| 这个作业属于哪个班级 | 数据结构-网络20 |
| ---- | ---- | ---- |
| 这个作业的地址 | DS博客作业02--栈和队列 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 学习栈和队列的结构设计及运算操作 |
| 姓名 | 余智康 |
目录
0. 展示PTA总分
1. 本章学习总结
2. PTA实验作业
3. 阅读代码
0.PTA得分截图

1.本周学习总结
1.1 栈
画一个栈的图形,介绍如下内容。
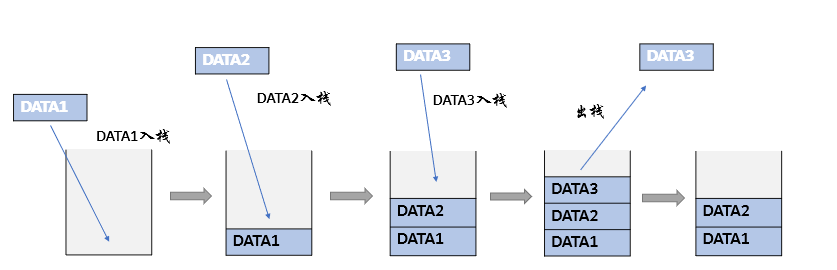
- 顺序栈的结构:
- 顺序栈是使用数组来存放栈内元素,需要一个整型变量top来记录目前栈顶的位置。
- 由于顺序栈需要考虑数组的容量,需要一个maxsize来记录最大能存放的数据个数
则,顺序栈的结构体定义如下:
typedef struct {
int data [MAXSIZE]; //以整型数据为例,若栈需要存放其他类型的数据,修改data[]的类型,如:char data[MAXSIZE]
//MAXSIZE 可以用 #define 来定义,这样便于修改。也可以直接用整型数代替,如:int data[12]
int top; //栈空时,top的值为-1
int maxSize = MAXSIZE; //存放最大数据个数,便于判断栈满情况
}SqStack, * stack;
- 顺序栈的操作函数:
- 判断栈空:
bool stack_empty(stack sta) //如果栈空,返回 1.否则返回 0
{
if(sta -> top == -1) return true;
else return false;
}
- 判断栈满:
bool stack_full(stack sta) //如果栈满,返回 1.否则返回 0
{
if(sta -> top == sta -> maxSize - 1) return true;
else return false;
}
- 进栈:
bool stack_push(stack sta, int x) //进栈成功,返回 1, 失败返回 0
{
if(sta -> top == sta -> maxSize - 1) //栈满情况,入栈失败
return false;
sta -> data [ ++ sta -> top] = x;
return true;
}
- 出栈:
bool stack_pop(stack sta, int &e) //出栈成功,将出栈的元素保存在e中, 返回 1, 失败返回 0
{
if(sta -> top == -1) //栈空情况,出栈失败
return false;
e = sta -> data[ sta -> top --];
return true;
}
- 共享栈:
- 介绍:
- 顺序栈需要考虑栈的容量,而栈的容量又不总会恰恰好与所填入的数据元素的个数相同,从而会产生空间的不足或是浪费
- 为增大空间的利用率,有了顺序栈的一种新的形态——“共享栈”
借用《大话数据结构》作者的比喻,普通的顺序栈就像是单身公寓,独立的卧室、厨卫、客厅。而共享栈好比双人套房,各自独立的卧室,共享的客厅、厨卫。
-
特点:
-
共享栈的两个栈顶 top1 和 top2 分别从 -1 和 MAXSIZ (栈的最大容量)开始
-
当 top1 + 1 == top2 时,栈满
-
共享栈的结构体定义中有两个整型的top变量,top1,top2
-
在进栈和入栈的函数中,需要输入一个用来判断入栈1还是栈2的变量
-
图像:
-
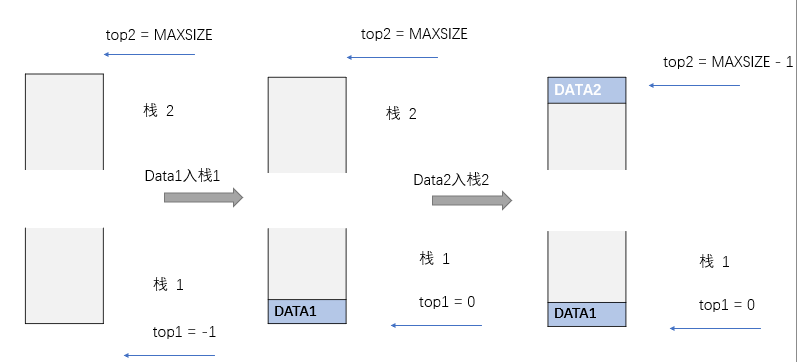
//代码, 部分细节与顺序表相同
/*入栈*/ bool sta_push(stack sta, int x, int sta_select)
{
if (sta->top1 + 1 == sta->top2)
return false; //栈满
if (sta_select == 1)
sta->data[++sta->top1] = x;
else if (sta_select == 2)
sta->data[--sta->top2] = x;
return true
}
/*出栈*/ bool sta_pop(stack sta, int &e, int sta_select)
{
