20200917-3 白名单
此作业的要求参见作业要求 20200917-3 白名单
本次作业的全部代码可以在codinghttps://e.coding.net/bluestudio/whitelist/whitelist.git , git@e.coding.net:bluestudio/whitelist/whitelist.git。
the git url of this project: https://e.coding.net/bluestudio/whitelist/whitelist.git or git@e.coding.net:bluestudio/whitelist/whitelist.git
WHY BAD CODING!!!! F**K Service.
该作业在截至时间后发生了题目描述修改,请自行关注
白名单 SPEC
老杨因为留作业太多被学生投诉下岗了,去面试,刚好你是公司的面试官。出了道题,题目要求如下(别忙着答题,现在是背景,作业的要求还在后面)。
1) 程序名brute,按照下面的要求读入两个文件。
文件 whitelist,包含1列整数10个,随机生成(要求老杨自己想办法),通过命令行参数指出文件名。
文件 q,包含1列整数1000个,随机生成(也要求老杨自己想办法),通过控制台读入。
2) 在文件q中查找所有不在whitelist中的整数,定向输出到一个文件中。
(读到此处,你见老杨面露困惑,出于多年,不,一年,不,半年的师生情谊,你补充道,“杨老师,您就当这是从交易记录q中查找不符合白名单whitelist的非法交易。”老杨感激地点点头。)
3) 写一份如何部署运行代码的readme。
老杨写成如下代码:
//brute.cpp
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int w_1m = 1000000;
int w[w_1m];
bool is_match(int t, int w[], int w_length)
{
for (int i = 0; i < w_length; i++)
{
if (t != w[i])
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// brute -w whitelist < T
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (argc != 3 || strcmp(argv[1], "-w"))
{
return 1;
}
// init w
//// for(int i=0;i<w_1m)
//// {
//// w[i]=-1; //填充非法数据
//// }
ifstream infile;
infile.open(argv[2]);
int i = 0;
cout << argv[2] << endl;
while (infile >> w[i++])
{
}
int w_length = i - 1;
cout << w_length << endl;
// check t
int t = 0;
while (cin >> t)
{
if (is_match(t, w, w_length))
{
cout << t << endl;
}
}
}
由于数据老杨也得自己想办法,所以老杨又写了两段代码生成数据,代码如下:
//create.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << rand() << "\n";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
readme文档如下:
readme.md
安装vs;
配置环境变量;
编译create.cpp文件;
执行“create >whitelist”生成文件whitelist;
将create.cpp中的for循环中的“10”改为1000;
重新编译create.cpp文件;
执行“create >q”生成文件q;
编译brute.cpp文件;
执行“brute -w q < whitelist > output”
老杨有多年的指导学生的经验,所以会使用多种语言编程。既然是面试,就想着多多展示自己,所以老杨又用C#解了这道题,代码如下:
//foo.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.IO;
namespace foo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
DateTime beforDT = System.DateTime.Now;
if(args.Count() < 1)
return;
string path = args[0];
string[] sm = File.ReadAllLines(path);
int[] p = new int[sm.Length];
//Console.WriteLine(sm.Length);
int[] array = new int[1000000];
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
array[i] = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
}
for(int i = 1;i < sm.Length; ++i)
