深入解析:手写MyBatis第100弹:注入黑科技:手动制造异常+强制返回值,深度测试MyBatis重试与插件容错机制
故障注入测试深度实战:模拟异常与强制返回的调试艺术
「IDEA故障注入黑科技:手动制造异常+强制返回值,深度测试MyBatis重试与插件容错机制」
故障注入:主动测试的艺术
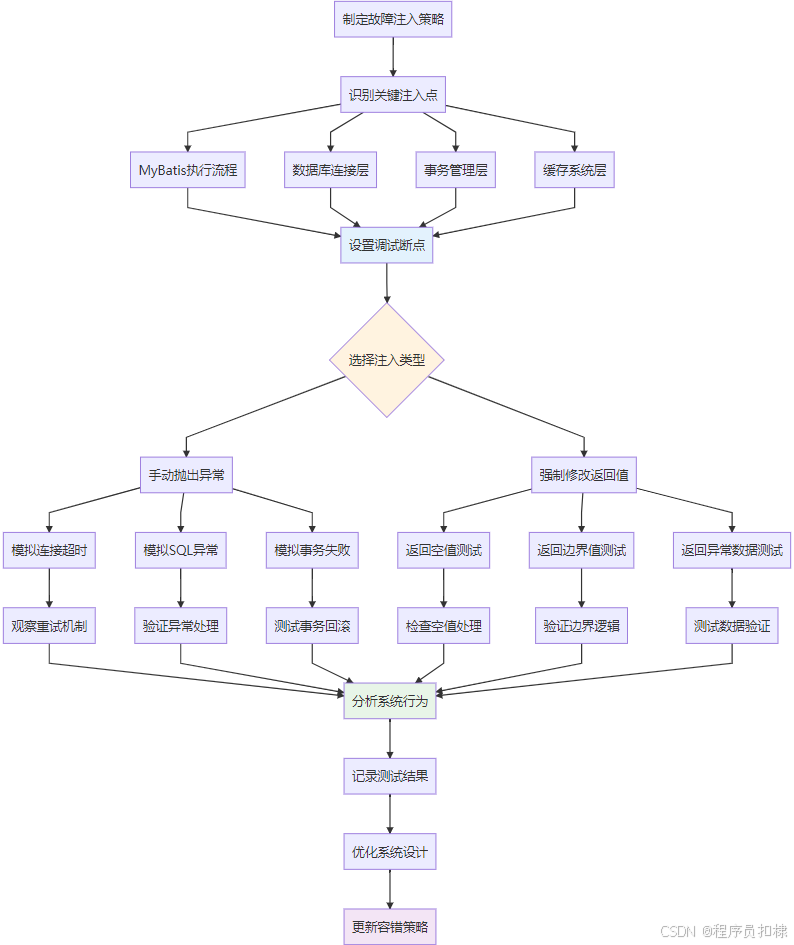
在复杂的分布式系统中,故障是不可避免的。传统的被动调试方法往往在问题发生后才进行排查,而故障注入测试则采用主动出击的策略,在受控环境中模拟各种异常场景,提前发现和修复潜在问题。这种"破坏性"的测试方法,对于构建健壮的MyBatis应用至关重要。
(❁´◡`❁)您的点赞➕评论➕收藏⭐是作者创作的最大动力
支持我:点赞+收藏⭐️+留言欢迎留言讨论
(源码 + 调试运行 + 问题答疑)
有兴趣可以联系我。文末有免费源码
免费获取源码。
更多内容敬请期待。如有需要可以联系作者免费送
更多源码定制,项目修改,项目二开可以联系作者
点击可以进行搜索(每人免费送一套代码):千套源码目录(点我)2025元旦源码免费送(点我)
我们常常在当下感到时间慢,觉得未来遥远,但一旦回头看,时间已经悄然流逝。对于未来,尽管如此,也应该保持一种从容的态度,相信未来仍有许多可能性等待着我们。
手动抛出异常:深度测试异常处理机制
模拟数据库连接超时
数据库连接超时是生产环境中常见的故障场景,通过手动抛出异常可以系统性地测试MyBatis的重试和容错机制:
public class ConnectionTimeoutSimulator {
@Test
public void testConnectionTimeoutHandling() {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
try {
// 在调试器中手动抛出SQLTimeoutException
User user = mapper.findById(1L);
fail("Should have thrown SQLTimeoutException");
} catch (Exception e) {
// 验证异常处理逻辑
assertTrue(e.getCause() instanceof SQLTimeoutException);
assertEquals("Connection timeout simulated", e.getCause().getMessage());
// 测试重试机制
verify(retryTemplate, times(3)).execute(any(RetryCallback.class));
}
}
}
// 在MyBatis执行关键点设置调试断点
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
@Override
public List doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter,
RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler,
BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = getConnection(ms.getStatementLog());
// 调试点:在这里手动抛出SQLTimeoutException
// 右键点击断点 → "More" → 勾选 "Suspend: Thread"
// 在 "Evaluate and log" 中输入:
// throw new SQLTimeoutException("Connection timeout simulated");
PreparedStatement stmt = prepareStatement(connection, ms, boundSql);
return query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
private Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
// 调试点:模拟连接获取超时
Connection conn = transaction.getConnection();
// 手动异常注入点:
// if (System.currentTimeMillis() % 2 == 0) {
// throw new SQLTimeoutException("Connection acquisition timeout");
// }
if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
return ConnectionLogger.newInstance(conn, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return conn;
}
}
} 测试MyBatis重试机制
通过异常注入验证重试策略的有效性:
public class RetryMechanismTester {
private int simulatedFailureCount = 0;
@Test
public void testRetryOnTransientFailures() {
UserMapper mapper = sqlSessionFactory.openSession().getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 模拟瞬时故障场景
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
User user = mapper.findById(1L);
System.out.println("Attempt " + (i + 1) + " succeeded");
break;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Attempt " + (i + 1) + " failed: " + e.getMessage());
if (i == 4) {
fail("All retry attempts failed");
}
}
}
}
// 在调试器中模拟瞬时故障
public User simulateTransientFailure(Long id) {
