shell脚本练习2——循环语句(for、while、until循环等的应用)
1.计算从1到100所有整数的和
#/bin/bash #Calculate the sum of all integers from 1 to 100 a=1 sum=0 while [ $a -le 100 ] do sum=$[$a+$sum] let a++ done echo "1到100的和为:$sum"
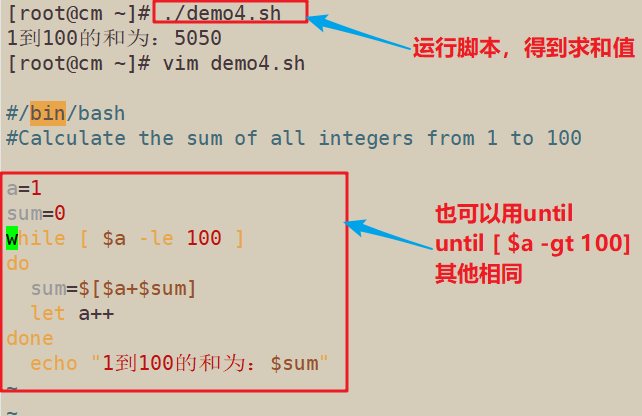
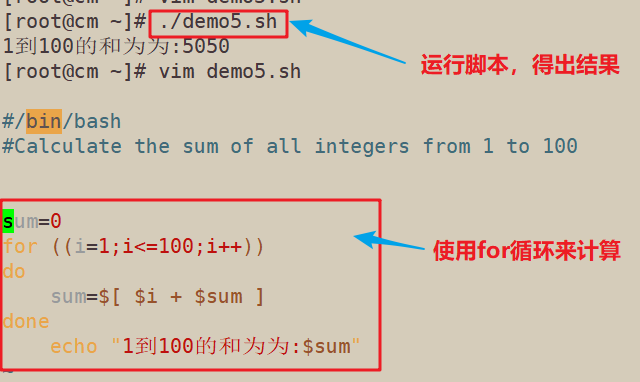
#/bin/bash
#Calculate the sum of all integers from 1 to 100
sum=0
for ((i=1;i<=100;i++))
do
sum=$[ $i + $sum ]
done
echo "1到100的和为为:$sum"
2.提示用户输入一个小于100的整数,并计算从1到该数之间所有整数的和
#!/bin/bash #Prompts the user to enter an integer less than 100 and calculates the sum of all integers from 1 to that number read -p "请输入一个小于100的整数:" num sum=0 for ((i=1;i<=$num;i++)) do sum=$[$sum+$i] done echo "1到$num的和为:$sum"
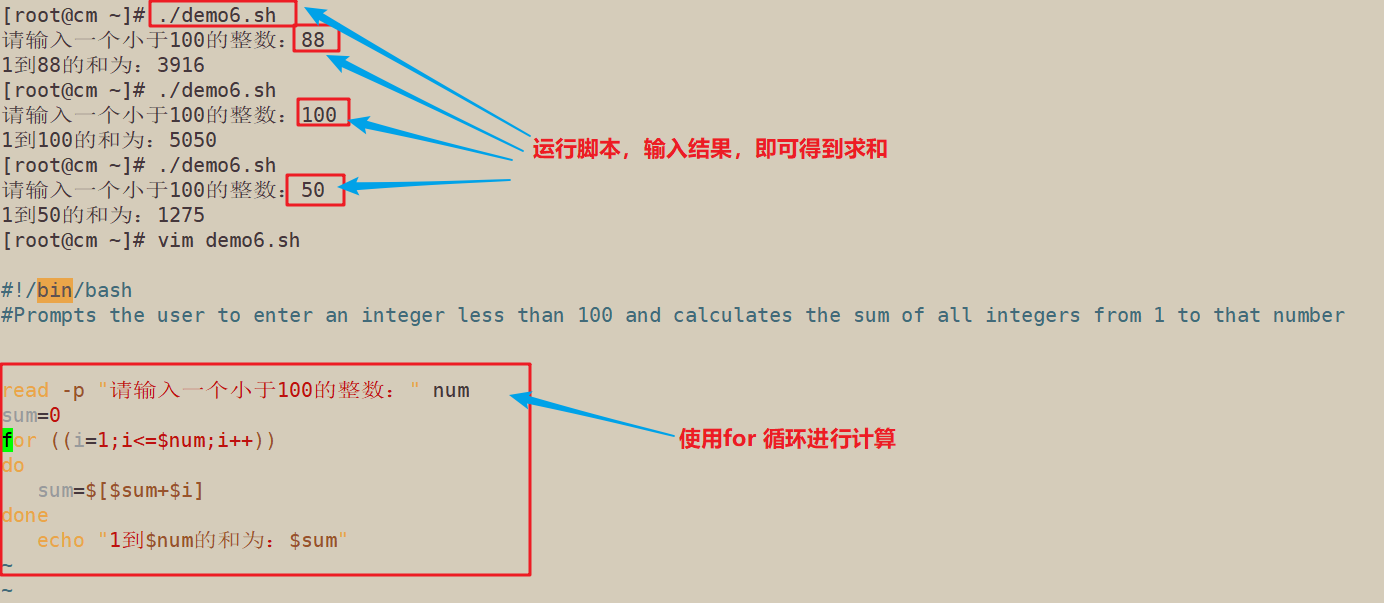
