【图论基础题】
【图论基础题】
哎哎全是结论题大佬呜呜呜啊啊啊呜呜呜
画图可得
Tree Jumps
https://codeforces.com/contest/2070/problem/D
思路
考虑单点贡献为上一层的贡献扣掉父节点贡献
最后将全部结点贡献相加即可
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
ll abss(ll a){return a>0?a:-a;}
ll max_(ll a,ll b){return a>b?a:b;}
ll min_(ll a,ll b){return a<b?a:b;}
bool cmpll(ll a,ll b){return a>b;}
const int N=300001;
const ll mod=998244353;
int t;
int n;
void solve(){
cin>>n;
/*拒绝屎山数学写法 拥抱树形dp 从我做起*/
vector<int> p(n+1,0);
//!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!空间不要开太大!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
vector<int> q[n+1];//直接存每一层是哪些节点
vector<int> s(n+1,0);//s存第几层
p[1]=1;
s[1]=1;
q[1].push_back(1);
int maxlev=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
cin>>p[i];
s[i]=s[p[i]]+1;
q[s[i]].push_back(i);
maxlev=max_(maxlev,s[i]);
}
ll ans=0;
vector<ll> dp(n+1,0);
//每个节点对答案的贡献是扣掉自己父亲节点的个数
dp[1]=1;
ll res=0;
for(auto son:q[2]){
dp[son]=1;
res=(res+1)%mod;
}
//cout<<res<<endl;
for(int i=3;i<=maxlev;i++){
for(auto son:q[i]){
dp[son]=(res-dp[p[son]]+mod)%mod;
}
res=0;
for(auto son:q[i]){
res=(res+dp[son])%mod;
}
//cout<<endl;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
//cout<<dp[i]<<" ";
ans=(ans+dp[i])%mod;
}
//cout<<endl;
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>t;
while(t--) solve();
return 0;
}
Trapmigiano Reggiano
https://codeforces.com/contest/2071/problem/C
手玩一下可得
思路
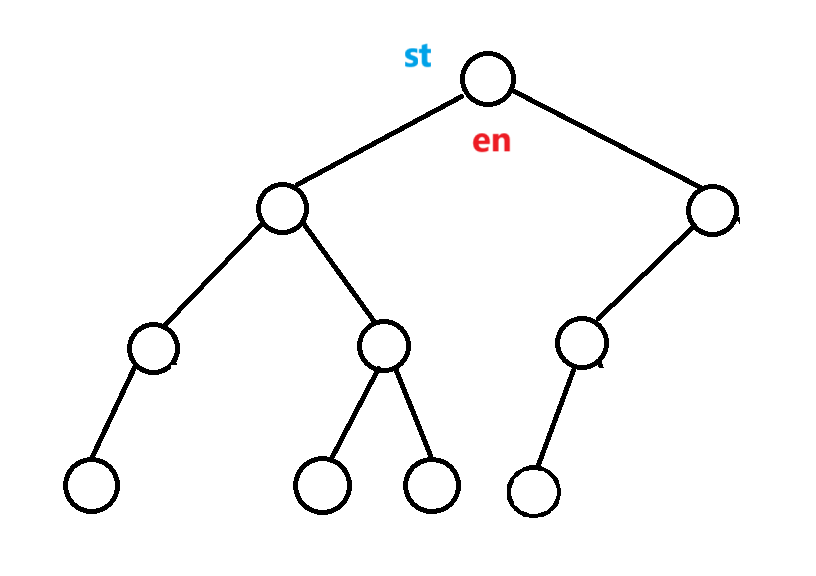
根据相对位置拉来拉去->考虑固定一个 讨论另一个的性质
所有结点都要被遍历一遍->考虑先后顺序
考虑将en作为根节点 随便放几个st的位置手玩
->抓住关键结论:节点不会拉到比最后一层还下面的位置
->结论:讨论层数 按层数从下到上依次输出节点就是结果

代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
ll abss(ll a){return a>0?a:-a;}
ll max_(ll a,ll b){return a>b?a:b;}
ll min_(ll a,ll b){return a<b?a:b;}
bool cmpll(ll a,ll b){return a>b;}
int t;
int n,st,en;
void solve(){
cin>>n>>st>>en;
vector<int> tr[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++){
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
tr[u].push_back(v);
tr[v].push_back(u);
}
/*
将树分成三块:
(1)st阵营
(2)en阵营
(3)st和en之间的
*/
//先找到st到en的路径
queue<PII> q;
vector<int> tree[n+1];
q.push({en,1});
tree[1].push_back(en);
vector<bool> st(n+1,0);
st[en]=1;
int maxlev=0;
while(!q.empty()){
auto t=q.front();
int no=t.first;
int cen=t.second;
maxlev=max(maxlev,cen);
q.pop();
for(auto son:tr[no]){
if(!st[son]){
int cen_=cen+1;
st[son]=1;
tree[cen_].push_back(son);
q.push({son,cen_});
}
}
}
for(int i=maxlev;i>=1;i--){
for(auto son:tree[i]){
cout<<son<<" ";
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>t;
