} on it.
* @param doc the DOM document
* @param resource the resource descriptor (for context information)
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions
* @see #setDocumentReaderClass
* @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions
*/
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 创建一个 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader, 用于读取 BeanDefinition
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}20
1
/**2
* Register the bean definitions contained in the given DOM document.3
* Called by {@code loadBeanDefinitions}.4
* <p>Creates a new instance of the parser class and invokes5
* {@code registerBeanDefinitions} on it.6
* @param doc the DOM document7
* @param resource the resource descriptor (for context information)8
* @return the number of bean definitions found9
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors10
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions11
* @see #setDocumentReaderClass12
* @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions13
*/14
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {15
// 创建一个 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader, 用于读取 BeanDefinition16
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();17
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();18
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));19
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;20
}其中documentReader调用registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));,
registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) 方法:
/**
* This implementation parses bean definitions according to the "spring-beans" XSD
* (or DTD, historically).
* <p>Opens a DOM Document; then initializes the default settings
* specified at the {@code <beans/>} level; then parses the contained bean definitions.
*/
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
}13
1
/**2
* This implementation parses bean definitions according to the "spring-beans" XSD3
* (or DTD, historically).4
* <p>Opens a DOM Document; then initializes the default settings5
* specified at the {@code <beans/>} level; then parses the contained bean definitions.6
*/7
8
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {9
this.readerContext = readerContext;10
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");11
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();12
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);13
}该方法从文档对象Document中获取根元素,最后调用 DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root) 进行注册。
该doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root)方法:
/**
* Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element.
*/
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
preProcessXml(root);
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}33
1
/**2
* Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element.3
*/4
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {5
// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In6
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,7
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create8
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,9
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.10
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.11
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;12
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);13
14
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {15
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);16
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {17
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(18
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);19
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {20
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {21
logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +22
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());23
}24
return;25
}26
}27
}28
29
preProcessXml(root);30
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);31
postProcessXml(root);32
this.delegate = parent;33
}该方法最重要的是倒数第三行的:parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate)方法:
/**
* Parse the elements at the root level in the document:
* "import", "alias", "bean".
* @param root the DOM root element of the document
*/
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}25
1
/**2
* Parse the elements at the root level in the document:3
* "import", "alias", "bean".4
* @param root the DOM root element of the document5
*/6
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {7
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {8
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();9
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {10
Node node = nl.item(i);11
if (node instanceof Element) {12
Element ele = (Element) node;13
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {14
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);15
}16
else {17
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);18
}19
}20
}21
}22
else {23
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);24
}25
}该方法就是一个解析XML 文档的步骤,核心是调用 parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate)
而 parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) 方法主要是调用processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate)方法
processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate)方法:
/**
* Process the given bean element, parsing the bean definition
* and registering it with the registry.
*/
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// 创建一个 BeanDefinitionHolder
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
// 执行容器通知事件
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}22
1
/**2
* Process the given bean element, parsing the bean definition3
* and registering it with the registry.4
*/5
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {6
// 创建一个 BeanDefinitionHolder7
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);8
if (bdHolder != null) {9
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);10
try {11
// Register the final decorated instance.12
// 执行容器通知事件13
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());14
}15
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {16
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +17
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);18
}19
// Send registration event.20
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));21
}22
}其中,该静态方法registerBeanDefinition(BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry):
/**
* Register the given bean definition with the given bean factory.
* @param definitionHolder the bean definition including name and aliases
* @param registry the bean factory to register with
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException if registration failed
*/
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// Register bean definition under primary name.
