计算机网络自顶向下
计算机网络自顶向下
课程主页:[https://gaia.cs.umass.edu/kurose_ross/index.php]
课程视频:b站计算机网络自顶向下英文字幕
课程作业:[https://gaia.cs.umass.edu/kurose_ross/wireshark.php]
Introduction
Overview
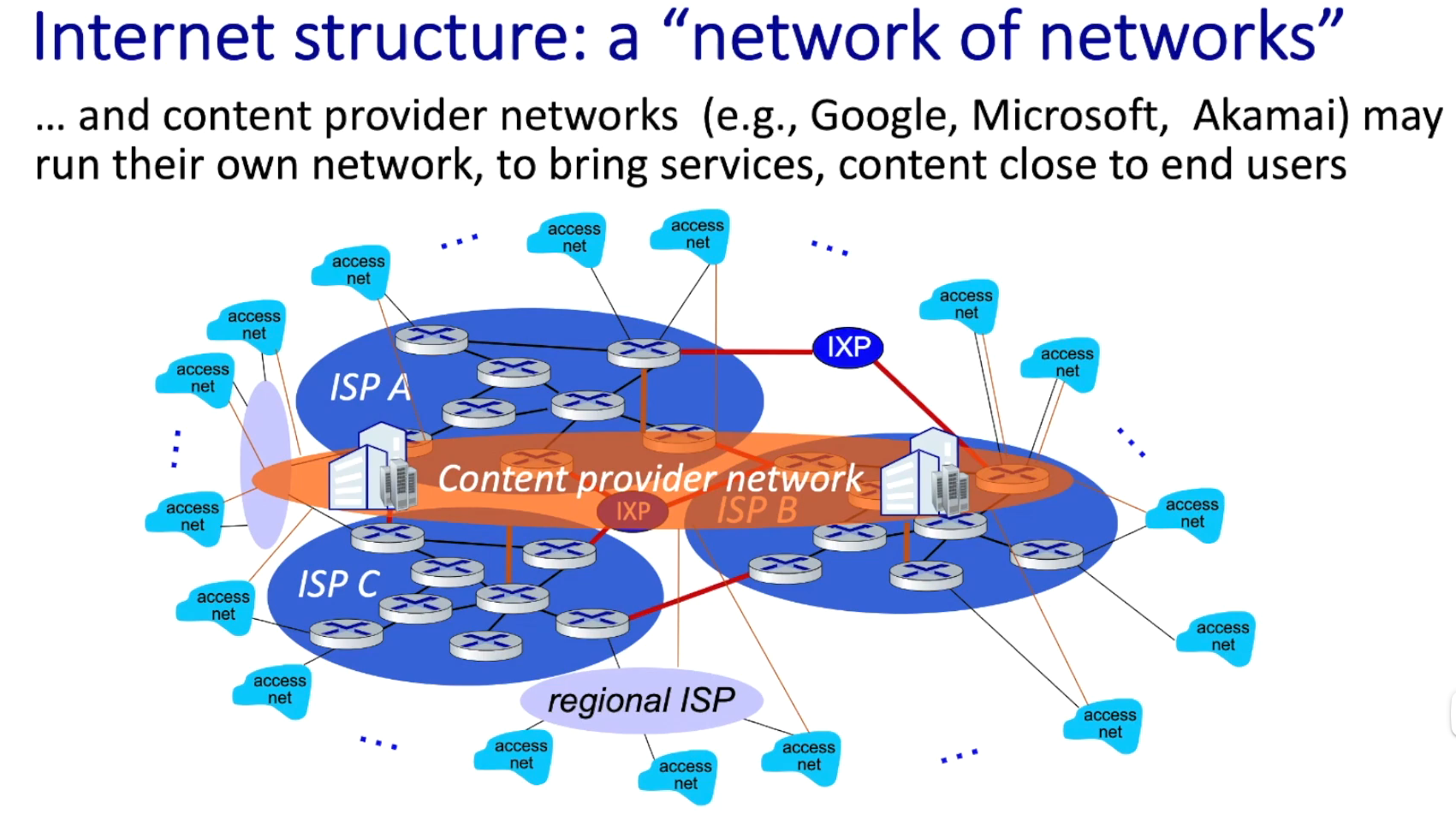
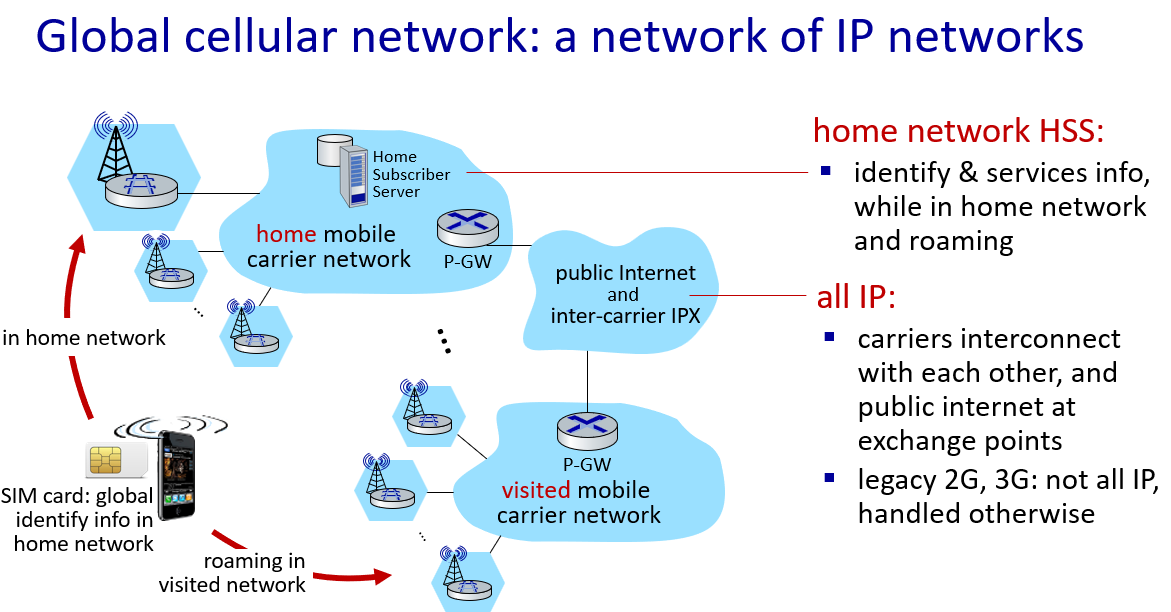
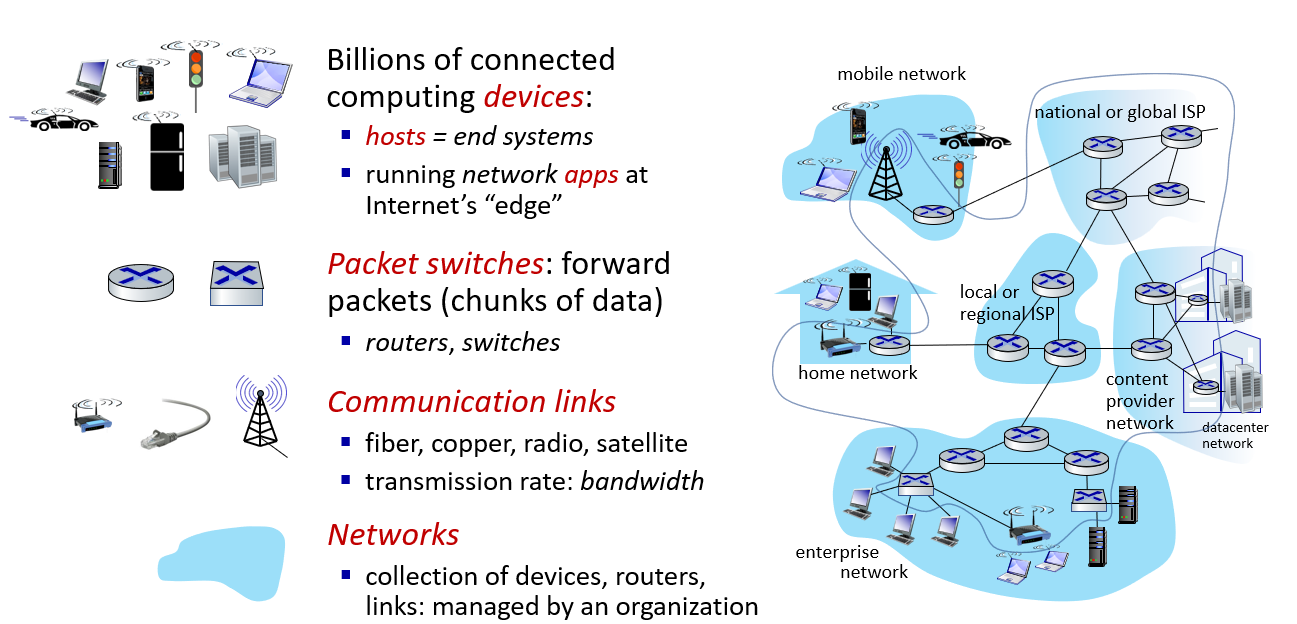
what is internet
a network of networks
edge:devices connect to internet (host)
inside:packet switches (what make network actually a network, forward date packet, two type:routers and switchers)
inks
networks
internet as a platform provide interface for app to send and receive information
what is protocol
protocol control everything in network
sepecefic message sepecefic action
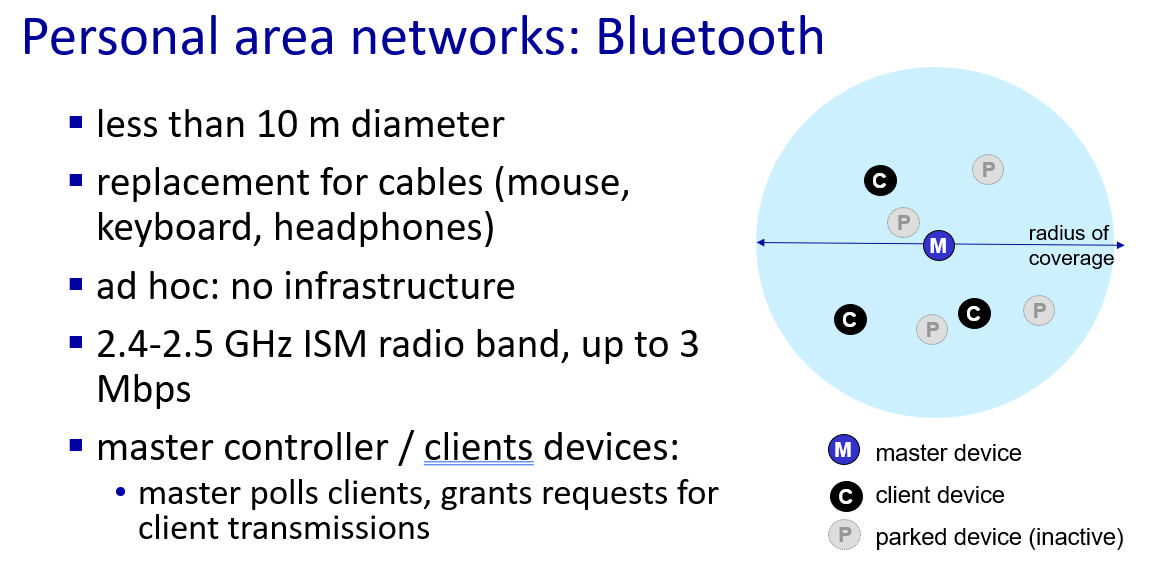
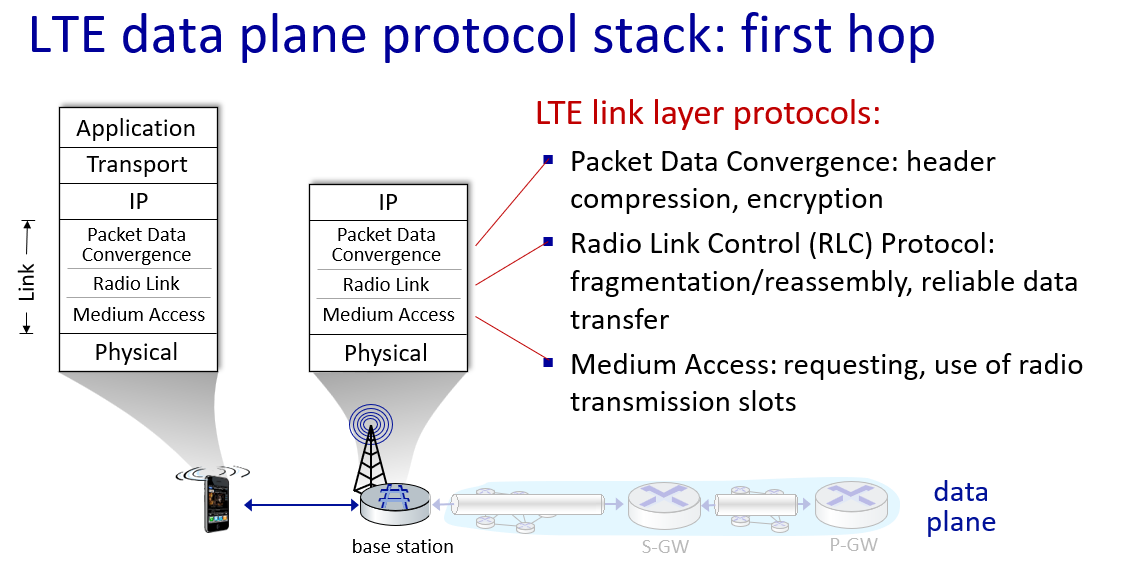
Network edge: hosts, access network, physical media
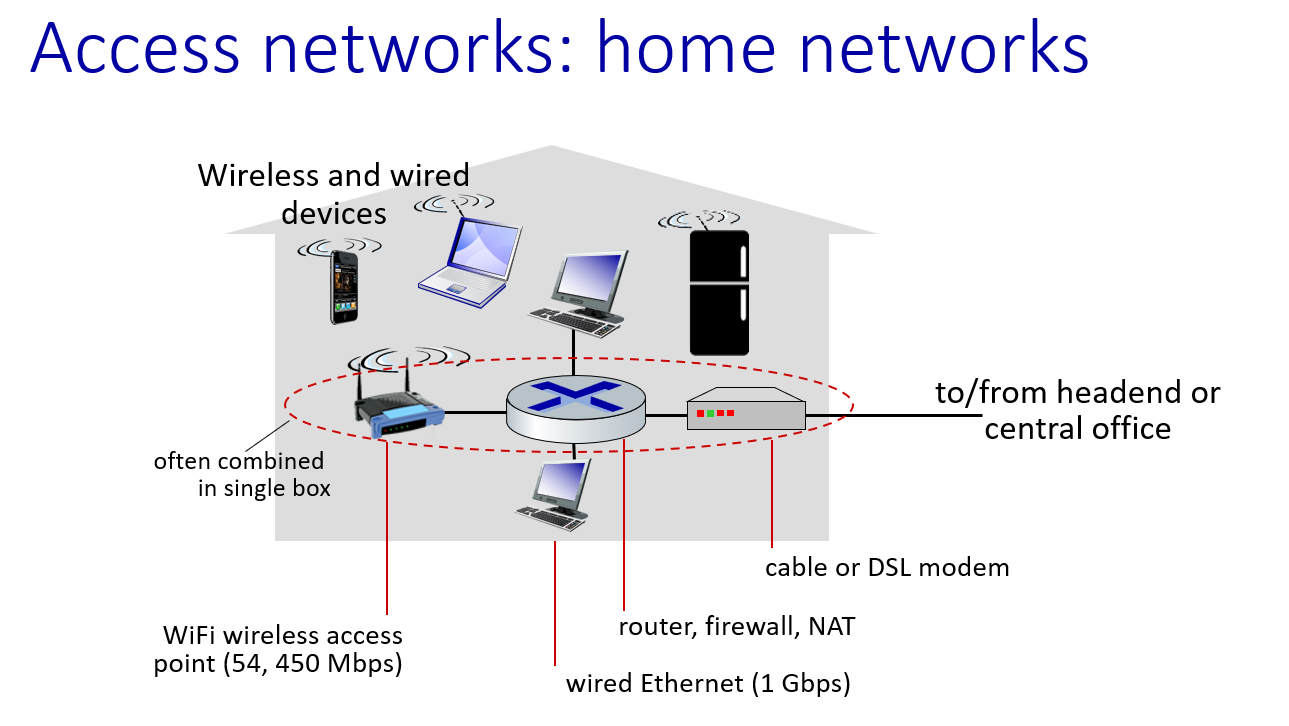
access networks: connect device or home network into large network(first layer)
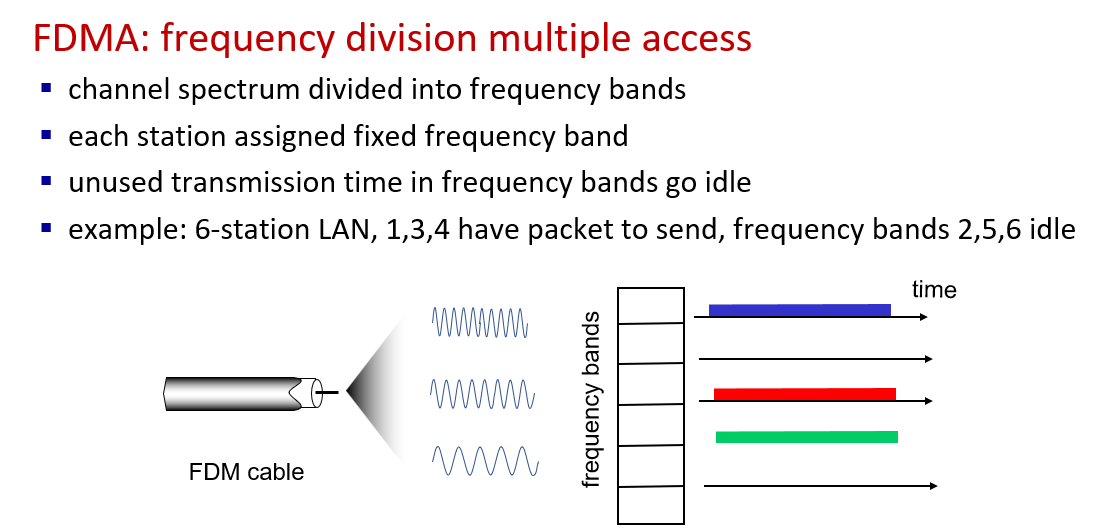
two metric:transmission rate(bits per second) & what degree we must share the network
- cable network: frequency division multiplexing \asymmetric(fast downstream slow upstream) \shared with your neighbor

- dsl network: digital subsctiber line(use existing telephone line) \asymmetric \not shared(connect directly to DSL central office) \slow(and with distance entending will be slower)
- wireless network:local area network(wifi) \wide-area cellular access network
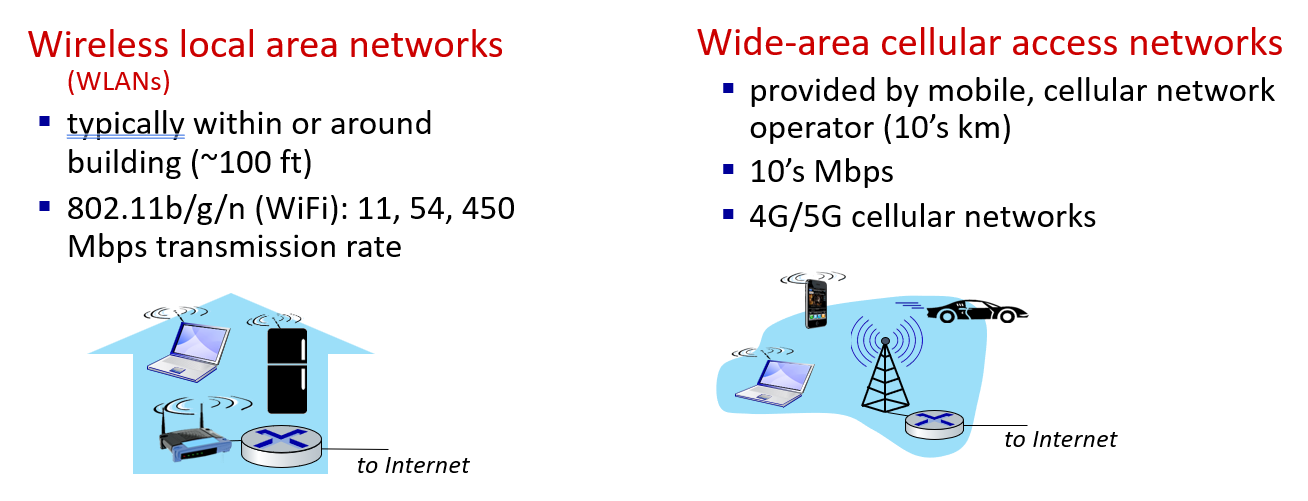
- home networks:
- enterprise networks: have multiple switchers and routers
- data center networks:very different
send packets: message break into smaller packets,each have a header(protocol dictate the header is what)
physical media: copper wire(copper,100M) \ fiber optics(expensive,10-100G,low error rate) \radio links(propagate freely,wireless,distance)
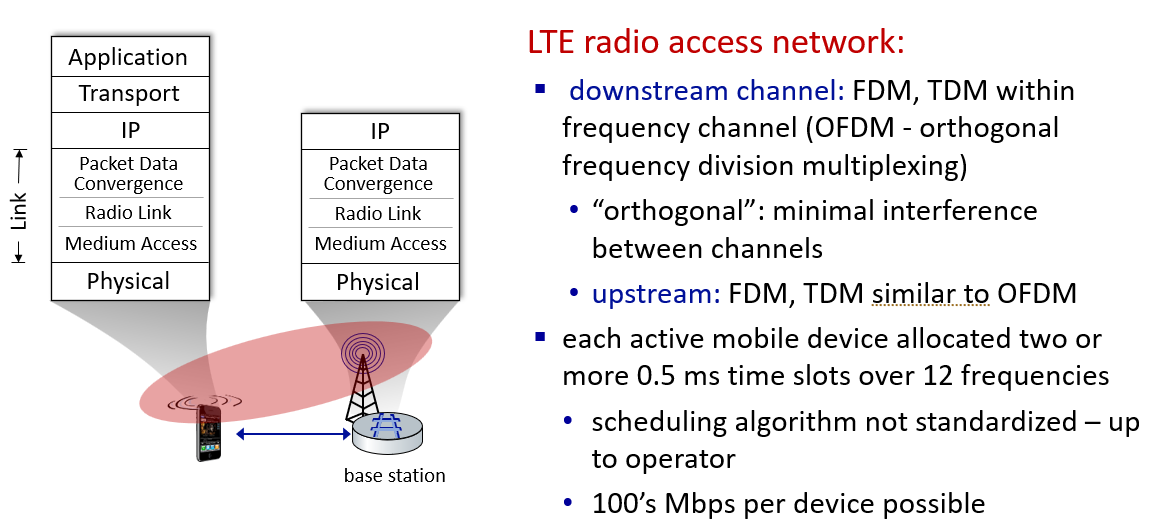
Network core: packet/circuit switching, internet structure
forwarding and rounting
local forward table and global rount alogrithm
store and forward
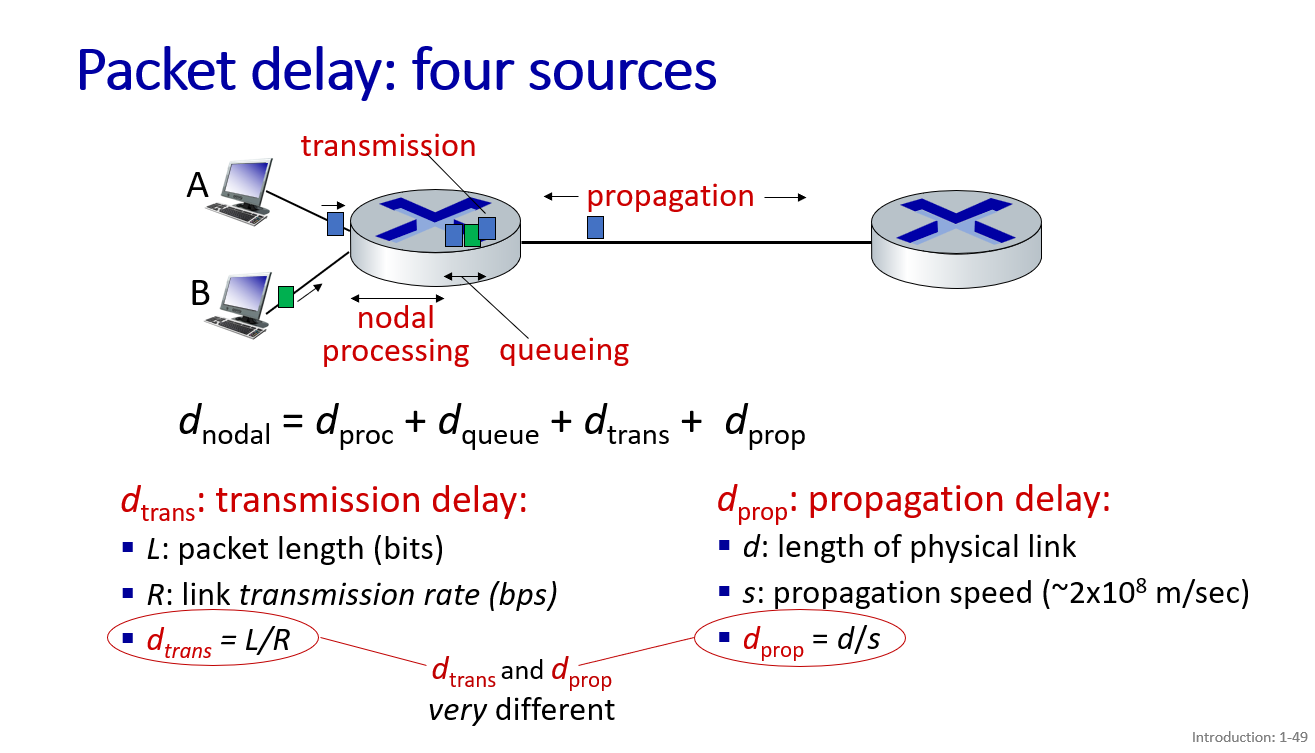
package delay and lost
circuit switching:telephone network(call -> ensure exclusive use ->no delay or lost)
FDM or TDM
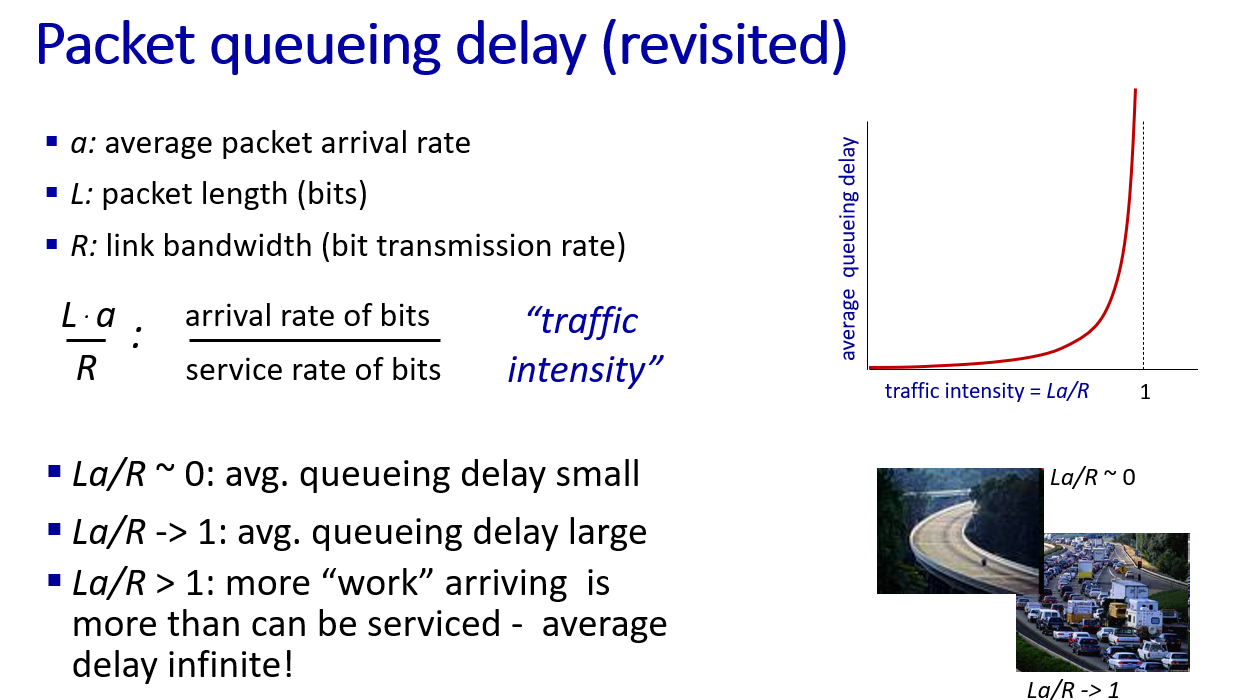
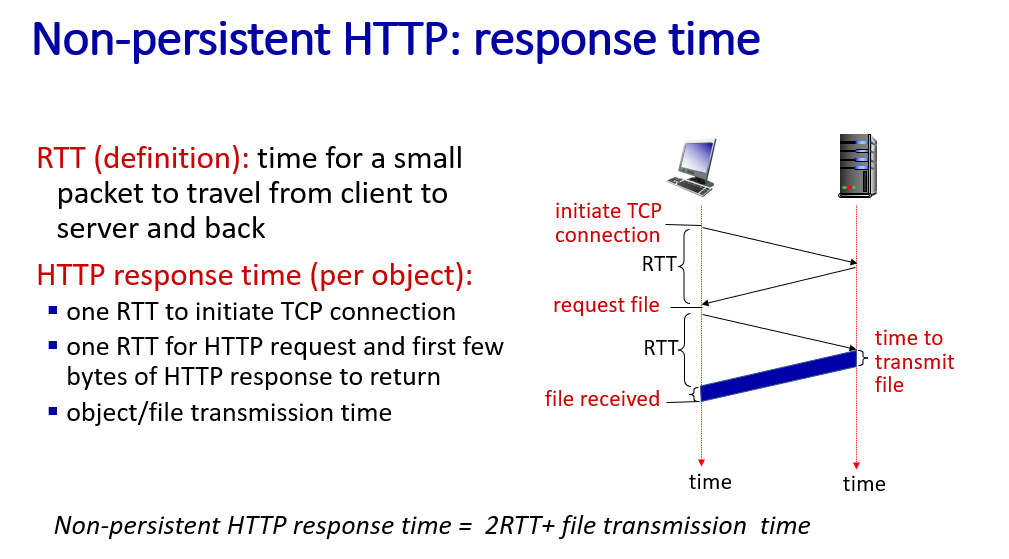
Performance: loss, delay, throughput
trace router:measure the round trip time rtt
throughput:bit per sec fluid throw pipes bottleneck pipe
Protocol layers, service models
layer: explicit reference modularized
encapsalute
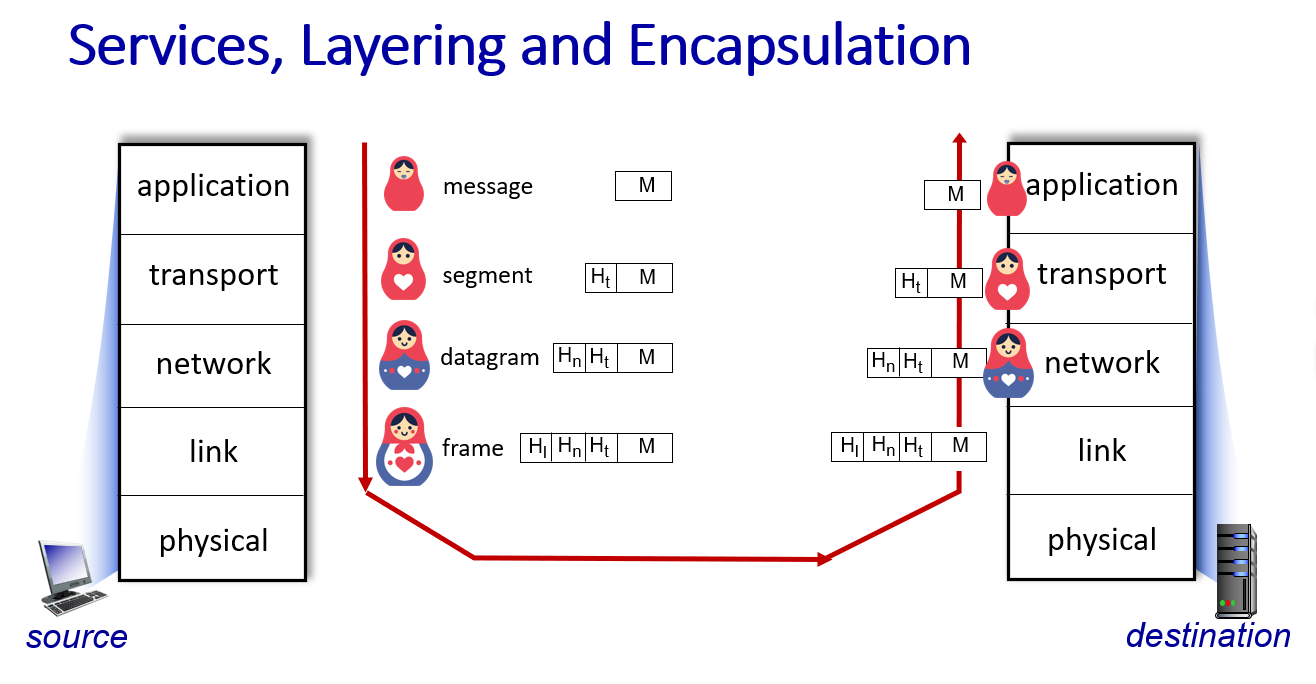
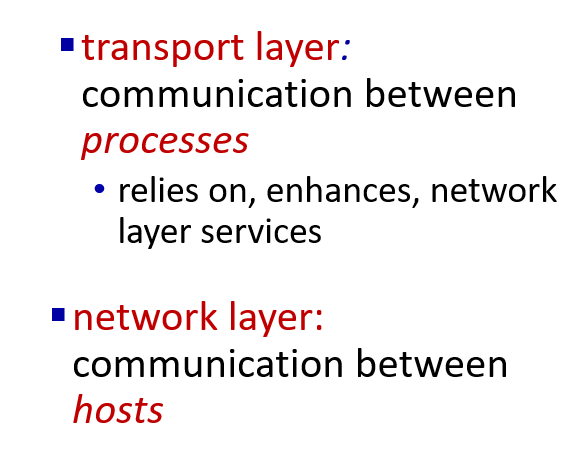
Transport layer transfer message from one process to another
Network layer transfer message from one host to another
Security
bad act:packet interception、fake indentity、denial of service

History
Application layer

HTTP:hypertext transfer protocol between web client and sever
SMTP:simple mail t p
DNS:domain name system translate domain name to 32 bit IP address
write network app only need to know two things:
- what service can transport layer provide
- what the application API look like to transport layer
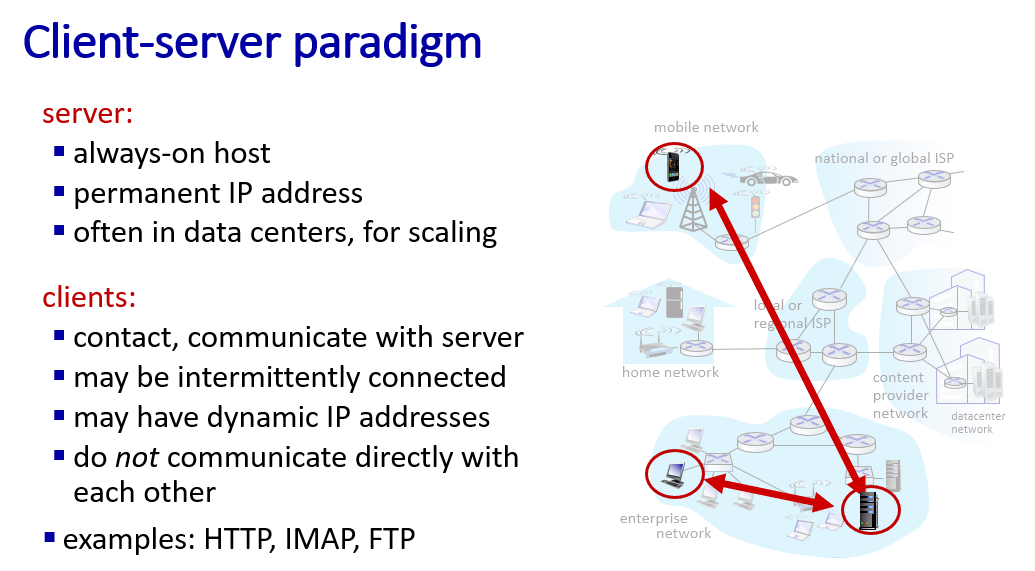
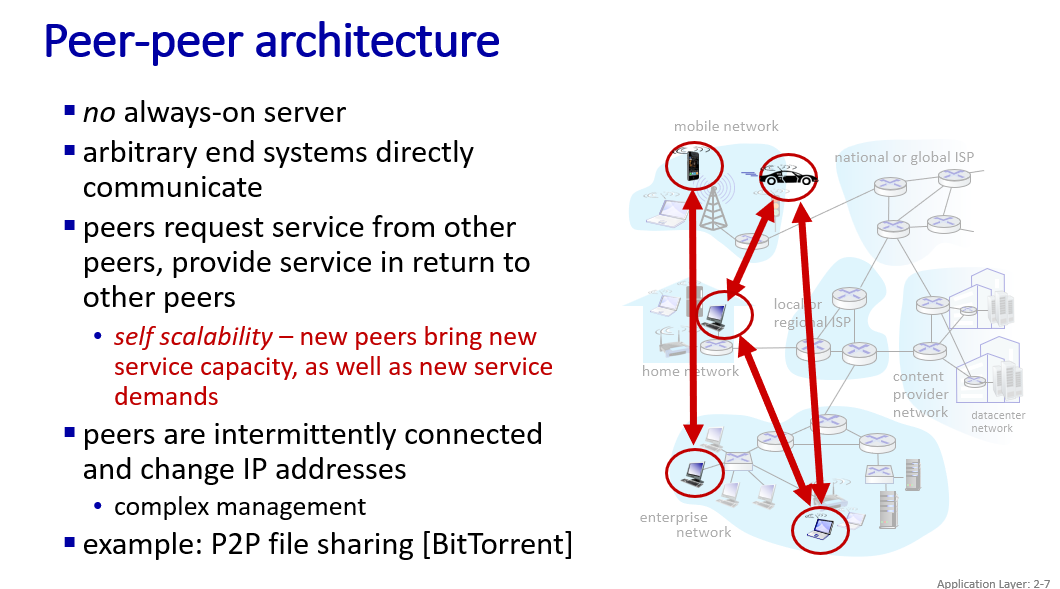
two sytle network app to interact:
- client-server model
- peer to peer model
app send and receive message through a socker API
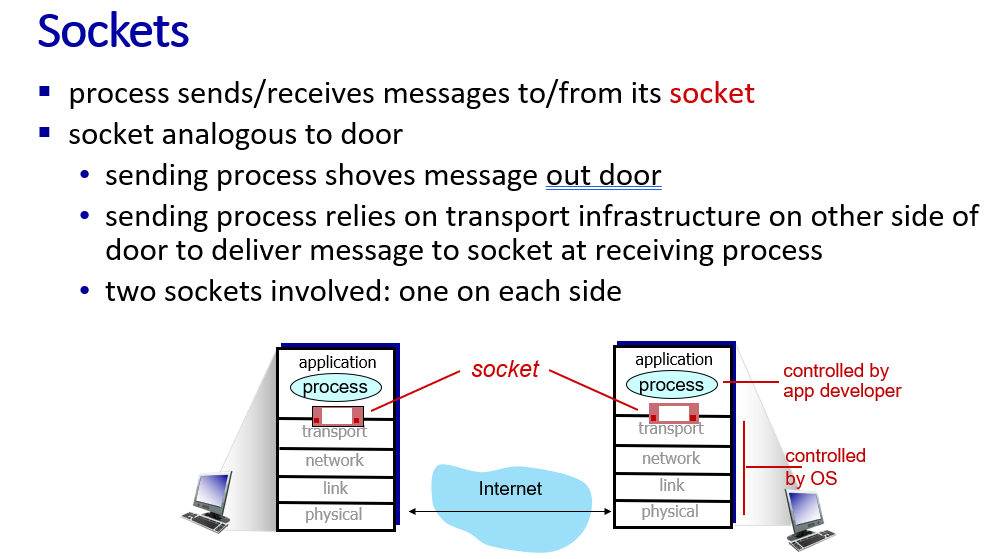
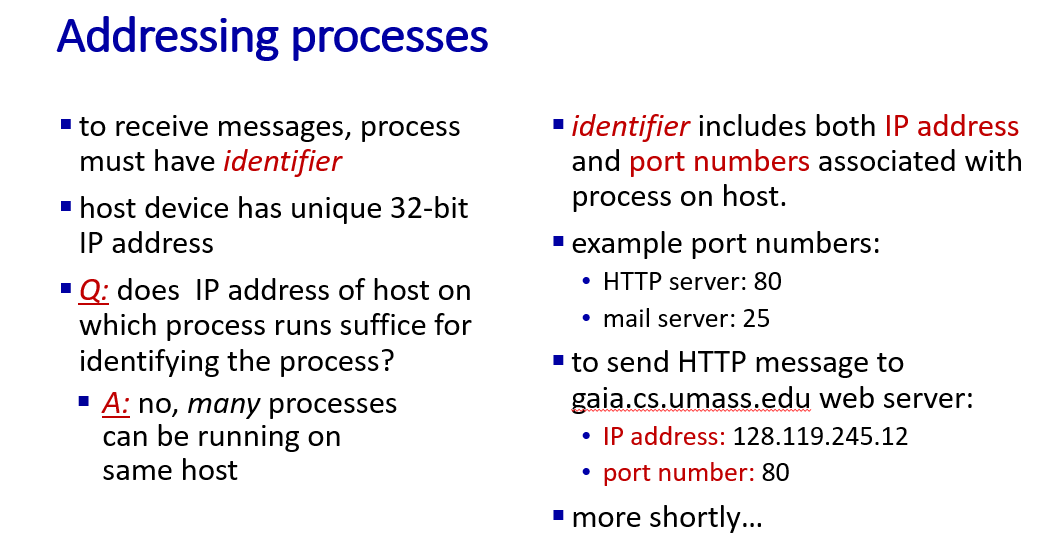
Address information includes two part:
- IP address
- port number
transport layer protocol
we can add protocol over the UDP
TLS(transport layer security) can be added over transport layer protocol to ensure security
Web and HTTP
Web
web:html & reference(jpg,html,java,audio...) stored on web servers
these objects are addressed by a url (host&path)
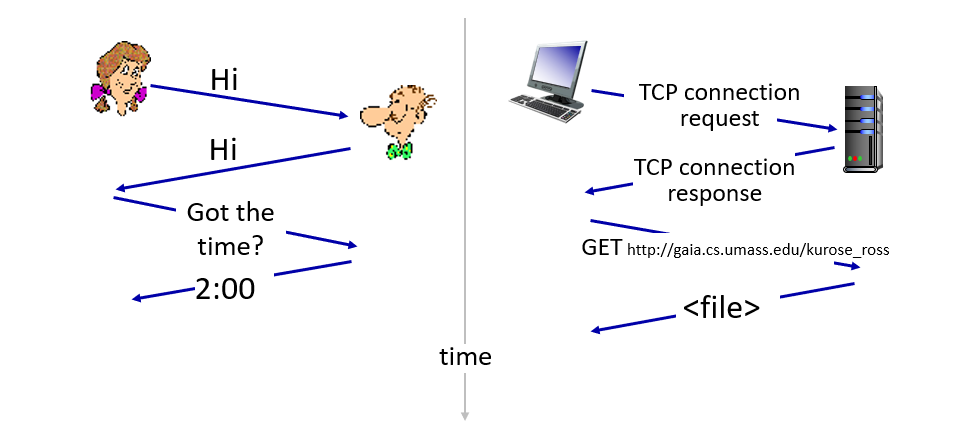
HTTP
known as hypertext transfer protocol
http is client-server model
http use the transport service by TCP
http is stateless : server donot maintain state ,just single request for an object and a single reply , http donot consider multistep transaction problem
two type HTTP connections
- persistent: TCP open -> multiple object sent over TCP connection -> TCP closed
- non persistent: TCP open -> at most one object sent over TCP connection -> TCP closed
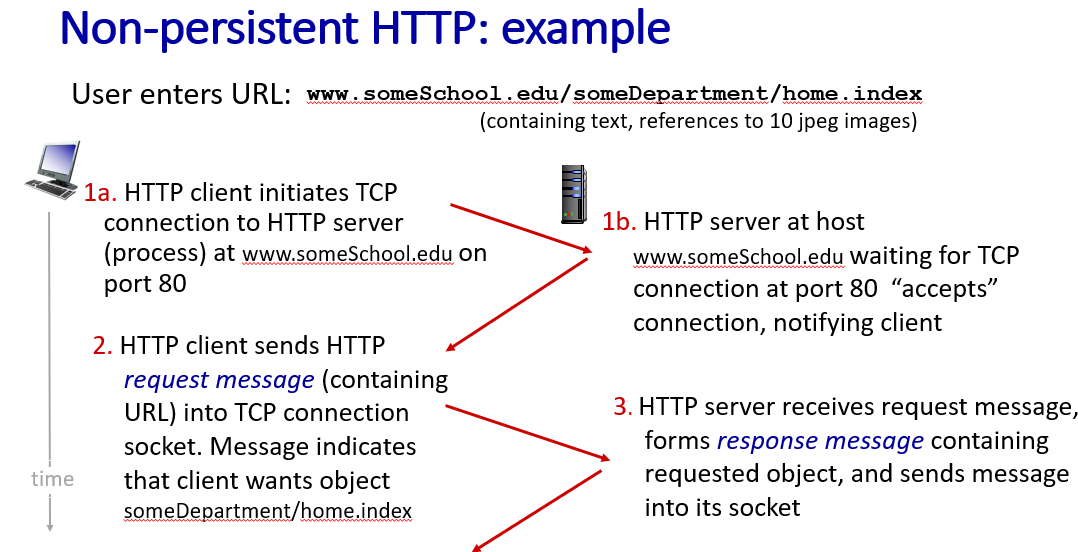