{
int temp = Convert.ToInt32(sm[i]);
if(find(temp, array) == -1)
Console.WriteLine(temp);
}
DateTime afterDT = System.DateTime.Now;
TimeSpan ts = afterDT.Subtract(beforDT);
Console.WriteLine("DateTime: {0}ms.", ts.TotalMilliseconds);
}
static int find(int key, int[] array)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
if(key == array[j])
return key;
}
return -1;
}
}
}
readme文档如下:
readme.md
安装vs;
编译create.cpp文件;
执行“create >whitelist”生成文件whitelist;
将create.cpp中的for循环中的“10”改为1000;
重新编译create.cpp文件;
执行“create >q”生成文件q;
编译.cs文件;
执行“foo q <whitelist >output”。
你读了一遍老杨的readme.md文件,看了看老杨生成数据的代码,建议到:“为什么不用命令行参数决定生成的数据量的大小呢?”你说完这句话之后老杨有点儿疑惑,你赶紧补充说:“你把for循环中的10替换成1000有点儿麻烦啊,何不把它定义成一个变量呢?在控制台进行输入。”老杨恍然大悟,马上修改了create.cpp和readme.md。
作业0(5分)
Q1: 修改create.cpp文件,改成由命令行参数确定生成的数据的数据量。修改readme.md的对应部分。(要求贴出修改之后的代码和read.md。)
A:
修改后的代码如下:
// add注释文本后的代码段(主观意义上)为修改的代码
//create.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string> // add
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// add
// default counter of random number,
// with default value 10 (create 10 numbers)
int counter = 10;
// add
// try to get counter form argument
if (3 == argc && 0 == strcmp("-n", argv[1])) {
try {
counter = std::stoi(argv[2]);
}
catch (const char* msg) {
cerr << msg << endl;
}
}
// create random number
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < counter; i++)
{
cout << rand() << "\n";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
修改后的read.md如下:
readme.md
安装vs;
配置环境变量;
编译create.cpp文件;
执行“create >whitelist”生成文件whitelist,默认包含10个随机数;
执行“create -n N >whitelist”生成文件whitelist,包含N个随机数;
编译brute.cpp文件;
执行“brute -w whitelist < q > output”
运行截图如下:
fig 1: create程序默认参数运行

fig 2: create程序指定参数为15运行

你看了一下代码,又说道:“老杨,你这结果倒是能对……但是”。你觉得代码的执行效率会比较低。但是你想引导他独立完成修改,你说:“我认为你应该profile一下你的代码,找到代码最慢的地方。”
profile?还好老杨看过《构建之法》,那本书中提到过效能分析。不过老杨不明白为啥要进行效能分析,但毕竟是在面试也不好把太多疑义说出来。所以只好照做。
作业1(10分)
Q2: 对上面两段老杨写的代码任选其一进行profile,观察现象(要求有截图记录)。
A:
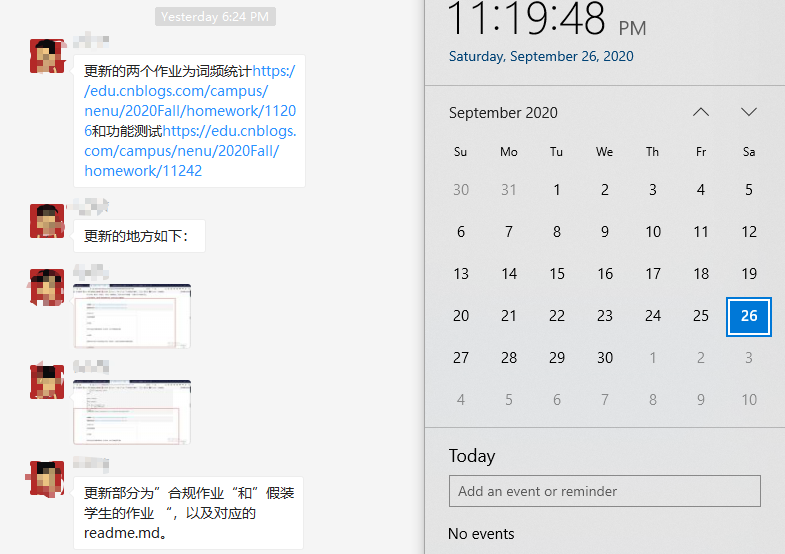
profile结果如下图所示。可以发现,该程序本身运行的时间并不多,外部代码占用较多运行时间。程序自身的代码中,输入数据部分占用较多时间。但由于程序运行时间过短(main function: 1unit),并不能准确反应占用情况。
PS:
原始代码的is_match()有逻辑错误,修改为:
bool is_match(int t, int w[], int w_length)
{
// search every number in array w, test t not same as anyone in array w.
// if have one same as t, return false and exit function;
// if not found any one same as t until last, return true and exit function.