switch (sta_select)
{
case 1:
if (sta->top1 == -1)
return false; //栈1空
e = sta->data[sta->top1--];
return true;
case 2:
...
}
}
- 链栈的结构:
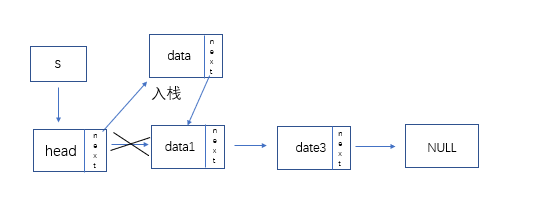
-
介绍;
- 链栈顾名思义是用链表来存放数据元素的栈,数据元素的入栈和出栈即是对链表的插入和删除
- 与顺序栈相比,链栈不需要考虑栈满的状态
- 为满足先进后出的原则,链栈一般使用尾插法实现入栈
-
链栈的结构体:
typedef struct linkNode{
int data; //以整型数据为例,若栈需要存放其他类型的数据,修改data的类型,如:char data
struct linkNode* next;
}LiNode, *LiStack;
- 链栈的操作与单链表类似:
- 链栈的初始化:
void InitStack(LiStack &s)
{
s = new LiNode;
s -> next = NULL;
}
- 链栈的销毁:
void DestroyStack(LiStack &s)
{
LiStack node;
while ( s! = NULL)
{
node = s;
s = s -> next;
delete node;
}
}
- 链栈的空:
bool StackEmpty(LiStack s)
{
if(s == NULL)
return true;
else
return false;
}
- 链栈的进栈:
void StackPush( LiStack &s, int x) // x 进栈
{
LiStack temp;
temp = new LiNode;
temp -> data = x;
temp -> next = s -> next;
s -> next = temp;
}
- 链栈的出栈:
bool StackPop( LiStack &s, int &e) //出栈,并将栈顶元素赋值给e
{
LiStack temp = s -> next;
if (s -> next == NULL)
return false; //需要判断空栈的情况,一开始我忘记了判断链表为空
e = s -> next -> data;
s -> next = s -> next -> next;
delete temp;
return true;
}
1.2 栈的应用
-
后缀表达式
-
大致思路:
- 给每个符号设定优先级
- 遇到符号时,判断符号与栈顶符号的优先级,决定将符号入栈,还是将出栈
- 当符号优先级高于栈顶符号的优先级时,该符号入栈。
- 若符号优先级低于栈顶符号优先级时,出栈,直到该符号的优先级高于栈顶符号
- 未避免空栈的影响,可以将'#'的优先级设为最低,并将'#'放置在栈底
-
具体思路:
- 需要考虑负数的情况(类似于上学期的切分表达式):负数会出现在第一个数或者是括号后面,可以使用标志(flag)来处理
- 需要考虑小数、以及十位数及以上的情况:可以在处理数字字符的if分支中使用continue
- 需要考虑符号和栈顶符号相同时优先度的判断:每个优先级可以设置间隔为2,栈外面的符号优先级减1
- 需要考虑括号的情况:可以将括号的优先度设为仅比'#'高,当遇到左括号'('时,不进行优先度判断,直接入栈
- 需要考虑优先级的设置:创建数组存放(level['#'] = -4;)(一开始我想使用动态分配7个位置存放优先度的,节省点空间。只是DEV和VS可以通过,但PTA会出现段错误,就改成直接分配128个位置给level[]了
-
主要代码:
for (count = 0; count < formula_mid.size(); count++)
{
if (flag) //负号的处理
{
flag = 0;
if (formula_mid[count] == '+')
{
continue;
}
else if (formula_mid[count] == '-')
{
formula_back += formula_mid[count];
continue;
}
}
if (formula_mid[count] == '(') //括号的处理
{
flag = 1;
op_sta.push('(');
continue;
}