- at 1a,1b no http message is send ,just tcp. in 2 http request message is send
- persitent http connection donot close the TCP connection after send the response message
HTTP messages
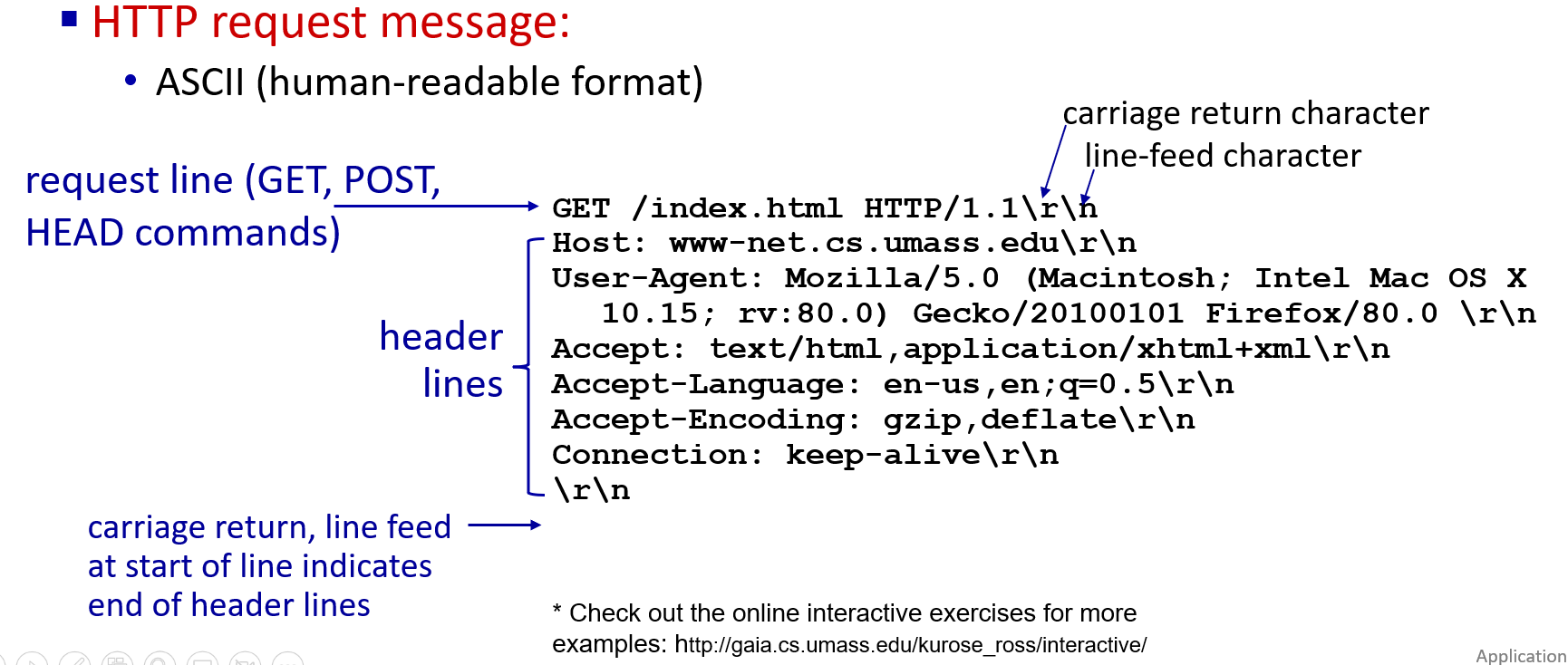
- requests messages
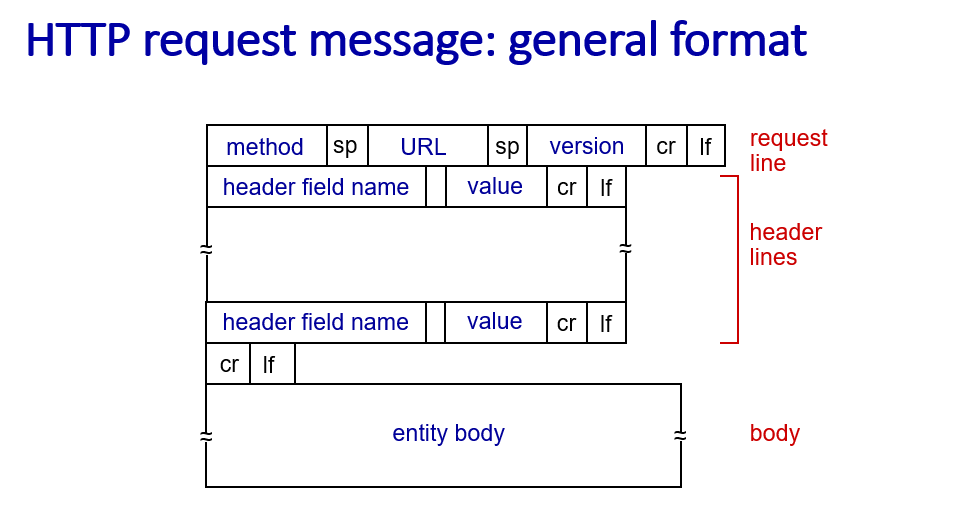
method:POST,GET,PUT,HEAD
- response

status code:200 OK, 301 Moved Permanently, 400 Bad Request, 404 Not Found, 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
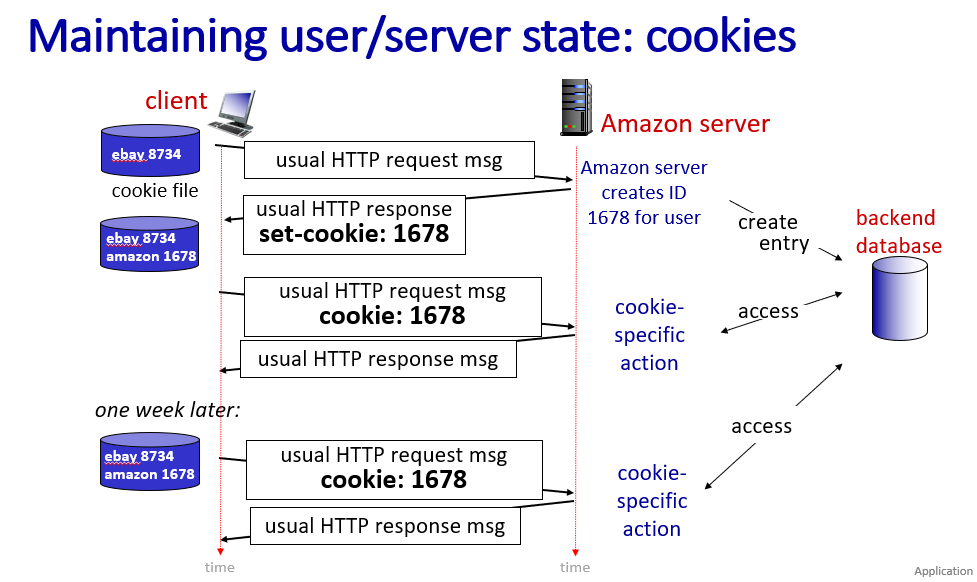
cookies
http is stateless
use cookies to maintain user/server state
four components possibly contain cookie:
- cookie header line of HTTP response message
- cookie header line of next HTTP request message
- cookie file kept on user's host,managed by browser
- back-end database at Web site
Web caches
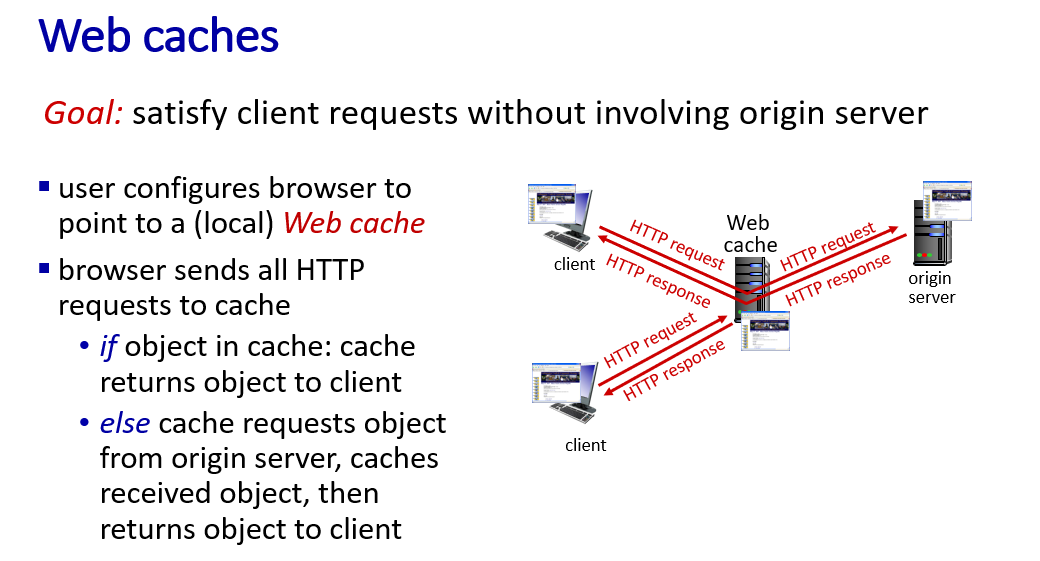


Conditional HTTP GET
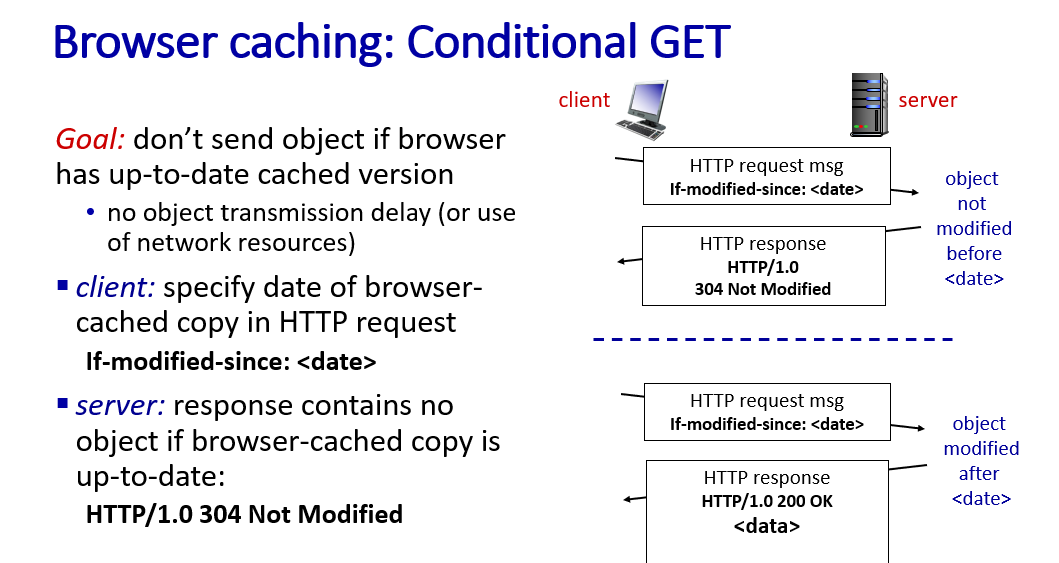
Q:How to know the cached version is up-to-date?
A:Request message contain a if-modified-since information,indicate the last time user search for the same content
HTTP2 / HTTP3
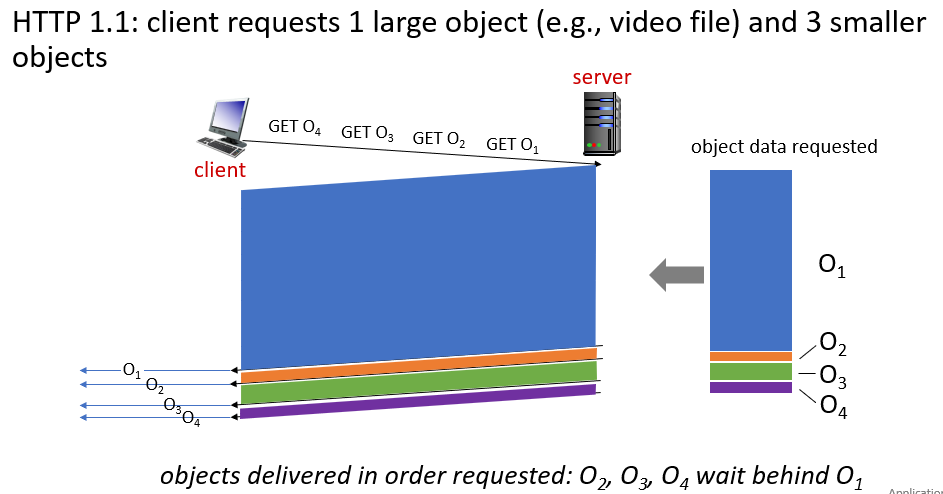
http 2
- the transmission order can be client-specified
- server can send unrequested objects to
- client, large objects can be divide into frames, reduce head of line delay
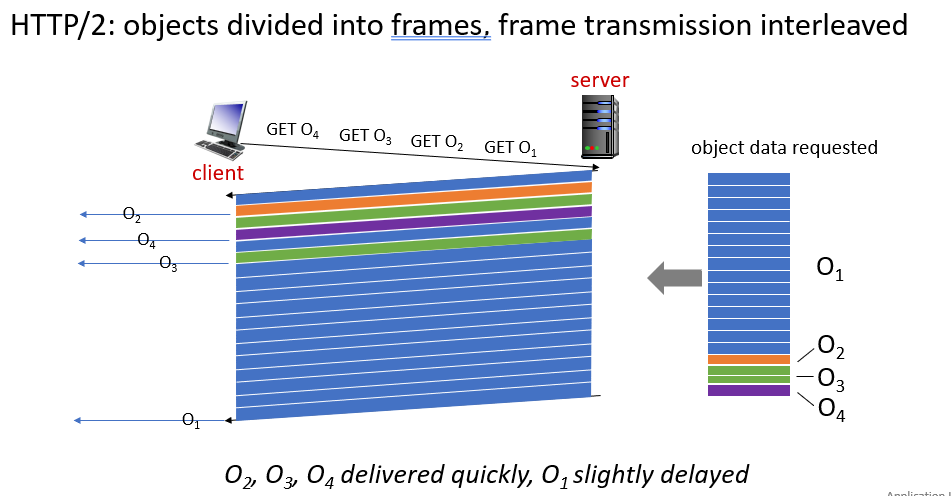
http 3
- address loss of security on TCP
- recovery from packet loss
E-mail, SMTP, IMAP
jump
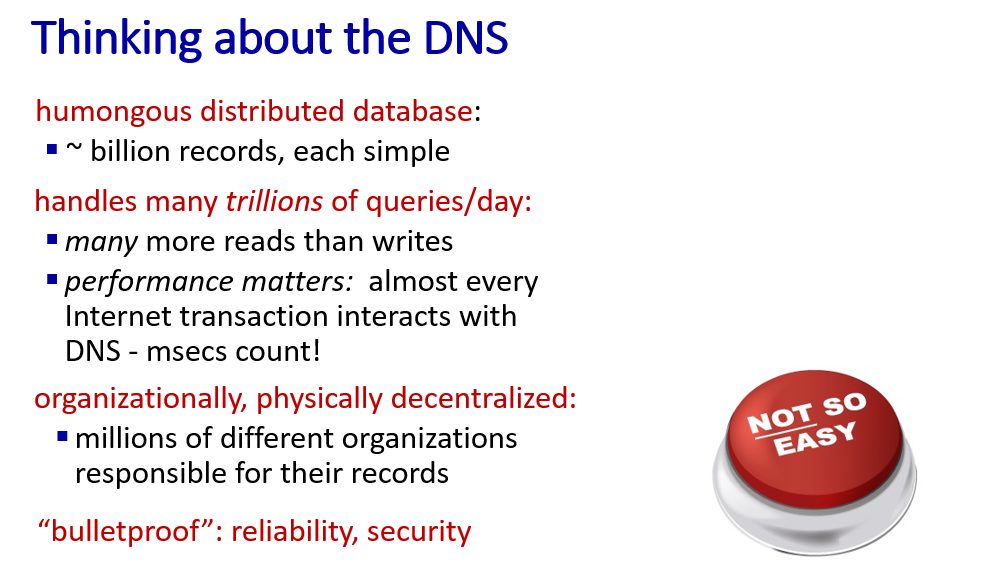
DNS
domain name -> ip address
DNS is a distributed database(better performance )
-
DNS structure
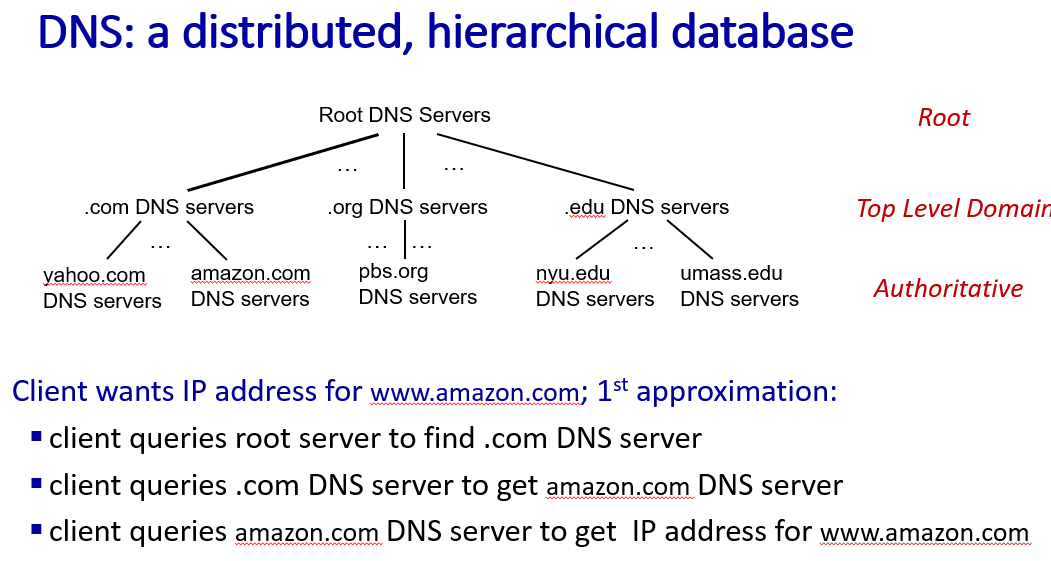 from top to bottom
from top to bottom- root name servers:where the translate begin
- TLD:top level Domain(.com, .org, .ner, ......)
- authoritative DNS servers:by organization themselves, translate responsiblity ends
- Local DNS name servers: associate to every host , cache name to address pair or forward request
-
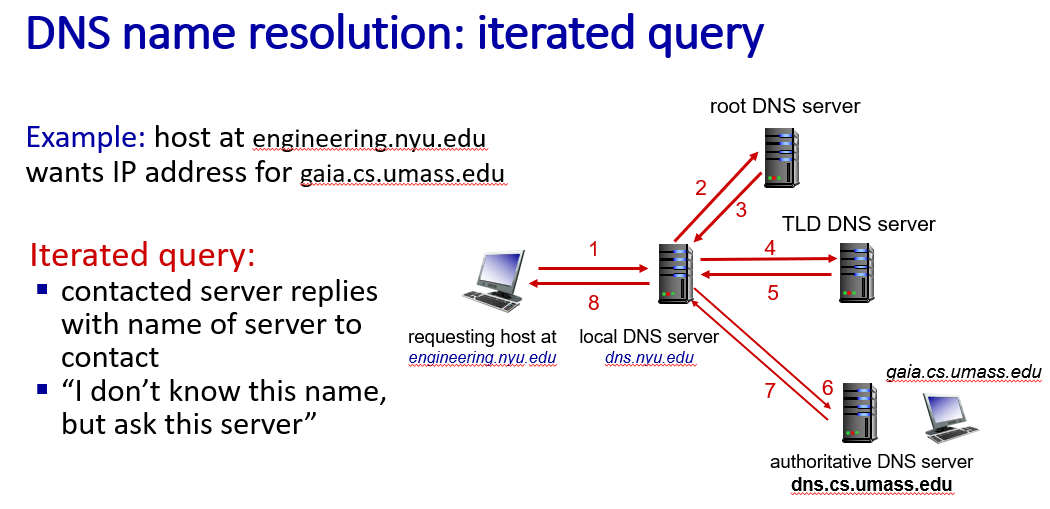
DNS resolution
- iterated query
- recursive query
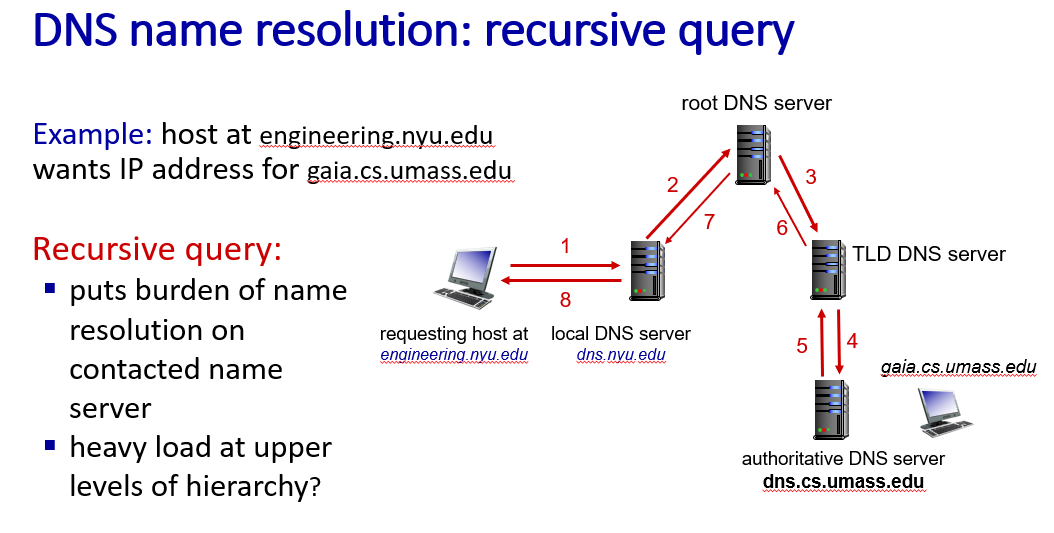 not common used (for the heavy traffic of root DNS server)
not common used (for the heavy traffic of root DNS server)
- iterated query
Local DNS server caching DNS information for a while
if named host changes IP address, may not be known Internet-wide until all TTLs(the time to live) expire! (why new domain name publish page)
best-effort name-to-address translation:donot bother to clear out-of-date DNS information considering the cost and complication
DNS records:(name, value, type, ttl)
- type
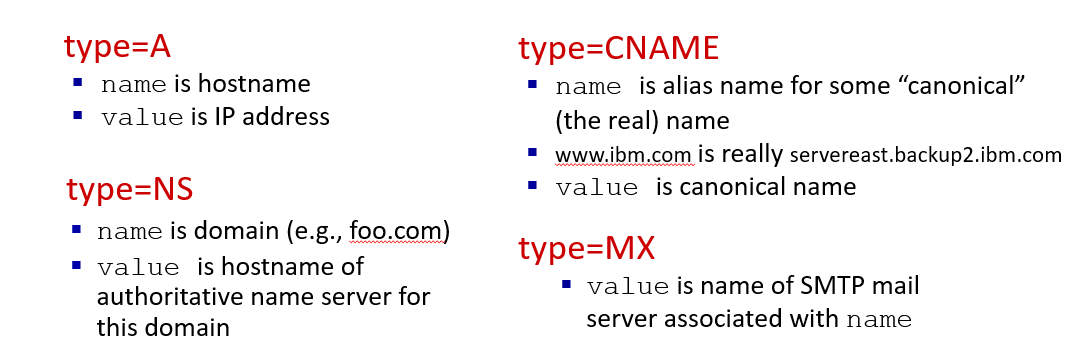
DNS protocol
P2P
How much time to distribute file (size F) from one server to N peers?
- server-client method
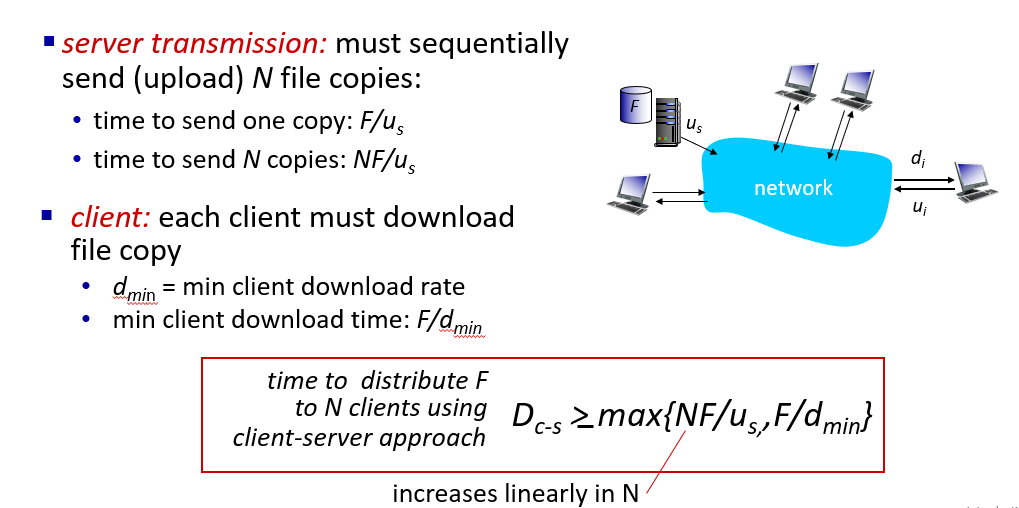
- peer-to-peer method
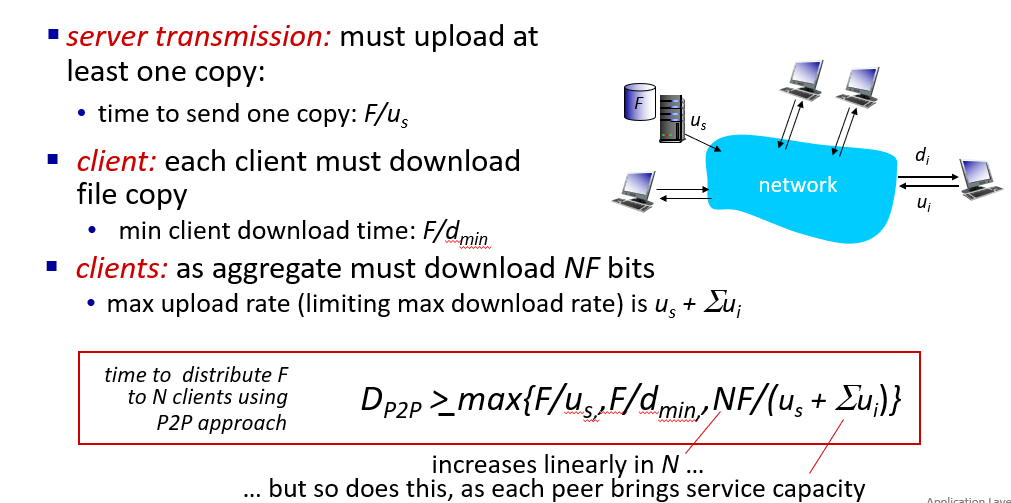
case:download speed greater than upload speed
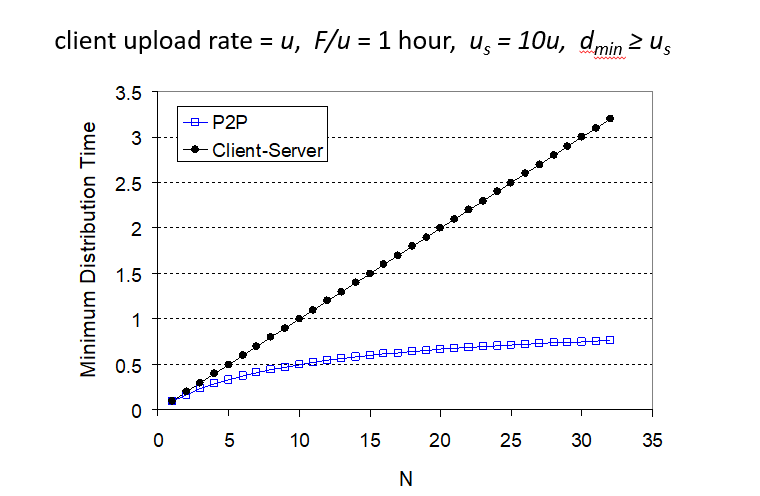
P2P application

video streaming
stream video:user donot need to download the whole video to watch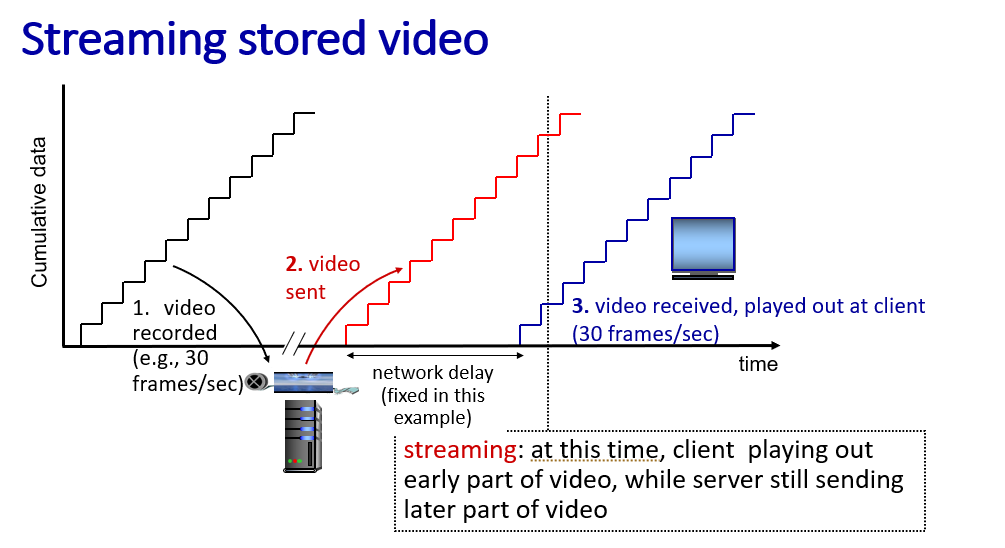
challenge:
- scale-how to reach billion users?
- heterogeneity-different users with different bandwidth
solution: distributed,app-level infrastructure
challenge:
- continuous playout constraint,but network delays are variable

- client interactivity:pause, fast-forward, rewind, jump
- video packets may be lost, retransmitted(more delay)
solution
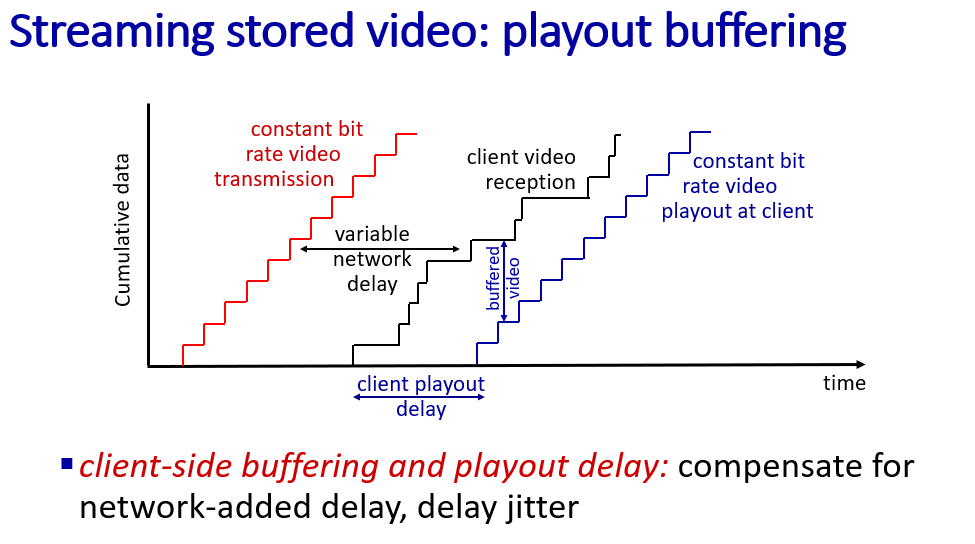
- solve variable delay
 solve limitted bandwidth
solve limitted bandwidth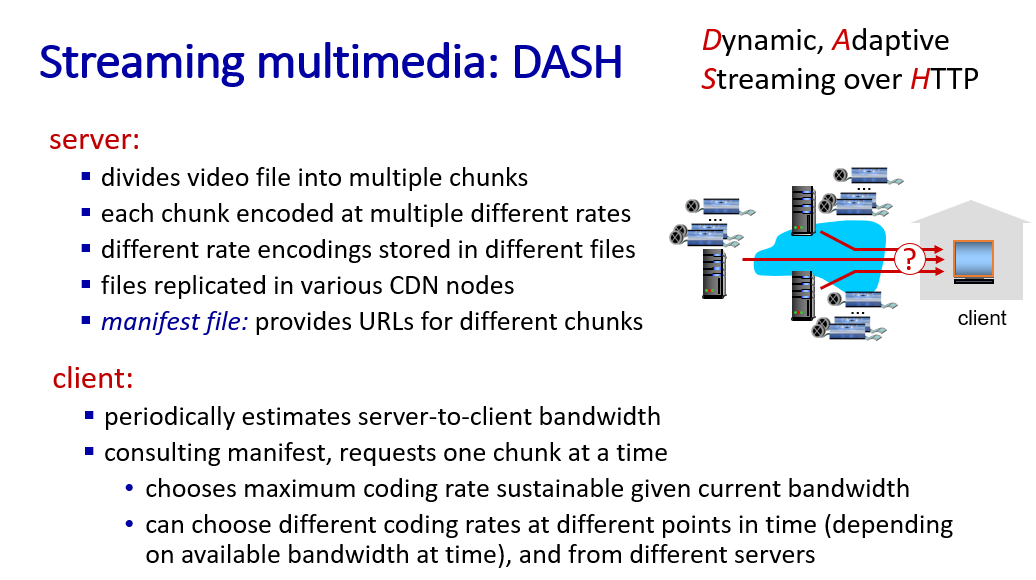
socket programing
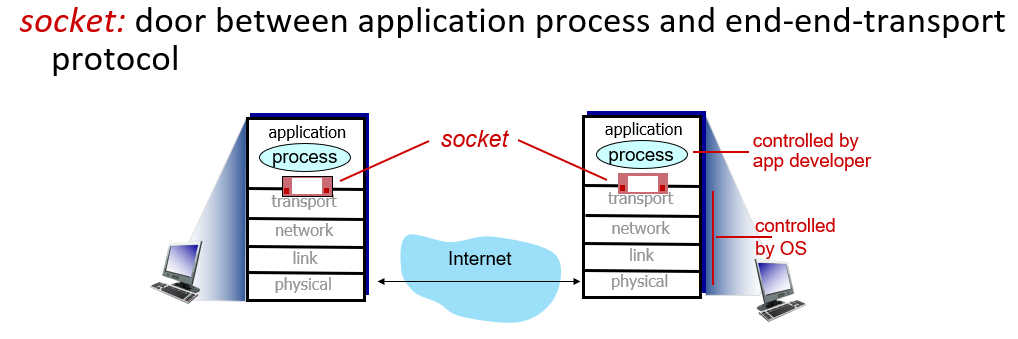
- transport layer are controlled by OS, while app layer are in outside of OS
- socket is the only api for app to get message from transport layer
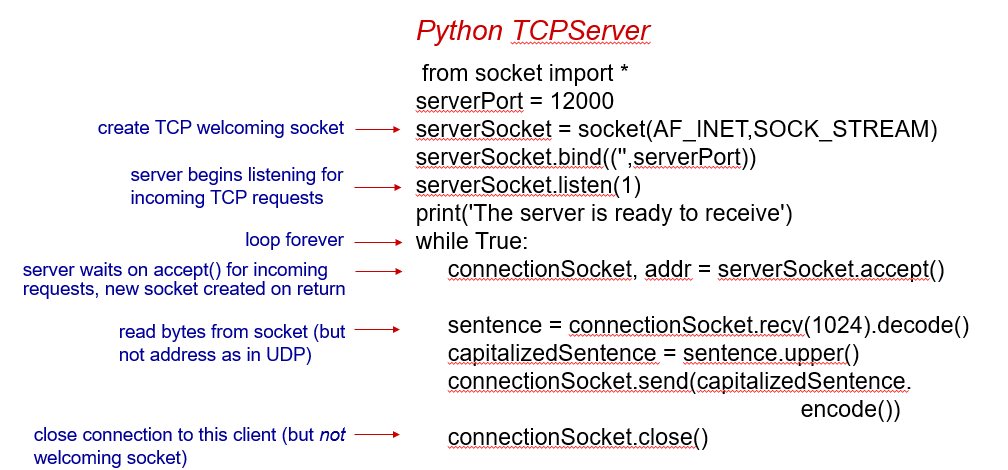
A program to send/recieve message and convert it to uppercase
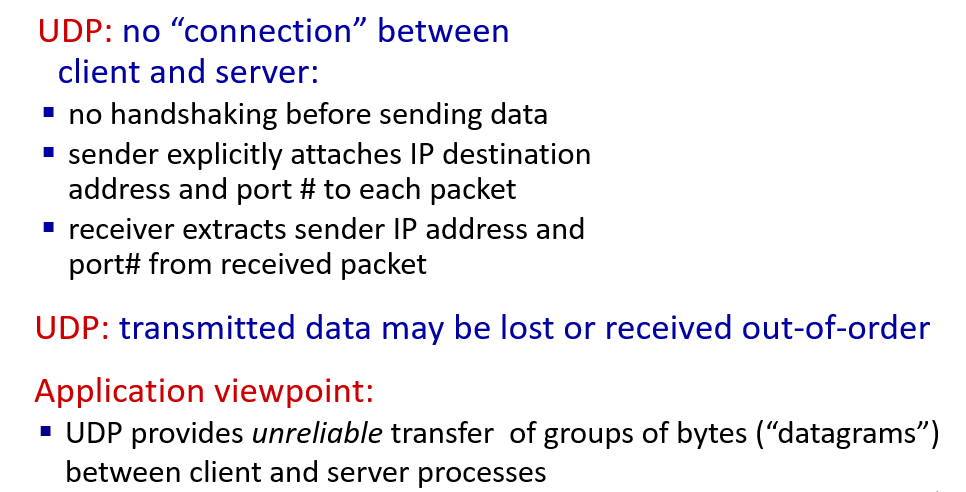
UDP
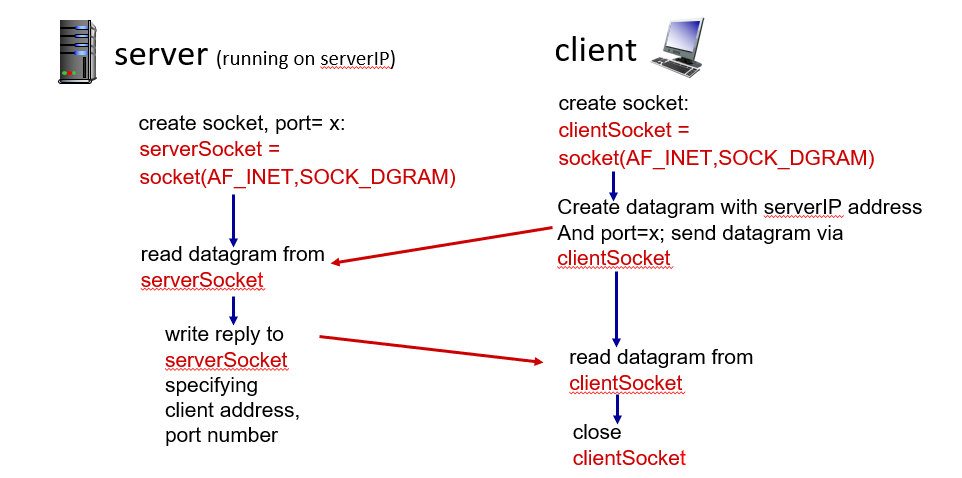
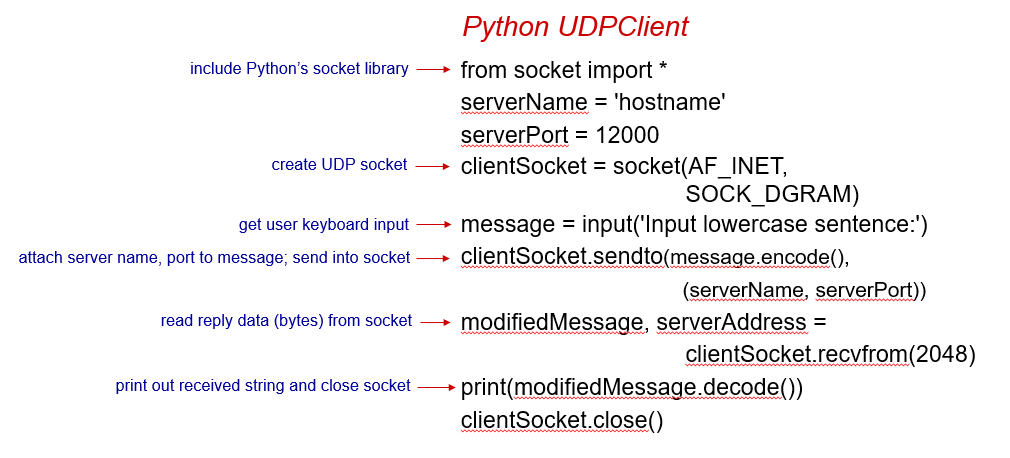
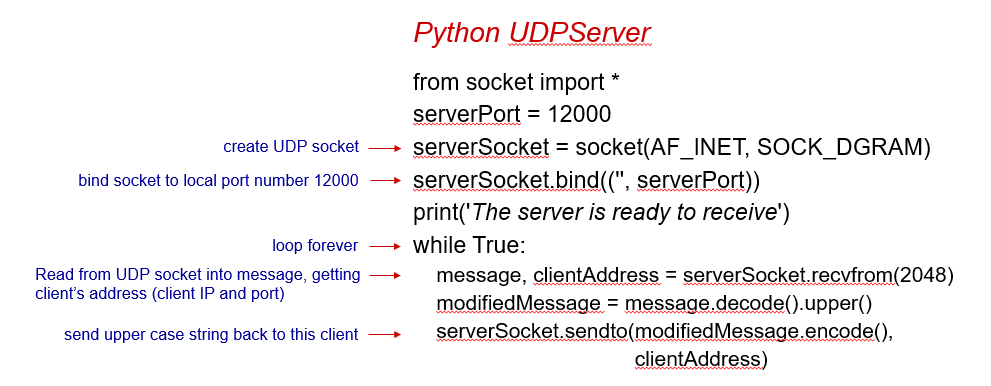
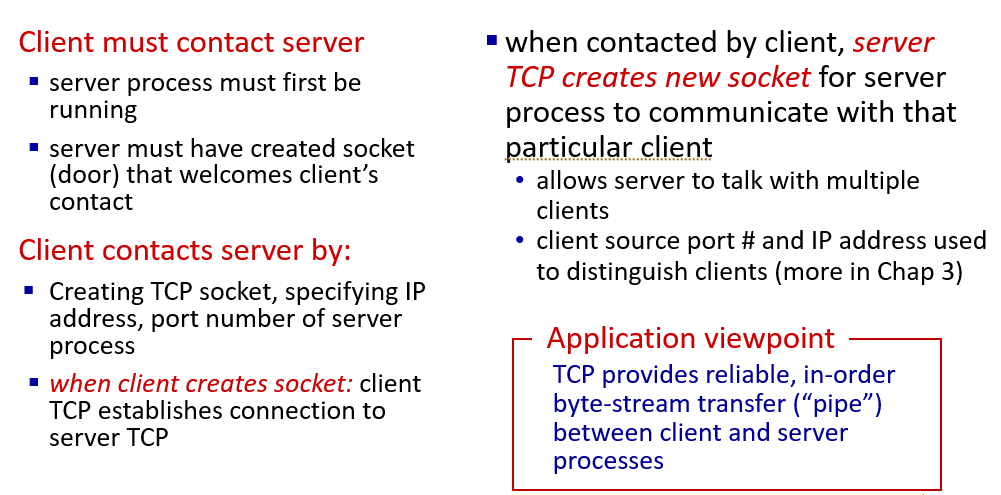
TCP
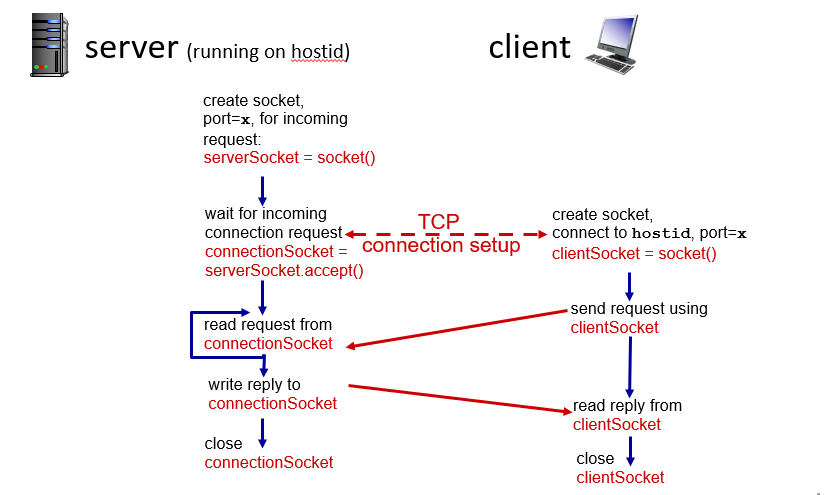
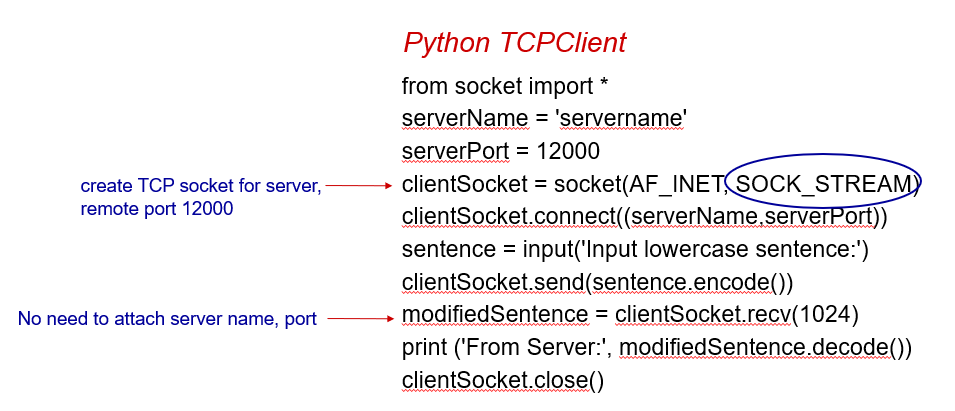
Transport layer
overview
the transport layer provide logical communication between application processes running on different hosts
- logical : despite the untrustable physical medium
- application:Multiplexing and demultiplexing

