Blog作业01
题目集1~3总结
一、前言
前三次题目集的知识点基本涵盖了JAVA的大部分基础语法,以及初步的面向对象编程思想,题目量不多,但是每一个题目的难度普遍较上一个学期有着更高的要求,更加考察学生对程序设计的要求,而不是停留在上一个学期一般,对语法的考察。
二、设计与分析
输入三角形三条边,判断该三角形为什么类型的三角形。
输入格式:
在一行中输入三角形的三条边的值(实型数),可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔,其中三条边的取值范围均为[1,200]。
输出格式:
(1)如果输入数据非法,则输出“Wrong Format”; (2)如果输入数据合法,但三条边不能构成三角形,则输出“Not a triangle”; (3)如果输入数据合法且能够成等边三角形,则输出“Equilateral triangle”; (3)如果输入数据合法且能够成等腰直角三角形,则输出“Isosceles right-angled triangle”; (5)如果输入数据合法且能够成等腰三角形,则输出“Isosceles triangle”; (6)如果输入数据合法且能够成直角三角形,则输出“Right-angled triangle”; (7)如果输入数据合法且能够成一般三角形,则输出“General triangle”。
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
50 50 50.0输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Equilateral triangle输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
60.2 60.2 80.56输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Isosceles triangle输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0.5 20.5 80输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format我的答案:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double[] angle = new double[3];
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){ //输入三边长度
double x = input.nextDouble();
if(x <= 200.0 && x >= 1.0){
angle[i] = x;
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++){ //将三边按大小排序
for(int j = 0; j < 2-i; j++){
if(angle[j] > angle[j+1]){
double temp = angle[j];
angle[j] = angle[j+1];
angle[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
//判断是否构成三角形
if(angle[0] + angle[1] < angle[2] || Math.abs(angle[0]+angle[1] - angle[2]) < 1e-6){
System.out.println("Not a triangle");
return;
}
//判断是否等边
if(Math.abs(angle[0] - angle[1]) < 1e-6 && Math.abs(angle[1] - angle[2]) < 1e-6 ){
System.out.println("Equilateral triangle");
return;
}
//判断是否等腰直角
if(Math.abs(angle[0]*angle[0] + angle[1]*angle[1] - angle[2]*angle[2]) < 1e-6 && Math.abs(angle[0] - angle[1]) < 1e-6){
System.out.println("Isosceles right-angled triangle");
return;
}
//判断是否等腰
if( Math.abs(angle[0] - angle[1]) < 1e-6||Math.abs(angle[2] - angle[1]) < 1e-6){
System.out.println("Isosceles triangle");
return;
}
//判断是否直角
if(Math.abs(angle[0]*angle[0] + angle[1]*angle[1] - angle[2]*angle[2]) < 1e-6){
System.out.println("Right-angled triangle");
return;
}
else{
System.out.println("General triangle");
}
}
}
我的分析
输入年月日的值(均为整型数),输出该日期的下一天。 其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1820,2020] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取值范围为[1,31] 。 注意:不允许使用Java中和日期相关的类和方法。
要求:Main类中必须含有如下方法,签名如下:
public static void main(String[] args);//主方法