for (int i = 0; i < w_length; i++)
{
if (t == w[i])
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
fig 3: profile-1 结果
你是一个好人,为了让老杨知道为什么要对代码进行profile,于是你在原来的题目的基础上做出了修改,修改之后的题要求如下:
1) 读入两个文件,一个用控制台,一个用命令行参数指出文件名。
文件 biggerwhitelist,包含1列整数1M个,随机生成(要求老杨自己想办法),通过命令行参数指出文件名。
文件 biggerq,包含1列整数10M个,随机生成(也要求老杨自己想办法),通过控制台读入。
2) 在文件biggerq中查找所有不在biggerwhitelist中的整数,重定向输出到一个文件中。
3) 写一份如何部署运行代码的readme。
老杨看了一下,发现只是数据量变大了,代码不用变。于是换了数据又运行了一遍自己的代码,发现跑了很久(大概10分钟)还没结果。由于是在面试,老杨急坏了。这个时候作为面试官的你知道目的已经达成了,于是告诉老杨:“你看,知道为啥让你profile了吧,你还是再profile一次吧。”
PS:
命令行操作如下:
# 创建1M随机数文件biggerwhitelist
.\create.exe -n 1000000 > biggerwhitelist
# 创建10M随机数文件biggerwhitelist
.\create.exe -n 10000000 > biggerq
作业2(10分)
Q3: 以biggerwhitelist和biggerq作为输入,对作业1中选择的代码再次进行profile,找到代码执行最“慢”的地方,截图为证并文字说明。
A:
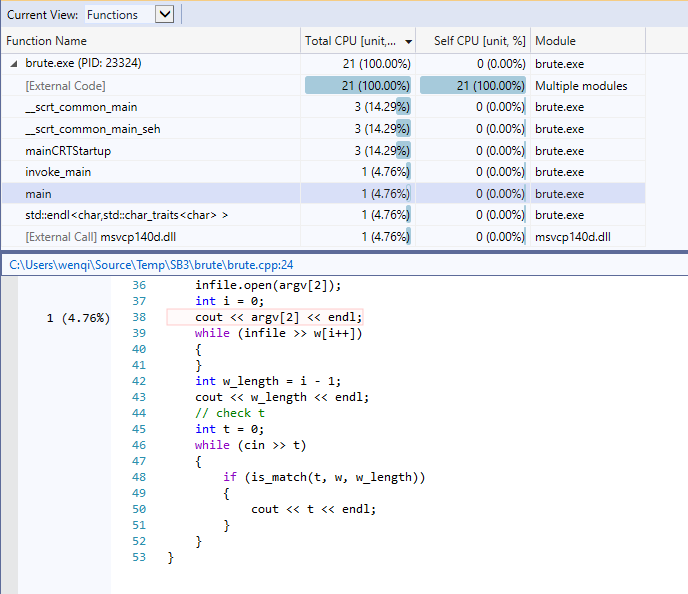
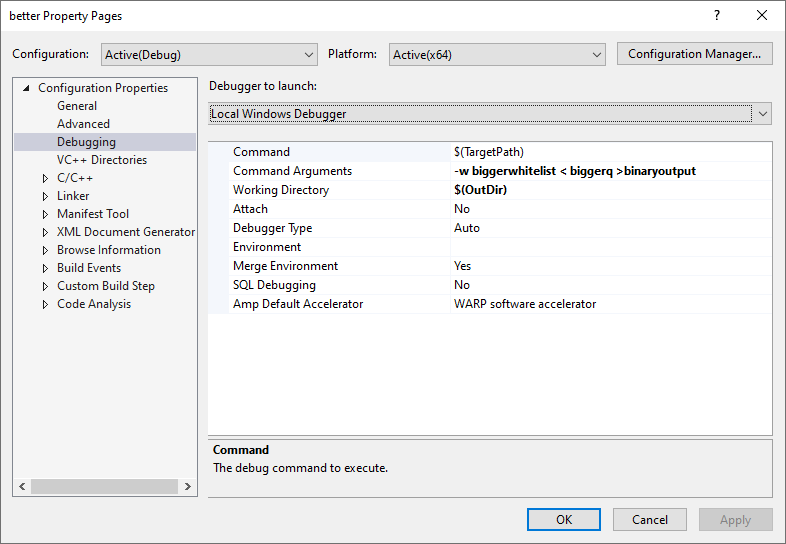
- 修改项目命令行属性,进行profile,属性设置如下图所示。
fig 4: profile 2 项目命令行属性
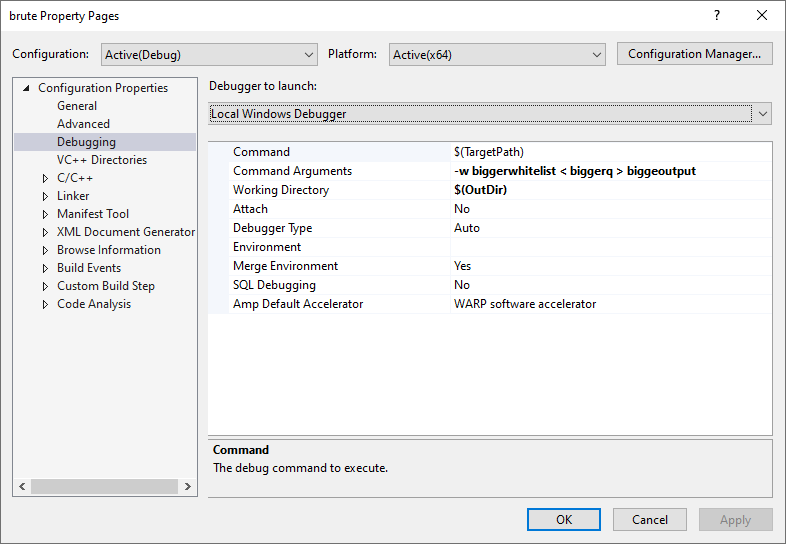
- 配置profile
fig 5: profile 2 配置
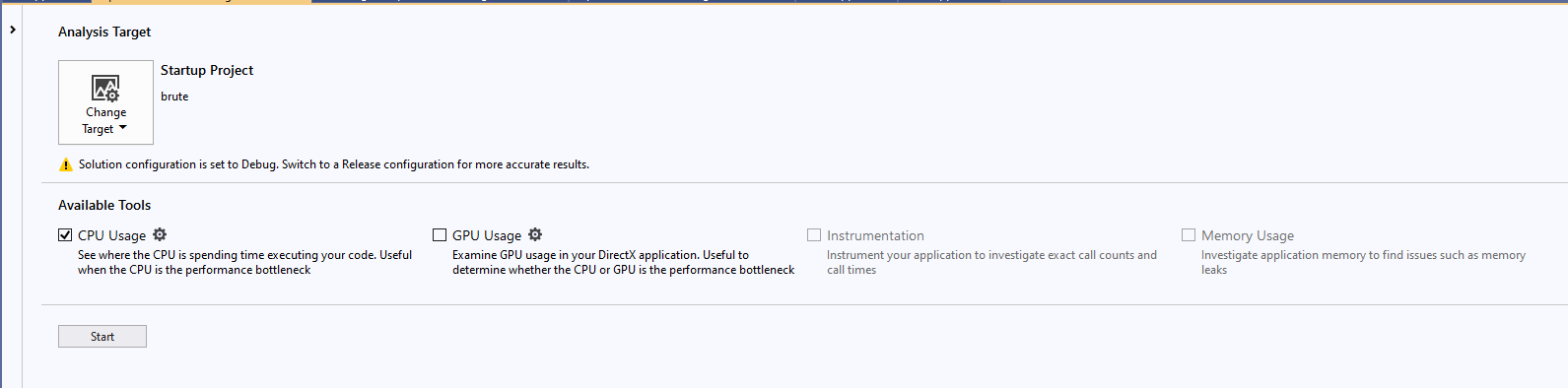