#!/bin/bash #Prompts the user to enter an integer less than 100 and calculates the sum of all integers from 1 to that number read -p "请输入一个小于100的整数:" num sum=0 a=1 #while [ $a -le $num ] until [ $a -gt $num ] do sum=$[$sum+$a] let a++ done echo "1到$num的和为:$sum"

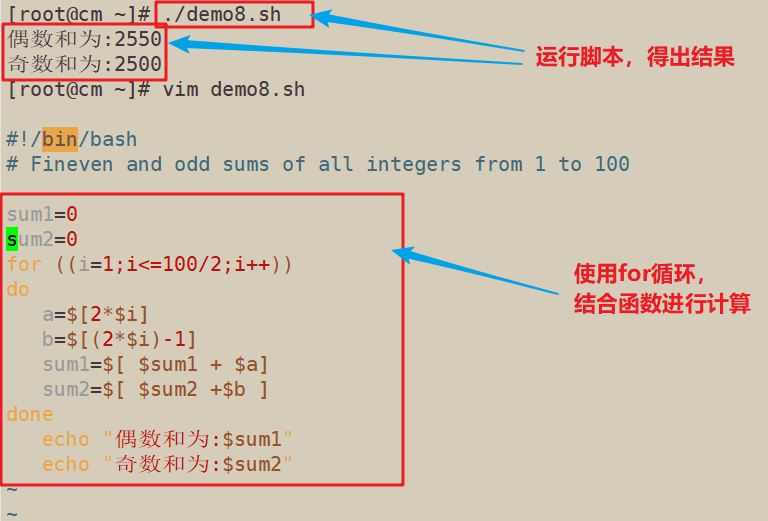
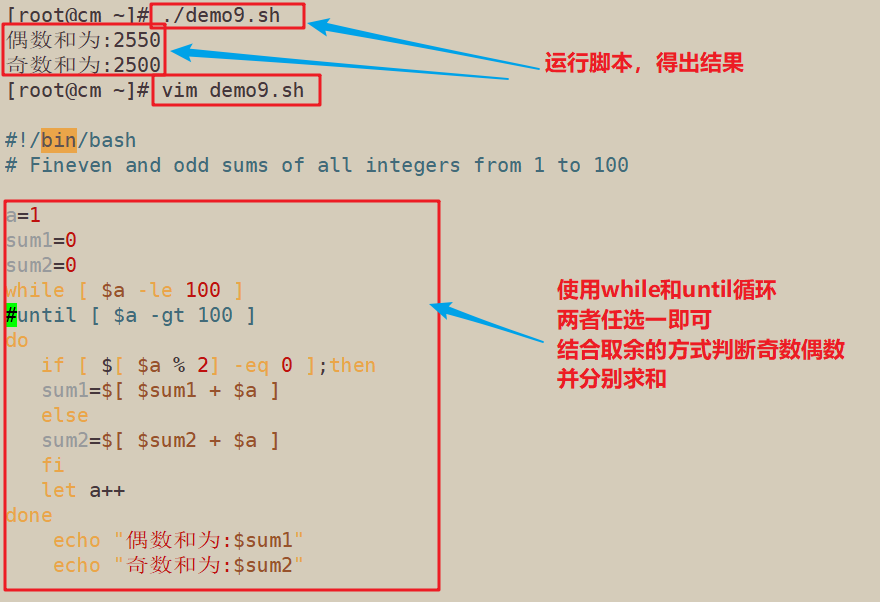
3.求从1到100所有整数的偶数和、奇数和
#!/bin/bash # Fineven and odd sums of all integers from 1 to 100 sum1=0 sum2=0 for ((i=1;i<=100/2;i++)) do a=$[2*$i] b=$[(2*$i)-1] sum1=$[ $sum1 + $a] sum2=$[ $sum2 +$b ] done echo "偶数和为:$sum1" echo "奇数和为:$sum2"
#!/bin/bash
# Fineven and odd sums of all integers from 1 to 100
a=1
sum1=0
sum2=0
while [ $a -le 100 ]
#until [ $a -gt 100 ]
do
if [ $[ $a % 2] -eq 0 ];then
sum1=$[ $sum1 + $a ]
else
sum2=$[ $sum2 + $a ]
fi
let a++
done
echo "偶数和为:$sum1"
echo "奇数和为:$sum2"
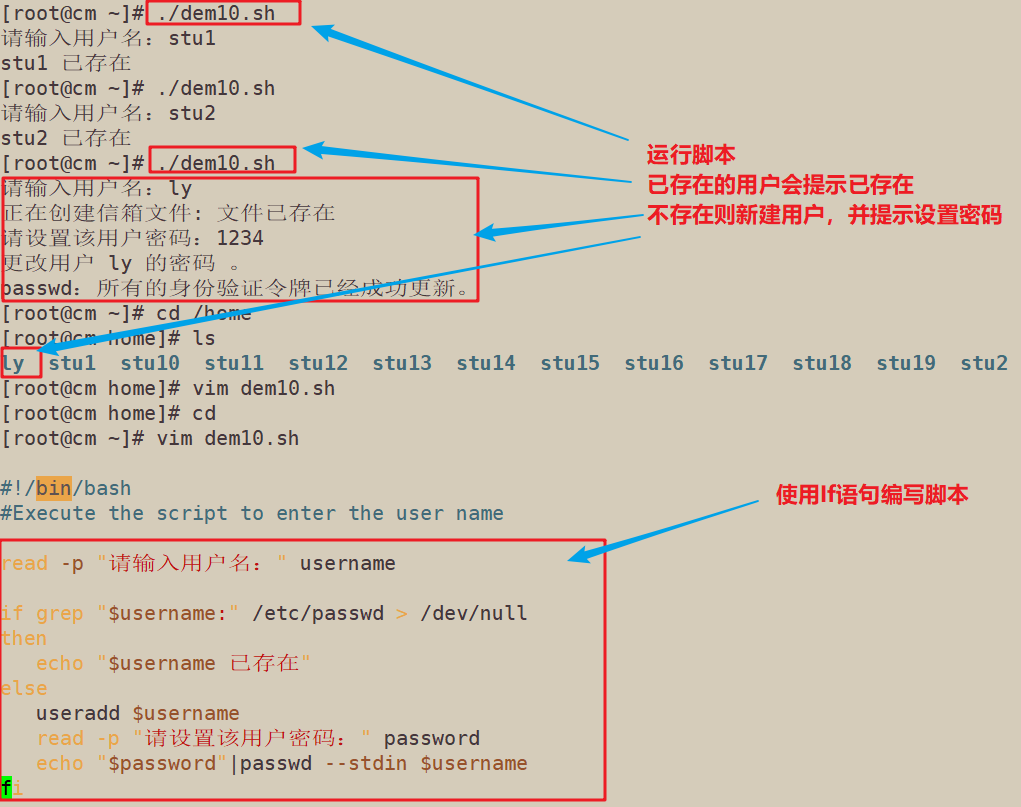