// 调试点:前两次调用失败,第三次成功
simulatedFailureCount++;
if (simulatedFailureCount <= 2) {
// 手动抛出异常:new SQLTransientException("Database temporarily unavailable")
throw new SQLTransientException("Database temporarily unavailable");
}
return new User(id, "RecoveredUser", "recovered@example.com");
}
}强制修改方法返回值:测试边界场景
验证插件链的容错性
MyBatis的插件机制基于责任链模式,通过强制修改返回值可以测试插件在各种场景下的行为:
public class PluginChainTester {
@Test
public void testPluginChainWithModifiedReturn() {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 测试正常流程
User normalUser = mapper.findById(1L);
assertNotNull(normalUser);
// 在调试器中强制返回null,测试空值处理
User nullUser = mapper.findById(999L); // 不存在的ID
// 调试点:在方法返回时强制设置为null
// 右键断点 → "More" → 在 "Return" 中输入 "null"
assertNull("Should return null for non-existent user", nullUser);
}
}
// 测试拦截器对修改返回值的处理
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
public class LoggingInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
try {
Object result = invocation.proceed();
// 调试点:强制修改查询结果
// 在result变量上设置观察点,手动修改为测试值
if (result instanceof List) {
List resultList = (List) result;
if (resultList.isEmpty()) {
// 手动注入测试数据
// result = Arrays.asList(new User(-1L, "TestUser", "test@example.com"));
}
}
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 测试异常处理插件
System.err.println("Interceptor caught exception: " + e.getMessage());
throw e;
}
}
}边界值测试场景
通过强制返回值测试各种边界条件:
public class BoundaryValueTester {
public void testExtremeScenarios() {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
ProductMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(ProductMapper.class);
// 场景1:空结果集处理
List emptyList = mapper.findByCategory("NonExistentCategory");
// 调试点:强制返回空列表
// 在return语句处设置断点,修改返回值为 "Collections.emptyList()"
assertTrue(emptyList.isEmpty());
// 场景2:超大结果集
List largeList = mapper.findByCategory("PopularCategory");
// 调试点:模拟返回10000条记录
// 修改返回值创建大型列表测试内存和分页
assertEquals(10000, largeList.size());
// 场景3:特殊值测试
Product specialProduct = mapper.findById(0L); // 边界ID值
// 调试点:强制返回包含特殊字符的对象
// 修改product名称包含特殊字符: "Test\u0000Product"
assertNotNull(specialProduct);
}
} 故障注入在连接池测试中的应用
模拟连接池耗尽场景
测试连接池在极端情况下的行为:
public class ConnectionPoolStressTester {
@Test
public void testConnectionPoolExhaustion() throws InterruptedException {
DataSource dataSource = getDataSource();
int poolSize = getPoolMaxSize(dataSource);
List connections = new ArrayList<>();
// 占用所有连接
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
connections.add(dataSource.getConnection());
}
// 测试获取额外连接的场景
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Future future = executor.submit(() -> {
// 这个调用应该阻塞或抛出异常
return dataSource.getConnection();
});
try {
Connection extraConn = future.get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 如果到达这里,说明连接池行为异常
fail("Should not acquire extra connection");
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
