探究Google力推的JetPack库<四>---------Navigation、Paging
经过之前的Jetpack学习,目前对于架构这块的组件只剩下最后三个木有学习了,如下:

所以接下来继续对剩下的库进行学习。
Navigation:
了解:
基本使用:
这里主要是Fragment之间的来回导航,先来看一下最终的效果:

也就是有三个Fragment,第一个跳到第二个;然后第二个既可以跳回第一个,又能跳到第三个;而第三个则又可以跳回到第二个,如果像这种跳转平常实现的话会比较麻烦,这里咱们来看一下具体怎么用导航组件来实现这样的效果:
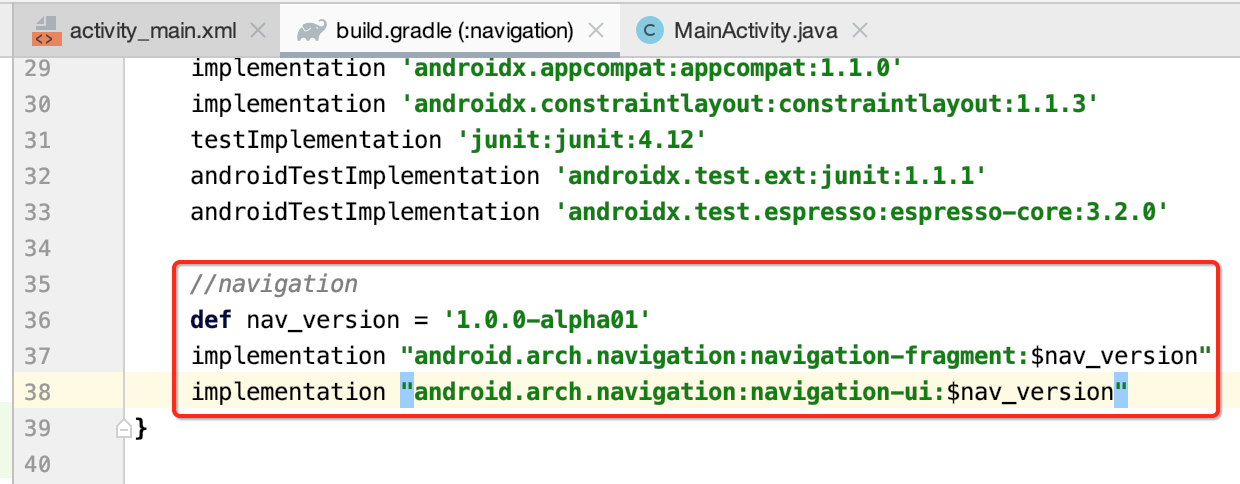
先来添加依赖:
MainActivity:
然后再来搭建主Activity:
package com.android.navigation; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <!-- app:defaultNavHost="true" 拦截系统back键,在fragment中就可以用back回退上一个fragment app:navGraph="@navigation/nav_graph_main" 连接使用nav_graph_main.xml,获取fragment之间的导航结构 --> <fragment android:id="@+id/my_nav_host_fragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:name="androidx.navigation.fragment.NavHostFragment" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent" app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" app:defaultNavHost="true" app:navGraph="@navigation/nav_graph_main"/> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
其中它需要依赖于一个导航配置文件:
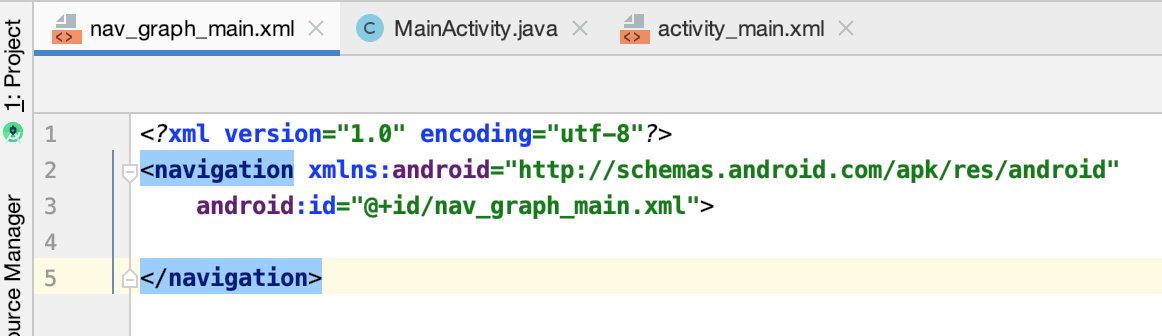
目前这配置文件里面先不配,待会用到时再配,很明显导航的规则肯定需要在这里来定义的:
其中它还有一个拖拉拽的视图:
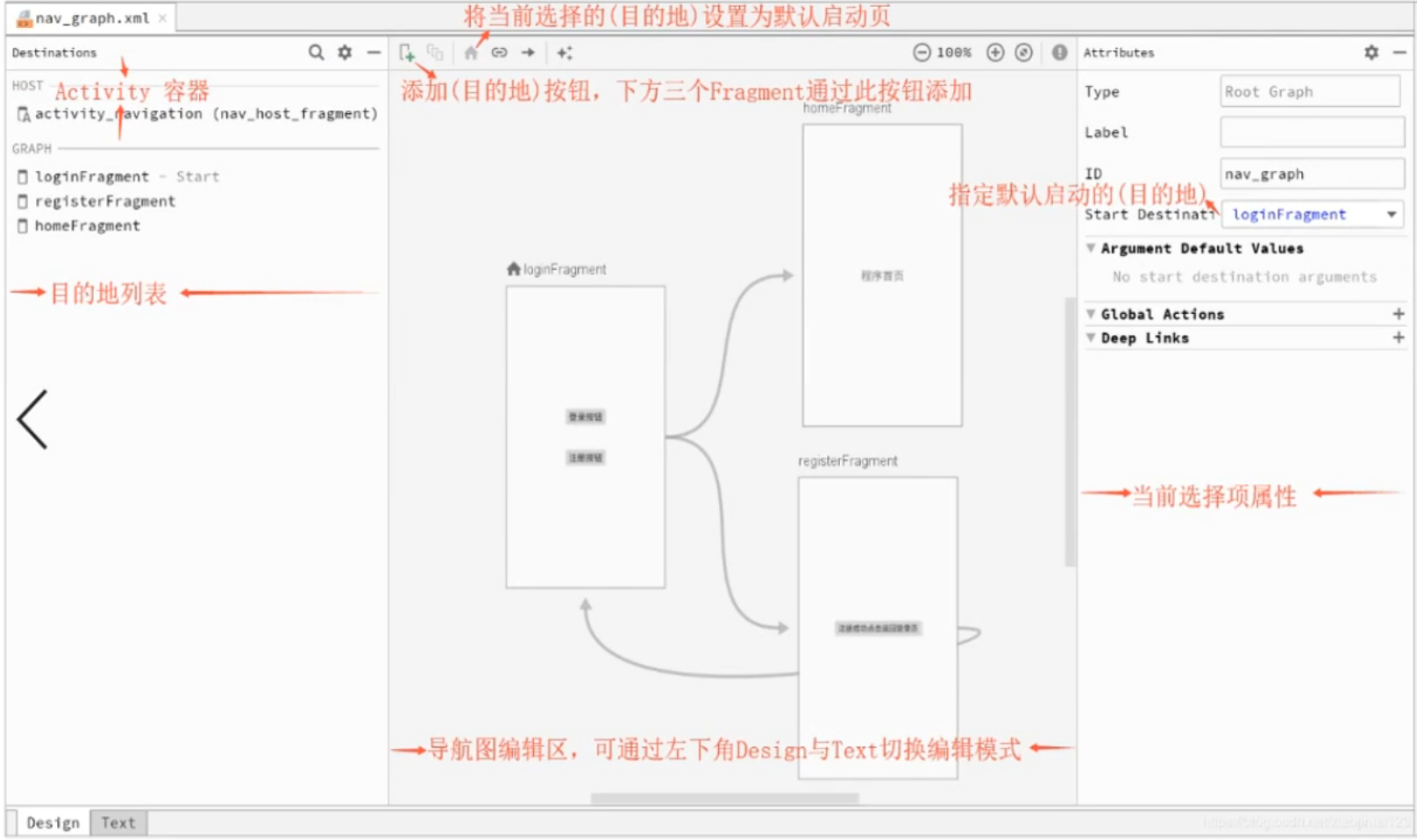
要学的话还是以xml的形式学,就像学布局一样,这样其实实现起来效率更高。
另外这里有一个小细节,就是如果我们平常一个界面只能显示一个Fragment的话,按back键默认是不是直接将当前的Activity给退出了?所以说这里需要配置一下来可以控制back的动作:
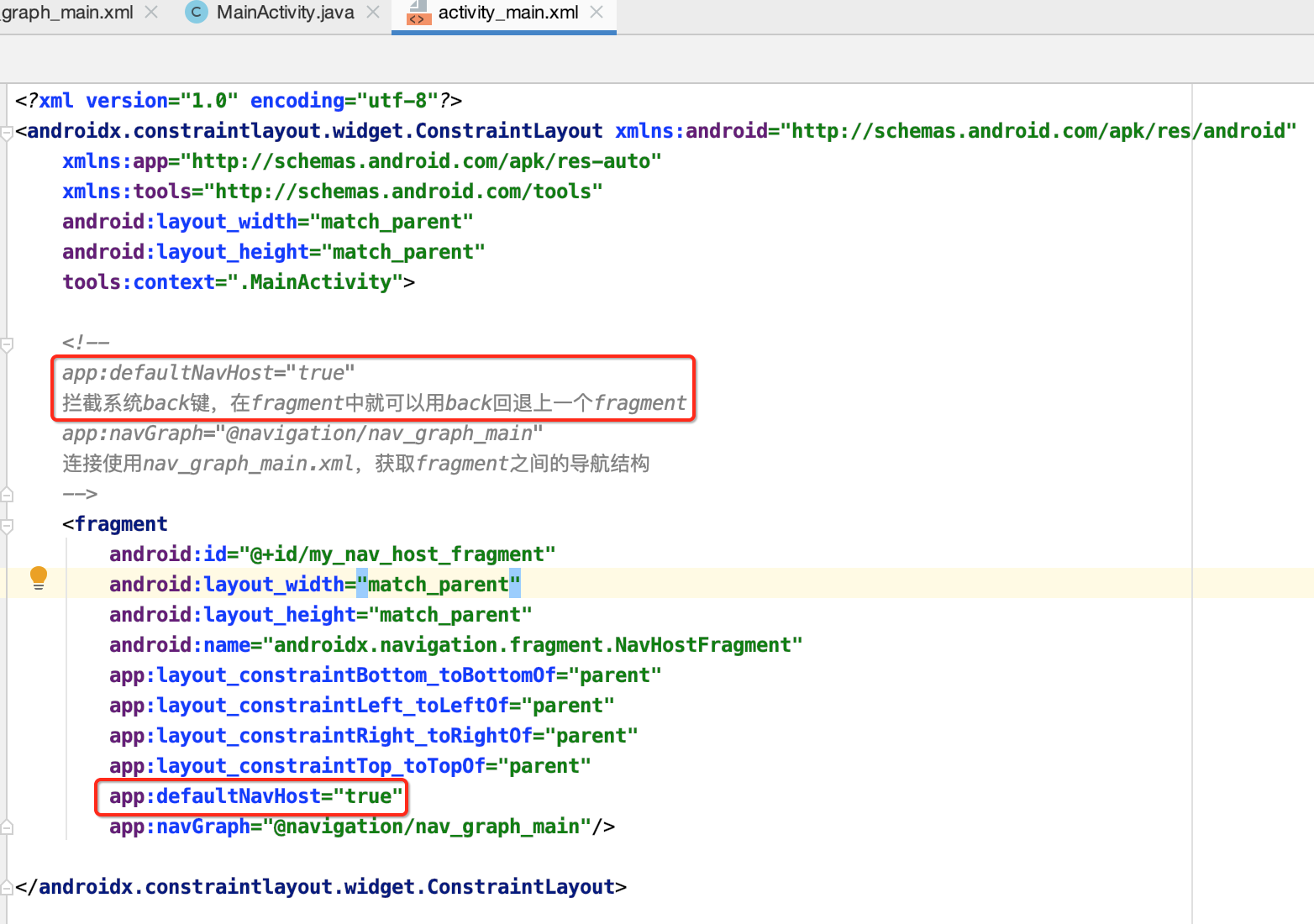
建立Fragments:
如效果所示,涉及到三个Fragment,所以这里先定义一下:
package com.android.navigation; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.LayoutInflater; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; import android.widget.Button; import androidx.annotation.NonNull; import androidx.annotation.Nullable; import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment; public class MainPage1Fragment extends Fragment { @Nullable @Override public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main_page1, container, false); } @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState); Button btn = view.findViewById(R.id.btn); btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { //TODO } }); } }
fragment_main_page1.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/main" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:id="@+id/message" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="MainPage1Fragment" android:textSize="20sp" android:textStyle="bold" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="跳转MainPage2Fragment" android:textAllCaps="false" /> </LinearLayout>
package com.android.navigation; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.LayoutInflater; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; import android.widget.Button; import androidx.annotation.NonNull; import androidx.annotation.Nullable; import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment; public class MainPage2Fragment extends Fragment { @Nullable @Override public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main_page2, container, false); } @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState); Button btn = view.findViewById(R.id.btn); btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { //TODO } }); Button btn2 = view.findViewById(R.id.btn2); btn2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { //TODO } }); } }
fragment_main_page2.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginLeft="8dp" android:layout_marginRight="8dp" android:layout_marginBottom="16dp" android:text="MainPage2Fragment" android:textSize="20sp" android:textStyle="bold" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginStart="8dp" android:layout_marginLeft="8dp" android:layout_marginEnd="8dp" android:layout_marginRight="8dp" android:text="返回MainPage1Fragment" android:textAllCaps="false" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginStart="8dp" android:layout_marginLeft="8dp" android:layout_marginEnd="8dp" android:layout_marginRight="8dp" android:text="前往MainPage3Fragment" android:textAllCaps="false" /> </LinearLayout>
package com.android.navigation; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.LayoutInflater; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; import android.widget.Button; import androidx.annotation.NonNull; import androidx.annotation.Nullable; import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment; public class MainPage3Fragment extends Fragment { @Nullable @Override public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main_page3, container, false); } @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState); Button btn = view.findViewById(R.id.btn); btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { //TODO } }); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginLeft="8dp" android:layout_marginRight="8dp" android:layout_marginBottom="16dp" android:text="MainPage3Fragment" android:textSize="20sp" android:textStyle="bold" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginStart="8dp" android:layout_marginLeft="8dp" android:layout_marginEnd="8dp" android:layout_marginRight="8dp" android:text="跳到MainPage2Fragment" android:textAllCaps="false"/> </LinearLayout>
定义导航配置:
接下来咱们则来配置一下导航规则了,具体如何配置呢?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/nav_graph_main.xml" app:startDestination="@id/page1Fragment"> <fragment android:id="@+id/page1Fragment" android:name="com.android.navigation.MainPage1Fragment" android:label="fragment_page1" tools:layout="@layout/fragment_main_page1"> <!-- action:程序中使用id跳到destination对应的类 --> <action android:id="@+id/action_page2" app:destination="@id/page2Fragment" /> </fragment> <fragment android:id="@+id/page2Fragment" android:name="com.android.navigation.MainPage2Fragment" android:label="fragment_page2" tools:layout="@layout/fragment_main_page2"> <action android:id="@+id/action_page1" app:destination="@id/page1Fragment" /> <action android:id="@+id/action_page3" app:destination="@id/page3Fragment" /> </fragment> <fragment android:id="@+id/page3Fragment" android:name="com.android.navigation.MainPage3Fragment" android:label="fragment_page3" tools:layout="@layout/fragment_main_page3"> <action android:id="@+id/action_page2" app:destination="@id/page2Fragment" /> </fragment> </navigation>
其可视视图为:
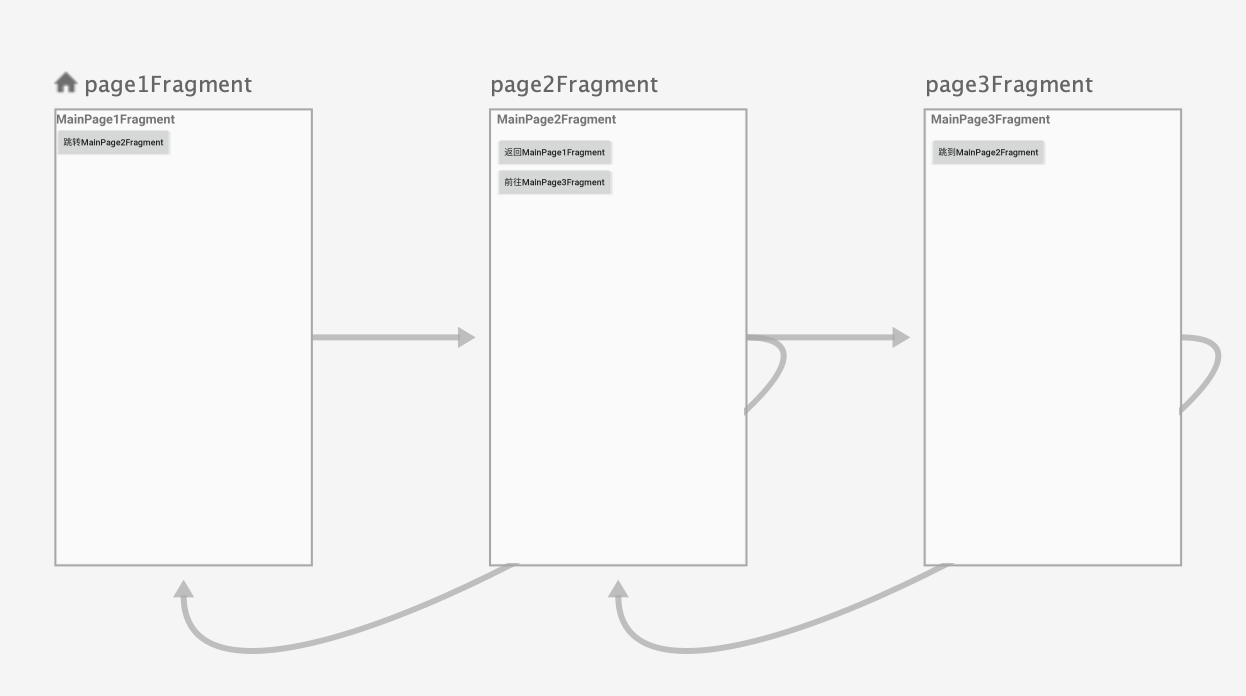
其中大致解释一下其配置:


好,接下来咱们则来完成点击事件:
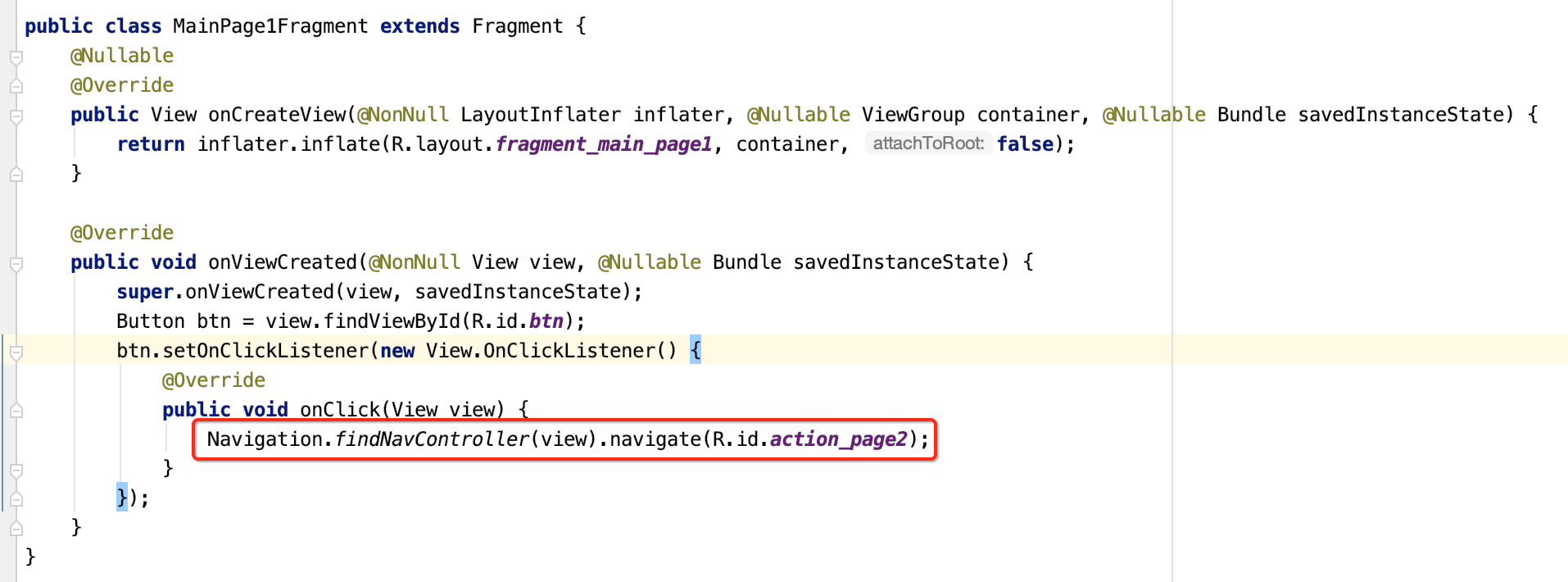
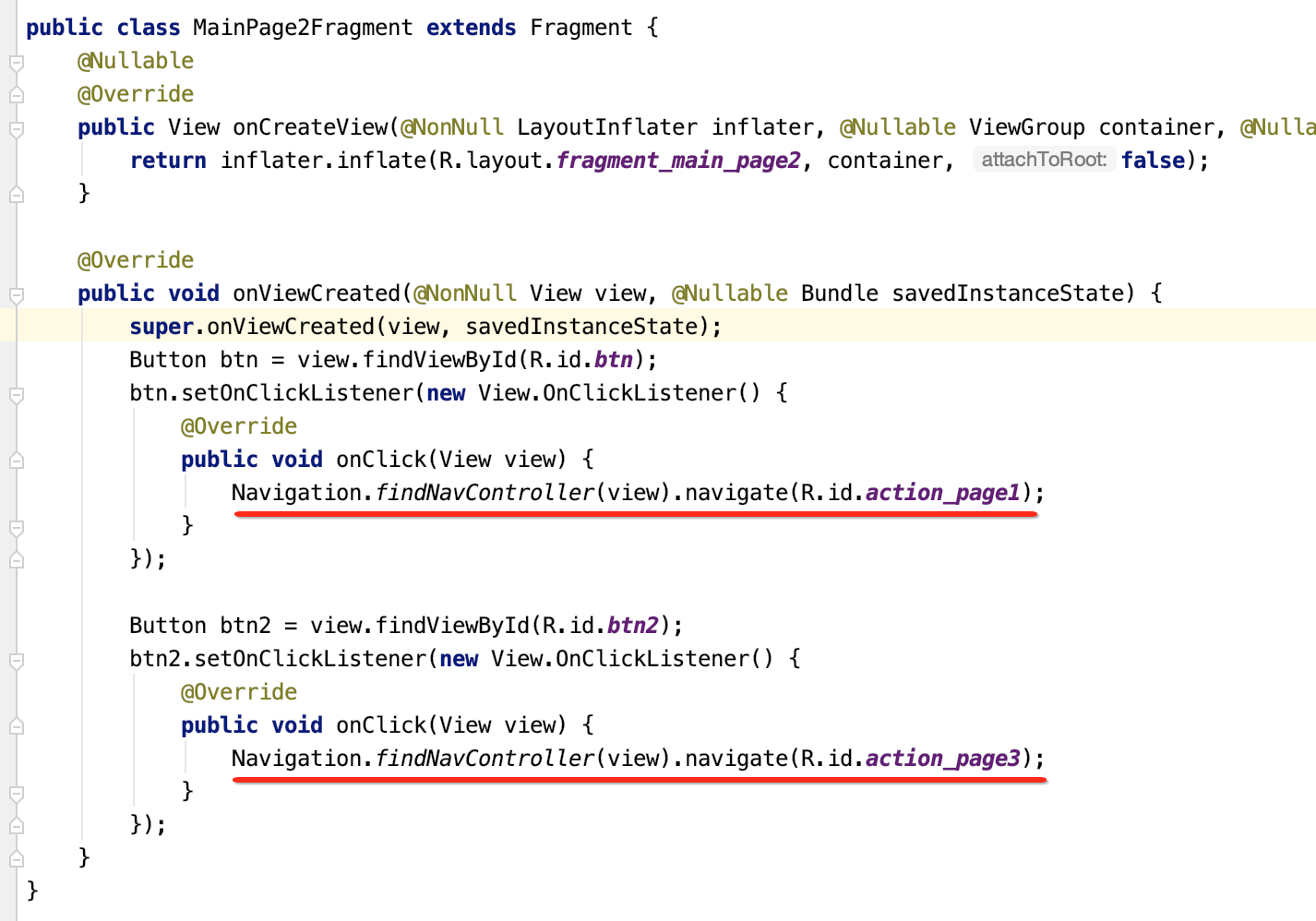
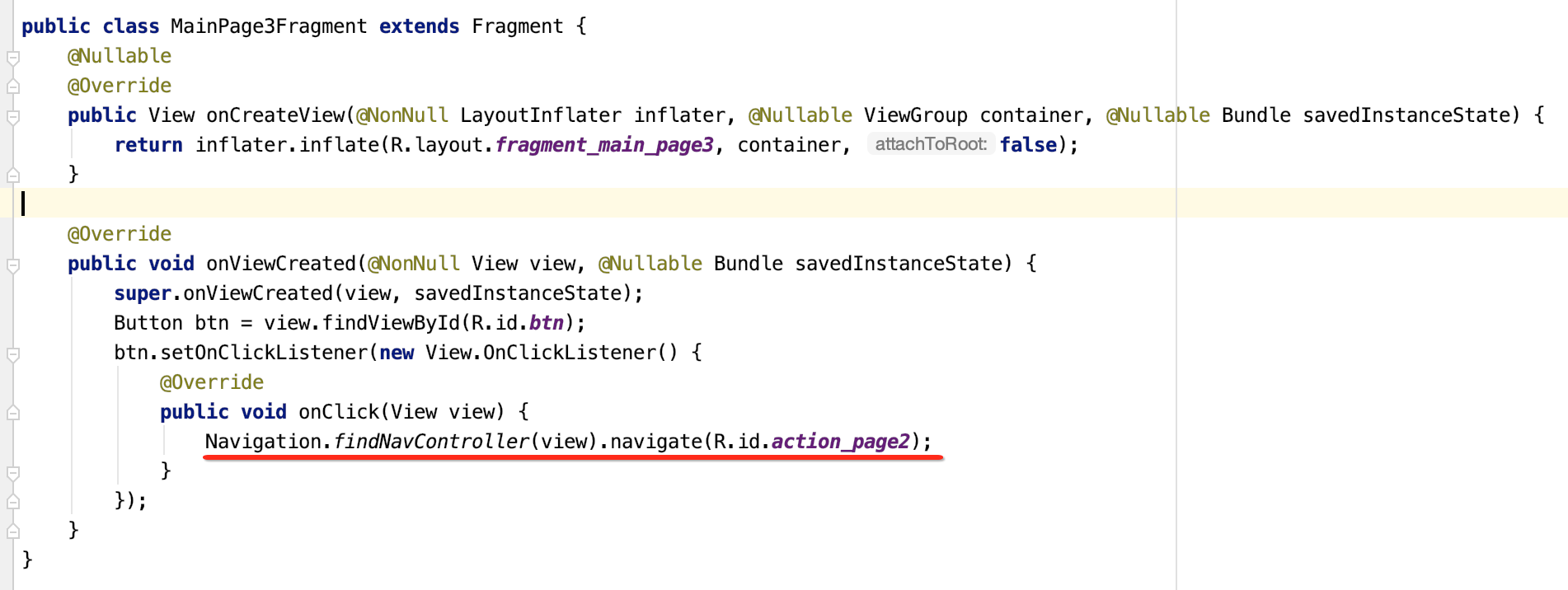
其中关于回退到上一个Fragment其实还有另一种写法:
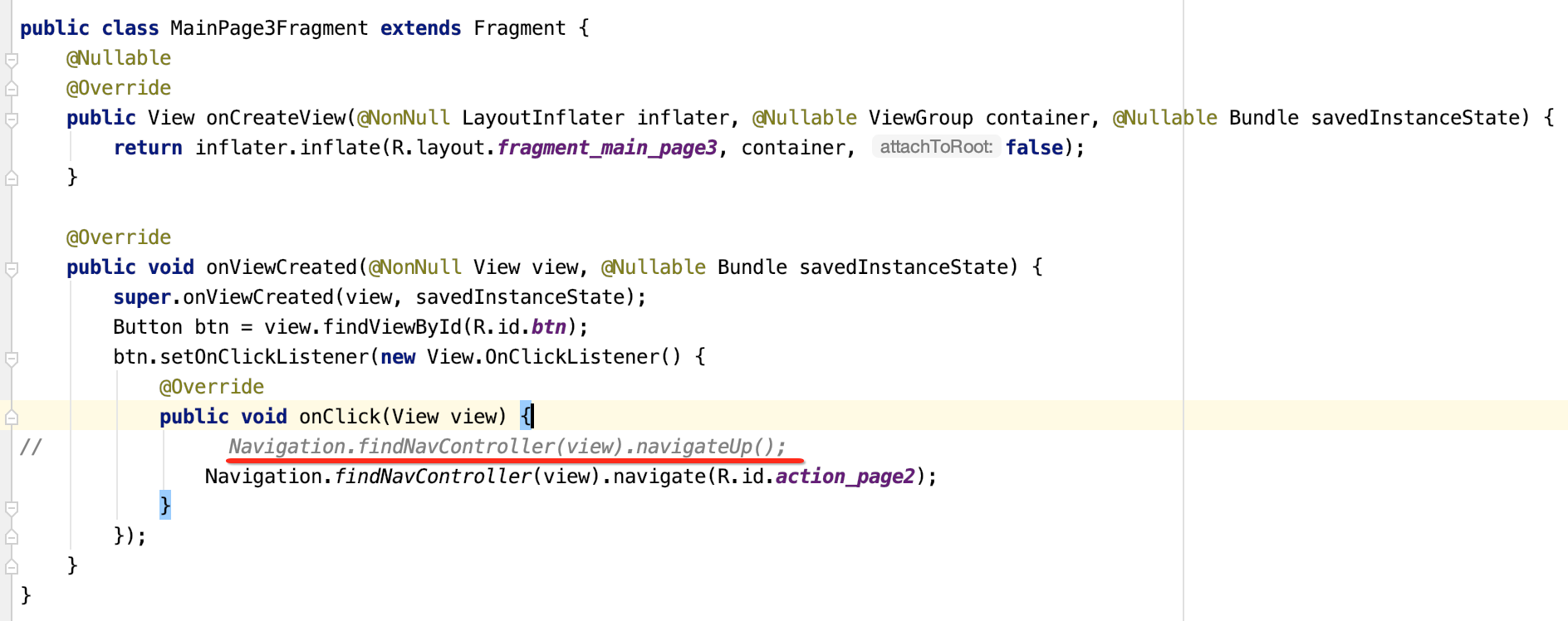
那有一个问题思考一下,光跳转不带参数么?其实各Fragment之间的数据共享可以使用LiveData既可,以上就已经完成了整个Fragment的导航了,整体使用确实简单,另外关于细节还有很多,这个待实际工作需要时再进一步探究。
原理剖析:
对于上面导航功能的实现它底层是如何实现的呢?下面开始进行源码解读:
NavController对象和NavHostFragment的关系:
这里从哪里开始分析起呢?看主Activity的布局:
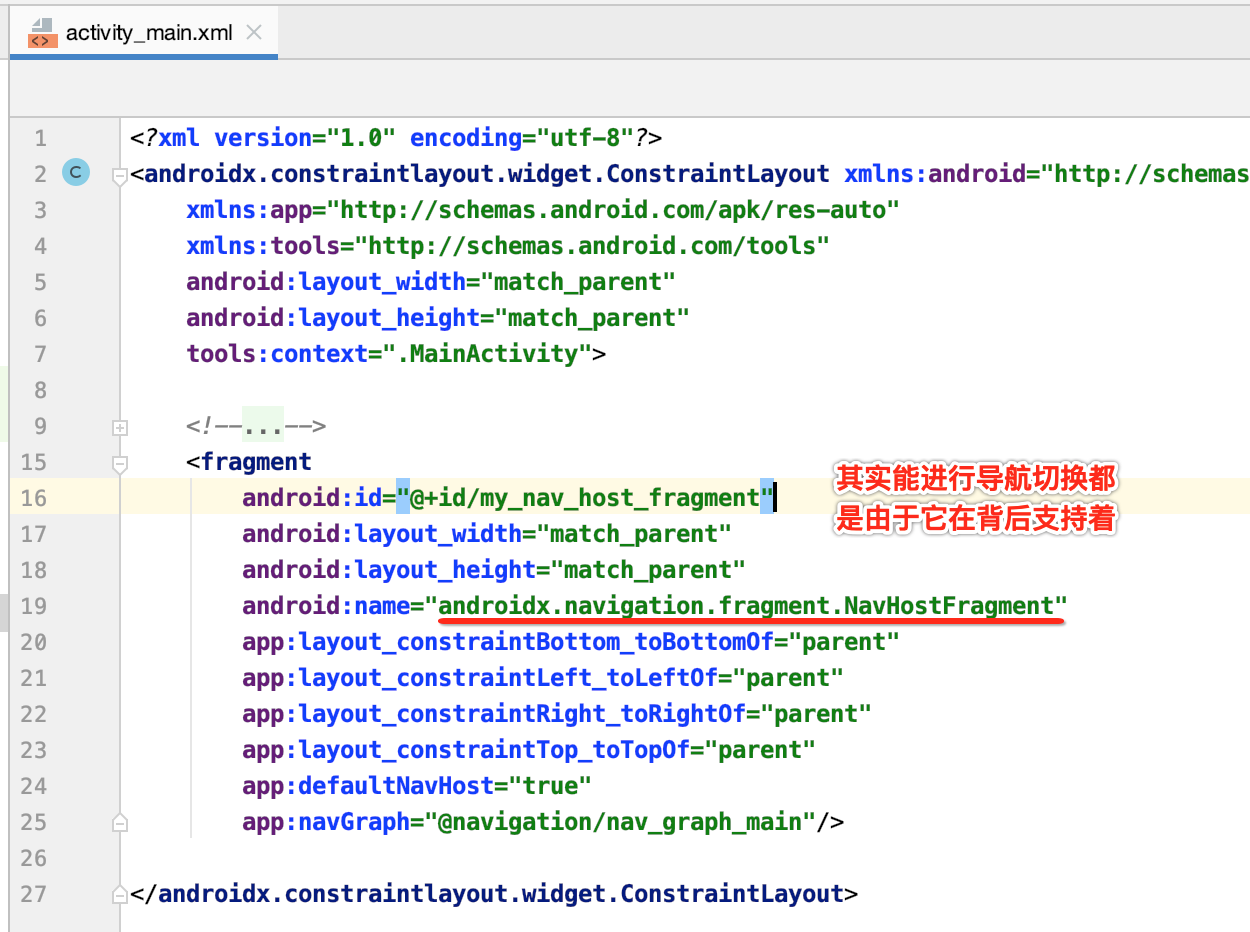
所以将它作为分析的入口:
1、NavHostFragment的创建:
(1)初始化Bundle,并且将graphResId,startDestinationArgs存储在Bundle中。
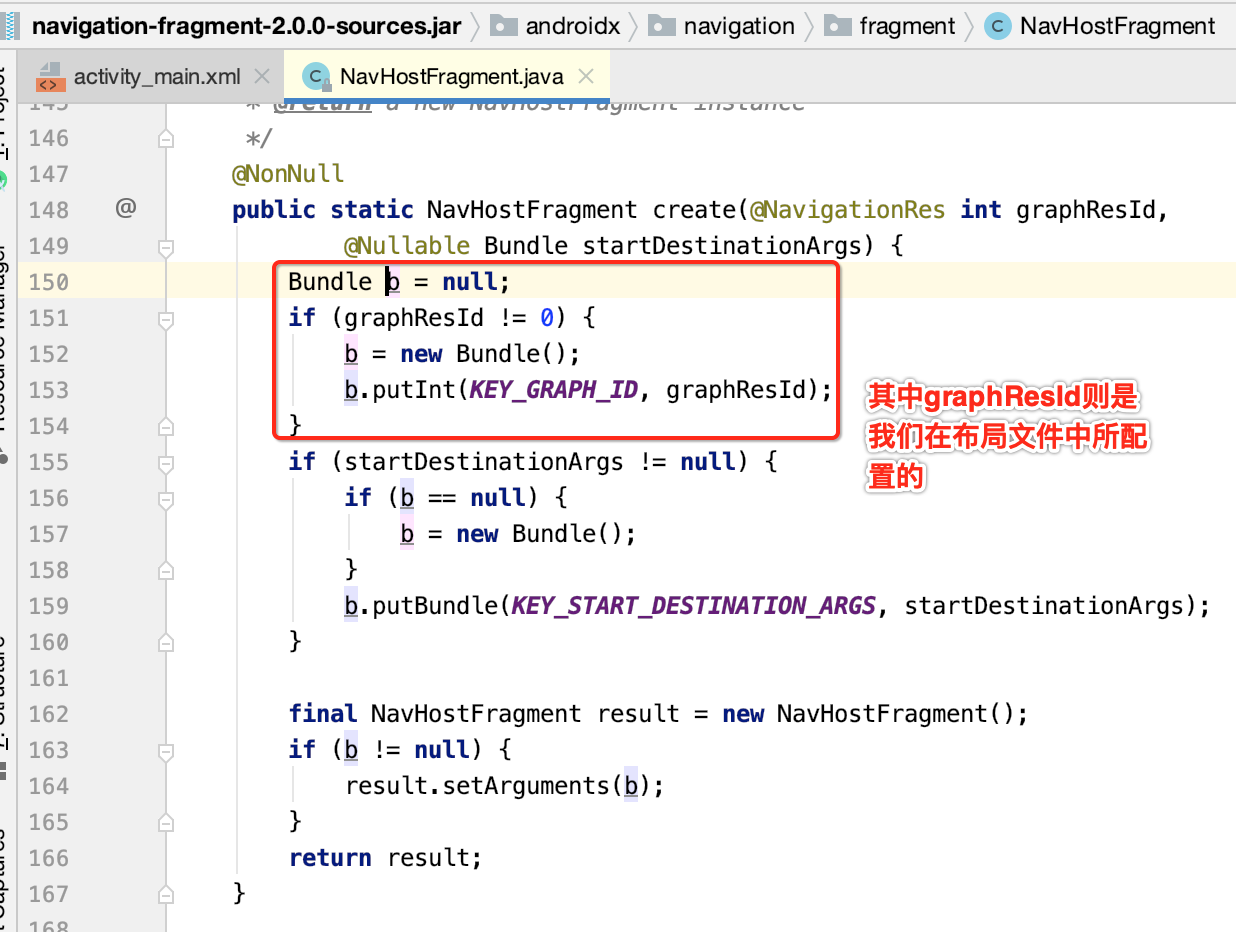