// 从bean的持有者那里获取了beanName
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
// 将bena的名字和 BeanDefinition 注册
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}24
1
/**2
* Register the given bean definition with the given bean factory.3
* @param definitionHolder the bean definition including name and aliases4
* @param registry the bean factory to register with5
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException if registration failed6
*/7
public static void registerBeanDefinition(8
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)9
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {10
11
// Register bean definition under primary name.12
// 从bean的持有者那里获取了beanName13
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();14
// 将bena的名字和 BeanDefinition 注册15
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());16
17
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.18
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();19
if (aliases != null) {20
for (String alias : aliases) {21
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);22
}23
}24
}其注册接口registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)的DefaultListableBeanFactory类的实现:
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (existingDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName +
"': There is already [" + existingDefinition + "] bound.");
}
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
if (this.manualSingletonNames.contains(beanName)) {
Set<String> updatedSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.manualSingletonNames);
updatedSingletons.remove(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames = updatedSingletons;
}
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase -- 最终放进这个map 实现注册
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);// 走这里 // private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}77
1
2
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)3
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {4
5
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");6
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");7
8
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {9
try {10
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();11
}12
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {13
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,14
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);15
}16
}17
18
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);19
if (existingDefinition != null) {20
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {21
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,22
"Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName +23
"': There is already [" + existingDefinition + "] bound.");24
}25
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {26
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE27
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {28
logger.warn("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +29
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +30
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");31
}32
}33
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {34
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {35
logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +36
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +37
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");38
}39
}40
else {41
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {42
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +43
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +44
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");45
}46
}47
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);48
}49
else {50
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {51
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)52
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {53
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);54
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);55
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);56
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);57
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;58
if (this.manualSingletonNames.contains(beanName)) {59
Set<String> updatedSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.manualSingletonNames);60
updatedSingletons.remove(beanName);61
this.manualSingletonNames = updatedSingletons;62
}63
}64
}65
else {66
// Still in startup registration phase -- 最终放进这个map 实现注册67
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);// 走这里 // private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);68
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);69
this.manualSingletonNames.remove(beanName);70
}71
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;72
}73
74
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {75
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);76
}77
}该方法可以说是注册bean的最后一步,将beanName和 beanDefinition 放进一个 ConcurrentHashMap(256) 中。
前面忽略了beanDefinition 的创建,beanDefinition 是在DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) 方法中,在这里创建了 BeanDefinitionHolder, 而创建了 BeanDefinitionHolder实例中解析Bean并将Bean 保存在该对象中。
该实例会调用 parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) 方法,该方法用于解析XML文件并创建一个 BeanDefinitionHolder 返回,该方法会调用 parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean) 方法, 我们看看该方法:
/**
* Parse the bean definition itself, without regard to name or aliases. May return
* {@code null} if problems occurred during the parsing of the bean definition.
*/
@Nullable
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
String className = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
// 类全限定名称
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
String parent = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
try {
// 创建
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return null;
}55
1
/**2
* Parse the bean definition itself, without regard to name or aliases. May return3
* {@code null} if problems occurred during the parsing of the bean definition.4
*/5
6
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(7
Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean) {8
9
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));10
11
String className = null;12
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {13
// 类全限定名称14
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();15
}16
String parent = null;17
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {18
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);19
}20
21
try {22
// 创建23
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);24
25
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);26
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));27
28
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);29
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());30
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());31
32
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);33
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);34
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);35
36
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());37
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));38
39
return bd;40
}41
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {42
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);43
}44
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {45
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);46
}47
catch (Throwable ex) {48
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);49
}50
finally {51
this.parseState.pop();52
}53
54
return null;55
}该方法从XML元素中取出 class 元素,然后拿着className调用 createBeanDefinition(className, parent) 方法,该方法核心是调用 BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.createBeanDefinition 方法,我们看看该方法:
/**
* Create a new GenericBeanDefinition for the given parent name and class name,
* eagerly loading the bean class if a ClassLoader has been specified.
