集合类之HashMap详解
首先说一下我对HashMap的认识。(基于jdk1.8)
1.HashMap是继承AbstractMap类,AbstractMap又是实现Map接口。实现了Serializable接口,因此它支持序列化,实现了Cloneable接口,能被克隆。
2.HashMap的底层实现是用哈希表,而Java中实现哈希表的数据结构是数组+链表。其中,当链表达到一定长度,会使用到红黑树。(需要继续了解红黑树)
3.在HashMap中,有几个重要的性能参数,比如loadFactor加载因子0.75,还有一个threshold阈值(threshold=loadFactor*桶数量),初始大小16=1<<4,其他的还有下面详细讲。
4.简单地讲一下HashMap中将<key,value>看成一个Node类对象(实现的是Map.Entry<K,V>的接口),里面包括hash,key,value,next属性,put(key,value)时,HashMap会根据hash(key.hashCode())的值,确定该node对象所在数组中的位置,如果不同的hash(key)映射到相同的数组位置,就使用尾插法插入到链表中。get(key)时,会根据hash(key)确定在数组的位置,该位置上的链表有多个值,使用key.equal(k)确定key所在位置,返回node对象,读取它的v。(大致应该是这样,还有细节需要再看看)
5.HashMap是非线程安全的,只使用于单线程环境下,多线程环境下可以采用concurrent并发包下的concurrentHashMap。
6.HashMap初始化的长度使16,扩容2倍,即使再扩容,也是2的n次方。
HashMap构造方法有:
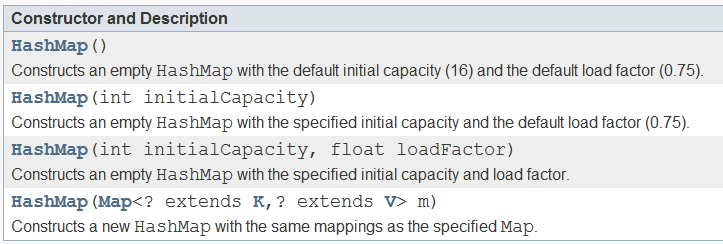
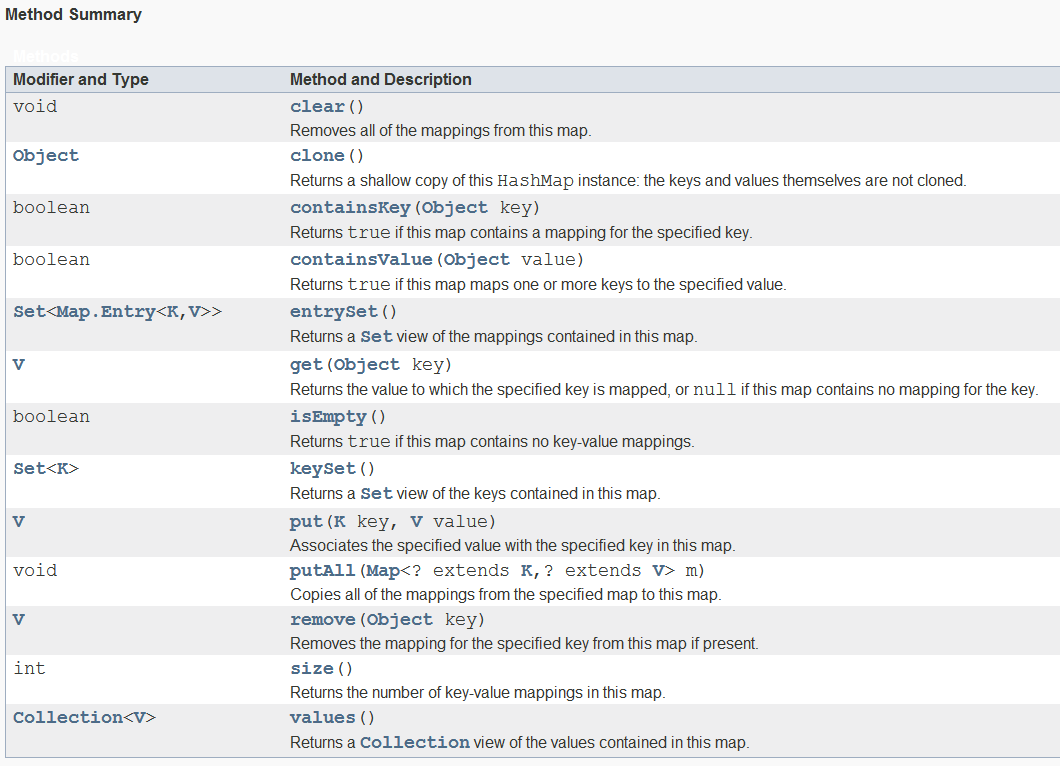
HashMap的方法有:
常用的方法有put(key,value),get(key),size(),containKey(key),containValue(value).