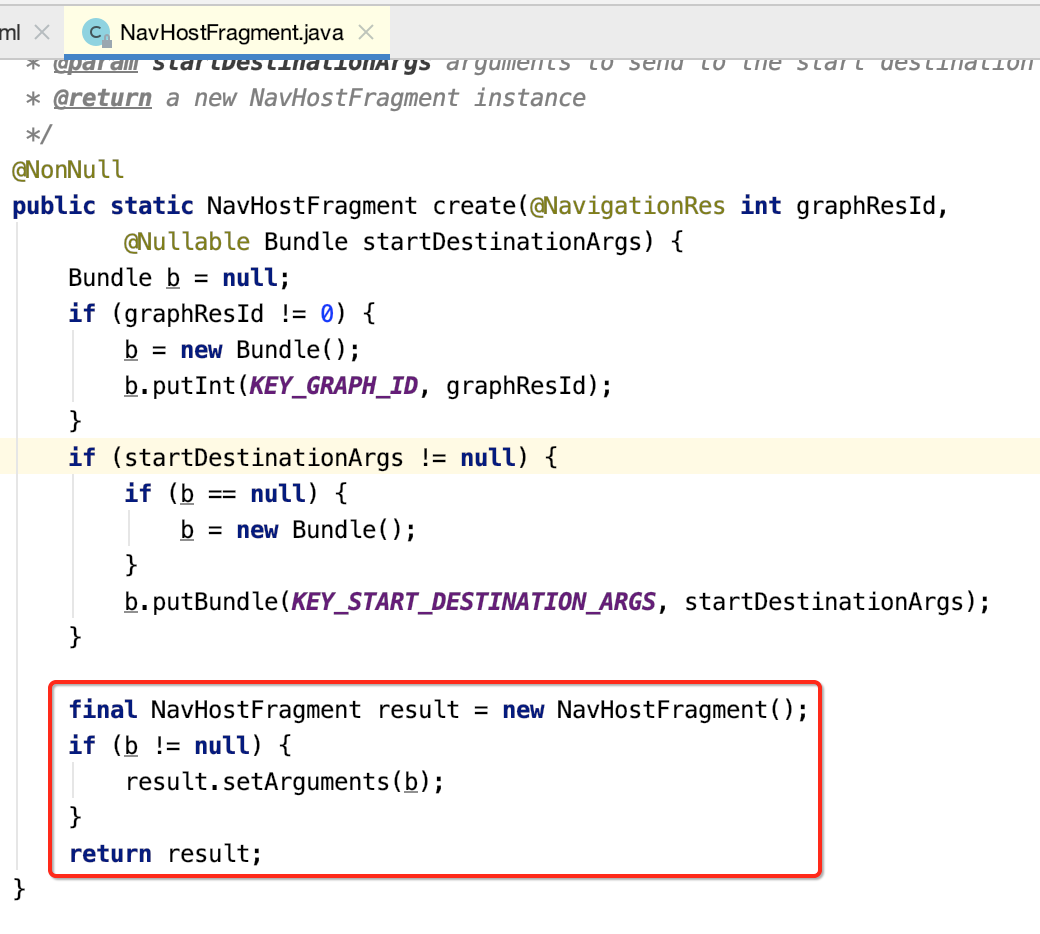
(2)返回NavHostFragment实例。
2.XML文件的属性解析:
接下来则需要解析一下XML的属性,也就是:
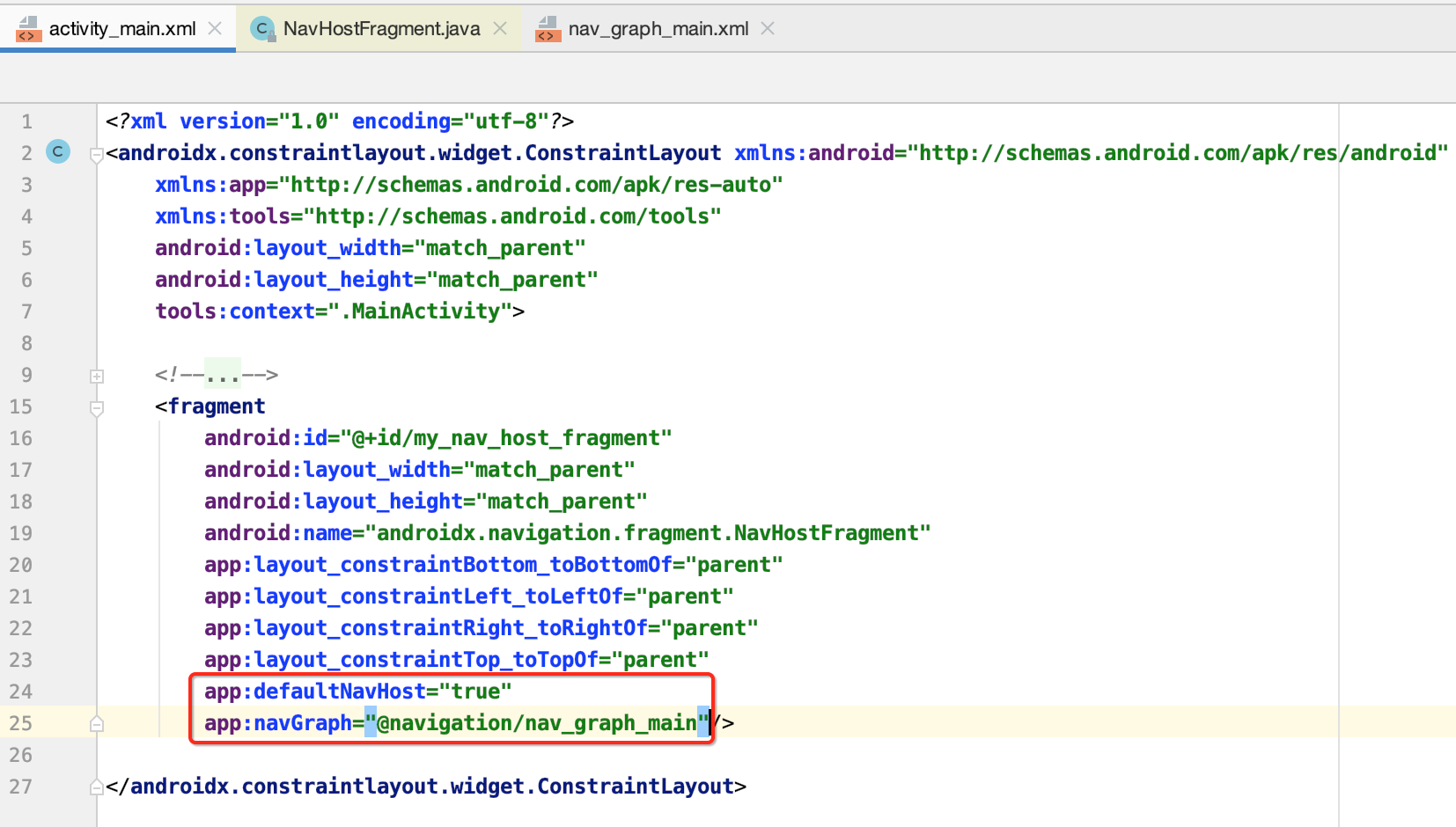
则会在这块进行,解析方式跟咱们自定义属性一样的:
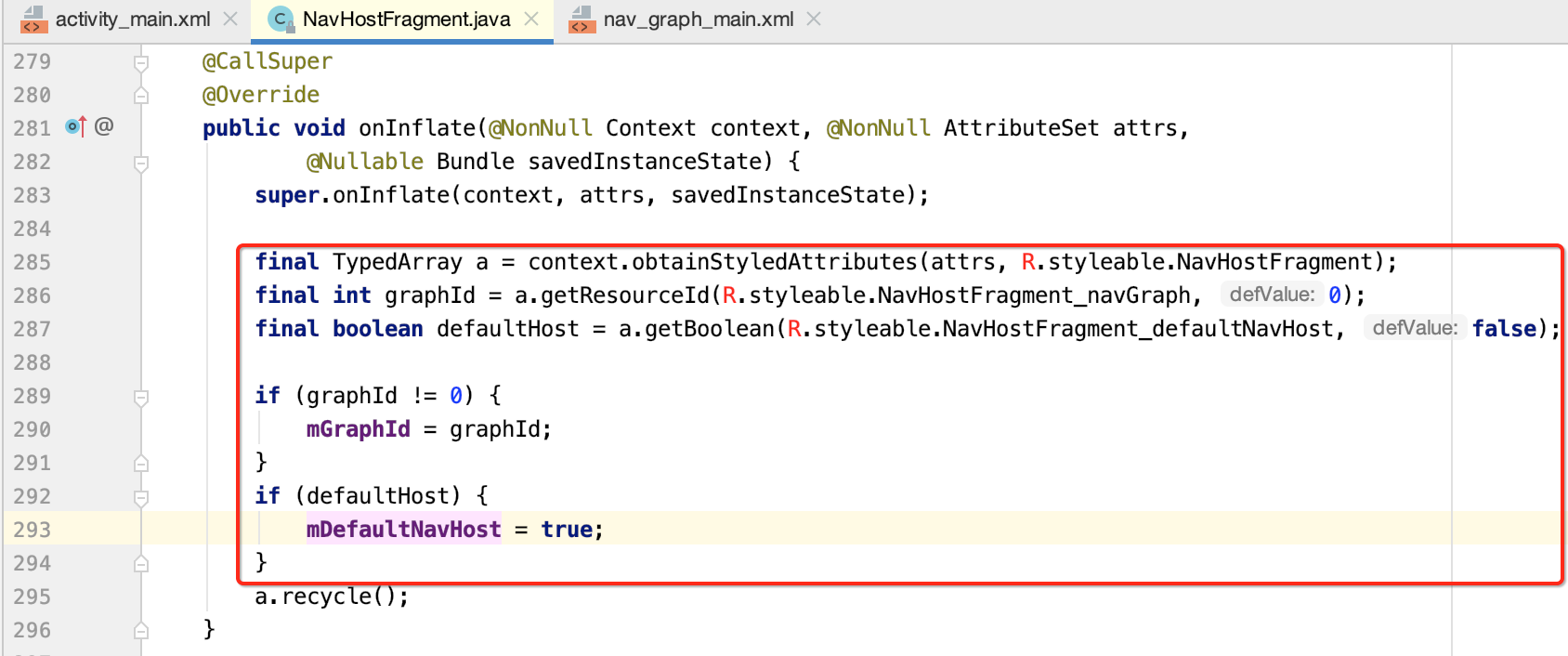
(调用时机:Fragment所关联的Activity在执行setContentView时)
3.导航初始化:NavController在这里被创建,并且NavHostFragment中有一个NavController对象。
而如果让这个Fragment要显示出来,则会执行它的生命周期方法了,首先是onCreate(),看它里面做了啥?
(1)初始化NavController,NavController为导航的控制类,核心类。
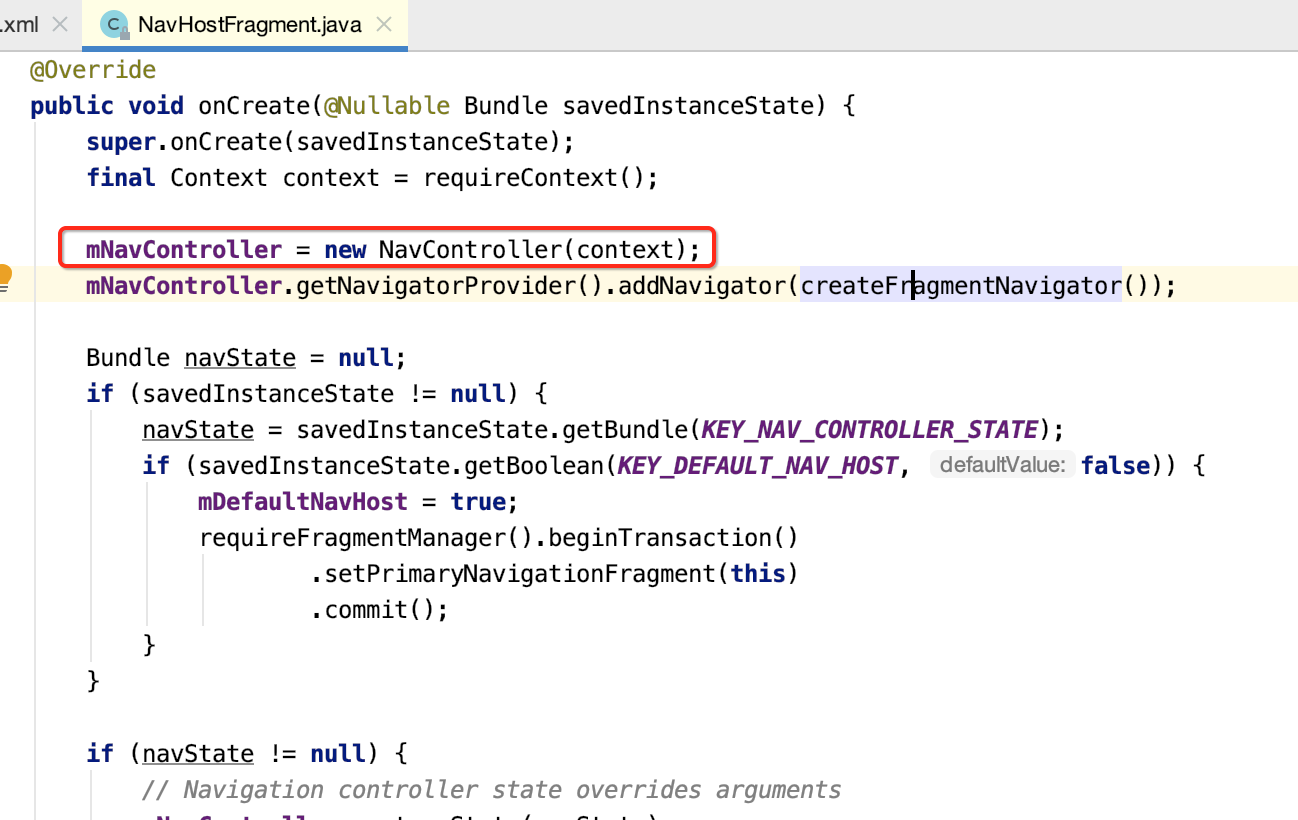
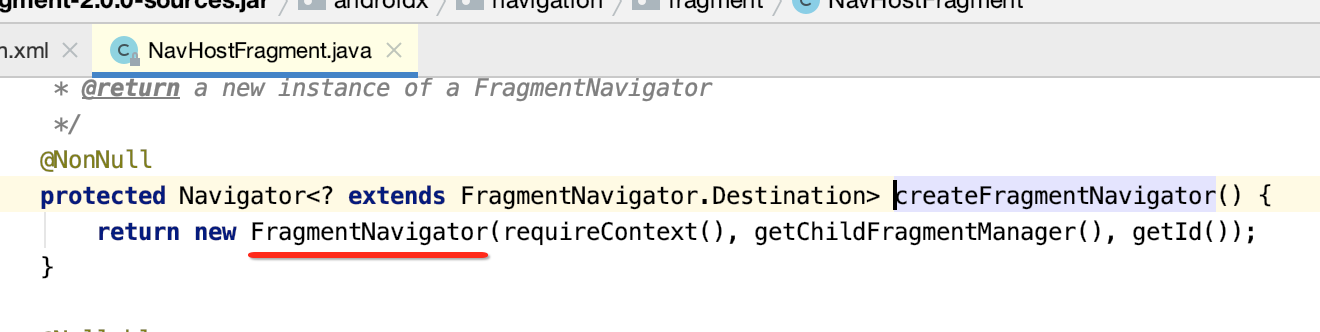
(2)在NavigatorProvider中以键值对保存FragmentNavigator类至HashMap当中。该类之后会做介绍。

咱们跟进去看一下:
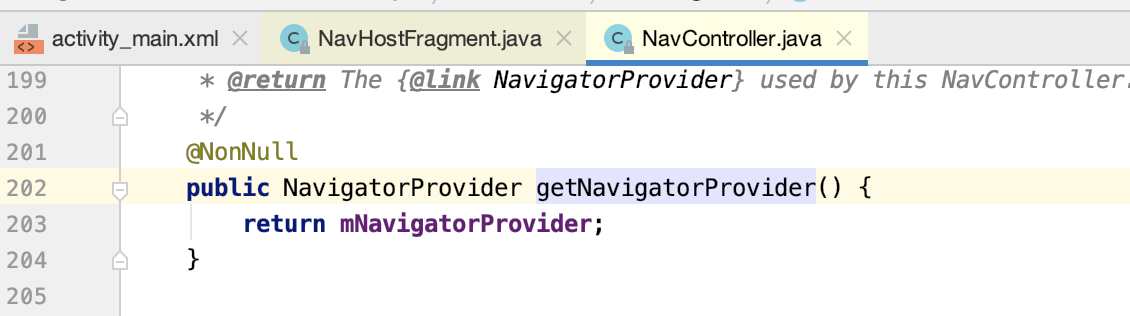
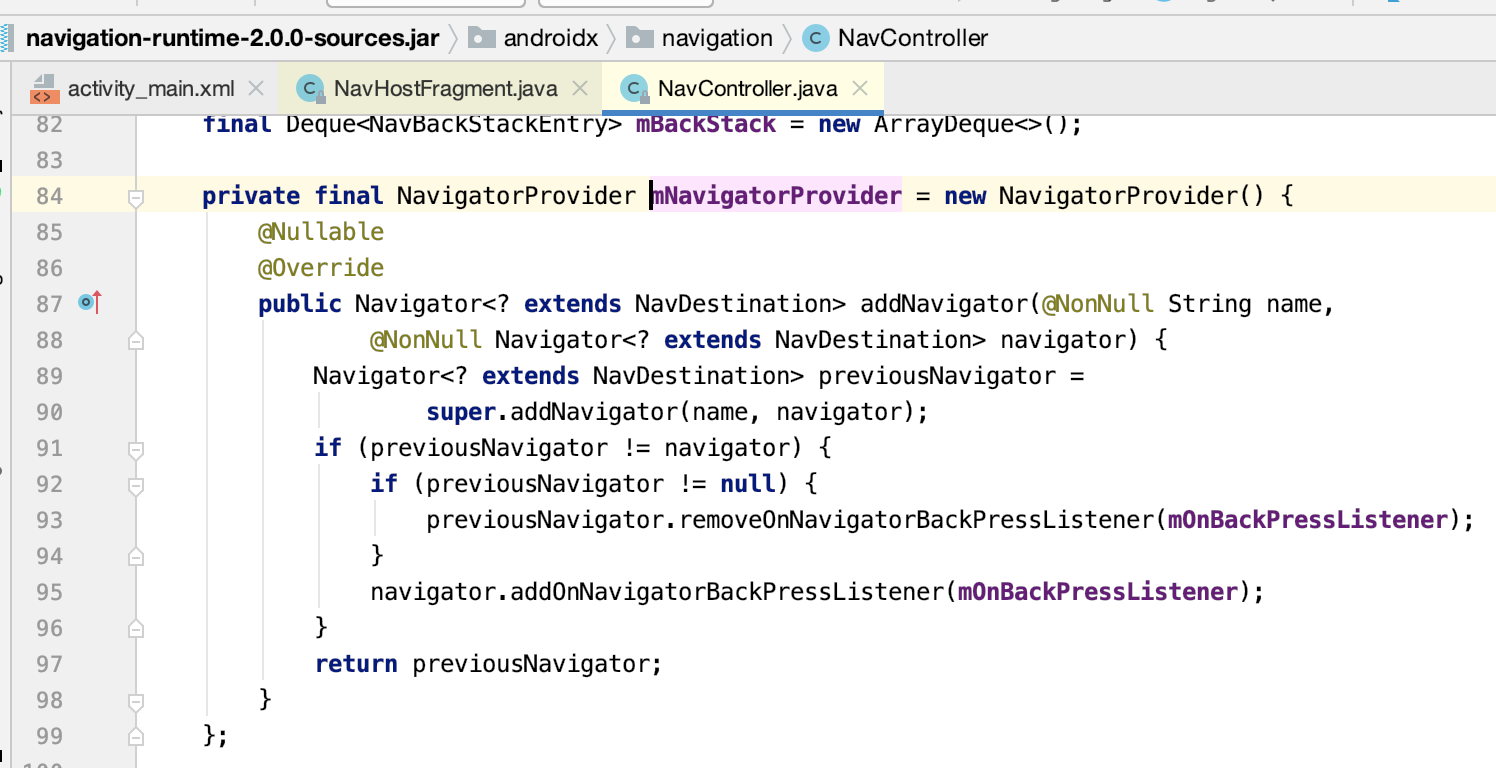

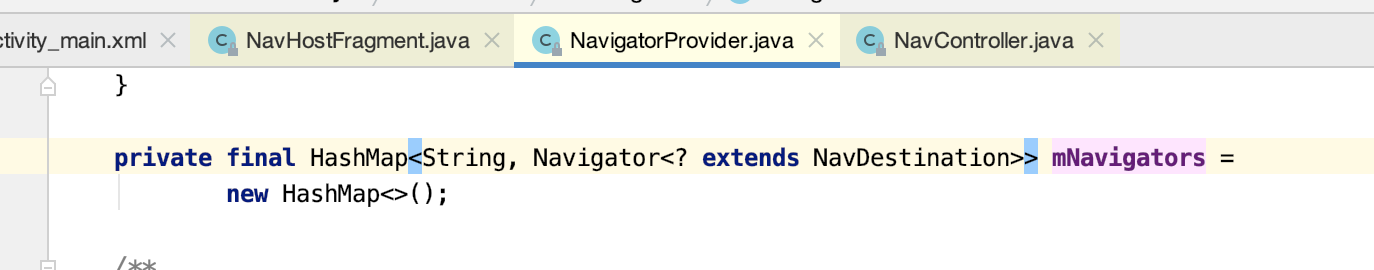
而添加的对象为:
(3)savedInstanceState不为空时候,恢复controller的状态
好,回到主流程继续往下分析:
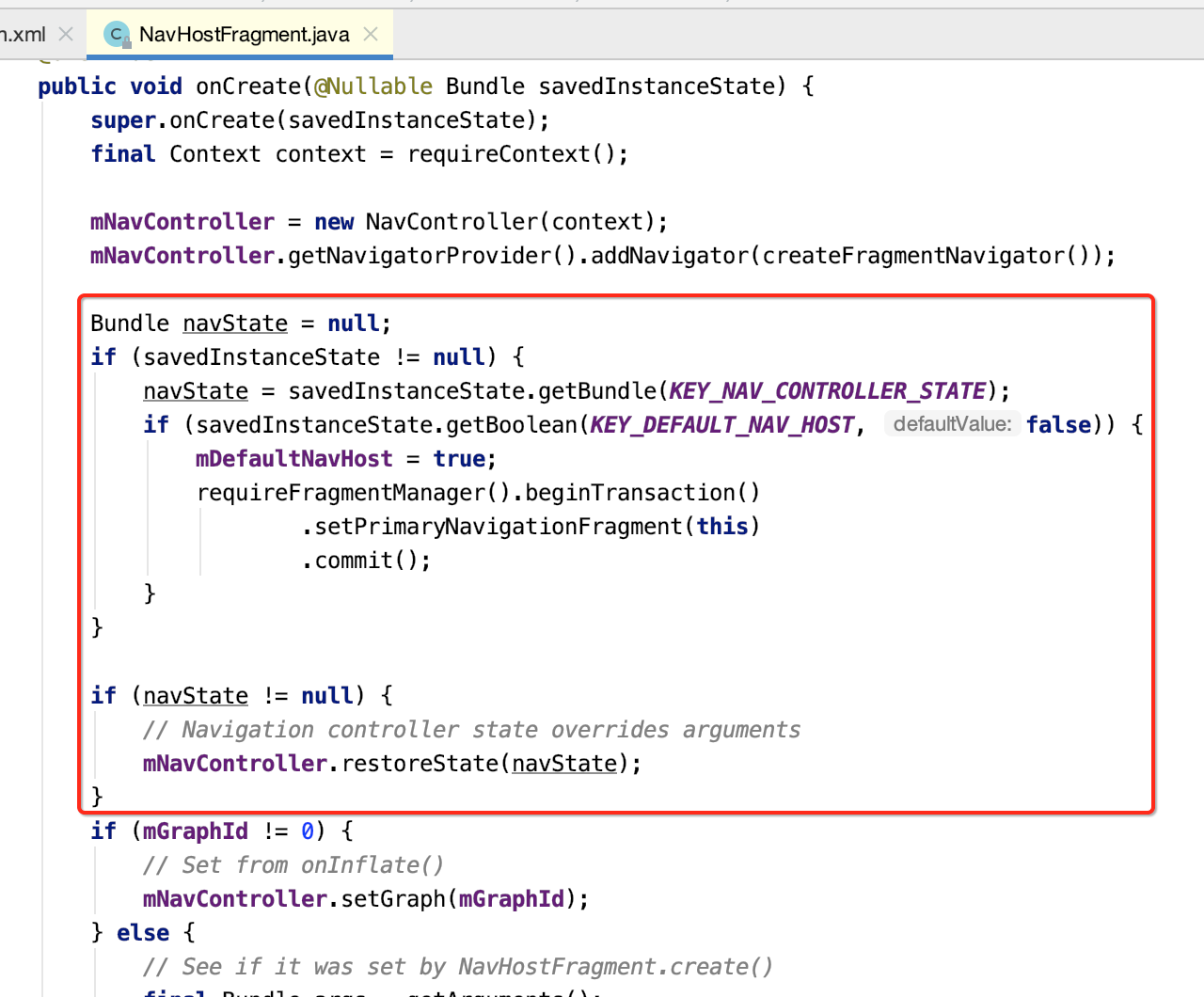
当mDefaltNavHost为true,将会被设置为主导航fragment。可以拦截返回键事件(back事件)。