// 期望的行为:获取连接超时
System.out.println("Correctly timed out waiting for connection");
} finally {
// 清理连接
connections.forEach(conn -> {
try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { /* ignore */ }
});
executor.shutdown();
}
}
// 在连接获取方法中注入故障
public class FaultInjectingDataSource implements DataSource {
private final DataSource realDataSource;
private boolean injectFailure = false;
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// 调试点:手动控制故障注入
if (injectFailure) {
throw new SQLTransientConnectionException("Connection pool exhausted");
}
return realDataSource.getConnection();
}
public void setInjectFailure(boolean injectFailure) {
this.injectFailure = injectFailure;
}
}
} 事务管理器的故障注入测试
模拟事务回滚场景
测试事务在各种故障场景下的回滚行为:
public class TransactionFailureTester {
@Test
public void testTransactionRollbackOnFailure() {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
OrderMapper orderMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OrderMapper.class);
try {
// 开始事务
User user = new User("TestUser", "test@example.com");
userMapper.insert(user);
// 调试点:在订单创建前手动抛出异常
// 设置断点并抛出 RuntimeException("Simulated business failure")
Order order = new Order(user.getId(), BigDecimal.valueOf(100.0));
orderMapper.insert(order);
sqlSession.commit();
fail("Transaction should have rolled back");
} catch (Exception e) {
// 验证事务回滚
sqlSession.rollback();
assertTrue(e.getMessage().contains("Simulated business failure"));
// 验证数据一致性:用户记录应该不存在
SqlSession newSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
User insertedUser = newSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class).findByName("TestUser");
assertNull("User should not be inserted due to rollback", insertedUser);
newSession.close();
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}缓存系统的故障注入
测试缓存一致性问题
模拟缓存失效、脏读等场景:
public class CacheFailureTester {
@Test
public void testCacheConsistencyUnderFailure() {
SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
UserMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 会话1查询并缓存数据
User user1 = mapper1.findById(1L);
assertNotNull(user1);
// 模拟缓存失效:在调试器中手动清除缓存
// 在 Cache 的 getObject 方法中设置断点,强制返回 null
sqlSession1.clearCache();
// 会话2修改数据
user1.setEmail("updated@example.com");
mapper2.updateUser(user1);
sqlSession2.commit();
// 测试会话1的缓存是否正确处理了失效
User cachedUser = mapper1.findById(1L);
// 调试点:验证缓存重新加载逻辑
assertEquals("updated@example.com", cachedUser.getEmail());
sqlSession1.close();
sqlSession2.close();
}
// 测试二级缓存故障场景
public void testSecondLevelCacheFailure() {
// 模拟分布式缓存故障
Cache secondLevelCache = configuration.getCache("com.example.UserMapper");
// 调试点:手动使缓存失效
secondLevelCache.clear();
// 测试缓存重新构建过程
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
User user = mapper.findById(1L); // 应该触发缓存重建
long duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
// 验证缓存重建后的性能