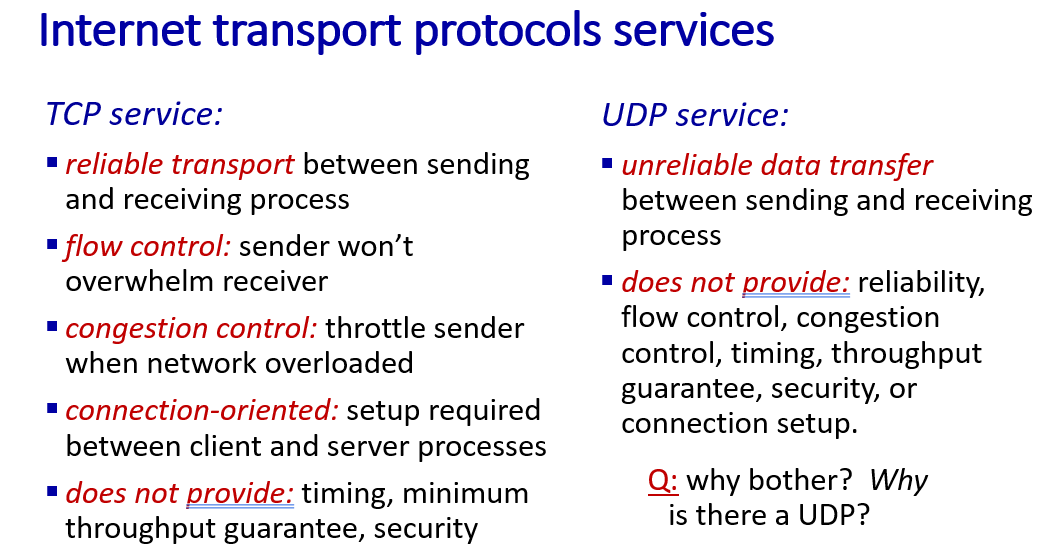
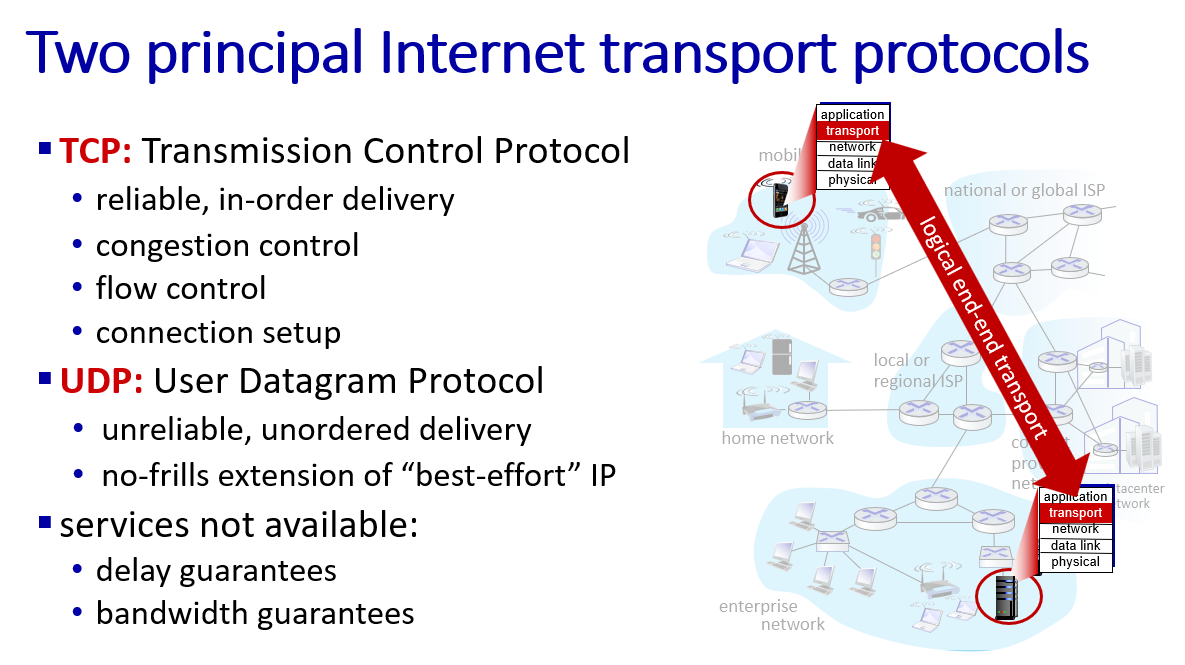
two transport layer protocol:
- UDP
- TCP
Multiplexing and demultiplexing
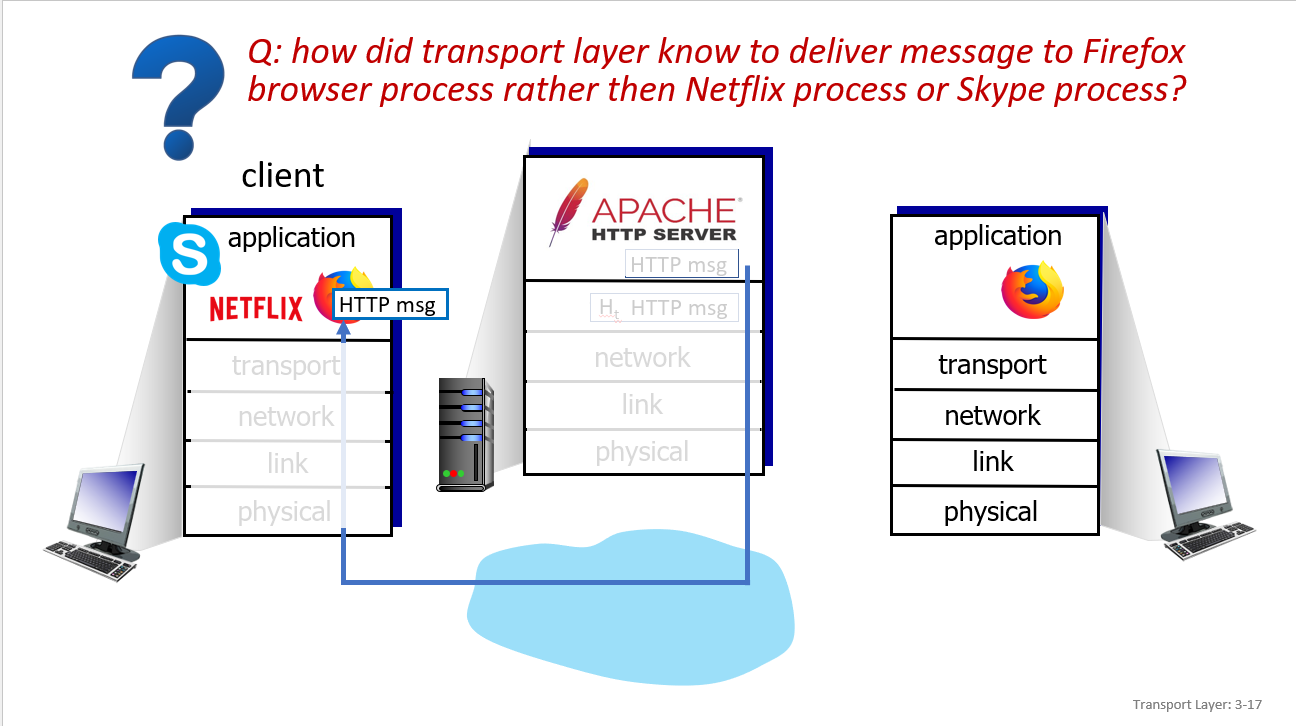
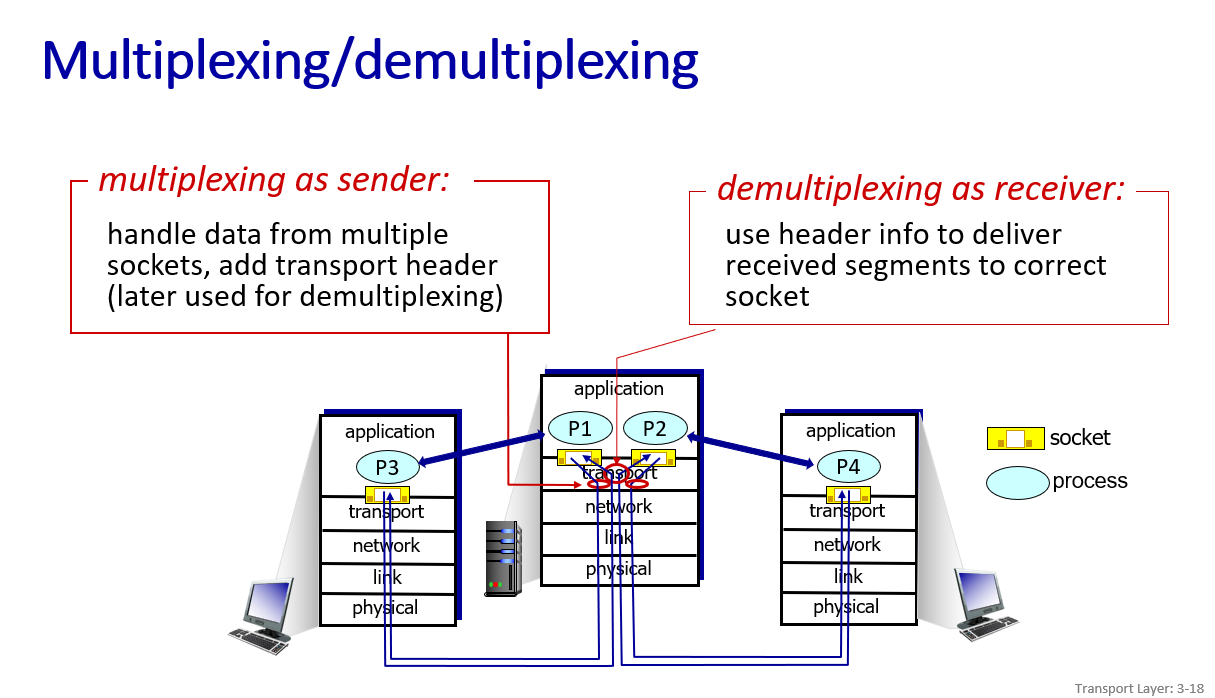
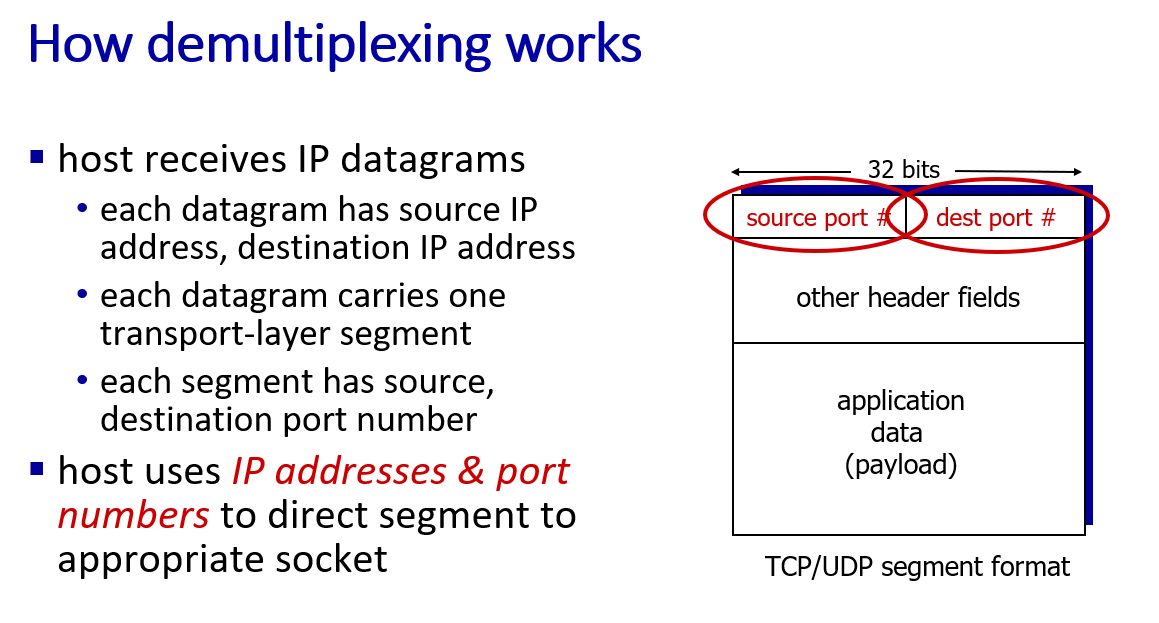
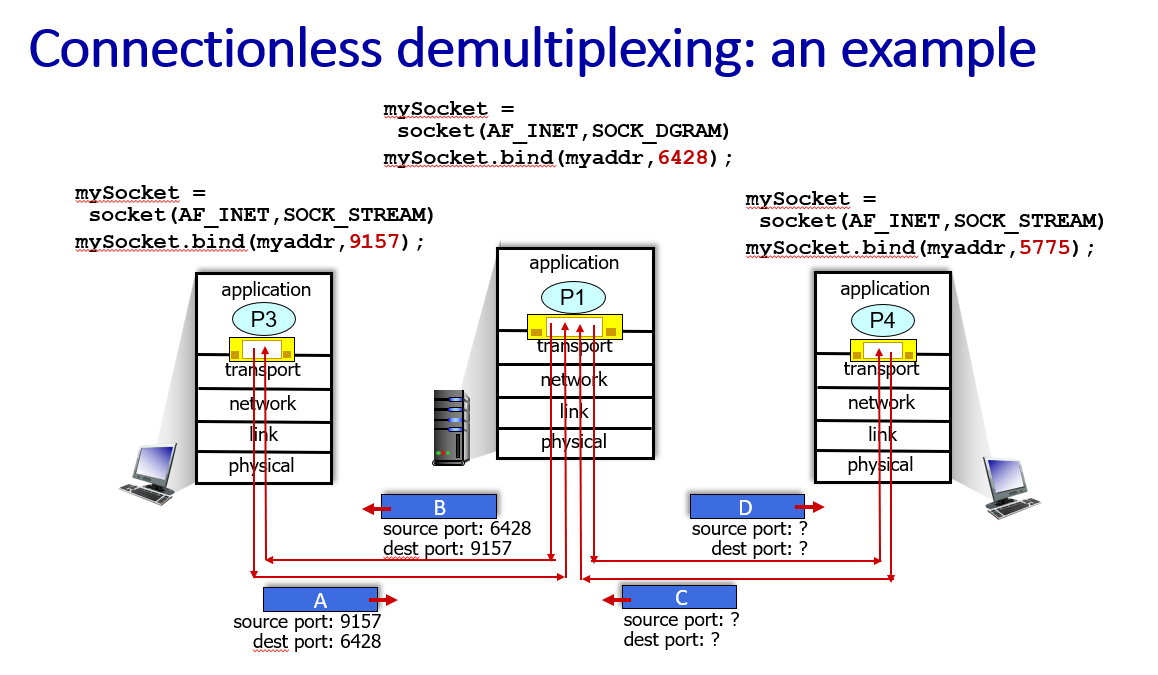
UDP:use dest.port to determine(message with same dest.port go to same socket)
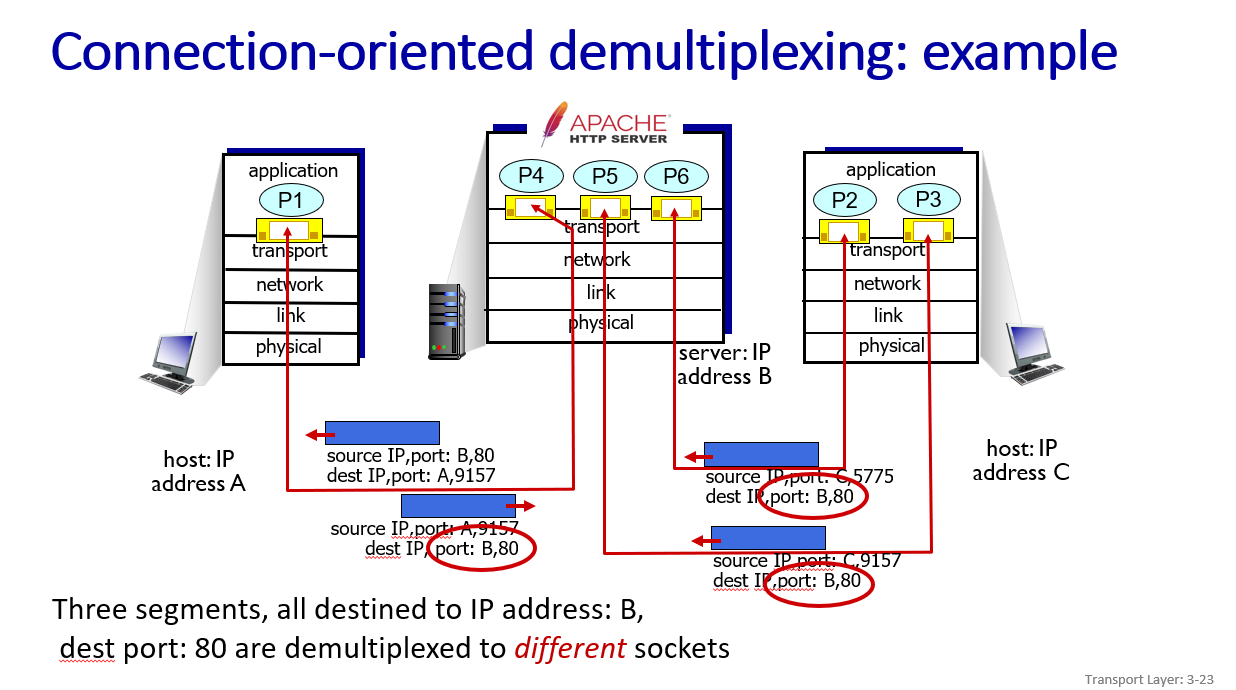
TCP:use 4-turple(source IP address, source port number, dest IP address, dest port number) to determine socket(each socket associated with a different connecting client)
Connectionless transport: UDP
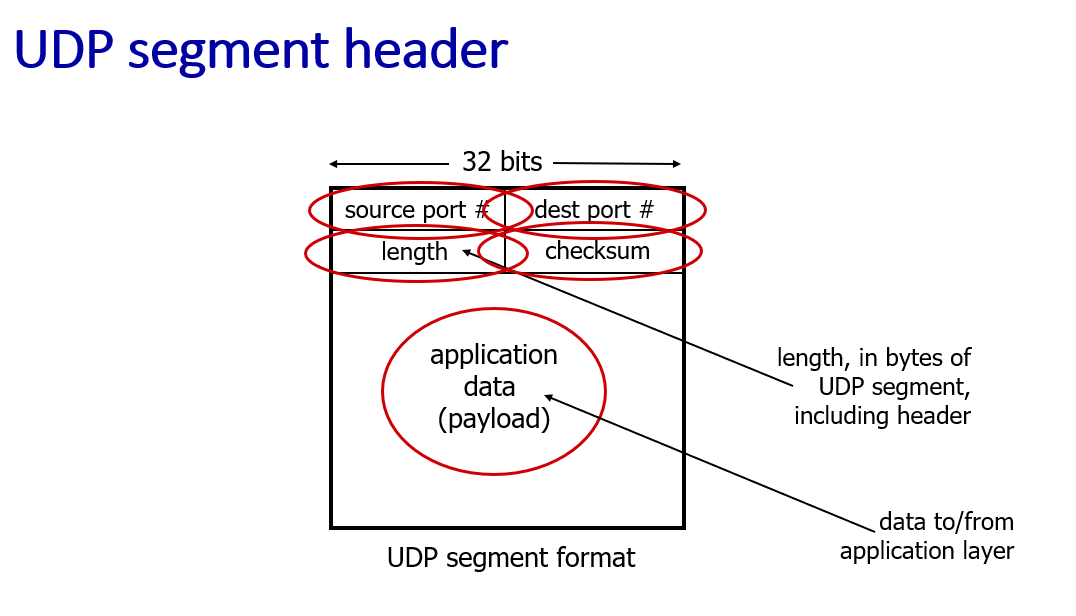
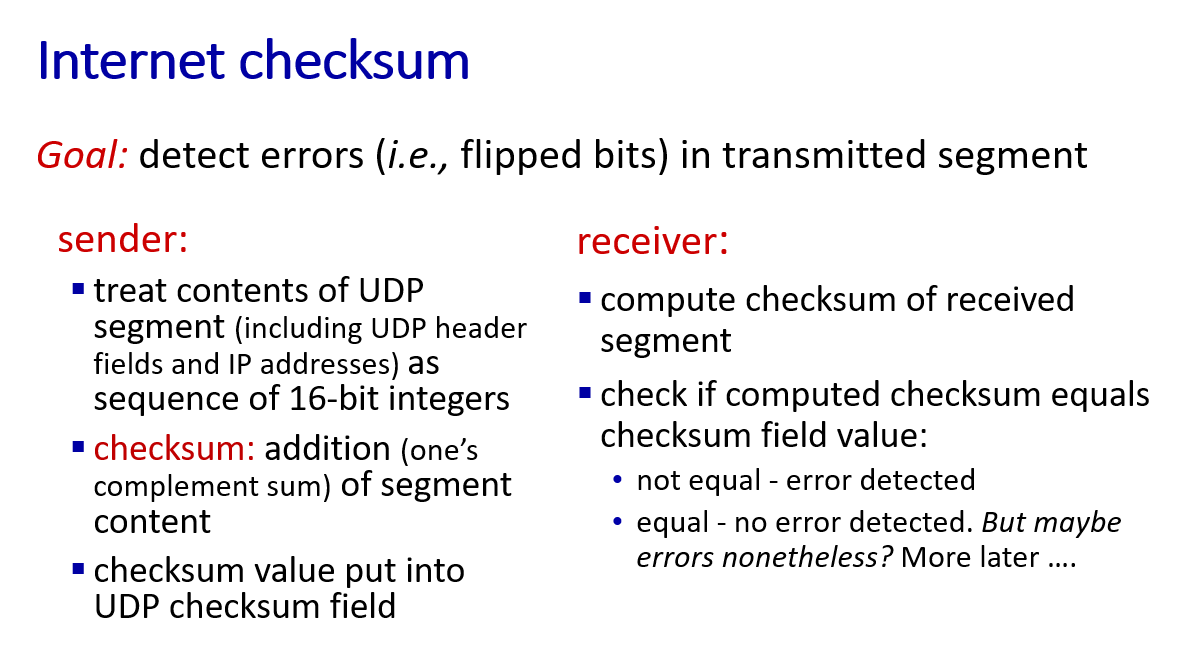
checksum:
Principles of reliable data transfer
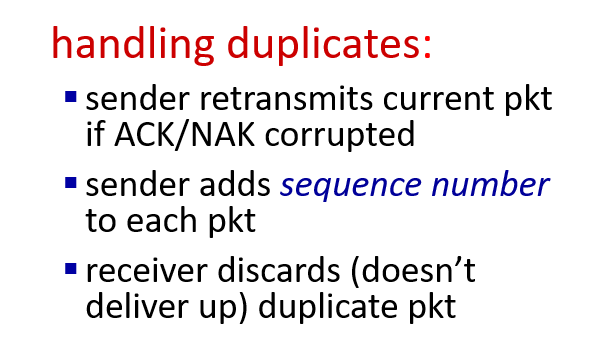
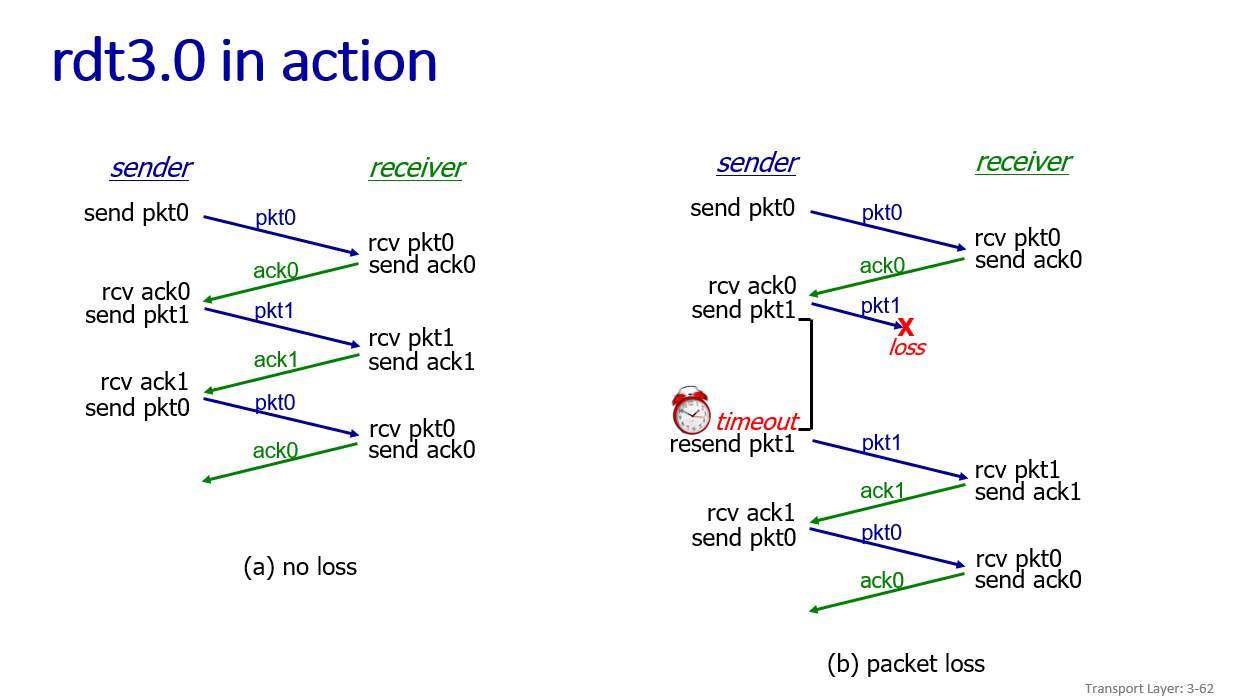
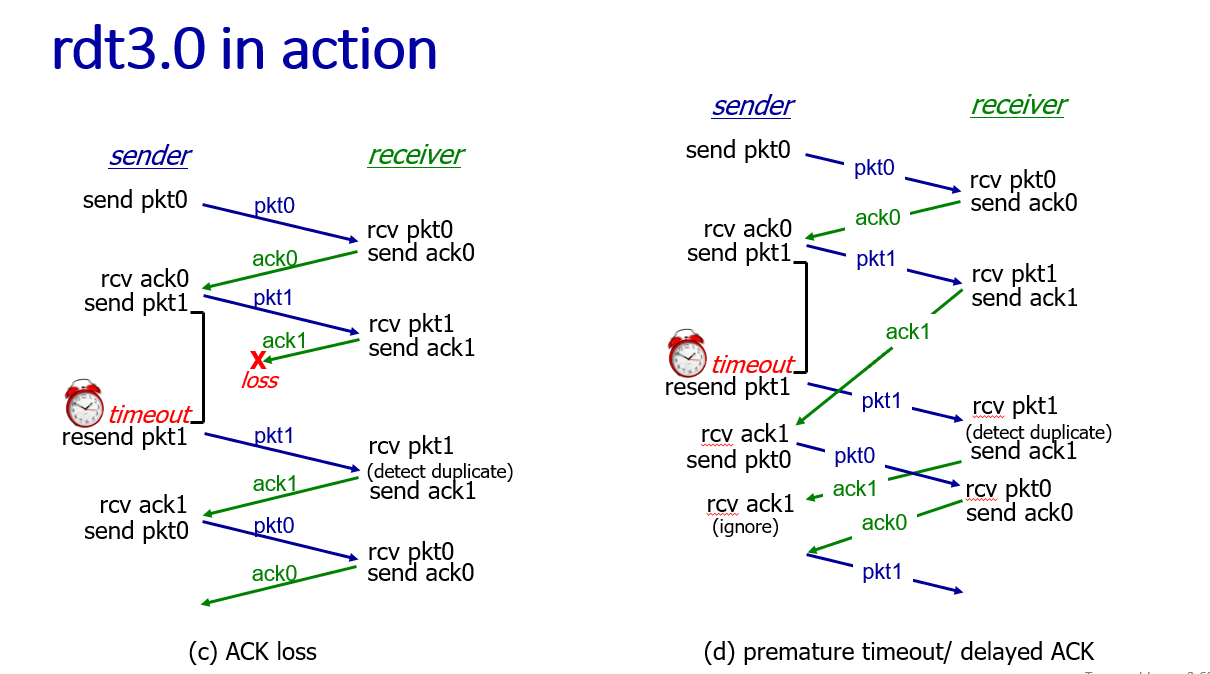
RDT 3.0 ptotocol:sender waits "reasonable" amount of time for acknowlege(sender seq # add to pkt
,recevier must specify sequnce of packet being ACKed, in case that the packet just delayed or deliver up duplicate pkt)
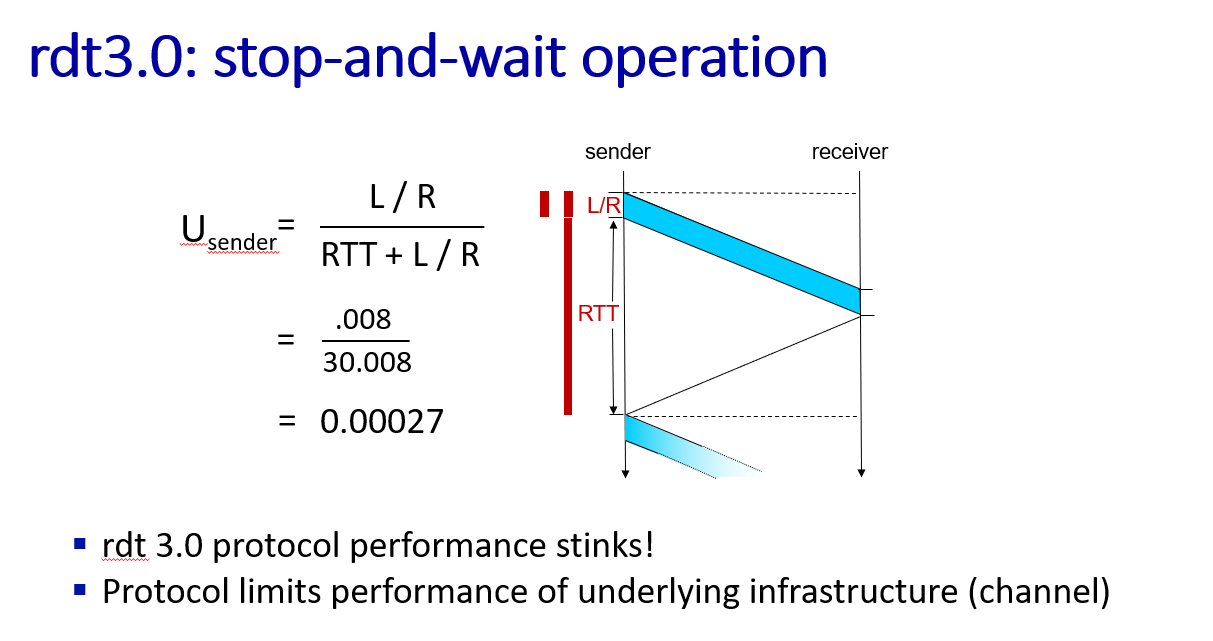
Performance

improve method:pipelined protocols operation
pipelining: sender allows multiple, “in-flight”, yet-to-be-acknowledged packets
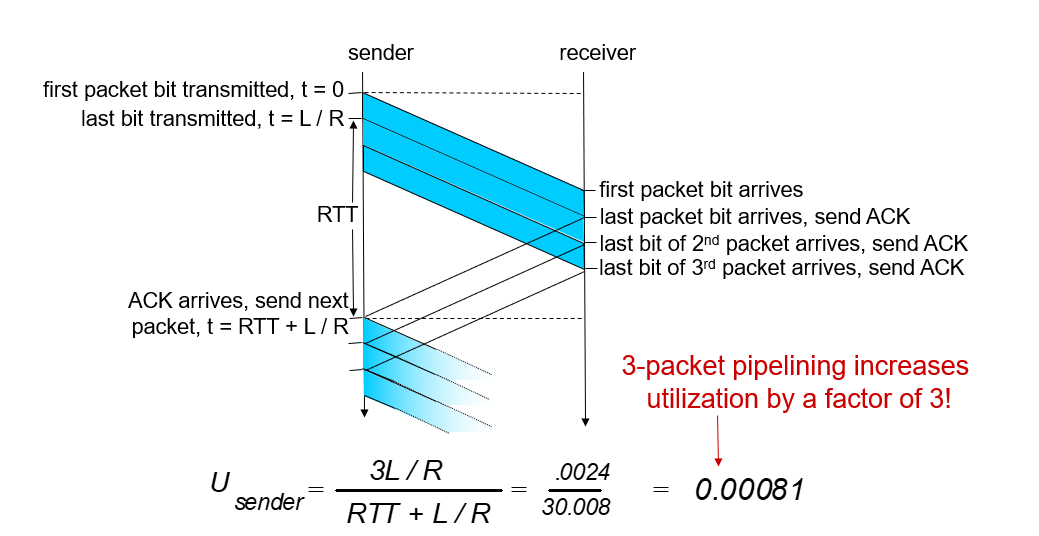
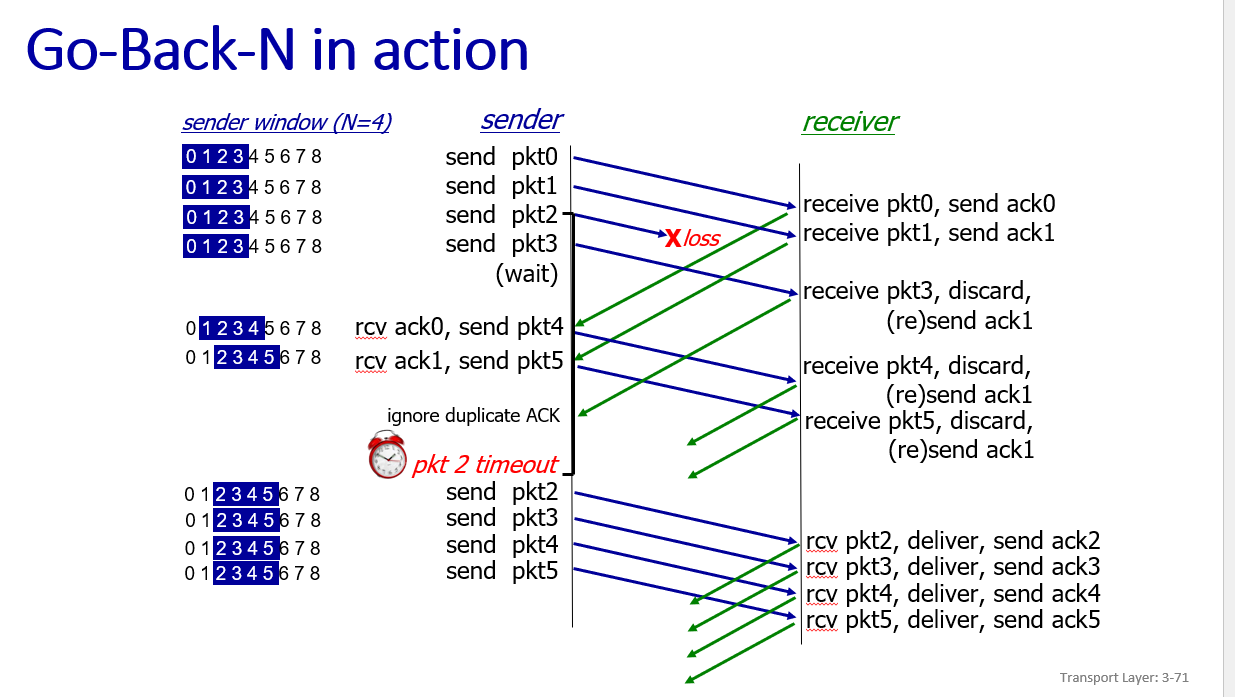
- Go-back-N(cumulative ACK)
recevier: need only remember rcv_base,always send it when receive higher order packet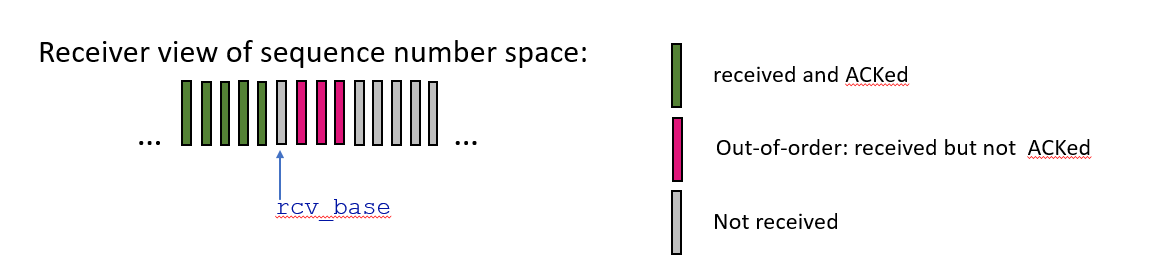 sender: on receiving ACK(n): move window forward to begin at n+1,when timeout send all packets in window
sender: on receiving ACK(n): move window forward to begin at n+1,when timeout send all packets in window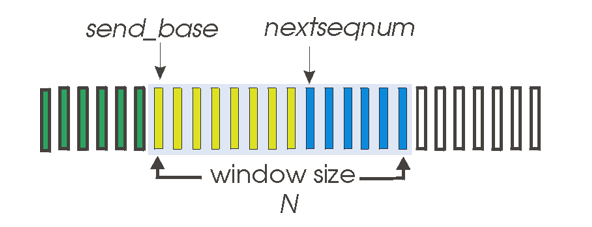
- Selective repeat
receiver: individually acknowledges all correctly received packets, buffer out-of-order packet
sender: maintains timer for each unACKed pkt

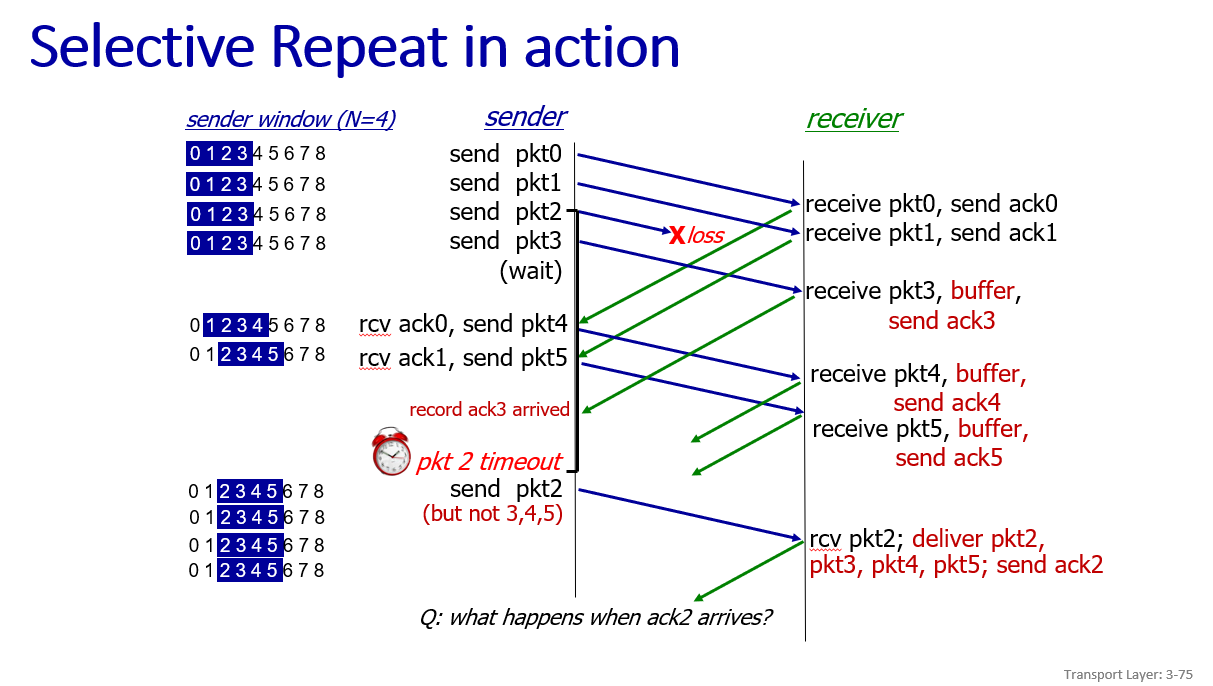
dilema: sometime very wrong
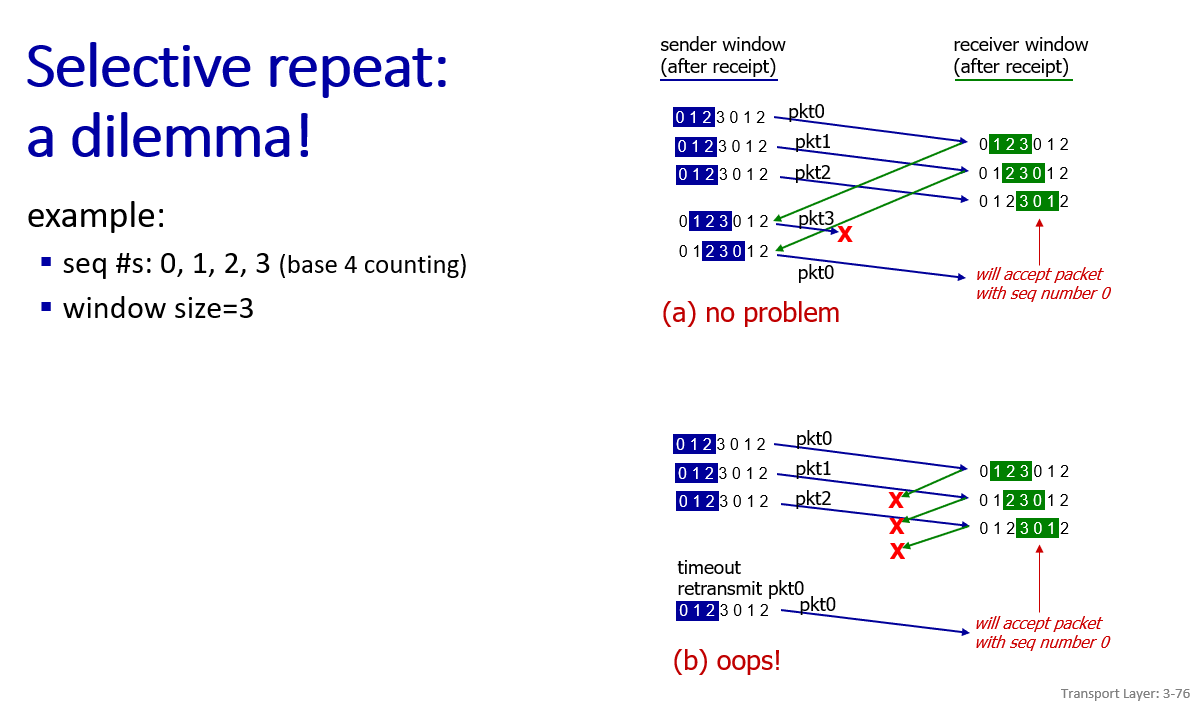

when window size is smaller than half of the seq size, can avoid problem in b, but can cause performance limit(short pipeline).
further discussion:here is a blogconclusion: sender window + receiver window size <= sequence size
Connection-oriented transport: TCP

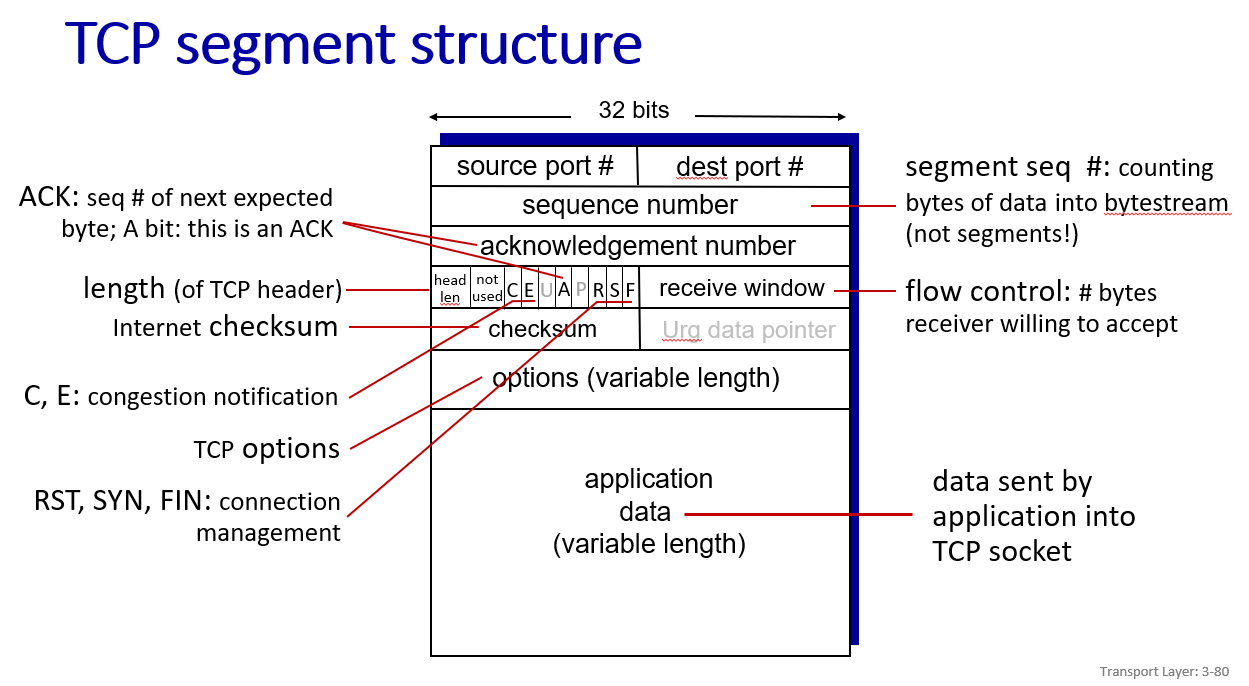
little different in ack and seq definition
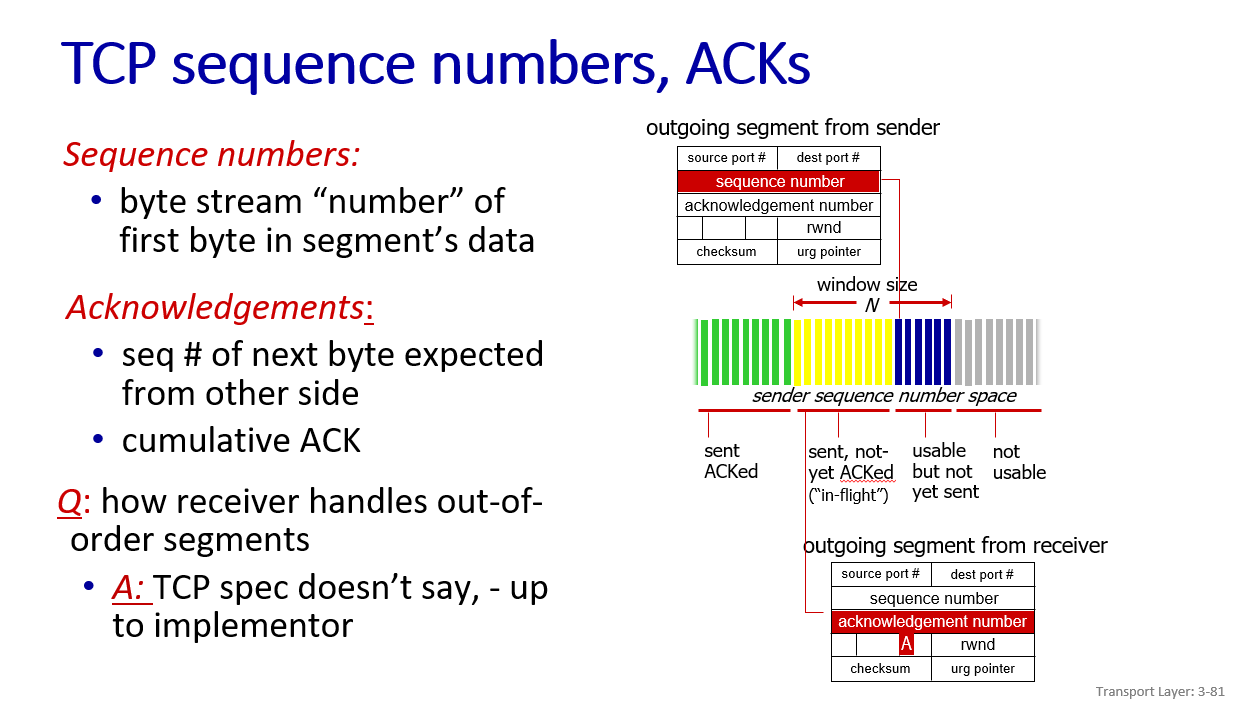
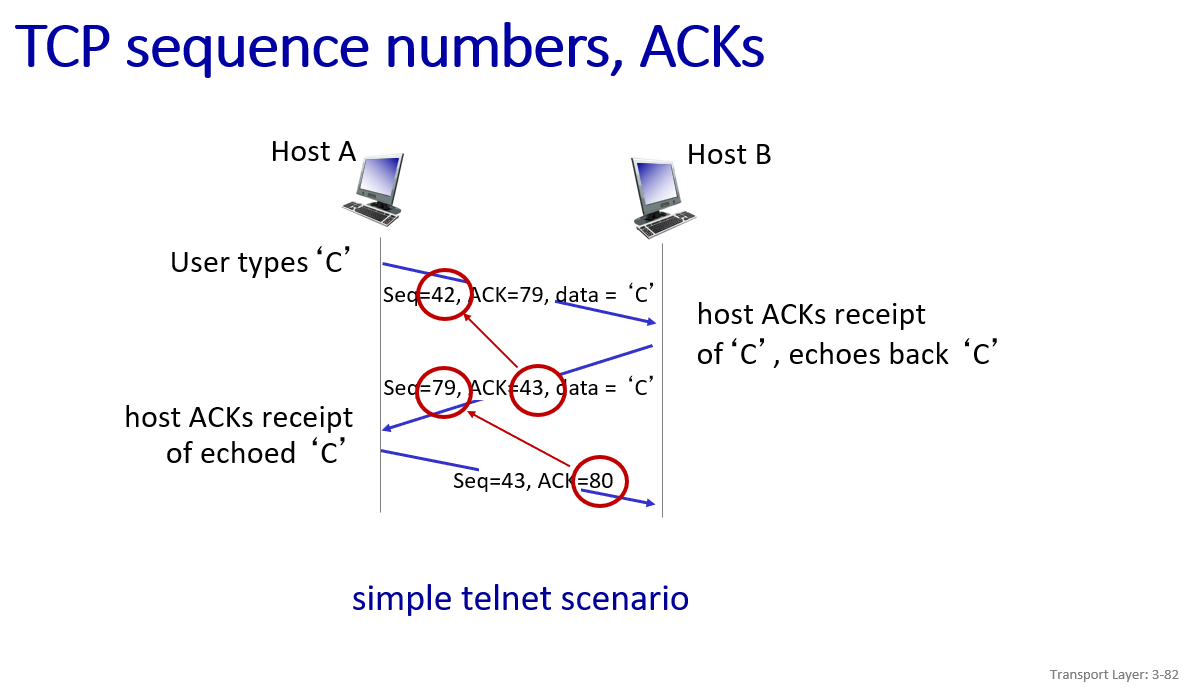
ACK=Seq+1:cause C is an 1 byte data
how to set reasonable timeout value
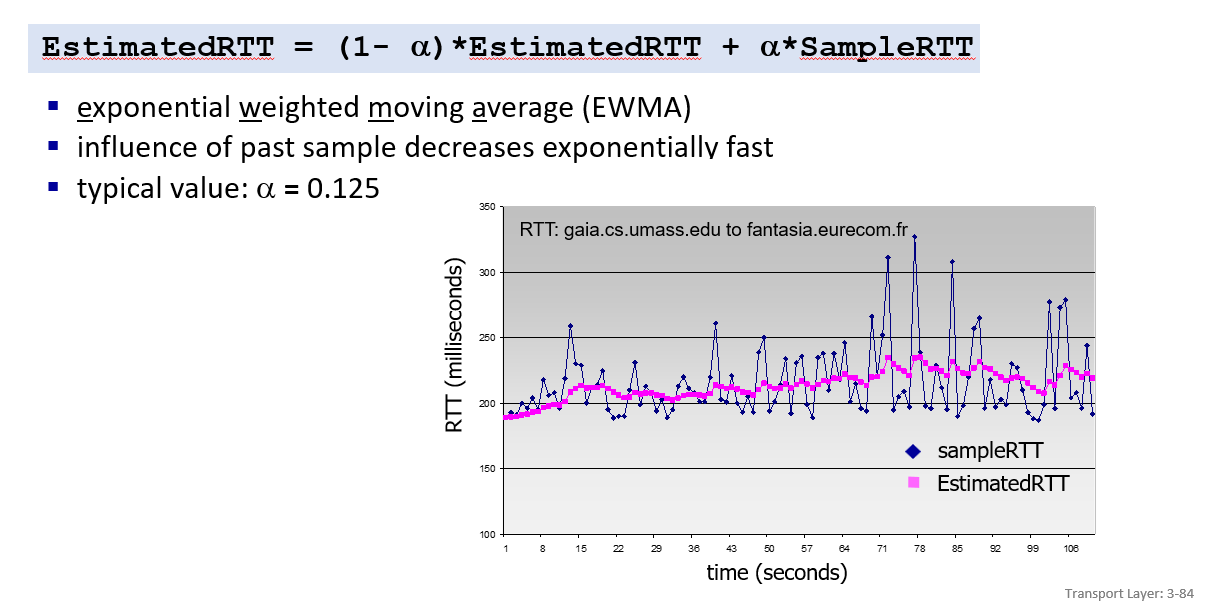
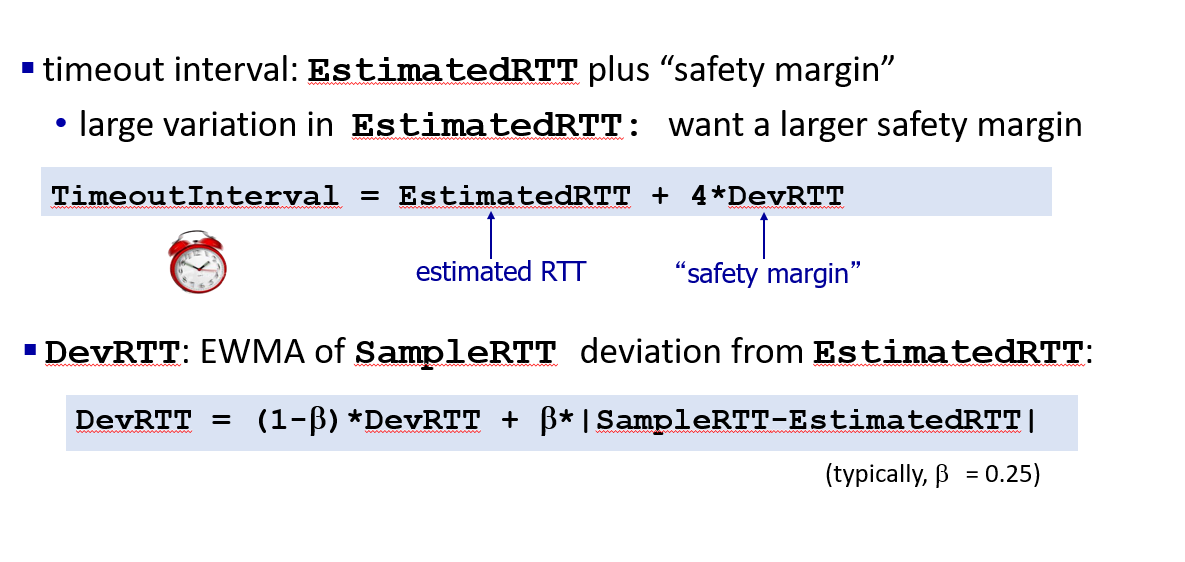
TCP action:
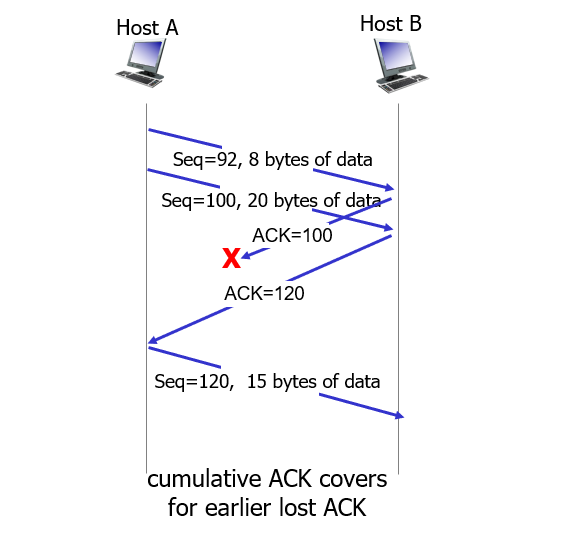
- Rather than immediately ACKnowledig this segment, many TCP implementations will wait for half a second for another in-order segment to arrive, and then generate a single cumulative ACK for both segments – thus decreasing the amount of ACK traffic. The arrival of this second in-order segment and the cumulative ACK generation that covers both segments is the second row in this table.
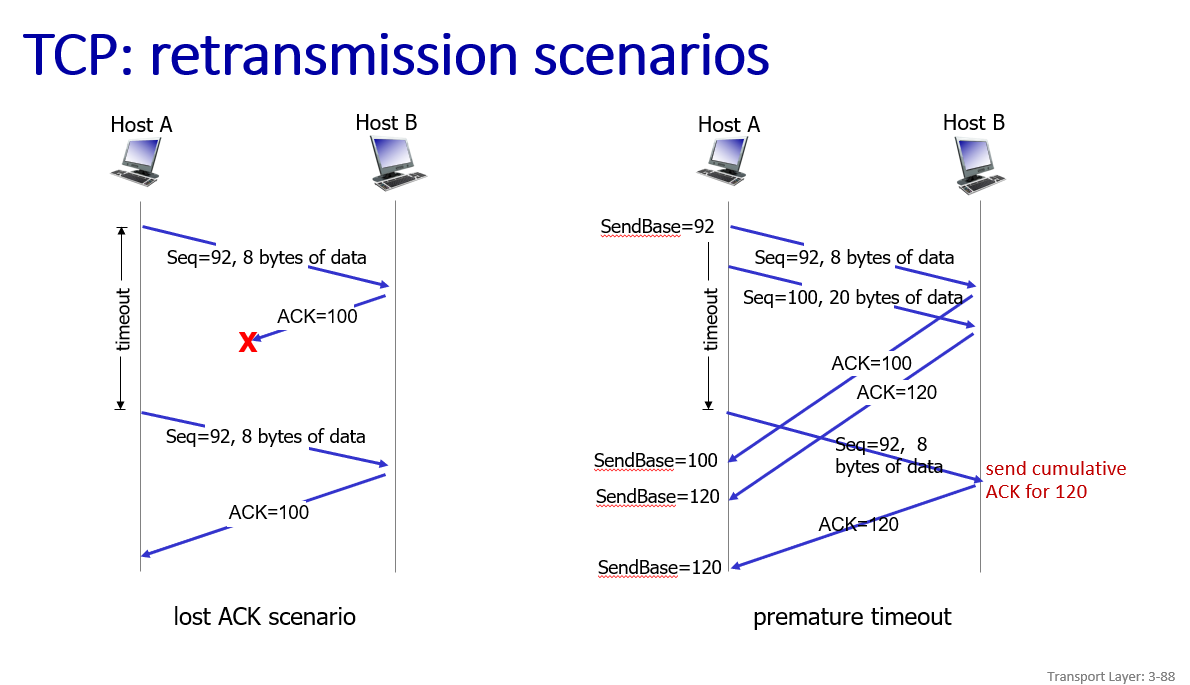
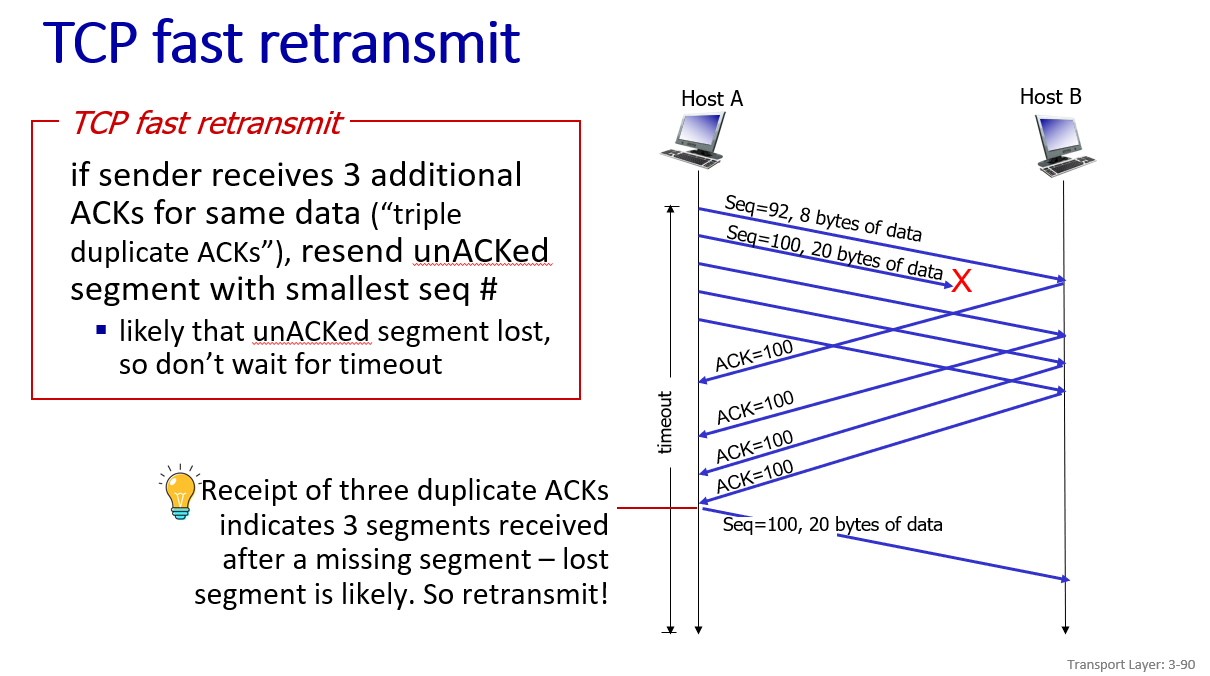
improve:fast retransmit,in example below there is no need to wait for timeout
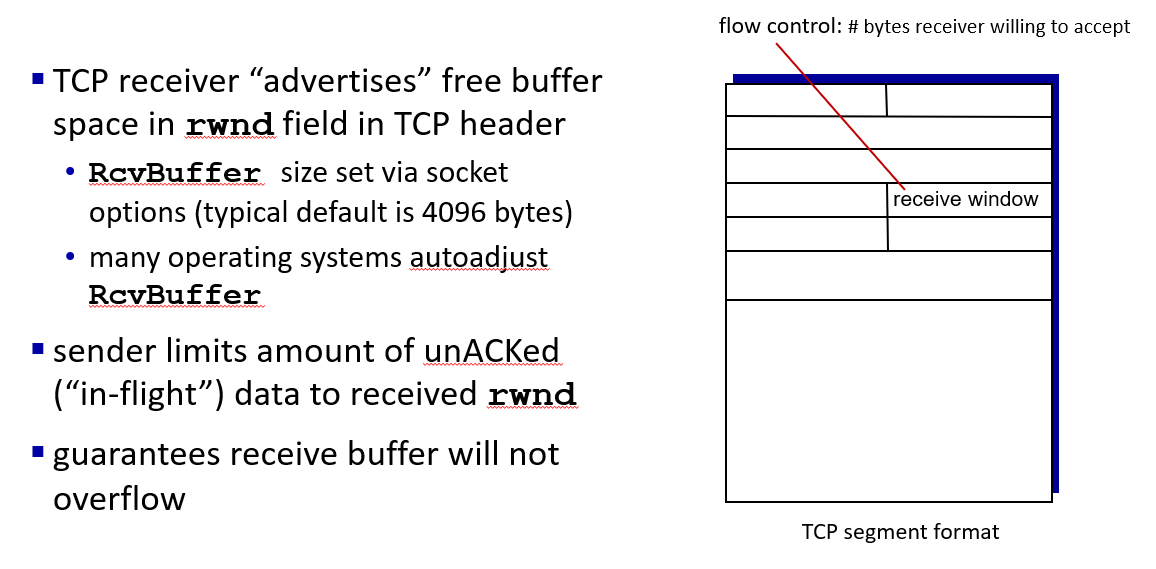
flow control
speed matching between single sender and receiver
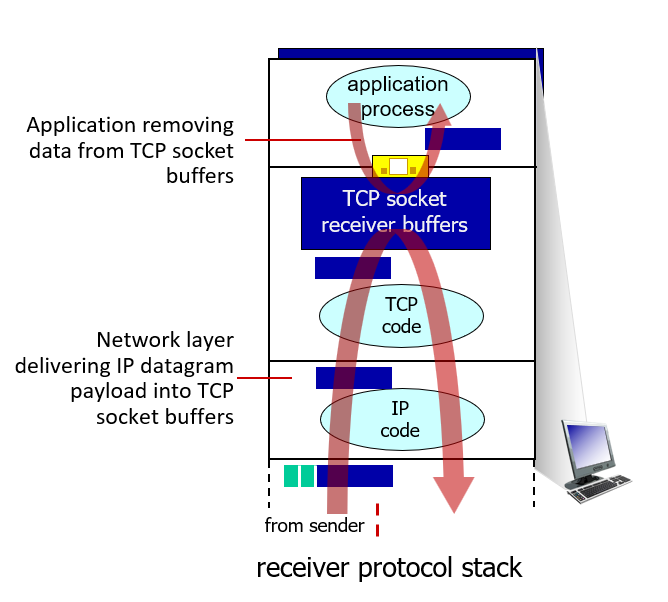
no one really want to drink from a fire hose