(4)将graph设置给navController,构建NavGraph。下面会单独分析该模块。

4.NavHostFragment.onCreateView():
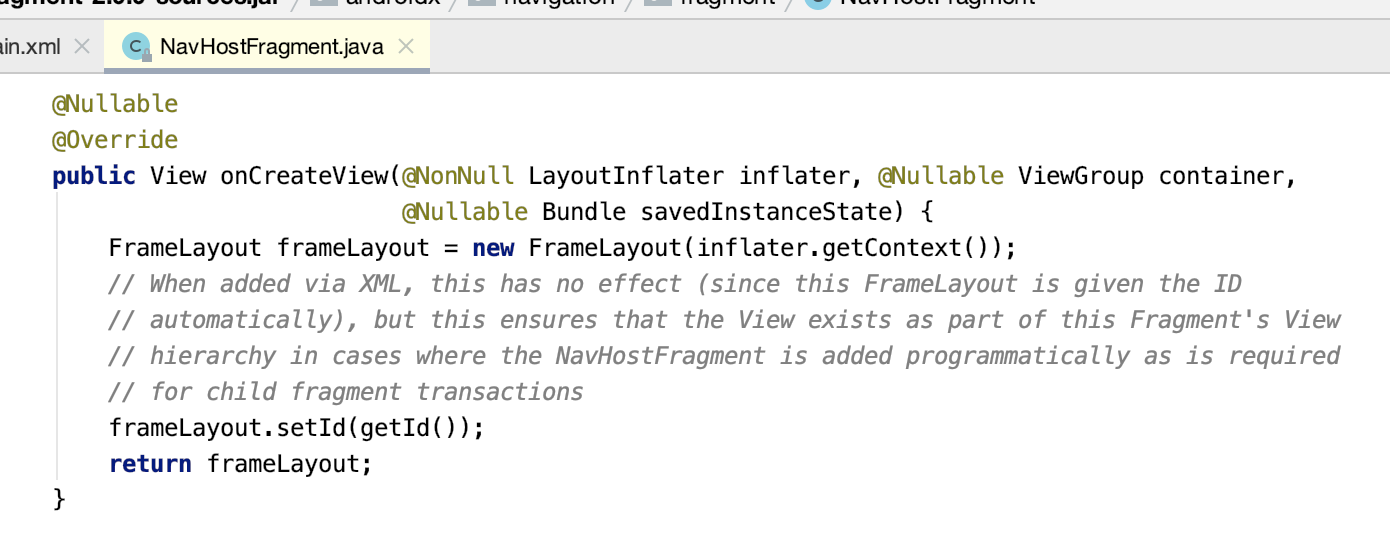
该NavHostFragment的视图就只有一个FrameLayout布局, 在NavHostFragment的创建时,为它创建一个FrameLayout作为导航界面的载体。
5.NavHostFragment.onViewCreated():
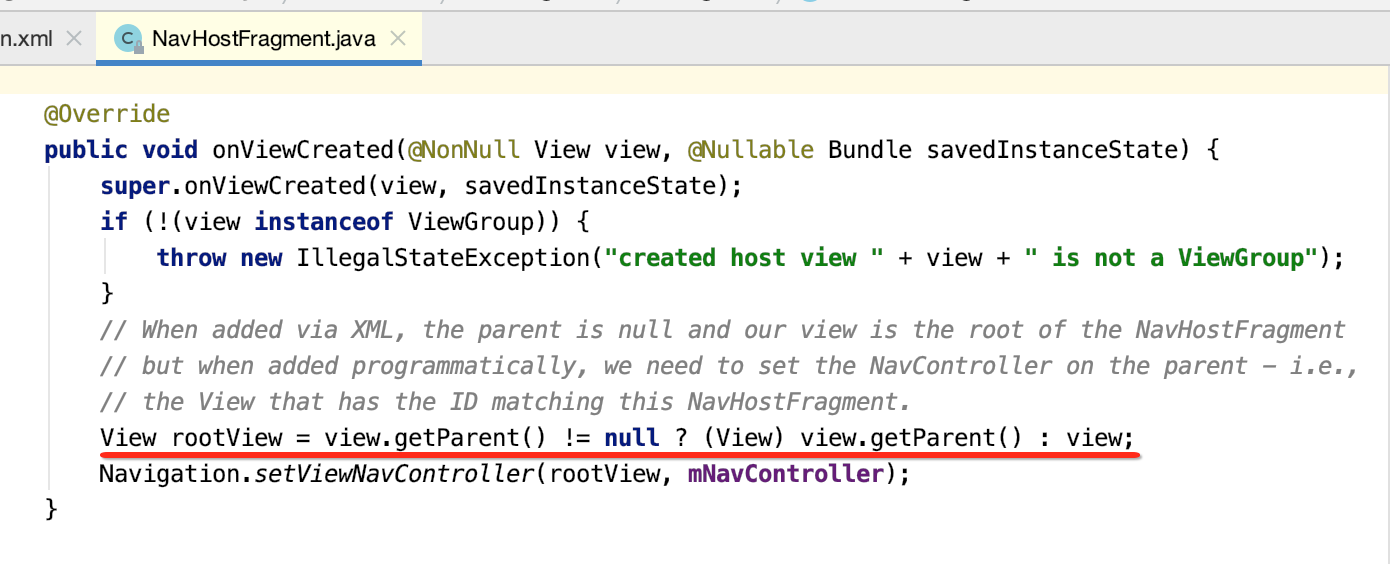
这是啥意思?其实是这样的:
(1)当通过XML添加时,父View是null,我们的view就是NavHostFragment的根。
(2)但是当以代码方式添加时,需要在父级上设置NavController。
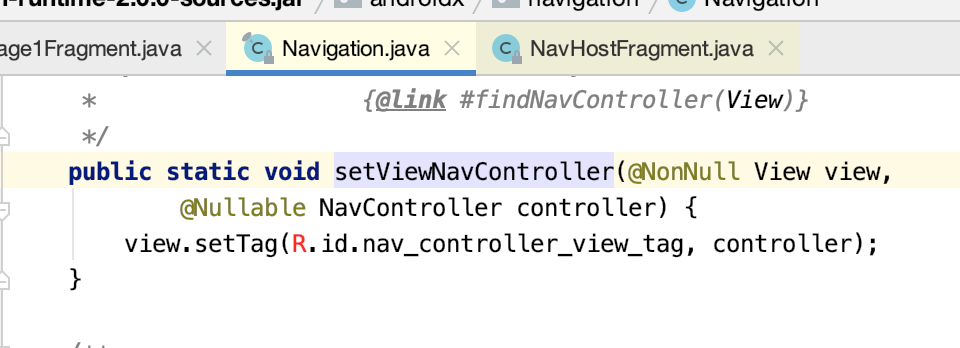
6.Navigation.setViewNavController():
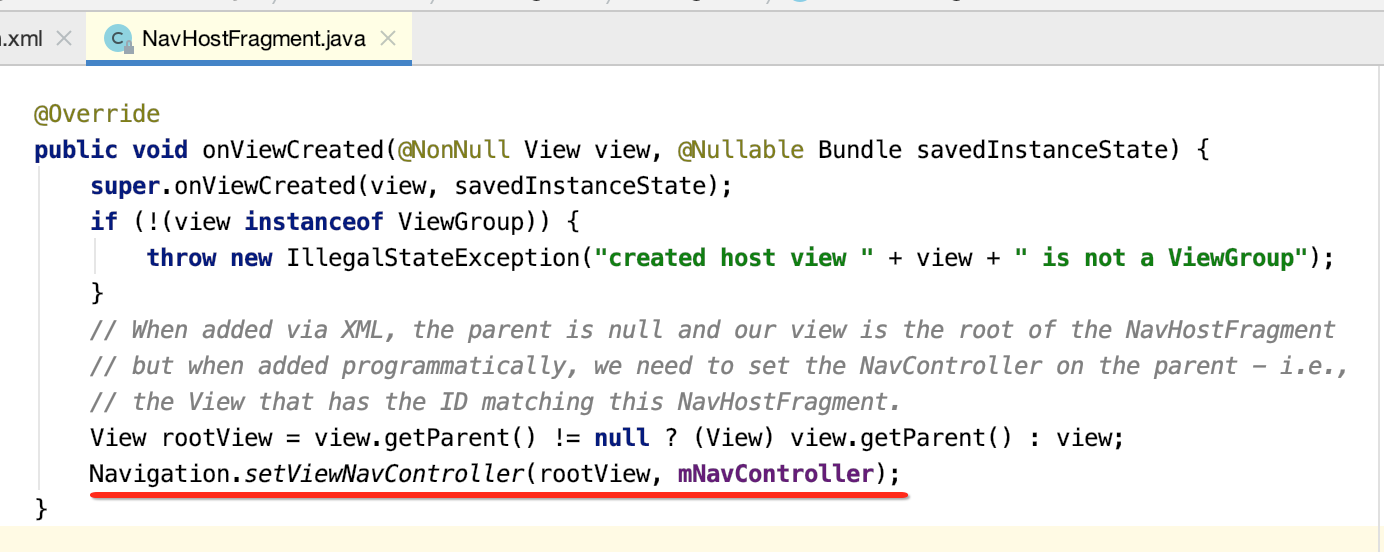
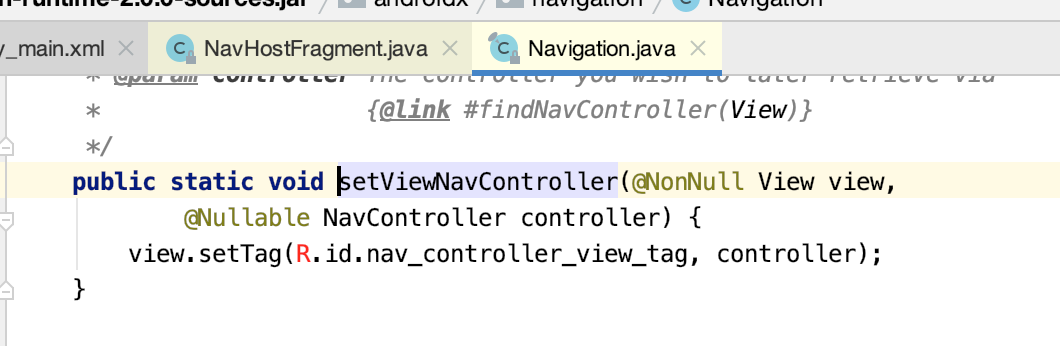
主要是将NavController对象设置为rootView的tag。方便以后递归遍历到NavController对象,确保NavController对象的唯一。
获取NavController:
我们在具体导航时的代码写法是这样的:
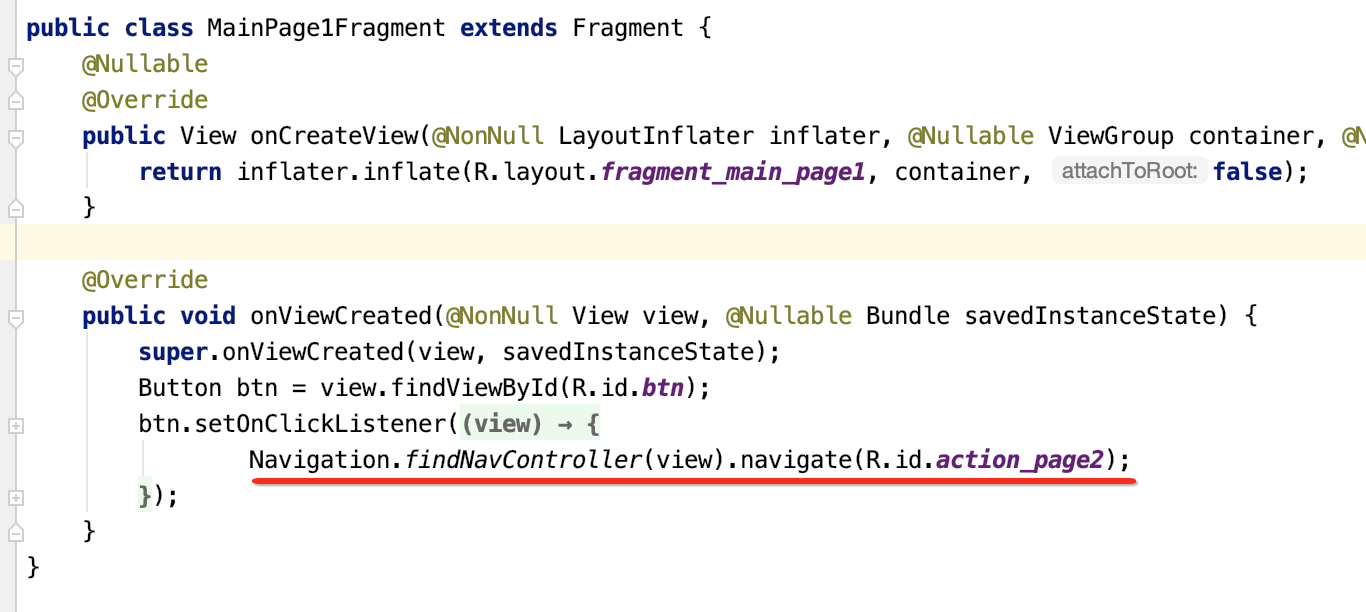
所以咱们来看一下findNavController()方法的细节:
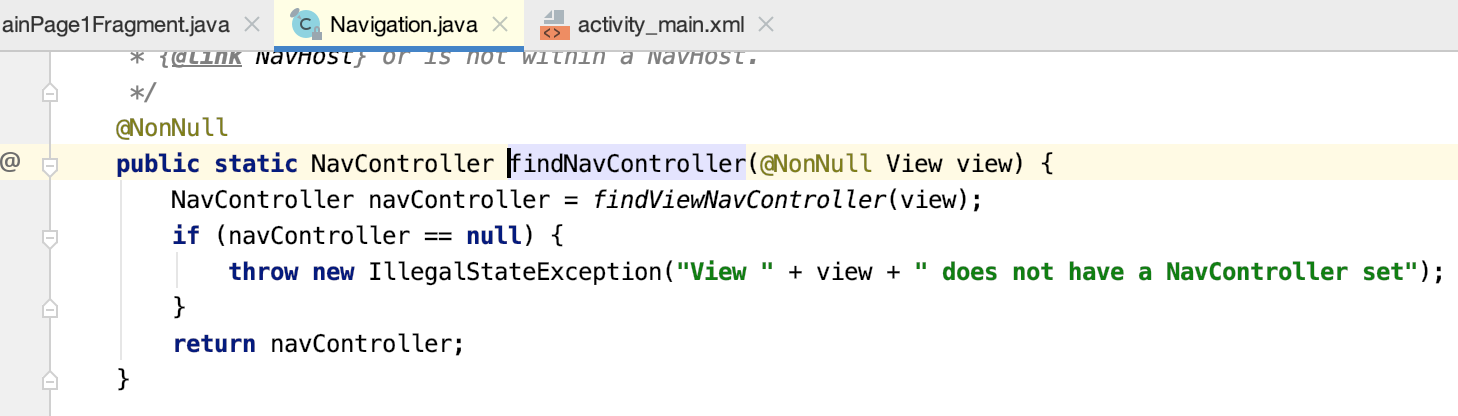
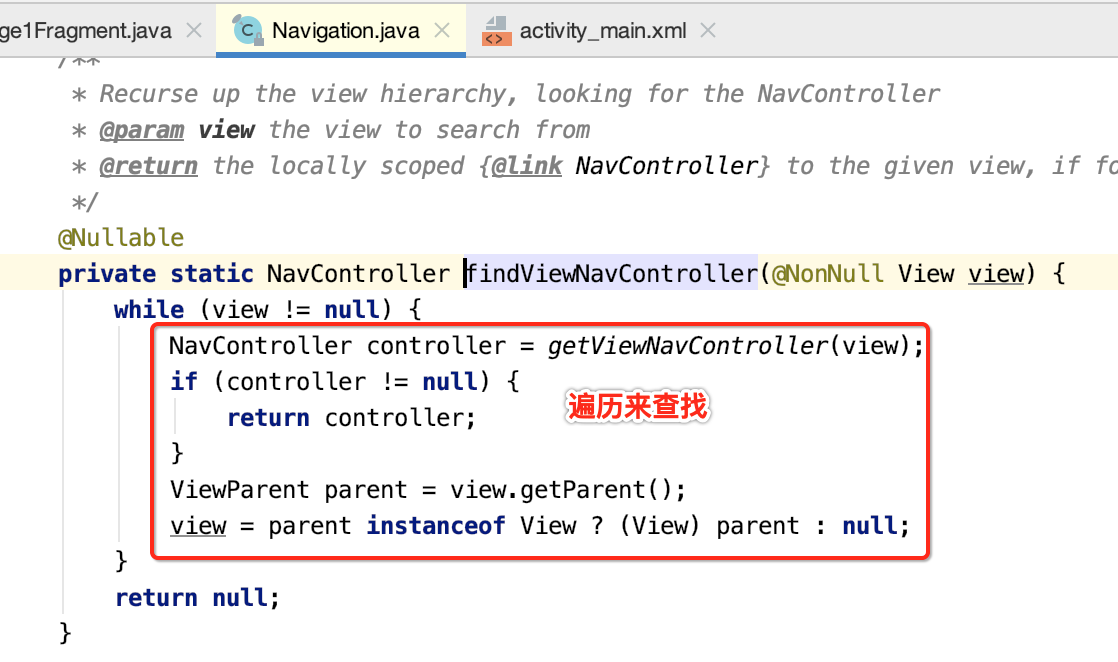

此时的这个tag就是我们之前在onViewCreated()中设置的:

也就是最终会获得它:
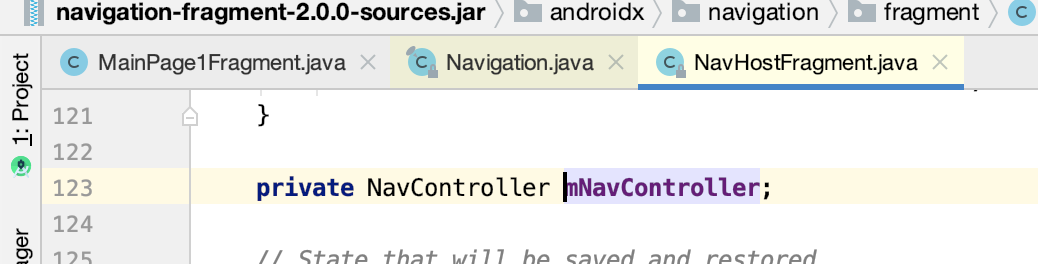
NavController是如何参与到导航事件的?
此时则需要回到这块代码进行进一步分析:
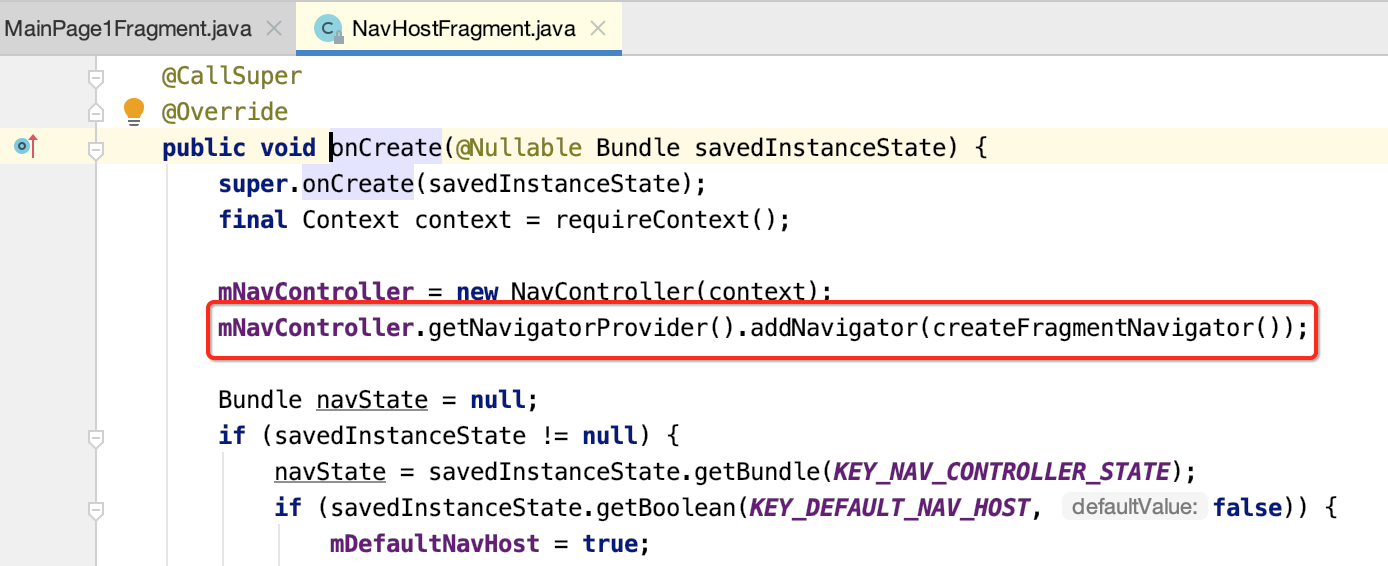
1.其中mNavigatorProvider是NavController中的全局变量,内部通过HashMap键值对的形式保存Navigator类。
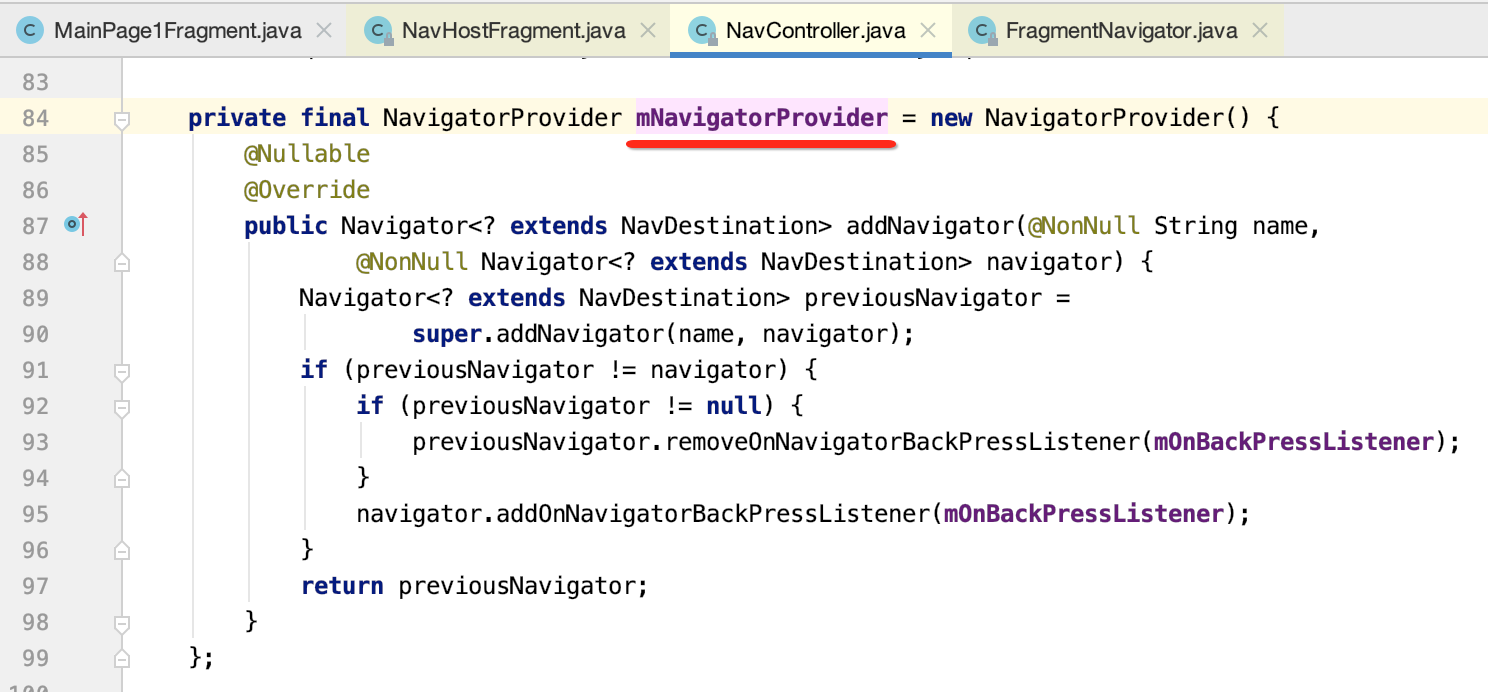
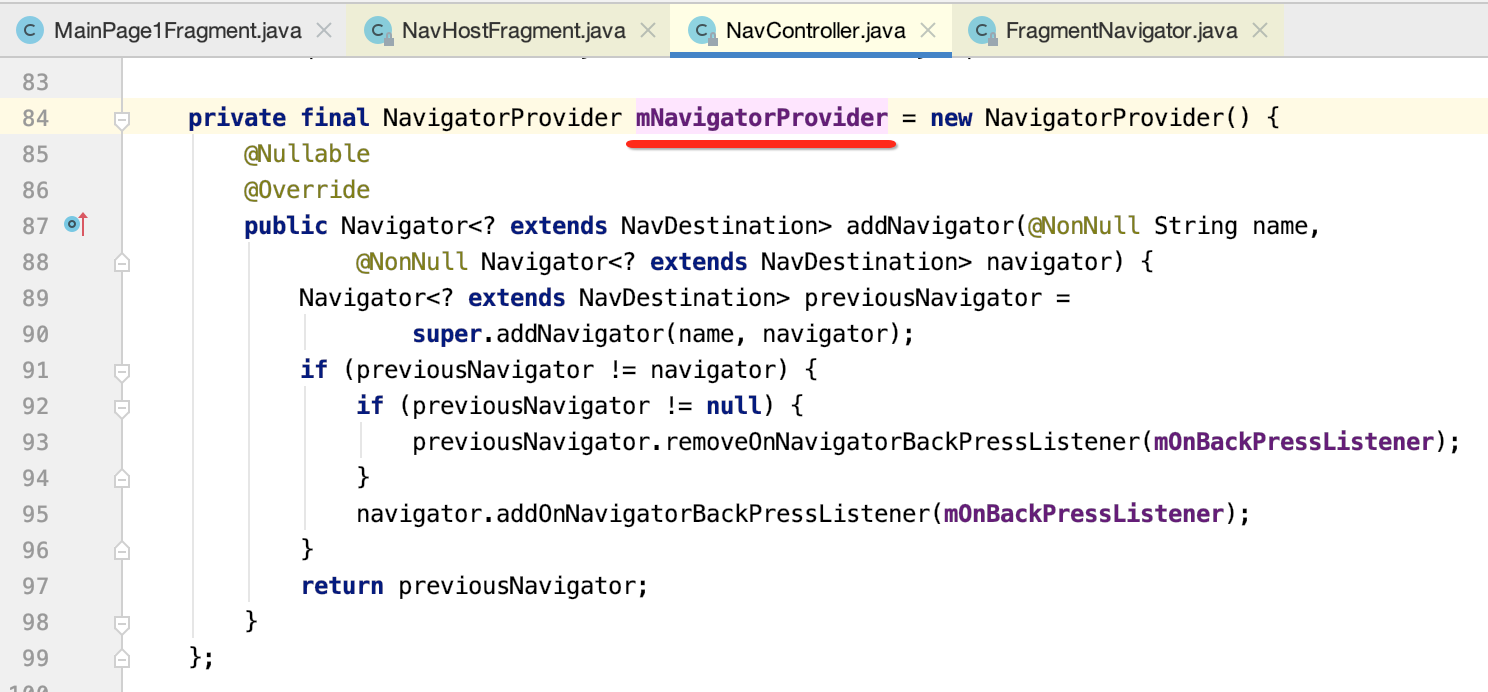
其中可以看到添加了一个导航返回的监听了:

2.createFragmentNavigator方法,构建了FragmentNavigator对象,其中抽象类Navigator还有个重要的实现类ActivityNavigator和NavGraphNavigator。
这两个类的对象在NavController的构造方法中被添加。

