1514. Path with Maximum Probability
You are given an undirected weighted graph of n nodes (0-indexed), represented by an edge list where edges[i] = [a, b] is an undirected edge connecting the nodes a and b with a probability of success of traversing that edge succProb[i].
Given two nodes start and end, find the path with the maximum probability of success to go from start to end and return its success probability.
If there is no path from start to end, return 0. Your answer will be accepted if it differs from the correct answer by at most 1e-5.
Example 1:
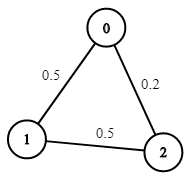
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.2], start = 0, end = 2 Output: 0.25000 Explanation: There are two paths from start to end, one having a probability of success = 0.2 and the other has 0.5 * 0.5 = 0.25.
Example 2:
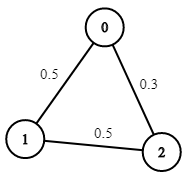
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.3], start = 0, end = 2 Output: 0.30000
Example 3:
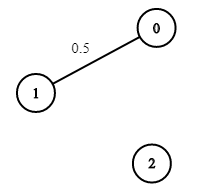
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1]], succProb = [0.5], start = 0, end = 2 Output: 0.00000 Explanation: There is no path between 0 and 2.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 10^40 <= start, end < nstart != end0 <= a, b < na != b0 <= succProb.length == edges.length <= 2*10^40 <= succProb[i] <= 1- There is at most one edge between every two nodes.
class Node { public int id; public double prob; public Node(int id, double prob) { this.id = id; this.prob = prob; } } class Solution { public double maxProbability(int n, int[][] edges, double[] succProb, int start, int end) { Map<Integer, List<Node>> neighbors = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { neighbors.put(i, new ArrayList<>()); } for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) { int a = edges[i][0], b = edges[i][1]; double p = succProb[i]; neighbors.get(a).add(new Node(b, p)); neighbors.get(b).add(new Node(a, p)); } Map<Integer, Double> res = new HashMap<>(); Set<Integer> calculated = new HashSet<>(); PriorityQueue<Node> heap = new PriorityQueue<>((n1, n2) -> Double.compare(n2.prob, n1.prob));//最短路径每次找到最近(小)的点,那么最大prob就是每次找到最大的值作为确认(中转)点 heap.add(new Node(start, 1.0)); while (!heap.isEmpty()) { Node cur = heap.poll(); if (calculated.contains(cur.id)) { continue; } res.put(cur.id, cur.prob); calculated.add(cur.id); for (Node nxt : neighbors.get(cur.id)) { double newProb = cur.prob * nxt.prob; if (newProb > res.getOrDefault(nxt.id, 0.0)) { res.put(nxt.id, newProb); heap.add(new Node(nxt.id, newProb)); } } } return res.getOrDefault(end, 0.0); } }
用dijistra算法,此算法包括一个Node class,是要把离start点的node和probability记录下来。
一个map做的graph,一个hashset做的用来保存已经计算过的节点的数组,一个priorityqueue用来永远取得与start的prob最大点的队列,然后bfs
总结:
We are asked to calculate the maximum prob between two nodes, then we think about bellman-ford or dijistra algorithm, cuz floyd-warshall will must TLE.
Then we choose dijistra:
In this algorithm, we used an object Node to store the destination node and prob. And used a map to store the graph, we use Map<from, Node>, node contains the to-node and prob/
And we need a priorityqueue to maintain the biggest prob to the start node. And by default the node to itself is 1.0 prob
And we need a Set to store the nodes that already visited.
And we need a map to store the result of <to-node, biggest prob> who points to the start node.




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号