实验分析
经实验发现,本项目由于存在文本数据中经常会在上下句同时出现一个实体的问题,pipline 模式的抽取方法不适用于本项目,故采用联合抽取的方法。以下为该模块的技术路线:
-
数据的进一步处理:
- 本项目中,在处理时发现,对于自己指向自己的"独立实体"关系,模型存在尾实体不正确的现象,但是联合抽取模型的实体识别部分是可以预测出此类头实体的,所以一旦有其参与的独立实体的关系预测,将不在下游关系抽取中出现,故剥离之。
- 由于文本的特殊性,有一些数据是比较适合用模板规则去解决的,故将这些数据剥离,未来预测时直接用规则补充,降低标注成本和模型学习成本和复杂度。
-
对前期实验的改进:
- 在原本的模型中,面对密集的三元组提取和大跨度的三元组提取,往往效果欠佳。此时加入BiLSTM, BiGRU, BiSRU比对效果,将上下文信息引入模型。
- 引入相对位置编码,以解决大跨度三元组问题。
- 同时引入自注意力机制或扩张卷积神经网络,经实验选择了后者。
-
联合抽取方式:
- 选择头实体映射到关系、尾实体方案。先抽取头实体h,再抽取对应的关系r和尾实体t。
- 采用联合解码,在序列编码层上叠加统一解码器,直接解码得到关系三元组信息。
-
编码:
- 采用Bert,项目使用Bert-base-chinese 预训练模型即可。
-
使用指针网络:
- 本项目使用层叠指针网络CasRel。设计编码端为基于BERT的编码层以获取上下文语义信息对字/词进行表征。
- 解码端包括头实体识别层、关系与尾实体联合识别层。
- CasRel对于关系抽取任务的拆分方式不同,头实体映射到关系、尾实体共享参数的方式。
- 训练时,CasRel基于共享参数的情况下,分开训练头实体和给定关系下的尾实体。
- 预测时,CasRel以联合的方式识别头实体和相应关系下的尾实体。
以下为CasRel训练过程示意图:
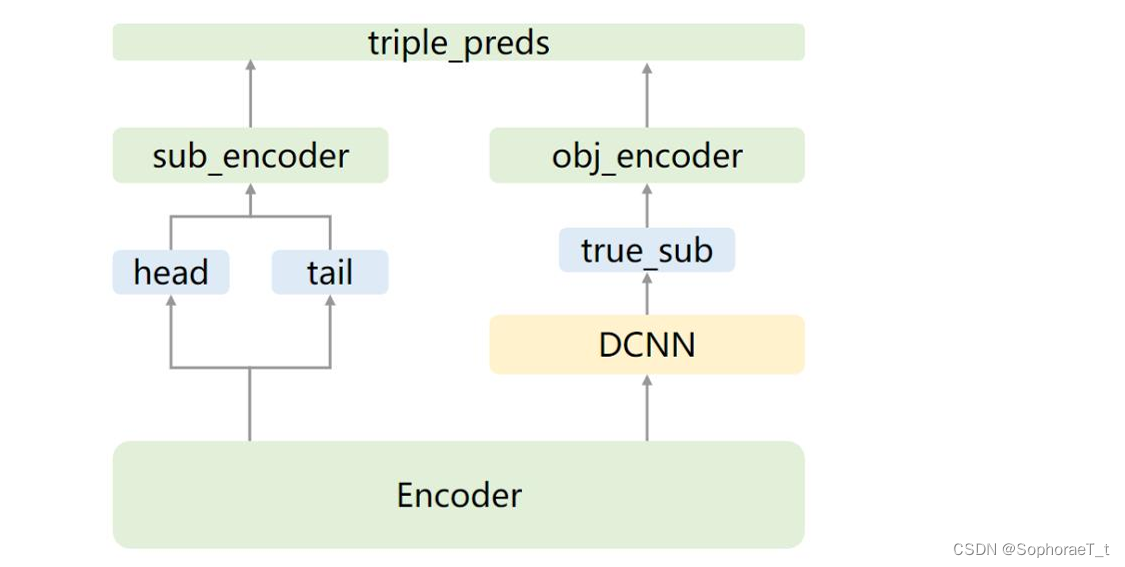
具体设计
1. 数据预处理
- 数据收集与标注:从文本数据中提取实体和关系对,并进行人工标注,以构建高质量的数据集。
- 数据清洗:去除噪声数据,标准化实体名称。
2. 模型设计
- 编码端:基于Bert的编码层
- 使用 Bert-base-chinese 预训练模型作为编码层。
- 将文本输入到Bert模型中,获取每个字/词的上下文表示向量。
- 引入相对位置编码:在Bert模型的基础上,添加相对位置编码以增强模型对位置关系的感知能力。相对位置编码可以帮助模型更好地理解文本中的依赖关系。
- 引入扩张卷积网络:使用扩张卷积(Dilated Convolution)来捕捉更大范围的上下文信息。扩张卷积通过在卷积核之间引入空洞,从而在不增加计算量的情况下扩大感受野。
- 解码端:头实体识别层与关系与尾实体联合识别层
- 设计一个头实体识别层,负责识别文本中的头实体。
- 设计一个关系与尾实体联合识别层(基于CasRel),该层同时识别头实体与尾实体之间的关系,并抽取相应的尾实体。
3. 联合抽取方法
采用联合抽取的方法,直接从文本中同时抽取实体和关系,避免了传统管道方法中的误差累积问题。
- CasRel模型:使用CasRel(Cascade Relation Extraction)模型,该模型通过级联的方式,先识别头实体,然后根据头实体来识别关系和尾实体。这个方法可以有效降低模型的学习成本和复杂度。
4. 模型训练
- 训练数据准备:使用标注好的数据集对模型进行训练。数据集需要包含实体和关系的标签。
- 损失函数设计:设计合适的损失函数,平衡实体识别和关系抽取的精度。
- 优化算法:选择合适的优化算法(如Adam)来优化模型参数。
5. 模型评估与优化
- 评估指标:使用Precision, Recall, F1-score等指标评估模型性能。
- 模型调优:根据评估结果,调整模型参数和结构,优化模型性能。
6. 应用与部署
- 将训练好的模型应用于实际数据,进行实体和关系抽取,构建知识图谱。
- 部署模型,提供API或服务接口,支持在线知识抽取和查询。
模型训练代码
import json
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertModel, AdamW
# 加载数据
def load_data(file_path):
data = []
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
data.append(json.loads(line.strip()))
return data
# 转换数据
def convert_data_to_model_input(data):
sentences = []
head_labels = []
tail_labels = []
rel_labels = []
for doc in data:
for item in doc['content']:
sentence = item['tokens']
sentences.append(sentence)
length = len(sentence)
head_label = [0] * length
tail_label = [0] * length
rel_label = [0] * length
for candidate in doc['candidates']:
if candidate['sent_id'] == doc['content'].index(item):
start, end = candidate['offset']
if start < length and end < length:
head_label[start] = 1
tail_label[end] = 1
for i in range(start, end + 1):
rel_label[i] = 1
head_labels.append(head_label)
tail_labels.append(tail_label)
rel_labels.append(rel_label)