* @param parentName the name of the parent bean, if any
* @param className the name of the bean class, if any
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for loading bean classes
* (can be {@code null} to just register bean classes by name)
* @return the bean definition
* @throws ClassNotFoundException if the bean class could not be loaded
*/
public static AbstractBeanDefinition createBeanDefinition(
@Nullable String parentName, @Nullable String className, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 泛型的bean定义,也就是最终生成的bean定义。
GenericBeanDefinition bd = new GenericBeanDefinition();
bd.setParentName(parentName);
if (className != null) {
if (classLoader != null) {
// 设置Class 对象
bd.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(className, classLoader));
}
else {
bd.setBeanClassName(className);
}
}
return bd;
}27
1
/**2
* Create a new GenericBeanDefinition for the given parent name and class name,3
* eagerly loading the bean class if a ClassLoader has been specified.4
* @param parentName the name of the parent bean, if any5
* @param className the name of the bean class, if any6
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for loading bean classes7
* (can be {@code null} to just register bean classes by name)8
* @return the bean definition9
* @throws ClassNotFoundException if the bean class could not be loaded10
*/11
public static AbstractBeanDefinition createBeanDefinition(12
String parentName, String className, ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {13
14
// 泛型的bean定义,也就是最终生成的bean定义。15
GenericBeanDefinition bd = new GenericBeanDefinition();16
bd.setParentName(parentName);17
if (className != null) {18
if (classLoader != null) {19
// 设置Class 对象20
bd.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(className, classLoader));21
}22
else {23
bd.setBeanClassName(className);24
}25
}26
return bd;27
}该方法创建一个 Definition 的持有者,然后设置该持有者的Class对象,该对象就是我们在配置文件中配置的Class对象。最后返回。
#############创建Bean实例并构建Bean的依赖关系网###########################################
我们刚刚创建了Bean工厂,并创建 BeanDefinitions 放进Map里,以beanName为key。那么我们现在有了Bean定义,但还没有实例,也没有构建Bean与Bean之间的依赖关系。
我们知道,构建依赖关系是 IOC 的一个重要的任务,我们怎么能放过。那么是在哪里做的呢?在 refresh() 方法的finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory) 方法中。该方法中重要的一步是 : beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(),我们有必要看看该方法实现:
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>)
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}56
1
2
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {3
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {4
logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);5
}6
7
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.8
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.9
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);10
11
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...12
for (String beanName : beanNames) {13
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);14
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {15
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {16
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);17
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {18
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;19
boolean isEagerInit;20
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {21
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>)22
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,23
getAccessControlContext());24
}25
else {26
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&27
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());28
}29
if (isEagerInit) {30
getBean(beanName);31
}32
}33
}34
else {35
getBean(beanName);36
}37
}38
}39
40
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...41
for (String beanName : beanNames) {42
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);43
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {44
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;45
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {46
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {47
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();48
return null;49
}, getAccessControlContext());50
}51
else {52
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();53
}54
}55
}56
}该方法首先循环所有的BeanNames,并且调用getBean(beanName);方法,该方法实际上就是创建bean并递归构建依赖关系。该方法会调用 doGetBean(name, null, null, false),我们进入该方法查看,该方法很长,楼主挑选重要代码:
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
* @param name the name of the bean to retrieve
* @param requiredType the required type of the bean to retrieve
* @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments
* (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one)
* @param typeCheckOnly whether the instance is obtained for a type check,
* not for actual use
* @return an instance of the bean
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}167
1
/**2
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.3
* @param name the name of the bean to retrieve4
* @param requiredType the required type of the bean to retrieve5
* @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments6
* (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one)7
* @param typeCheckOnly whether the instance is obtained for a type check,8
* not for actual use9
* @return an instance of the bean10
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created11
*/12
("unchecked")13
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, final Class<T> requiredType,14