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) ;//判断year是否为闰年,返回boolean类型
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day);//判断输入日期是否合法,返回布尔值
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) ; //求输入日期的下一天输入格式:
在一行内输入年月日的值,均为整型数,可以用一到多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
- 当输入数据非法及输入日期不存在时,输出“Wrong Format”;
- 当输入日期合法,输出下一天,格式如下:Next date is:年-月-日
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2020 3 10输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Next date is:2020-3-11输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2025 2 10输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
我的答案:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int year;
static int month;
static int day;
//主方法
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
year = input.nextInt();
month = input.nextInt();
day = input.nextInt();
if (!checkInputValidity(year,month,day)){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else
nextDate(year,month,day);
}
//判断year是否为闰年,返回boolean类型
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year){
return (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0;
}
//判断输入日期是否合法,返回布尔值
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day){
//判断年份是否合理
if(year < 1820 || year > 2020){
return false;
}
//判断月份是否合理
if(month <= 0 || month > 12){
return false;
}
//判断日期是否合理
if (month == 1 || month == 3 || month == 5 || month == 7 || month == 8 || month == 10 || month == 12) {
return day > 0 && day <= 31;
}
else if (month == 2) {
if (isLeapYear(year))
return day > 0 && day <= 29;
else
return day > 0 && day <= 28;
}
else{
return day > 0 && day <= 30;
}
}
//求输入日期的下一天
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) {
//大月
if (month == 1 || month == 3 || month == 5 || month == 7 || month == 8 || month == 10 || month == 12) {
if (day==31) {
day = 1;
month++;
}
else
day++;
}
//闰月
else if (month == 2) {
if(isLeapYear(year)){
if (day == 29){
day = 1;
month++;
}
else {
day++;
}
}
else {
if(day == 28){
day = 1;
month++;
}
else {
day++;
}
}
}
//平月
else {
if(day == 30){
day = 1;
month++;
}
else {
day++;
}
}
if(month==13){
month = 1;
year++;
}
System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
}
}
我的分析
输入年月日的值(均为整型数),同时输入一个取值范围在[-10,10] 之间的整型数n,输出该日期的前n天(当n > 0时)、该日期的后n天(当n<0时)。
其中年份取值范围为 [1820,2020] ,月份取值范围为[1,12] ,日期取值范围为[1,31] 。
注意:不允许使用Java中任何与日期有关的类或方法。
输入格式:
在一行中输入年月日的值以及n的值,可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
- 当输入的年、月、日以及n的值非法时,输出“Wrong Format”;
- 当输入数据合法时,输出“n days ago is:年-月-日”