basic idea:receiver inform the sender how much free buffer space there is, and sender limit send no more than this amount of data(rwnd:receive window)
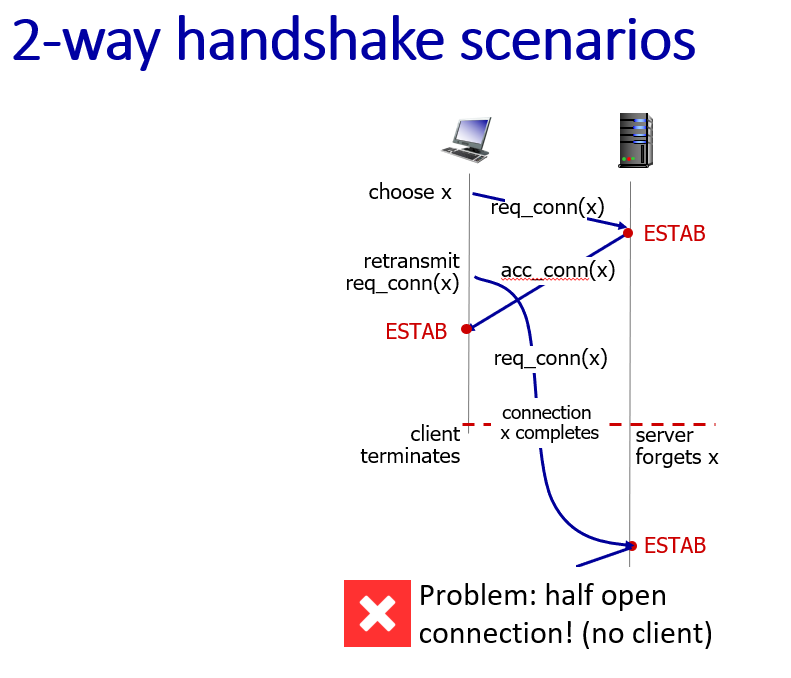
connection management
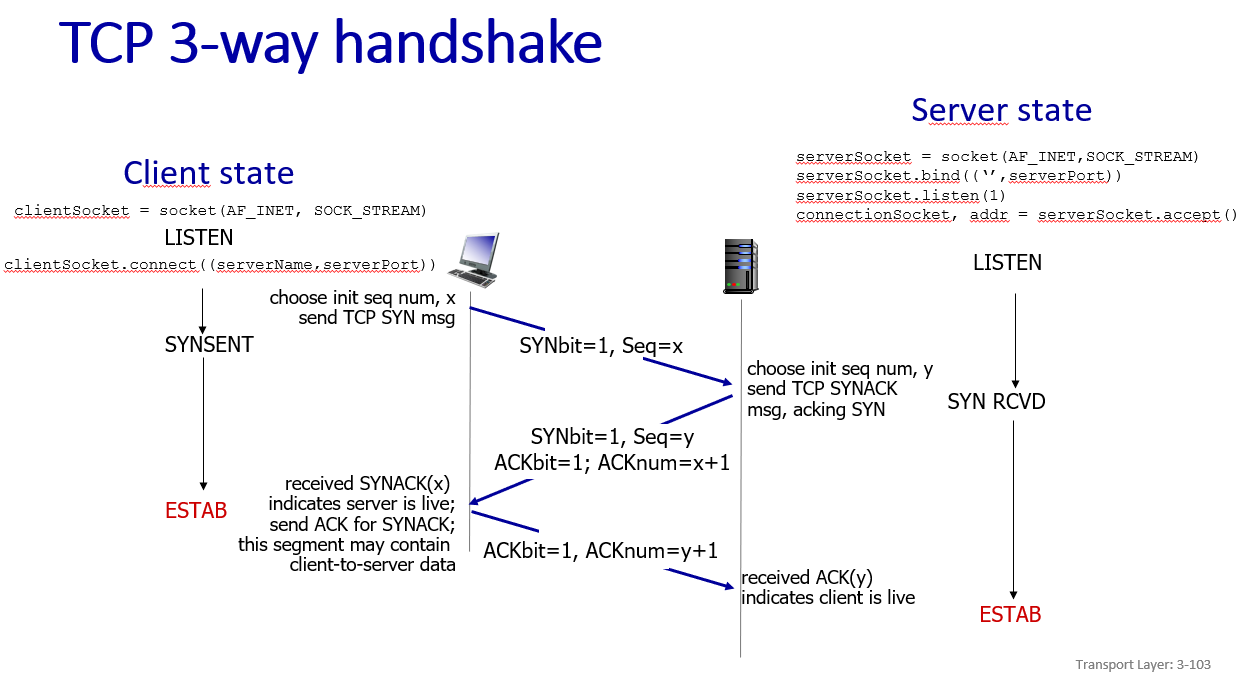
three way handshake:send one mes and receive one mes to ESTAB(establish)

Principles of congestion control
-
cause and cost of congestion:
between multiple (too many)senders send too fast and aggregate: data arrival rate exceeds transmission rate thus queue

-
a scenario
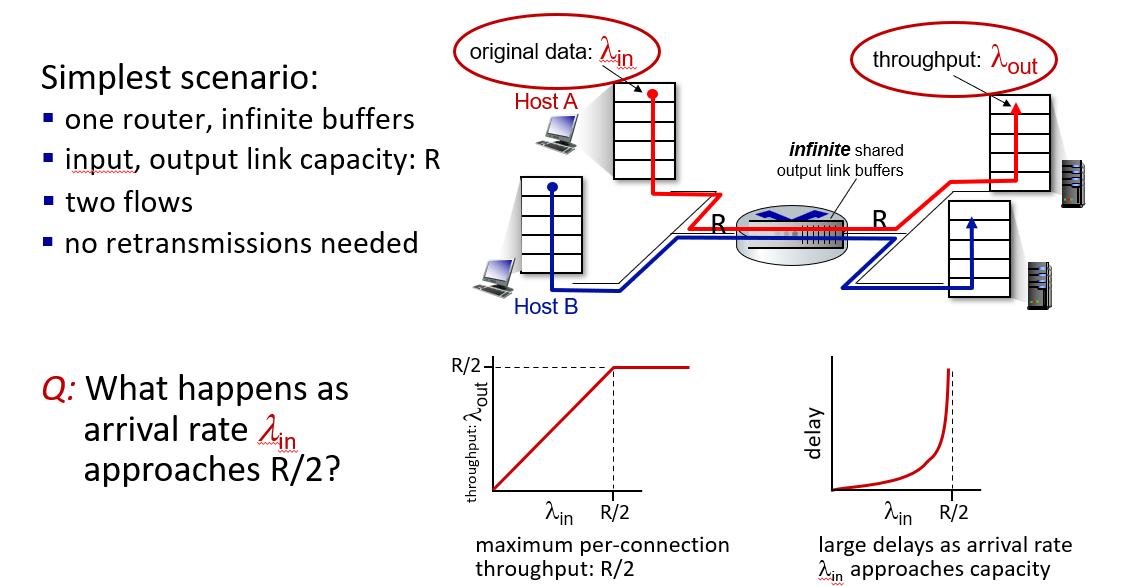
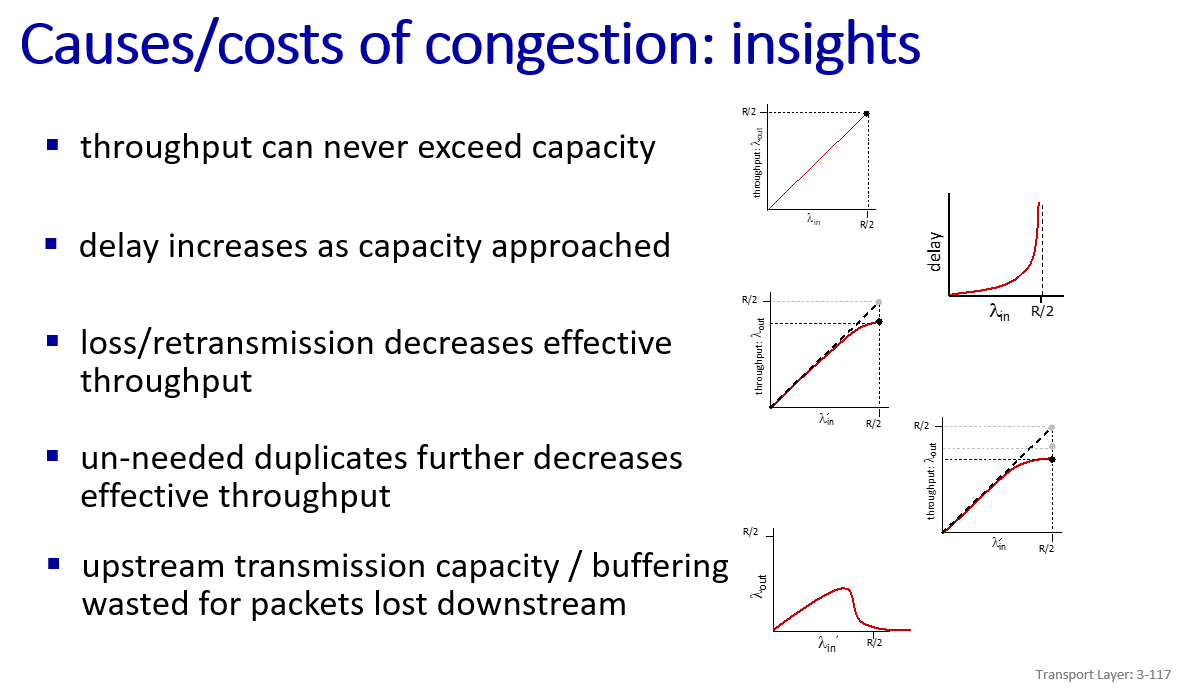
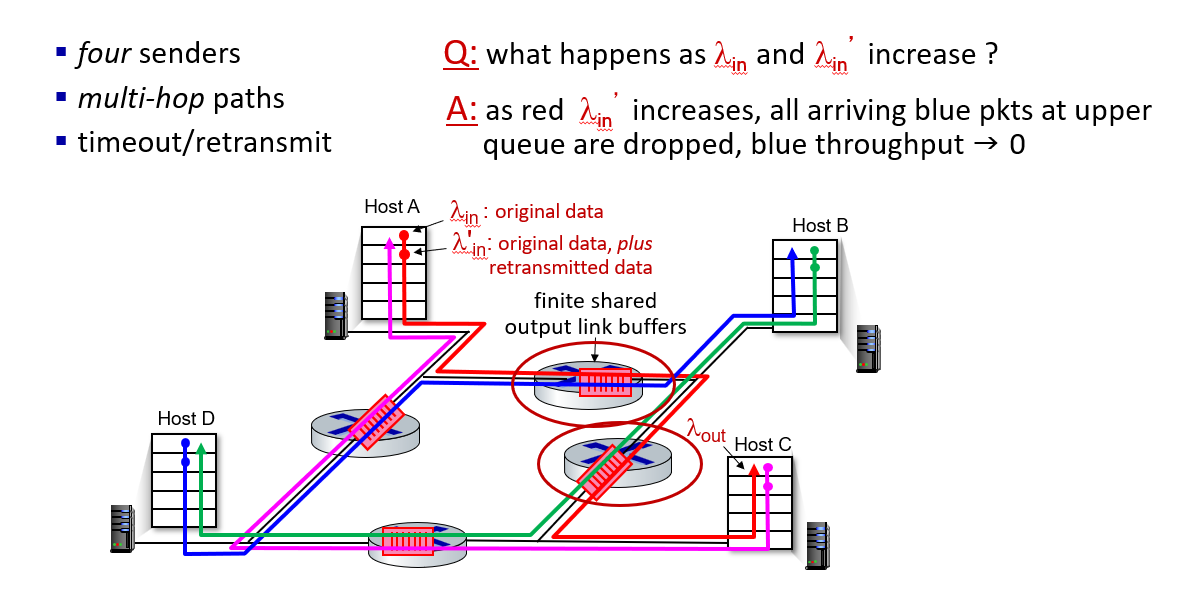
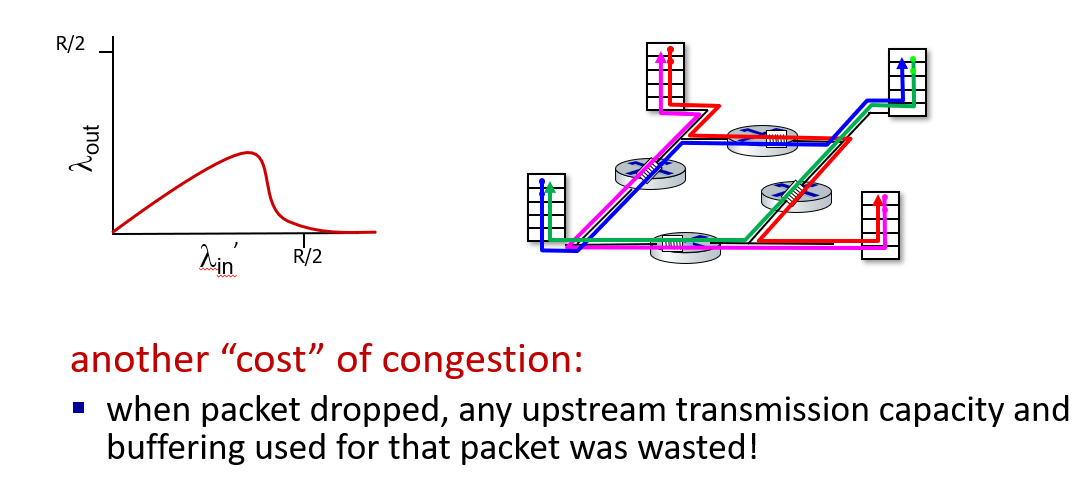
-
how to deal with congestion:
the former method doesnot get information from network layer, while the latter does
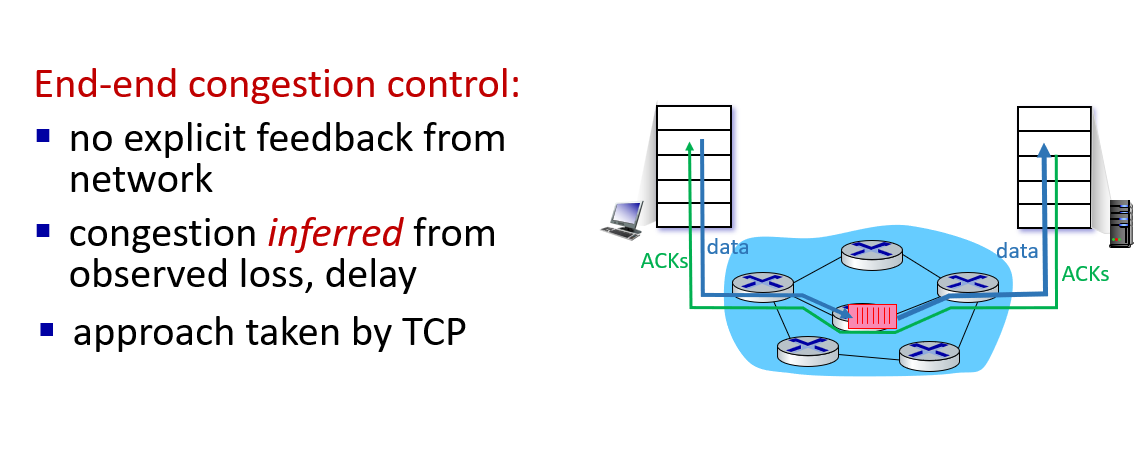
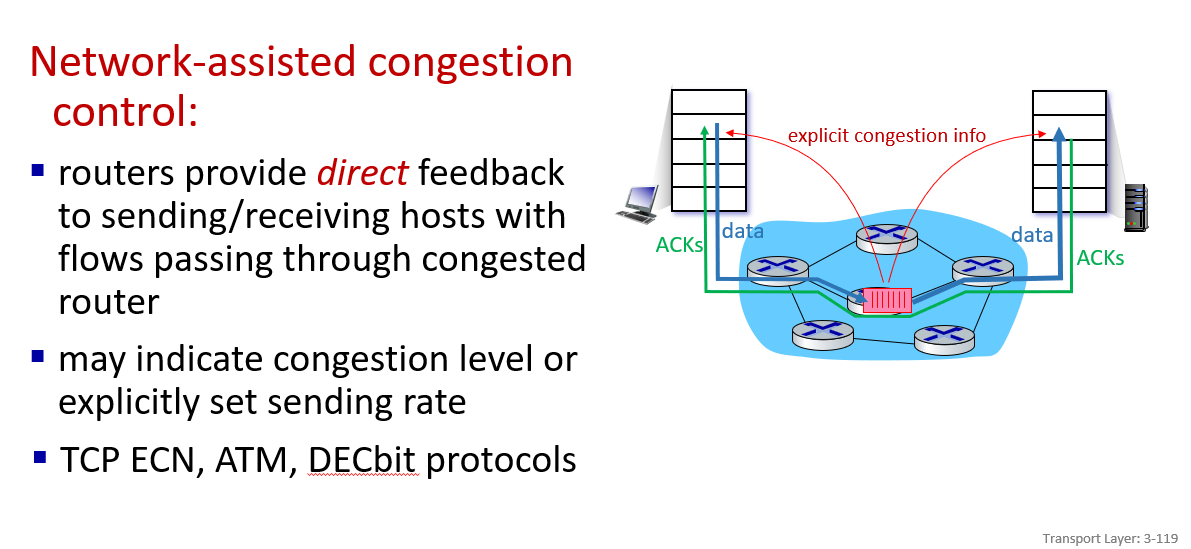
TCP congestion control
congestion base on lost
- AIMD:
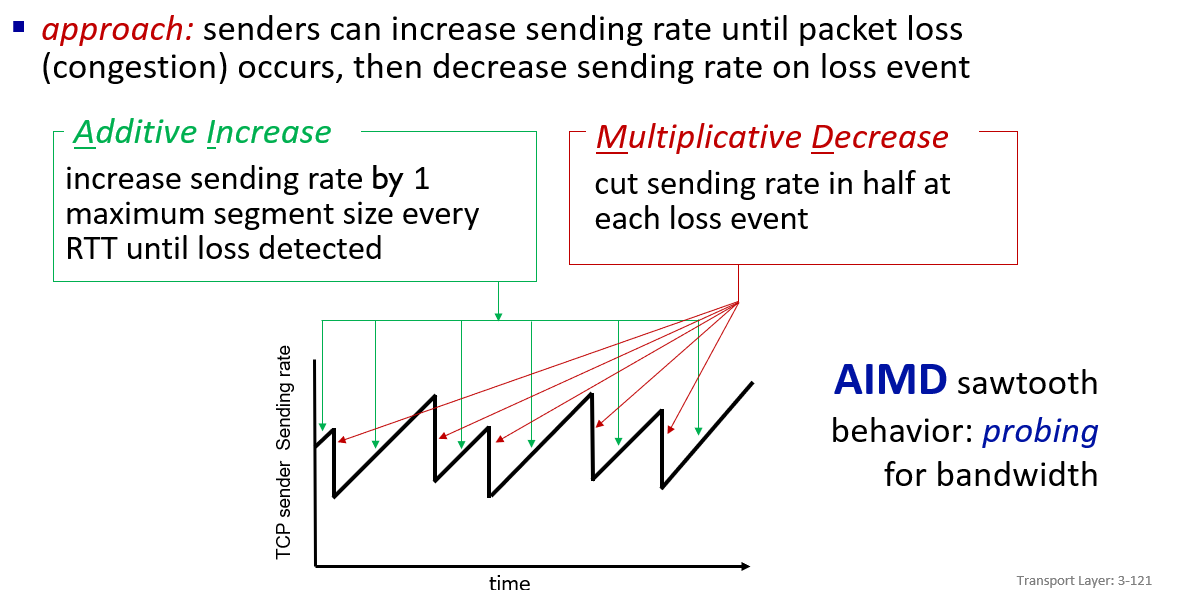
two type of lost,M is different



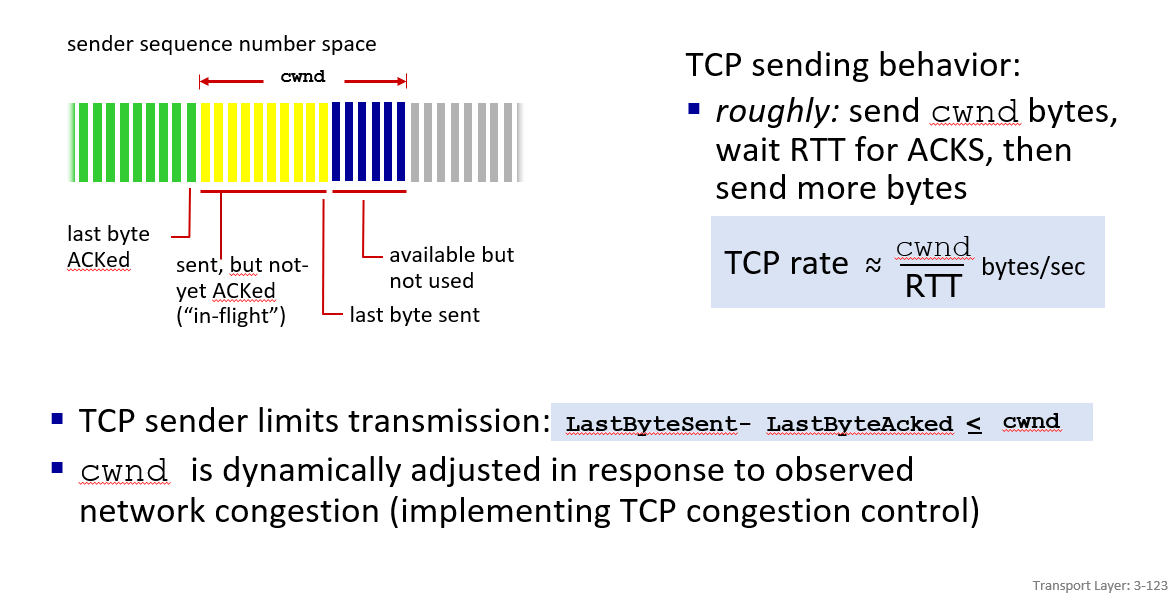
by adjust cwnd(congestion window) size to control
notice that in TCP,ACK is the byte number,so cwnd is in terms of bytes as well as rwnd.
TCP slow start
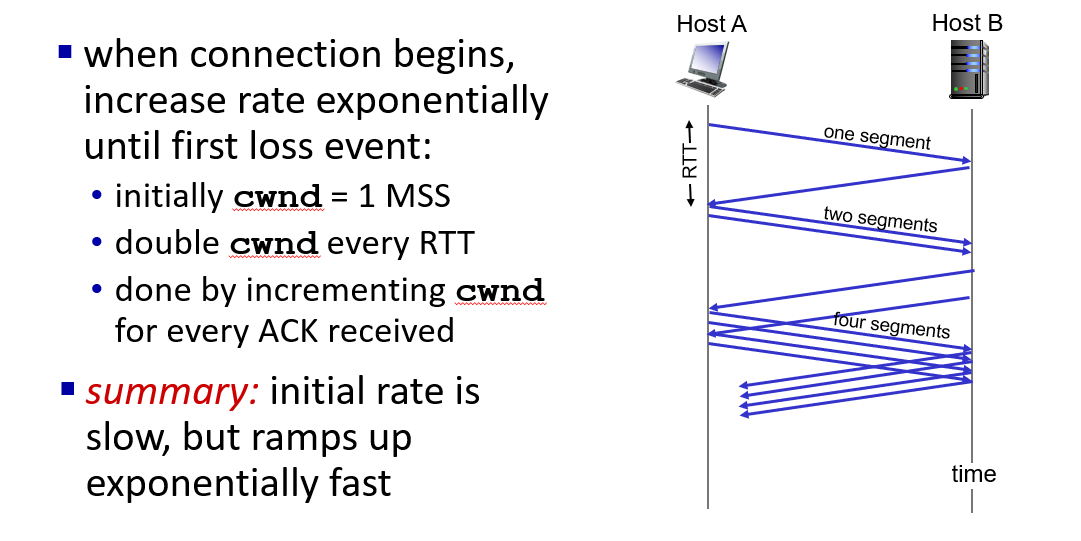
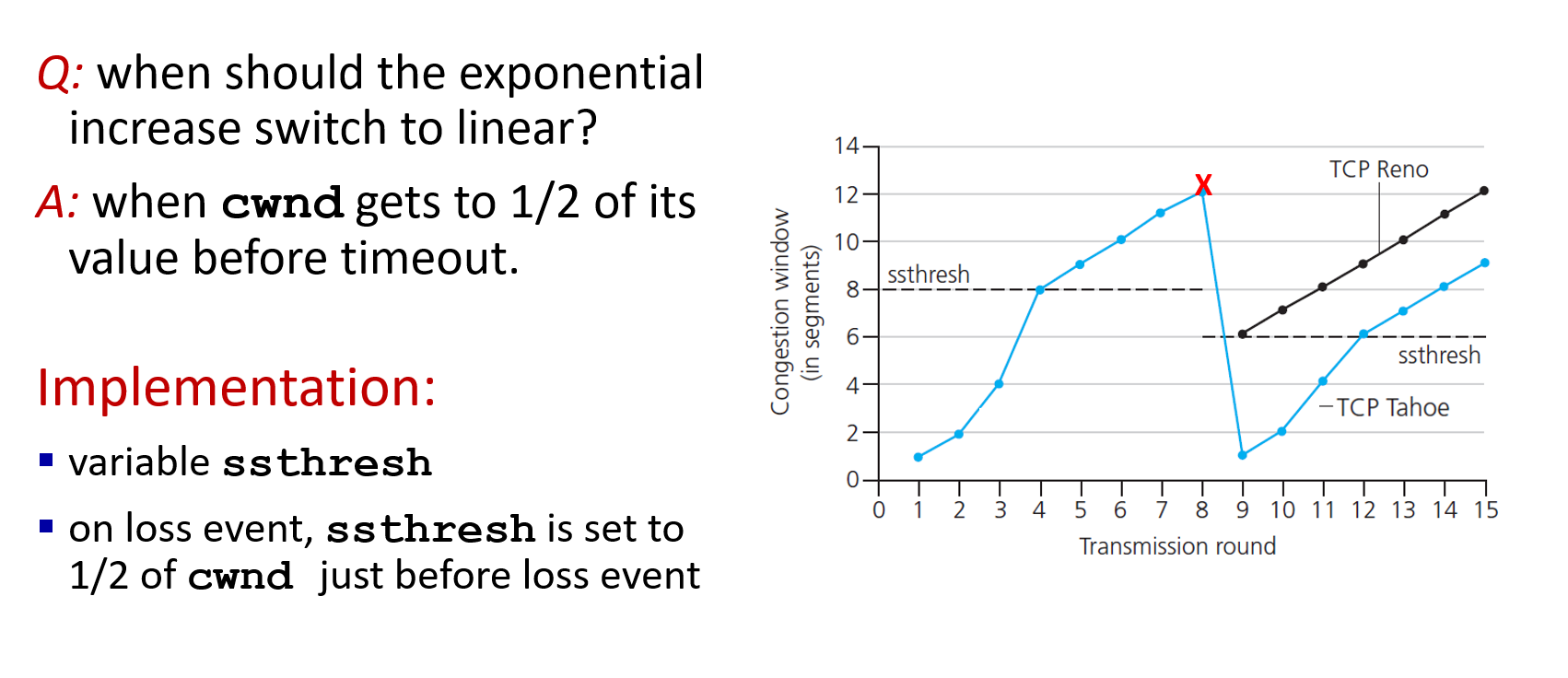
set SS the value of half of cwnd when timeout loss
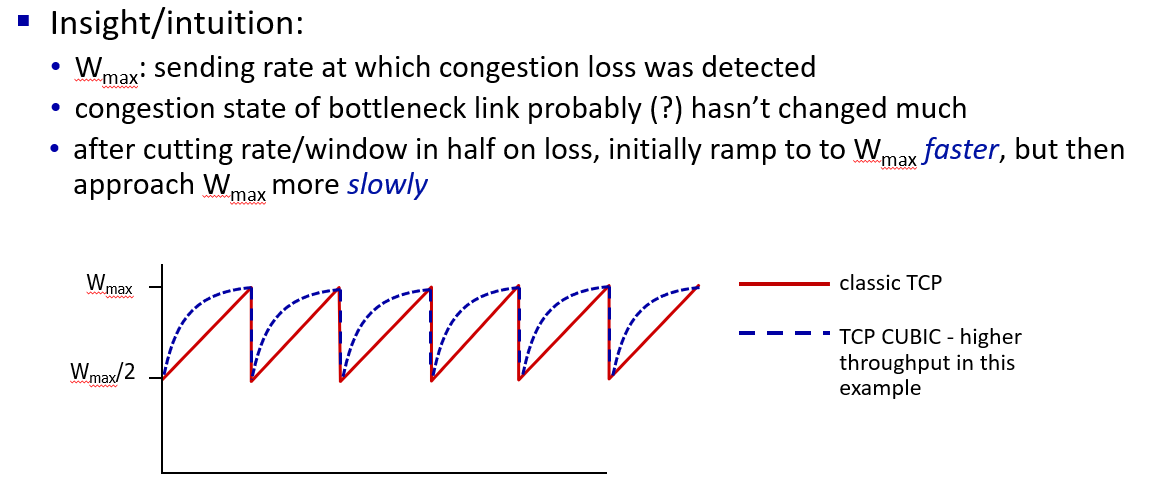
- CUBIC:
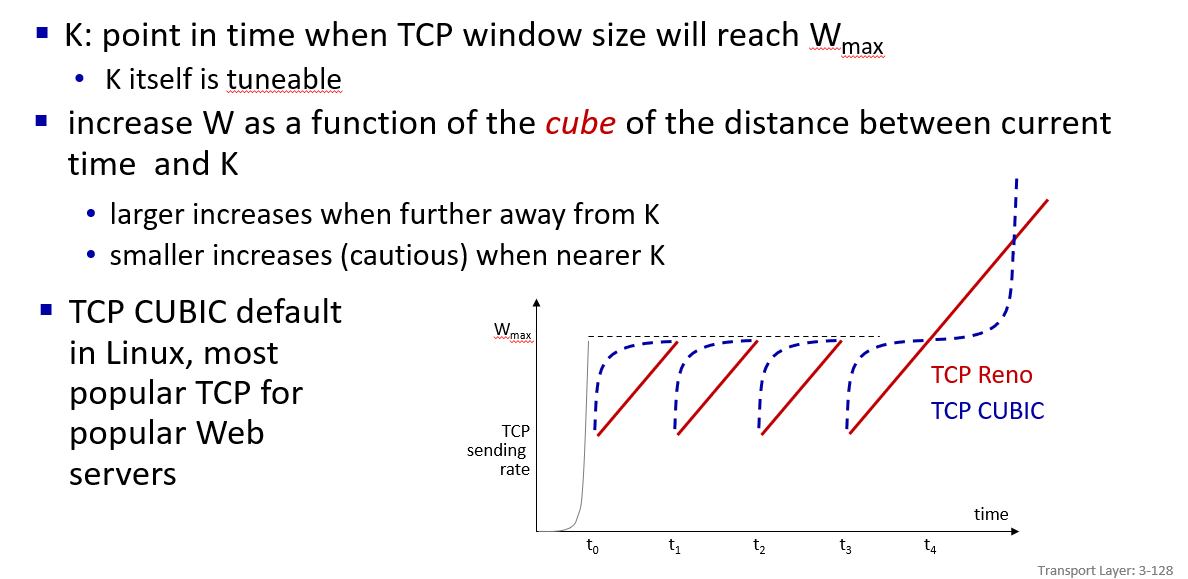
cubic function
K:future time (x offset of cubic funtion)
W:loss detected sending rate (y offset of cubic funtion)
congestion base on delay
considering bottlelink behavior, if RTTmin then uncongested , else congested.
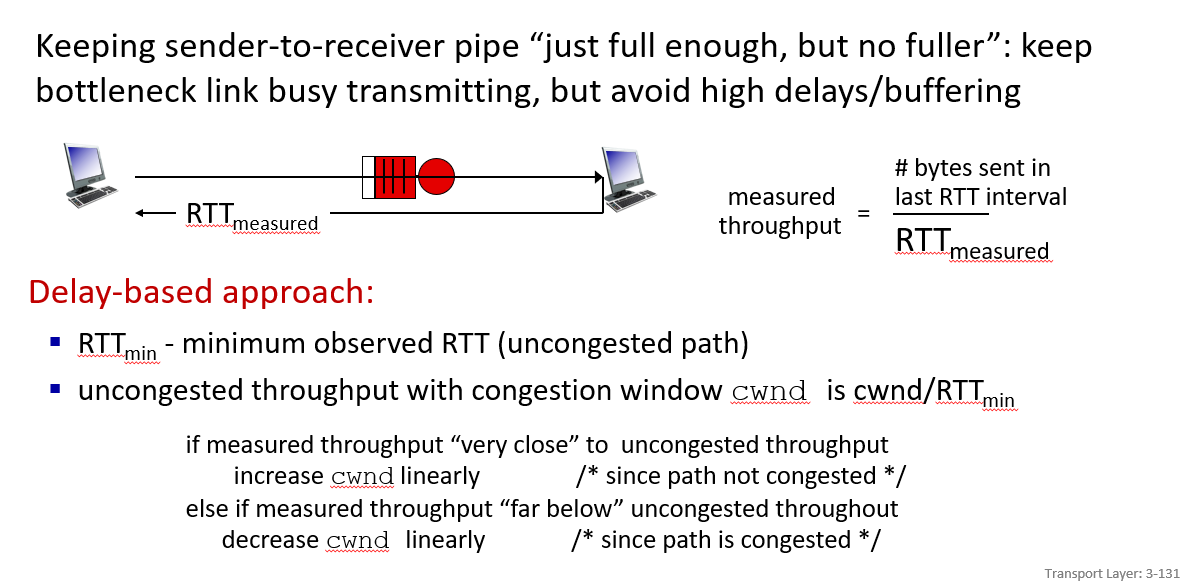