while(t--) solve();
return 0;
}
树上问题
https://codeforces.com/gym/105158/submit
【有向图】
【强联通分量(能连双边的)】用并查集缩点
统计出入度 入度为0的块有且只有1个且这个块的大小就是答案
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
ll abss(ll a){return a>0?a:-a;}
ll max_(ll a,ll b){return a>b?a:b;}
ll min_(ll a,ll b){return a<b?a:b;}
bool cmpll(ll a,ll b){return a>b;}
int n;
struct DSU{
vector<int> p,sz;
//建立并查集
DSU(int n):p(n + 1),sz(n + 1,1){for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)p[i] = i;}
//找父亲+合并
int find(int x){return (p[x] == x) ? x : p[x] = find(p[x]);}
//查找是否相同
bool same(int x,int y){return find(x) == find(y);}
//合并两集合
bool merge(int x,int y){
x = find(x),y = find(y);
if(x == y)return false;
sz[x] += sz[y];
p[y] = x;
return true;
}
//查询集合内数量
int size(int x){return sz[find(x)];}
};
void solve(){
cin>>n;
vector<int> a(n+1,0);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
//并查集缩点
DSU dsu(n);
//邻接表存图
vector<int> g[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
if(a[u]*2>=a[v] && a[v]*2>=a[u]){
//缩点合并
dsu.merge(u,v);
}
//做单向边
else if(a[u]*2>=a[v]){
g[v].push_back(u);
}
else if(a[v]*2>=a[u]){
g[u].push_back(v);
}
}
//统计出入度:注意缩点->先找父亲
set<PII> st;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(auto son:g[i]){
int fu=dsu.find(i),fv=dsu.find(son);
if(fu==fv) continue;
st.insert({fu,fv});
}
}
vector<int> chu(n+1,0),ru(n+1,0);
for(auto son:st){
chu[son.first]++;
ru[son.second]++;
}
//有且只有一个入度为0的强联通块 为答案
//否则答案为0
int flag=0;
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int fa=dsu.find(i);
if(i!=fa) continue;//只有fa==i的才是连通块的父亲
if(ru[fa]==0){
flag++;
ans=dsu.size(fa);
}
}
if(flag!=1) cout<<"0"<<endl;
else cout<<ans<<endl;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--) solve();
return 0;
}
Kirei Attacks the Estate
https://codeforces.com/contest/2114/problem/E
分析。考虑多种情况。->结论

int n;
void solve(){
cin>>n;
vector<ll> a(n+1,0);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
vector<int> g[n+1];
vector<ll> dpmax(n+1,0),dpmin(n+1,0);
vector<ll> ans(n+1,0);
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
dpmax[1]=a[1],dpmin[1]=a[1];
ans[1]=a[1];
std::function<void(int, int)> dfs;
dfs=[&](int u,int fa) -> void{
for(auto son:g[u]){
if(son!=fa){
dpmax[son]=max_(a[son],a[son]-dpmin[u]);
dpmin[son]=min_(a[son],a[son]-dpmax[u]);
ans[son]=dpmax[son];
dfs(son,u);
}
}
};
dfs(1,-1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cout<<ans[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号