实验4 汇编应用编程和c语言程序反汇编分析
实验内容
1. 实验任务1
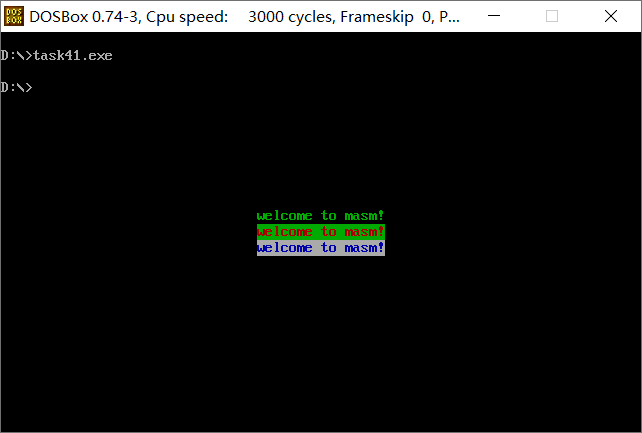
教材「实验9 根据材料编程」(P187-189) 编程:在屏幕中间分别显示绿色、绿底红色、白底蓝色的字符串'welcome to masm!'。
assume cs:code
data segment
db "welcome to masm!"
data ends
code segment
start: mov ax,data
mov ds,ax
mov cx,16
mov ax,0b800h
mov es,ax
mov bx,720h
mov di,0
s1: mov ah,2
mov al,ds:[0+di]
mov es:[bx],ax
add bx,2
inc di
loop s1
mov bx,7c0h
mov di,0
mov cx,16
s2: mov ah,24h
mov al,ds:[0+di]
mov es:[bx],ax
add bx,2
inc di
loop s2
mov bx,860h
mov di,0
mov cx,16
s3: mov ah,71h
mov al,ds:[0+di]
mov es:[bx],ax
add bx,2
inc di
loop s3
mov ax,4c00h
int 21h
code ends
end start
运行结果如下:
2. 实验任务2
编写子程序printStr,实现以指定颜色在屏幕上输出字符串。调用它,完成字符串输出。 子程序printSar 功能:以指定颜色在屏幕上(从屏幕左上角开始)输出字符串 要求:字符串以0结尾 入口参数 字符串的起始地址—> ds: si (其中,字符串所在段的段地址—> ds, 字符串起始地址 的偏移地址—> si 字符串颜色—> al 出口参数:无 使用任意文本编辑器,录入汇编源程序task2.asm。
assume cs:code, ds:data
data segment
str db 'try', 0//以0结尾
data ends
code segment
start:
mov ax, data
mov ds, ax//data段用作数据段
mov si, offset str//取变量str为偏移地址
mov al, 2//颜色指定为绿色
call printStr//进入子程序
mov ah, 4ch
int 21h
printStr:
push bx
push cx
push si
push di//保留现场
mov bx, 0b800H
mov es, bx
mov di, 0
s: mov cl, [si]
mov ch, 0
jcxz over//当cx=0即扫描到字符串结尾0,退出
mov ch, al
mov es:[di], cx
inc si
add di, 2
jmp s
over: pop di
pop si
pop cx
pop bx
ret//退出子程序恢复现场
code ends
end start
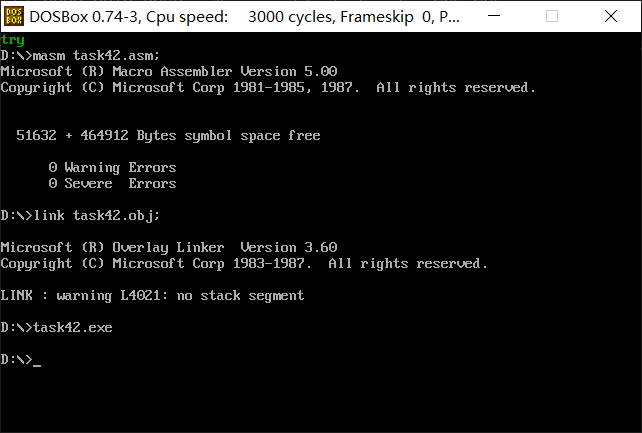
实验结果:
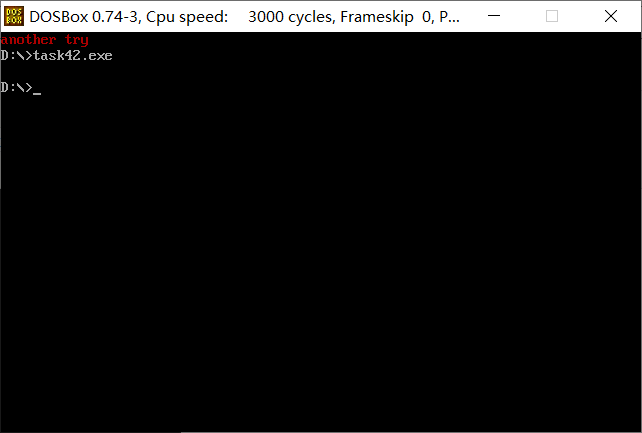
把line3改为:
str db 'another try', 0
把line12改为:
mov al, 4//字体改成红色
基于运行结果,理解源代码,以及,组合使用转移指令call和ret实现子程序的原理与方法。
具体地,在 line18-40中: line19-22, line36-39,这组对称使用的push、pop,这样用的目的是什么?
line30的功能是什么?