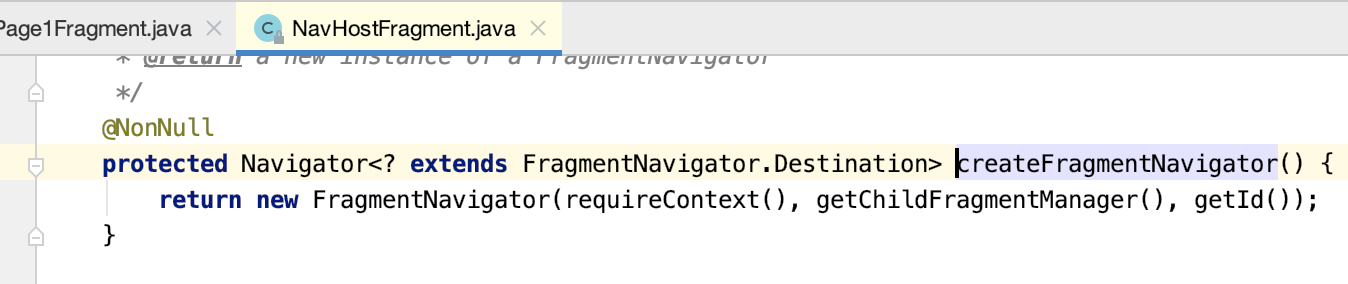
而FragmentNavigator看下它的类结构:
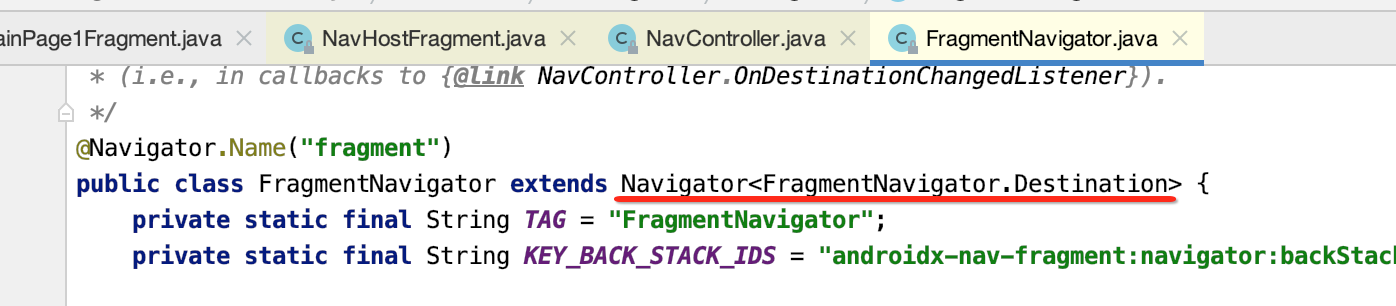
而这个抽象类Navigator有几个继承子类:

3.其中Navigator类的作用是:能够实例化对应的NavDestination,并且能够实现导航功能,拥有自己的回退栈。构建NavGraph,在构建NavController的时候,我们还调用了NavController.setGraph(graphId)方法,该方法主要是构建NavGraph。

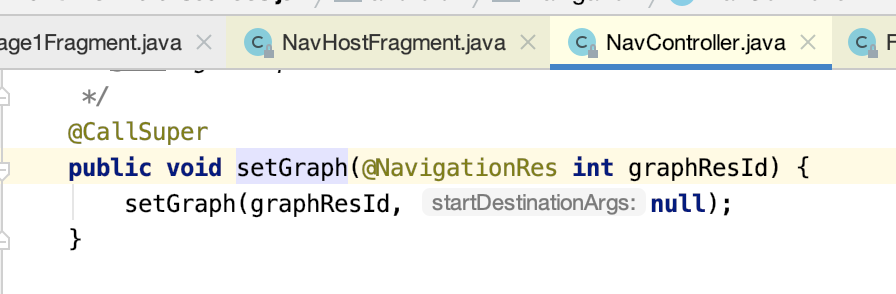
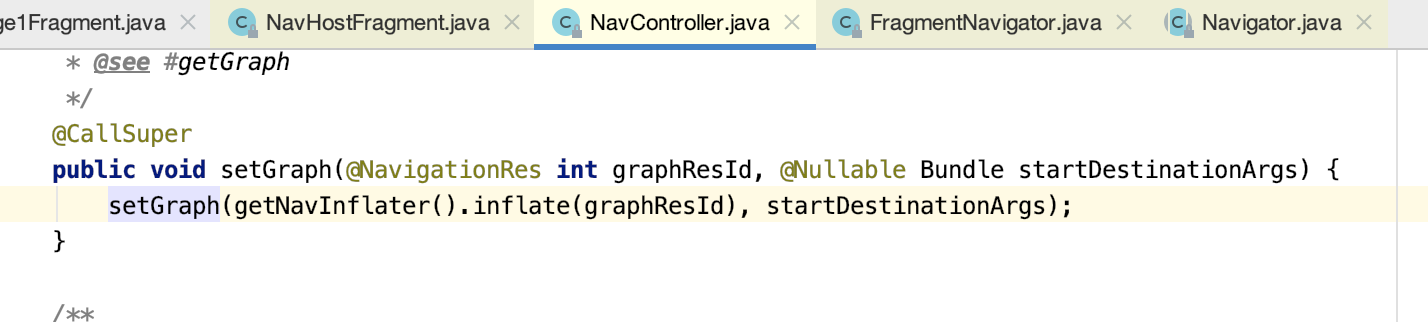
其中调用getNavInflater方法创建NavInflater对象,用于解析导航配置xml:

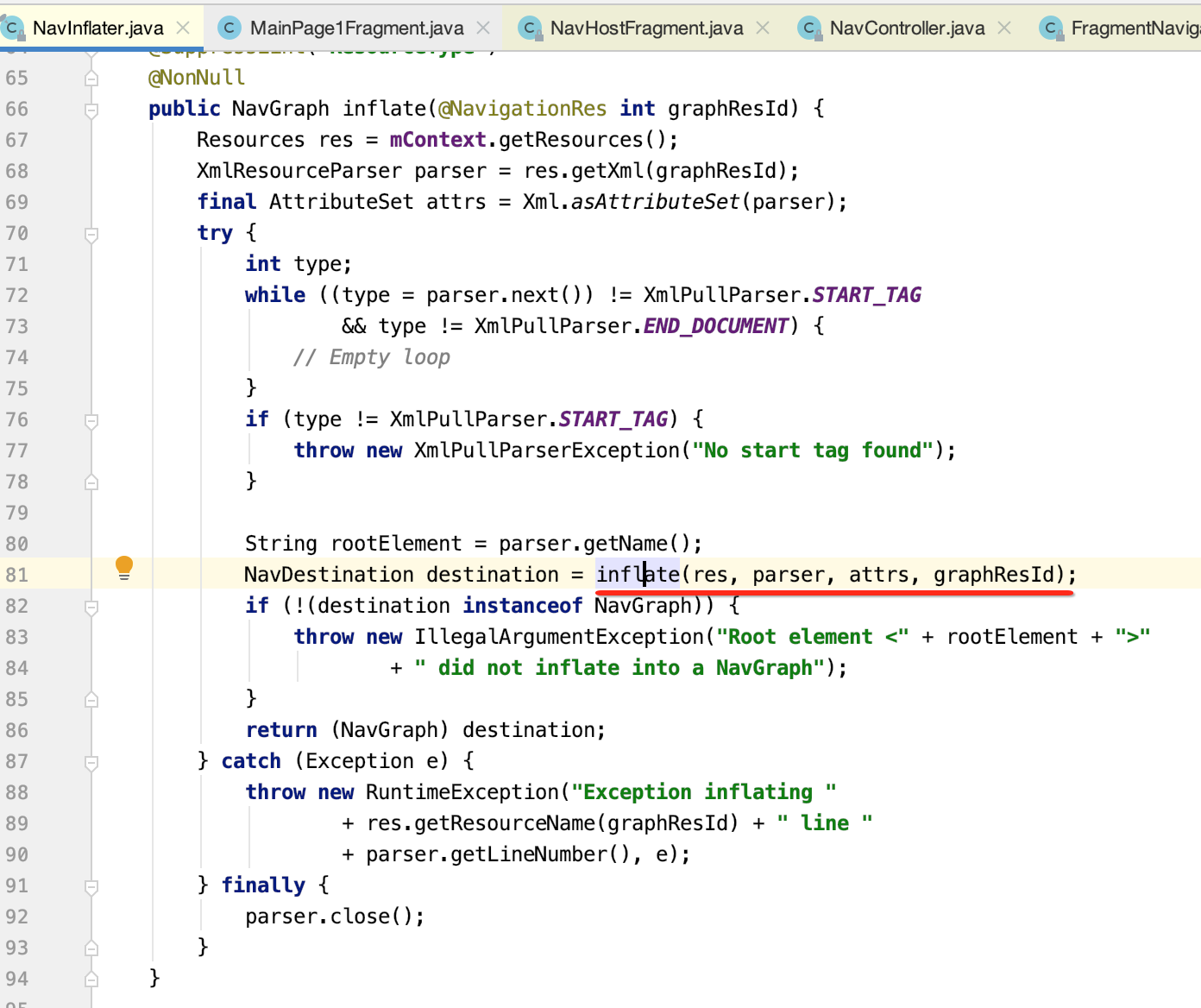
4. NavInflater.inflate():
根据传入的XML资源id构建NavGraph,NavGraph组成Fragment路由的导航地图,而NavDestination代表了导航的每一个目的地。在解析完NavDestination后,需要要求NavDestination为NavGraph,即NavGraph是NavDestination的子类。而且在NavGraph内部存储了NavDestination信息。
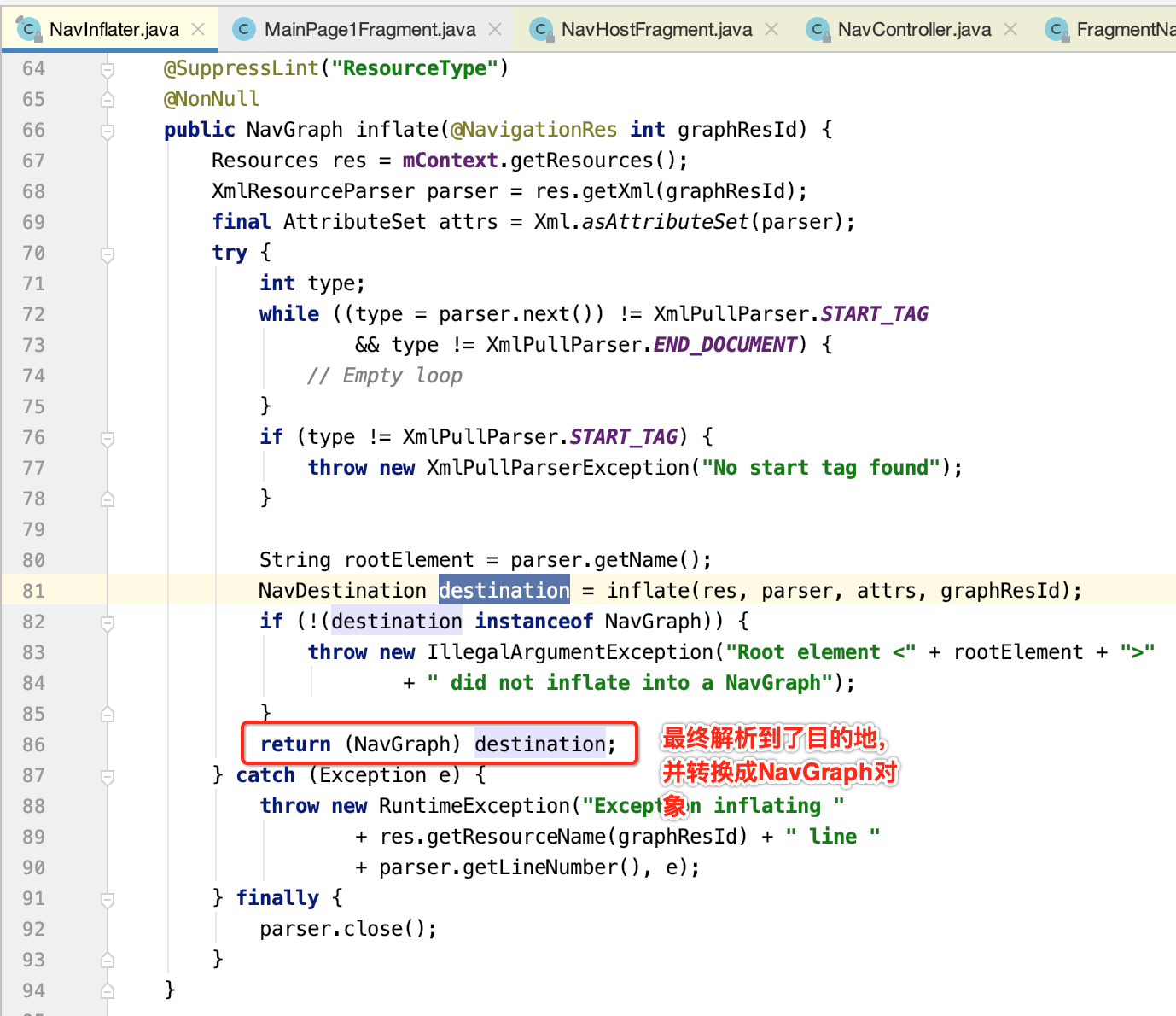
5.上面的inflate方法内部会继续调用inflate方法。
下面具体看一下它的细节:
(1)getNavigator方法获取都Navigator实例,该实例在构建NavController是被添加进去,这里获取的是FragmentNavigator对象。
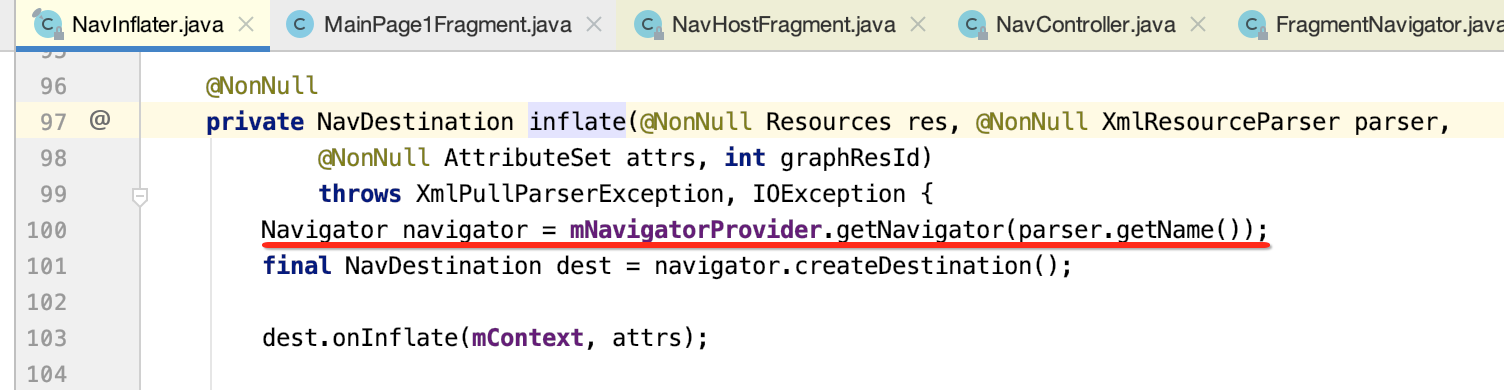
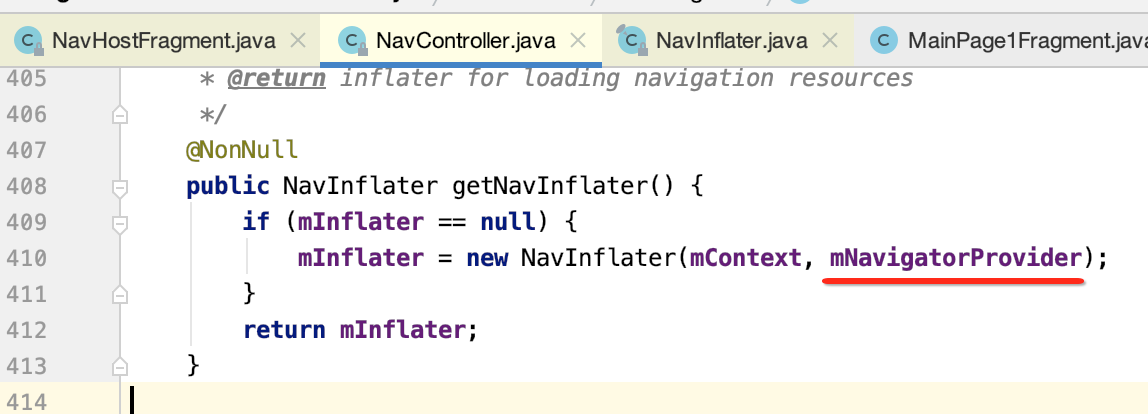
(2)createDestination方法,会调用FragmentNavigator的createDestination构建Destination对象。
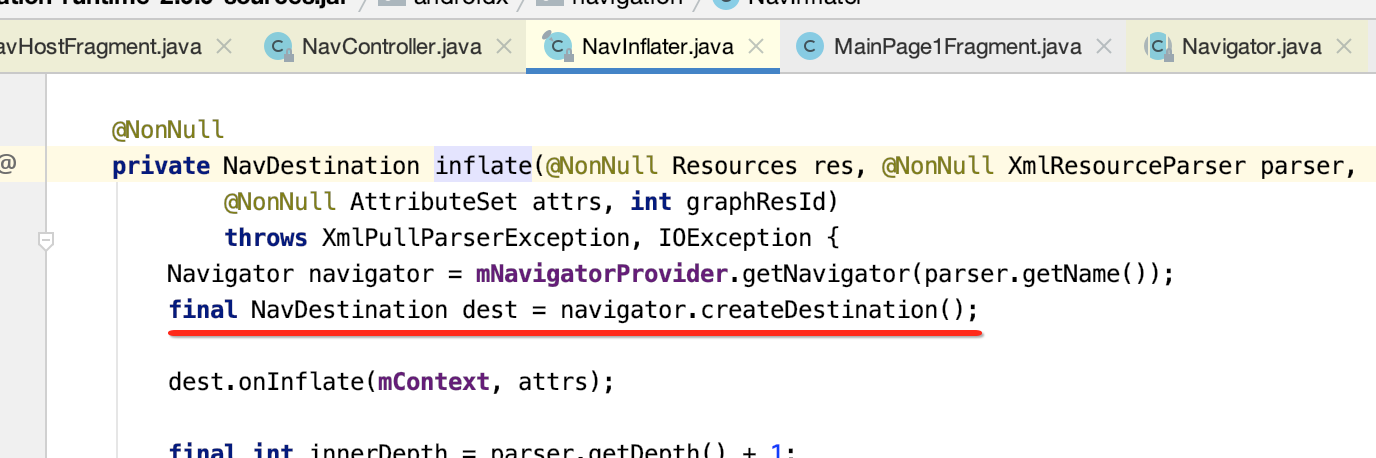
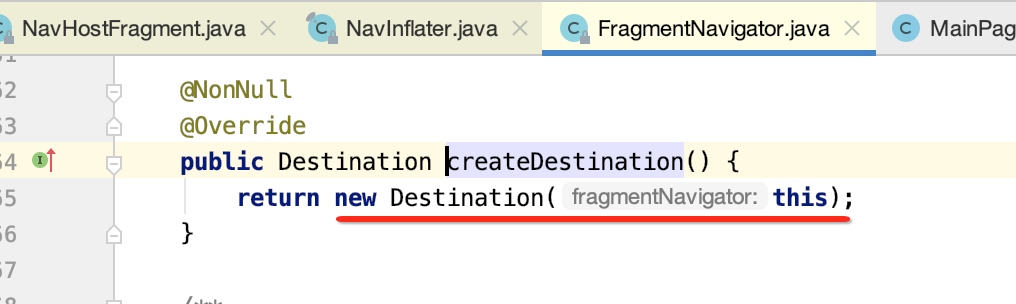
(3)onInflate方法,调用FragmentNavigator.Destination的方法获取设置的Fragment的类名。

(4)while循环内部通过递归构建导航图。
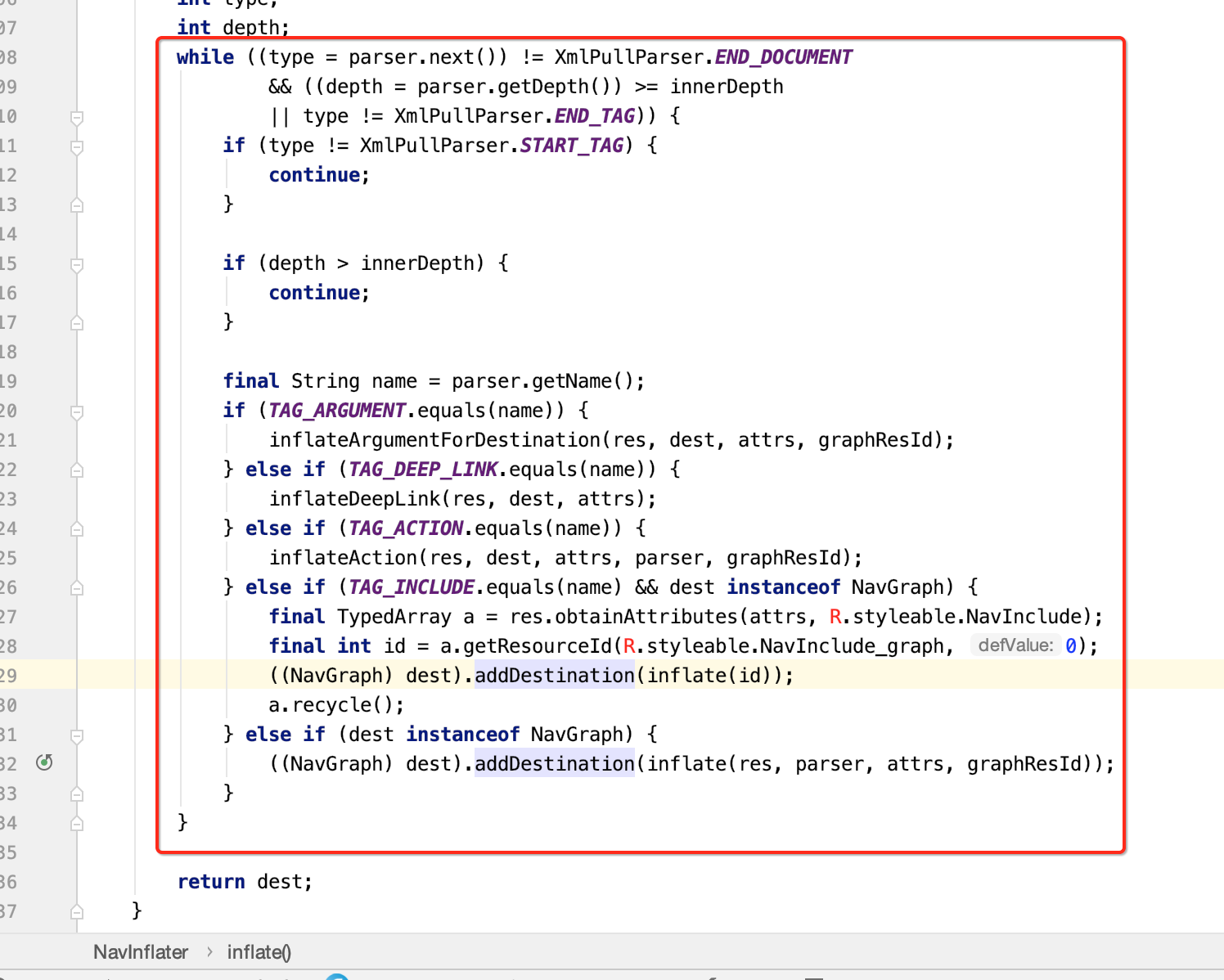
6.通过NavInflater类之后,解析了XML文件构建整个Graph之后,下面回到setGraph方法主流程上来,在解析完XML后会调用setGraph方法。
(1)popBackStackInternal方法将旧的导航图全部出栈。
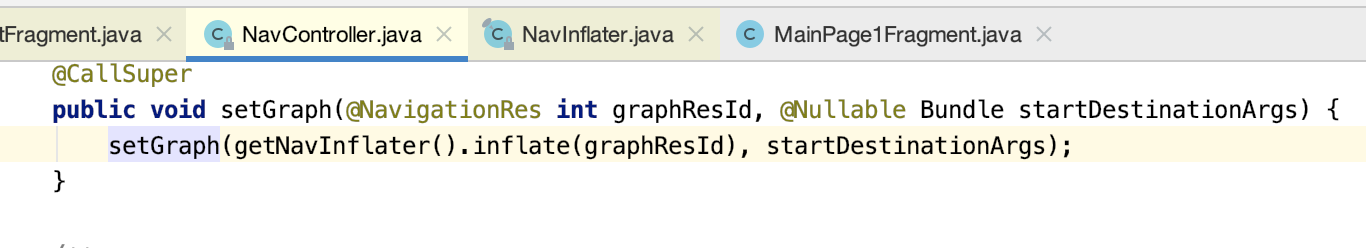