BBR:Bottleneck Bandwidth and Round-trip propagation time
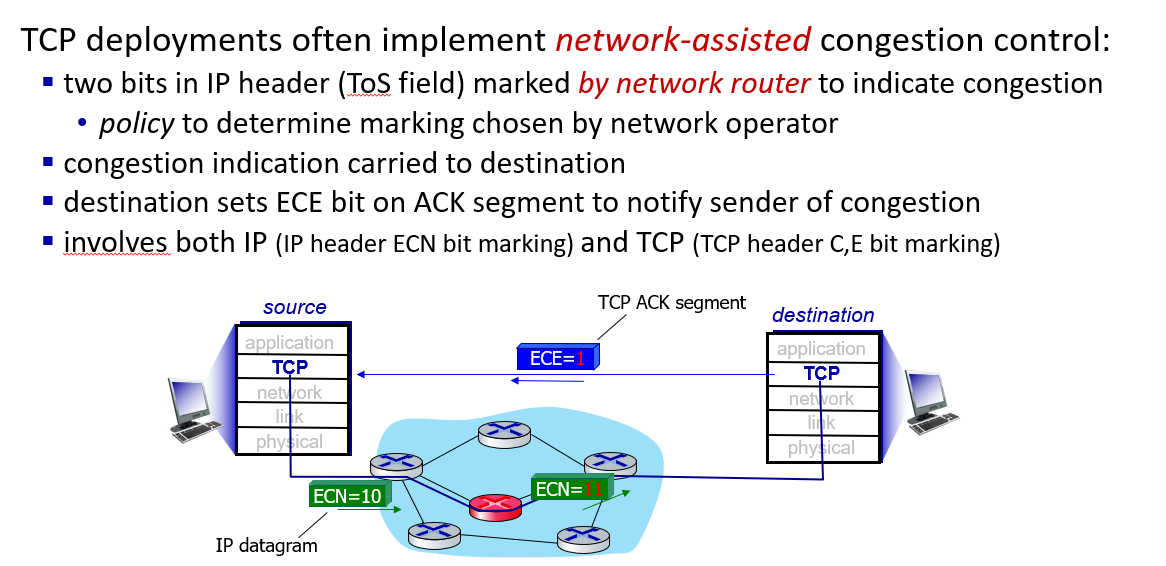
Explicit congestion notification (ECN)
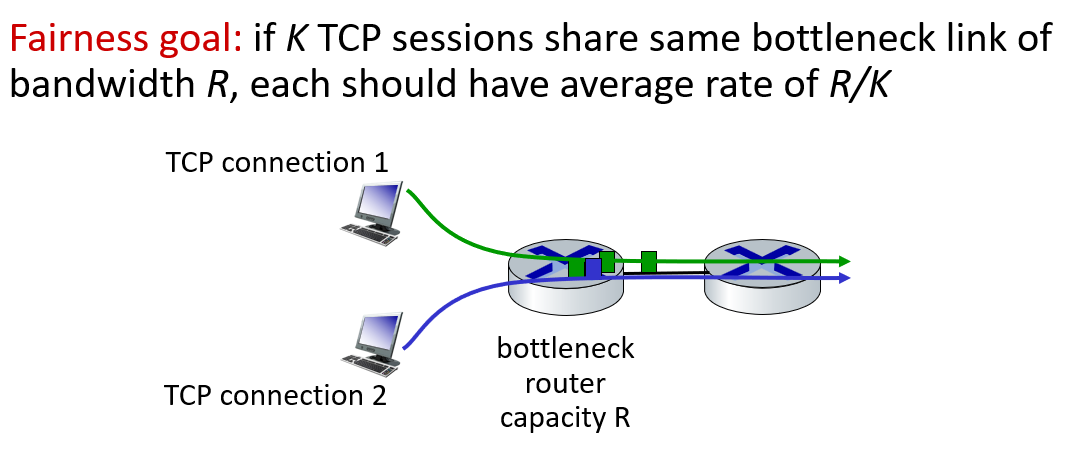
TCP fairness
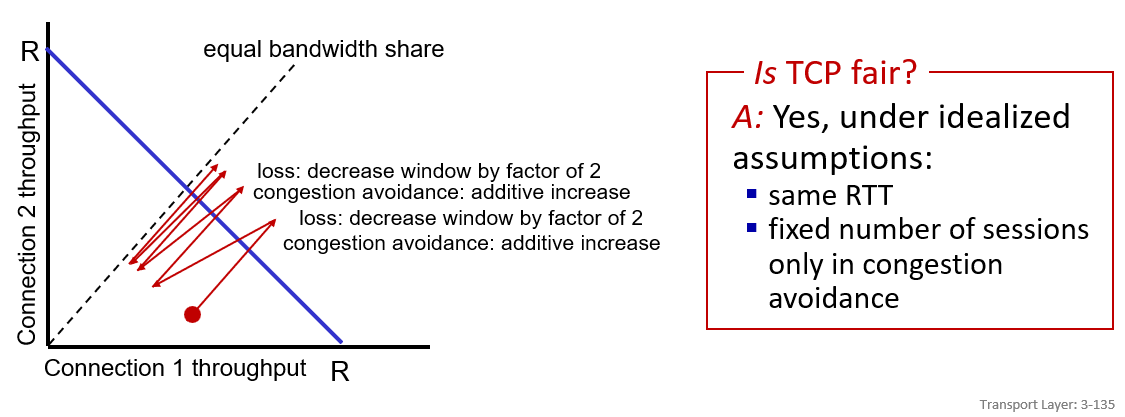
although TCP is fair,UDP and parallel TCP is not fair and may strave out the TCP connection.
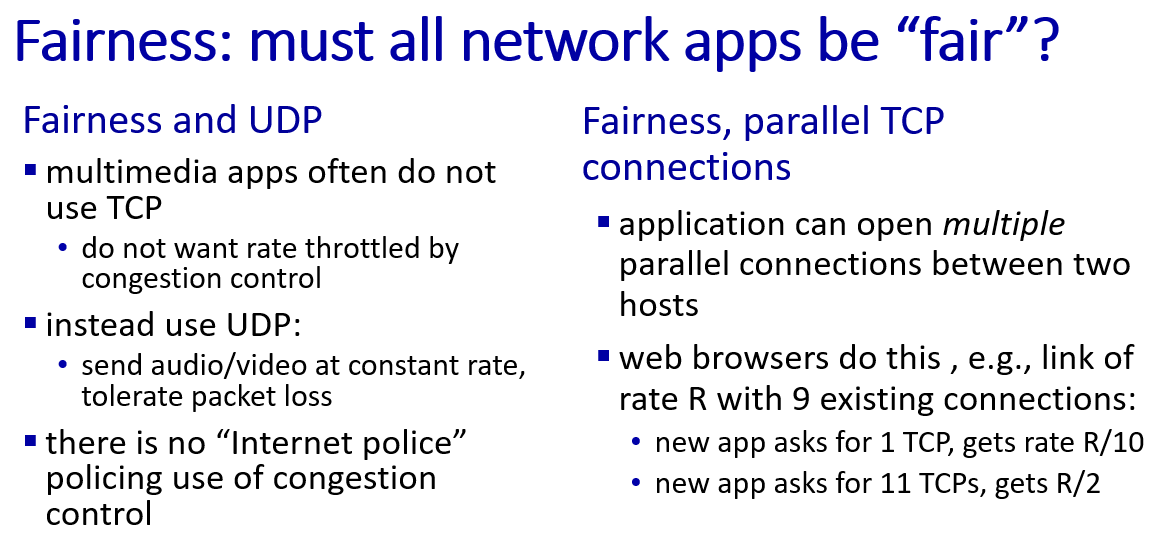
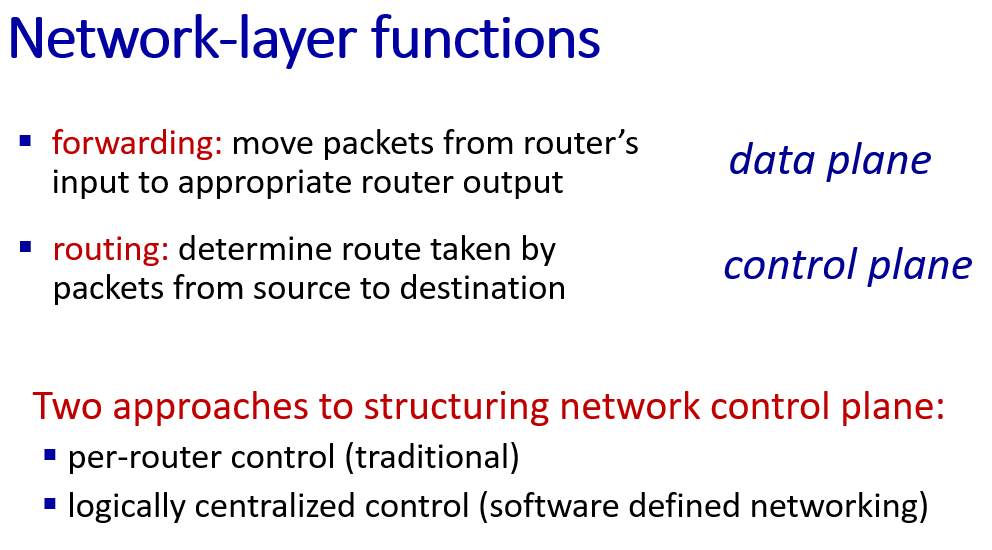
Network layer: Data plane
Nerwork layer overview
what network layer do:
- in service view:what service it provide for the upper layer
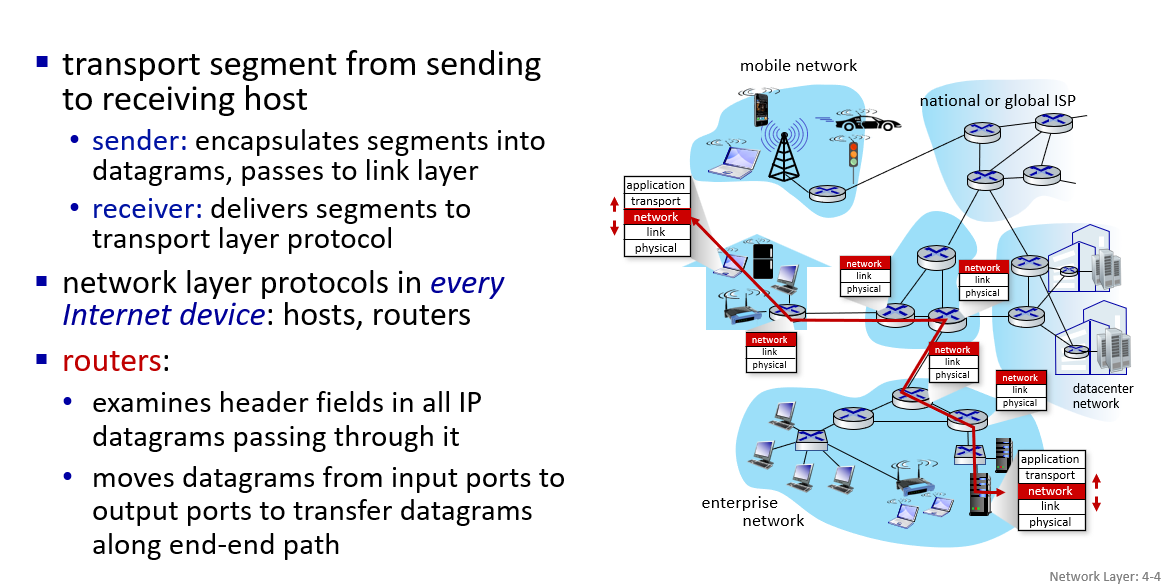
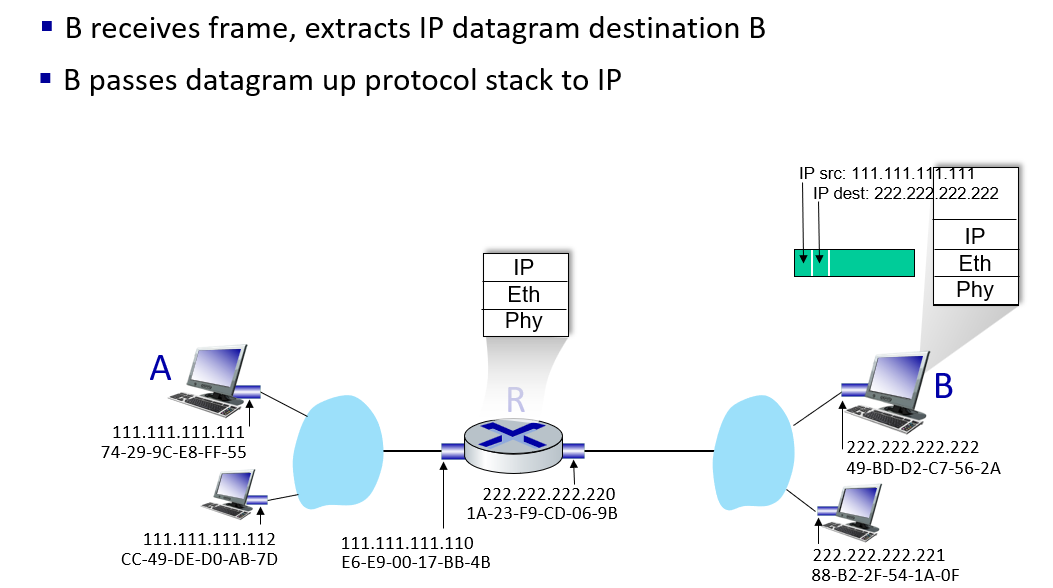
in network edge:sender add IP address to datagram,receiver extracts checksum and deliver to transport layer
in network core:forward datagram from input link to output link(not easy)
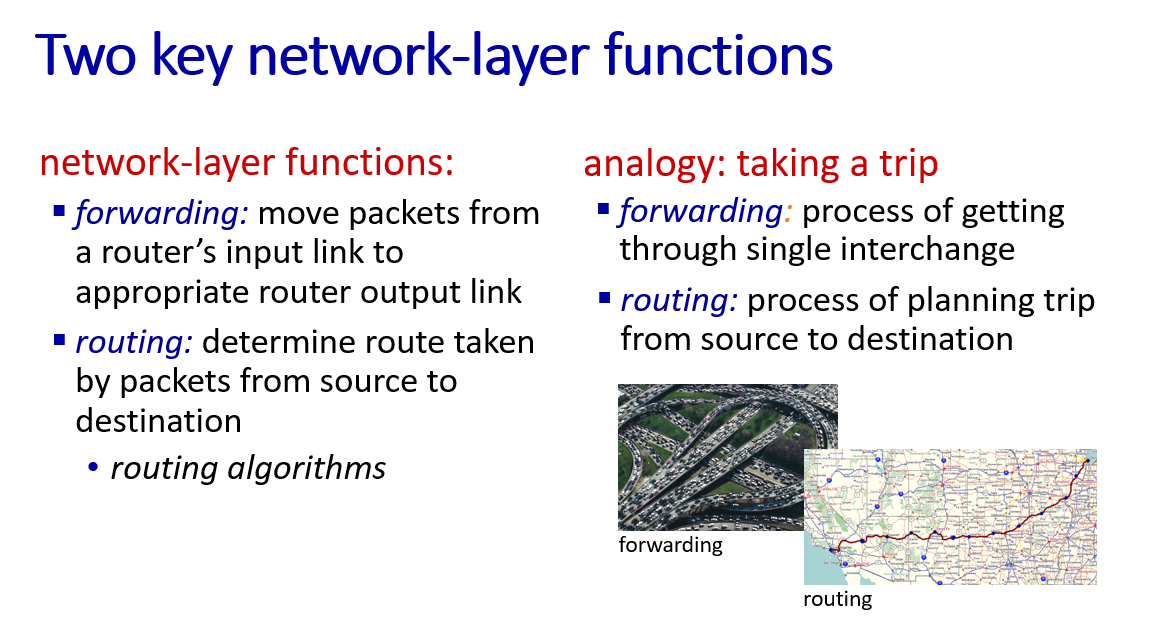
network layer divided into two topic:
- data plane(forwarding)
- control plane(routing)
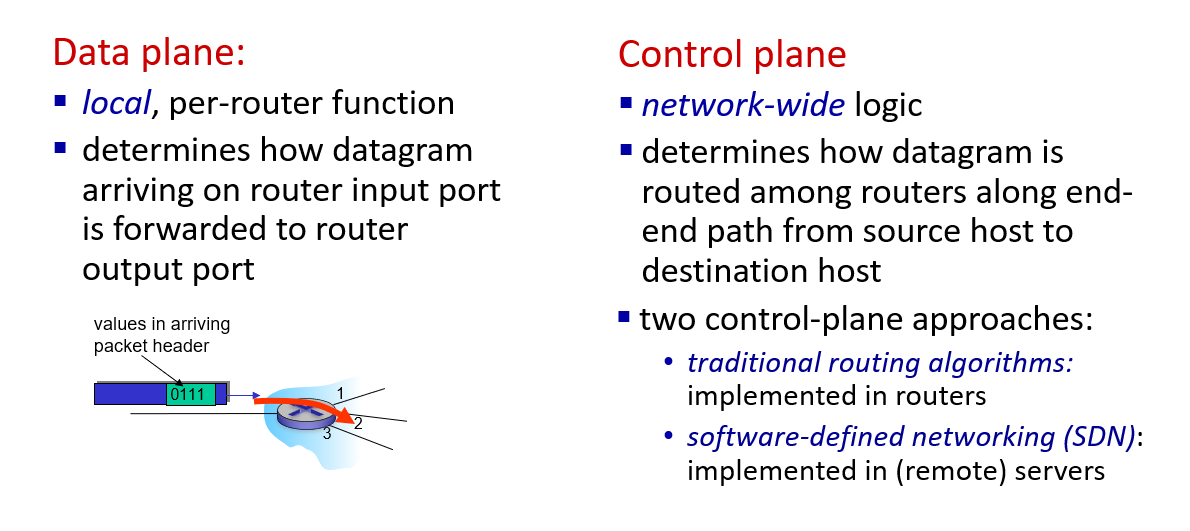
two control-plane approaches:
- (router compute the local forwarding table)
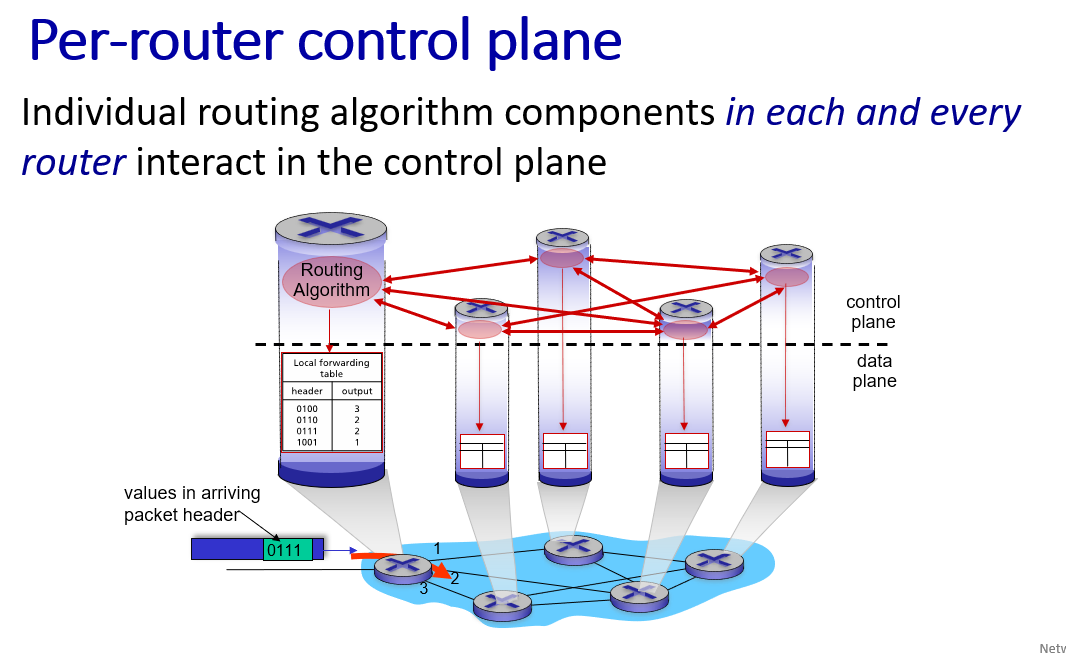
- (Remote Controller distributes the local forwarding table to each router)
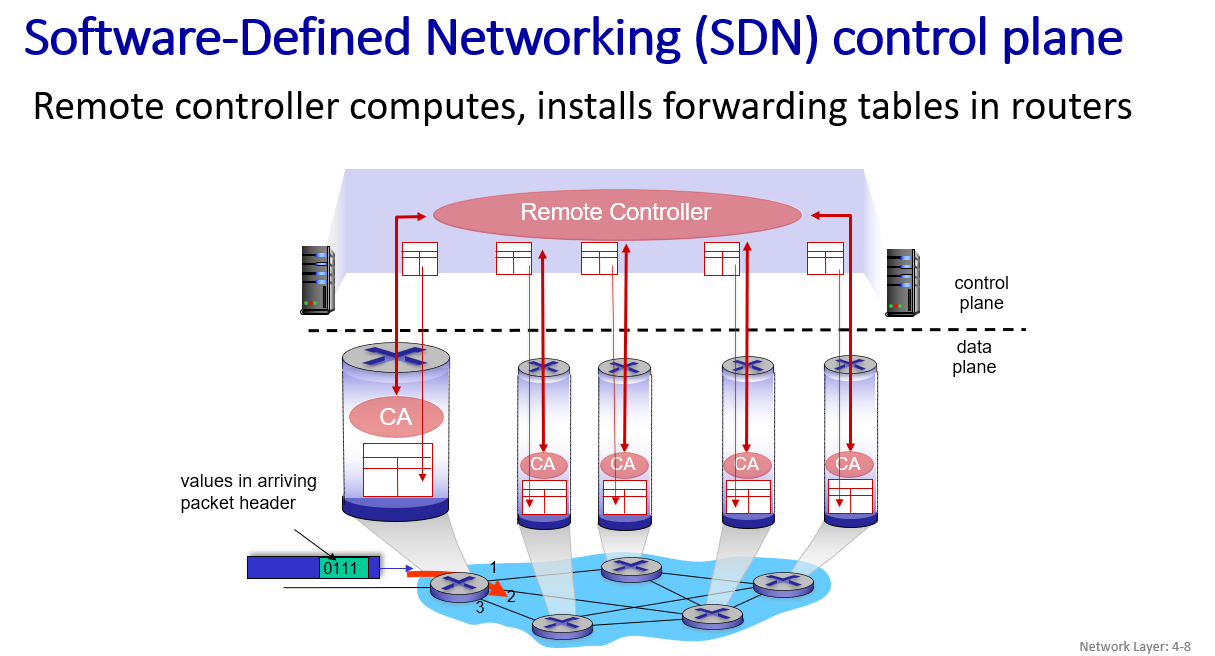
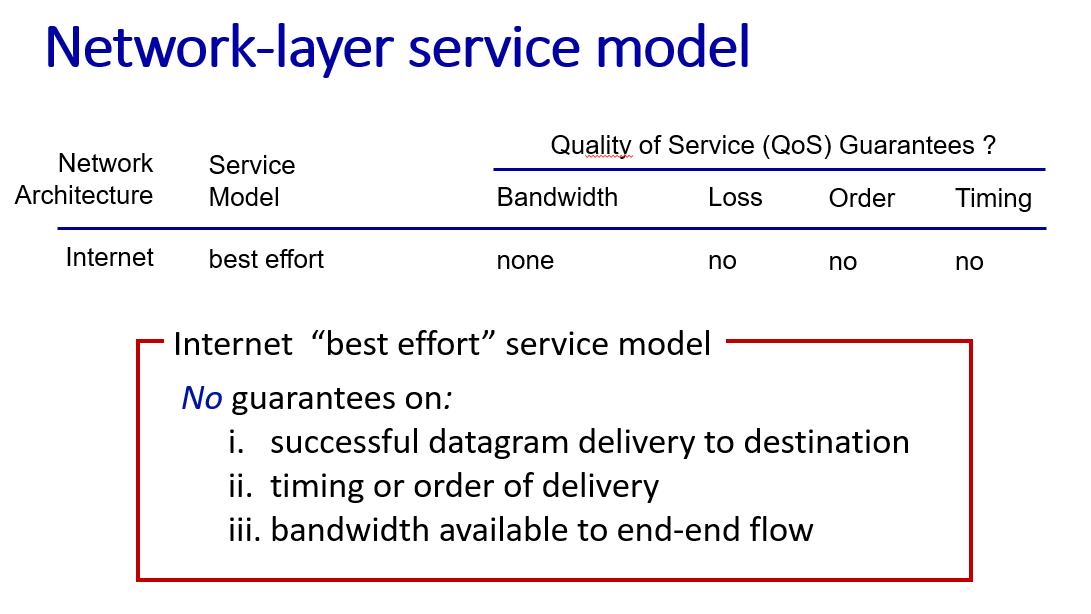
how to understand best-effort

What’s inside a router
how forwarding function implement?
Router architecture
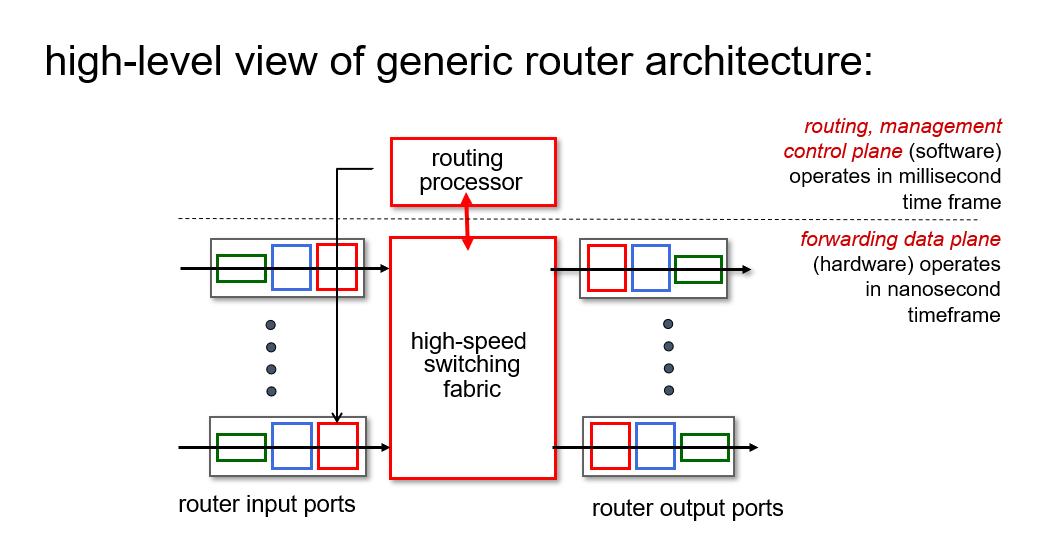
Input Port
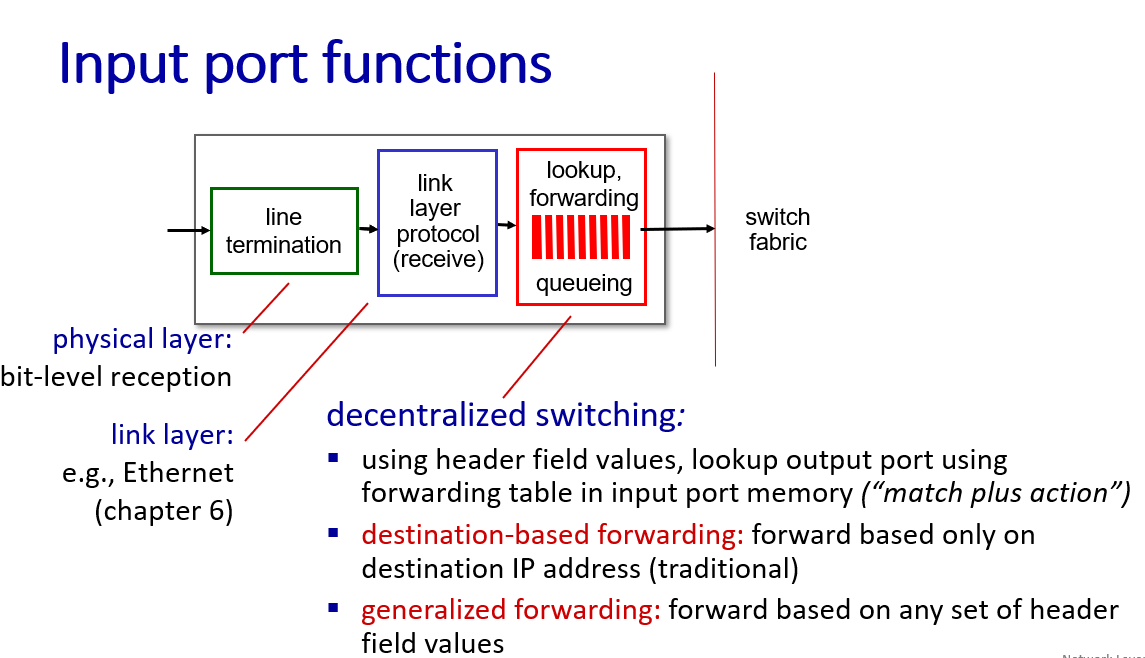
hardware implementation

Swithing fabrics
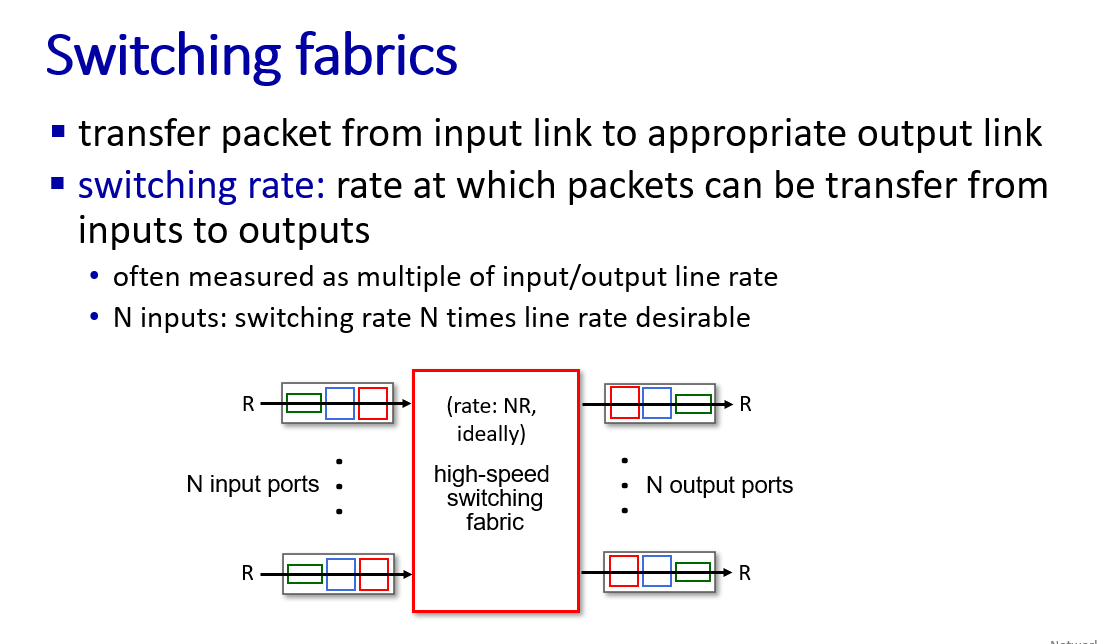
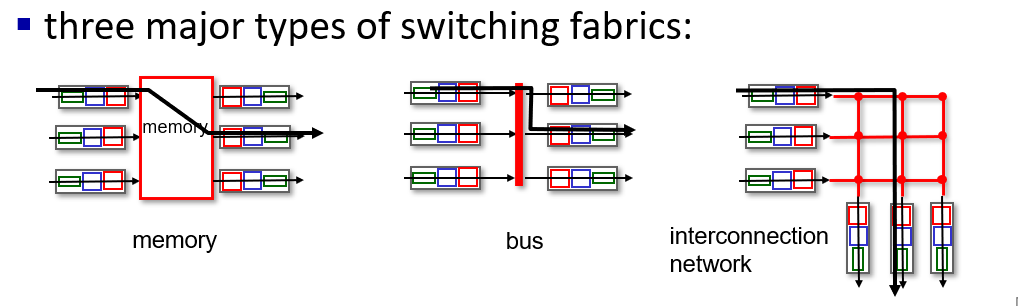
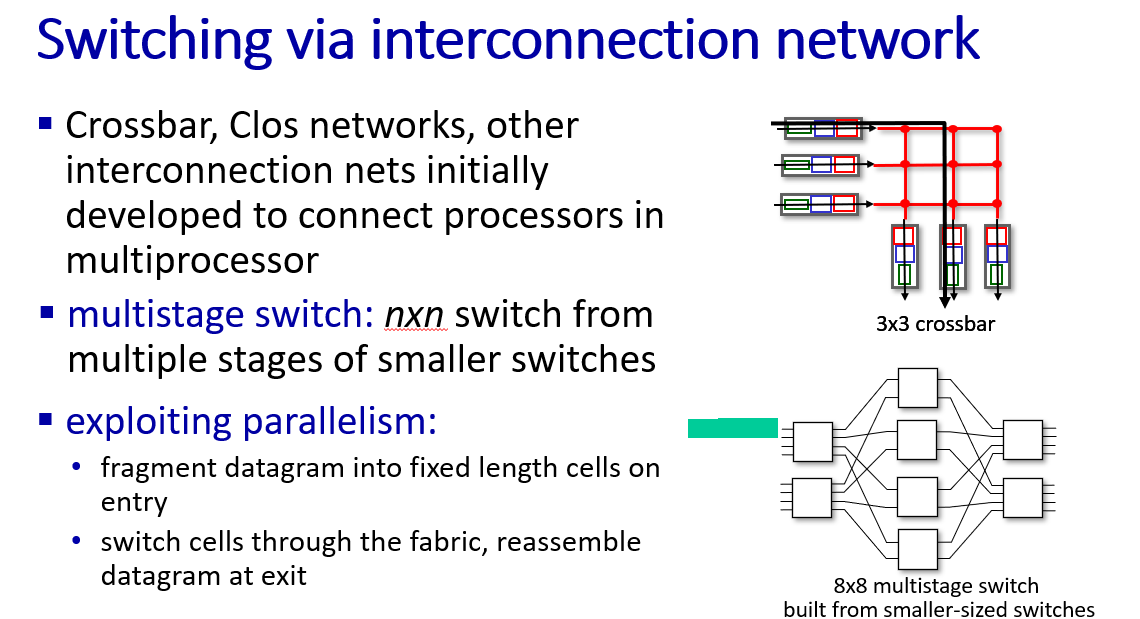
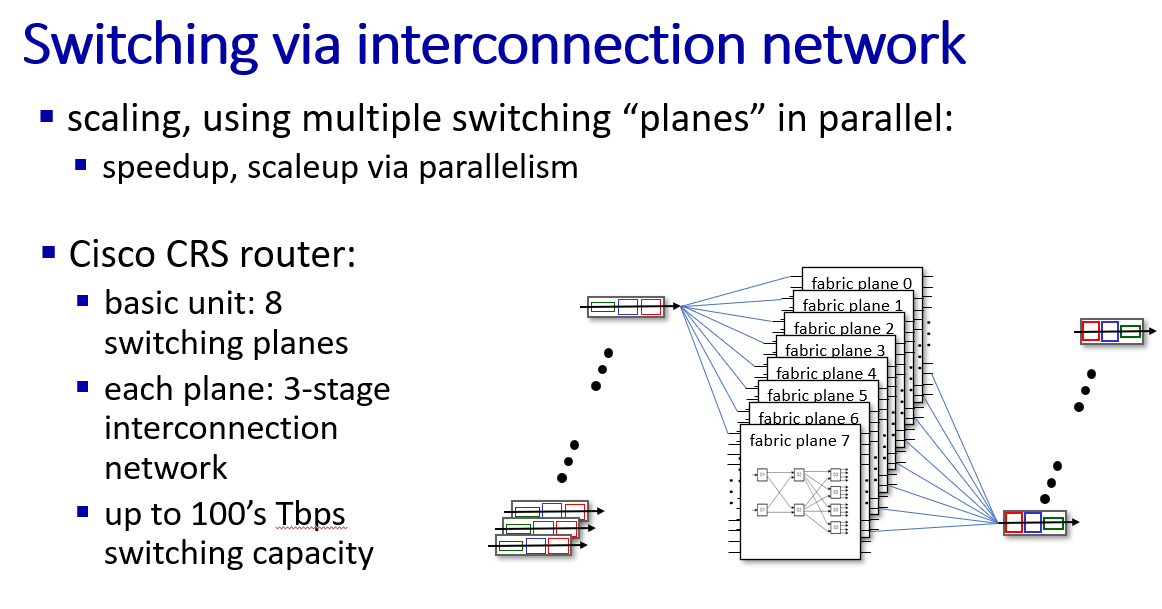
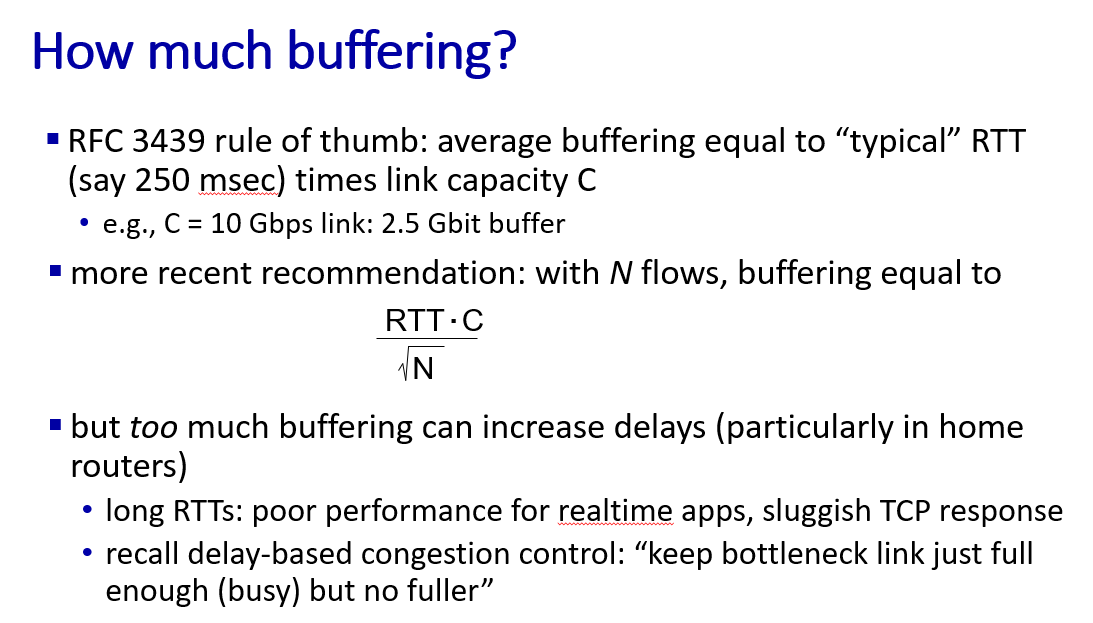
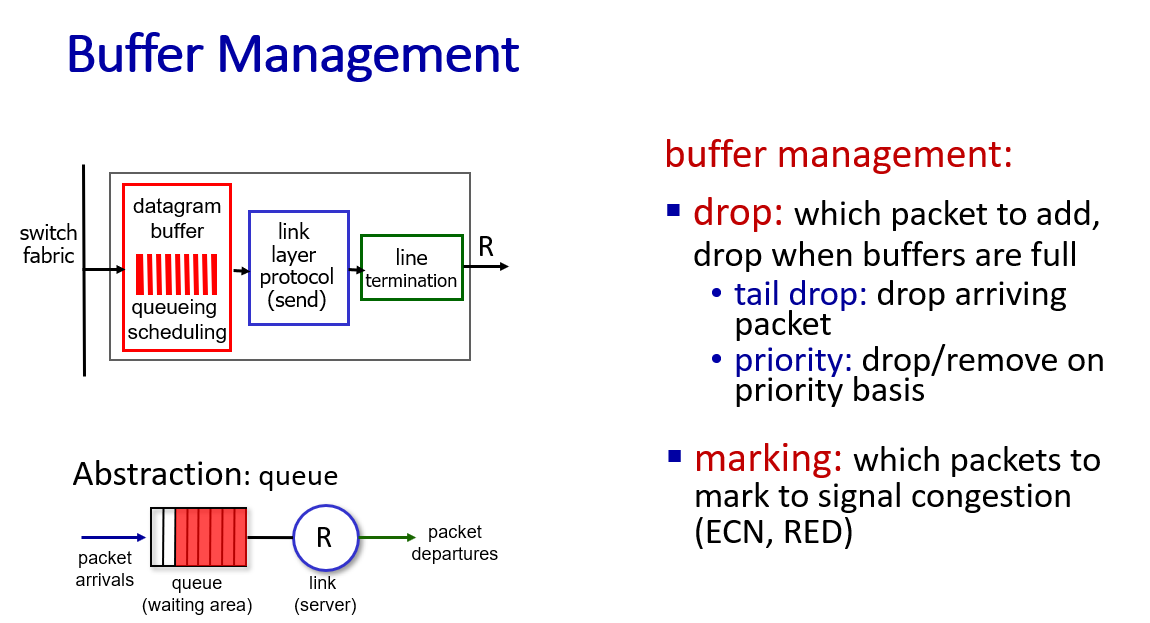
buffer management, scheduling
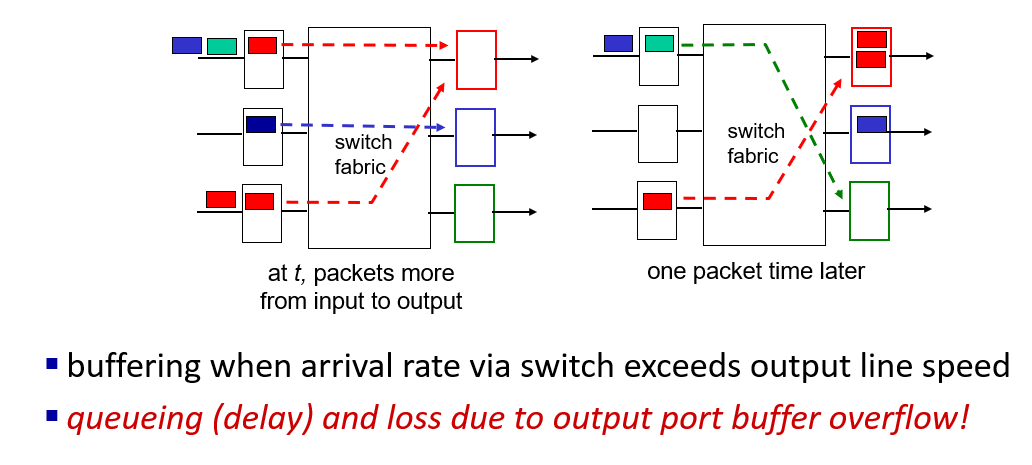
to mitigate packet loss and packet delay
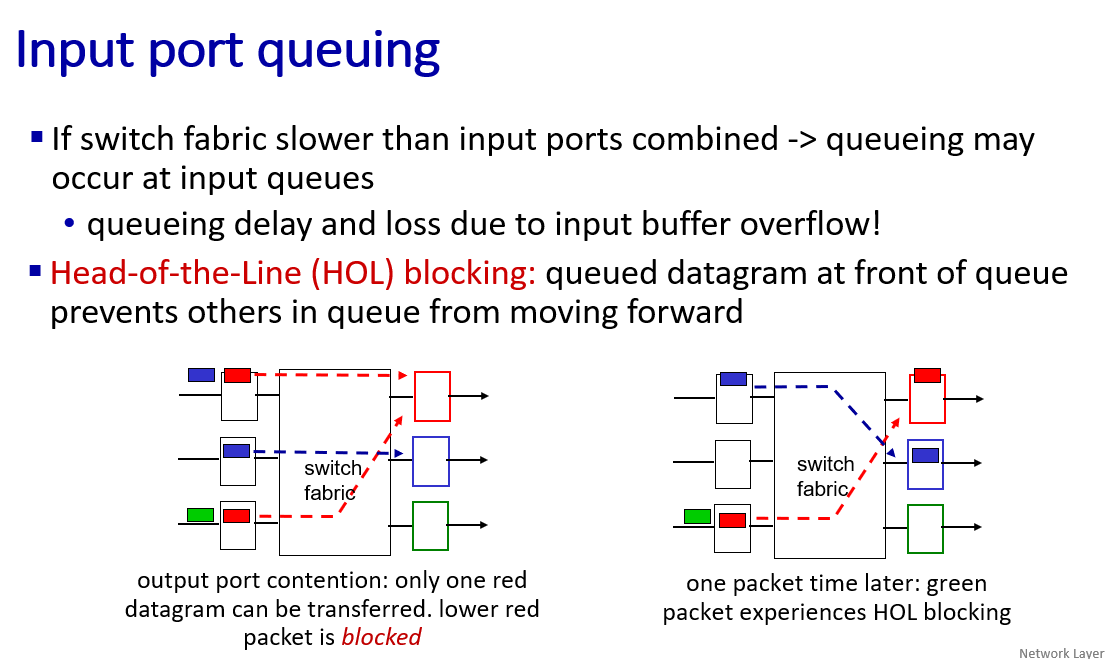
the green packet experience the head of line blocking
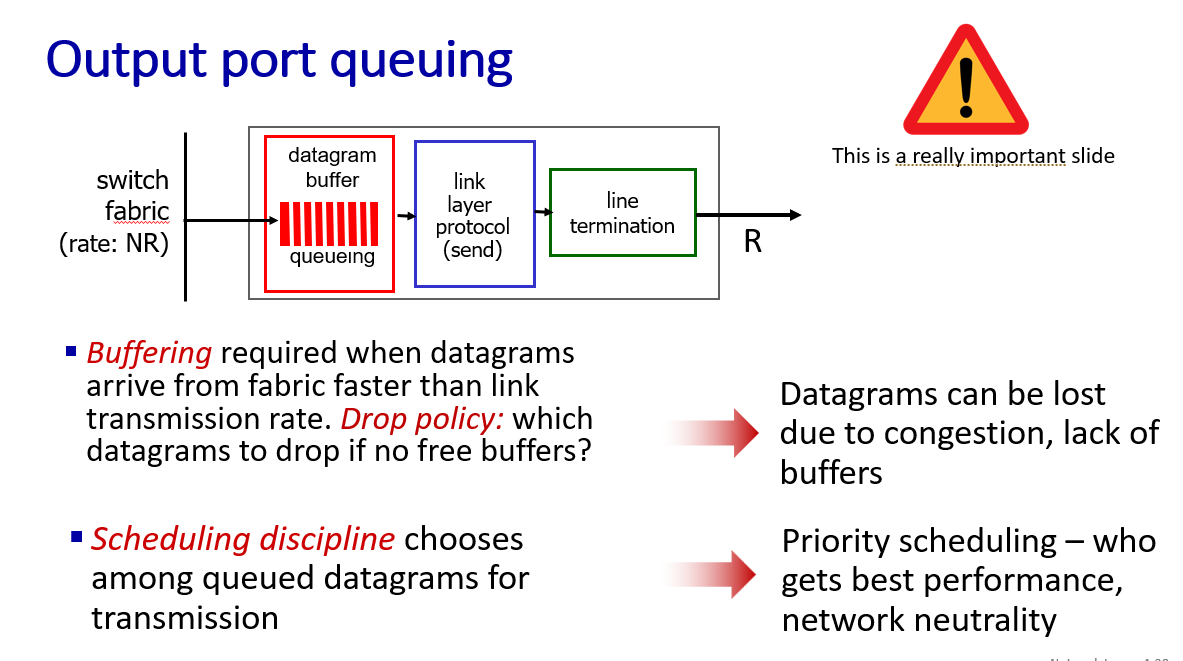

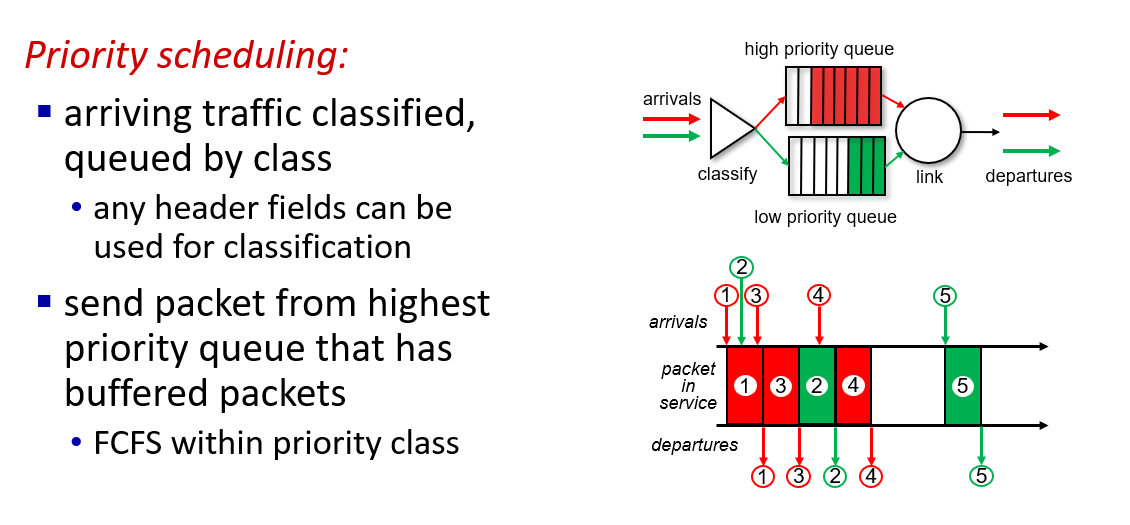
- FCFS:FIFO
- priority
- RR
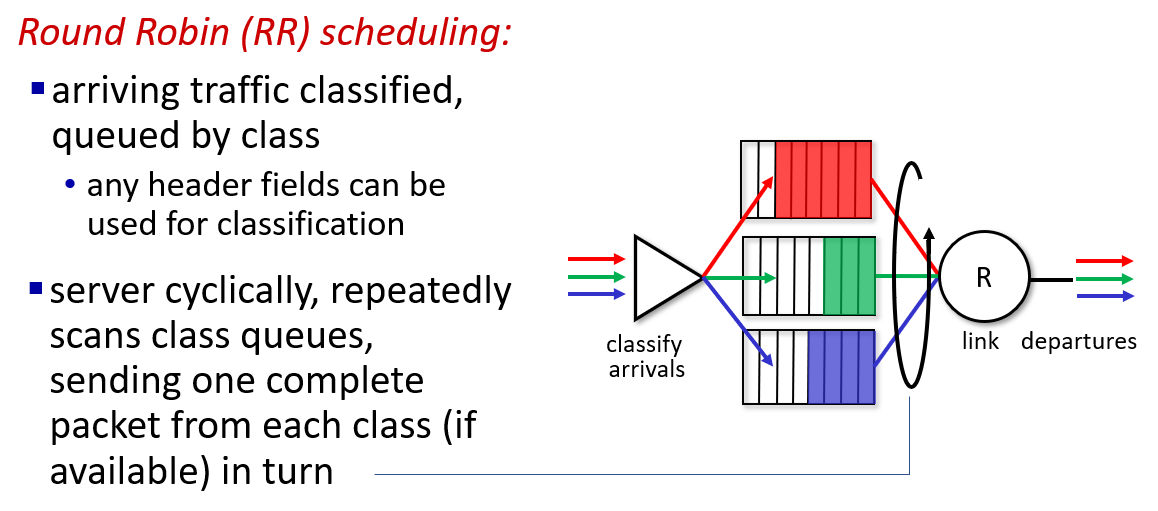
- WFQ
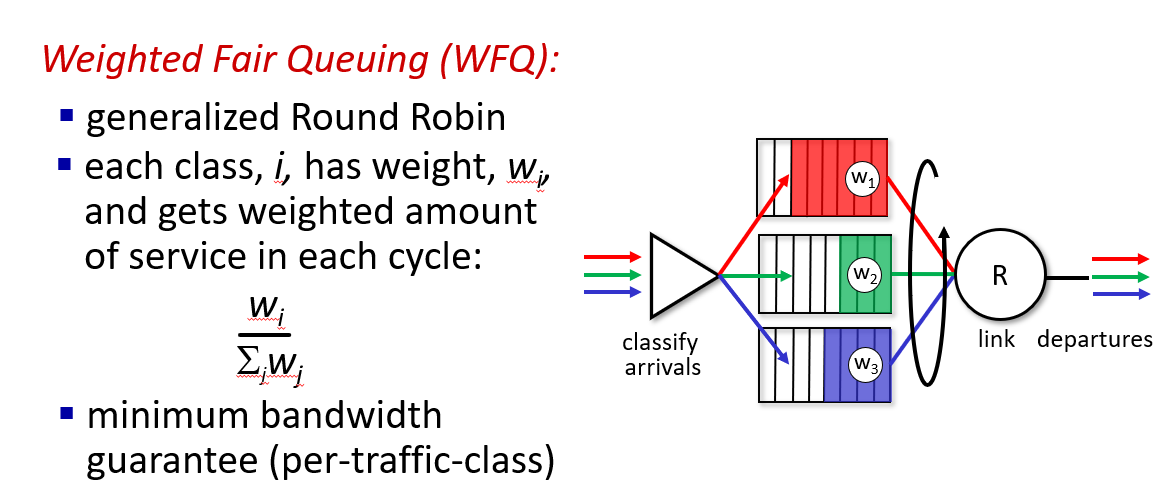
IP: the Internet Protocol
about:
- datagram format
- addressing
- packet handling
IPv4:
head length 这个字段占4位,它的单位是32位字(4字节),因此可以表示的首部长度的范围是0到15个32位字
offset 字段表示当前片段在原始数据包中的位置。单位是8字节
length 用于指示整个IP数据报(包括IP首部和数据部分)的总长度。这个字段占16位,单位是字节,但数据包最大字节数为MTU。
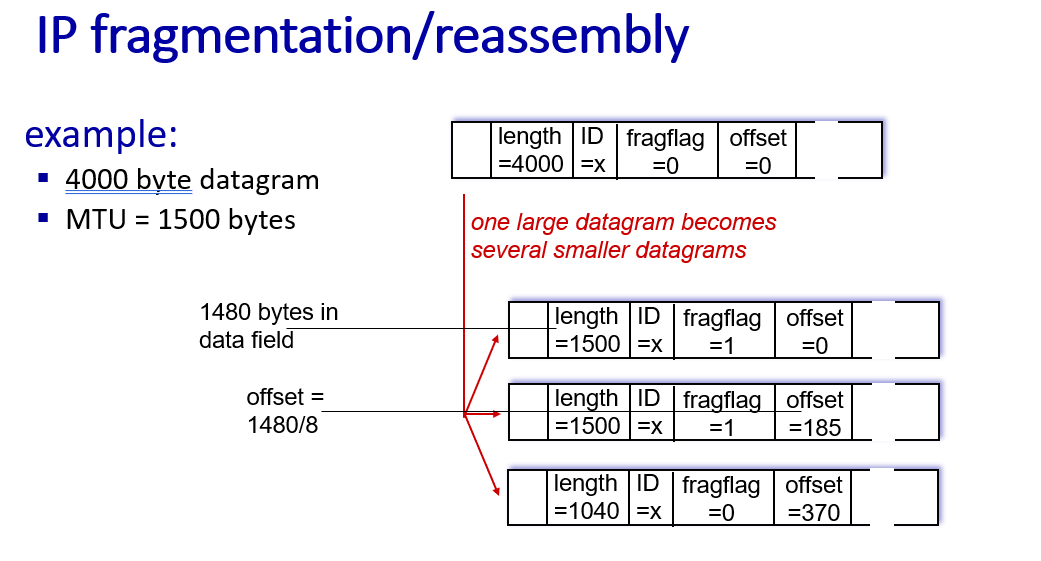
MTU:network links have MTU (max. transfer size) - largest possible link-level frame
MSS:TCP报文段中报文的最大长度为1460=1500-20-20
185*8=1480 bytes
addressing:
IP address identify interface
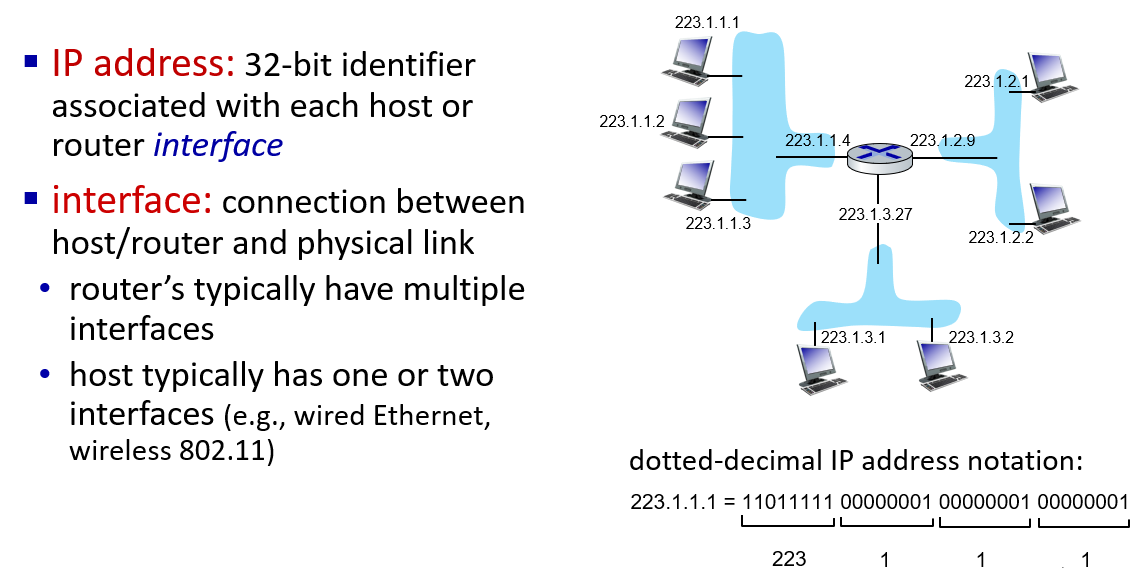
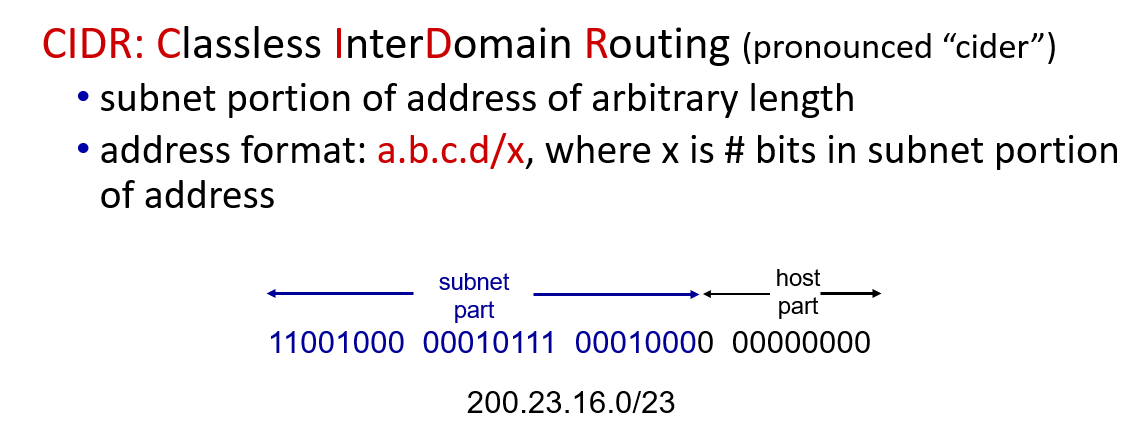
how to get one IP address