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2018 6 19 8 输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
8 days ago is:2018-6-11输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2018 6 19 -8 输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
-8 days ago is:2018-6-27
我的答案:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
//主方法
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = input.nextInt();
int month = input.nextInt();
int day = input.nextInt();
int x = input.nextInt();
if(x < -10 || x > 10){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
if (!checkInputValidity(year,month,day)) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
findObjectDay(year,month,day,x);
}
//判断year是否为闰年,返回boolean类型
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year){
return (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0;
}
//判断输入日期是否合法,返回布尔值
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day){
//判断年份是否合理
if(year < 1820 || year > 2020){
return false;
}
//判断月份是否合理
if(month <= 0 || month > 12){
return false;
}
//判断日期是否合理
if (month == 1 || month == 3 || month == 5 || month == 7 || month == 8 || month == 10 || month == 12) {
return day > 0 && day <= 31;
}
else if (month == 2) {
if (isLeapYear(year))
return day > 0 && day <= 29;
else
return day > 0 && day <= 28;
}
else{
return day > 0 && day <= 30;
}
}
//求输入日期的上一天
public static void pastDate(int year,int month,int day, int object) {
if(object < 0) {
object = -object;
}
for (int i = 0; i < object; i++){
//前一个月是大月
if ( month == 1 || month == 2 || month == 4 || month == 6 || month == 8 || month == 9 || month == 11) {
if(day == 1){
day = 31;
month--;
}
else {
day--;
}
}
//前一个月是闰月
else if(month == 3){
if (isLeapYear(year)){
if (day==1){
day = 29;
month--;
}
else {
day--;
}
}
else {
if (day==1){
day = 28;
month--;
}
else {
day--;
}
}
}
//前一个月是平月
else {
if (day==1){
day = 30;
month--;
}
else {
day--;
}
}
if(month==0){
month = 12;
year--;
}
}
System.out.println(object+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
}
//下N天日期
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day, int object) {
if(object < 0){
object = -object;
}
for(int i = 0; i < object; i++){
//大月
if (month == 1 || month == 3 || month == 5 || month == 7 || month == 8 || month == 10 || month == 12) {
if (day==31) {
day = 1;
month++;
}
else
day++;
}
//闰月
else if (month == 2) {
if(isLeapYear(year)){
if (day == 29){
day = 1;
month++;
}
else {
day++;
}
}
else {
if(day == 28){
day = 1;
month++;
}
else {
day++;
}
}
}
//平月
else {
if(day == 30){
day = 1;
month++;
}
else {
day++;