return sentences, head_labels, tail_labels, rel_labels
# 填充标签
def pad_labels(labels, max_length):
padded_labels = []
for label in labels:
if len(label) > max_length:
padded_label = label[:max_length]
else:
padded_label = label + [0] * (max_length - len(label))
padded_labels.append(padded_label)
return padded_labels
# 定义CasRel模型
class CasRelModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, bert_model_name):
super(CasRelModel, self).__init__()
self.bert = BertModel.from_pretrained(bert_model_name)
self.head_extractor = nn.Linear(self.bert.config.hidden_size, 2)
self.tail_extractor = nn.Linear(self.bert.config.hidden_size, 2)
self.rel_extractor = nn.Linear(self.bert.config.hidden_size, 2)
def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask):
outputs = self.bert(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
sequence_output = outputs.last_hidden_state
head_logits = self.head_extractor(sequence_output)
tail_logits = self.tail_extractor(sequence_output)
rel_logits = self.rel_extractor(sequence_output)
return head_logits, tail_logits, rel_logits
# 检查GPU是否可用
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device("cuda")
print(f"Using GPU: {torch.cuda.get_device_name(0)}")
else:
device = torch.device("cpu")
print("Using CPU")
# 加载数据
data = load_data('legal_documents.jsonl')
sentences, head_labels, tail_labels, rel_labels = convert_data_to_model_input(data)
# 定义最大长度并填充标签
max_length = 512
head_labels = pad_labels(head_labels, max_length)
tail_labels = pad_labels(tail_labels, max_length)
rel_labels = pad_labels(rel_labels, max_length)
# 定义模型并转移到GPU
model = CasRelModel('bert-base-chinese').to(device)
# 初始化BERT tokenizer
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-chinese')
input_ids = []
attention_masks = []
# Tokenize sentences并转移到GPU
for sentence in sentences:
inputs = tokenizer(sentence, is_split_into_words=True, return_tensors='pt', padding='max_length', max_length=max_length, truncation=True)
input_ids.append(inputs['input_ids'])
attention_masks.append(inputs['attention_mask'])
input_ids = torch.cat(input_ids).to(device)
attention_masks = torch.cat(attention_masks).to(device)
# 将标签转移到GPU
head_labels = torch.tensor(head_labels).to(device)
tail_labels = torch.tensor(tail_labels).to(device)
rel_labels = torch.tensor(rel_labels).to(device)
# 定义优化器和损失函数
optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=2e-5)
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 定义batch size
batch_size = 8
# 训练模型
for epoch in range(3):
model.train()
for i in range(0, len(input_ids), batch_size):
batch_input_ids = input_ids[i:i + batch_size]