0.0.0.0:not have a IP address yet
255.255.255.255:broadcast to all interface in a subnet


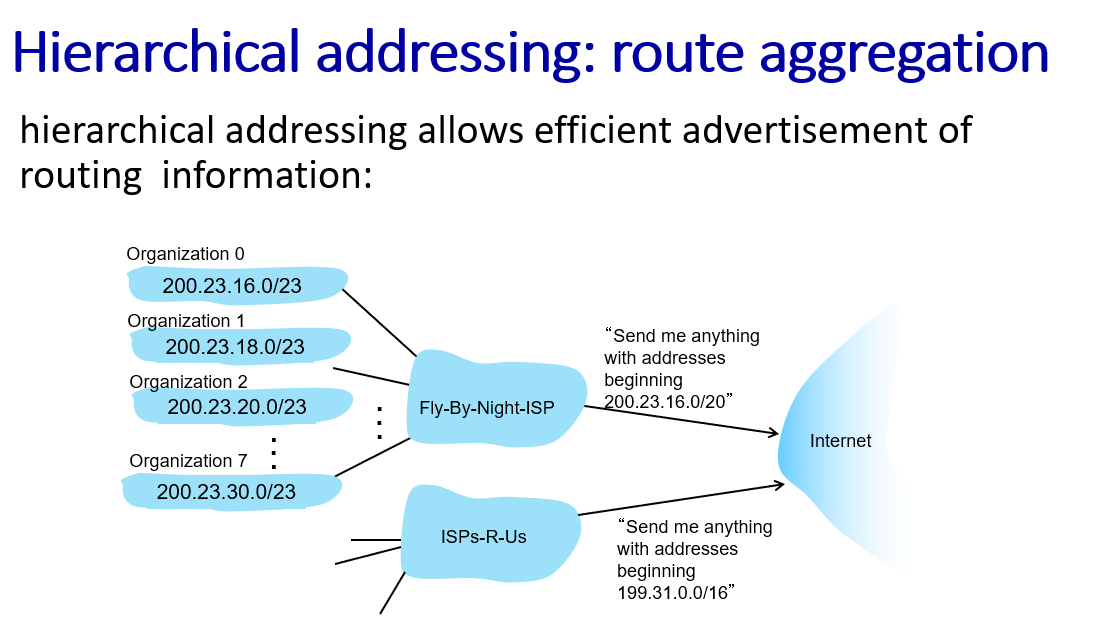
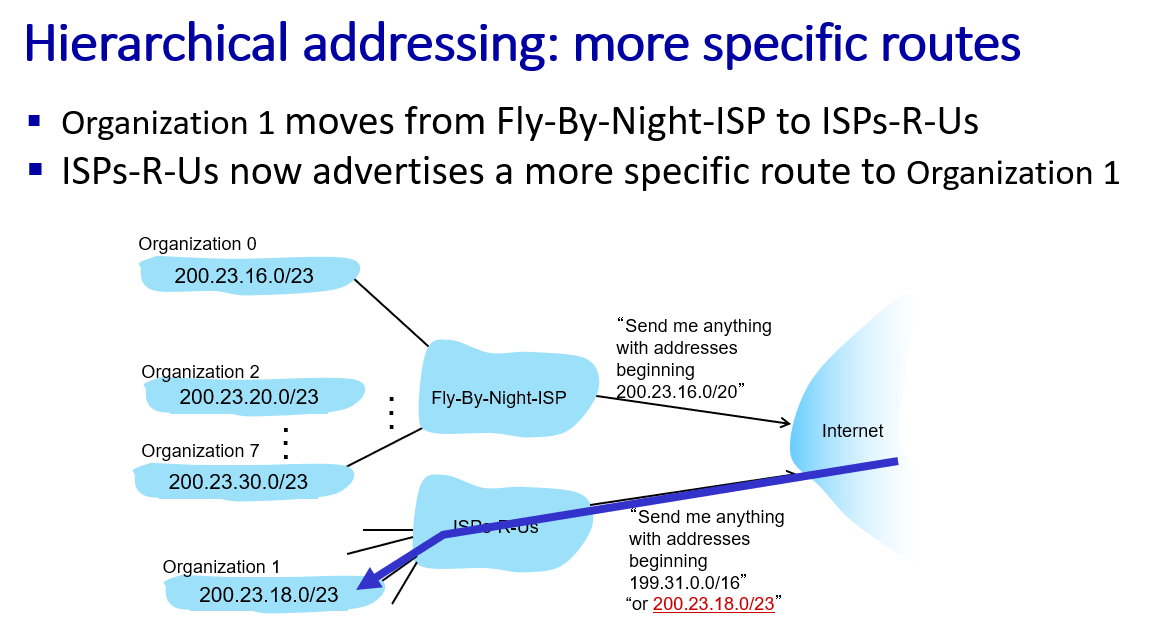

NAT
network address translation:all devices in local network share just one IPv4 address as far as outside world is concerned
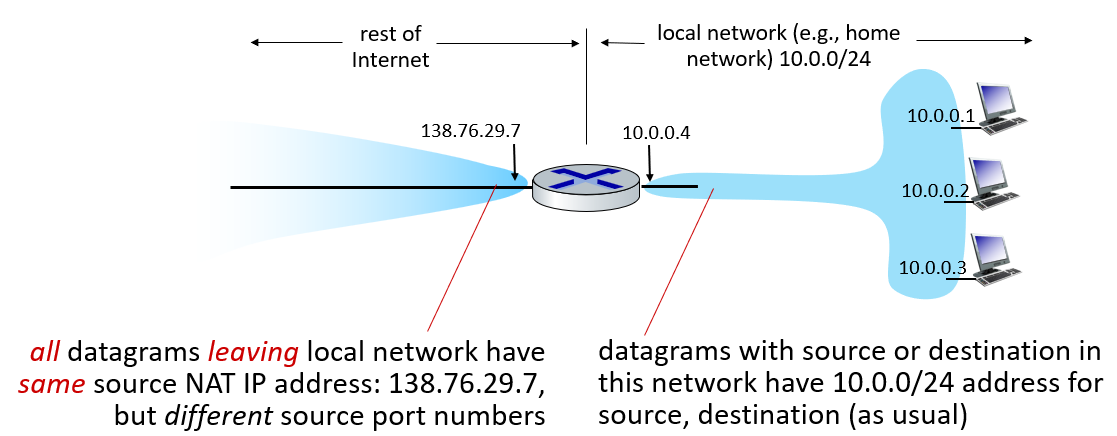

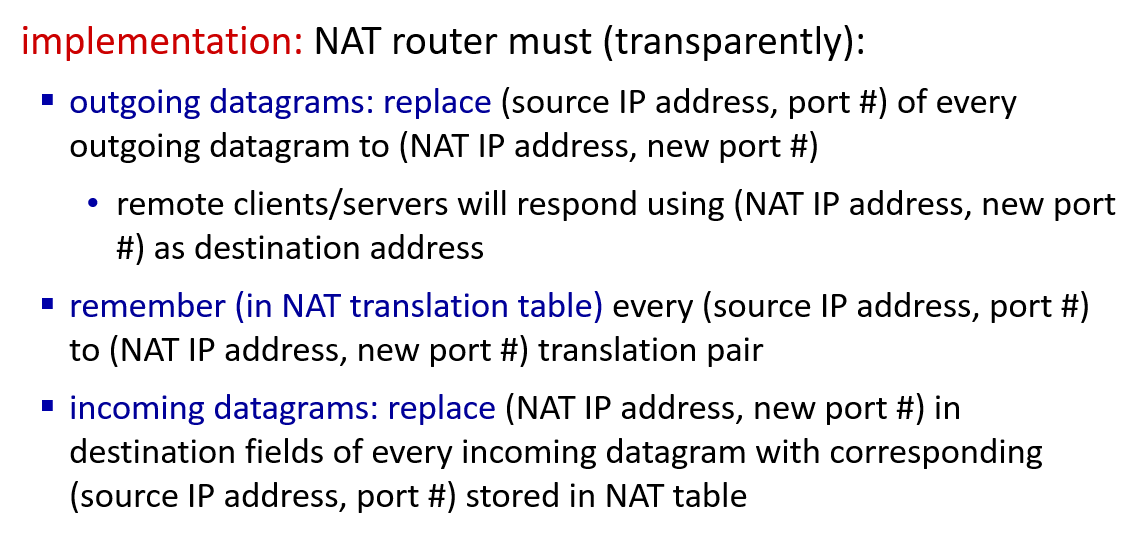
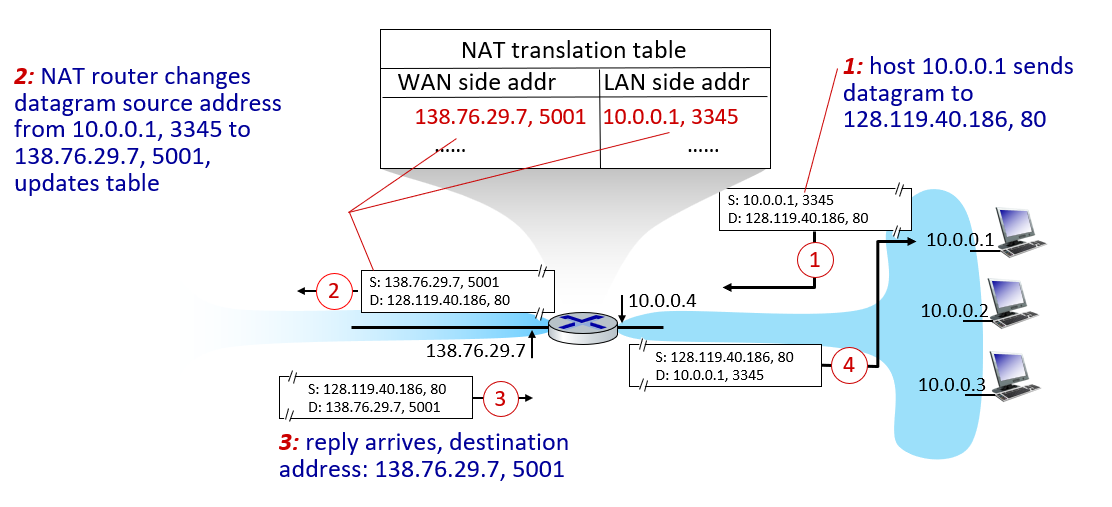
how to implement NAT
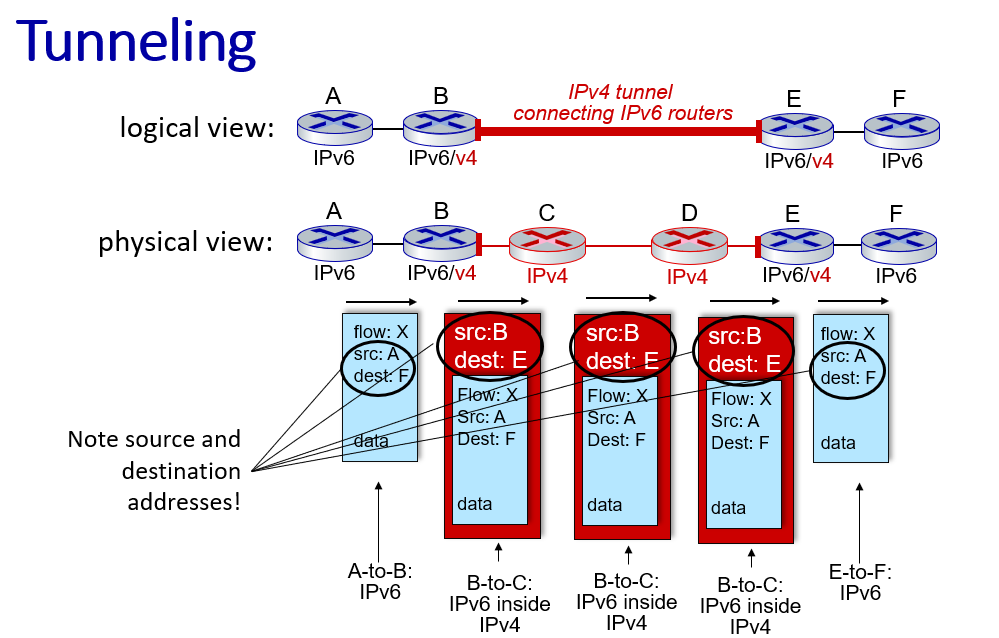
IPv6

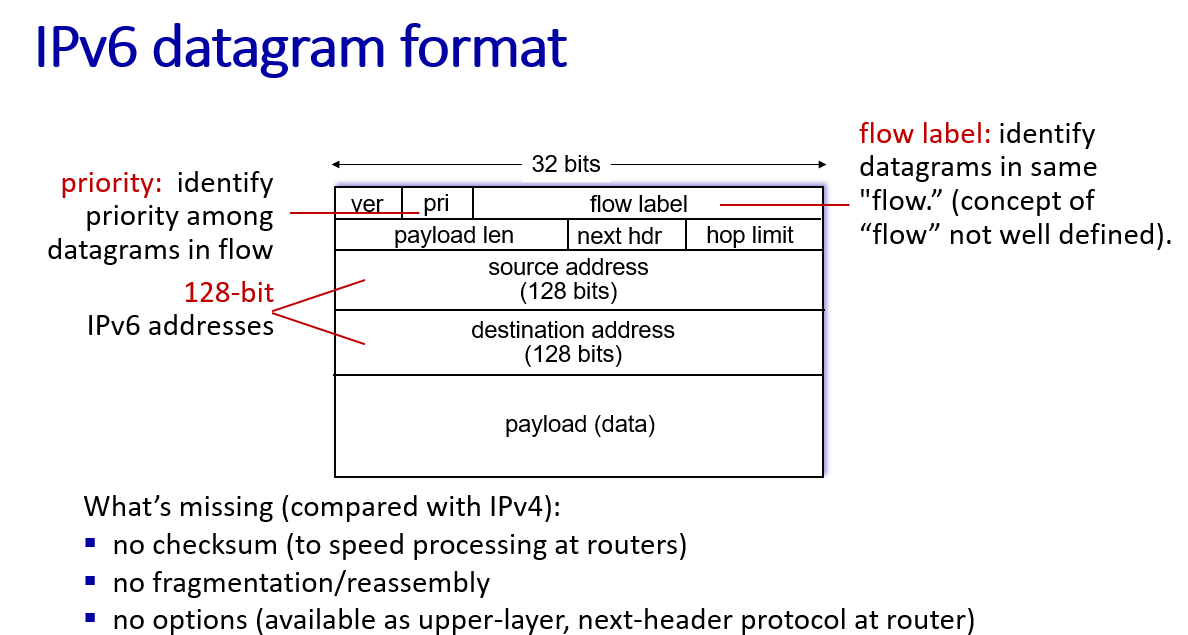
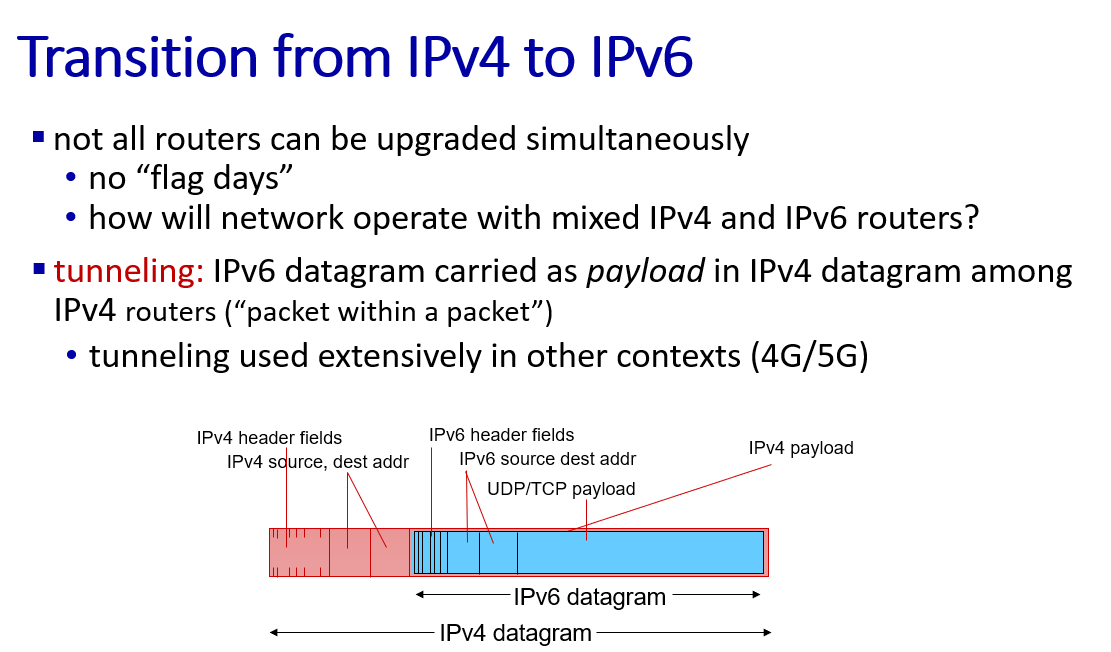
because F is a IPv6(128 bit) address and cannot contain in an IPv4 datagram.
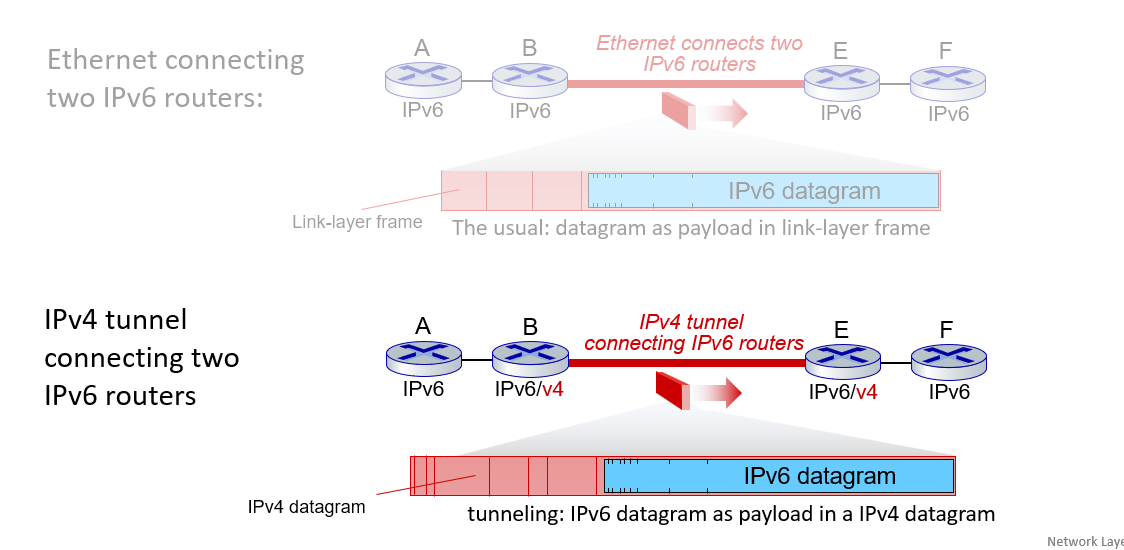
therefore the IPv4 header can be considered as a linker layer header.
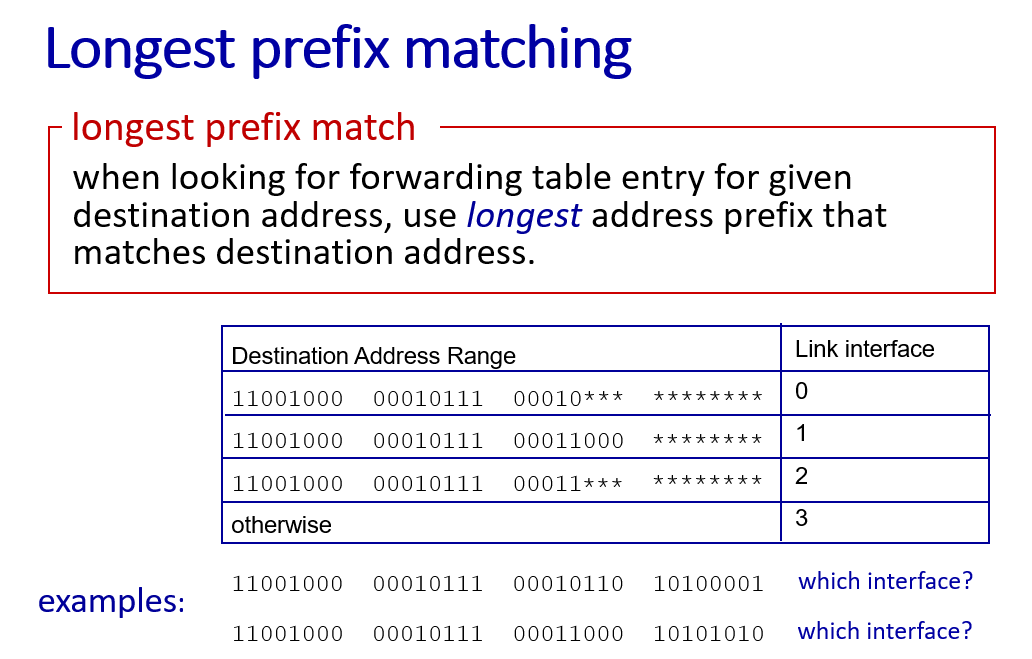
Generalized Forwarding
match+action
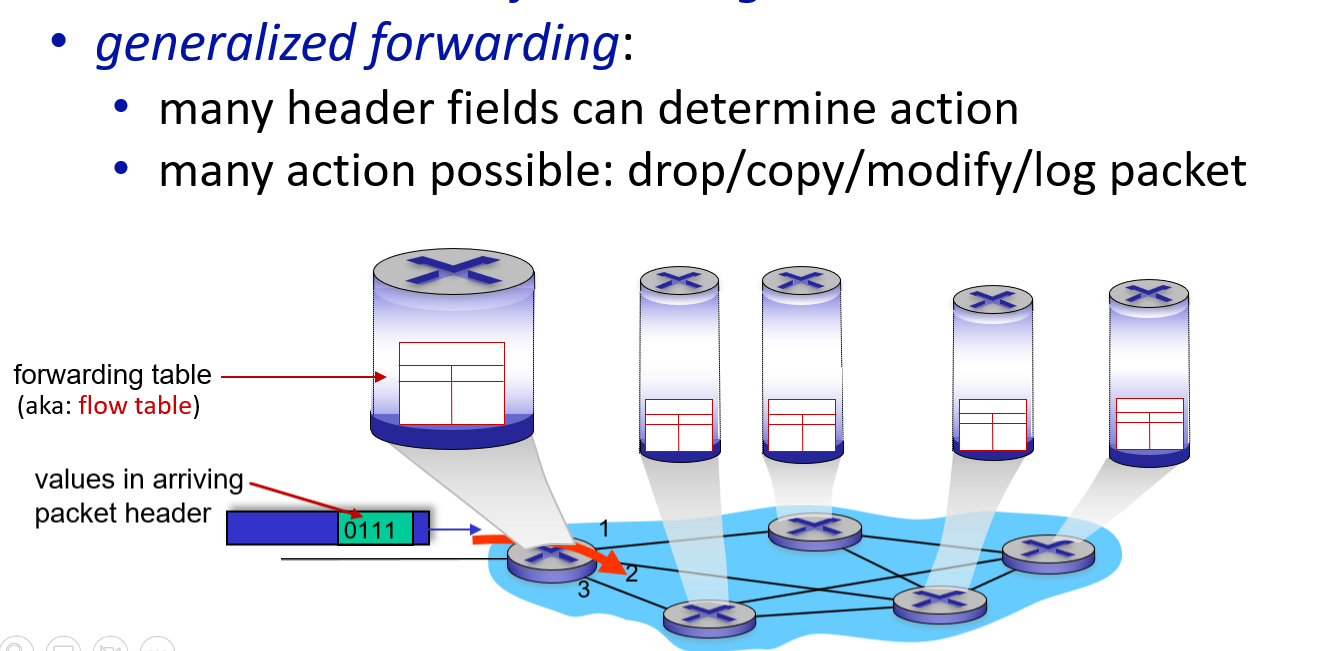
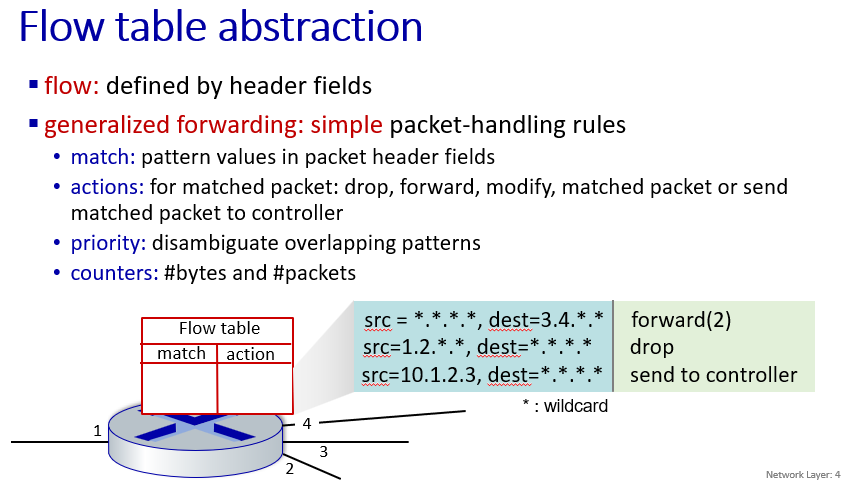
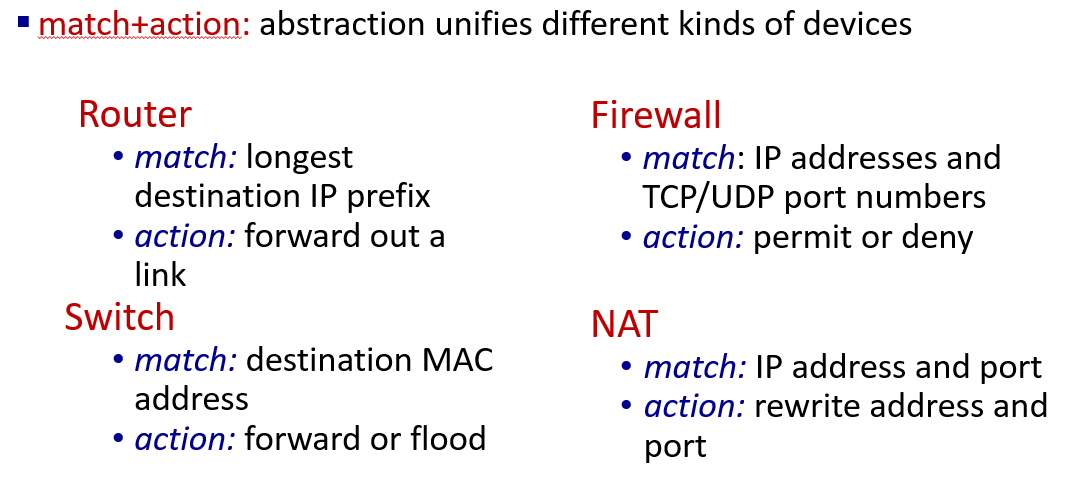
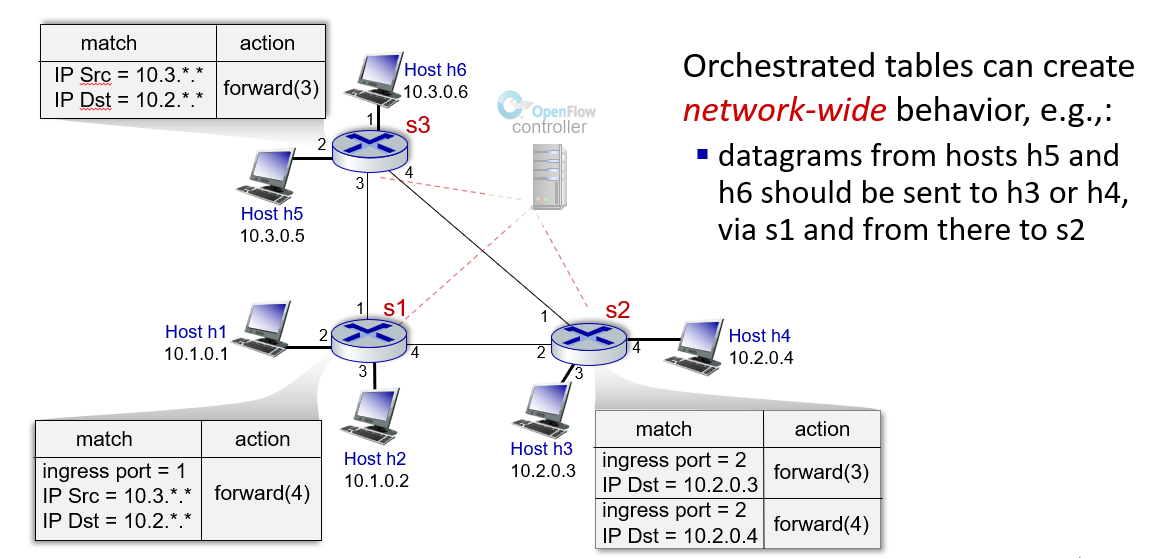
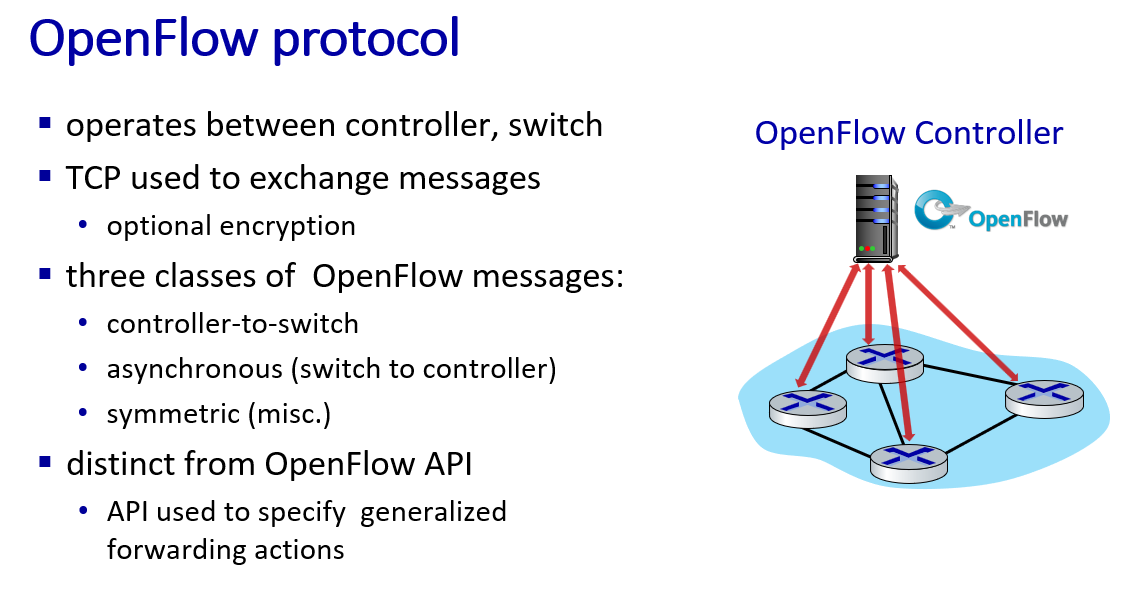
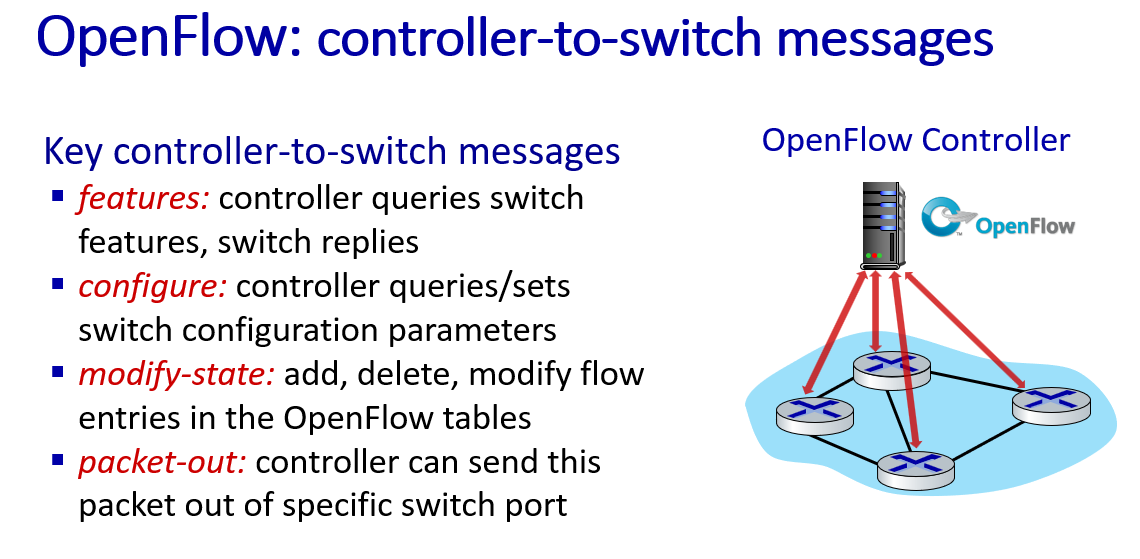
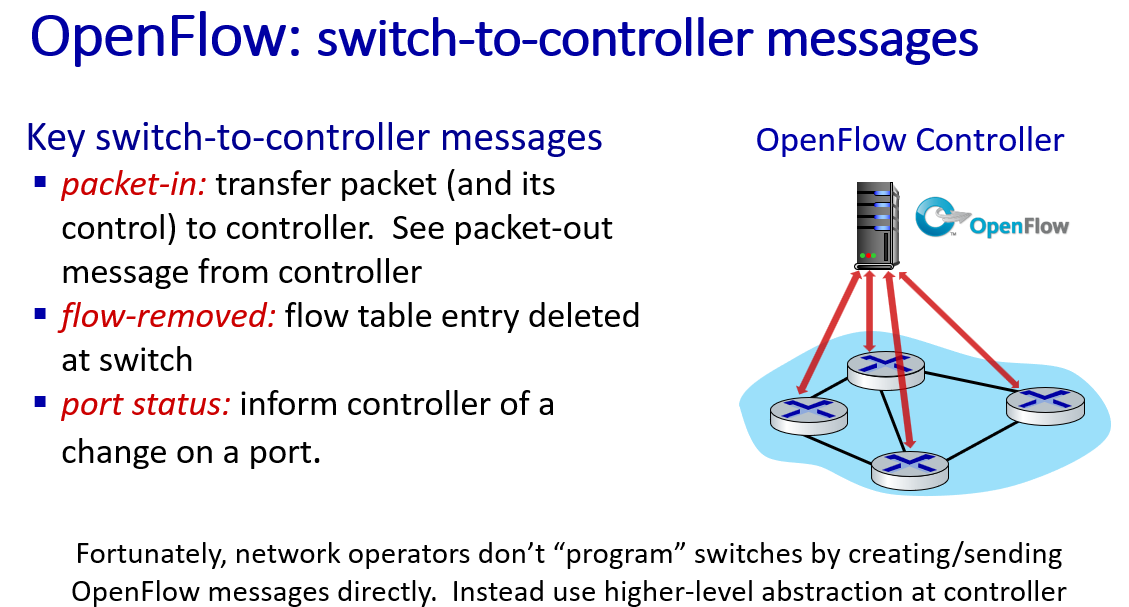
generalized forwarding standard: OpenFlow
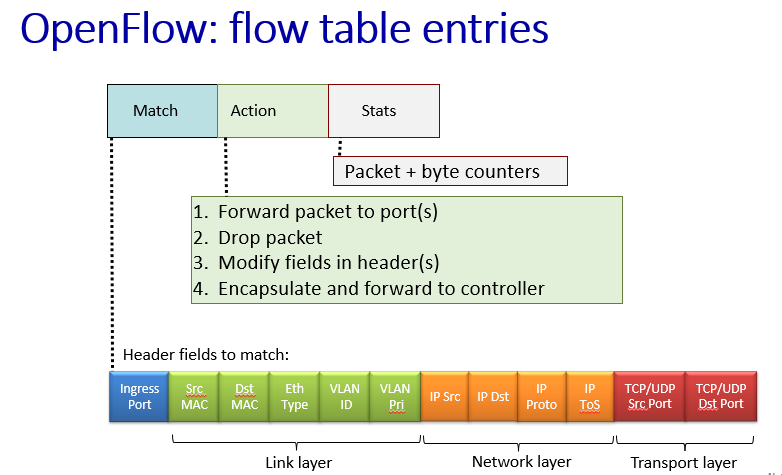
OpenFlow: examples
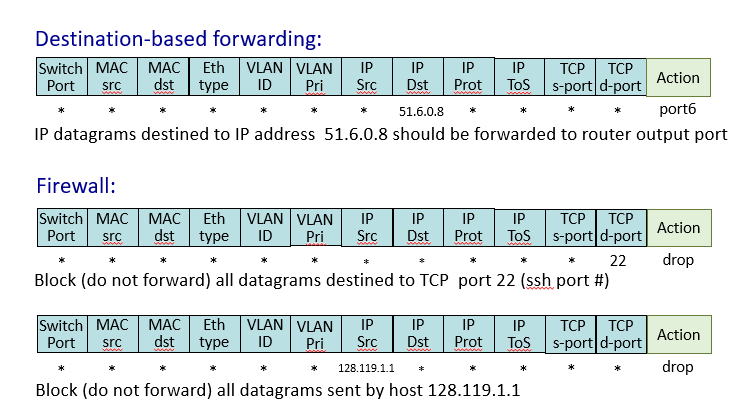
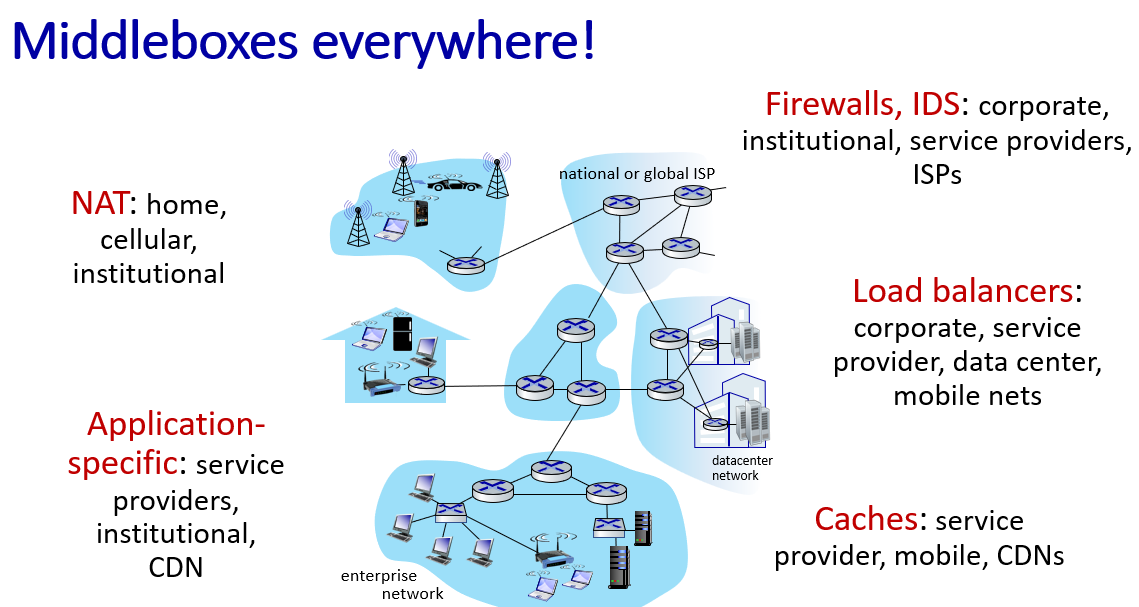
Middleboxes

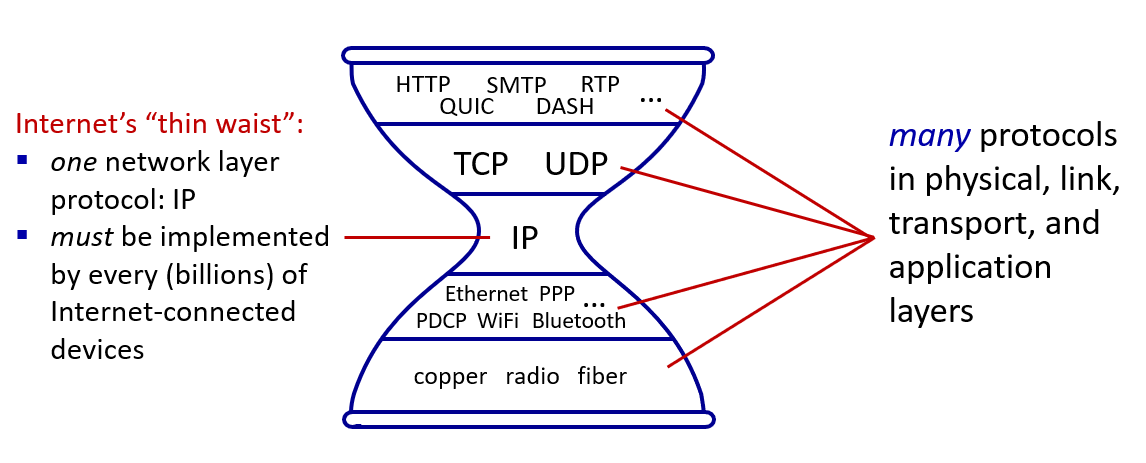

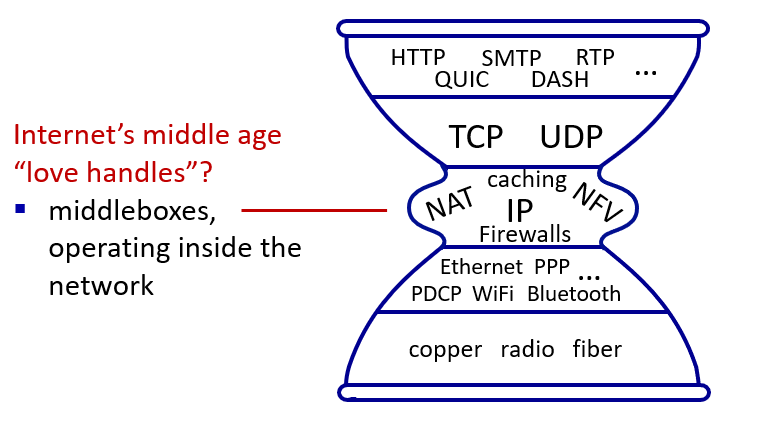
Network layer Architectural

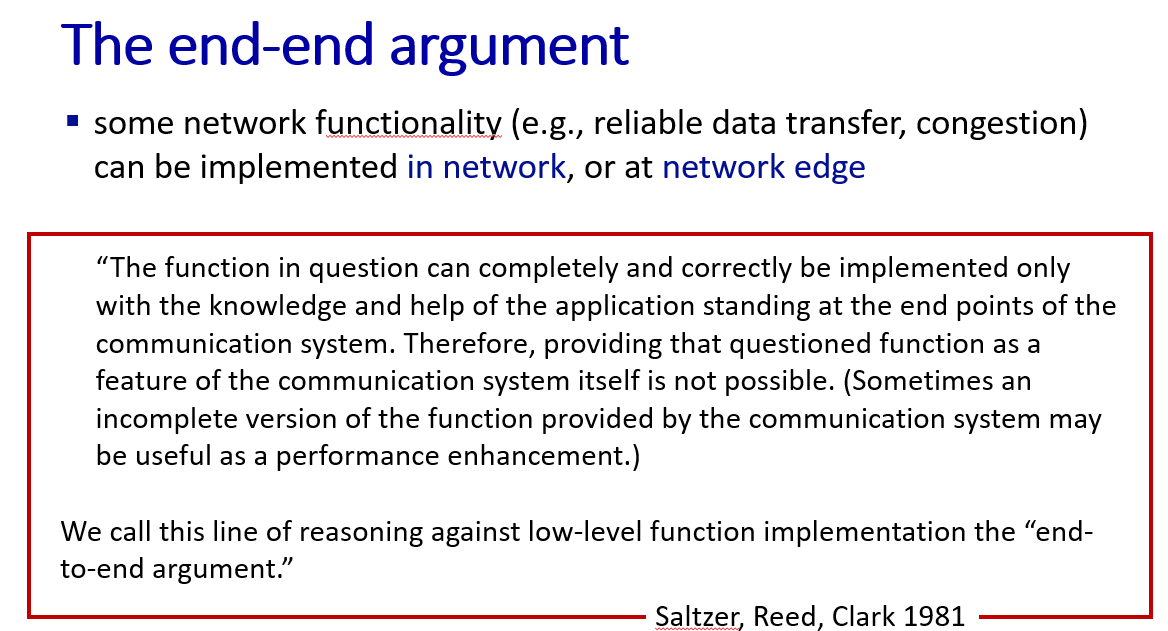
with middle boxes(mostly programable whiteboxes)
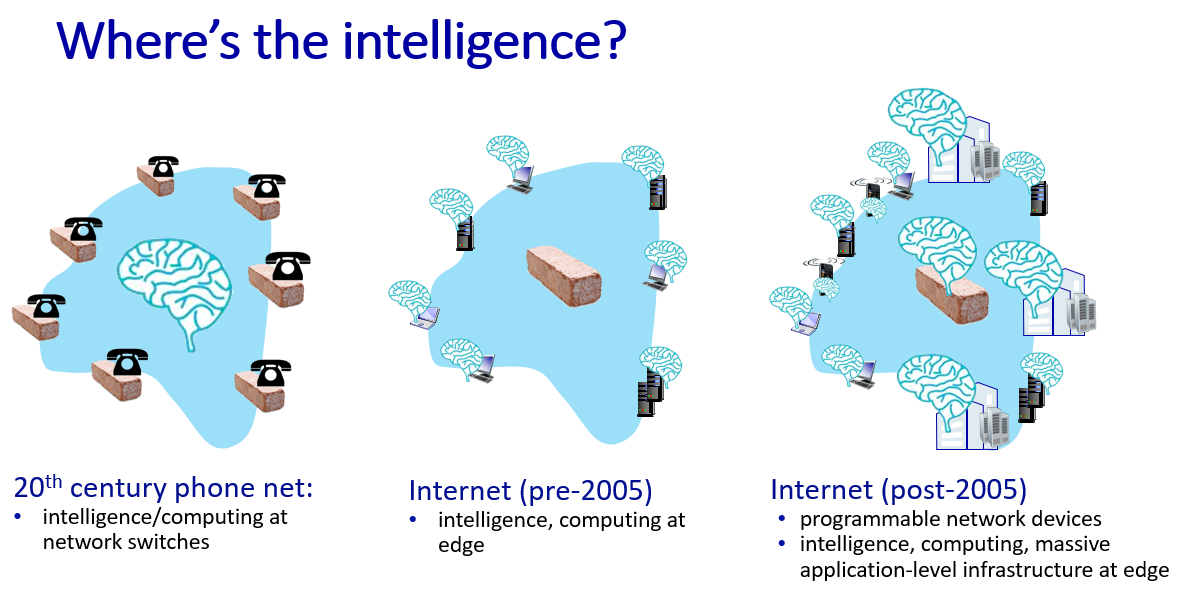