4.执行脚本输入用户名,若该用户存在,输出提示该用户已存在;若该用户不存在,提示用户输入密码,建立用户并设立其密码
#!/bin/bash #Execute the script to enter the user name read -p "请输入用户名:" username if grep "$username:" /etc/passwd > /dev/null then echo "$username 已存在" else useradd $username read -p "请设置该用户密码:" password echo "$password"|passwd --stdin $username fi
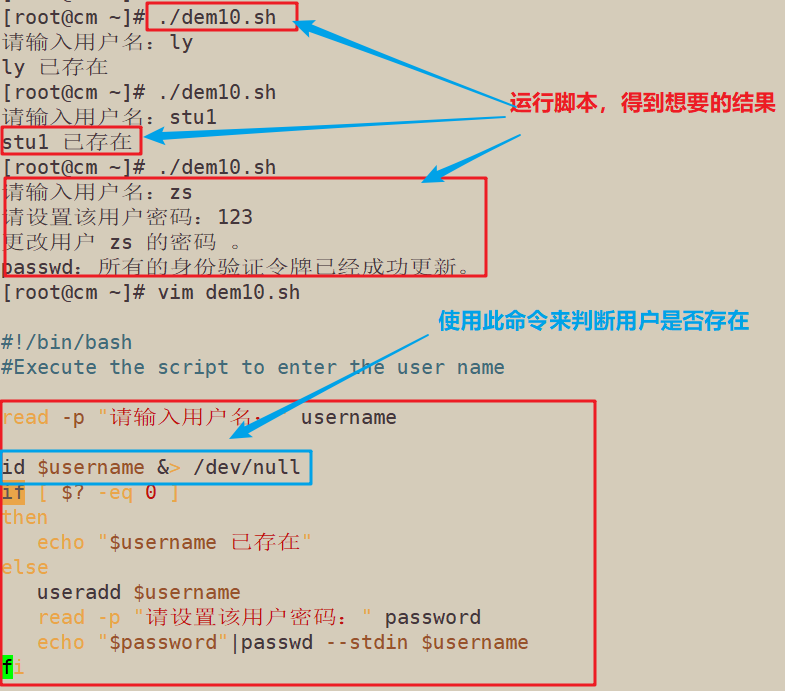
#!/bin/bash #Execute the script to enter the user name read -p "请输入用户名:" username id $username &> /dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ] then echo "$username 已存在" else useradd $username read -p "请设置该用户密码:" password echo "$password"|passwd --stdin $username fi
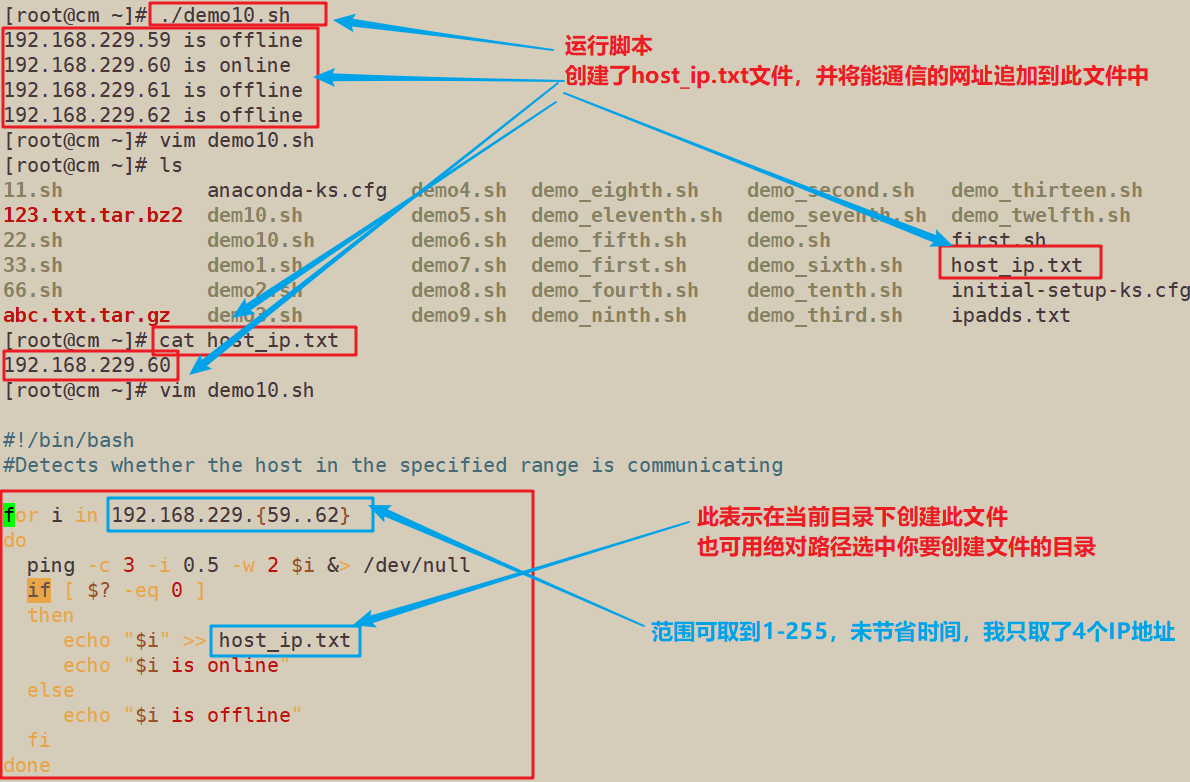
5.检测指定范围主机是否通信,并将通信的主机ip输出到文件host_ip中
#!/bin/bash
#Detects whether the host in the specified range is communicating
for i in 192.168.229.{59..62}
do
ping -c 3 -i 0.5 -w 2 $i &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
echo "$i" >> host_ip.txt
echo "$i is online"
else
echo "$i is offline"
fi
done
多线程操作(for循环)
#!/bin/bash
#Detects whether the host in the specified range is communicating
for i in 192.168.229.{1..255}
do
{
ping -c 3 -i 0.5 -w 2 $i &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
echo "$i" >> host_ip.txt
echo "$i is online"
else
echo "$i is offline"
fi
}&
done
wait
cat /root/host_ip.txt

wait是等待前面的后台任务全部完成才往下执行,否则程序本身是不会等待的,这样对后面依赖前面任务结果的命令 来说就可能出错
6.用户输入密码,脚本判断密码是否正确,输入正确提示正确信息,连续输错3次则报警
#!/bin/bash
#Determine if the password was entered correctly
read -p "请输入密码:" first
for i in {1..3}
do
read -p "请再次输入密码:" second
if [ $first == $second ]
then
echo "输入的密码正确!"
exit
else
echo "输入的密码有误!"
fi
done
echo "错误次数过多,退出程序!"