assertTrue("Cache should be rebuilt", duration < 1000);
sqlSession.close();
}
}故障注入测试的最佳实践
系统化的测试策略
建立完整的故障注入测试体系:
故障分类:
瞬时故障(网络抖动、数据库暂时不可用)
持久故障(数据库连接失败、磁盘空间不足)
逻辑故障(业务规则违反、数据一致性問題)
注入时机:
启动阶段(应用初始化时)
运行时(业务处理过程中)
关闭阶段(应用关闭时)
影响范围:
组件级别(单个Mapper或Service)
服务级别(整个业务功能)
系统级别(影响多个服务)
自动化故障注入框架
构建自动化的故障注入测试框架:
public class AutomatedFaultInjection {
private static final Map rules = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public static void registerFaultRule(String pointcut, FaultInjectionRule rule) {
rules.put(pointcut, rule);
}
public static Object injectFault(String pointcut, Object originalResult) {
FaultInjectionRule rule = rules.get(pointcut);
if (rule != null && rule.shouldInject()) {
if (rule.shouldThrowException()) {
throw rule.getExceptionToThrow();
} else {
return rule.getModifiedResult();
}
}
return originalResult;
}
// 在MyBatis关键点插入故障注入
public class FaultAwareExecutor extends SimpleExecutor {
@Override
public List doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter,
RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler,
BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
// 故障注入点
String pointcut = "executor.query:" + ms.getId();
try {
List result = super.doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
return (List) injectFault(pointcut, result);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
if (e.getCause() instanceof SQLException) {
throw (SQLException) e.getCause();
}
throw e;
}
}
}
} 生产环境故障注入的谨慎应用
在生产环境进行故障注入需要极其谨慎的策略:
public class ProductionFaultInjection {
private static final double INJECTION_PROBABILITY = 0.001; // 0.1%的概率
public static boolean shouldInjectFault() {
// 只在极小概率下注入故障,避免影响正常用户
return Math.random() < INJECTION_PROBABILITY;
}
public static void safeFaultInjection(String scenario) {
if (shouldInjectFault()) {
log.warn("Injecting controlled fault for scenario: {}", scenario);
// 执行受控的故障注入
injectControlledFault(scenario);
}
}
private static void injectControlledFault(String scenario) {
// 在生产环境中只注入可安全处理的故障
switch (scenario) {
case "TIMEOUT":
// 模拟轻微延迟,不模拟完全失败
try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { /* ignore */ }
break;
case "CACHE_MISS":
// 只清除特定缓存条目
clearSpecificCacheEntries();
break;
default:
// 生产环境不模拟严重故障
log.debug("Skipping severe fault injection in production");
}
}
}总结
故障注入测试是一种强大的质量保障手段,它通过主动引入故障来验证系统的容错能力和恢复机制。在MyBatis应用开发中,通过手动抛出异常和强制修改返回值,我们可以:
验证异常处理:确保系统能够优雅地处理各种故障场景
测试重试机制:验证重试策略的有效性和正确性
检查边界条件:测试系统在各种极端情况下的行为
提升系统韧性:通过提前发现问题来增强系统的稳定性
掌握故障注入测试技巧,不仅能够提升代码质量,更能培养预防性编程的思维方式,这是在构建高可用分布式系统中不可或缺的核心能力。
(❁´◡`❁)您的点赞➕评论➕收藏⭐是作者创作的最大动力
支持我:点赞+收藏⭐️+留言欢迎留言讨论
(源码 + 调试运行 + 问题答疑)
有兴趣可以联系我。文末有免费源码
学习知识需费心,
整理归纳更费神。
源码免费人人喜,
码农福利等你领!常来我家多看看,
网址:扣棣编程,
感谢支持常陪伴,
点赞关注别忘记!山高路远坑又深,
大军纵横任驰奔,
谁敢横刀立马行?
唯有点赞+关注成!
往期文章推荐:
基于Springboot + vue实现的学生宿舍信息管理系统
免费获取宠物商城源码--SpringBoot+Vue宠物商城网站系统
【2025小年源码免费送】



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号