final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {15
16
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);17
Object bean;18
19
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.20
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);21
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {22
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {23
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {24
logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +25
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");26
}27
else {28
logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");29
}30
}31
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);32
}33
34
else {35
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:36
// We're assumably within a circular reference.37
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {38
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);39
}40
41
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.42
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();43
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {44
// Not found -> check parent.45
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);46
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {47
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(48
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);49
}50
else if (args != null) {51
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.52
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);53
}54
else {55
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.56
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);57
}58
}59
60
if (!typeCheckOnly) {61
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);62
}63
64
try {65
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);66
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);67
68
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.69
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();70
if (dependsOn != null) {71
for (String dep : dependsOn) {72
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {73
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,74
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");75
}76
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);77
try {78
getBean(dep);79
}80
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {81
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,82
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);83
}84
}85
}86
87
// Create bean instance.88
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {89
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {90
try {91
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);92
}93
catch (BeansException ex) {94
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there95
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.96
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.97
destroySingleton(beanName);98
throw ex;99
}100
});101
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);102
}103
104
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {105
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.106
Object prototypeInstance = null;107
try {108
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);109
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);110
}111
finally {112
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);113
}114
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);115
}116
117
else {118
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();119
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);120
if (scope == null) {121
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");122
}123
try {124
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {125
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);126
try {127
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);128
}129
finally {130
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);131
}132
});133
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);134
}135
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {136
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,137
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +138
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",139
ex);140
}141
}142
}143
catch (BeansException ex) {144
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);145
throw ex;146
}147
}148
149
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.150
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {151
try {152
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);153
if (convertedBean == null) {154
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());155
}156
return convertedBean;157
}158
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {159
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {160
logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +161
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);162
}163
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());164
}165
}166
return (T) bean;167
}其中部分重要代码截图:
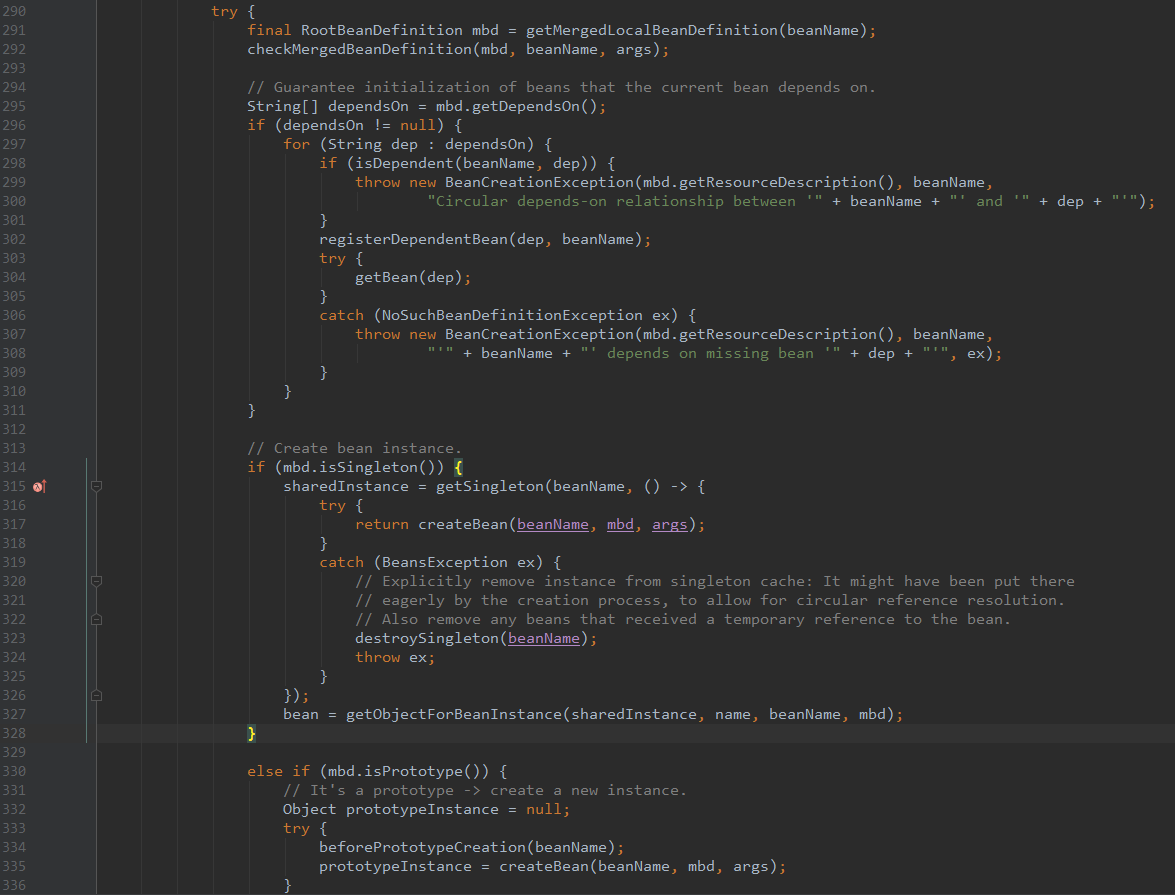
可以看到,该方法首先会获取依赖关系,拿着依赖的BeanName 递归调用 getBean方法,直到调用 getSingleton 方法返回依赖bean,而 getSingleton 方法的参数是 createBean 返回的实例,该createBean 方法内部调用 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean 方法:
/**
* Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened
* at this point, e.g. checking {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callbacks.