对称使用push和pop指令是为避免在循环体中改变原来寄存器中的相关数据故而利用栈进行保存与执行完毕的恢复。
line30的功能是
把设置好颜色属性的字符送入显存。
3. 实验任务3
使用任意文本编辑器,录入汇编源程序task3.asm。 子程序num2str: 功能:把0~2559之间的任意整数转换成数字字符串,例如,把1984转换成'1984' 入口参数 要转换的整数 —> ax 数字字符串的起始地址 —> ds:di (其中:数字字符串所在段的段地址—> ds,字符串 起始地址的偏移地址—>di) 出口参数:无
assume cs:code, ds:data
data segment
x dw 1984
str db 16 dup(0)
data ends
code segment
start:
mov ax, data
mov ds, ax
mov ax, x//被除数设置为1984
mov di, offset str//数字串设为偏移地址
call num2str
mov ah, 4ch
int 21h
num2str:
push ax
push bx
push cx
push dx
mov cx, 0
mov bl, 10
s1:
div bl//除以10
inc cx
mov dl, ah//余数传递给dl
push dx//保存当前的低位数字
mov ah, 0
cmp al, 0//商与0作比较
jne s1//商不为0则跳转到s1
s2:
pop dx
or dl, 30h//数字转字符
mov [di], dl
inc di
loop s2
pop dx
pop cx
pop bx
pop ax
ret
code ends
end start
子任务1
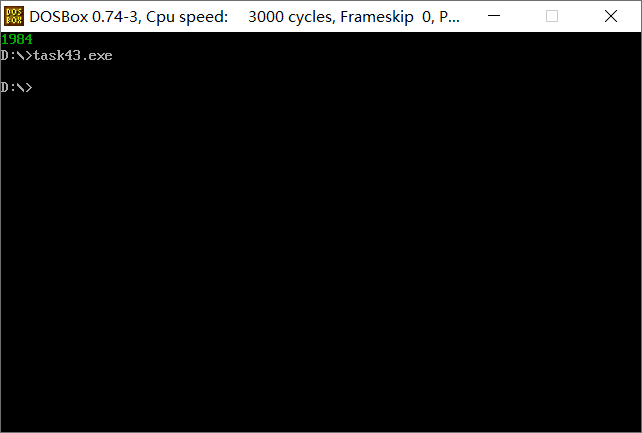
对task3.asm进行汇编、链接,得到可执行程序后,在debug中使用u命令反汇编,使用g命令执行 到line15(程序退出之前),使用d命令查看数据段内容,观察是否把转换后的数字字符串'1984'存放 在数据段中str标号后面的单元。
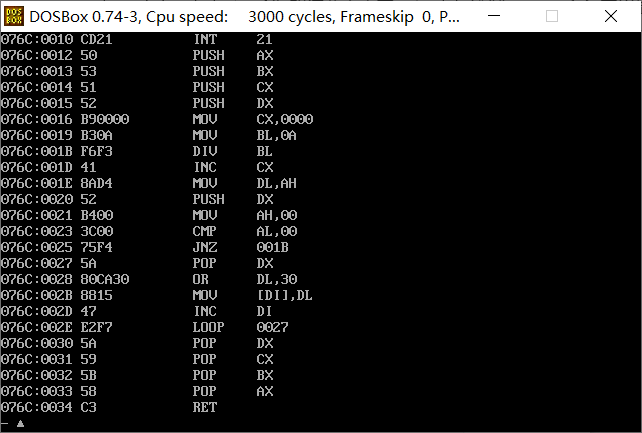
-d命令查看

子任务2
对task3.asm源代码进行修改、完善,把task2.asm中用于输出以0结尾的字符串的子程序加进来, 实现对转换后的字符串进行输出。
assume cs:code, ds:data
data segment
x dw 1984
str db 16 dup(0)
data ends
code segment
start:
mov ax, data
mov ds, ax
mov ax, x
mov di, offset str
call num2str
mov bx, 0b800H
mov es, bx
mov si,2
mov di,0
push bx
push cx
push si
push di
s: mov cl, [si]
mov ch, 0
jcxz over
mov ch, 2
mov es:[di], cx
inc si
add di,2
jmp s
over: pop di
pop si
pop cx
pop bx
mov ah, 4ch
int 21h
num2str:
push ax
push bx
push cx
