987. Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
Example 1:
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0):
Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1);
The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2);
The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1);
The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:
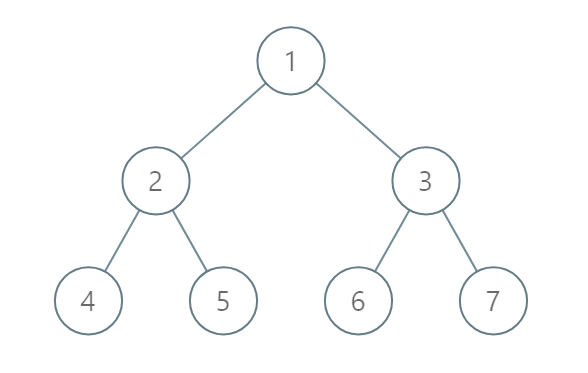
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme.
However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
- The tree will have between 1 and
1000nodes. - Each node's value will be between
0and1000.
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { class Node { TreeNode root; int x, y; public Node(TreeNode root, int x, int y) { this.root = root; this.x = x; this.y = y; } } public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList(); if(root == null) return res; Map<Integer, List<Node>> map = new HashMap(); Node c = new Node(root, 0, 0); Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList(); q.offer(c); int minx = 0; int maxx = 0; while(!q.isEmpty()) { Node cur = q.poll(); minx = Math.min(cur.x, minx); maxx = Math.max(cur.x, maxx); map.computeIfAbsent(cur.x, a -> new ArrayList()).add(cur); if(cur.root.left != null) { q.offer(new Node(cur.root.left, cur.x - 1, cur.y - 1)); } if(cur.root.right != null) { q.offer(new Node(cur.root.right, cur.x + 1, cur.y - 1)); } } int index = 0; for(int i = minx; i <= maxx; i++) { Collections.sort(map.get(i), (a, b) -> a.y == b.y ? a.root.val - b.root.val : b.y - a.y); res.add(new ArrayList()); for(Node node : map.get(i)) { res.get(index).add(node.root.val); } index++; } return res; } }
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AUQL0R-ibEw
首先重新弄一个Node,包含了TreeNode和x、y坐标
然后用bfs来遍历所有的点并添加到map(x coord,List)中。因为我们最后要求从x最小到最大输出,所以为方便起见直接把minx和maxx持续更新了
因为可能两个点的位置相同,所以我们按x输出时,比较两个点的y,如果相同就先输出val小的那个,否则先输出高度高的。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号