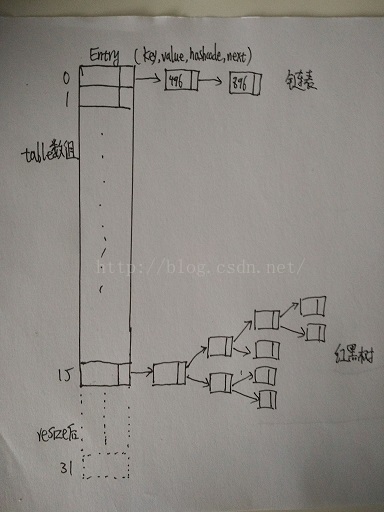
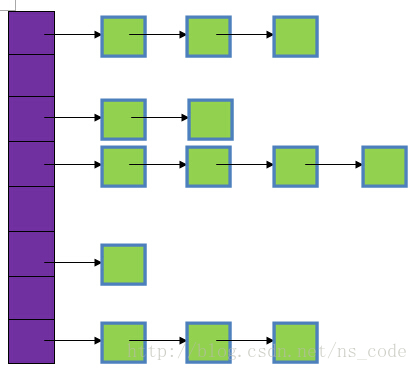
一、了解HashMap数据结构
本着负责任的态度,在网上找了两个比较形象的图
地址:https://blog.csdn.net/brycegao321/article/details/52527236 和 https://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/36034955
可以看出,HashMap底层实现是哈希表(HashTable),java中哈希表(HashTable)是数组和链表的结合体。
如果在同一个数组位置上,插入Node类对象,使用尾插法,插入链表中。
可以看一下Node类在HashMap源码中是什么样的:
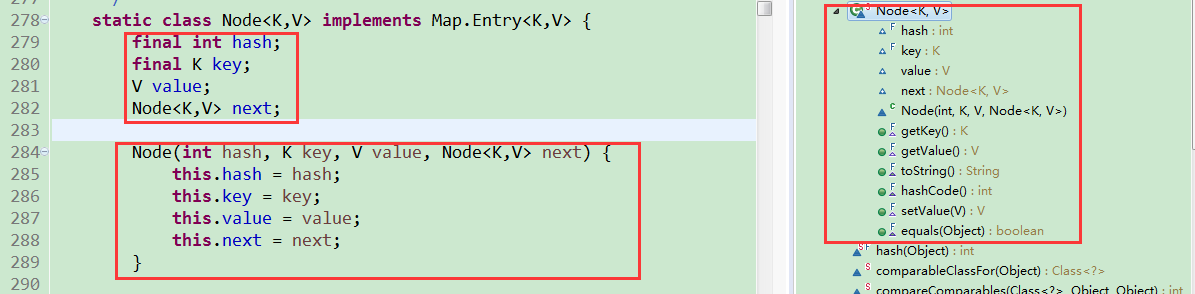
这就可以看到,HashMap是如何把<key,value>当成一个整体来处理。Node类中包含的属性有hash,key,value,next。hash是通过hash(key)方法得到的,用于确定该对象在哈希数组中的位置( (n - 1) & hash );key是键,是不可重复的;value是值,可以被重新赋值;next是在数组位置上使用链表,指向下一个。
二、常用方法put,get的内部实现
(1)put
先看源码:
1 /** 2 * Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map. 3 * If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old 4 * value is replaced. 5 * 6 * @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated 7 * @param value value to be associated with the specified key 8 * @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or 9 * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>. 10 * (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map 11 * previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.) 12 */ 13 public V put(K key, V value) { 14 return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); 15 }
再看put调用的putVal():
1 /** 2 * Implements Map.put and related methods 3 * 4 * @param hash hash for key 5 * @param key the key 6 * @param value the value to put 7 * @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value 8 * @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode. 9 * @return previous value, or null if none 10 */ 11 final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, 12 boolean evict) { 13 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; 14 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) 15 n = (tab = resize()).length; 16 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) //如果该位置了没有元素,直接声明一个新的元素,放到该位置上 17 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 18 else { 19 Node<K,V> e; K k; 20 if (p.hash == hash && 21 ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))//如果存在hash与key值相等的元素,保存下来,后面进行修改键值的操作 22 e = p; 23 else if (p instanceof TreeNode) //如果node是红黑树的节点,那么交给红黑树进行添加node 24 e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); 25 else { 26 for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { 27 if ((e = p.next) == null) {//如果p->next为空,便将键值放入此处。 