* <p>Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a
* factory method, and autowiring a constructor.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
* @return a new instance of the bean
* @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created
* @see #instantiateBean
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
*/
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}111
1
/**2
* Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened3
* at this point, e.g. checking {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callbacks.4
* <p>Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a5
* factory method, and autowiring a constructor.6
* @param beanName the name of the bean7
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean8
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation9
* @return a new instance of the bean10
* @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created11
* @see #instantiateBean12
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod13
* @see #autowireConstructor14
*/15
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args)16
throws BeanCreationException {17
18
// Instantiate the bean.19
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;20
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {21
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);22
}23
if (instanceWrapper == null) {24
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);25
}26
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();27
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();28
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {29
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;30
}31
32
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.33
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {34
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {35
try {36
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);37
}38
catch (Throwable ex) {39
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,40
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);41
}42
mbd.postProcessed = true;43
}44
}45
46
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references47
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.48
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&49
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));50
if (earlySingletonExposure) {51
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {52
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +53
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");54
}55
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));56
}57
58
// Initialize the bean instance.59
Object exposedObject = bean;60
try {61
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);62
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);63
}64
catch (Throwable ex) {65
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {66
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;67
}68
else {69
throw new BeanCreationException(70
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);71
}72
}73
74
if (earlySingletonExposure) {75
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);76
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {77
if (exposedObject == bean) {78
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;79
}80
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {81
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);82
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);83
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {84
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {85
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);86
}87
}88
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {89
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,90
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +91
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +92
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +93
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +94
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +95
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");96
}97
}98
}99
}100
101
// Register bean as disposable.102
try {103
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);104
}105
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {106
throw new BeanCreationException(107
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);108
}109
110
return exposedObject;111
}该方法很长,我们重点关注以下2行代码:
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args) 创建实例。
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper) , 该方法用于填充Bean,该
方法可以就是说就是发生依赖注入的地方。
createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args):
/**
* Create a new instance for the specified bean, using an appropriate instantiation strategy:
* factory method, constructor autowiring, or simple instantiation.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance
* @see #obtainFromSupplier
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
* @see #instantiateBean
*/
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
Supplier<?> instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();
if (instanceSupplier != null) {
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);
}
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
if (resolved) {
if (autowireNecessary) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// Need to determine the constructor...
Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}61
1
/**2
* Create a new instance for the specified bean, using an appropriate instantiation strategy:3
* factory method, constructor autowiring, or simple instantiation.4
* @param beanName the name of the bean5
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean6
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation7
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance8
* @see #obtainFromSupplier9
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod10
* @see #autowireConstructor11
* @see #instantiateBean12
*/13
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) {14
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.15
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);16
17
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {18
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,19
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());20
}21
22
Supplier<?> instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();23
if (instanceSupplier != null) {24
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);25
}26
27
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {28
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);29
}30
31
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...32
boolean resolved = false;33
boolean autowireNecessary = false;34
if (args == null) {35
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {36
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {37
resolved = true;38
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;39
}40
}41
}42
if (resolved) {43
if (autowireNecessary) {44
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);45
}46
else {47
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);48
}49
}50
51
// Need to determine the constructor...52
Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);53
if (ctors != null ||54
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||55
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {56
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);57
}58
59
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.60
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);61
}该方法的doc注释是这样介绍的:为指定的bean创建一个新的实例,使用适当的实例化策略:工厂方法、构造函数自动装配或简单实例化。
我们看,该方法首先创建Class 对象,然后获取构造器对象,最后调用 instantiateBean(beanName, mbd) 方法,
instantiateBean(beanName, mbd) 方法实现:
/**
* Instantiate the given bean using its default constructor.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance
*/
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance;
final BeanFactory parent = this;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () ->
getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent),
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent);
}
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
}27
1
/**2
* Instantiate the given bean using its default constructor.3
* @param beanName the name of the bean4
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean5
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance6
*/7
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd) {8
try {9
Object beanInstance;10
final BeanFactory parent = this;11
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {12
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () ->13
getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent),14
getAccessControlContext());15
}16
else {17
beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent);18
}19
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance);20
initBeanWrapper(bw);21
return bw;22
}23
catch (Throwable ex) {24
throw new BeanCreationException(25
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Instantiation of bean failed", ex);26
}27
}该方法核心逻辑是 beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent),携带BeanName ,RootBeanDefinition ,发挥的策略对象是 SimpleInstantiationStrategy,该方法内部调用静态方法 BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse), 组后调用 Constructor 的 newInstance 方法, 也就是最终使用反射创建了该实例:
/**
* Convenience method to instantiate a class using the given constructor.
* <p>Note that this method tries to set the constructor accessible if given a
* non-accessible (that is, non-public) constructor, and supports Kotlin classes
* with optional parameters and default values.