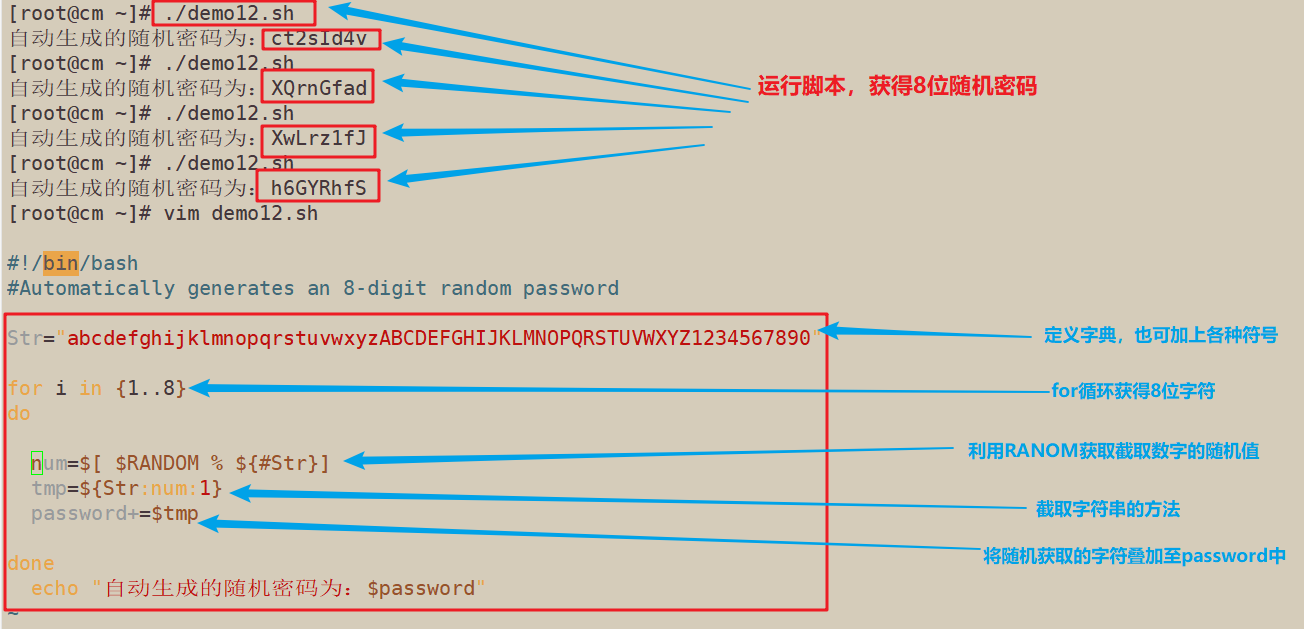
7.编写能够自动生成一个8位随机密码的脚本
#!/bin/bash
#Automatically generates an 8-digit random password
Str="abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ1234567890"
for i in {1..8}
do
num=$[ $RANDOM % ${#Str}]
tmp=${Str:num:1}
password+=$tmp
done
echo "自动生成的随机密码为:$password"
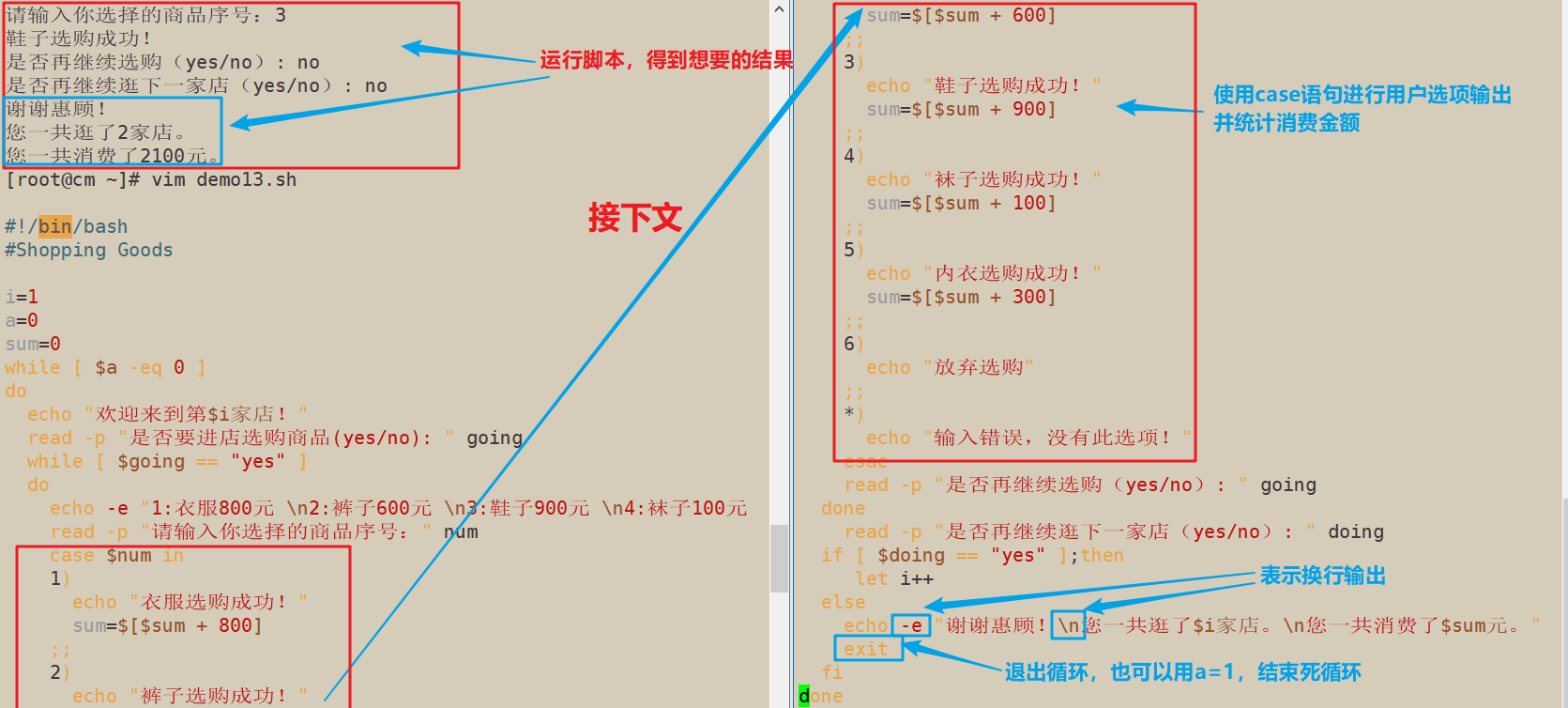
8.写个逛淘宝选购商品脚本,每家商店有五种商品选购(衣服800元,裤子600元,鞋子900元,内衣300元,袜子100元),每次选购完或不买都会提示用户是否继续逛下一家商店,如果不再继续逛的话进行购物车结算总额。
#!/bin/bash
#Shopping Goods
i=1
a=0
sum=0
while [ $a -eq 0 ]
do
echo "欢迎来到第$i家店!"
read -p "是否要进店选购商品(yes/no): " going
while [ $going == "yes" ]
do
echo -e "1:衣服800元 \n2:裤子600元 \n3:鞋子900元 \n4:袜子100元 \n5:内衣300元 \n6:放弃选购"
read -p "请输入你选择的商品序号:" num
case $num in
1)
echo "衣服选购成功!"
sum=$[$sum + 800]
;;
2)
echo "裤子选购成功!"
sum=$[$sum + 600]
;;
3)
echo "鞋子选购成功!"
sum=$[$sum + 900]
;;
4)
echo "袜子选购成功!"
sum=$[$sum + 100]
;;
5)
echo "内衣选购成功!"
sum=$[$sum + 300]
;;
6)
echo "放弃选购"
;;
*)
echo "输入错误,没有此选项!"