28 p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 29 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st //如果链表长度超过桶数,便构造红黑树 30 treeifyBin(tab, hash); 31 break; 32 } 33 if (e.hash == hash && 34 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) // 35 break; 36 p = e; 37 } 38 } 39 if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key 40 V oldValue = e.value; 41 if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) 42 e.value = value; 43 afterNodeAccess(e); 44 return oldValue; 45 } 46 } 47 ++modCount; 48 if (++size > threshold) //The number of key-value mappings contained in this map. 49 resize(); 50 afterNodeInsertion(evict); 51 return null; 52 }
对于源码注释 有大神的博客写的很详细 针对1.8的
https://zhongfucheng.bitcron.com/post/javaji-chu/hashmapjiu-shi-zhe-yao-jian-dan-yuan-ma-pou-xi
值得注意的是对于node节点在链表中插入的方式,应该是1.7之前采用的是头插法,1.8改成尾插法。
自己描述一遍:当调用put(xxx,xxx)的时候,HashMap会根据hash(key)来确定对应数组位置上是否为空,如果为空,直接将Node对象添加到链表中;如果不为空,则遍历链表,(1)如果遍历的key和hash(key)都相等,则说明是对应key的新值换旧值;(2)如果遍历的节点是TreeNode类的实例,说明链表已经变成红黑树,调用对应红黑树的操作;(3)如果遍历node->next未空,则在尾部插入新的Node。
补充一点:关于hash(key)的源码:
/** * Computes key.hashCode() and spreads (XORs) higher bits of hash * to lower. Because the table uses power-of-two masking, sets of * hashes that vary only in bits above the current mask will * always collide. (Among known examples are sets of Float keys * holding consecutive whole numbers in small tables.) So we * apply a transform that spreads the impact of higher bits * downward. There is a tradeoff between speed, utility, and * quality of bit-spreading. Because many common sets of hashes * are already reasonably distributed (so don't benefit from * spreading), and because we use trees to handle large sets of * collisions in bins, we just XOR some shifted bits in the * cheapest possible way to reduce systematic lossage, as well as * to incorporate impact of the highest bits that would otherwise * never be used in index calculations because of table bounds. */ static final int hash(Object key) { int h; return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); }
得到key的hashCode,与keyhashCode的高16位做异或运算。
原因是:(拷贝的大佬的)
我们是根据key的哈希值来保存在散列表中的,我们表默认的初始容量是16,要放到散列表中,就是0-15的位置上。
也就是tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]。可以发现的是:在做&运算的时候,仅仅是后4位有效~那如果我们key的哈希值
高位变化很大,低位变化很小。直接拿过去做&运算,这就会导致计算出来的Hash值相同的很多。 而设计者将key的哈希值的高位也做了运算(与高16位做异或运算,使得在做&运算时,此时的低位实际上是高位与
低位的结合),这就增加了随机性,减少了碰撞冲突的可能性!