* @param ctor the constructor to instantiate
* @param args the constructor arguments to apply (use {@code null} for an unspecified
* parameter if needed for Kotlin classes with optional parameters and default values)
* @return the new instance
* @throws BeanInstantiationException if the bean cannot be instantiated
* @see Constructor#newInstance
*/
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException {
Assert.notNull(ctor, "Constructor must not be null");
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);
return (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(ctor.getDeclaringClass()) ?
KotlinDelegate.instantiateClass(ctor, args) : ctor.newInstance(args));
}
catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is it an abstract class?", ex);
}
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is the constructor accessible?", ex);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Illegal arguments for constructor", ex);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Constructor threw exception", ex.getTargetException());
}
}
33
1
/**2
* Convenience method to instantiate a class using the given constructor.3
* <p>Note that this method tries to set the constructor accessible if given a4
* non-accessible (that is, non-public) constructor, and supports Kotlin classes5
* with optional parameters and default values.6
* @param ctor the constructor to instantiate7
* @param args the constructor arguments to apply (use {@code null} for an unspecified8
* parameter if needed for Kotlin classes with optional parameters and default values)9
* @return the new instance10
* @throws BeanInstantiationException if the bean cannot be instantiated11
* @see Constructor#newInstance12
*/13
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException {14
Assert.notNull(ctor, "Constructor must not be null");15
try {16
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);17
return (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(ctor.getDeclaringClass()) ?18
KotlinDelegate.instantiateClass(ctor, args) : ctor.newInstance(args));19
}20
catch (InstantiationException ex) {21
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is it an abstract class?", ex);22
}23
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {24
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is the constructor accessible?", ex);25
}26
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {27
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Illegal arguments for constructor", ex);28
}29
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {30
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Constructor threw exception", ex.getTargetException());31
}32
}33
该方法会判断是否是 Kotlin 类型。如果不是,则调用构造器的实例方法。
到这里,我们的实例已经创建。但是我们的实例的依赖还没有设置,刚刚我们在 doCreateBean方法说关心以下2行代码:
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args) 创建实例。
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper) , 该方法用于填充Bean,该方法可以就是说就是发生依赖注入的地方。
我们已经解析了第一个,现在看第二个方法:
/**
* Populate the bean instance in the given BeanWrapper with the property values
* from the bean definition.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param bw the BeanWrapper with bean instance
*/
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
if (pvs != null) {
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}87
1
/**2
* Populate the bean instance in the given BeanWrapper with the property values3
* from the bean definition.4
* @param beanName the name of the bean5
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean6
* @param bw the BeanWrapper with bean instance7
*/8
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {9
if (bw == null) {10
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {11
throw new BeanCreationException(12
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");13
}14
else {15
// Skip property population phase for null instance.16
return;17
}18
}19
20
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the21
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,22
// to support styles of field injection.23
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;24
25
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {26
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {27
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {28
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;29
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {30
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;31
break;32
}33
}34
}35
}36
37
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {38
return;39
}40
41
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);42
43
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||44
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {45
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);46
47
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.48
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {49
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);50
}51
52
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.53
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {54
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);55
}56
57
pvs = newPvs;58
}59
60
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();61
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);62
63
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {64
if (pvs == null) {65
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();66
}67
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);68
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {69
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {70
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {71
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;72
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);73
if (pvs == null) {74
return;75
}76
}77
}78
}79
if (needsDepCheck) {80
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);81
}82
}83
84
if (pvs != null) {85
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);86
}87
}该方法核心逻辑是
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null),
即获取该bean的所有属性,也就是我们配置property元素。最后执行 applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs) 方法。
/**
* Apply the given property values, resolving any runtime references
* to other beans in this bean factory. Must use deep copy, so we
* don't permanently modify this property.