(2)调用onGraphCreated主要是显示一个导航Fragment视图。

7.onGraphCreated方法
(1)恢复之前的导航状态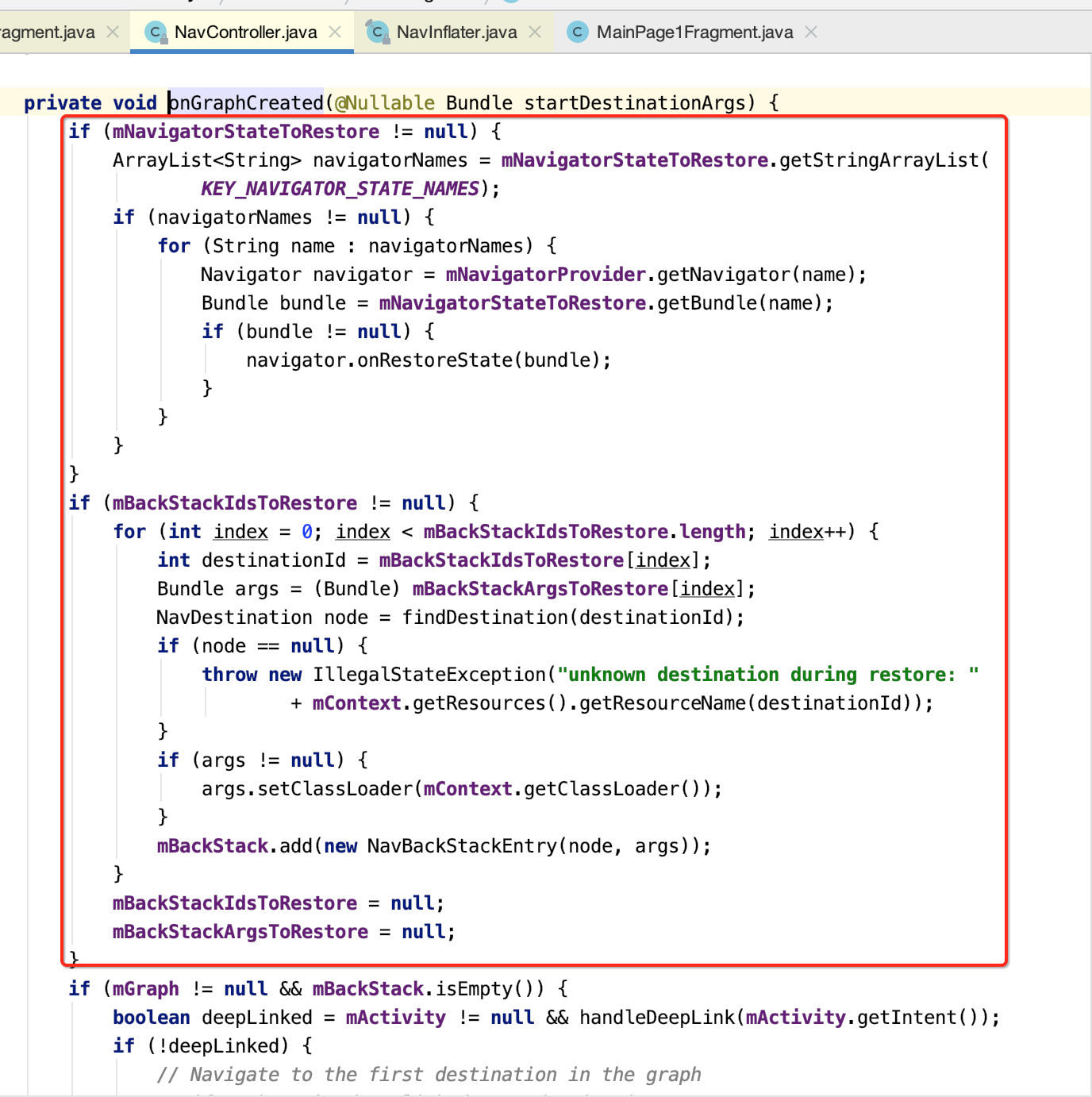
其中可以看到将目标对象放到了一个回退栈当中了:
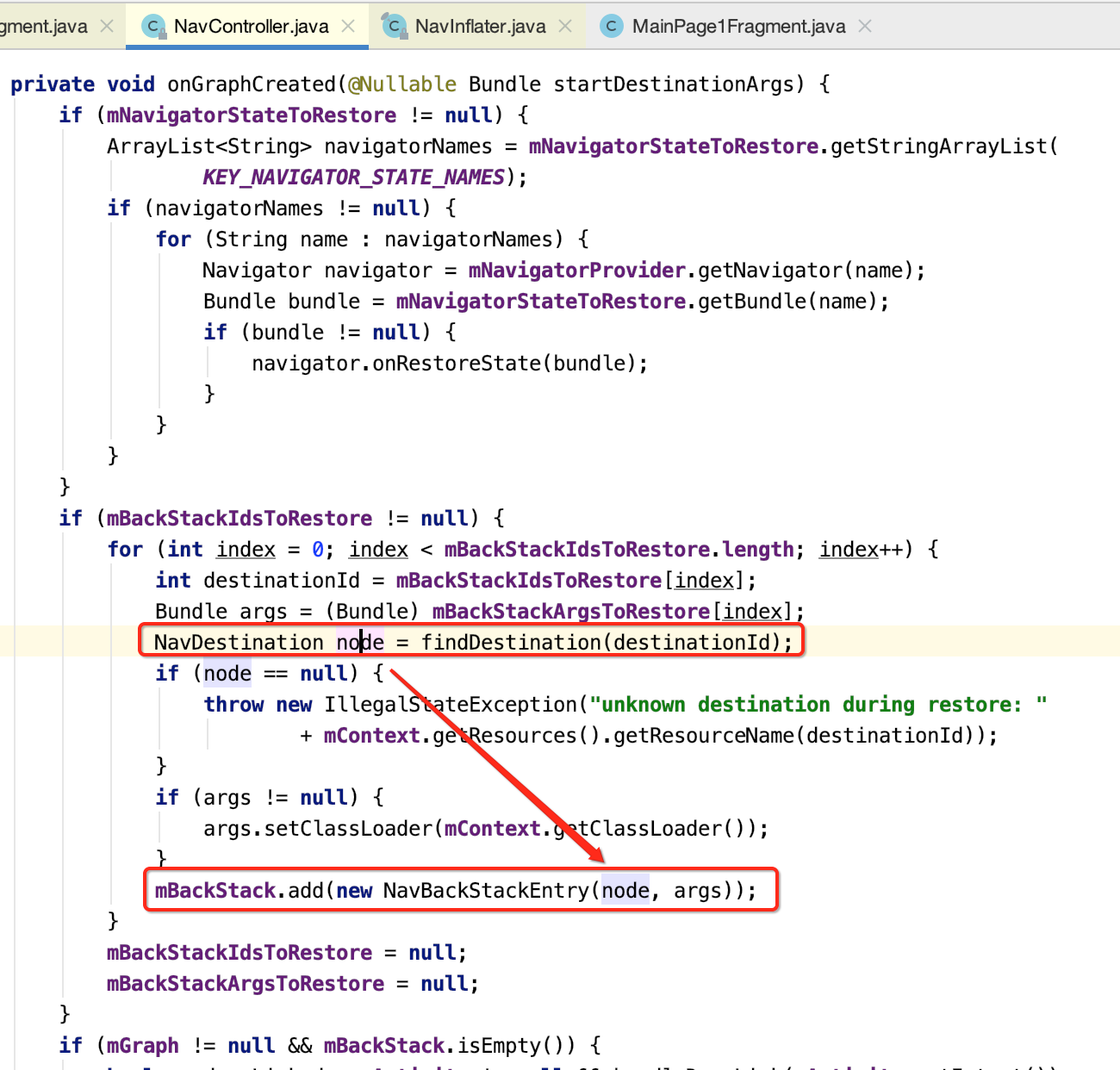
这点就是一个非常核心的导航思想了,也就是都会根据这个回退栈来进行导航处理。
(2)调用navigate方法,显示第一个Fragment。即在Navigation文件里,属性app:startDestination的Fragment。所以最终都会走到navigate导航方法。

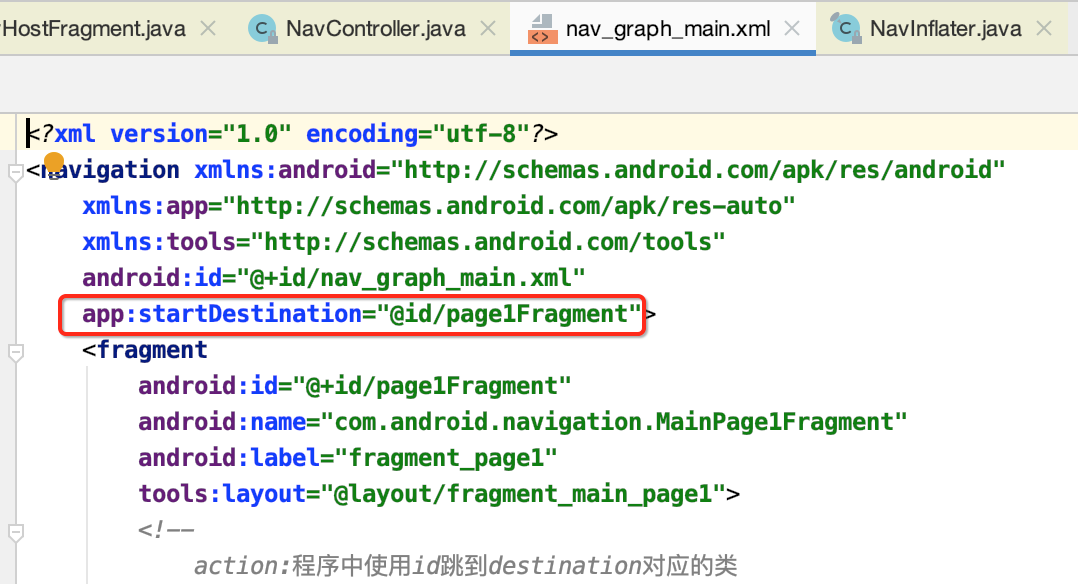
最终导航的细节下面则会详细分析。
导航 navigate():
1.在构建和获取到NavController对象以及NavGraph之后,下面是使用它来实现真正的导航了。下面从navigate开始分析。在navigate方法内部会查询到NavDestination,然后根据不同的Navigator实现页面导航。

下面来分析一下这个导航的细节:
(1)如果回退栈为null返回NavGraph,不为null返回回退栈中的最后一项。
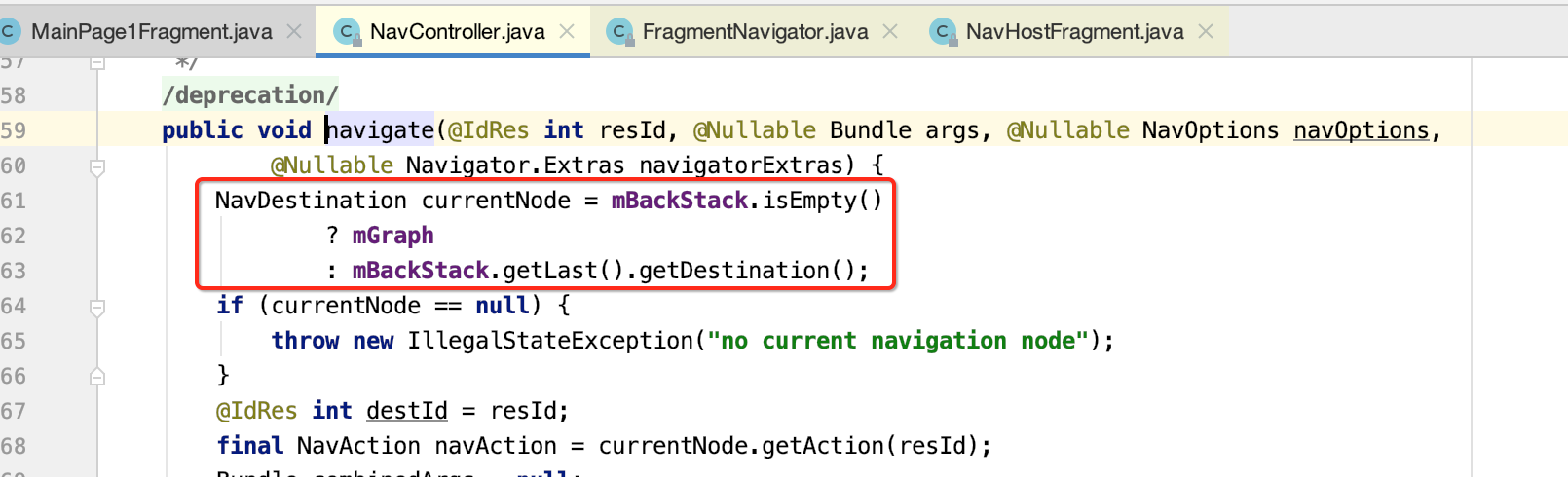
(2)根据id,获取对应的NavAction。然后在通过NavAction获取目的地id。
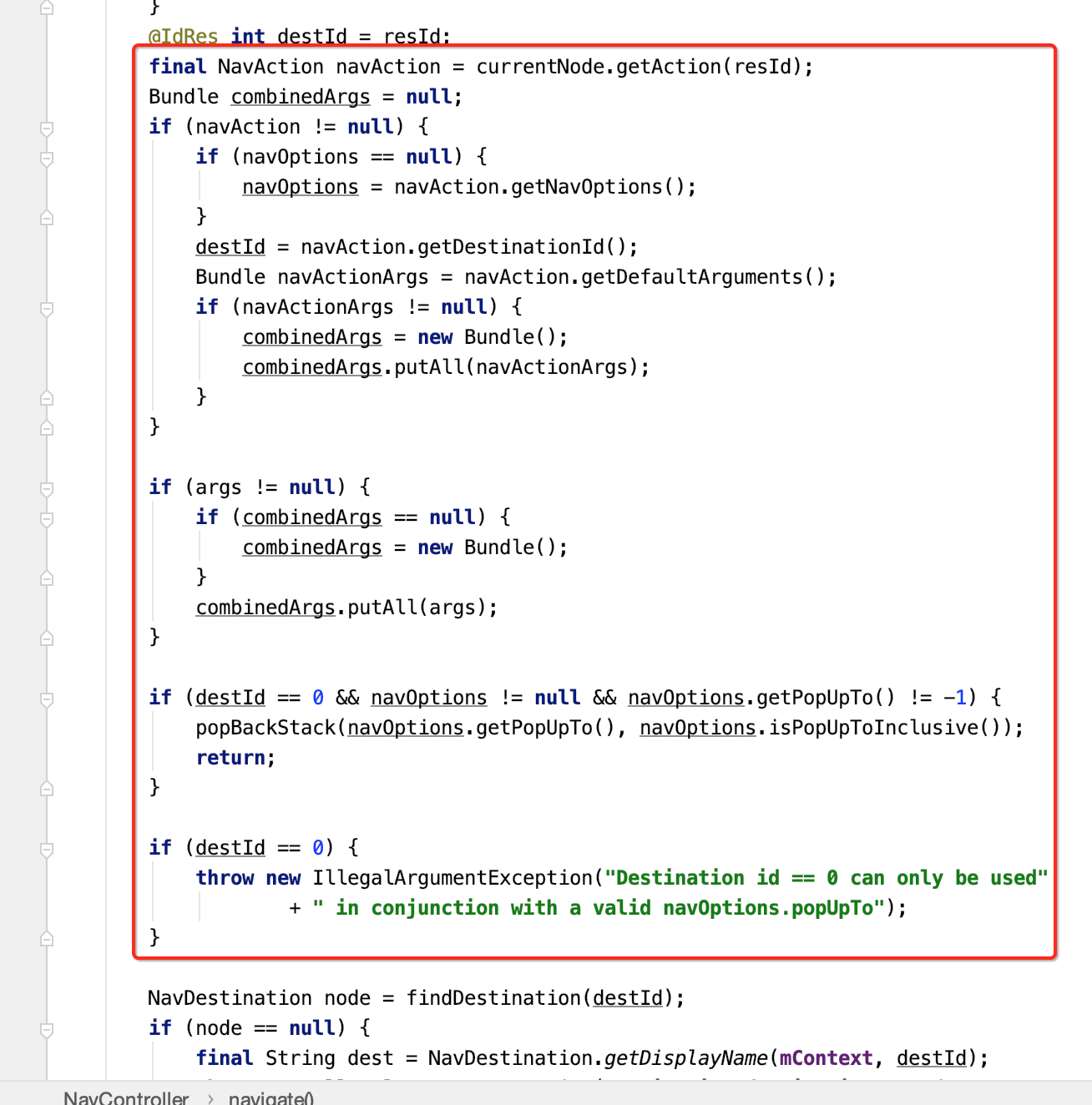
(4)利用目的地ID属性,通过findDestination方法,找到准备导航的目的地。
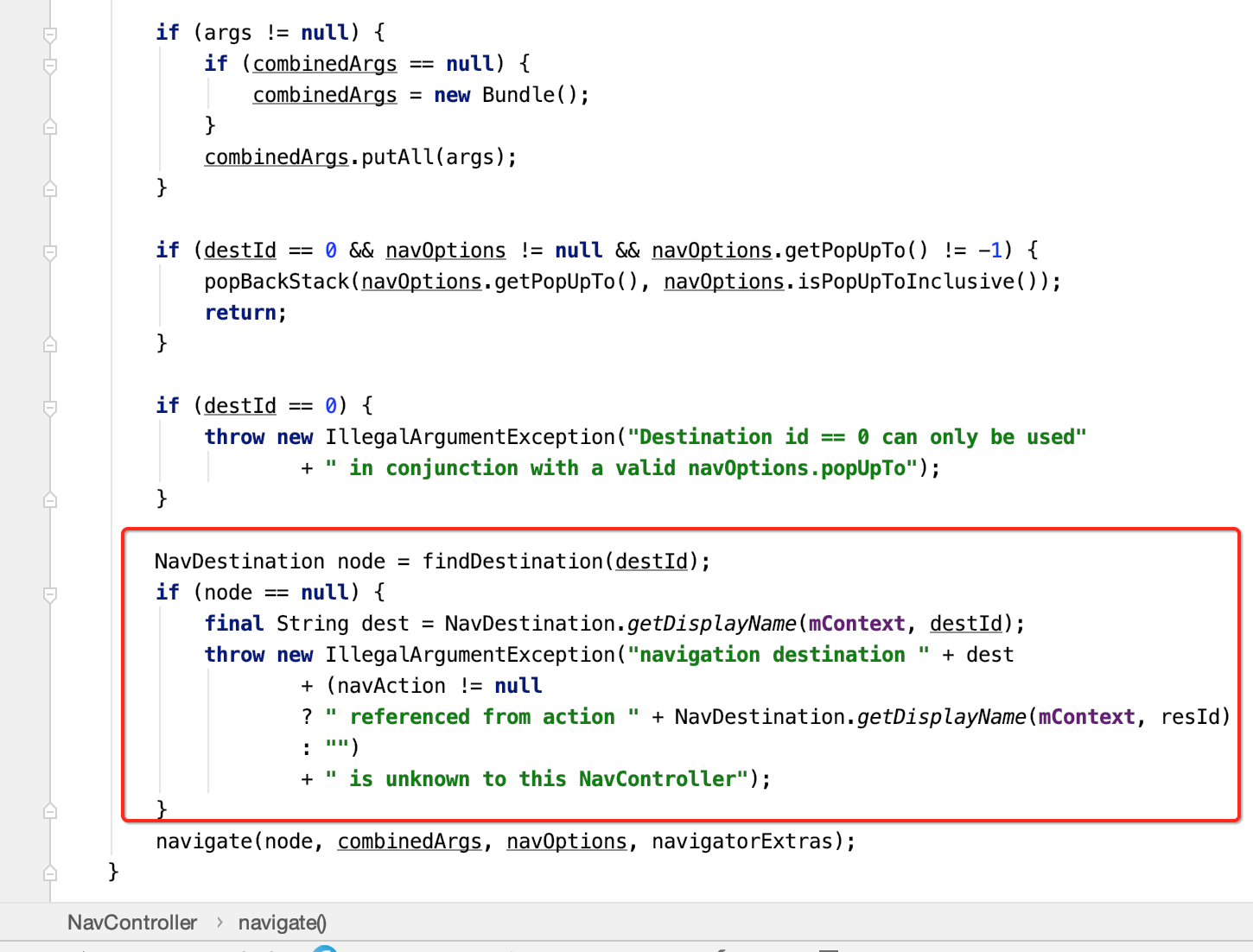
最终会调用到这个navigate方法():
(5)根据导航目的地的名字,调用getNavigator方法,获取Navigator对象。这里对应的是FragmentNavigator。
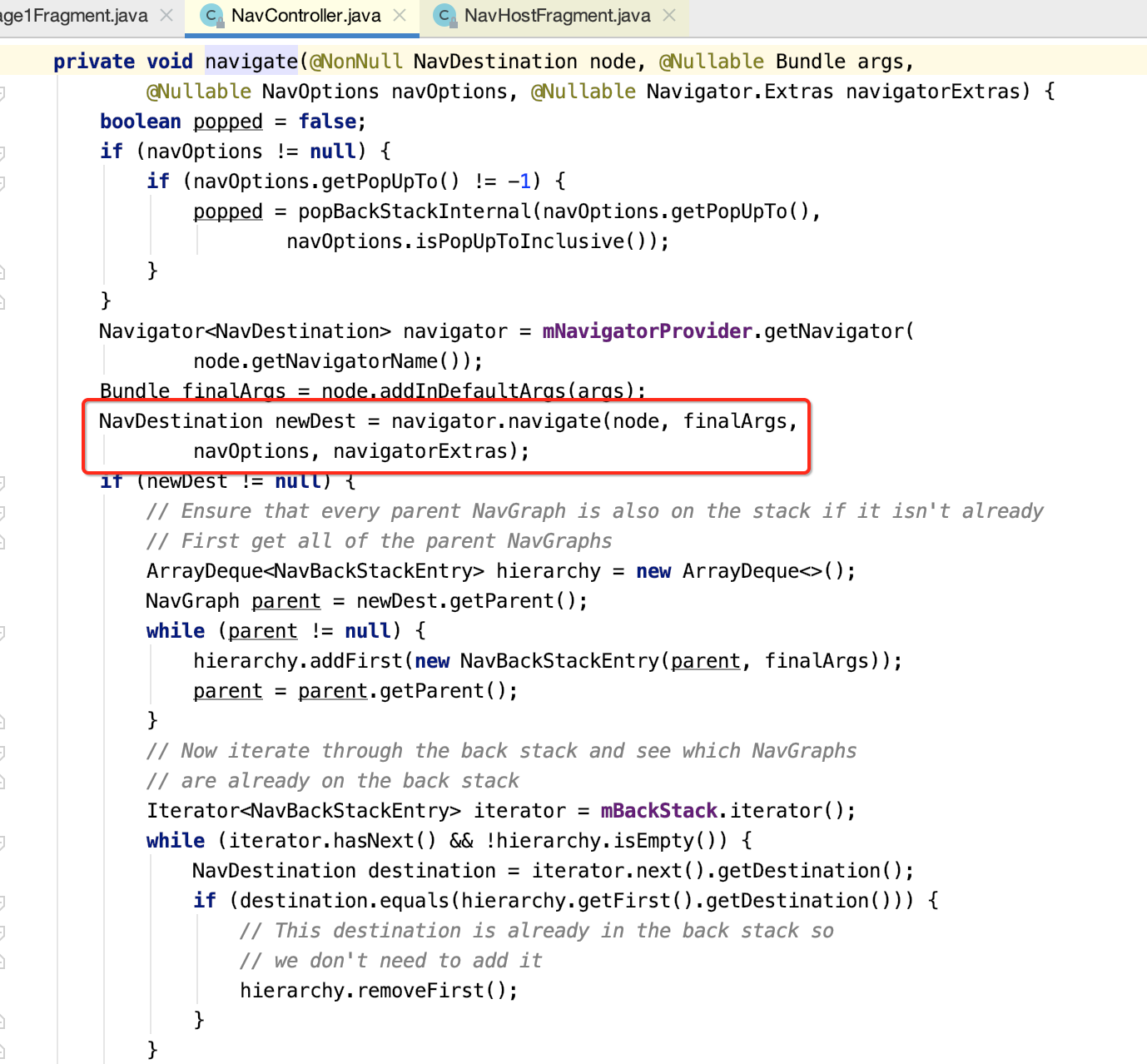
2.FragmentNavigator的实现
通过以上的分析,又来到了Navigator 的子类FragmentNavigator类。下面来看看FragmentNavigator.navigate的方法。
(1)调用instantiateFragment,通过反射机制构建Fragment实例
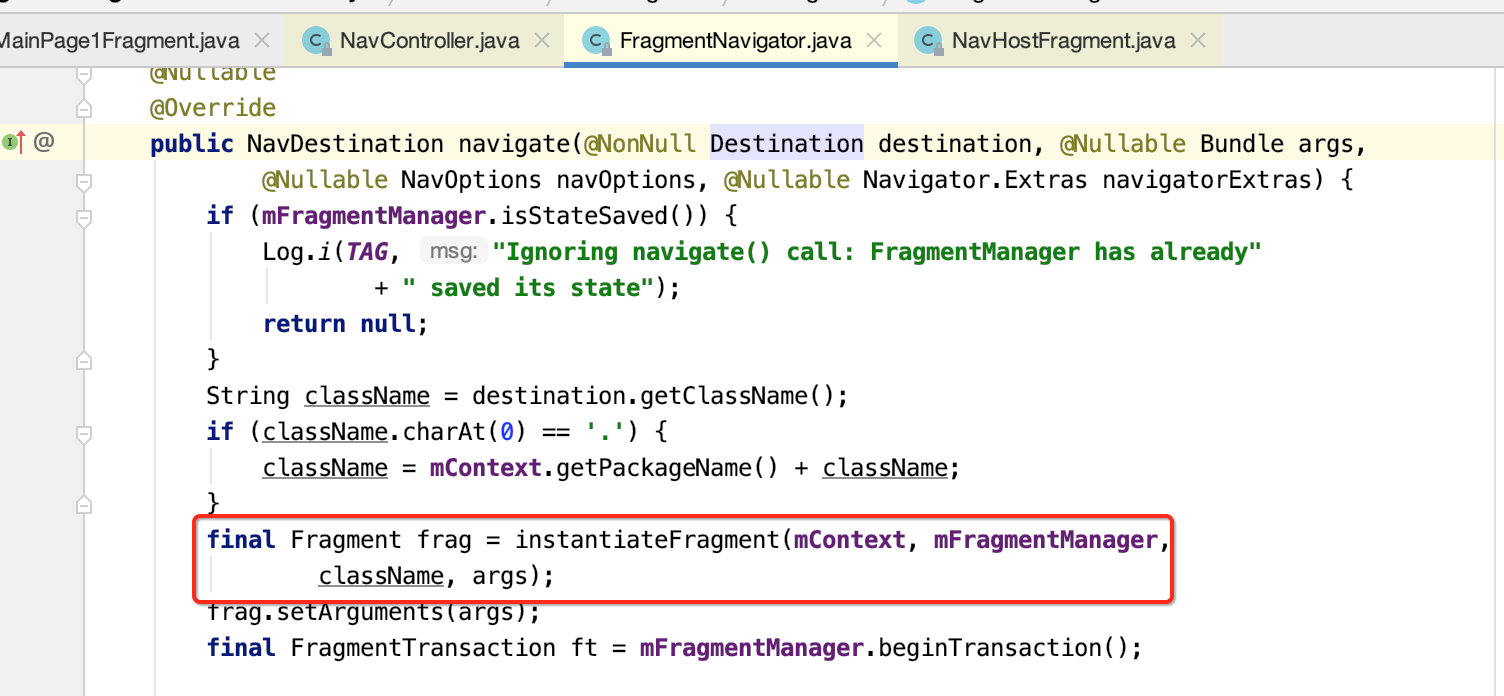