}
}
if(month==13){
month = 1;
year++;
}
}
System.
out.println(-object+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
}
public static void findObjectDay(int year, int month, int day, int object){
if(object == 0){
System.out.println(object+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
}
else if (object < 0)
nextDate(year,month,day,object);
else
pastDate(year,month,day,object);
}
}
我的分析:
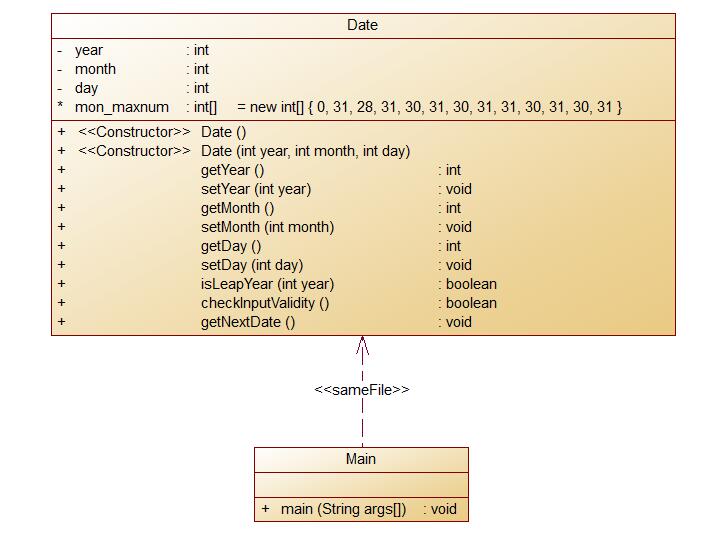
定义一个类Date,包含三个私有属性年(year)、月(month)、日(day),均为整型数,其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1900,2000] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取值范围为[1,31] 。 注意:不允许使用Java中和日期相关的类和方法,否则按0分处理。
要求:Date类结构如下图所示:
输入格式:
在一行内输入年月日的值,均为整型数,可以用一到多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
- 当输入数据非法及输入日期不存在时,输出“Date Format is Wrong”;
- 当输入日期合法,输出下一天,格式如下:Next day is:年-月-日
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1912 12 25输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Next day is:1912-12-26输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2001 2 30输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Date Format is Wrong
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Date today = new Date();
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
today.setYear(input.nextInt());
today.setMonth(input.nextInt());
today.setDay(input.nextInt());
if (!today.checkInputValidity(today.getYear(), today.getMonth(), today.getDay())){
System.out.println("Date Format is Wrong");
}
else
today.nextDate(today.getYear(), today.getMonth(), today.getDay());
}
}
class Date {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
//主方法
void setYear(int year){
this.year = year;
}
int getYear(){
return year;
}
void setMonth(int month){
this.month = month;
}
int getMonth(){
return month;
}
void setDay(int day){
this.day = day;
}
int getDay(){
return day;
}
//判断year是否为闰年,返回boolean类型
boolean isLeapYear(int year){
return (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0;
}
//判断输入日期是否合法,返回布尔值
boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day){
//判断年份是否合理
if(year < 1900 || year > 2000){
return false;
}
//判断月份是否合理
if(month <= 0 || month > 12){
return false;
}
//判断日期是否合理
if (month == 1 || month == 3 || month == 5 || month == 7 || month == 8 || month == 10 || month == 12) {
return day > 0 && day <= 31;
}
else if (month == 2) {
if (isLeapYear(year))
return day > 0 && day <= 29;
else
return day > 0 && day <= 28;
}
else{
return day > 0 && day <= 30;
}
}
//求输入日期的下一天
void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) {
//大月