if ((formula_mid[count] >= '0' && formula_mid[count] <= '9') || formula_mid[count] == '.') // 小数和多位数的处理
{
formula_back += formula_mid[count];
continue;
}
if(!((formula_mid[count] >= '0' && formula_mid[count] <= '9') || formula_mid[count] == '.')) //其他符号处理
{
while (level[formula_mid[count]] - 1 < level[op_sta.top()]) //小于栈顶优先度,出栈
{
if (op_sta.top() == '(')
{
op_sta.pop(); // 括号不入后缀表达式
continue;
}
formula_back += ' ';
formula_back += op_sta.top();
op_sta.pop();
}
if (level[formula_mid[count]] - 1 > level[op_sta.top()]) //大于,除了')'外,入栈
{
if (formula_mid[count] == ')')
continue;
op_sta.push(formula_mid[count]);
}
}
formula_back += ' ';
}
//栈内剩余元素
while (!op_sta.empty() && op_sta.top() != '#')
{
formula_back += ' ';
formula_back += op_sta.top();
op_sta.pop();
}
cout << formula_back;
return 0;
}
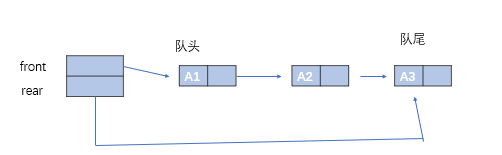
1.3 队列(
- 顺序队列

-
介绍:
- 顺序队列:front位置为队头元素,rear的位置为队尾元素的后一位
- 队空条件:front == rear
- 队满条件:rear == MAXSIZE - 1
-
顺序队列的结构:
typedef struct queue{
int data[MAXSIZE];
int front,rear;
}Queue;
- 顺序队列初始化:
void InitQueue(SqQueue &q)
{
q = new Queue;
q -> front = q -> rear = -1;
}
- 顺序队列入队:
bool PushQueue(SqQueue &q, int x)
{
if(q -> rear == MAXSIZE -1)
return false;
q -> data[q->rear++] = x;
return true;
}
- 顺序队列出队:
bool PopQueue(SqQueue &q, int &e)
{
if(q -> rear == q -> front)
return false;
e = q -> data[q->front++];
return true;
}
- 环形队列

-
介绍:
- 环形,空间利用率大,解决的顺序队列存在的“假溢出”的问题
- 队空条件:front == rear
- 队满条件:(rear + 1) % MAXSIZE == front
-
环形队列列初始化:
void InitQueue(SqQueue &q)
{
q = new Queue;
q -> front = q -> rear = 0;
}
- 环形队列入队:
bool PushQueue(SqQueue &q, int x)
{
if((q > rear + 1) % MAXSIZE == q -> front)
return false;
q -> rear = (q -> rear + 1) % MAXSIZE;
q -> data[q->rear] = x;
return true;
}
- 环形队列出队:
bool PopQueue(SqQueue &q, int &e)
{
if(q -> front == q-> rear)
return false;
e = q -> data[q->front];
q -> front = (q->front + 1) % MAXSIZE;
return true;
}
- 链队列

-