esac
read -p "是否再继续选购(yes/no): " going
done
read -p "是否再继续逛下一家店(yes/no): " doing
if [ $doing == "yes" ];then
let i++
else
echo -e "谢谢惠顾!\n您一共逛了$i家店。\n您一共消费了$sum元。"
exit
fi
done
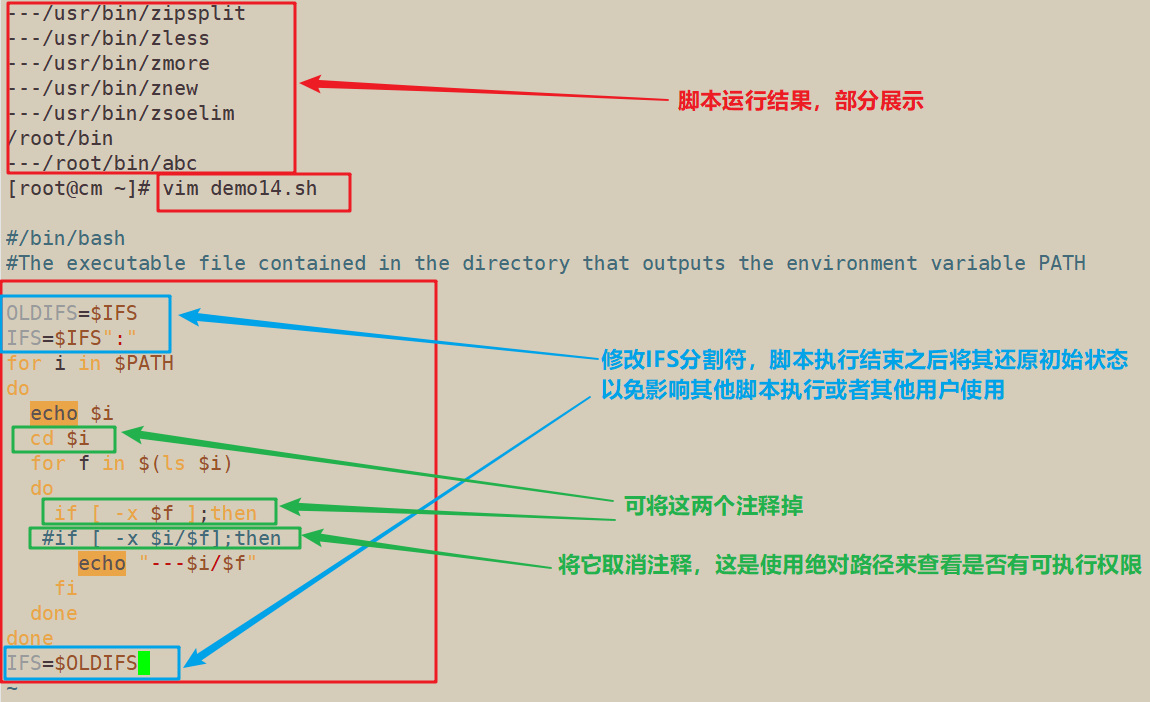
9、输出环境变量PATH 的目录所包含的可执行文件
#/bin/bash
#The executable file contained in the directory that outputs the environment variable PATH
OLDIFS=$IFS
IFS=$IFS":"
for i in $PATH
do
echo $i
cd $i
for f in $(ls $i)
do
if [ -x $f ];then
#if [ -x $i/$f];then
echo "---$i/$f"
fi
done
done
IFS=$OLDIFS
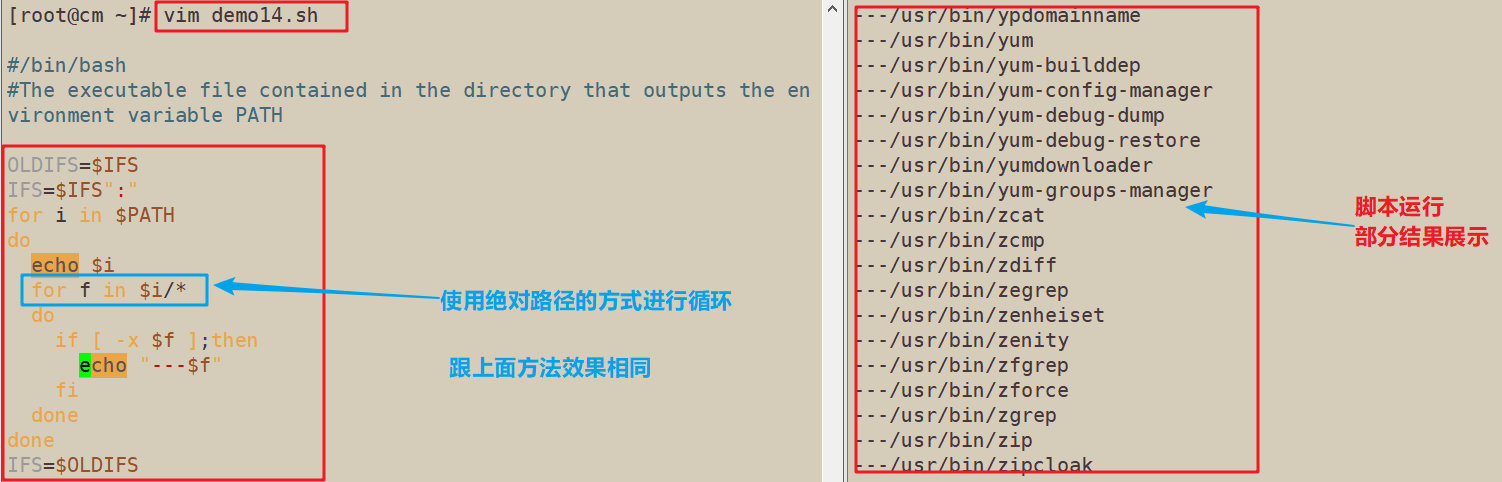
#/bin/bash
#The executable file contained in the directory that outputs the environment variable PATH
OLDIFS=$IFS
IFS=$IFS":"