batch_attention_masks = attention_masks[i:i + batch_size]
batch_head_labels = head_labels[i:i + batch_size]
batch_tail_labels = tail_labels[i:i + batch_size]
batch_rel_labels = rel_labels[i:i + batch_size]
optimizer.zero_grad()
head_logits, tail_logits, rel_logits = model(batch_input_ids, batch_attention_masks)
head_loss = loss_fn(head_logits.view(-1, 2), batch_head_labels.view(-1))
tail_loss = loss_fn(tail_logits.view(-1, 2), batch_tail_labels.view(-1))
rel_loss = loss_fn(rel_logits.view(-1, 2), batch_rel_labels.view(-1))
loss = head_loss + tail_loss + rel_loss
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(f'Epoch {epoch}, Batch {i // batch_size}, Loss: {loss.item()}')
print("Training complete!")
# 定义评估和提取实体关系的函数
def extract_entities_and_relations(model, tokenizer, sentences, max_length=512):
model.eval()
entities_relations = []
for sentence in sentences:
inputs = tokenizer(sentence, is_split_into_words=True, return_tensors='pt', padding='max_length', max_length=max_length, truncation=True)
input_ids = inputs['input_ids'].to(device)
attention_mask = inputs['attention_mask'].to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
head_logits, tail_logits, rel_logits = model(input_ids, attention_mask)
head_predictions = torch.argmax(head_logits, dim=-1).cpu().numpy().flatten()
tail_predictions = torch.argmax(tail_logits, dim=-1).cpu().numpy().flatten()
rel_predictions = torch.argmax(rel_logits, dim=-1).cpu().numpy().flatten()
entities = []
relations = []
for idx, token in enumerate(sentence):
if head_predictions[idx] == 1:
entity_start = idx
for j in range(idx, len(sentence)):
if tail_predictions[j] == 1:
entity_end = j
entities.append("".join(sentence[entity_start:entity_end + 1]))
break
current_relation = []
for idx, token in enumerate(sentence):
if rel_predictions[idx] == 1:
current_relation.append(token)
else:
if current_relation:
relations.append("".join(current_relation))
current_relation = []
entities_relations.append({
'sentence': sentence,
'entities': entities,
'relations': relations
})
return entities_relations
# 提取实体和关系
extracted_data = extract_entities_and_relations(model, tokenizer, sentences)
# 保存提取结果到文件
output_file = 'extracted_entities_relations.jsonl'
with open(output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for item in extracted_data:
f.write(json.dumps(item, ensure_ascii=False) + '\n')
print(f"Extracted data saved to {output_file}")
初步结果
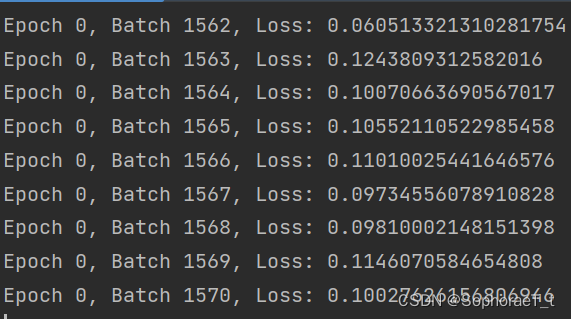
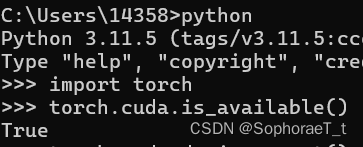
由于数据集数量巨大,使用cpu速度较慢(初步计算每轮训练要两天),在改用gpu训练的过程中遇到问题,命令行中cuda是正常的,pycharm中cuda就识别不到。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号