介绍:
-
入队使用尾插法
-
队空条件:front == rear == NULL
-
队满条件:不考虑
-
-
链队的结构:
//数据结点
typedef struct qNode{
int data;
struct qNode *next;
}QNode;
//头尾指针
typedef struct{
QNode *front;
QNode *rear;
}LinkQueue;
- 链队的入队:
void PushQueue(LinkQueue &Q, int x)
{
QNode* temp = new QNode;
temp -> data = x;
Q.rear => next = temp;
Q,rear = Q.rear -> next;
Q.rear -> next = NULL;
}
- 链队的出队:
bool PopQueue(LinkQueue &Q, int &e)
{
QNode* temp = Q.front -> next;
Q -> front -> next = temp => next;
e = temp -> data;
delete temp;
}
1.4 队列的应用(
- 报数游戏
- 思路:
- 建立队列1,里面存放编号1~N的人,
- 开始报数,删除的人放入del_thing[]数组中,未被删除的出队列1,进入队列2
- 返回队列2,并把队列2赋值给队列1,删除队列2,新建队列2
- 循环步骤2、3,直到所有人都被删除
- 主要代码:
if (game.del_num >= game.maxSize) //超出,输出错误,结束程序
{
cout << "error!" << endl;
return 0;
}
while (game.del_count < game.maxSize) //步骤4,即循环步骤2、3
{
queue <int> que_empty;
que = *PushQueue(game, que, que_empty);
while (!que_empty.empty())
{
que_empty.pop();
}
}
// 主要函数, 将人放在que中
queue <int>* PushQueue(GAME& game, queue<int> que_1, queue<int>& que_2)
{
while (!que_1.empty())
{
game.count_num++;
if (game.count_num % game.del_num == 0)
{
game.del_thing[game.del_count++] = que_1.front();
que_1.pop();
continue;
}
que_2.push(que_1.front());
que_1.pop();
}
return &que_2;
}
2.PTA实验作业
2.1 符号配对
https://gitee.com/welcome_to_tommrow/pta-code/blob/master/7-3 符号配对.cpp
2.1.1 解题思路及伪代码
- 解题思路:
- 将输入放入string字符串中,再进行遍历
- 遍历时,发现左半符号,则左半符号入栈。
- 遍历判断符号时,需要判断当前位置和下一个位置的符号,以便发现注释符(/**/)
- 对于注释符,为了方便操作,可以使用其它非题中的符号代为入栈。当然,直接入栈也是可以的,相差不多
- 遇到右边符号时,先检查栈内是否为空,若为空,则缺少左符号,返回false
- 反之,再与栈顶符号比对。若符合,则出栈,不符合,输出缺少右符号,返回false
- 当遍历完成之后,检查栈内是否还有元素,若仍有元素,输出缺少右符号,返回false
- 伪代码:
for count = 0 to procedure.size()
// push stack
// 1)
if procedure[count] == '/' && procedure[count+1] == '*'
push stack
push stack
continue
end if
// 2)
else if sign_left[1].find(procedure[count]) < 3 && >= 0
push stack
continue
end else if
// pop stack, (need to check whether stack is empty or not?)
