装饰器模式
装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern)是在不必改变原类文件且不使用继承的情况下,动态地扩展一个对象的功能。通过创建了一个装饰类,用来包装原有的类,来通过额外的功能。
- 抽象组件(Component):抽象接口,规范接收附加功能的对象。
- 具体构件(Concrete Component):接收附加功能的类。
- 装饰(Decorator):持有 Component 对象的实例,并实现与 Component 接口一致的接口。
- 具体装饰(Concrete Decorator):负责给组件对象添加上附加的功能。
UML:

Cast:以火锅为例
HotPot:火锅抽象类(Component)

1 public abstract class HotPot { 2 3 protected String description; 4 private int price = 0; 5 6 public String getDescription() { 7 return description; 8 } 9 10 public void setDescription(String description) { 11 this.description = description; 12 } 13 14 public int getPrice() { 15 return price; 16 } 17 18 public void setPrice(int price) { 19 this.price = price; 20 } 21 22 // 计费方法 23 public abstract int cost(); 24 }
各种锅底:(ConcreteComponent)

1 // 经典麻辣锅底 2 public class ClassifySpicy extends HotPot { 3 public ClassifySpicy() { 4 setPrice(101); 5 setDescription("经典麻辣锅底 ¥" + 101); 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 public int cost() { 10 return super.getPrice(); 11 } 12 } 13 14 // 清油锅底 15 public class Oily extends HotPot { 16 17 public Oily() { 18 setPrice(78); 19 setDescription("清油锅底 ¥" + getPrice()); 20 } 21 22 @Override 23 public int cost() { 24 return super.getPrice(); 25 } 26 } 27 28 // 番茄清油锅底 29 public class TomatoOily extends HotPot { 30 public TomatoOily() { 31 setPrice(101); 32 setDescription("番茄清油锅底 ¥" + getPrice()); 33 } 34 35 @Override 36 public int cost() { 37 return super.getPrice(); 38 } 39 }
Decorator:

1 public class Decorator extends HotPot { 2 private HotPot obj; 3 protected int num; 4 public Decorator(HotPot hotPot) { 5 this.obj = hotPot; 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 public int cost() { 10 return obj.cost() + this.getPrice(); 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 public String getDescription() { 15 return obj.getDescription() + super.getDescription(); 16 } 17 }
各种配菜(ConcreteDecorator):

1 // 生菜 2 public class Lettuce extends Decorator { 3 public Lettuce(HotPot hotPot, int... num) { 4 super(hotPot); 5 if (num.length != 0) 6 this.num = num[0]; 7 else 8 this.num = 1; 9 setPrice(this.num * 10); 10 setDescription("\n生菜 x " + this.num + "\t ¥" + getPrice()); 11 } 12 } 13 14 // 金针菇 15 public class EnokiMushroom extends Decorator { 16 public EnokiMushroom(HotPot hotPot, int... num) { 17 super(hotPot); 18 if (num.length != 0) 19 this.num = num[0]; 20 else 21 this.num = 1; 22 setPrice(this.num * 14); 23 setDescription("\n金针菇 x " + this.num + "\t ¥" + getPrice()); 24 } 25 } 26 27 // 藕片 28 public class LotusRoot extends Decorator { 29 public LotusRoot(HotPot hotPot, int... num) { 30 super(hotPot); 31 if (num.length != 0) 32 this.num = num[0]; 33 else 34 this.num = 1; 35 setPrice(this.num * 10); 36 setDescription("\n藕片 x " + this.num + "\t ¥" + getPrice()); 37 } 38 } 39 40 // 鹌鹑蛋 41 public class QuailEgg extends Decorator { 42 public QuailEgg(HotPot hotPot, int... num) { 43 super(hotPot); 44 if (num.length != 0) 45 this.num = num[0]; 46 else 47 this.num = 1; 48 setPrice(this.num * 14); 49 setDescription("\n鹌鹑蛋 x " + this.num + "\t ¥" + getPrice()); 50 } 51 } 52 53 // 肥牛 54 public class BeefRoll extends Decorator { 55 public BeefRoll(HotPot hotPot, int... num) { 56 super(hotPot); 57 if (num.length != 0) 58 this.num = num[0]; 59 else 60 this.num = 1; 61 setPrice(this.num * 35); 62 setDescription("\n肥牛 x " + this.num + "\t ¥" + getPrice()); 63 } 64 } 65 66 // 鸭血 67 public class GooseBlood extends Decorator { 68 public GooseBlood(HotPot hotPot, int... num) { 69 super(hotPot); 70 if (num.length != 0) 71 this.num = num[0]; 72 else 73 this.num = 1; 74 setPrice(this.num * 21); 75 setDescription("\n鸭血 x " + this.num + "\t ¥" + getPrice()); 76 } 77 } 78 79 // 毛肚 80 public class HairyBelly extends Decorator { 81 public HairyBelly(HotPot hotPot, int... num) { 82 super(hotPot); 83 if (num.length != 0) 84 this.num = num[0]; 85 else 86 this.num = 1; 87 setPrice(this.num * 31); 88 setDescription("\n毛肚 x " + this.num + "\t ¥" + getPrice()); 89 } 90 } 91 92 // 虾滑 93 public class ShrimpPaste extends Decorator { 94 public ShrimpPaste(HotPot hotPot, int... num) { 95 super(hotPot); 96 if (num.length != 0) 97 this.num = num[0]; 98 else 99 this.num = 1; 100 setPrice(this.num * 28); 101 setDescription("\n虾滑 x " + this.num + "\t ¥" + getPrice()); 102 } 103 }
Client:

1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 HotPot order = new ClassifySpicy(); 3 4 order = new Lettuce(order); 5 order = new EnokiMushroom(order, 2); 6 order = new LotusRoot(order); 7 order = new QuailEgg(order); 8 order = new BeefRoll(order, 2); 9 order = new GooseBlood(order); 10 order = new HairyBelly(order); 11 order = new ShrimpPaste(order); 12 13 System.out.println(order.getDescription()); 14 System.out.println("------------------\n合计:\t\t¥" + order.cost()); 15 16 17 }
运行结果:
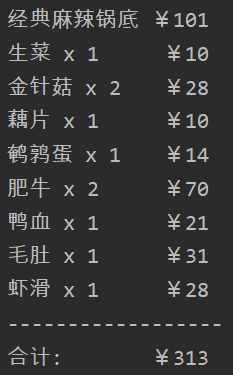
优点:
装饰类和被装饰类可以独立发展,不会相互耦合,符合开闭原则
装饰器模式是继承的一个替代模式,符合合成复用原则
装饰器模式可以动态扩展一个实现类的功能
缺点:
比继承更加灵活机动的特性,也意味着更加多的复杂性。
会产生较多的细粒度对象过度使用,会使程序变得很复杂。
装饰器模式针对抽象组件(Component)编程。如果要针对具体组件编程,就应该重新思考应用的架构,以及装饰者是否合适。当然也可以改变Component接口,增加新的公开的行为,实现“半透明”的装饰者模式。在实际项目中要做出最佳选择
适用情况:
需要扩展一个类的功能,或给一个类添加附加职责。
需要动态的给一个对象添加功能,且这些功能可以再动态的撤销。
当不能采用生成子类的方法进行扩充时。一种情况是,可能有大量独立的扩展,为支持每一种组合将产生大量的子类,使得子类数目呈爆炸性增长。另一种情况可能是因为类定义被隐藏,或类定义不能用于生成子类。
模式简化:
如果只有一个Concrete Component类而没有抽象的Component接口时,可以让Decorator继承Concrete Component。
如果只有一个Concrete Decorator类时,可以将Decorator和Concrete Decorator合并。
java IO 流是典型的装饰器模式
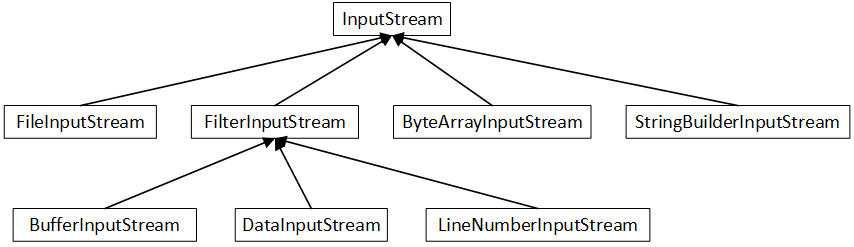
InputStream 是抽象类,对应 component
![]()
FileInputStream 对应 concreteComponent
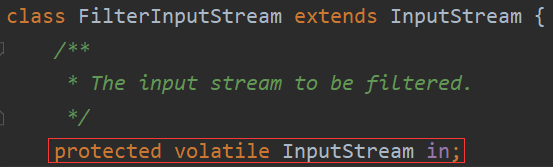
FilterInputStream 对应 Decorator,持有 InputStream(被修饰对象)
BufferInputStream、DataInputStream、LineNumberInputStream 对应 concreteDecorator




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号