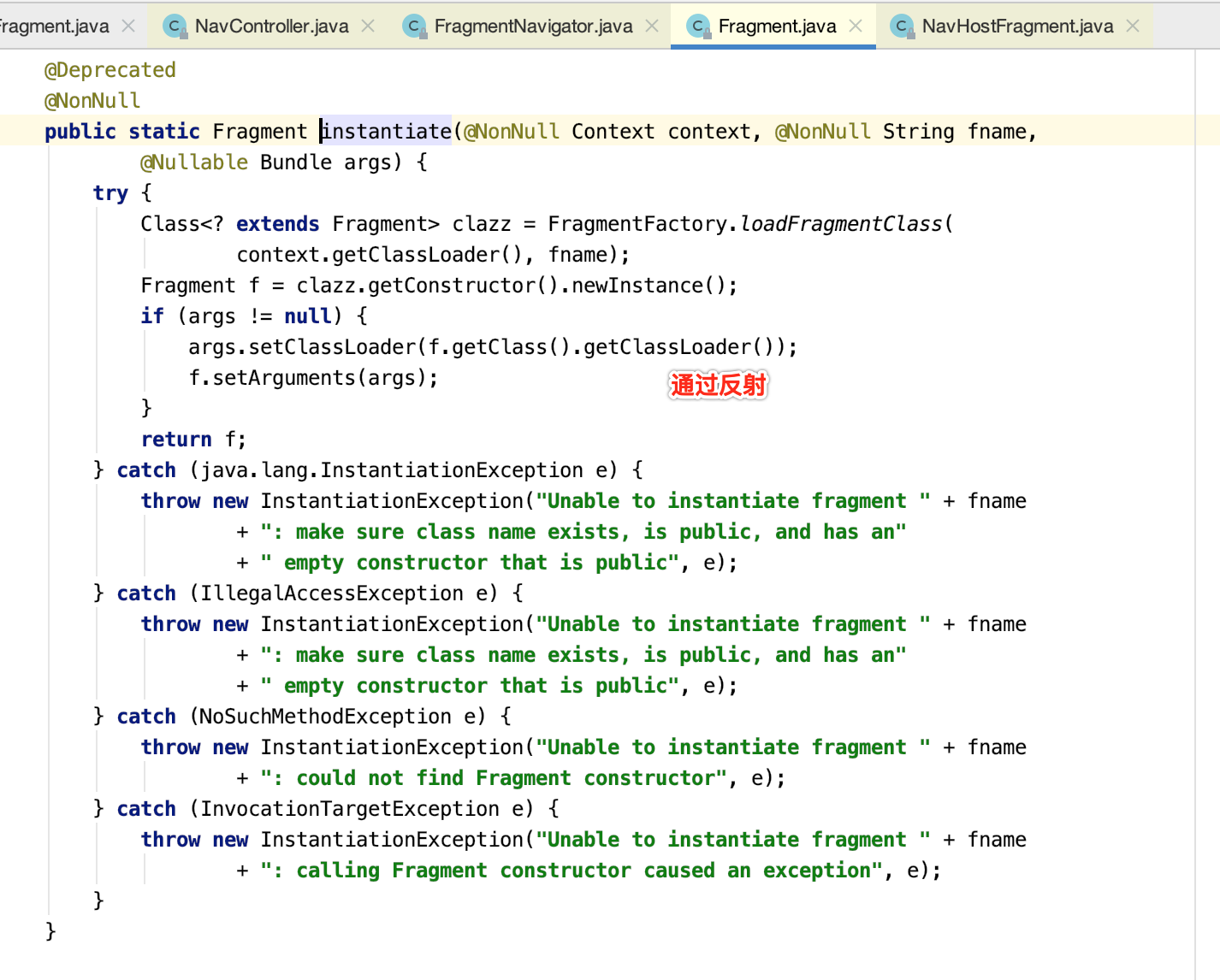
(2)处理进出场等动画逻辑
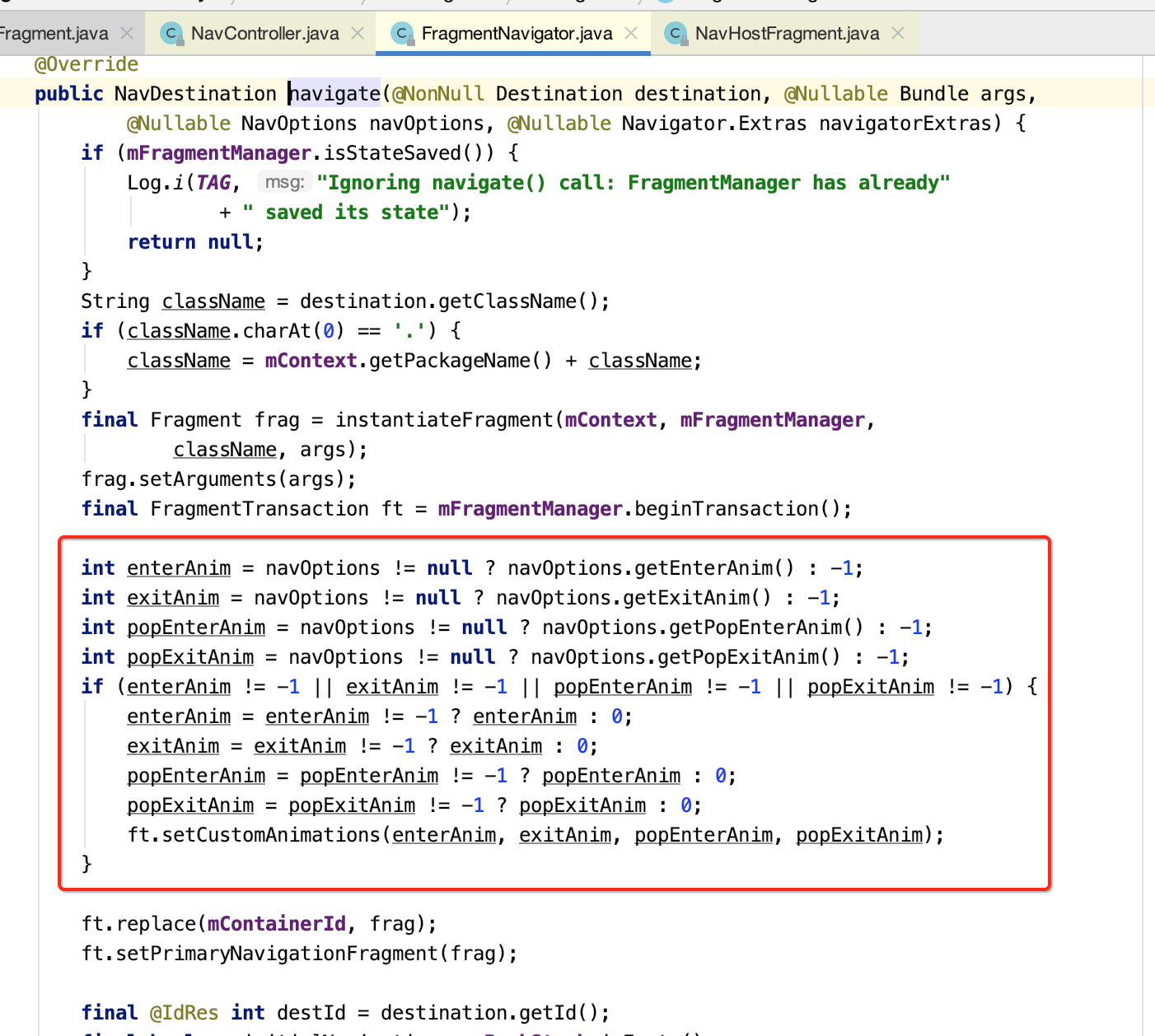
(3)最终调用FragmentManager来处理导航逻辑。
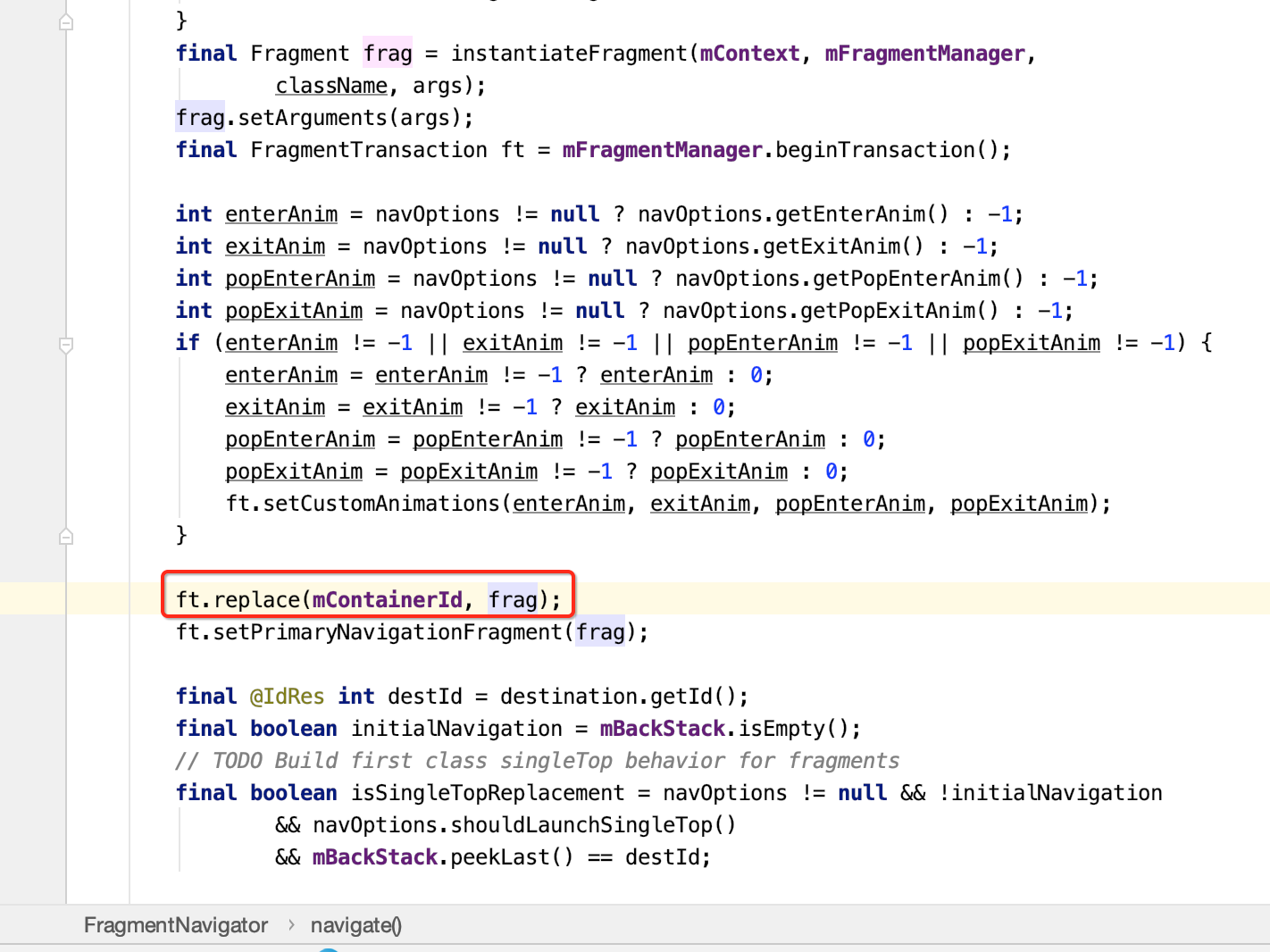
back退栈的处理:
实现原理总结:
(1)NavHostFragment 作为导航载体,在Activity的layout文件里被引用(或者在代码中动态),并且持有导航控制类NavController引用。
(2)NavController 将导航任务委托给Navigator类,Navigator类有两个重要的子类FragmentNavigator和ActivityNavigator子类。NavController类持有NavInflater类引用。
(3)NavInflater 负责解析Navgation文件,负责构建NavGraph导航图。
(4)NavDestination 存有各个目的地信息,在FragmentNavigator和ActivityNavigator内部分别对应一个Destination类,该类继承NavDestination。
(5)在页面导航时,fragment的操作还是交由FragmentManager在操作,activity交由startActivity执行。
Paging入门:
了解:
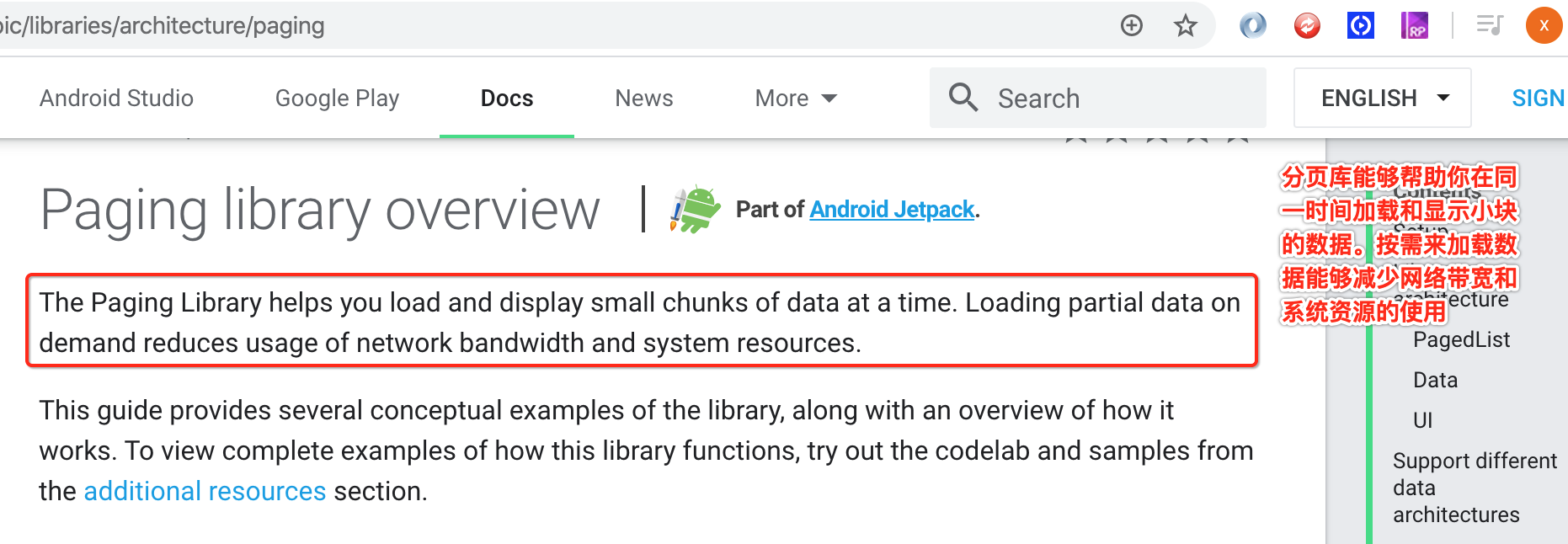
基本使用:
这里用它来实现一个很常见的RecycleView下拉自动分页加载数据的功能,看用了Paging框架之后使用跟我们平常使用有啥区别:
先添加依赖:
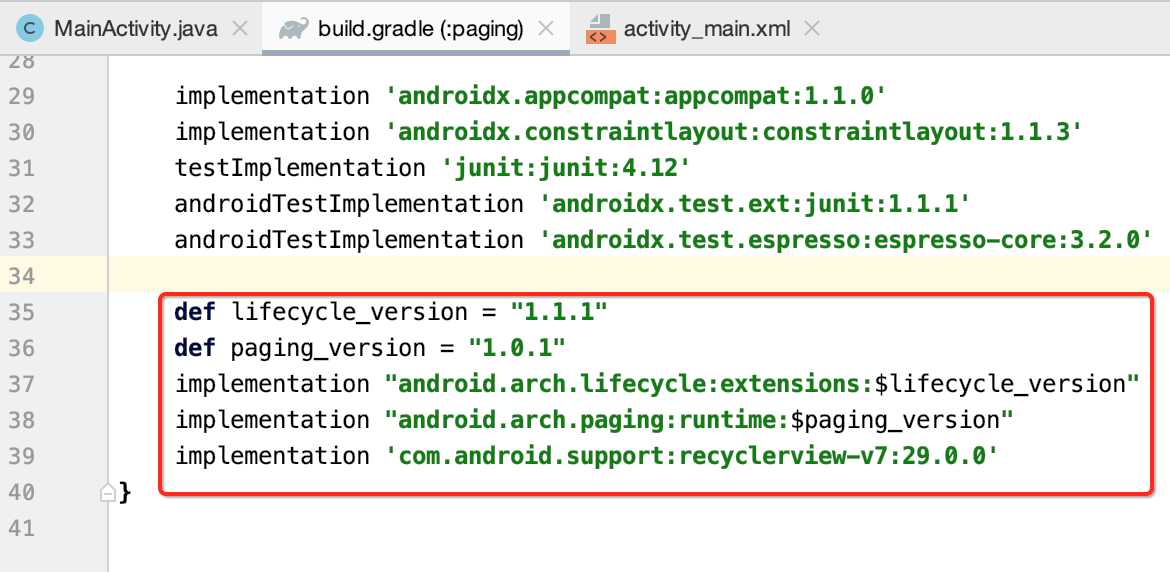
package com.android.paging; import android.os.Bundle; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private RecyclerView recyclerView; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.recyclerView); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView android:id="@+id/recyclerView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent" app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
接下来则新建一个实体:

package com.android.paging; import java.util.Objects; public class Concert { private String title; private String content; private String author; public String getTitle() { return title; } public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; } public String getContent() { return content; } public void setContent(String content) { this.content = content; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) { return true; } if (obj == null) { return false; } if (this.getClass() == obj.getClass()) { return true; } Concert concert = (Concert) obj; return Objects.equals(title, concert.title) && Objects.equals(content, concert.content) && Objects.equals(author, concert.author); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(title, content, author); } }
然后这里定义一个Adapter,此时当然得要用Paging相关的Adapter了,用普通的怎么可能能实现分页呢?代码如下:
package com.android.paging; import android.view.LayoutInflater; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; import android.widget.TextView; import androidx.annotation.NonNull; import androidx.paging.PagedListAdapter; import androidx.recyclerview.widget.DiffUtil; import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView; /** * PagedListAdapter:这个Adapter就是一个RecyclerView的Adapter。 * 不过我们在使用paging实现RecyclerView的分页加载效果, * 不能直接继承RecyclerView的Adapter,而是需要继承PagedListAdapter。 */ public class RecyclerAdapter extends PagedListAdapter<Concert, RecyclerAdapter.RecyclerViewHolder> { protected RecyclerAdapter() { super(DIFF_CALLBACK); } @NonNull @Override public RecyclerViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) { View view = LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()).inflate(R.layout.item_recyclerview, parent, false); return new RecyclerViewHolder(view); } @Override public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull RecyclerViewHolder holder, int position) { Concert concert = getItem(position); if (concert != null) { holder.mTitleTextView.setText(concert.getTitle()); holder.mAuthorTextView.setText(concert.getAuthor()); holder.mContentTextView.setText(concert.getContent()); } } public static class RecyclerViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder { TextView mTitleTextView; TextView mAuthorTextView; TextView mContentTextView; public RecyclerViewHolder(View itemView) { super(itemView); mTitleTextView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.title); mAuthorTextView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.author); mContentTextView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.content); } } //需要oldConcert与新 newConcert 比较才能得出变化的数据 private static DiffUtil.ItemCallback<Concert> DIFF_CALLBACK = new DiffUtil.ItemCallback<Concert>() { // 判断Item是否已经存在 @Override public boolean areItemsTheSame(Concert oldConcert, Concert newConcert) { return oldConcert.getTitle().equals(newConcert.getTitle()); } // 如果Item已经存在则会调用此方法,判断Item的内容是否一致 @Override public boolean areContentsTheSame(Concert oldConcert, Concert newConcert) { return oldConcert.equals(newConcert); } }; }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView android:id="@+id/title" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:gravity="center" android:textSize="20sp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/author" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:gravity="center" android:textSize="16sp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textSize="25sp" /> </LinearLayout>
其中标红处则是有别于平常的Adapter的,接下来则需要绑定数据了:
接下来则需要初始化列表数据呀,怎么往这个Adapter中添加数据呢,其它它里面有一个api:
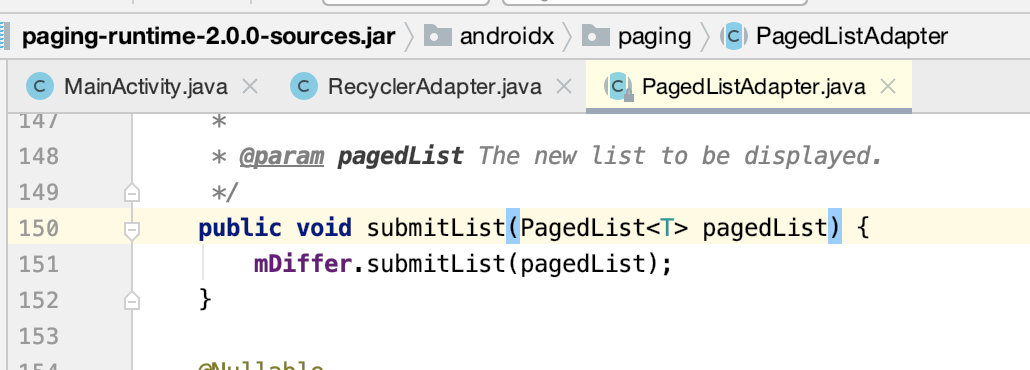
具体数据这块看一下用法,这里也不深入开展了,主要是对它有一个直观的了解,待之后有需要再进一步分析,写法会有些怪,但熟能生巧的事:
先来建立一个数据源:
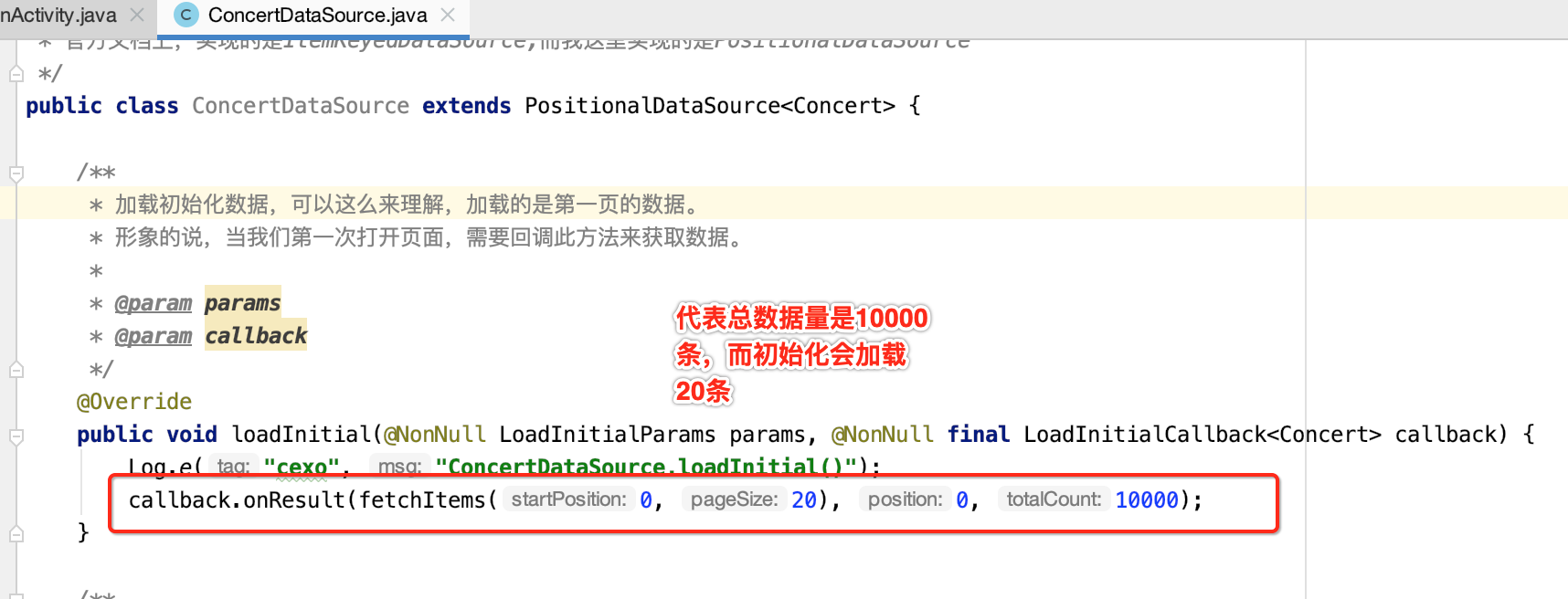
package com.android.paging; import android.util.Log; import androidx.annotation.NonNull; import androidx.paging.PositionalDataSource; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * DataSource:顾名思义,数据源,获取数据是通过它实现的。 * 官方文档上,实现的是ItemKeyedDataSource,而我这里实现的是PositionalDataSource */ public class ConcertDataSource extends PositionalDataSource<Concert> { /** * 加载初始化数据,可以这么来理解,加载的是第一页的数据。 * 形象的说,当我们第一次打开页面,需要回调此方法来获取数据。 * * @param params * @param callback */ @Override public void loadInitial(@NonNull LoadInitialParams params, @NonNull final LoadInitialCallback<Concert> callback) { Log.e("cexo", "ConcertDataSource.loadInitial()"); callback.onResult(fetchItems(0, 20), 0, 10000); } /** * 当有了初始化数据之后,滑动的时候如果需要加载数据的话,会调用此方法。 * * @param params * @param callback */ @Override public void loadRange(@NonNull LoadRangeParams params, @NonNull final LoadRangeCallback<Concert> callback) { Log.e("cexo", "ConcertDataSource.loadRange() startPosition:" + params.startPosition + ";loadSize:" + params.loadSize); callback.onResult(fetchItems(params.startPosition, params.loadSize)); } private List<Concert> fetchItems(int startPosition, int pageSize) { List<Concert> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = startPosition; i < startPosition + pageSize; i++) { Concert concert = new Concert(); concert.setAuthor("author = " + i); concert.setContent("content = " + i); concert.setTitle("title = " + i); list.add(concert); } return list; } }
这里稍加解释一下,也是第一次用:
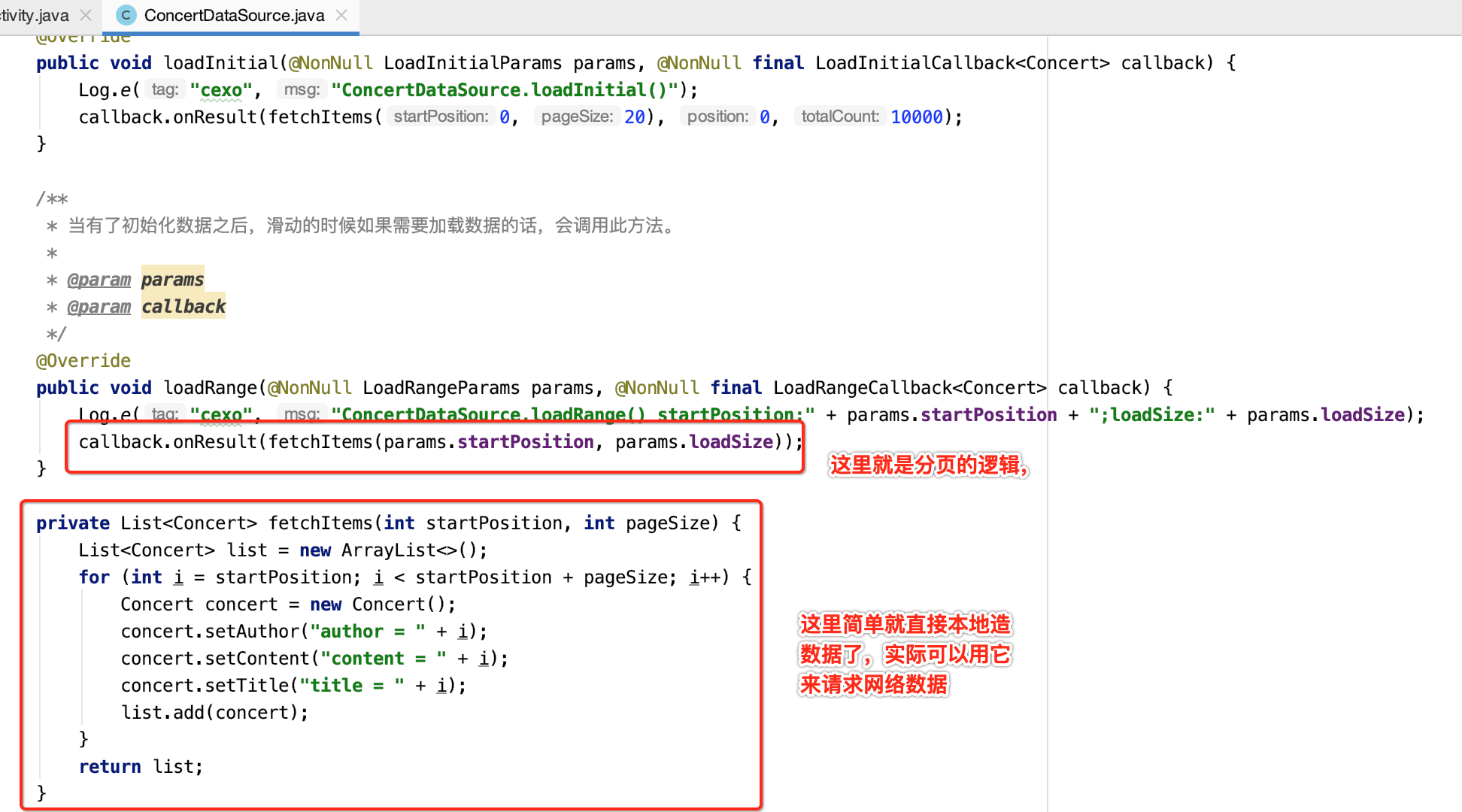
那定义了数据源了怎么用呢?需要一个工厂来创建这些数据:
package com.android.paging; import androidx.lifecycle.MutableLiveData; import androidx.paging.DataSource; public class ConcertFactory extends DataSource.Factory<Integer, Concert> { private MutableLiveData<ConcertDataSource> mSourceLiveData = new MutableLiveData<>(); @Override public DataSource<Integer, Concert> create() { ConcertDataSource concertDataSource = new ConcertDataSource(); mSourceLiveData.postValue(concertDataSource); return concertDataSource; } }
其中看到没,用LiveData保存的,那如果数据源有更新肯定也会及时收到通知的,接下来这工厂则在ViewModel中来使用了,如下:
package com.android.paging; import androidx.lifecycle.LiveData; import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel; import androidx.paging.DataSource; import androidx.paging.LivePagedListBuilder; import androidx.paging.PagedList; /** * PagedList: 数据源获取的数据最终靠PagedList来承载。 * 对于PagedList,我们可以这样来理解,它就是一页数据的集合。 * 每请求一页,就是新的一个PagedList对象。 */ public class ConcertViewModel extends ViewModel { private final LiveData<PagedList<Concert>> convertList; private DataSource<Integer, Concert> concertDataSource; public ConcertViewModel() { ConcertFactory concertFactory = new ConcertFactory(); concertDataSource = concertFactory.create(); convertList = new LivePagedListBuilder<>(concertFactory, 20).build(); } public void invalidateDataSource() { concertDataSource.invalidate(); } public LiveData<PagedList<Concert>> getConvertList() { return convertList; } }
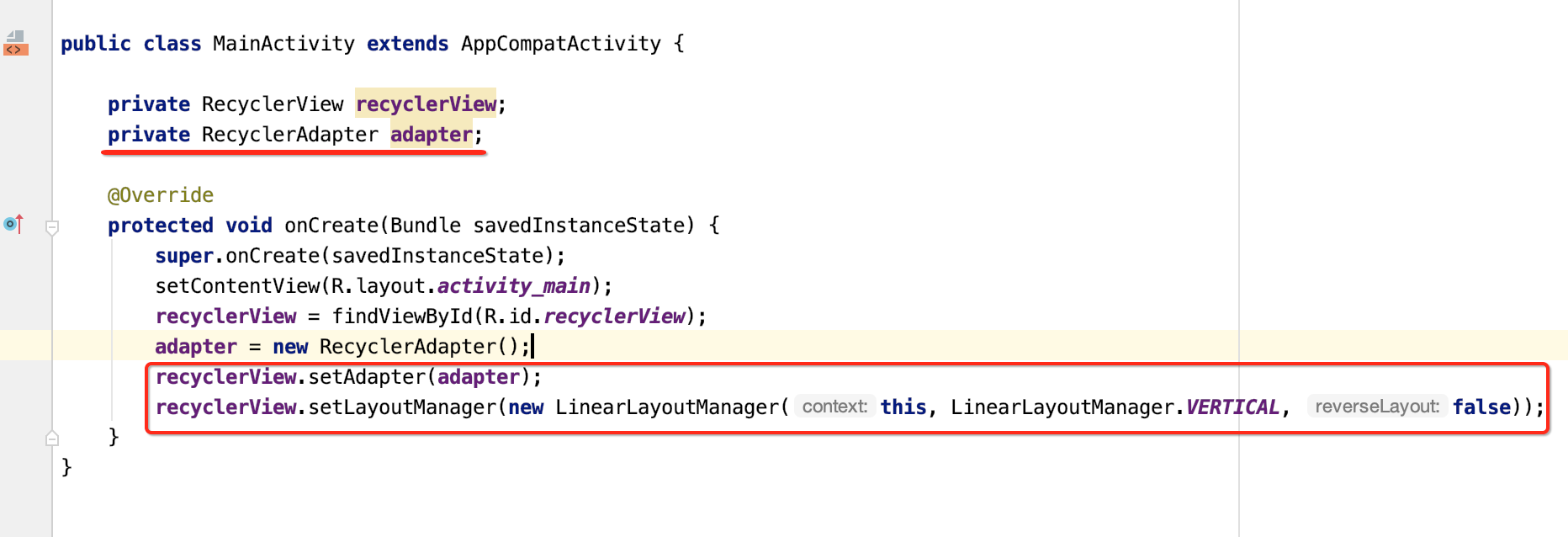
最终咱们就可以在Activity来调用了,如下:
package com.android.paging; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import androidx.annotation.Nullable; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import androidx.lifecycle.Observer; import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModelProviders; import androidx.paging.PagedList; import androidx.recyclerview.widget.LinearLayoutManager; import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private RecyclerView recyclerView; private RecyclerAdapter adapter; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.recyclerView); adapter = new RecyclerAdapter(); ConcertViewModel viewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(this).get(ConcertViewModel.class); viewModel.getConvertList().observe(this, new Observer<PagedList<Concert>>() { @Override public void onChanged(@Nullable PagedList<Concert> concerts) { adapter.submitList(concerts); Log.i("cexo", "数据更新了"); } }); recyclerView.setAdapter(adapter); recyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this, LinearLayoutManager.VERTICAL, false)); } }
好,下面来运行一下:
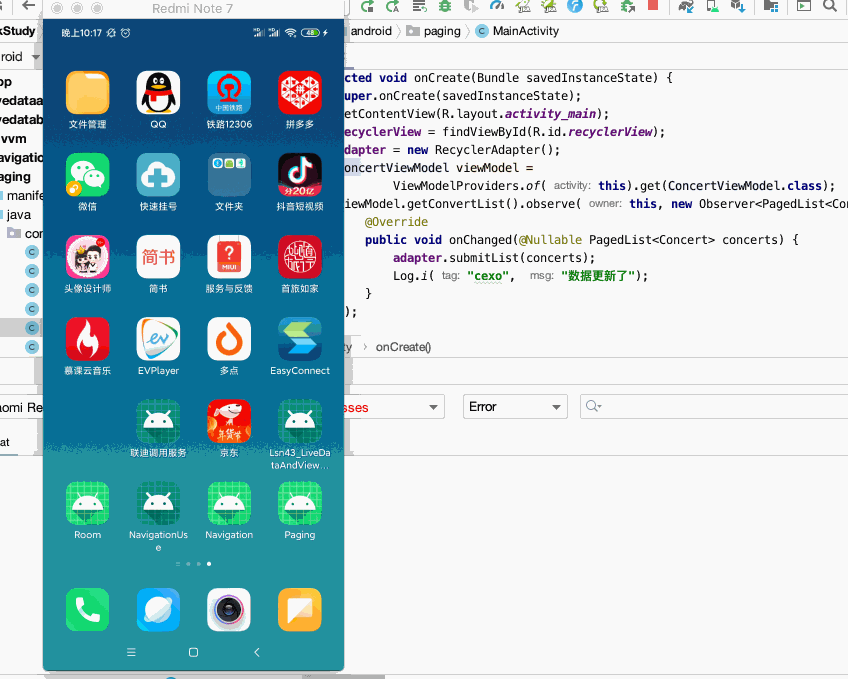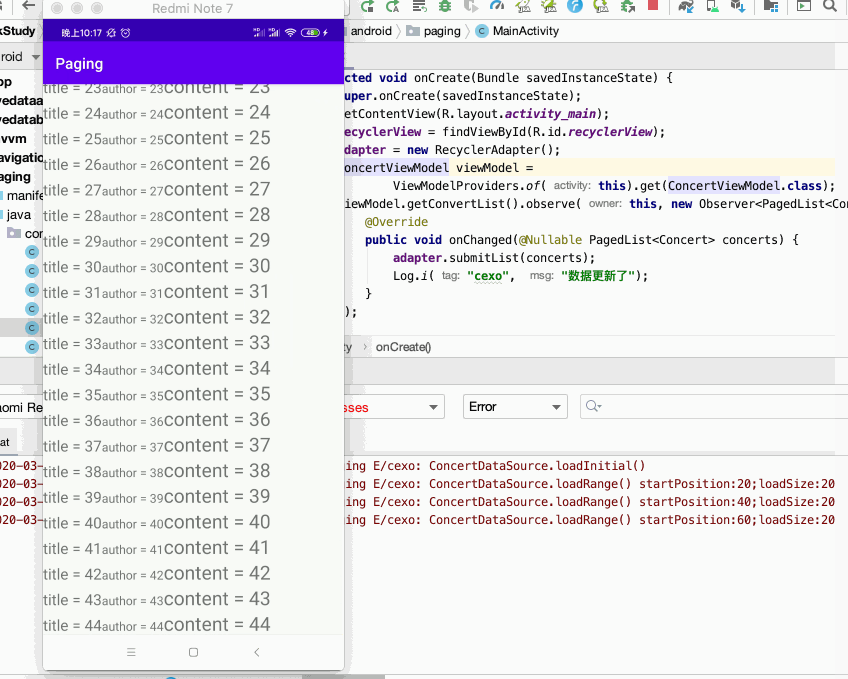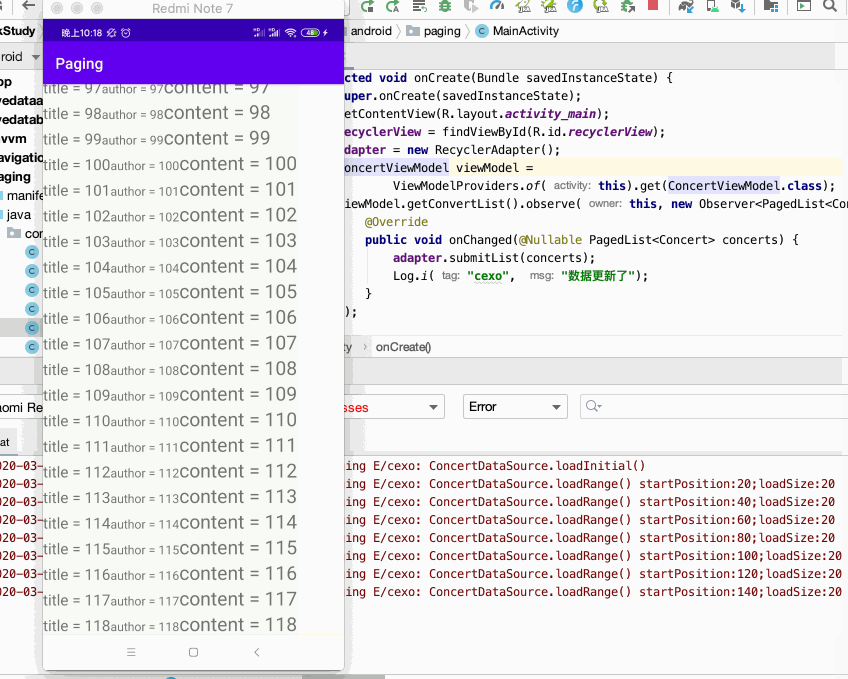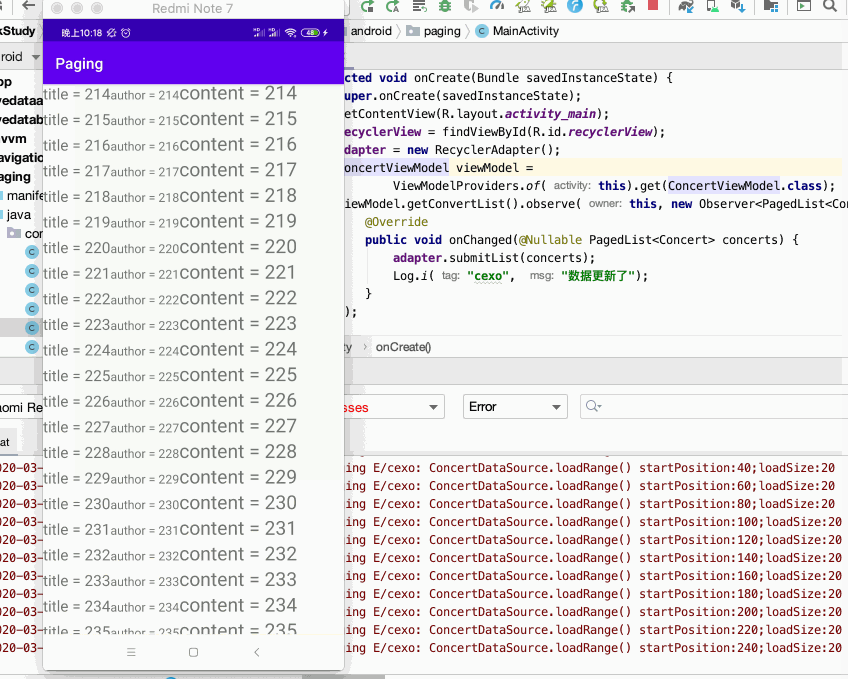
而什么分页容错处理我们完全不用客,我们只需管数据源如何加载,如何将数据显示在页面上,相当的简单,关于它的原理这块就不分析了,待之后在实际工作中用到它了到时再深入探究。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号