if (month == 1 || month == 3 || month == 5 || month == 7 || month == 8 || month == 10 || month == 12) {
if (day==31) {
day = 1;
month++;
}
else
day++;
}
//闰月
else if (month == 2) {
if(isLeapYear(year)){
if (day == 29){
day = 1;
month++;
}
else {
day++;
}
}
else {
if(day == 28){
day = 1;
month++;
}
else {
day++;
}
}
}
//平月
else {
if(day == 30){
day = 1;
month++;
}
else {
day++;
}
}
if(month==13){
month = 1;
year++;
}
System.out.println("Next day is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
}
}
我的分析:
编写程序性,实现对简单多项式的导函数进行求解。详见作业指导书。 OO作业3-3题目说明.pdf
输入格式:
在一行内输入一个待计算导函数的表达式,以回车符结束。
输出格式:
- 如果输入表达式不符合上述表达式基本规则,则输出“Wrong Format”。
- 如果输入合法,则在一行内正常输出该表达式的导函数,注意以下几点: 结果不需要排序,也不需要化简;
- 当某一项为“0”时,则该项不需要显示,但如果整个导函数结果为“0”时,则显示为“0”;
- 当输出结果第一项系数符号为“+”时,不输出“+”;
- 当指数符号为“+”时,不输出“+”;
- 当指数值为“0”时,则不需要输出“x^0”,只需要输出其系数即可。
输出格式见输入输出示例。
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
-2* x^-2+ 5*x^12-4*x+ 12输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
4*x^-3+60*x^11-4输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2*x^6-0*x^7+5输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
我的答案:
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String expression = input.nextLine();//输入表达式
if(checkChar(expression)||checkSpace(expression)){//检查是否含有非法字符和空格
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
return;
}
StringBuffer[] utils = new StringBuffer[100];
if(killSpace(expression).length()==0){//去空格
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
return;
}
splitExpression(utils,killSpace(expression));//将去空格后的表达式分割成一个个单项式
if(utils[0]==null){
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
return;
}
for(int i = 0; utils[i] != null; i++){
if(!Monomial.checkMonomial(utils[i])){//检查单项式是否合法
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
return;
}
}
Monomial[] monomials = new Monomial[utils.length];//封装到类
//monomials[0] = null;
for(int i = 0; utils[i]!=null; i++){
monomials[i] = new Monomial();
monomials[i].setMonomial(utils[i]);
monomials[i].derivation();
}
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; monomials[i]!=null; i++){
if(monomials[i].getMonomial()!=null)
result.append(monomials[i].getMonomial());
}
if(result.length() == 0){
System.out.print("0");
return;
}
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("x");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(expression);
if(result.charAt(0)=='+'){
result.delete(0,1);
}
System.out.print(result);
}
//检查是否含有非法字符
public static boolean checkChar(String expression){