* @param beanName the bean name passed for better exception information
* @param mbd the merged bean definition
* @param bw the BeanWrapper wrapping the target object
* @param pvs the new property values
*/
protected void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, PropertyValues pvs) {
if (pvs.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && bw instanceof BeanWrapperImpl) {
((BeanWrapperImpl) bw).setSecurityContext(getAccessControlContext());
}
MutablePropertyValues mpvs = null;
List<PropertyValue> original;
if (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues) {
mpvs = (MutablePropertyValues) pvs;
if (mpvs.isConverted()) {
// Shortcut: use the pre-converted values as-is.
try {
bw.setPropertyValues(mpvs);
return;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
}
original = mpvs.getPropertyValueList();
}
else {
original = Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues());
}
TypeConverter converter = getCustomTypeConverter();
if (converter == null) {
converter = bw;
}
BeanDefinitionValueResolver valueResolver = new BeanDefinitionValueResolver(this, beanName, mbd, converter);
// Create a deep copy, resolving any references for values.
List<PropertyValue> deepCopy = new ArrayList<>(original.size());
boolean resolveNecessary = false;
for (PropertyValue pv : original) {
if (pv.isConverted()) {
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
String propertyName = pv.getName();
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();
Object resolvedValue = valueResolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(pv, originalValue);
Object convertedValue = resolvedValue;
boolean convertible = bw.isWritableProperty(propertyName) &&
!PropertyAccessorUtils.isNestedOrIndexedProperty(propertyName);
if (convertible) {
convertedValue = convertForProperty(resolvedValue, propertyName, bw, converter);
}
// Possibly store converted value in merged bean definition,
// in order to avoid re-conversion for every created bean instance.
if (resolvedValue == originalValue) {
if (convertible) {
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
}
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else if (convertible && originalValue instanceof TypedStringValue &&
!((TypedStringValue) originalValue).isDynamic() &&
!(convertedValue instanceof Collection || ObjectUtils.isArray(convertedValue))) {
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);
deepCopy.add(pv);
}
else {
resolveNecessary = true;
deepCopy.add(new PropertyValue(pv, convertedValue));
}
}
}
if (mpvs != null && !resolveNecessary) {
mpvs.setConverted();
}
// Set our (possibly massaged) deep copy.
try {
bw.setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(deepCopy));
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);
}
}96
1
/**2
* Apply the given property values, resolving any runtime references3
* to other beans in this bean factory. Must use deep copy, so we4
* don't permanently modify this property.5
* @param beanName the bean name passed for better exception information6
* @param mbd the merged bean definition7
* @param bw the BeanWrapper wrapping the target object8
* @param pvs the new property values9
*/10
protected void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, PropertyValues pvs) {11
if (pvs.isEmpty()) {12
return;13
}14
15
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && bw instanceof BeanWrapperImpl) {16
((BeanWrapperImpl) bw).setSecurityContext(getAccessControlContext());17
}18
19
MutablePropertyValues mpvs = null;20
List<PropertyValue> original;21
22
if (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues) {23
mpvs = (MutablePropertyValues) pvs;24
if (mpvs.isConverted()) {25
// Shortcut: use the pre-converted values as-is.26
try {27
bw.setPropertyValues(mpvs);28
return;29
}30
catch (BeansException ex) {31
throw new BeanCreationException(32
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);33
}34
}35
original = mpvs.getPropertyValueList();36
}37
else {38
original = Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues());39
}40
41
TypeConverter converter = getCustomTypeConverter();42
if (converter == null) {43
converter = bw;44
}45
BeanDefinitionValueResolver valueResolver = new BeanDefinitionValueResolver(this, beanName, mbd, converter);46
47
// Create a deep copy, resolving any references for values.48
List<PropertyValue> deepCopy = new ArrayList<>(original.size());49
boolean resolveNecessary = false;50
for (PropertyValue pv : original) {51
if (pv.isConverted()) {52
deepCopy.add(pv);53
}54
else {55
String propertyName = pv.getName();56
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();57
Object resolvedValue = valueResolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(pv, originalValue);58
Object convertedValue = resolvedValue;59
boolean convertible = bw.isWritableProperty(propertyName) &&60
!PropertyAccessorUtils.isNestedOrIndexedProperty(propertyName);61
if (convertible) {62
convertedValue = convertForProperty(resolvedValue, propertyName, bw, converter);63
}64
// Possibly store converted value in merged bean definition,65
// in order to avoid re-conversion for every created bean instance.66
if (resolvedValue == originalValue) {67
if (convertible) {68
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);69
}70
deepCopy.add(pv);71
}72
else if (convertible && originalValue instanceof TypedStringValue &&73
!((TypedStringValue) originalValue).isDynamic() &&74
!(convertedValue instanceof Collection || ObjectUtils.isArray(convertedValue))) {75
pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue);76
deepCopy.add(pv);77
}78
else {79
resolveNecessary = true;80
deepCopy.add(new PropertyValue(pv, convertedValue));81
}82
}83
}84
if (mpvs != null && !resolveNecessary) {85
mpvs.setConverted();86
}87
88
// Set our (possibly massaged) deep copy.89
try {90
bw.setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(deepCopy));91
}92
catch (BeansException ex) {93
throw new BeanCreationException(94
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex);95
}96
}注意,现在的PropertyValues 都是字符串,没有值的,这个方法的作用就是获取值,关键代码:
Object resolvedValue = valueResolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(pv, originalValue)
该方法会获取 pvName 所对应的容器value,该方法内部会调用 BeanWrapperImpl的resolveReference(argName, ref) 方法,我们看看该方法:
/**
* Resolve a reference to another bean in the factory.
