1091. Shortest Path in Binary Matrix
In an N by N square grid, each cell is either empty (0) or blocked (1).
A clear path from top-left to bottom-right has length k if and only if it is composed of cells C_1, C_2, ..., C_k such that:
- Adjacent cells
C_iandC_{i+1}are connected 8-directionally (ie., they are different and share an edge or corner) C_1is at location(0, 0)(ie. has valuegrid[0][0])C_kis at location(N-1, N-1)(ie. has valuegrid[N-1][N-1])- If
C_iis located at(r, c), thengrid[r][c]is empty (ie.grid[r][c] == 0).
Return the length of the shortest such clear path from top-left to bottom-right. If such a path does not exist, return -1.
Example 1:
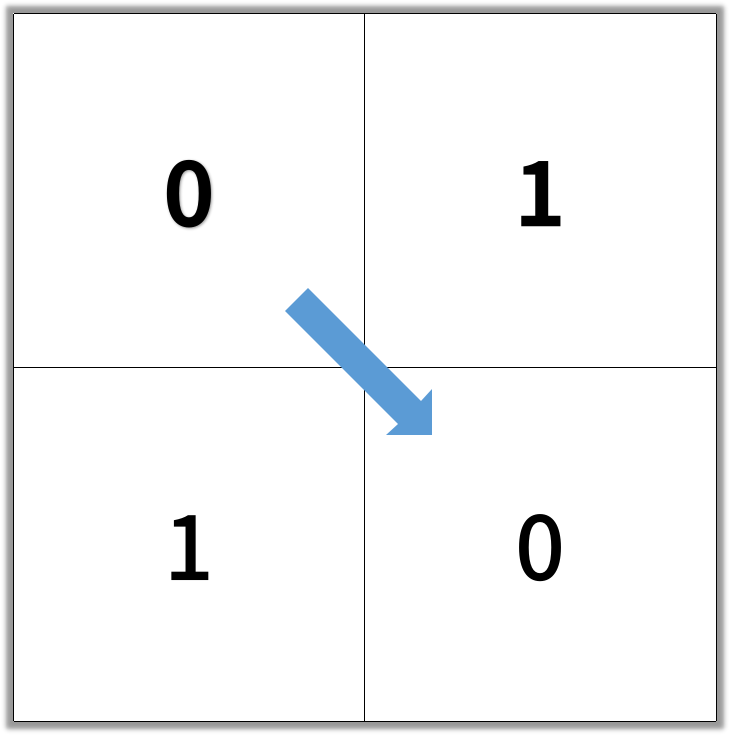
Input: [[0,1],[1,0]]
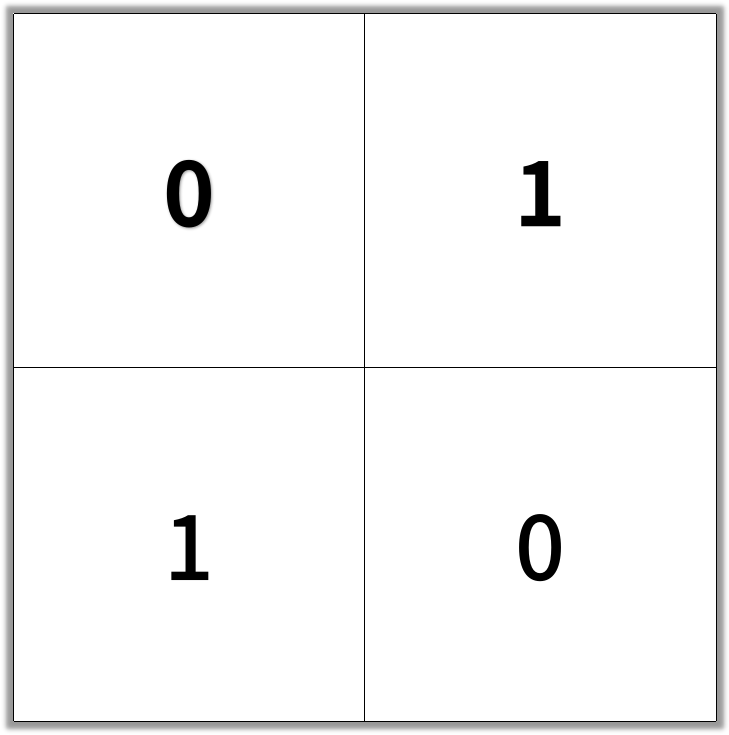 Output: 2
Output: 2
Example 2:
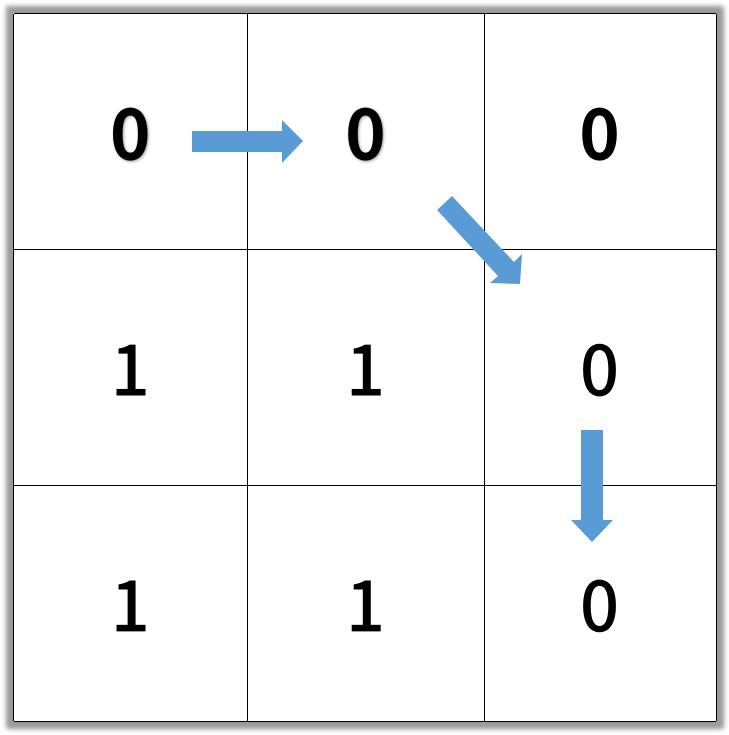
Input: [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]]
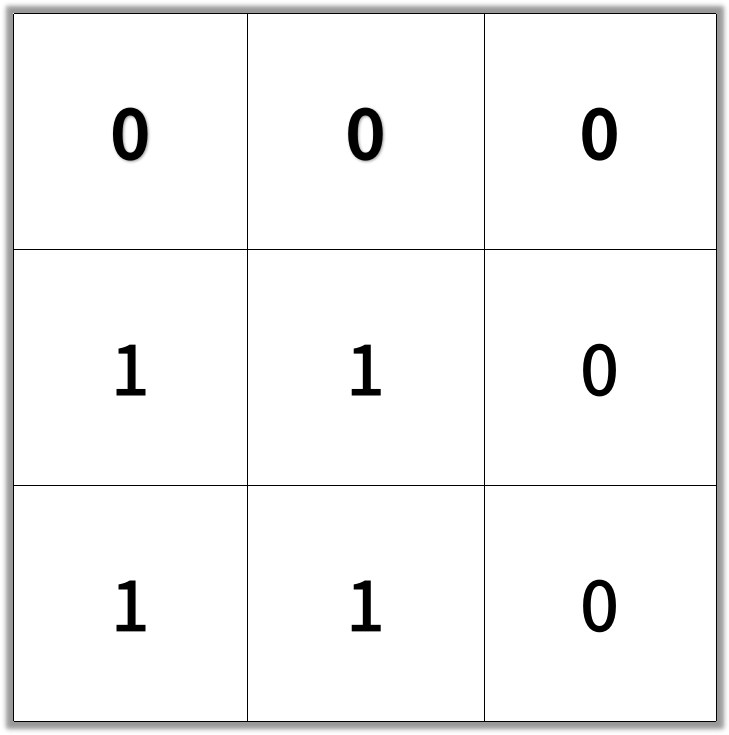 Output: 4
Output: 4
Note:
1 <= grid.length == grid[0].length <= 100grid[r][c]is0or1
class Solution { private int dir[][] = new int[][]{{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0},{1,-1},{-1,1},{-1,-1},{1,1}}; public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grid) { int m = grid.length; int n = grid[0].length; if(grid[0][0]==1 || grid[m-1][n-1]==1) { return -1; } boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n]; visited[0][0] = true; Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.add(new int[]{0,0}); int ans=0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); for(int i=0;i<size;i++) { int[] pop = queue.remove(); if(pop[0]==m-1 && pop[1]==n-1) { return ans+1; } for (int k=0;k<8;k++) { int nextX = dir[k][0]+pop[0]; int nextY = dir[k][1]+pop[1]; if(nextX>=0 && nextX<m && nextY>=0 && nextY<n && !visited[nextX][nextY] && grid[nextX][nextY]==0) { queue.add(new int[]{nextX,nextY}); visited[nextX][nextY]=true; } } } ans++; } return -1; } }
bfs处理无向图最短路径问题,dfs会TLE




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号