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("[^\\sx*\\-+^\\d]");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(expression);
return matcher.find();
}
//检查是否含有非法空格
public static boolean checkSpace(String expression){
//Pattern pattern0 = Pattern.compile("^[+-]\\s+\\d+.*");//检测开头整数
Pattern pattern1 = Pattern.compile("\\d\\s+\\d");//两数之间
//Pattern pattern2 = Pattern.compile("x\\s*\\^\\s*[+-]\\s+\\d");//指数
//Pattern pattern3 = Pattern.compile("^[+-]0$");//开头0为带符号
//Matcher matcher0 = pattern0.matcher(expression);
Matcher matcher1 = pattern1.matcher(expression);
//Matcher matcher2 = pattern2.matcher(expression);
//Matcher matcher3 = pattern3.matcher(expression);
return matcher1.find();
}
//去空格
public static String killSpace(String expression){
StringBuilder unSpaceExpression = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0; i < expression.length(); i++){
if(expression.charAt(i)!=32){
unSpaceExpression.append(expression.charAt(i));
}
}
return unSpaceExpression.toString();
}
//分割表达式
public static void splitExpression(StringBuffer[] utils, String unSpaceExpression){
for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < unSpaceExpression.length(); i++){
if(utils[j]==null){
utils[j] = new StringBuffer();
}
if ((unSpaceExpression.charAt(i) == '+' || unSpaceExpression.charAt(i)== '-') && i-1 >=0 && unSpaceExpression.charAt(i-1)!='^') {
j++;
}
if(utils[j]==null){
utils[j] = new StringBuffer();
}
utils[j].append(unSpaceExpression.charAt(i));
}
}
//合并单项式
}
//单项式类
class Monomial{
int type; //类型
private BigInteger coefficient; //系数
private BigInteger exponent; //指数
//检查单项式是否符合输入规范
static boolean checkMonomial(StringBuffer util){
Pattern pattern0 = Pattern.compile("^([+-]?)([1-9]\\d*)$"); //常数
Pattern pattern1 = Pattern.compile("^([+-]?)(?:x)$"); //+-x;
Pattern pattern2 = Pattern.compile("^([+-]?)([1-9]\\d*)(?:\\*)(?:x)$"); //-+ a * x;
Pattern pattern3 = Pattern.compile("^([-+]?)(?:x)(?:\\^)([-+]?)([1-9]\\d*)$"); //x^-+b;
Pattern pattern4 = Pattern.compile("^([+-]?)([1-9]\\d*)(?:\\*)(?:x)(?:\\^)([-+]?)([1-9]\\d*)$");//+- a * x ^ +- b;
//+-0
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^[+-]?0$");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(util.toString());
if(matcher.find()){
return true;
}
Matcher matcher0 = pattern0.matcher(util.toString());
if(matcher0.find())
return true;
Matcher matcher1 = pattern1.matcher(util.toString());
if(matcher1.find())
return true;
Matcher matcher2 = pattern2.matcher(util.toString());
if(matcher2.find())
return true;
Matcher matcher3 = pattern3.matcher(util.toString());
if(matcher3.find())