Network layer: Control plane
routing algorithms
computing shortest path or least cost path

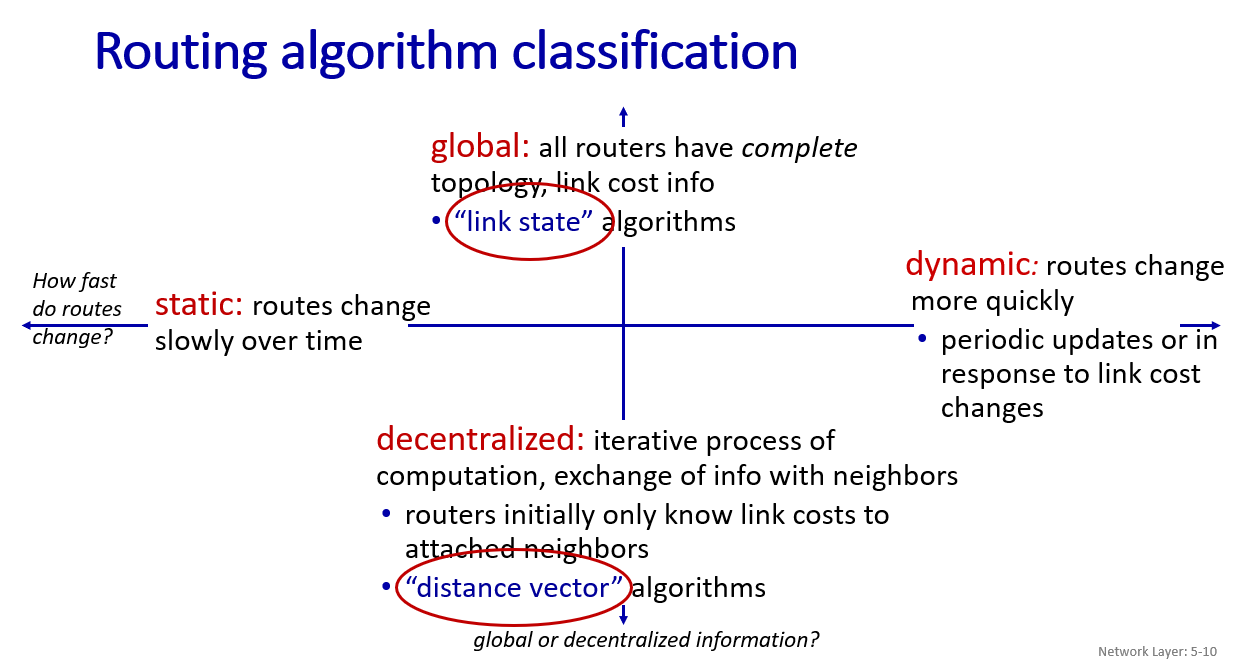
- link state(Dijkstra) algorithm

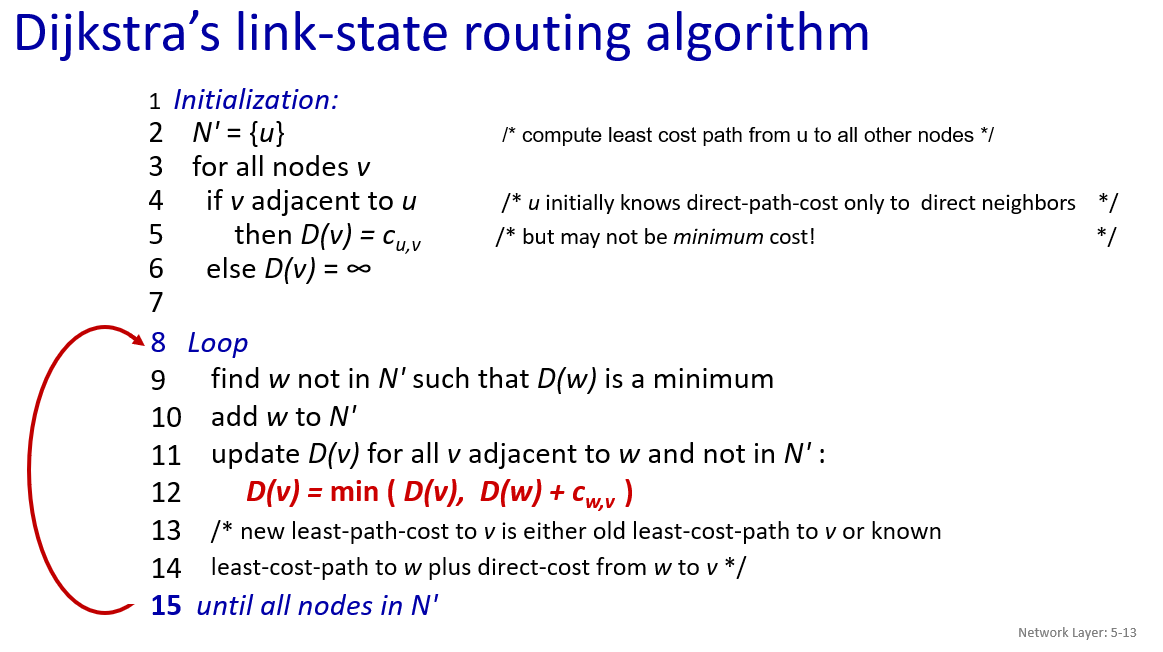
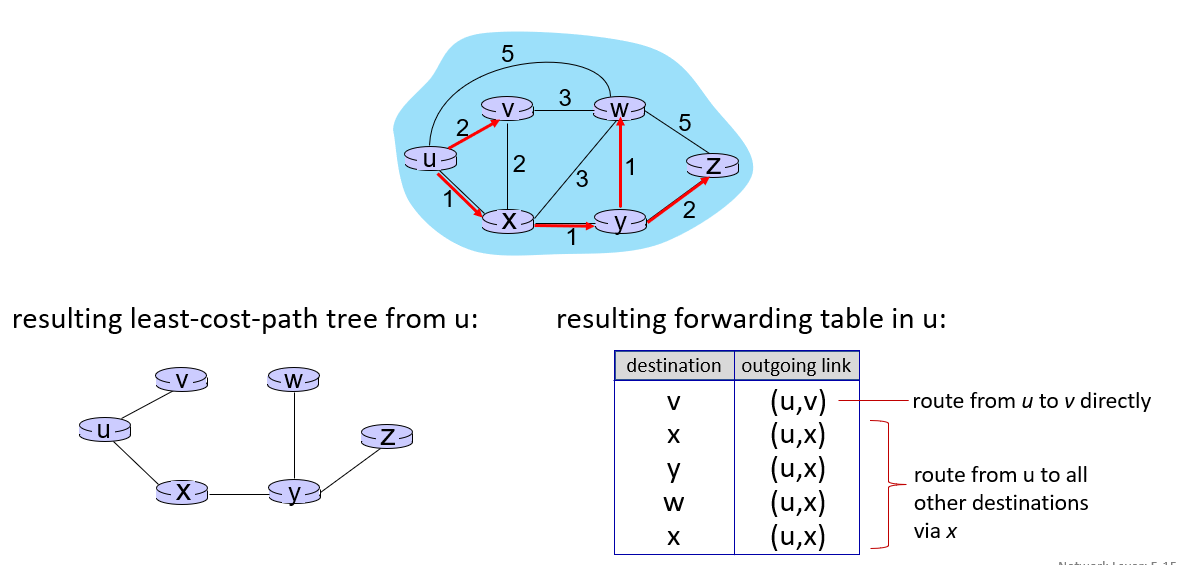
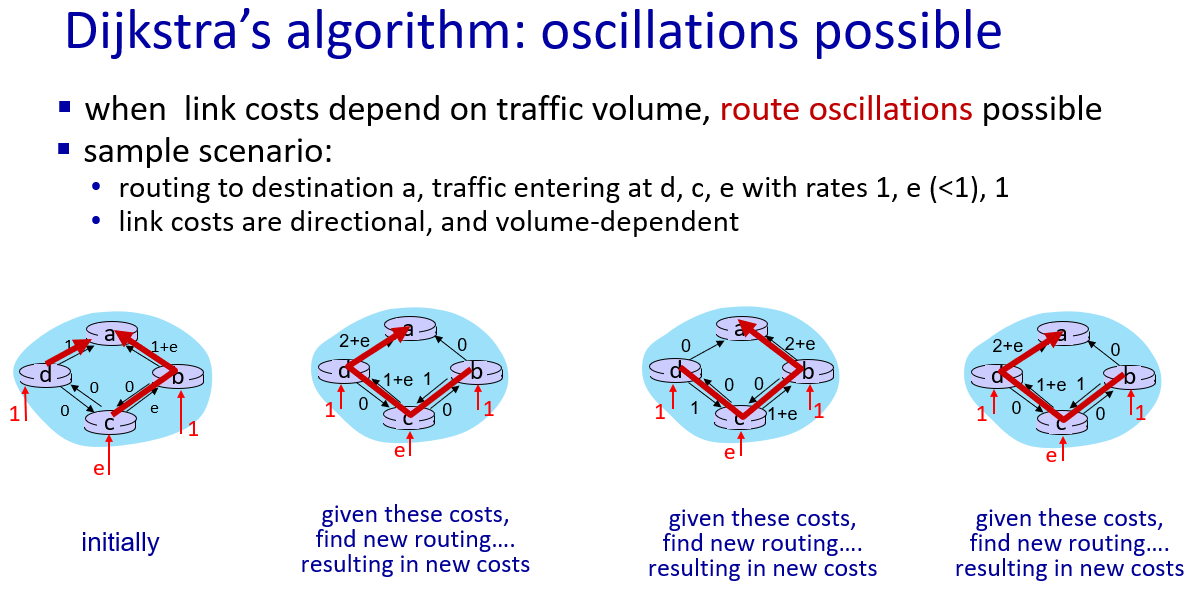
avoid define cost based on short-term load levels
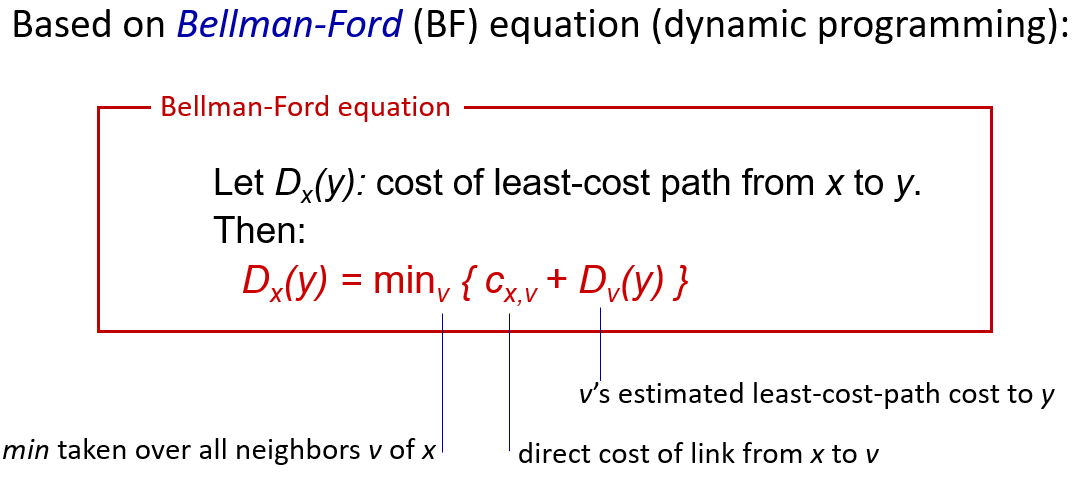
- distance vector(Bellman Ford) algorithm




and so on
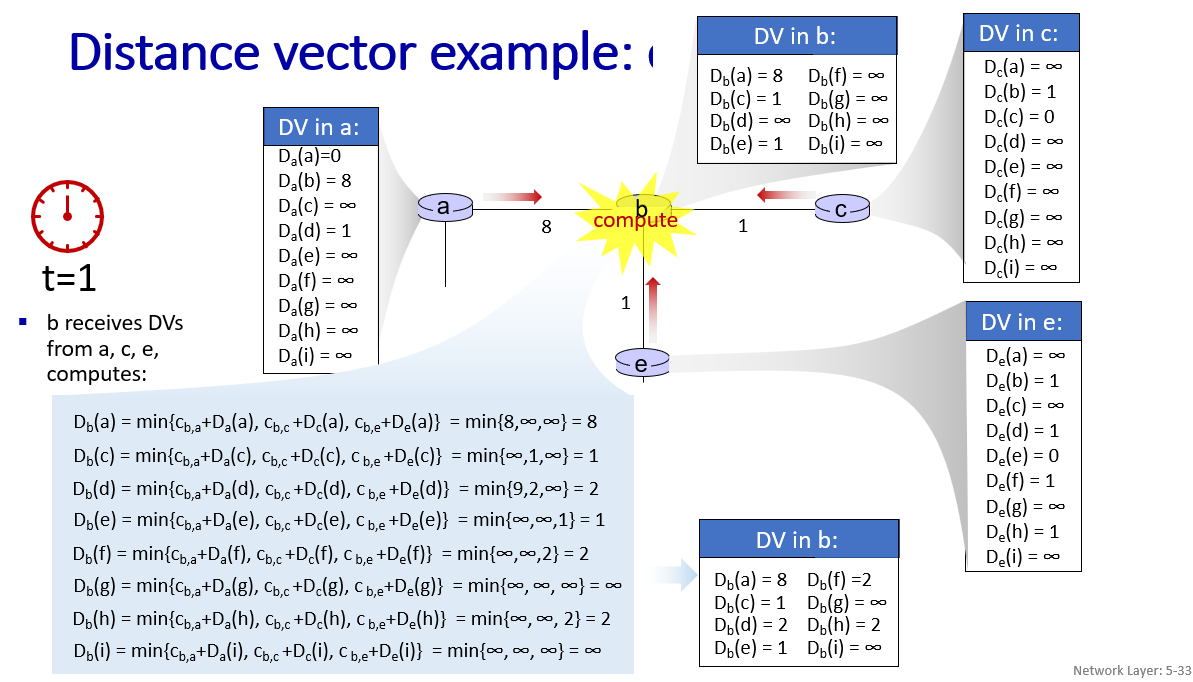
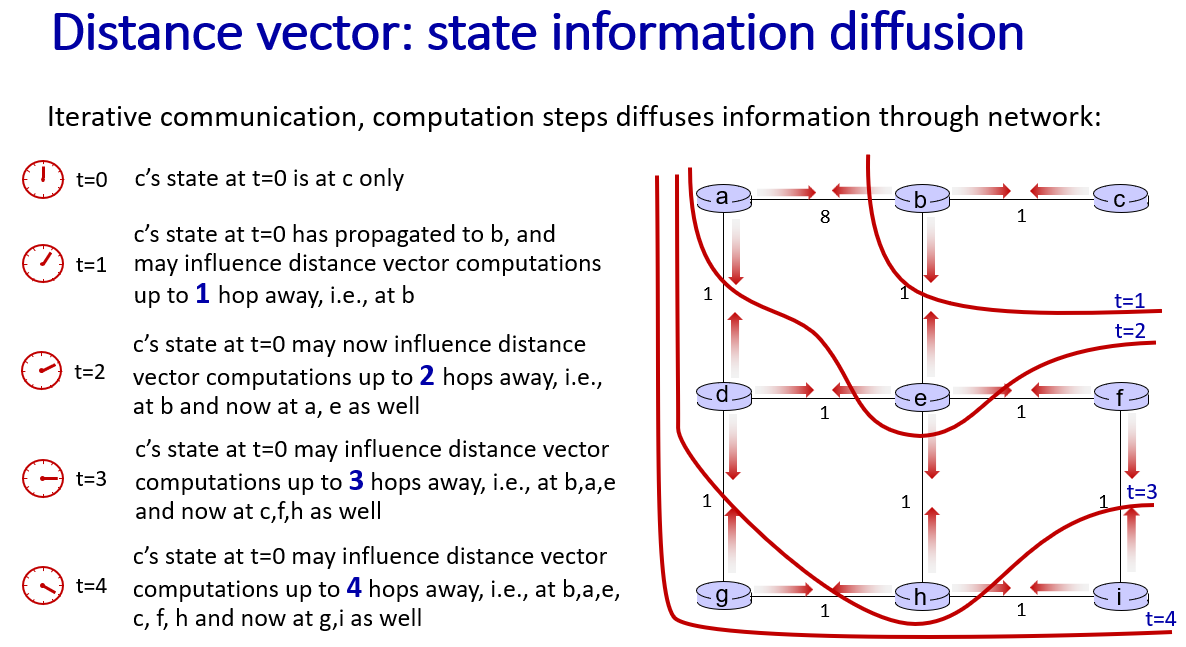
good news travel fast,but bad news travels slow.
the initial least cost path from z to x is 5.

what if not 60, but 6000000?
Internet routing in practice
considering two factors
- scale:billions of routers
- autonomy:allow network managers to choose how to route both within and outside their own network

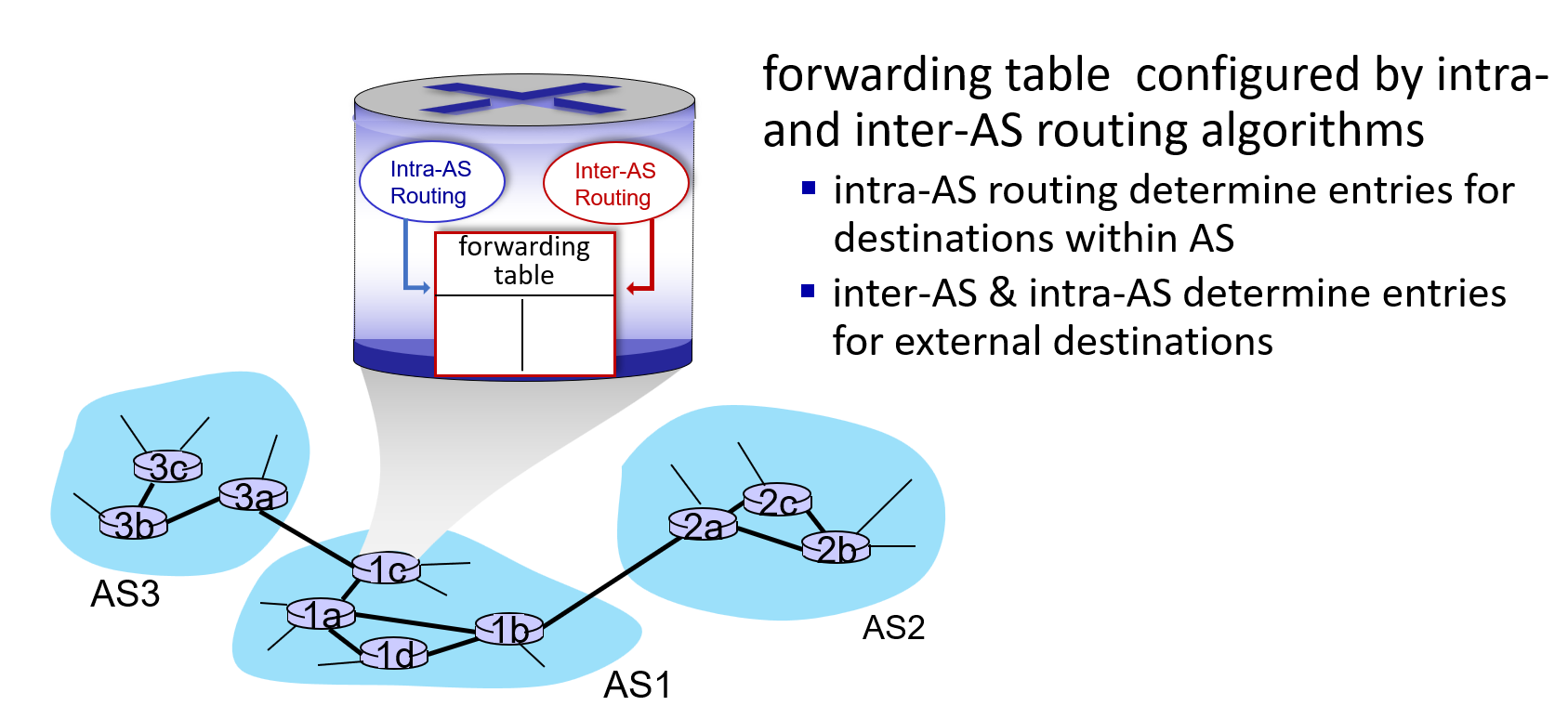
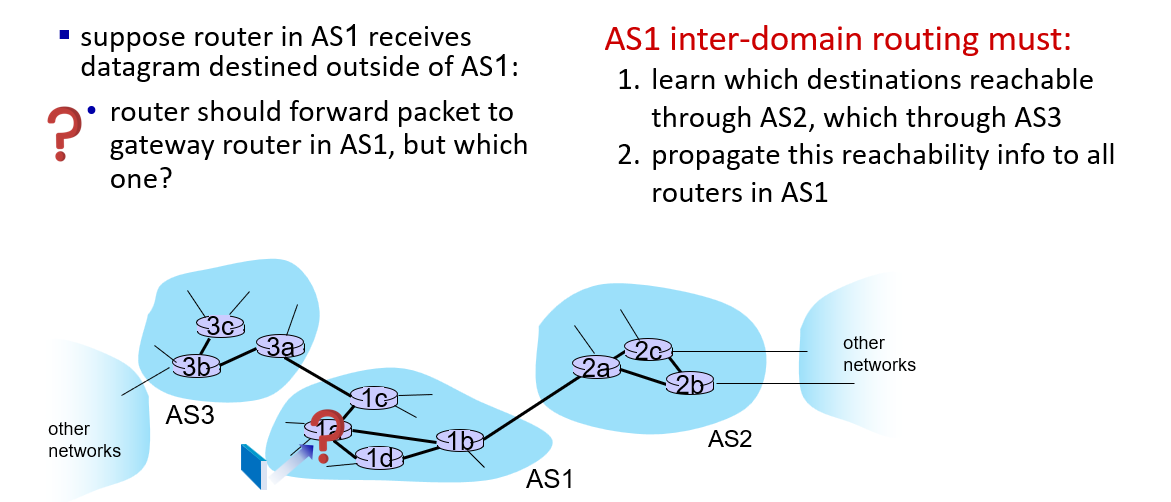
OSPF is the most widely used intra-AS protocol

the only inter-AS protocol:BGP —— the glue of network
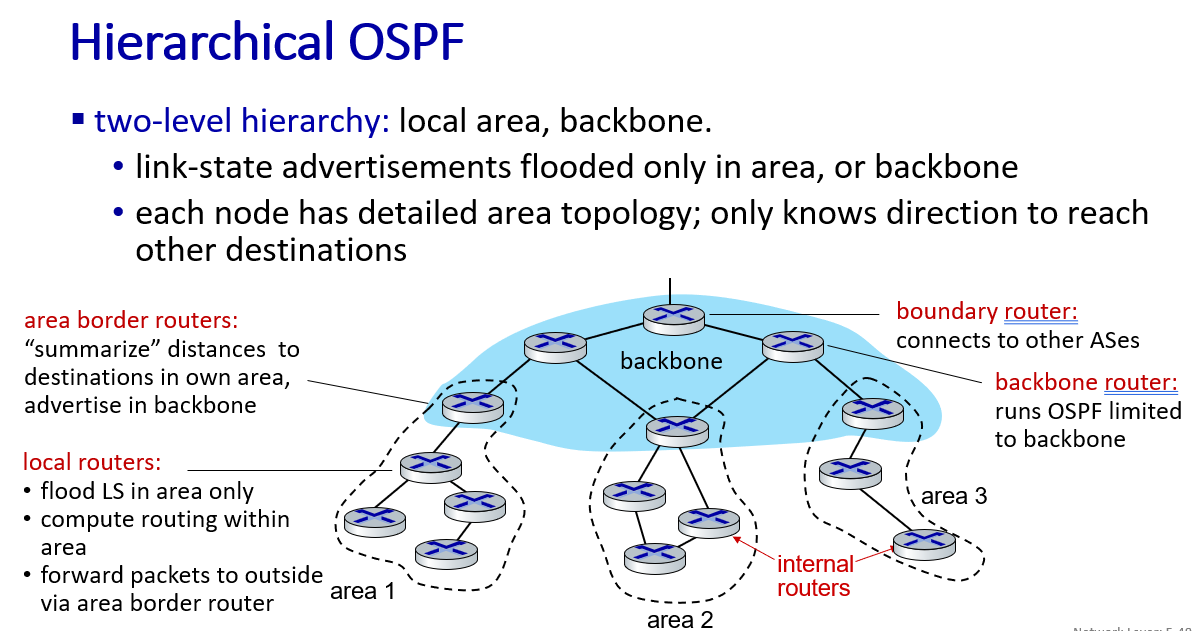
intra-ISP routing: OSPF

flood the link-state in its own area.
the area border routers may flood in multiple area
routing among ISPs: BGP

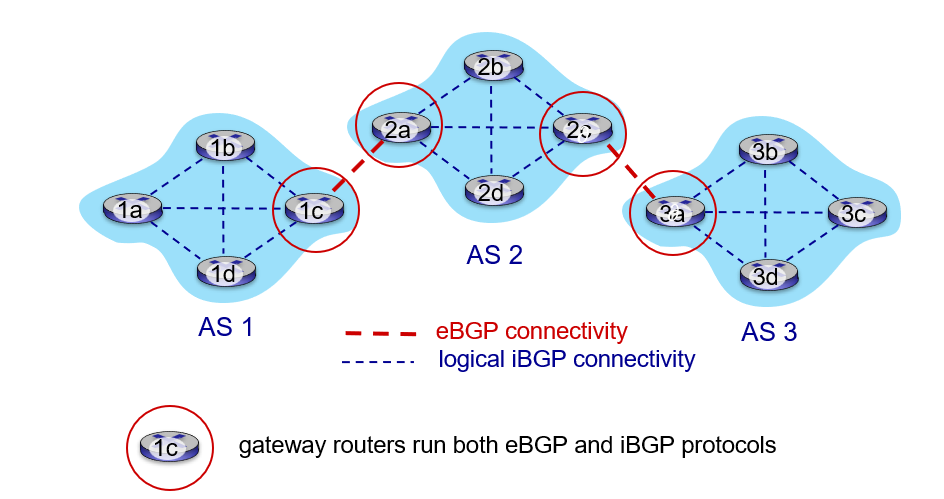
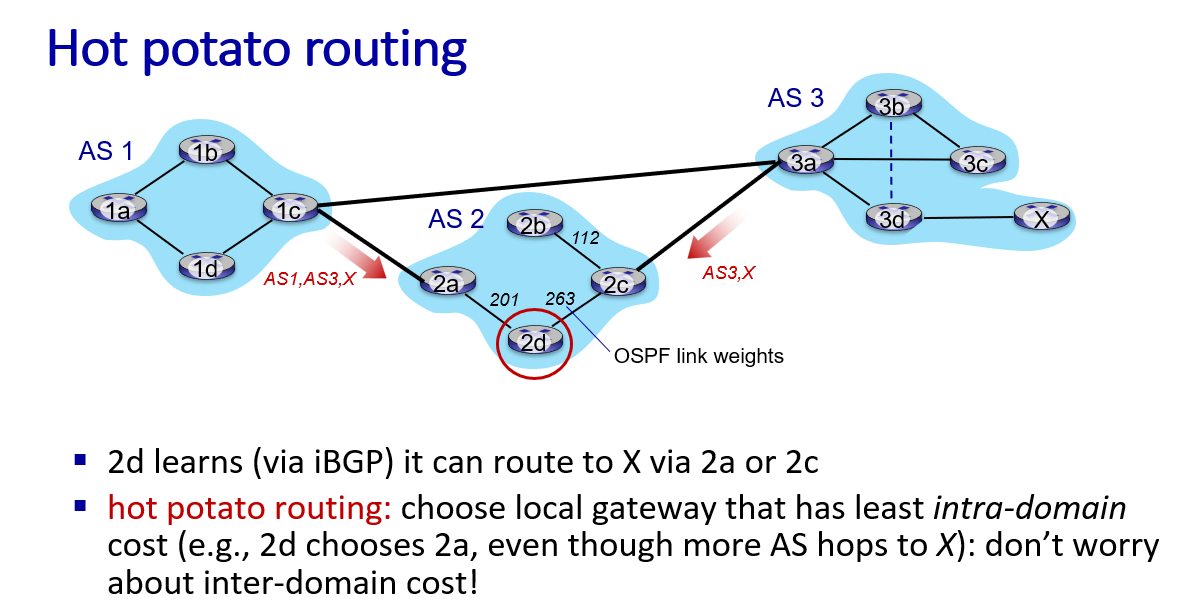
AS3 know it can reach x,so if it willing it advertise other gateway router path AS3 X.
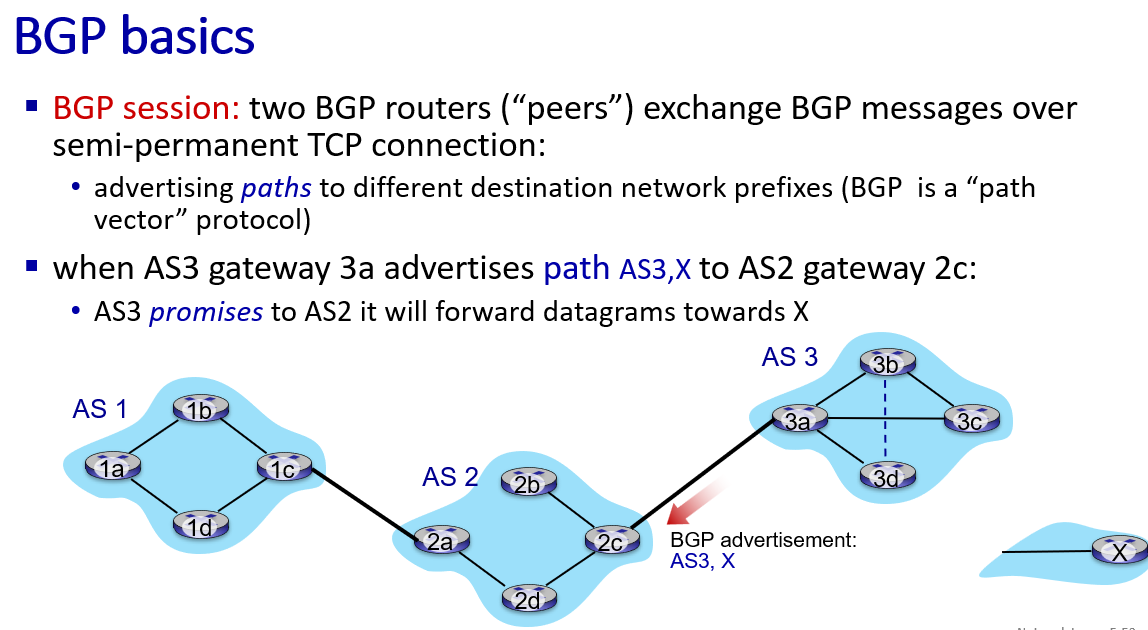
if ASa donot advertise it has a path to router such as w,then it will not have to forward inter-AS traffic which destination is w
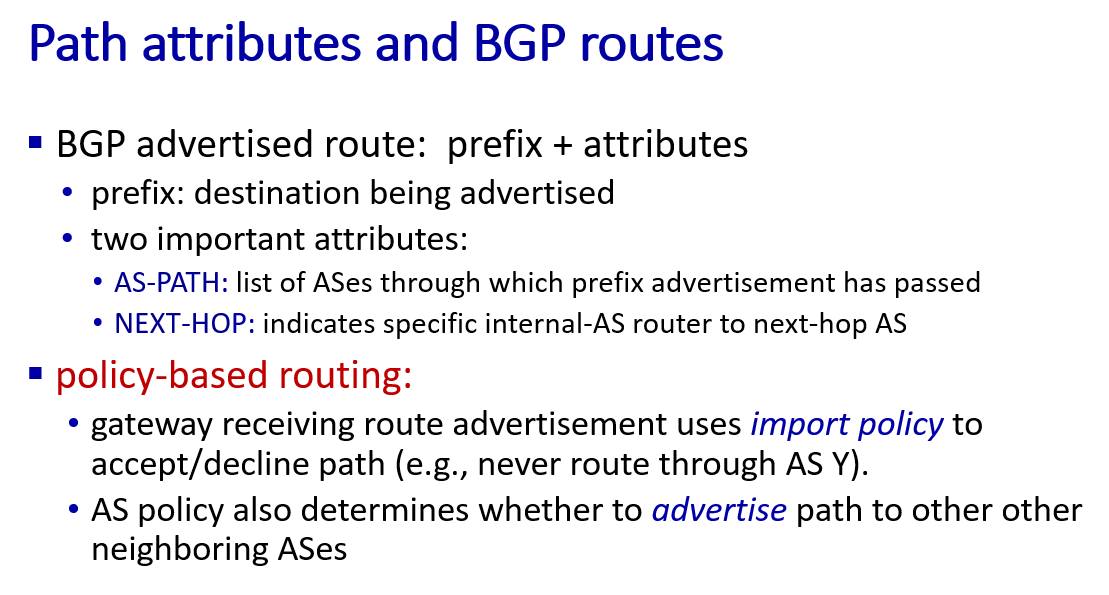
path advertisement AS2,AS3,X: prefix->X indicate the destination, AS-path-> AS2,AS2, NEXT-hop-> 2a, 3a
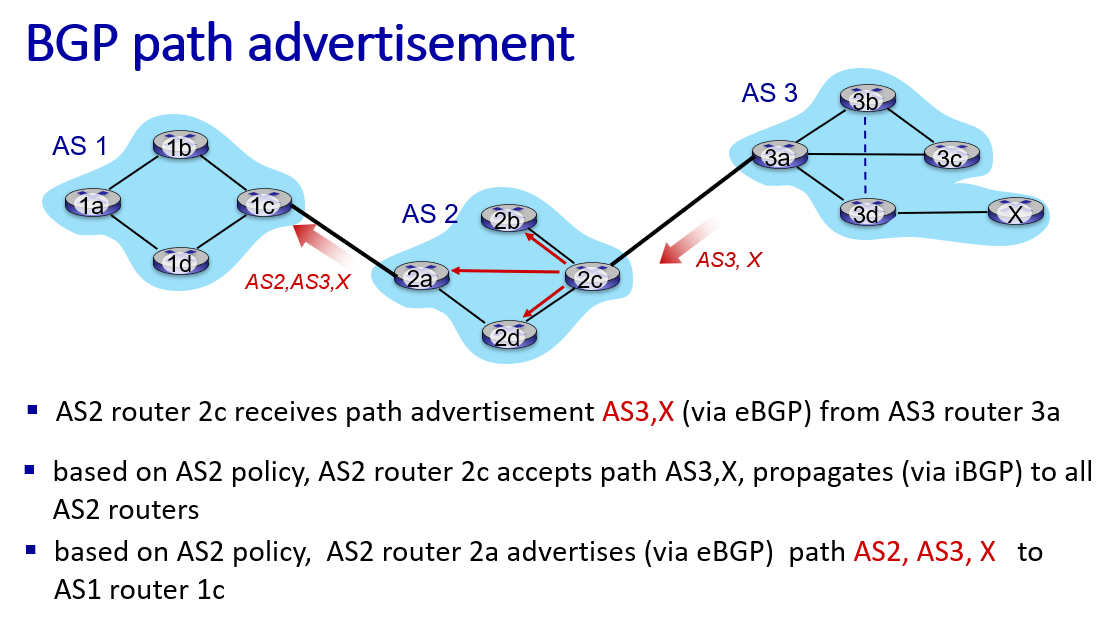
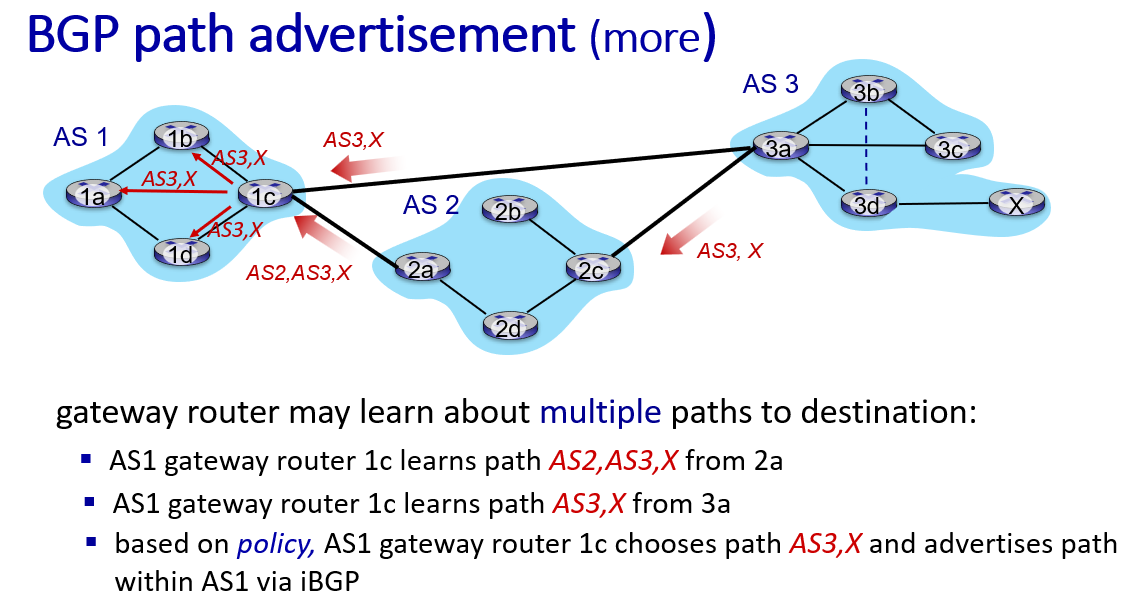

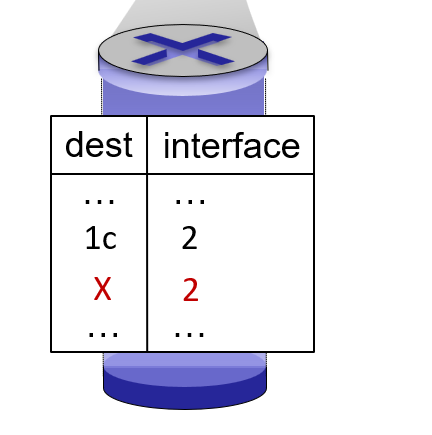
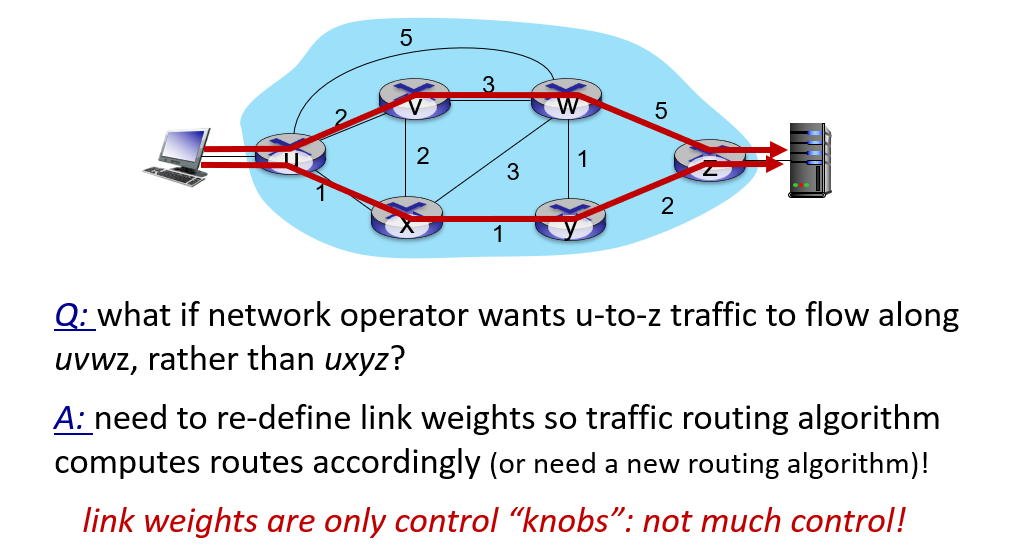
So how to design forward table?
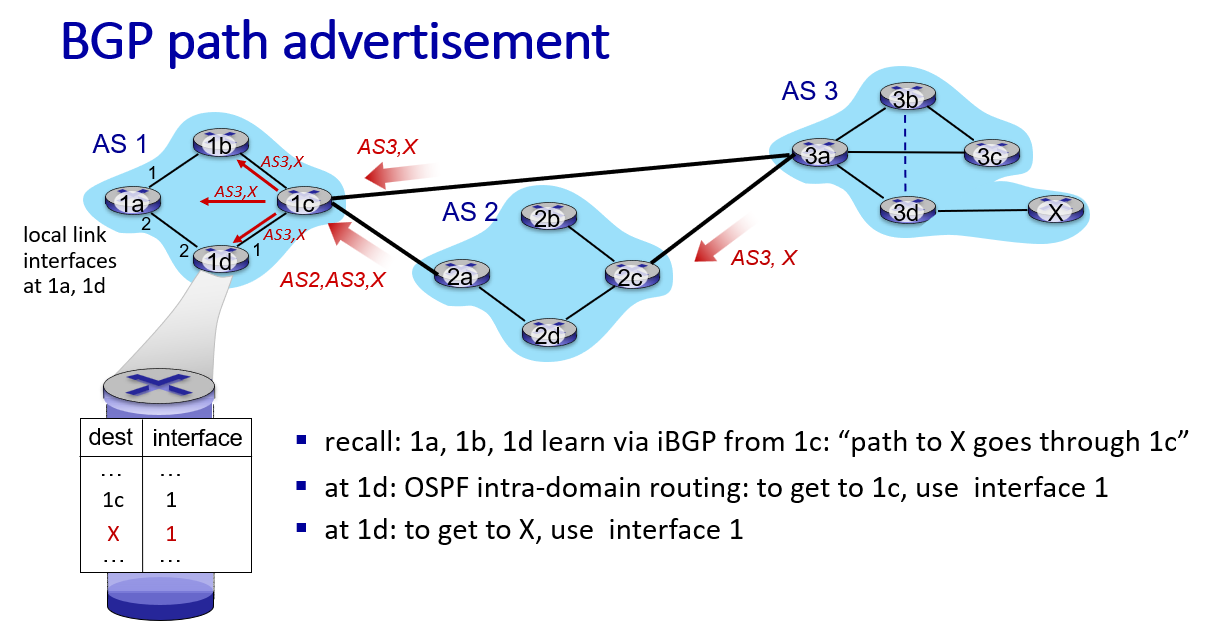
for 1a

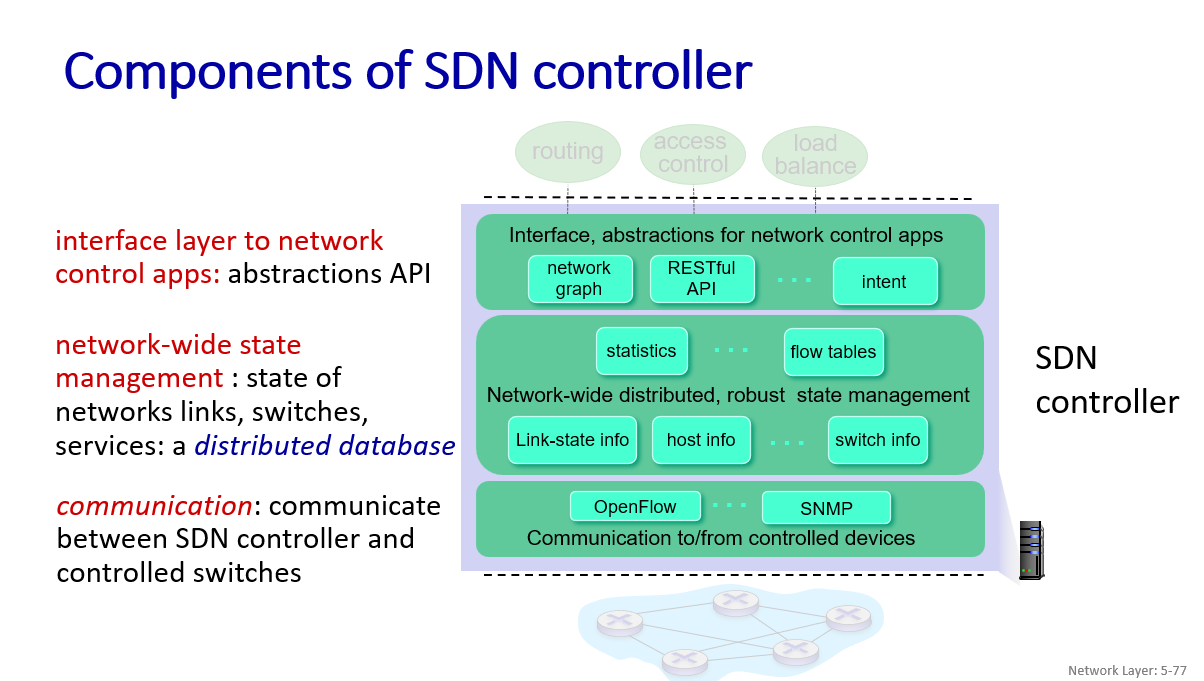
SDN control plane

- Traffic engineering(programming)
 while generalized forwarding plus SDN can be used to achieve any routing desired
while generalized forwarding plus SDN can be used to achieve any routing desired
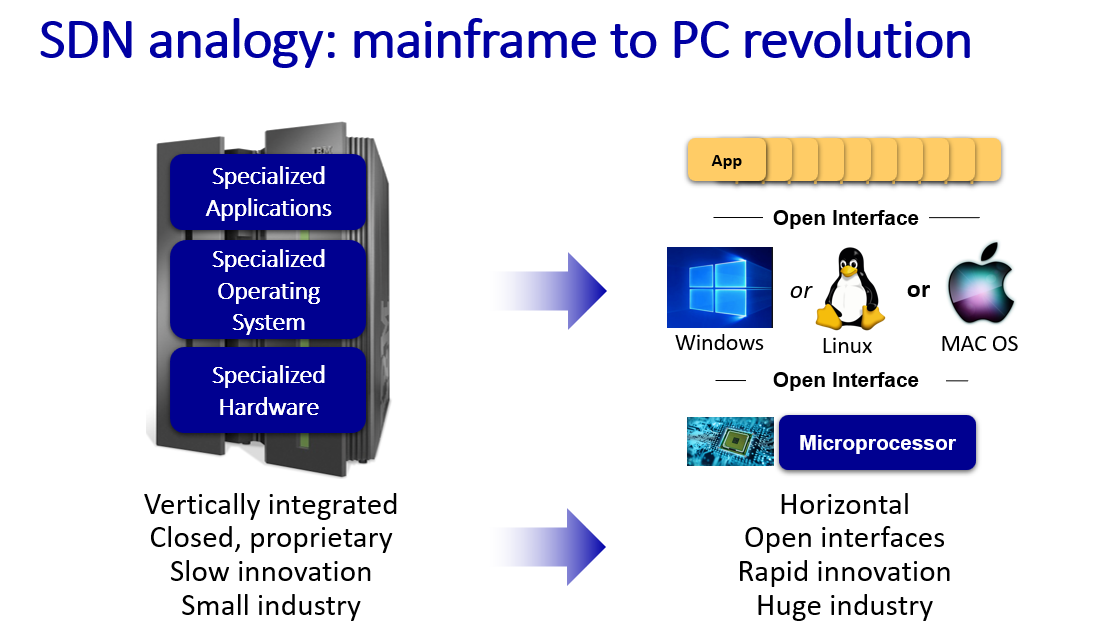
- open (non-proprietary)
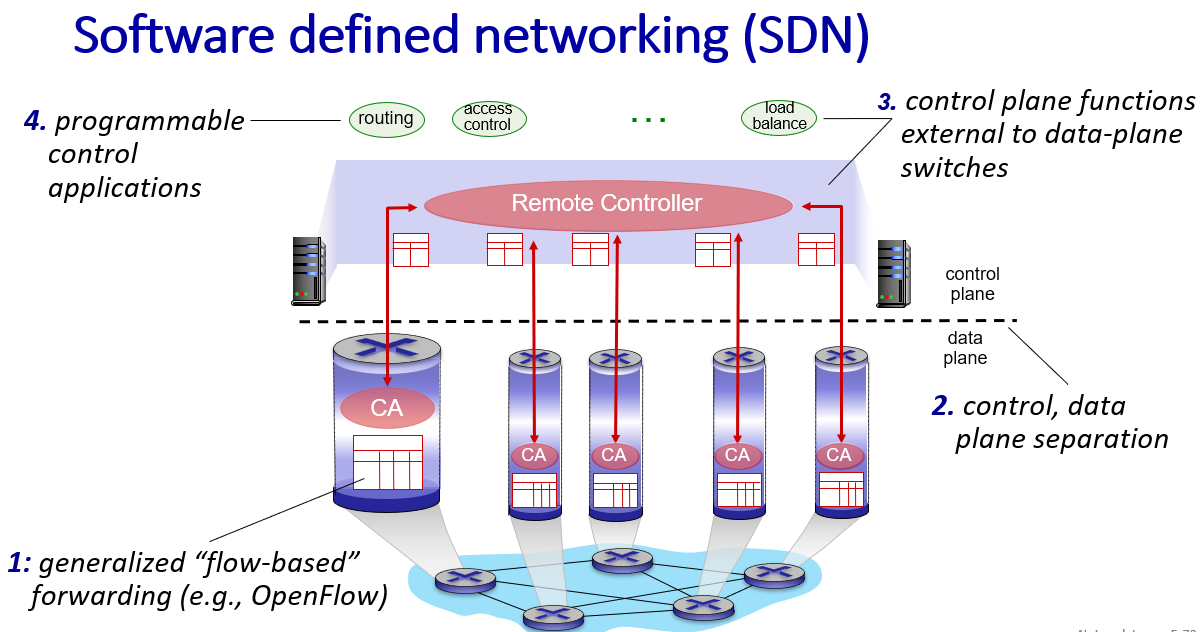
In Data-plane switches view:
- API for table-based switch control (e.g., OpenFlow) defines what is controllable, what is not.
- protocol for communicating with controller (e.g., OpenFlow)
network-control apps:
- “brains” of control: implement control functions using lower-level services, API provided by SDN controller
- unbundled: can be provided by 3rd party: distinct from routing vendor, or SDN controller
(network OS)

