并查集 笔记
原理
在线维护集合的合并和查询
int find(int x)
{
return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y)
{
fa[find(x)] = find(y);
}
时间复杂度
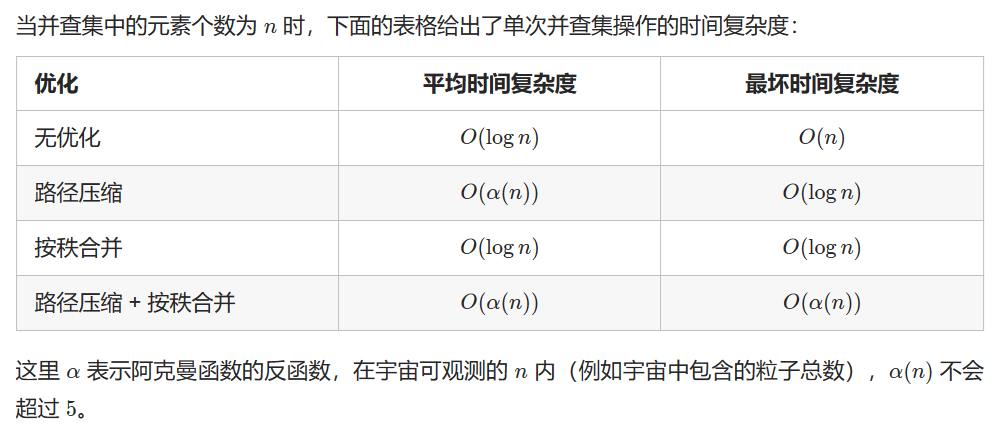
运用
1. P6121 [USACO16OPEN] Closing the Farm G
P3144 [USACO16OPEN] Closing the Farm S(逊版)
思路 \(\scr{Solution}\)
\(10pts\)
每一时刻关闭农场,求是否全联通。也就是维护将单个集合分成多个集合。
很容易想到爆搜算法,用 vector 邻接表建图,每次跑完图就将当前点的连边关系删去。复杂度 \(O(n^2)\)
只能拿 10pts ,居然有 WA qwq
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 3e3 + 10;
int n, m;
bool vis[N];
vector<int> g[N];
void dfs(int fa, int x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < g[x].size(); i ++)
{
int y = g[x][i];
if (y == fa || vis[y]) continue;
vis[y] = true;
dfs(x, y);
}
}
void cut(int x)
{
for (int i = 0; i <g[x].size(); i ++)
g[x][i] = -1;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
{
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
g[x].push_back(y);
g[y].push_back(x);
}
while (n --)
{
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
int x;
cin >> x;
vis[x] = true;
dfs(0, x);
bool flag = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
if (!vis[i])
{
flag = true;
break;
}
cout << (flag ? "NO" : "YES") << '\n';
cut(x);
}
return 0;
}
正着搜不好优化,考虑倒过来思考。
即一开始所有农场都是关闭的,从后往前,判断每一时刻打开一个农场,对应正着想的当前状态下该农场还未关闭。
而正着想是判断当前状态下是否因关闭该农场而被分成了多个集合。
那倒着想就是打开多个农场,判断是否有多个集合(连通块)!
这不就是并查集了吗 ......
每次打开一个农场,默认多了一个集合,再通过图遍历直接相连的点是否打开了,打开了但又不在同一集合里就用并查集合并,同时抹去该单点集合。
每次操作完后就留下了当前状态下打开了的相连农场的集合数量。
\(O(m)~\) done.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n, m, a[N], fa[N], ans[N];
bool vis[N];
vector<int> g[N];
int find(int x)
{
return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y)
{
fa[find(x)] = find(y);
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
{
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) fa[i] = i;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i --)
{
sum ++;
int k = a[i];
vis[k] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < g[k].size(); j ++)
{
int l = g[k][j];
if (find(k) != find(l) && vis[l])
{
merge(k, l);
sum --;
}
}
ans[i] = sum;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
cout << (ans[i] == 1 ? "YES" : "NO") << '\n';
return 0;
}
总结 \(\scr{Summary}\)
- 有些题目正着想好做但常常不够优,所以当发现正着想超时时可以试着倒着思考;
- 一些删边的问题可以转化为加边的问题来做,从而考虑并查集;
类似思想的题
2. P7991 [USACO21DEC] Connecting Two Barns S
思路 \(\scr{Solution}\)
\(50pts\)
相当于从 \(1\sim n\) 的一条通路被分成了多条断路,再将它们之间互相连接求最小费用。
可以用并查集维护集合关系,而至多可以连两条路就可以分成三种情况:
- 0 条,说明 1 和 n 已经连通,费用为 0;
- 1 条,将 1 和 n 所在集合直接连一条最小边;
- 2 条,选一个第三方集合作为桥,分别连接两条最小边;
易想到枚举所有其他集合再和 1、n所在集合暴力枚举打擂台,复杂度为 \(O(n^2)\),只能拿 50pts
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll N = 2e5 + 10, inf = LONG_LONG_MAX;
ll t, n, m, fa[N];
vector<ll> a[N];
void init()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
fa[i] = i;
a[i].clear();
}
}
ll find(int x)
{
return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y)
{
fa[find(x)] = find(y);
}
ll count(int x, int y)
{
ll ans = inf;
for (int i = 0; i < a[x].size(); i ++)
for (int j = 0; j < a[y].size(); j ++)
{
ll k = a[x][i], l = a[y][j];
ans = min(ans, (k - l) * (k - l));
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> t;
while (t --)
{
cin >> n >> m;