return true;
Matcher matcher4 = pattern4.matcher(util.toString());
return matcher4.find();
// if(matcher0.find())
// return true;
// if(matcher1.find())
// return true;
// if(matcher2.find())
// return true;
// if(matcher3.find())
// return true;
// if(matcher4.find())
// return true;
// // return matcher0.find() || matcher1.find() || matcher2.find() || matcher3.find() || matcher4.find();
// return false;
}
//为单项式对象属性赋值
void setMonomial(StringBuffer util){
Pattern pattern0 = Pattern.compile("^([+-]?)([1-9]\\d*)$"); //常数
Pattern pattern1 = Pattern.compile("^([+-]?)(?:x)$"); //+-x;
Pattern pattern2 = Pattern.compile("^([+-]?)([1-9]\\d*)(?:\\*)(?:x)$"); //-+ a * x;
Pattern pattern3 = Pattern.compile("^([-+]?)(?:x)(?:\\^)([-+]?)([1-9]\\d*)$"); //-+x^-+b;
Pattern pattern4 = Pattern.compile("^([+-]?)([1-9]\\d*)(?:\\*)(?:x)(?:\\^)([-+]?)([1-9]\\d*)$");//+- a * x ^ +- b;
Matcher matcher0 = pattern0.matcher(util);
Matcher matcher1 = pattern1.matcher(util);
Matcher matcher2 = pattern2.matcher(util);
Matcher matcher3 = pattern3.matcher(util);
Matcher matcher4 = pattern4.matcher(util);
//+-0
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^[-+]?0$");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(util.toString());
if(matcher.find()){
type = -1;
}
if(matcher0.find()){
type = 0;
coefficient = new BigInteger(matcher0.group(2));
if(matcher0.group(1).equals("-")){
coefficient = coefficient.subtract(coefficient).subtract(coefficient);
}
exponent = new BigInteger("0");
}
else if(matcher1.find()){
type = 1;
if(matcher1.group(1).equals("-"))
coefficient = new BigInteger("-1");
else
coefficient = new BigInteger("1");
exponent = new BigInteger("1");
}
else if(matcher2.find()){
type = 2;
coefficient = new BigInteger(matcher2.group(2));
if(matcher2.group(1).equals("-")){
coefficient = coefficient.subtract(coefficient).subtract(coefficient);
}
exponent = new BigInteger("1");
}
else if(matcher3.find()){
type = 3;
if(matcher3.group(1).equals("-"))
coefficient = new BigInteger("-1");
else
coefficient = new BigInteger("1");
exponent = new BigInteger(matcher3.group(3));
if(matcher3.group(2).equals("-")){
exponent = exponent.subtract(exponent).subtract(exponent);
}
}
else if(matcher4.find()){
type = 4;
coefficient = new BigInteger(matcher4.group(2));
if(matcher4.group(1).equals("-")){
coefficient = coefficient.subtract(coefficient).subtract(coefficient);
}
exponent = new BigInteger(matcher4.group(4));
if(matcher4.group(3).equals("-")){
exponent = exponent.subtract(exponent).subtract(exponent);
}
}
}
//对单项式进行求导操作