- 测试结果
fig 6: profile 2测试结果1
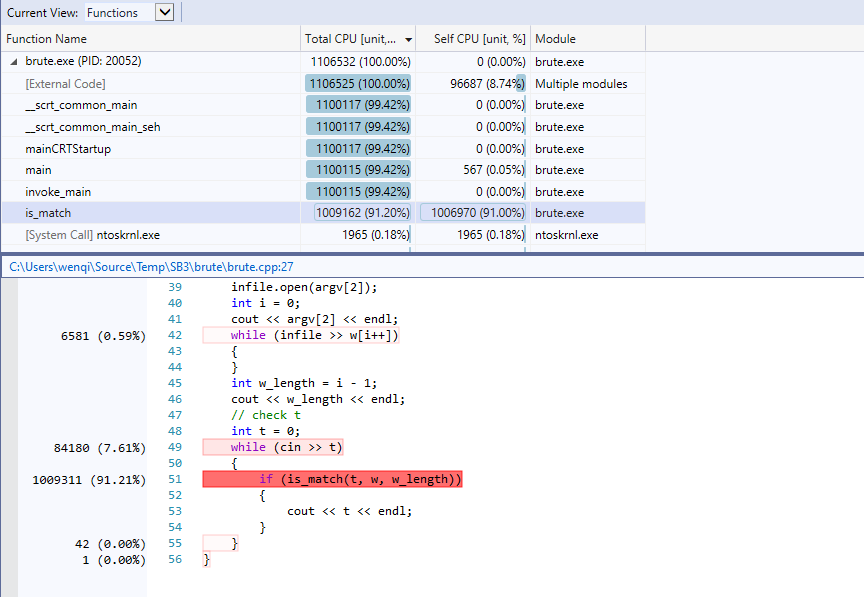
fig 7: profile 2测试结果2

- 分析
is_match()是性能的瓶颈所在,分析得知该程序需要大量的进行查找操作,但is_match()的实现算法为暴力穷举,效率低下,考虑使用更高效的查找算法,如二分查找。
老杨再次profile之后发现了代码最慢的地方在哪儿。这时候你说:“既然找到了最慢的地方,那就开始对你的代码进行优化吧。”对于这次引导的结果,你很得意。
作业3(10分)
Q4: 根据作业2找到的最慢的地方,优化作业1中你选择的代码,在保证输出结果正确的前提下,减少老杨程序运行的时间。(优化后的代码需要你提交到git上,作为教师的判断依据。优化后的程序的名字应该是better.cpp或者better.cs。)
A:
修改is_match()函数,使用二分算法,修改后的代码如下所示。同时,本次作业的全部代码可以在coding找到。注意,本代码在Visual Studio 2019编写、编译以及测试,但版本控制中只包含源码文件,请自行配置解决方案与项目。
bool is_match(int t, int w[], int w_length)
{
// binary search
int left = 0, right = w_length - 1, mid;
while (left <= right) {
mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (t == w[mid]) {
return false;
}
if (t > w[mid]) {
left = mid + 1;
}
else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return true;
}
老杨在优化了代码之后,发现果然代码运行“快”了很多,很是得意。这时候你想“好人”做到底,顺水推舟一把。你说:“对优化后的代码再profile一下吧。”老杨与你意见一致。
作业4(5分)
Q5: 对作业3优化后的代码进行profile,结果与作业2的结果做对比。画表格并文字说明。
A:
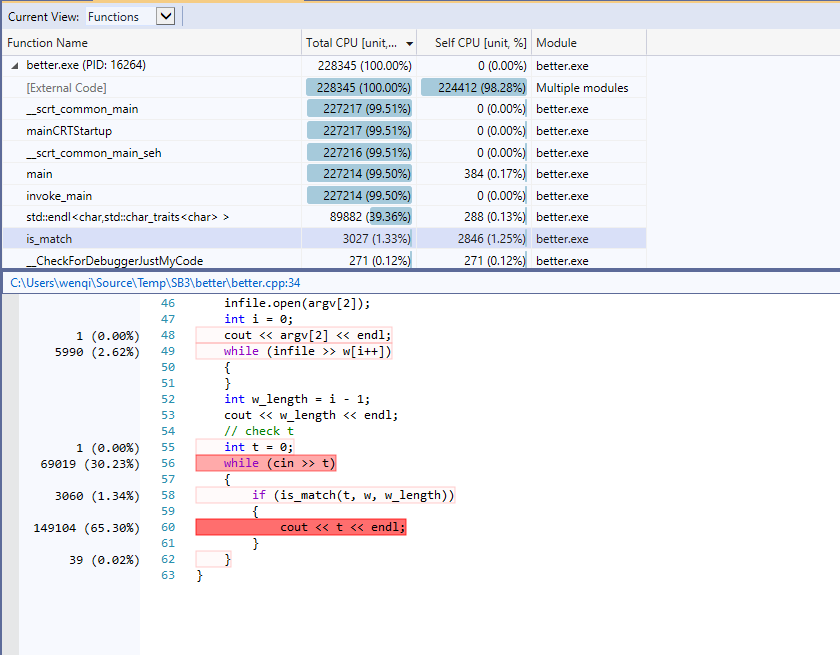