后面要再看一下当链表变成红黑树之后的操作。
(2)get 的源码分析
1 /** 2 * Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, 3 * or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key. 4 * 5 * <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key 6 * {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null : 7 * key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise 8 * it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.) 9 * 10 * <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i> 11 * indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also 12 * possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}. 13 * The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to 14 * distinguish these two cases. 15 * 16 * @see #put(Object, Object) 17 */ 18 public V get(Object key) { 19 Node<K,V> e; 20 return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; 21 }
再看getNode()源码:
1 /** 2 * Implements Map.get and related methods 3 * 4 * @param hash hash for key 5 * @param key the key 6 * @return the node, or null if none 7 */ 8 final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { 9 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; 10 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && 11 (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { 12 if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node 13 ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 14 return first; 15 if ((e = first.next) != null) { 16 if (first instanceof TreeNode) //如果是红黑树交给红黑树查找 17 return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); 18 do { 19 if (e.hash == hash && 20 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))//判断hash值是否相等和key是否相等 21 return e; 22 } while ((e = e.next) != null); 23 } 24 } 25 return null; 26 }
getNode的逻辑就相对比较简单啦,首先判断哈希表是否为空和数组对应位置是否为空,不为空则判断链表中第一个node是否是要找的,如果不是判断第一个node时候是TreeNode,如果不是则循环链表,根据hash是否相等,key.equals(k)来找到对应node返回。
三、如何扩容 resize()
resize在初始化时,会调用。在哈希表中的元素大于capacity*loadfactor时,也会调用。
1 final Node<K,V>[] resize() { 2 Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; 3 int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; 4 int oldThr = threshold; 5 int newCap, newThr = 0; 6 if (oldCap > 0) { 7 if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { 8 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 9 return oldTab; 10 } 11 else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && //oldCap << 1 扩容2倍 12 oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) 13 newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold 14 } 15 else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold 16 newCap = oldThr; 17 else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults 18 newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; 19 newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); 20 } 21 if (newThr == 0) { 22 float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor; 23 newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? 