void derivation(){
if (type == 0) {
coefficient = BigInteger.valueOf(0);
exponent = BigInteger.valueOf(0);
type = -1;
} else if (type == 1) {
exponent = BigInteger.valueOf(0);
type = 0;
} else if (type == 2) {
exponent = BigInteger.valueOf(0);
type = 0;
} else if (type == 3) {
coefficient = coefficient.multiply(exponent);
exponent = exponent.subtract(BigInteger.valueOf(1));
if (exponent.equals(BigInteger.valueOf(1))) {
type = 2;
}
else if (exponent.equals(BigInteger.valueOf(0))) {
type = 0;
}
else if(!coefficient.equals(BigInteger.valueOf(1))&&!coefficient.equals(BigInteger.valueOf(-1))){
type = 4;
}
} else if (type == 4) {
coefficient = coefficient.multiply(exponent);
if(coefficient.equals(BigInteger.valueOf(1))||coefficient.equals(BigInteger.valueOf(-1))){
type = 3;
}
exponent = exponent.subtract(BigInteger.valueOf(1));
if (exponent.equals(BigInteger.valueOf(1))) {
type = 2;
}
}
}
//返回单项式
String getMonomial(){
if (type == 0) {
if (coefficient.compareTo(BigInteger.valueOf(0)) == 1) {
return "+" + coefficient;
} else {
return "" + coefficient;
}
} else if (type == 1) {
if (coefficient.compareTo(BigInteger.valueOf(0)) == 1) {
return "+x";
} else {
return "-x";
}
} else if (type == 2) {//coefficient>0
if (coefficient.compareTo(BigInteger.valueOf(0)) == 1) {
return "+" + coefficient + "*x";
} else {
return "" + coefficient + "*x";
}
} else if (type == 3) {
if (coefficient.compareTo(BigInteger.valueOf(0)) == 1) {
//return "+" + coefficient + "*x^" + exponent;
return "x^" + exponent;
} else {
//return coefficient + "*x^" + exponent;
return "-x^" + exponent;
}
} else if (type == 4) {
if (coefficient.compareTo(BigInteger.valueOf(0)) == 1) {
return "+" + coefficient + "*x^" + exponent;
} else {
return coefficient + "*x^" + exponent;
}
}
return null;
}
}
我的分析:
心得:
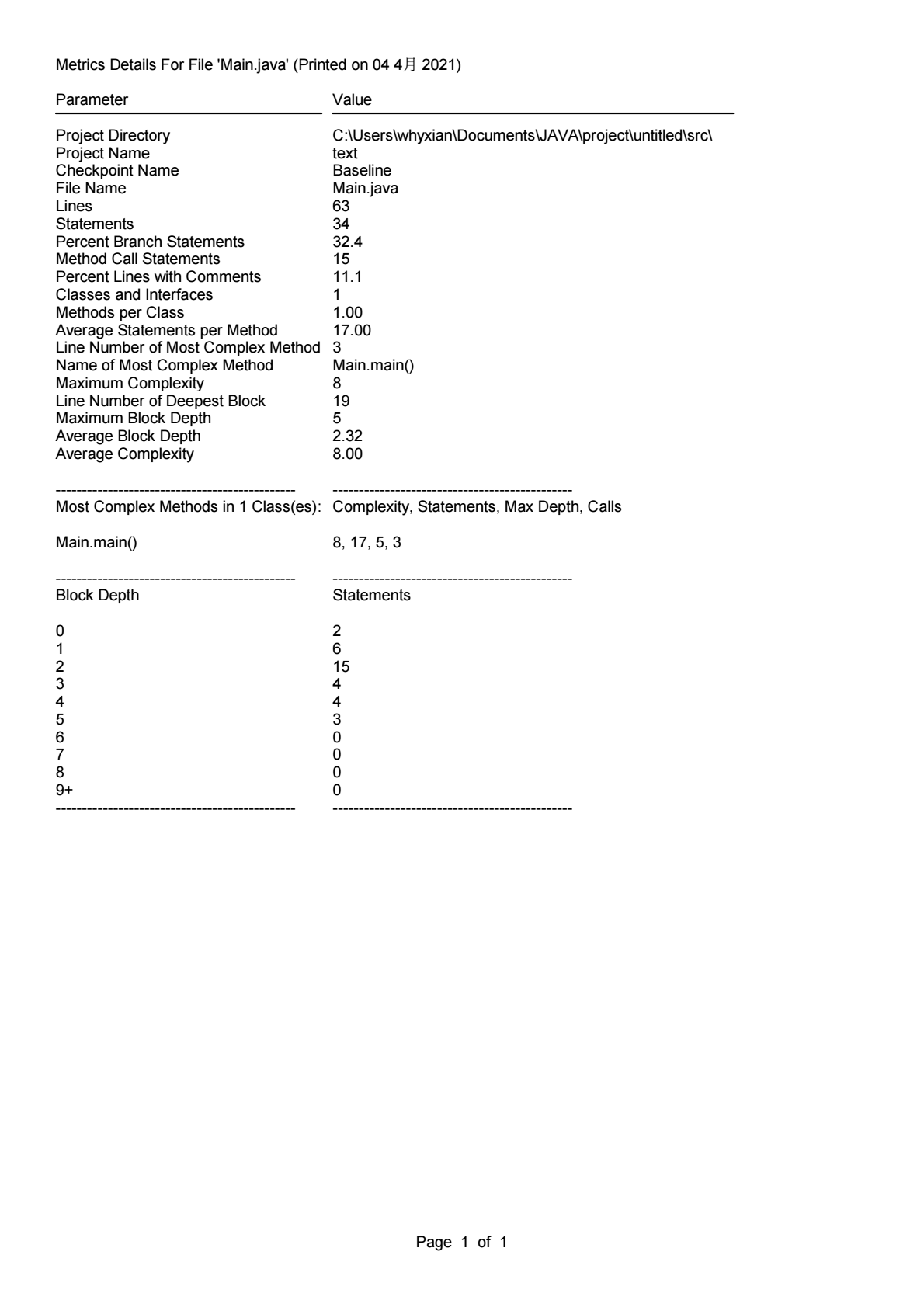
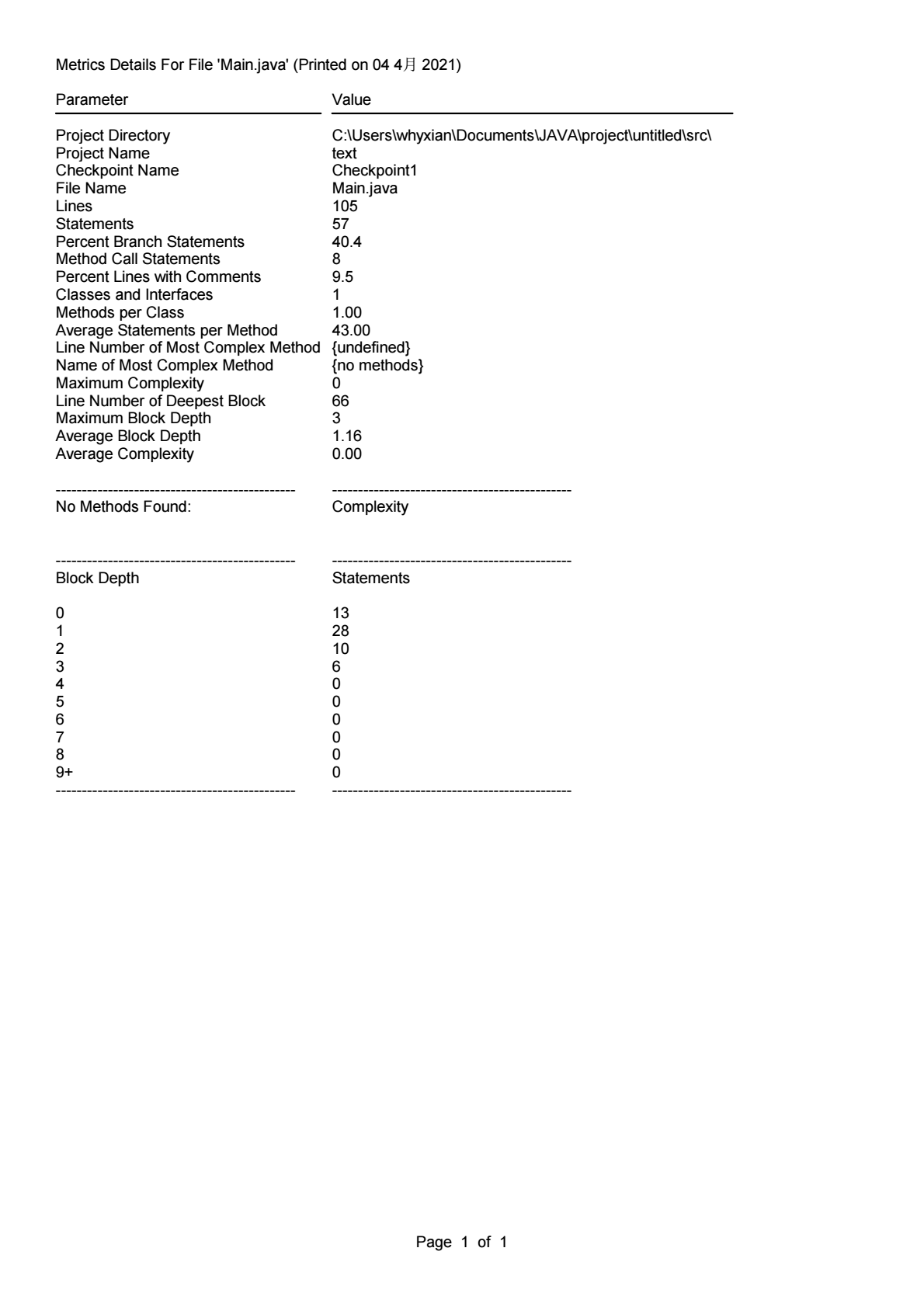
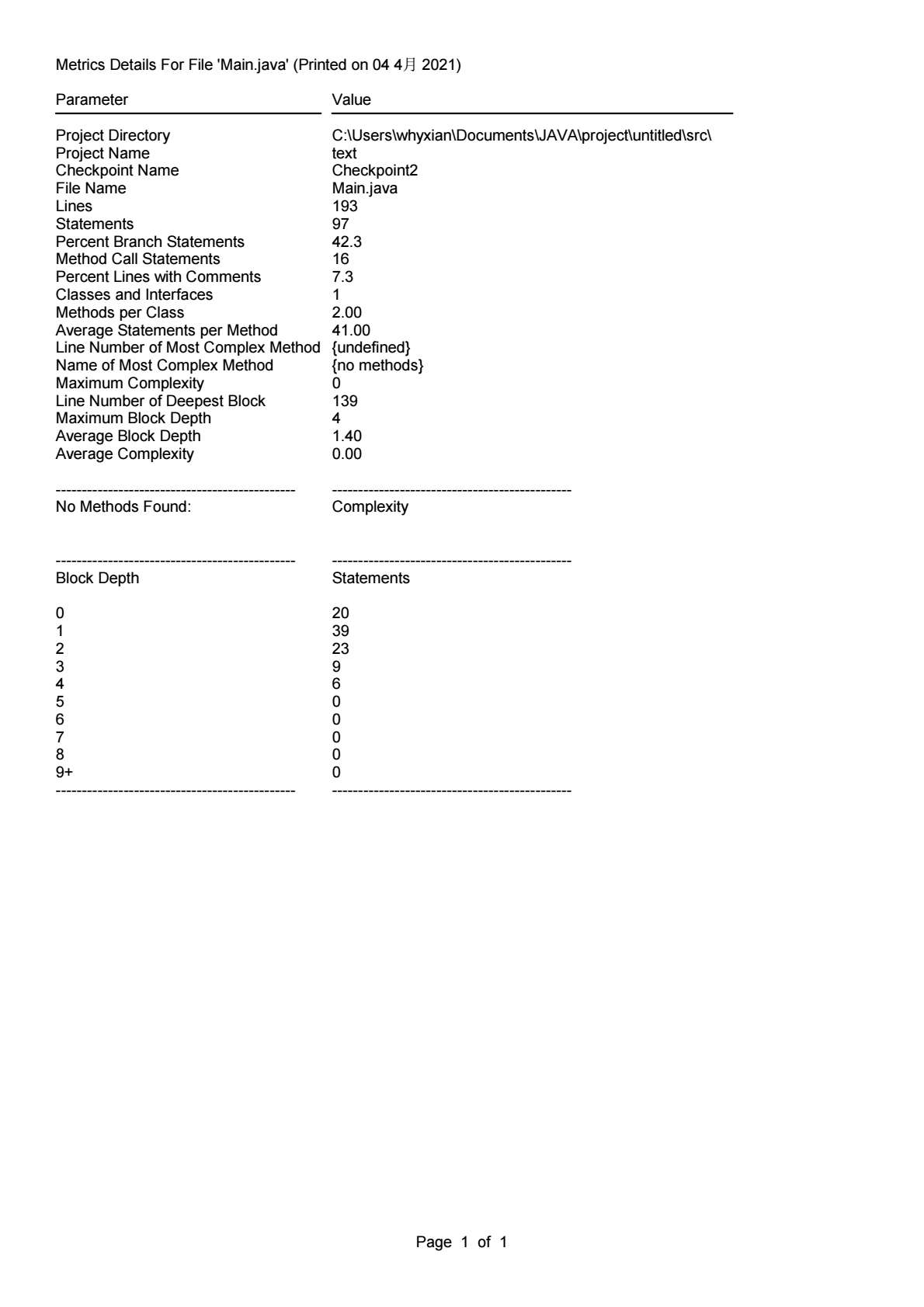
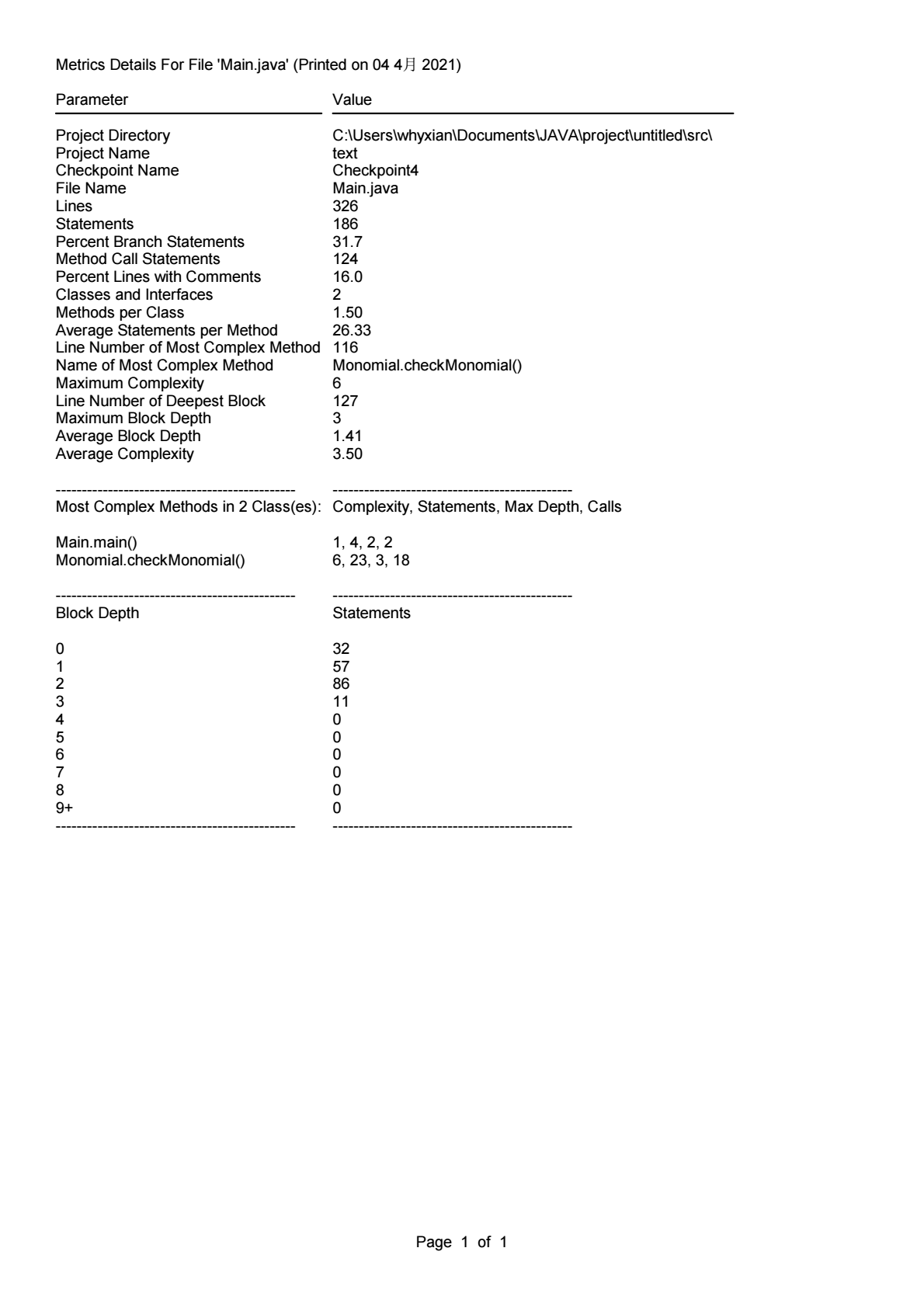
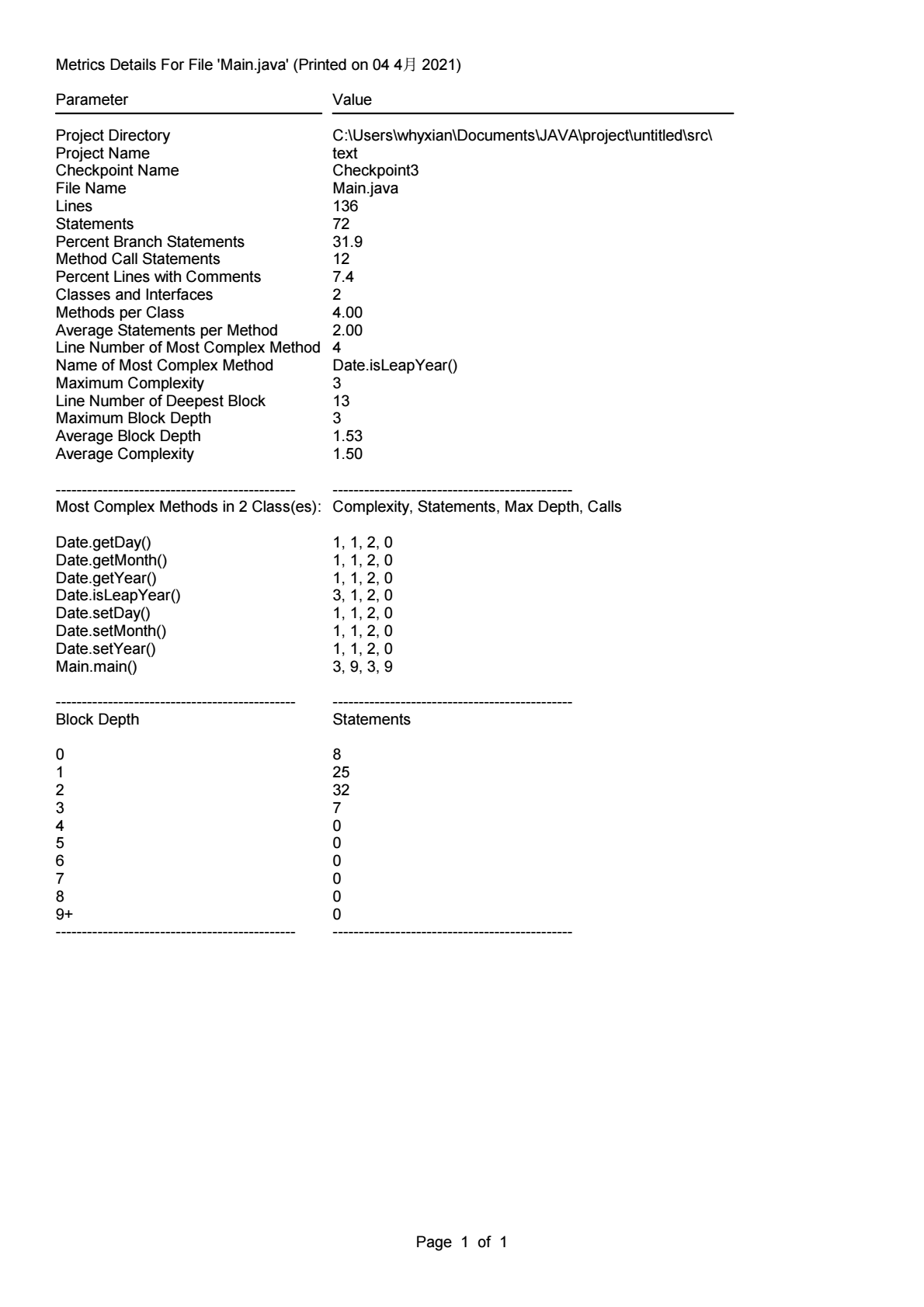
这几次作业的难度普遍跟上一学期不是一个量级,要是没有寒假前两个星期做课设的经验是很难有一个比较清晰的思路的,虽然涉及到类,但是很多题目依旧是可以通过C语言的基础解决的,但是的确是让我对JAVA的设计思想有了一个初步的认识。通过source monitor分析得出的结果可以看出,目前的编码水平还是存在着十分大的提升空间,以及对面向对象的程序设计缺乏更加深刻的认识,只是停留在初学者水平。
三、踩坑心得
这几次作业给我造成最大阻碍的就是题目集3的7-3,由于要使用到字符串数组,就不可避免的要注意指针问题,在初期编码过程中由于忽视的空指针的严重性,导致后期代码漏洞百出,几乎不可用,只能花费大量时间一条条代码调试找出指针漏洞全部堵上,因此在程序设计中每一条语句都要慎重考量,漏洞积少成多必将酿成大错,耗费大量时间。
四、改进建议
1、类的职责可以更加单一,分工可以更加明确
2、指针的使用可以更加合理
3、代码复用性有待提高
五、总结
1、学习到了java的基本语法
2、接触到了面向对象的基础思维
3、程序设计的思路更加清晰
4、掌握到了基本的调试方法
4、希望老师在题目结束后可以给出讲解




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号