push dx
mov cx, 0
mov bl, 10
s1:
div bl
inc cx
mov dl, ah
push dx
mov ah, 0
cmp al, 0
jne s1
s2:
pop dx
or dl, 30h
mov [di], dl
inc di
loop s2
pop dx
pop cx
pop bx
pop ax
ret
code ends
end start
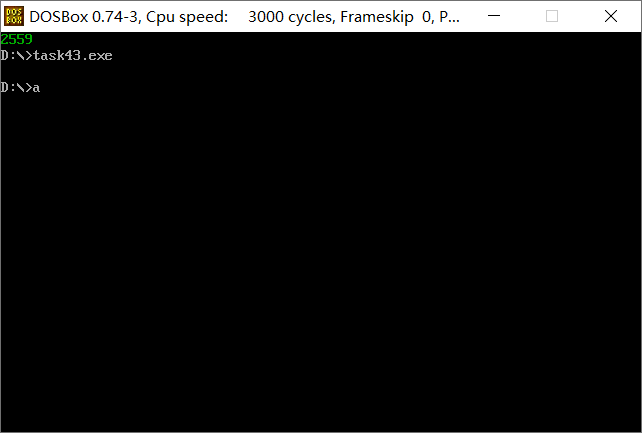
数据改为:
data segment
x dw 2559
str db 16 dup(0)
data ends
4. 实验任务4
使用任意文本编辑器,录入汇编源程序task4.asm。
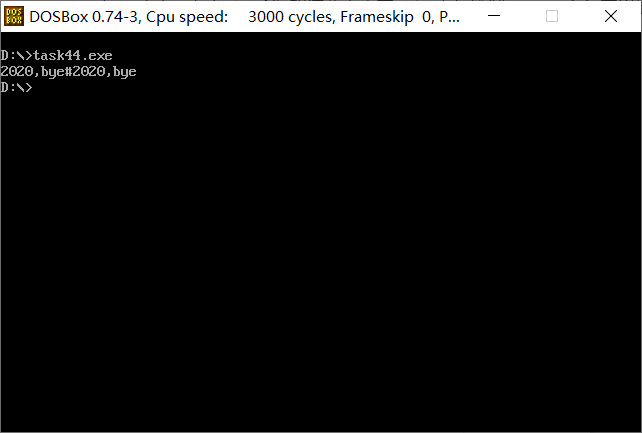
汇编、链接、运行程序,输入一个字符串并以#结束(比如,2020, bye#)观察运行结果。结合运行结 果,理解程序功能,了解软中断指令。
assume cs:code, ds:data
data segment
str db 80 dup(?)
data ends
code segment
start:
mov ax, data
mov ds, ax
mov si, 0
s1:
mov ah, 1
int 21h
mov [si], al
cmp al, '#'
je next
inc si
jmp s1
next:
mov cx, si
mov si, 0
s2: mov ah, 2
mov dl, [si]
int 21h
inc si
loop s2
mov ah, 4ch
int 21h
code ends
end start
输入2020,bye#
运行结果:
具体地: line12-19实现的功能是?
cmp用于判断是否输入结束,当所读取的当前字符为'#'读取结束,跳转到next部分,否则继续读入键盘输入的字符。
line21-27实现的功能是?
设置循环次数为读取的非‘#’字符个数将其在显示器上输出。
5. 实验任务5
在visual studio集成环境中,编写一个简单的包含有函数调用的c程序。代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
int sum(int, int);
int main() {
int a = 2, b = 7, c;
c = sum(a, b);
return 0;
}
int sum(int x, int y) {
return (x + y);
}
在line7, line13分别设置断点,在调试模式下,查看反汇编代码。 分析反汇编代码,从汇编的角度,观察高级语言中参数传递和返回值是通过什么实现的,以及,参数入 栈顺序,返回值的带回方式,等等。
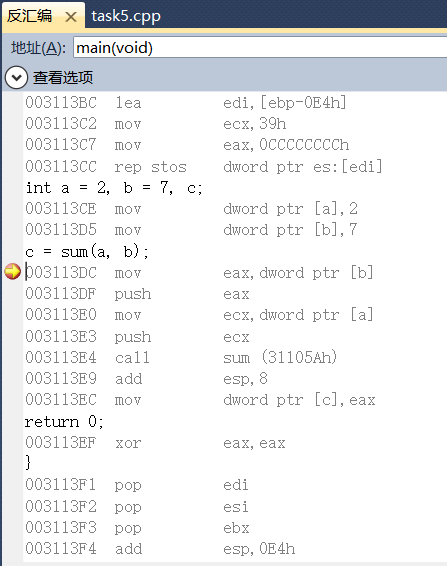
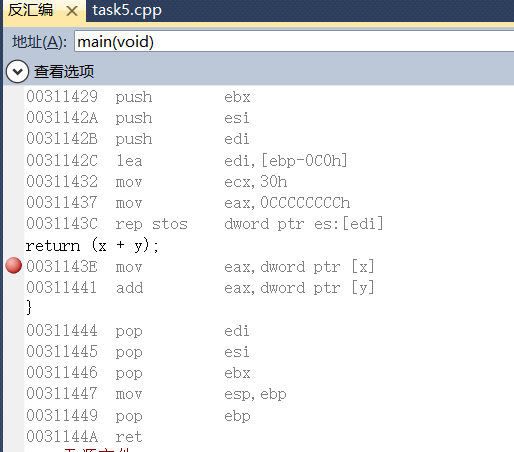
分析:高级语言中的参数传递是从双字数据ptr [a]、ptr [b]传入eax、ecx等寄存器,用call命令调用sun函数,最后返回真正的值为eax,再传入双字数据ptr[c]




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号