Faster R-CNN中的RPN的理解
RPN的作用
rpn是相对于选择性搜索策略做出的改进,该区域生成网络的输入是backbone的一个或多个特征层,维度不妨设为(B,C,H,W)先通过3x3的卷积将输入的特征图的特征进行融合,接着利用两个独立的1x1卷积输出objectness和boundingbox_regression。得到的objectness输出向量的维度为(B,K,H,W),其中k为每个cell上生成的anchors的个数。boundingbox_regression的向量的维度为(B,Kx4,H,W),它的值是proposal相对于anchor的相对偏移量。
注:"For simplicity we implement the cls layer as a two-class softmax layer. Alternatively, one may use logistic regression to produce k scores."作者提出objectness输出向量的维度也可以为为(B,Kx2,H,W),这样将问题看作是一种二分类问题。为简单期间,采用前者直接采用回归产生k的分数的方法。
RPN损失函数的定义
anchors的生成。对于一个尺寸为(B,C,H,W)的特征图而言,令每个cell生成k个anchors,则该特征层生成HxWxK个anchors。将anchors的坐标映射回原图,在原图上就会产生一系列高宽比不同的anchor框。为每一个anchor框分配一个class标签,代表它们是或者不是目标。有两种anchor框可以分配正标签:(1)anchor框和gtbox框的iou大于0.7(这个值是人为指定的)。(2)在某个gtbox匹配的所有anchor框中,该anchor具有最大的值,即使它的iou值小于阈值0.7。(个人认为这样做的原因是为每个gtbox框分配一个正样本,以期提高后续检测的召回率)。单个gtbox可以匹配多个anchors,而那些与gtbox计算的iou值小于0.3的anchor框被视为负样本。这样,可以将目标损失函数定义为:
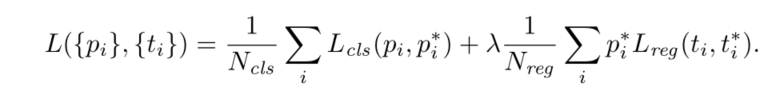
其中,i:一个batch中anchor的索引
pi:对于索引为i的anchor,预测其为object的概率
pi*:gtbox标签,当anchor为正样本时,标签值为1;当anchor为负样本时,标签值为0
ti:第i个anchor预测的bbox的坐标,即为proposal
ti*:与第i个positive anchor相关联的gtbox的坐标
Lcls:分类损失函数,计算二分类损失
pi**Lreg:回归损失,只有anchor为正样本时才会起作用,此时pi* *为1.Lreg为smooth L1函数
smooth L1损失函数定义
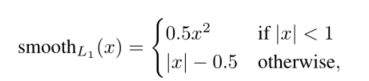
回归参数定义
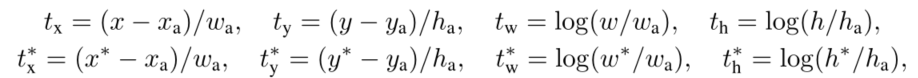
(tx,ty,tw,th)代表proposal(预测的bbox)相对于anchor坐标的偏移量
(tx,ty,tw,th)*代表gtbox相对于anchor坐标的偏移量
anchors采样操作
为了解决计算RPNloss正负样本的不均衡问题,先假设正样本占总样本的比例为0.5,如果数量不够则选择所有的正样本。负样本同理,每张图像上选取的样本数量总数设置为256(人为设定)。
代码如下所示:
class BalancedPositiveNegativeSampler(object):
"""
This class samples batches, ensuring that they contain a fixed proportion of positives
"""
def __init__(self, batch_size_per_image, positive_fraction):
# type: (int, float) -> None
"""
Arguments:
batch_size_per_image (int): number of elements to be selected per image
positive_fraction (float): percentage of positive elements per batch
"""
self.batch_size_per_image = batch_size_per_image
self.positive_fraction = positive_fraction
def __call__(self, matched_idxs):
# type: (List[Tensor]) -> Tuple[List[Tensor], List[Tensor]]
"""
Arguments:
matched idxs: list of tensors containing -1, 0 or positive values.
Each tensor corresponds to a specific image.
-1 values are ignored, 0 are considered as negatives and > 0 as
positives.
Returns:
pos_idx (list[tensor])
neg_idx (list[tensor])
Returns two lists of binary masks for each image.
The first list contains the positive elements that were selected,
and the second list the negative example.
"""
pos_idx = []
neg_idx = []
# 遍历每张图像的matched_idxs
for matched_idxs_per_image in matched_idxs:
# >= 1的为正样本, nonzero返回非零元素索引
# positive = torch.nonzero(matched_idxs_per_image >= 1).squeeze(1)
positive = torch.where(torch.ge(matched_idxs_per_image, 1))[0]
# = 0的为负样本
# negative = torch.nonzero(matched_idxs_per_image == 0).squeeze(1)
negative = torch.where(torch.eq(matched_idxs_per_image, 0))[0]
# 指定正样本的数量
num_pos = int(self.batch_size_per_image * self.positive_fraction)
# protect against not enough positive examples
# 如果正样本数量不够就直接采用所有正样本
num_pos = min(positive.numel(), num_pos)
# 指定负样本数量
num_neg = self.batch_size_per_image - num_pos
# protect against not enough negative examples
# 如果负样本数量不够就直接采用所有负样本
num_neg = min(negative.numel(), num_neg)
# randomly select positive and negative examples
# Returns a random permutation of integers from 0 to n - 1.
# 随机选择指定数量的正负样本
perm1 = torch.randperm(positive.numel(), device=positive.device)[:num_pos]
perm2 = torch.randperm(negative.numel(), device=negative.device)[:num_neg]
pos_idx_per_image = positive[perm1]
neg_idx_per_image = negative[perm2]
# create binary mask from indices
pos_idx_per_image_mask = torch.zeros_like(
matched_idxs_per_image, dtype=torch.uint8
)
neg_idx_per_image_mask = torch.zeros_like(
matched_idxs_per_image, dtype=torch.uint8
)
pos_idx_per_image_mask[pos_idx_per_image] = 1
neg_idx_per_image_mask[neg_idx_per_image] = 1
pos_idx.append(pos_idx_per_image_mask)
neg_idx.append(neg_idx_per_image_mask)
return pos_idx, neg_idx


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号