for i in $PATH
do
echo $i
for f in $i/*
do
if [ -x $f ];then
echo "---$f"
fi
done
done
IFS=$OLDIFS
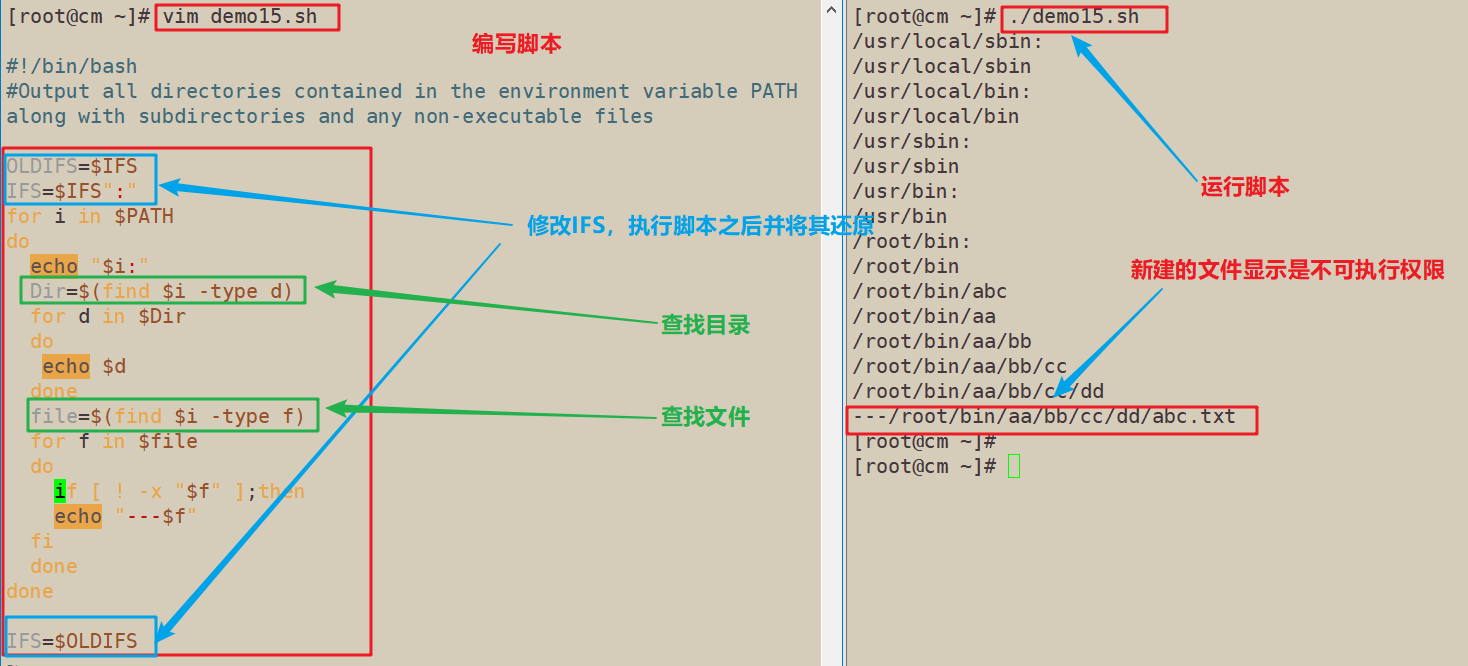
10、mkdir -p /root/bin/aa/bb/cc/dd ; touch /root/bin/aa/bb/cc/dd/abc.txt,输出环境变量PATH所包含的所有目录以及其中的子目录和所有不可执行文件
#!/bin/bash
#Output all directories contained in the environment variable PATH along with subdirectories and any non-executable files
OLDIFS=$IFS
IFS=$IFS":"
for i in $PATH
do
echo "$i:"
Dir=$(find $i -type d)
for d in $Dir
do
echo $d
done
file=$(find $i -type f)
for f in $file
do
if [ ! -x "$f" ];then
echo "---$f"
fi
done
done
IFS=$OLDIFS
将本人在工作学习中的一些知识记录并分享


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号