// situation 1: short of left_sign
// 1)
if procedure[count] == '*' && procedure[count+1] == '\'
if stack.empty() || !(stack.top == '*')
cout <<"NO\n" << "?-*/\n"
return false
end if
else if !(stack.top == '*')
cout << "NO\n" << sta_sign.top() << "-?\n"
return false;
end else
else if(stack.top == '*')
stack.pop
stack.pop
count++
continue
end else
end if
// 2)
if (position = sige_right[1].find(procedure[count])) < 3 && >=0
if stack.empty()
shour of stack_right
return false
end if
else if !(stack.top == sign_left[1][position])
if(sta_sign.top() == '*')
cout << "NO\n" << "/*-?\n"
else
cout << "NO\n" << sta_sign.top() << "-?\n"
return false;
else if(stack.top == sign_left[1][position])
stack.pop
end else
end if
end for
// situation 2: shor of left_sign
if !stack.empty()
// 1)
if stack.top == '*'
short of "/*"
return false
end if
else
position = sign_left[1].find(stack.top)
short of sign_right[1][position]
return false
end if
end if
2.1.2 总结解题所用的知识点
- C++中字符串的使用,以及输入一串带空格的字符串,放入变量line中
string line;
getline(cin, line);
line.empty();
line.find('A');
line.size();
- 入栈、出栈,以及栈空的判断
- 如何进行配对
2.2 银行业务队列简单模拟
https://gitee.com/welcome_to_tommrow/pta-code/blob/master/7-6 银行业务队列简单模拟.cpp
2.2.1 解题思路及伪代码
- 解题思路: 依编号分配A、B,然后A处理两只,B处理一只,直到某个为空,剩余处理
- 伪代码:
// PushQue 将数据由字符型改为整型,放入队列A 和队列B中
for i = 0 to line.size()
num = 0
if line[i] >= '0' && line[i] <= '9'
while line[i] >= '0' && line[i] <= '9' do
num = num = line[count++] - '0' + num * 10
end while
if num % 2 == 0
bank.que_B.push(num); //偶数编号存放入B中
else
bank.que_A.push(num); //奇数编号存放入A中
end if
end if
end for
//将处理完的,放入list数组中
while !bank.que_A.empty() && !bank.que_B.empty() do
time = 0
while !bank.que_A.empty() && time < 2
bank.list[count++] = bank.que_A.front();
bank.que_A.pop();
time++;
end while
bank.list[count++] = bank.que_B.front();
bank.que_B.pop();
end while
//若队列A不为空
while !bank.que_A.empty() do
bank.list[count++] = bank.que_A.front();
bank.que_A.pop();
end while
//若队列B不为空
while !bank.que_B.empty() do
bank.list[count++] = bank.que_B.front();
bank.que_B.pop();
end while
2.2.2 总结解题所用的知识点