24 (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); 25 } 26 threshold = newThr; 27 @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) 28 Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; 29 table = newTab; 30 if (oldTab != null) { 31 for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { 32 Node<K,V> e; 33 if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { 34 oldTab[j] = null; 35 if (e.next == null) 36 newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; 37 else if (e instanceof TreeNode) 38 ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); 39 else { // preserve order 40 Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; 41 Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; 42 Node<K,V> next; 43 do { 44 next = e.next; 45 if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { //决定e放到新哈希表的高位还是低位 46 if (loTail == null) 47 loHead = e; 48 else 49 loTail.next = e; 50 loTail = e; 51 } 52 else { 53 if (hiTail == null) 54 hiHead = e; 55 else 56 hiTail.next = e; 57 hiTail = e; 58 } 59 } while ((e = next) != null); 60 if (loTail != null) { 61 loTail.next = null; 62 newTab[j] = loHead; 63 } 64 if (hiTail != null) { 65 hiTail.next = null; 66 newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; 67 } 68 } 69 } 70 } 71 } 72 return newTab; 73 }
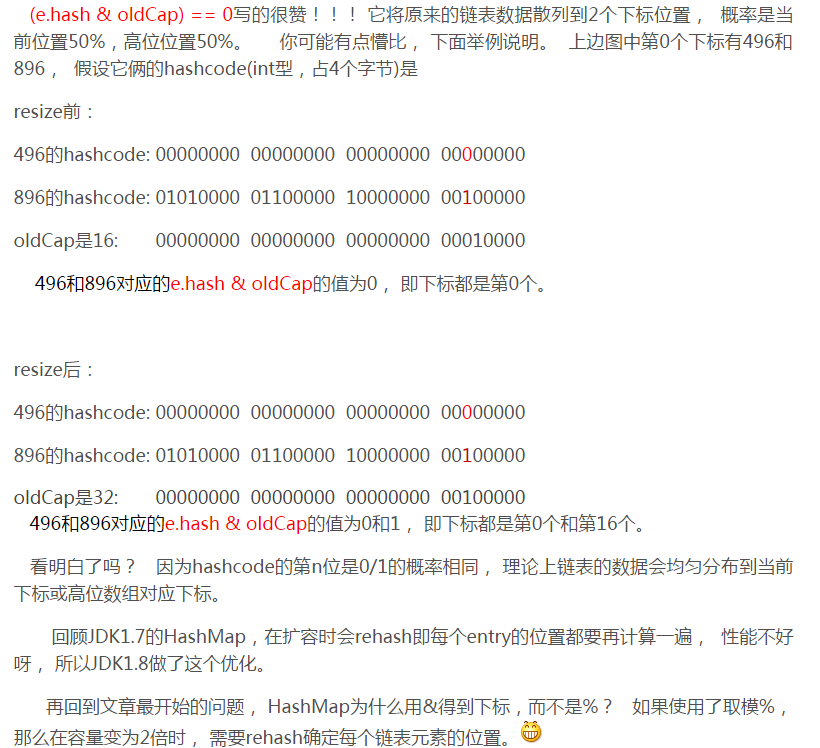
这里有点蒙逼的是旧哈希表复制到新的哈希表。这里jdk1.7和jdk1.8也有所不同,可以看一下 https://blog.csdn.net/brycegao321/article/details/52527236
之前听师兄说,复制会一个一个的拷贝,现在看来那是说的1.7,现在1.8是均匀的分布在新的哈希表的高位和低位,通过拷贝链表完成复制。
四、什么是fail-fast机制
我们知道HashMap是线程不安全的,因此在使用迭代器的过程中,如果有其他线程修改了HashMap,那么就会抛出ConcurrentModificationException,这就是所谓fail-fast策略。
涉及到的参数有modCount和expectedModCount,判断modCount和expertedModCount是否相等,如果不相等,表示有其他线程修改了HashMap,抛出异常。
transient int modCount; modCount修饰为transient,表示当对象存储时,它的值不需要维持。还有expectedModCount在源码中的定义: 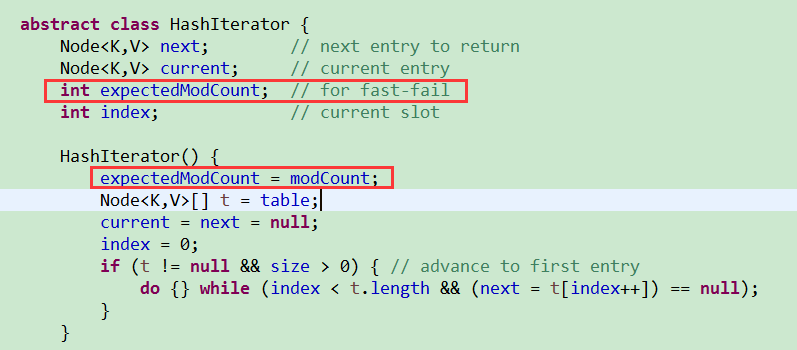
源码注释后续有空再加上,刚写博客,写的有点长有点乱。
五、还有几点需要注意
(1) 关于hash和equal的重写
https://blog.csdn.net/u010223904/article/details/46295439
前面说到了,HashMap的很多函数要基于equal()函数和hashCode()函数。hashCode()用来定位要存放的位置,equal()用来判断是否相等。
那么,相等的概念是什么?
Object版本的equal只是简单地判断是不是同一个实例。但是有的时候,我们想要的的是逻辑上的相等。比如有一个学生类student,有一个属性studentID,只要studentID相等,不是同一个实例我们也认为是同一学生。当我们认为判定equals的相等应该是逻辑上的相等而不是只是判断是不是内存中的同一个东西的时候,就需要重写equal()。而涉及到HashMap的时候,重写了equals(),就需要重写hashCode()
我们总结一下几条基本原则
1. 同一个对象(没有发生过修改)无论何时调用hashCode()得到的返回值必须一样。
如果一个key对象在put的时候调用hashCode()决定了存放的位置,而在get的时候调用hashCode()得到了不一样的返回值,这个值映射到了一个和原来不一样的地方,那么肯定就找不到原来那个键值对了。
2. hashCode()的返回值相等的对象不一定相等,通过hashCode()和equals()必须能唯一确定一个对象
不相等的对象的hashCode()的结果可以相等。hashCode()在注意关注碰撞问题的时候,也要关注生成速度问题,完美hash不现实
3. 一旦重写了equals()函数(重写equals的时候还要注意要满足自反性、对称性、传递性、一致性),就必须重写hashCode()函数。而且hashCode()的生成哈希值的依据应该是equals()中用来比较是否相等的字段
如果两个由equals()规定相等的对象生成的hashCode不等,对于hashMap来说,他们很可能分别映射到不同位置,没有调用equals()比较是否相等的机会,两个实际上相等的对象可能被插入不同位置,出现错误。其他一些基于哈希方法的集合类可能也会有这个问题
(2) TREEIFY_THRESHOLD=8 树状阈值
这是JDK1.8对HashMap的优化, 哈希碰撞后的链表上达到8个节点时要将链表重构为红黑树, 查询的时间复杂度变为O(logN)。
(3) 哈希表是非线程安全的
如果多线程同时访问哈希表, 且至少一个线程修改了哈希表的结构, 那么必须在访问hashmap前设置同步锁。(修改结构是指添加或者删除一个或多个entry, 修改键值不算是修改结构。) 一般在多线程操作哈希表时, 要使用同步对象封装map。 如果不封装Hashmap, 可以使用Collections.synchronizedMap 方法调用HashMap实例。 在创建HashMap实例时避免其他线程操作该实例, 即保证了线程安全。
Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap(...));



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号