init();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
{
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
merge(x, y);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) a[find(i)].push_back(i);
if (find(1) == find(n))
{
cout << 0 << '\n';
continue;
}
ll ans = inf;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
if (find(i) == find(1) || find(i) == find(n) || find(i) != i) continue;
ans = min(ans, count(find(i), find(1)) + count(find(i), find(n)));
}
cout << min(ans, count(find(1), find(n))) << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
显然是暴力枚举这还可以优化,而回想打擂台的目的是在1、n所在集合里找到与第三方集合里两两最近的点。
保留任意一个集合枚举,那另一个要找到与当前集合的点最近的点。
考虑 二分查找优化
此时就要求维护集合并且集合内有序,可以考虑用 set 实现。
不想手打二分(悲,所以用 .lower_bound(x) 函数可以直接查找第一个 \(\geqslant x\) 的数的地址。
但 set 没有查找第一个 \(< x\) 的函数,所以考虑在1、n所在集合 \(A\) 有 \(A_{i-1} < x \leqslant A_i\),且集合大小为 \(n_A\),设 \(x_j \in B\),且大小为 \(n_B\)
易得:
\(O(n\log \sqrt{n})~\) done.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll N = 2e5 + 10, inf = LONG_LONG_MAX;
ll t, n, m, fa[N];
set<ll> s[N];
void init()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
fa[i] = i;
s[i].clear();
}
}
ll find(int x)
{
return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y)
{
fa[find(x)] = find(y);
}
ll count(int x, int y)
{
ll ans = inf;
set<ll>::iterator i, j;
for (i = s[x].begin(); i != s[x].end(); i ++)
{
j = s[y].lower_bound(*i);
if (j != s[y].end()) ans = min(ans, (*j - *i) * (*j - *i));
if (j == s[y].end() || j != s[y].begin()) ans = min(ans, (*(-- j) - *i) * (*j - *i));
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> t;
while (t --)
{
cin >> n >> m;
init();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
{
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
merge(x, y);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) s[find(i)].insert(i);
if (find(1) == find(n))
{
cout << 0 << '\n';
continue;
}
ll ans = inf;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
if (find(i) == find(1) || find(i) == find(n) || find(i) != i) continue;
ans = min(ans, count(find(i), find(1)) + count(find(i), find(n)));
}
cout << min(ans, count(find(1), find(n))) << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
总结 \(\scr{Summary}\)
- 要熟知 STL 常用容器的特性,不仅可以简化思路,有时可以通过特性找到解题、优化思路;
3. P1840 Color the Axis
思路 \(\scr{Solution}\)
最先想到的肯定是直接模拟染色过程,每次暴力查找,时间为 \(O(nm)\), 直接 T 飞。
然鹅,当范围 \([l,r]\) 里的点都被染成黑色时,完全可以把这个集合看做一个点来进行下一次染色,这样大大压缩查找时间。
想到用并查集维护。
具体地,在下一次染色时该次染色就等价于压缩成点。
而每次查找从左到右,就可以把 \([l,r]\) 的点一一都合并到 \(r\) 作为根的集合,同时记录剩余点数。
注意:可能 \(r = n\),此时会越界到 \(n+1\) !
\(O(n+m)~\) done.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n, m, fa[N];
int find(int x)
{
return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y)
{
fa[find(x)] = find(y);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
int res = n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i ++) fa[i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
{
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
int a = find(l);
while (a <= r)
{
merge(a, a + 1);
a = find(a);
res --;
}
cout << res << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
总结 \(\scr{Summary}\)
- 注意越界问题啊啊啊!
类似思想的问题


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号