Java 多线程基础
方法1:写一个继承 Thread 的类,重写 run() 方法

1 public class MyThread1 extends Thread { 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 5 System.out.println("run: " + i); 6 try { 7 sleep(10); 8 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 9 e.printStackTrace(); 10 } 11 } 12 } 13 14 // main线程为主线程 15 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 16 17 MyThread1 myThread1 = new MyThread1();// 创建线程对象 18 19 myThread1.start();// 调用 start() 方法开启线程 20 21 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 22 System.out.println("main: " + i); 23 sleep(10); 24 } 25 } 26 }
方法2:实现 runnable 接口,重写 run() 方法

1 public class MyThread2 implements Runnable { 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 5 System.out.println("run: " + i); 6 try { 7 Thread.sleep(10); 8 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 9 e.printStackTrace(); 10 } 11 } 12 } 13 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 16 // 创建线程对象 17 MyThread2 myThread2 = new MyThread2(); 18 19 Thread myThread2Test = new Thread(myThread2); 20 21 myThread2Test.start();// 开启线程 22 23 for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 24 System.out.println("main: " + i); 25 try { 26 Thread.sleep(10); 27 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } 30 } 31 32 } 33 }
结果如下
1、 2、 3、
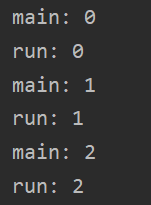
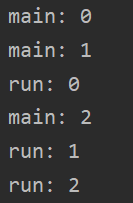
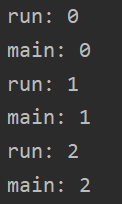
运行结果不同,因为线程开启不一定立即执行,各进程由CUP调度执行
View Code




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号