*/
@Nullable
private Object resolveReference(Object argName, RuntimeBeanReference ref) {
try {
Object bean;
String refName = ref.getBeanName();
refName = String.valueOf(doEvaluate(refName));
if (ref.isToParent()) {
if (this.beanFactory.getParentBeanFactory() == null) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Can't resolve reference to bean '" + refName +
"' in parent factory: no parent factory available");
}
bean = this.beanFactory.getParentBeanFactory().getBean(refName);
}
else {
bean = this.beanFactory.getBean(refName);
this.beanFactory.registerDependentBean(refName, this.beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof NullBean) {
bean = null;
}
return bean;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Cannot resolve reference to bean '" + ref.getBeanName() + "' while setting " + argName, ex);
}
}1
33
1
/**2
* Resolve a reference to another bean in the factory.3
*/4
5
private Object resolveReference(Object argName, RuntimeBeanReference ref) {6
try {7
Object bean;8
String refName = ref.getBeanName();9
refName = String.valueOf(doEvaluate(refName));10
if (ref.isToParent()) {11
if (this.beanFactory.getParentBeanFactory() == null) {12
throw new BeanCreationException(13
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,14
"Can't resolve reference to bean '" + refName +15
"' in parent factory: no parent factory available");16
}17
bean = this.beanFactory.getParentBeanFactory().getBean(refName);18
}19
else {20
bean = this.beanFactory.getBean(refName);21
this.beanFactory.registerDependentBean(refName, this.beanName);22
}23
if (bean instanceof NullBean) {24
bean = null;25
}26
return bean;27
}28
catch (BeansException ex) {29
throw new BeanCreationException(30
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,31
"Cannot resolve reference to bean '" + ref.getBeanName() + "' while setting " + argName, ex);32
}33
}其中有一行熟悉的代码:bean = this.beanFactory.getBean(refName),对,这里就是发生递归的地方。该方法会拿着属性名称从容器中获取实例。
我们回到 applyPropertyValues 方法。此时deepCopy 集合已经有值了,不再仅仅是字符串了。
然后调用 setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(deepCopy)) 方法, 该方法会调用 AbstractPropertyAccessor.setPropertyValues 方法完成注入,而该方法会循环元素列表, 循环中调用 setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) 方法, 该方法setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv)最后会调用 nestedPa.setPropertyValue(tokens, pv) 方法, 该方法又会调用 processLocalProperty(tokens, pv) 方法,该方法最后又会调用 ph.setValue(valueToApply) 方法,也就是BeanWrapperImpl.setValue() 方法,终于,我们要看到反射了,看到反射说明到了尽头。
@Override
public void setValue(final @Nullable Object value) throws Exception {
final Method writeMethod = (this.pd instanceof GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor ?
((GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor) this.pd).getWriteMethodForActualAccess() :
this.pd.getWriteMethod());
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
return null;
});
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () ->
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value), acc);
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException ex) {
throw ex.getException();
}
}
else {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value);
}
}
}1
24
1
2
public void setValue(final Object value) throws Exception {3
final Method writeMethod = (this.pd instanceof GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor ?4
((GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor) this.pd).getWriteMethodForActualAccess() :5
this.pd.getWriteMethod());6
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {7
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {8
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);9
return null;10
});11
try {12
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () ->13
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value), acc);14
}15
catch (PrivilegedActionException ex) {16
throw ex.getException();17
}18
}19
else {20
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);21
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value);22
}23
}24
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号