对修改is_match()更新算法后,对程序重新进行profile,测试结果如下图所示。可以看出,程序运行总体用时大大减少,对程序内部函数的统计数据进一步分析,可以看出is_match()函数不在是性能瓶颈,其运行时间远远低于输入输出。更新前后的profile对比如下表所示。
table 1: brute(old)于better(new) CPU占用对比表
| function | burter Total CPU[unit, %] |
better Total CPU[unit, %] |
burter Self CPU[unit, %] |
better Self CPU[unit, %] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| main | 1100115(97.42%) | 227214(99.50%) | 567(0.05) | 384(0.17%) |
| is_match | 1009162(91.6%) | 2027(1.33%) | 1006970(91.0%) | 2846(1.25%) |
- 配置项目命令行参数
fig 8: profile 3 项目命令行配置
- profile配置
fig 9: profile 2测试
- 测试结果
fig 10: profile 2 结果
最后,老杨发现了他原本代码的不足,并且对于你的引导表达了谢意。
但是,你还是犹豫要不要录用老杨。因为你觉得老杨的文档(readme),注释和代码风格有很大的问题,并且给老杨指了出来。
做业5(5分)
Q6: 你觉得老杨的文档(readme),注释和代码风格又哪些问题,该如何改进?
A:
-
函数未写注释。函数应当注释其作用,参数,返回值以及简要的逻辑和算法说明;
-
关键语句或语句块应当注释逻辑和算法说明;
-
readme没有说明程序作用,没有对编译环境、过程和参数做足够说明,也没有对程序的运行提供足够的文档说明。
Q7: 面试结束了,你和老杨握手,对他说出了面试的结果。你说的内容,不是今天的作业题,也许是若干年以后你想对当年教你的教师说的,也许是你希望未来的面试官对你说的。你想说的是什么呢?
A:
功能实现的不错,算法很好,代码可读性也高


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号