- 将字符型的数字转化为整型
while (line[count] >= '0' && line[count] <= '9')
{
num = line[count++] - '0' + num * 10;
}
- string类型字符串的遍历
for (count = 0; count < line.size(); count++)
{
...
}
- 两组数据的以不同的速度合并
while (!que_A.empty() && !que_B.empty())
{
time = 0;
while (!que_A.empty() && time < 2)
{
...
time++;
}
if (!bank.que_B.empty())
{
...
}
}
3.阅读代码
3.1 题目及解题代码
- 题目: 接雨水
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
输出:6
解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)
- 代码:
int trap(int* height, int heightSize) {
int n = heightSize;
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
int ans = 0;
int stk[n], top = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
while (top && height[i] > height[stk[top - 1]]) {
int stk_top = stk[--top];
if (!top) {
break;
}
int left = stk[top - 1];
int currWidth = i - left - 1;
int currHeight = fmin(height[left], height[i]) - height[stk_top];
ans += currWidth * currHeight;
}
stk[top++] = i;
}
return ans;
}
//作者:LeetCode-Solution
//链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/solution/jie-yu-shui-by-leetcode-solution-tuvc/
//来源:力扣(LeetCode)
//著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
3.2 该题的设计思路及伪代码
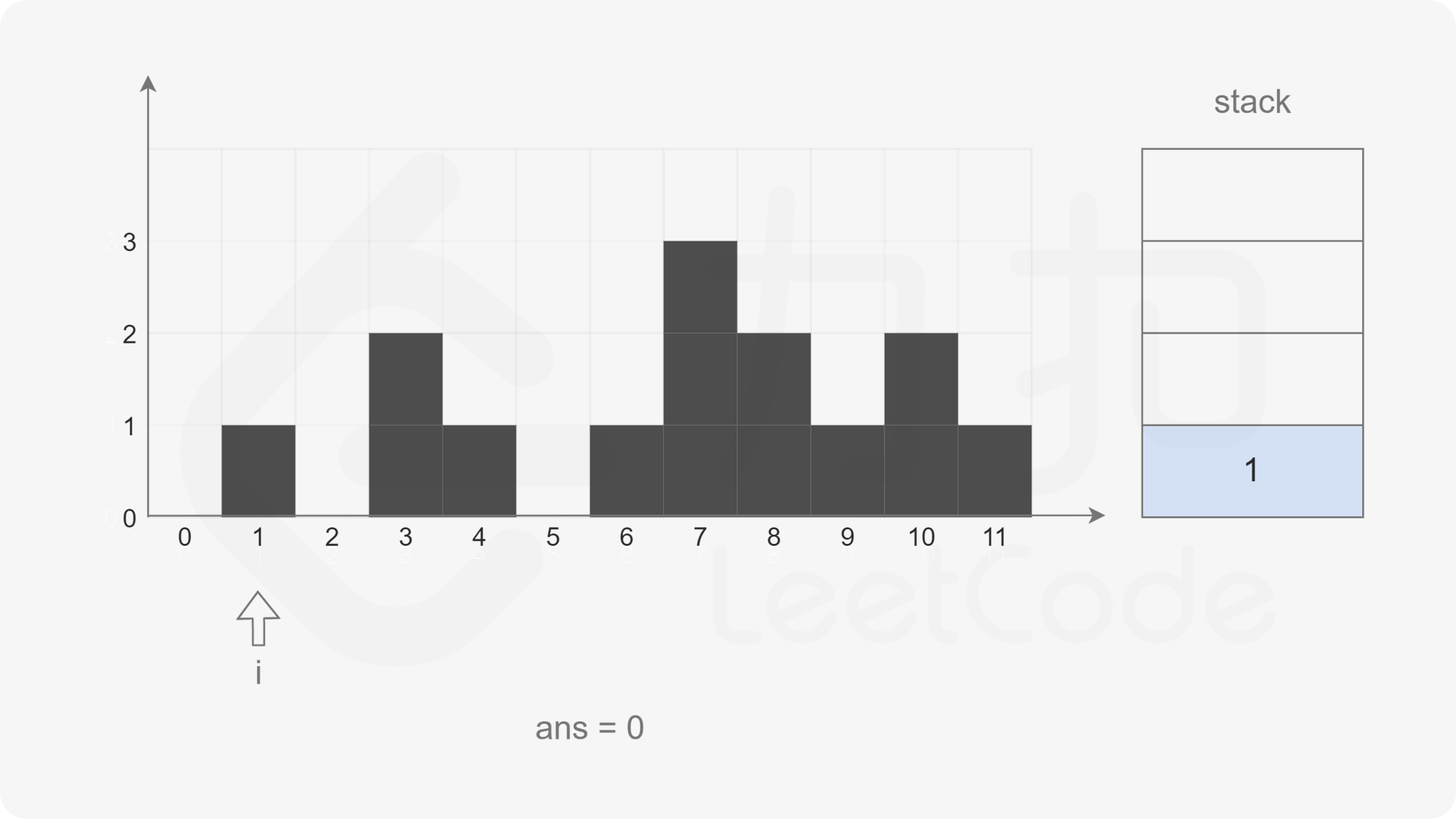
-
设计思路:
- 遍历数组height[],在栈内至少有两个元素的情况下,记栈顶元素下面的一个元素为left
- 当height[i] 小于等于 栈顶元素时入栈
- 当height[i] 大于栈顶元素height[top]时,得到雨水区域
- 宽度:i - left -1
- 高度:min(height[left],height[i]) - height[top]
- 即可根据高度和宽度得到雨水量
- 计算结束后,出栈,left成为新的栈顶,继续操作,直到栈为空,或是height[i] 小于等于 栈顶元素
-
伪代码:
int n = heightSize //最大宽度
if (n == 0) then
return 0
end if
int ans = 0
int stk[n], top = 0
for i = 0 to n-1
while top && height[i] > height[stk[top - 1]] do
int stk_top = stk[-top]
if(!top)
break
end if
int left = stk[top - 1]
int currWidth = i - left -1 //宽度
int currHeight = fmin(height[left], height[i]) - height[stk_top]; //高度
ans += currWidth * currHeight;
end while
stk[top++] = i
end for
return ans
3.3 分析该题目解题优势及难点。
- 优势:
- 条理清晰,便于理解
- 巧妙地利用了栈解决了雨水量的问题
- 难点:
- 如何利用栈完成雨水的测量
- 入栈的条件、出栈的条件,结束的条件




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号