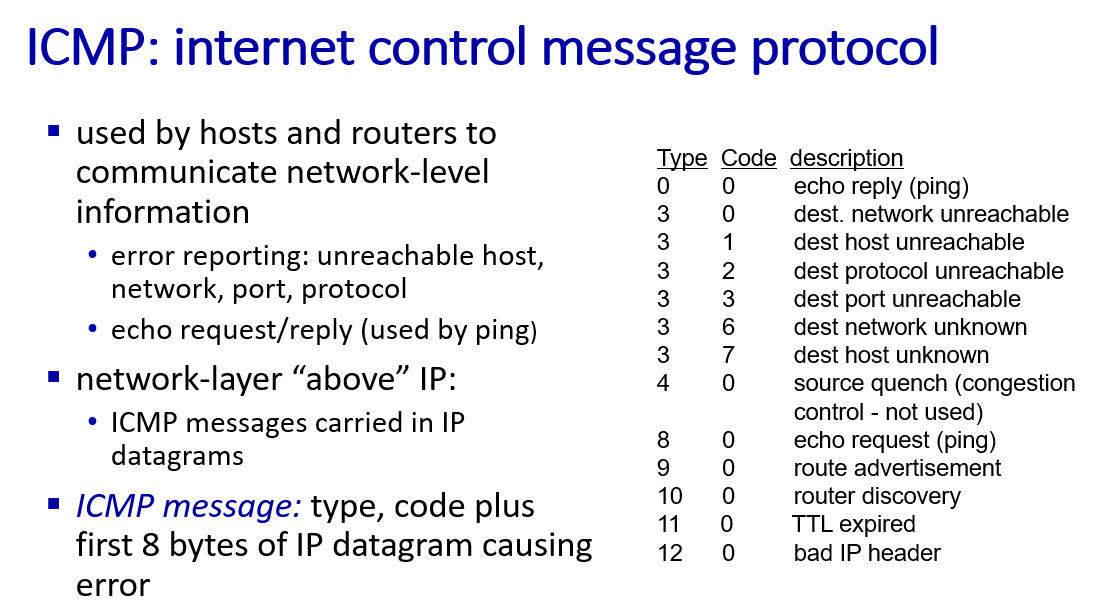
Internet Control Message Protocol
usually used to report error msg
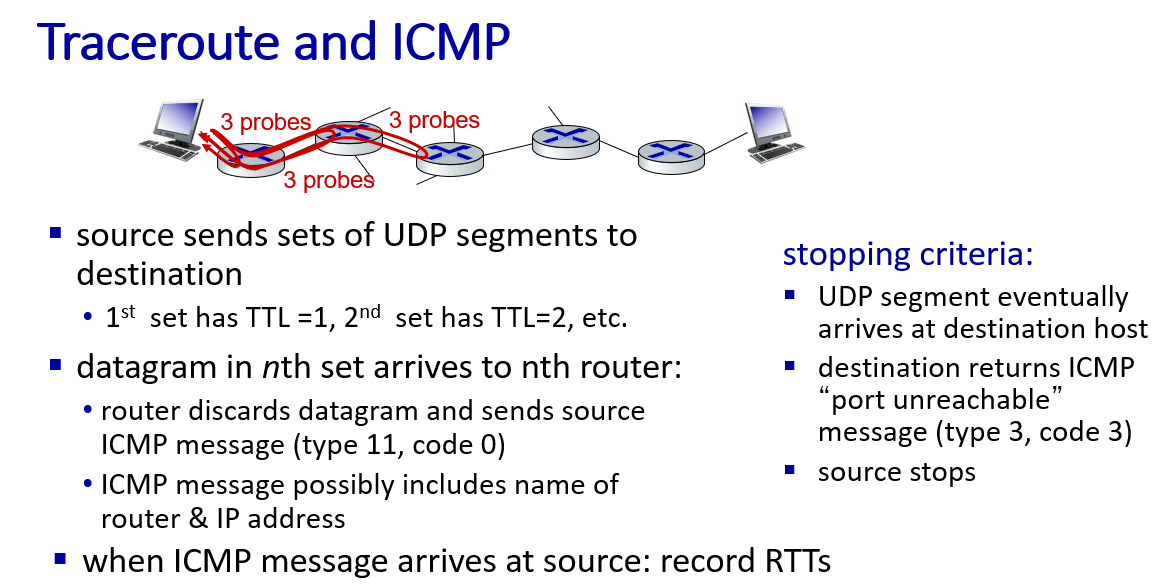
stopping criteria:when path is end(arrive destination), there is no need to evaluate RTT
network management, configuration

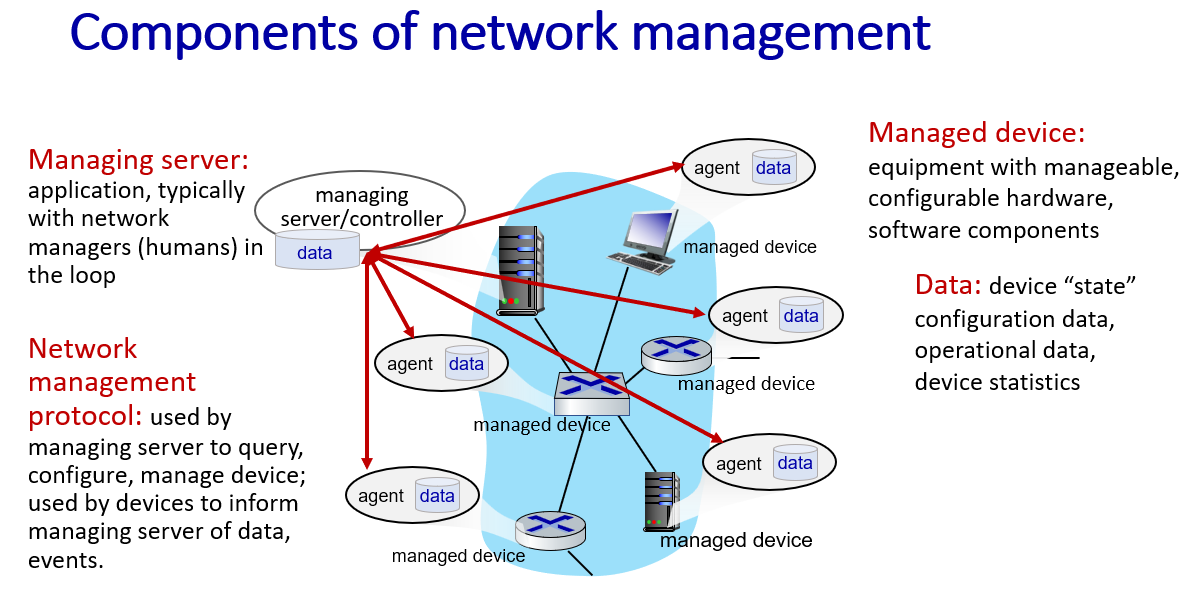
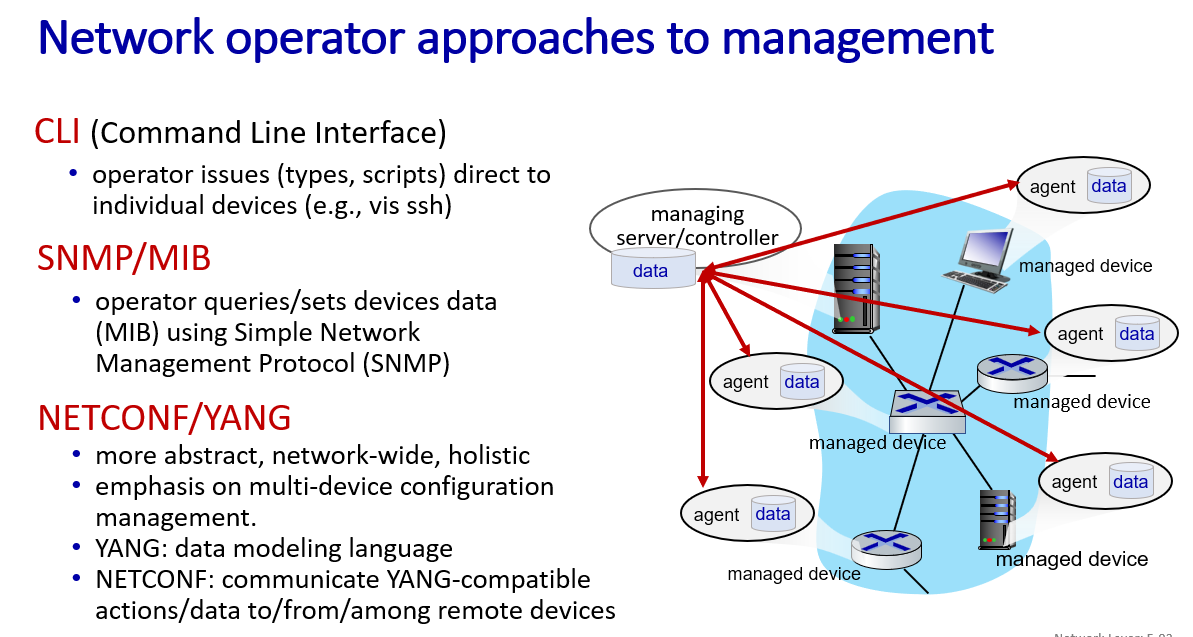
-
SNMP
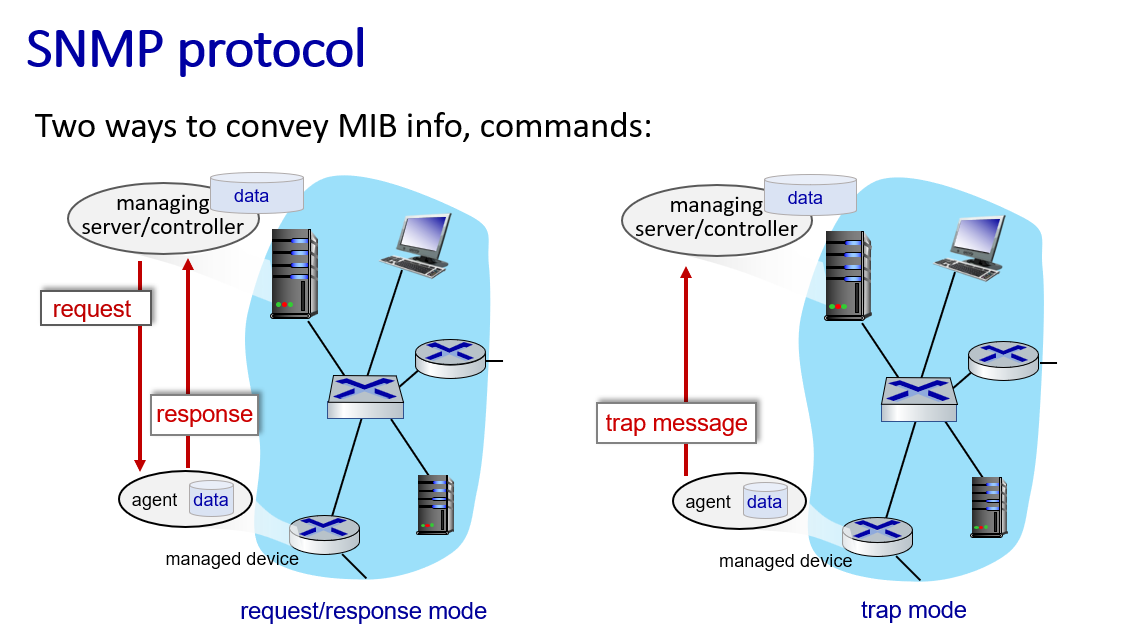
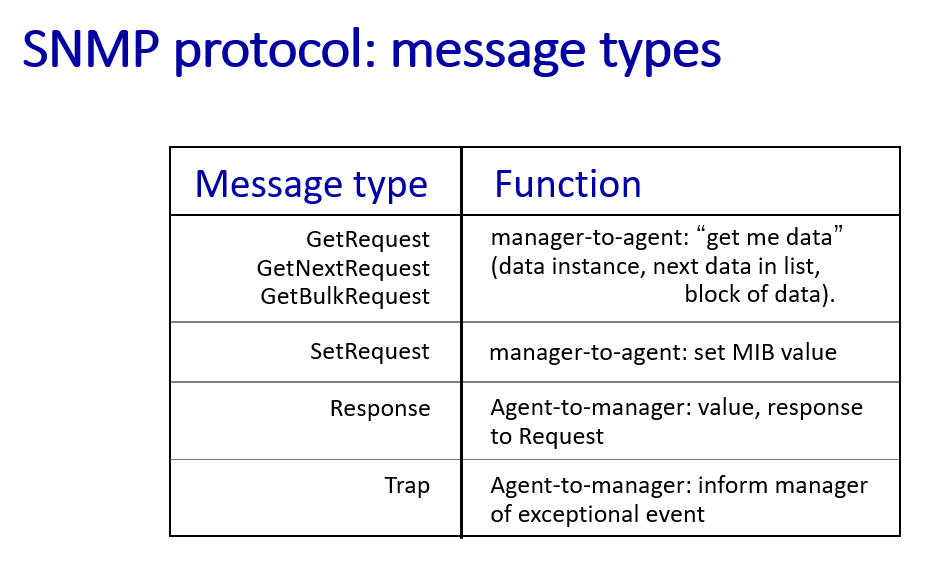
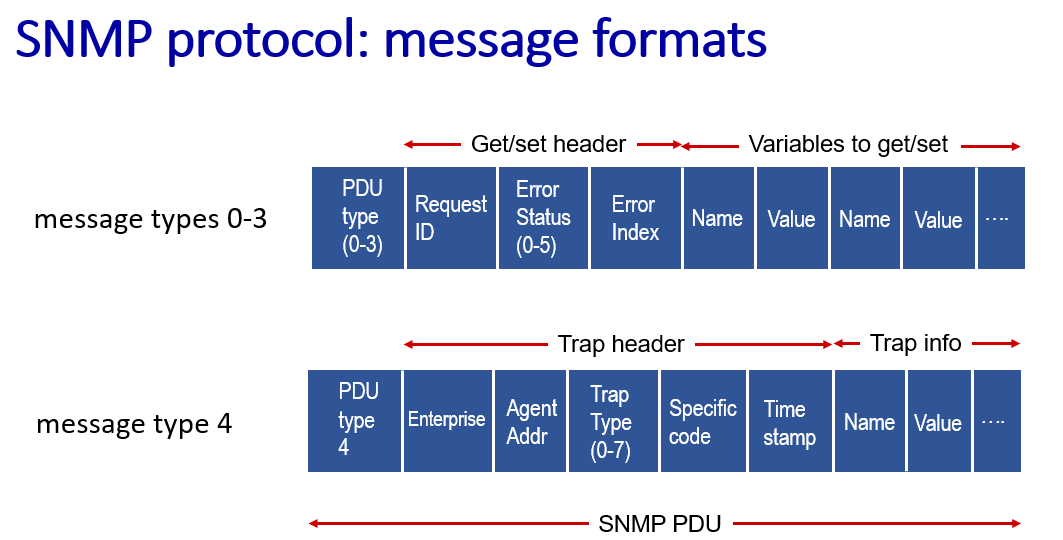
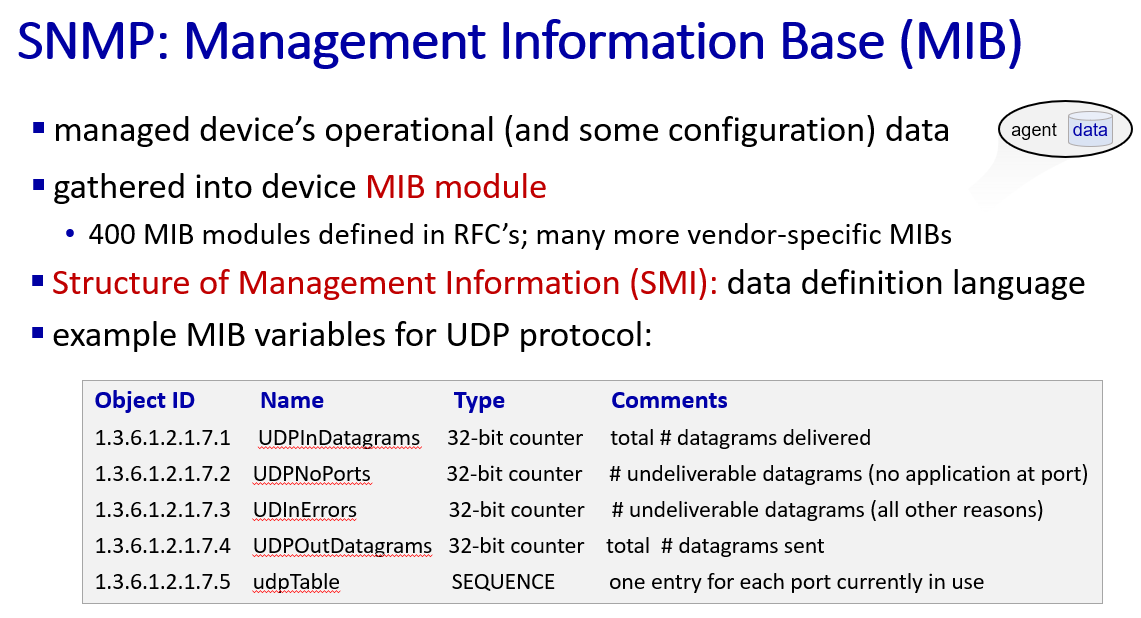
-
NETCONF

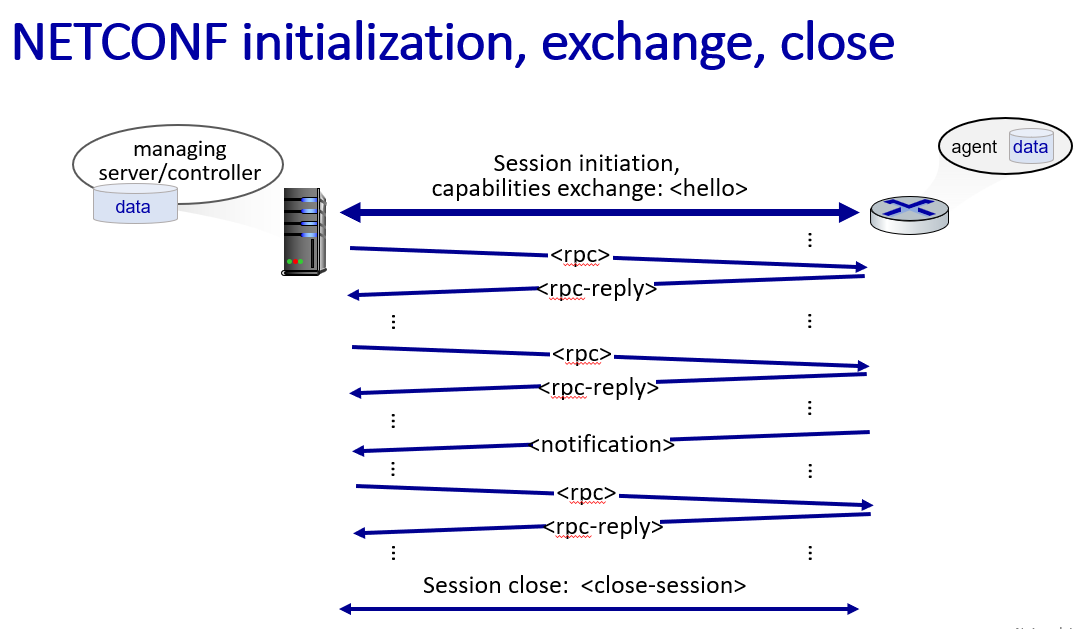


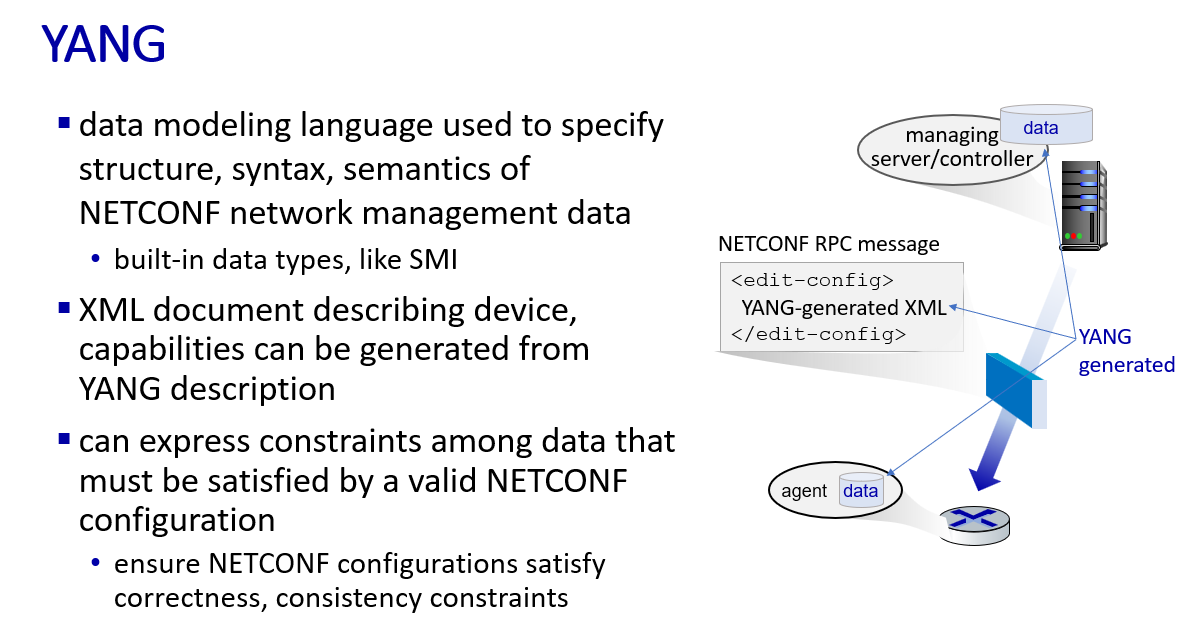
link layer
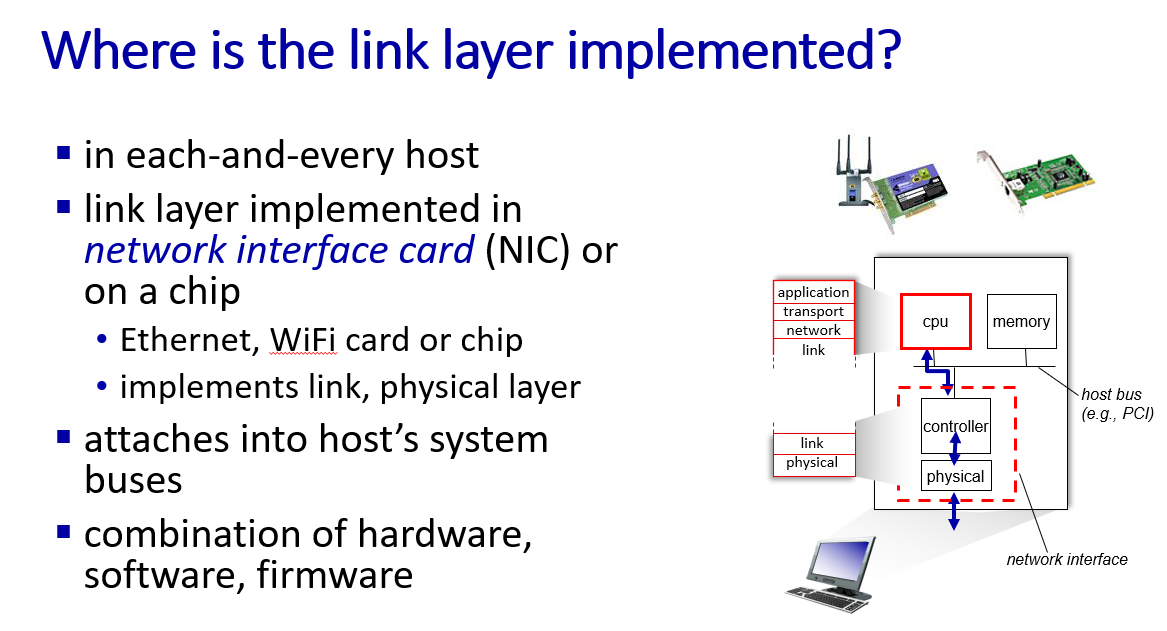
link layer introduction
principle and practice of link layer

terminology of link layer
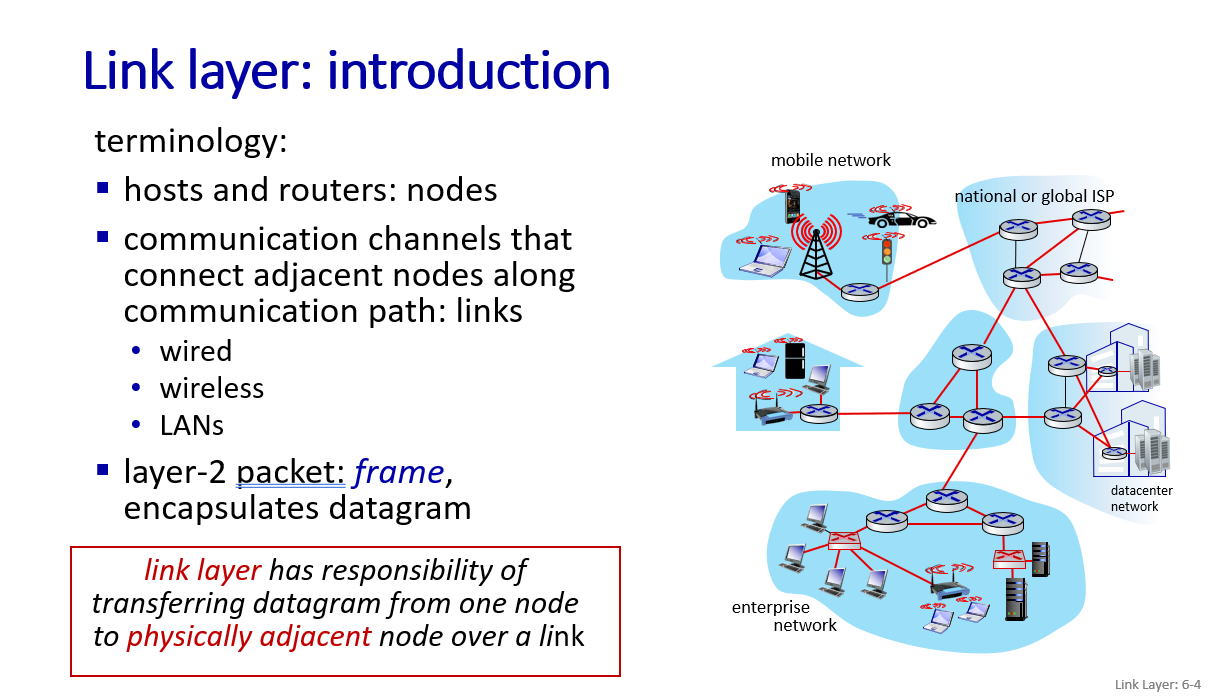
links donot contain routers which is also considered as nodes,only link, wireless and switches.
context of link layer
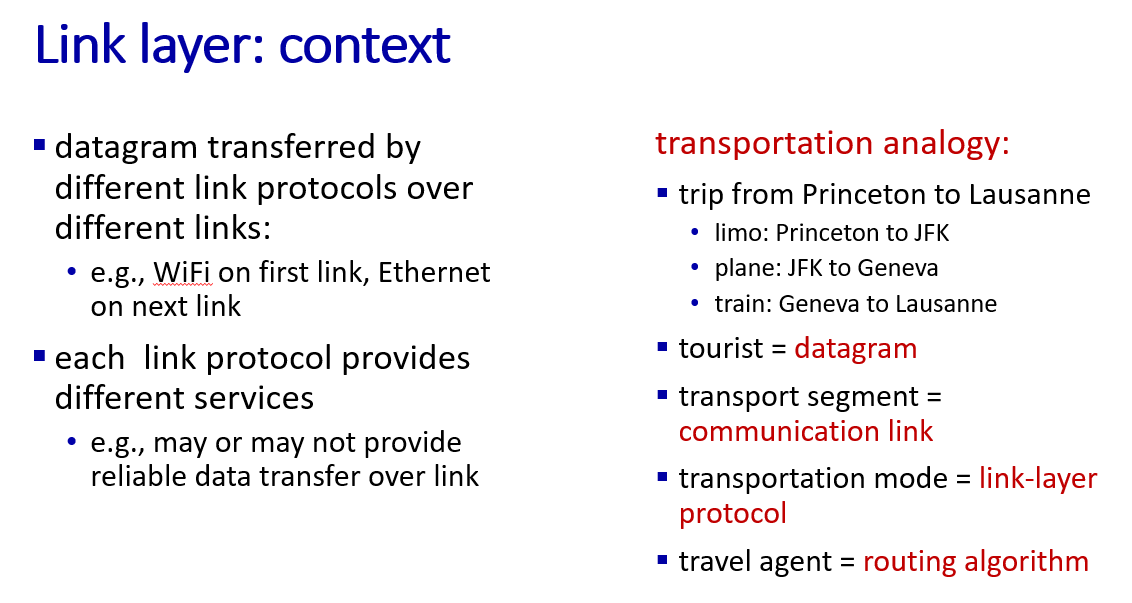
service of link layer
multiple access(MAC).
error control seldom used on low bit-error links, mostly on wireless links.
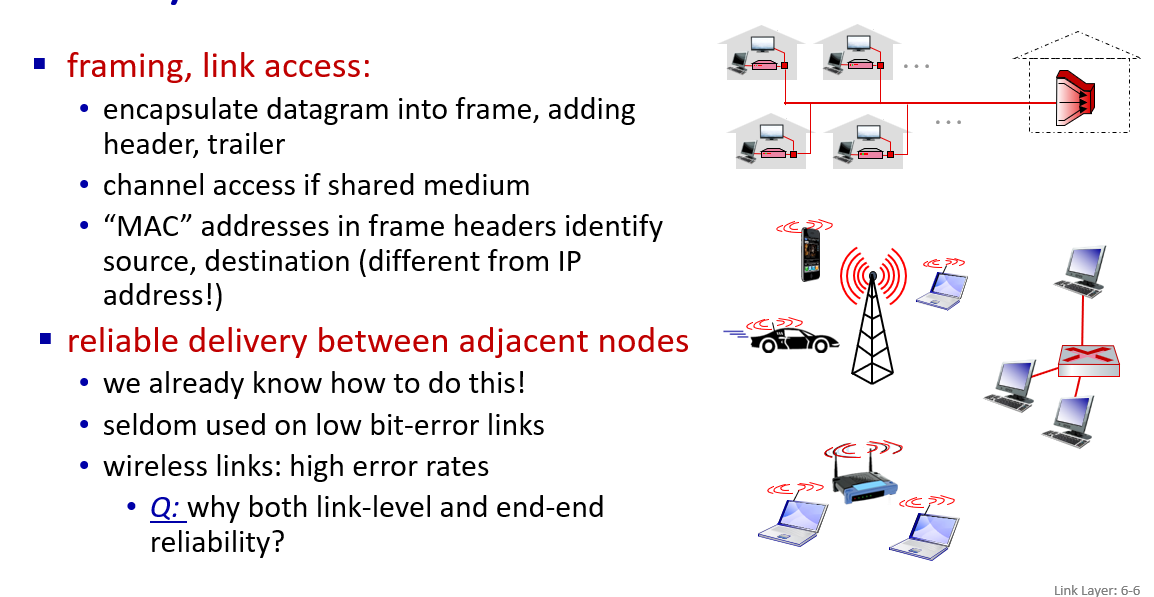
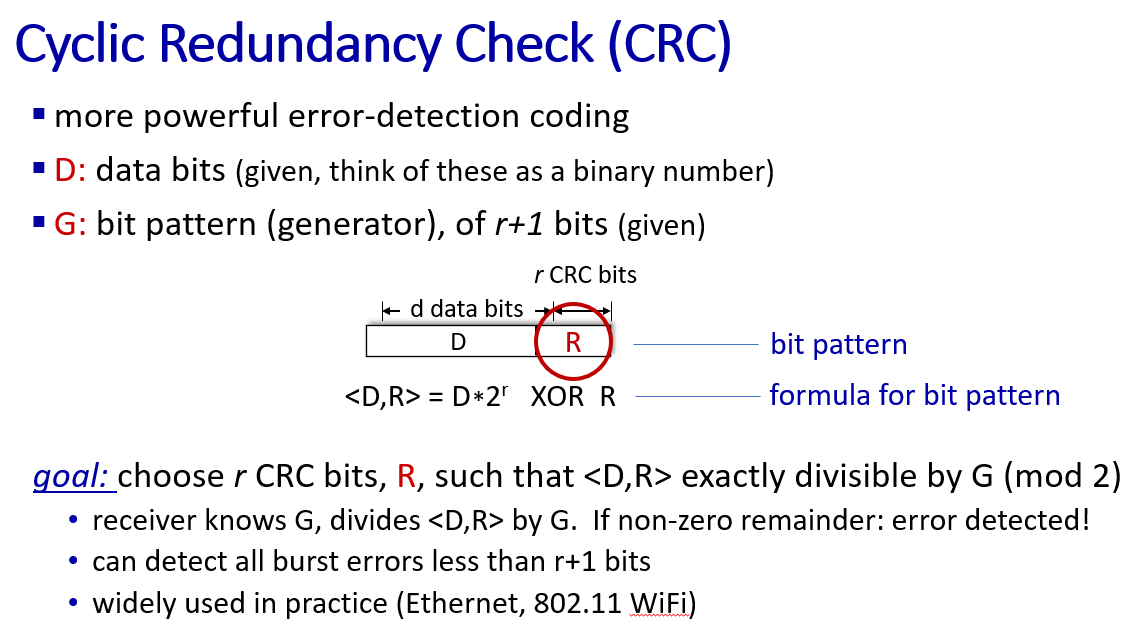
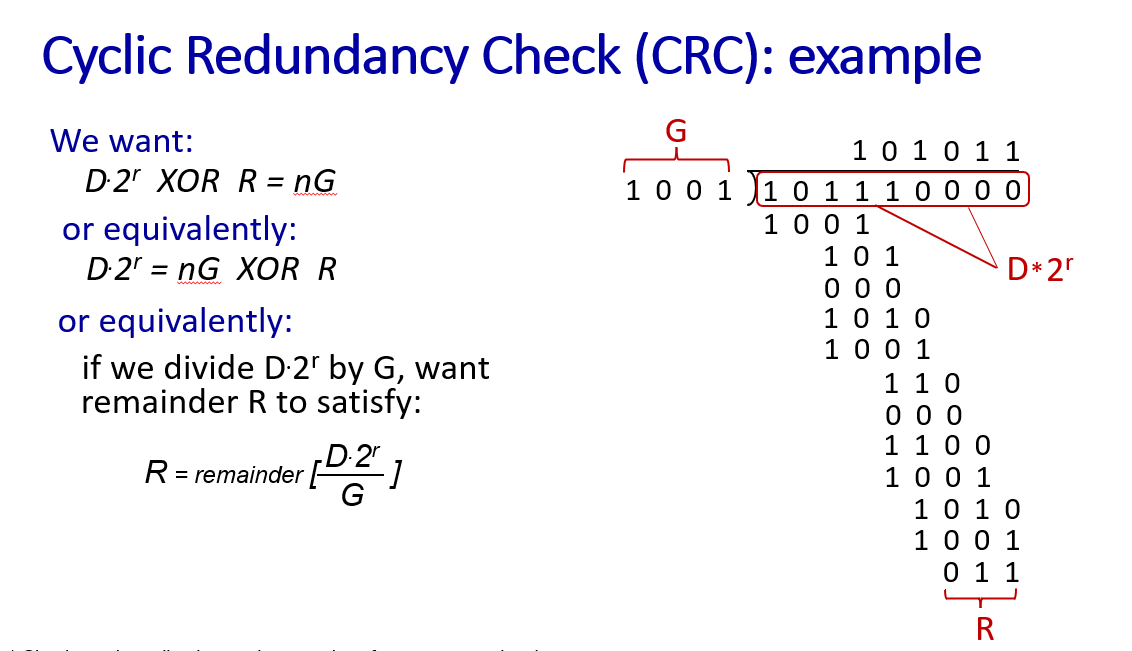
error detection, correction
in network layer we use checksum to detect errors in UDP segment, it is not very strong
but in link layer we use CRC, which is much stronger
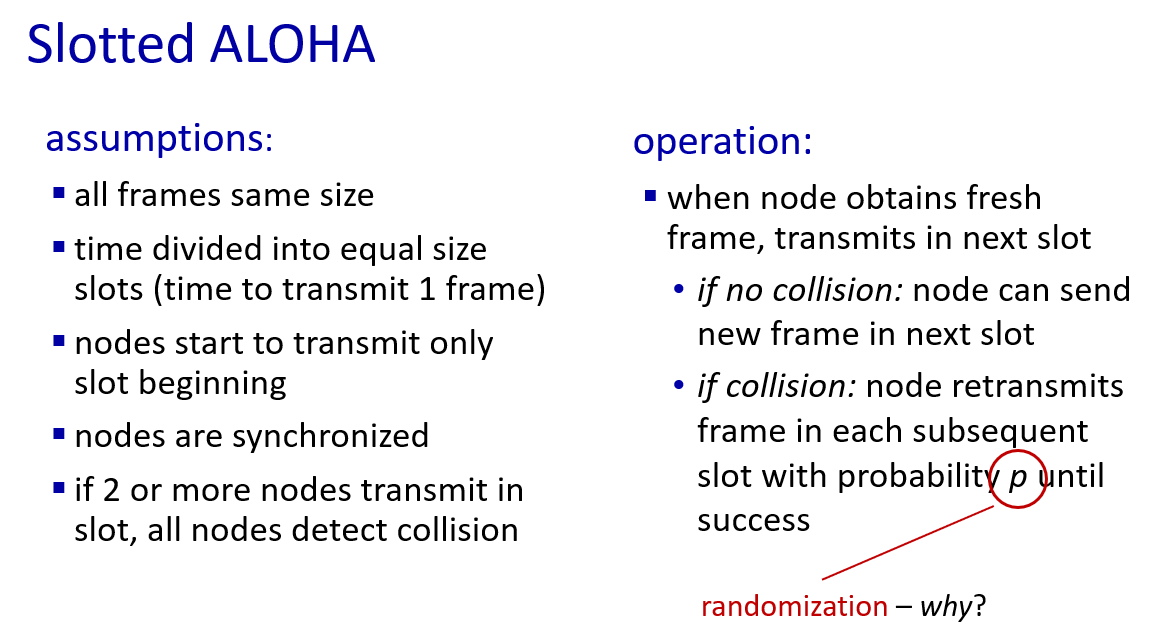
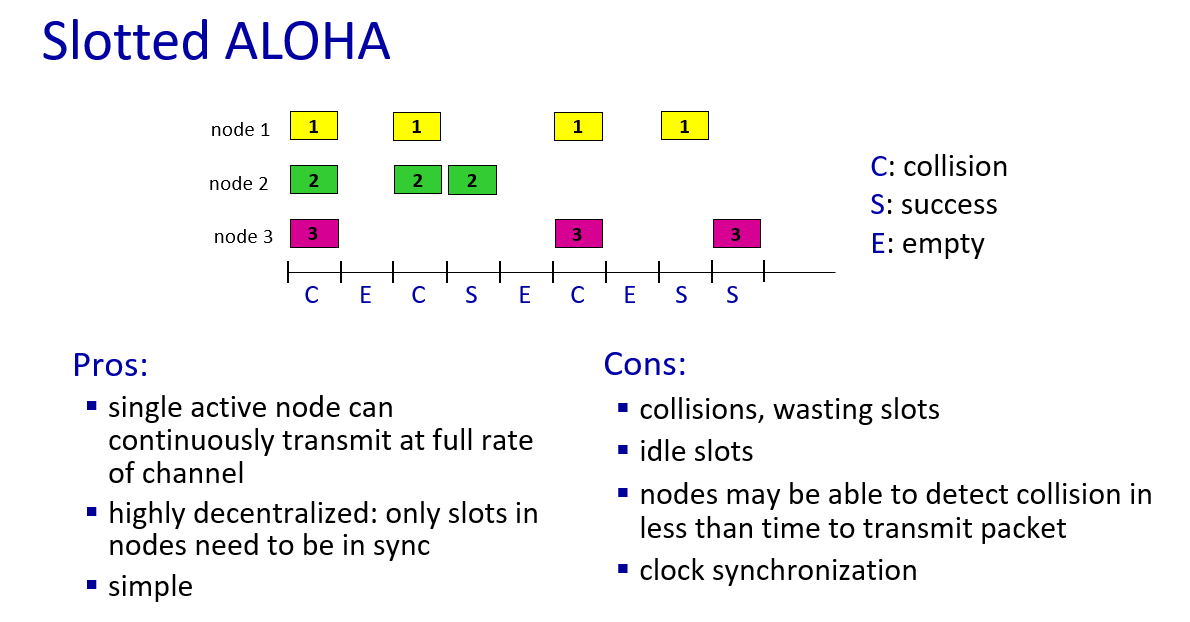
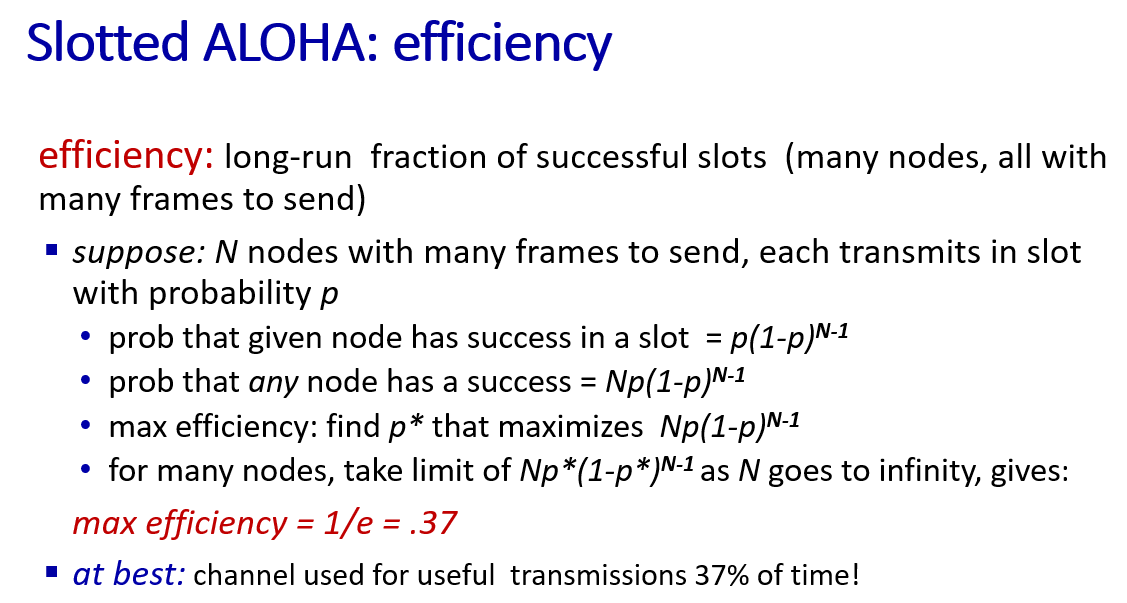
multiple access protocols
why multiple access protocol needed?
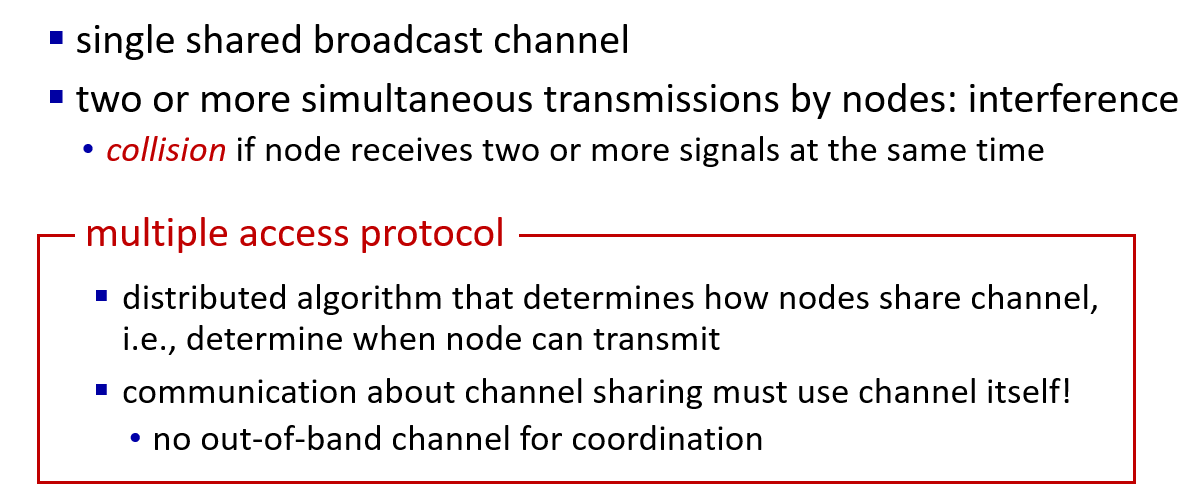
three type

- channel partitioning
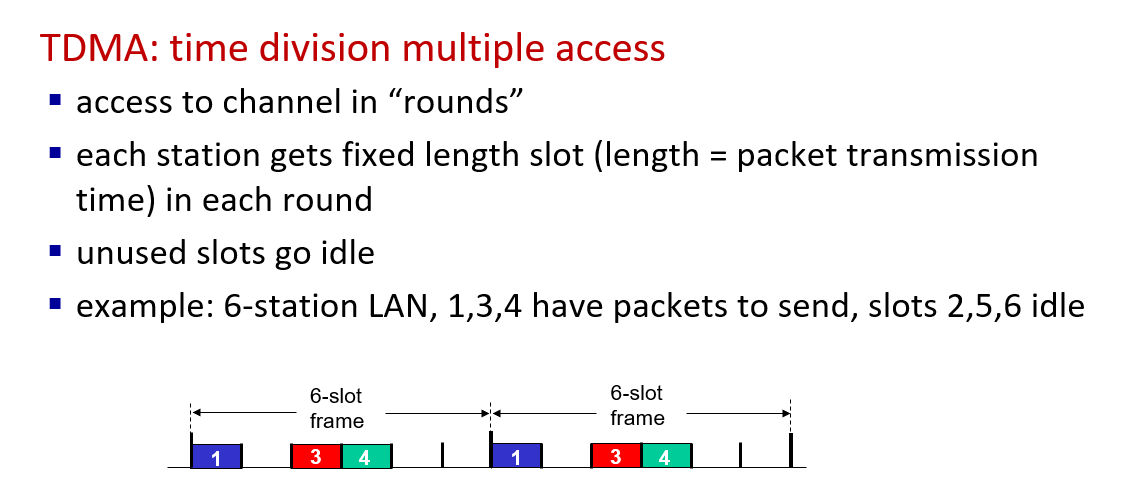
- Random access protocols




P坚持,当检测到信道空闲也只以一定概率来占用信道,这样可以在有多个等待者时避免冲突。(更加polite)

collision still exist
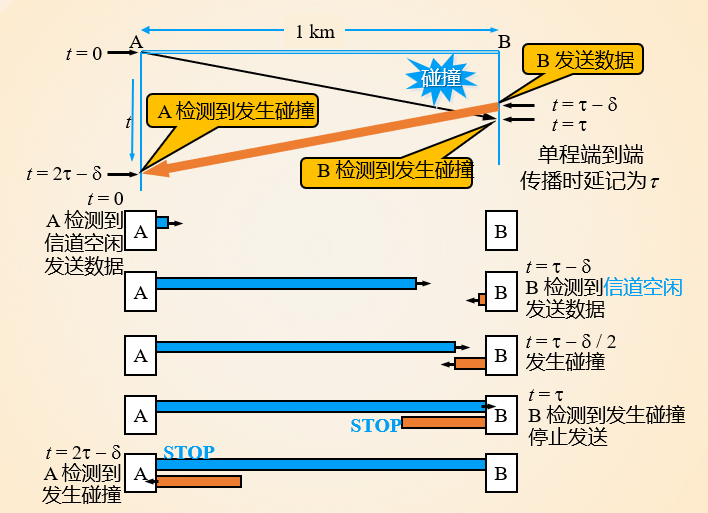
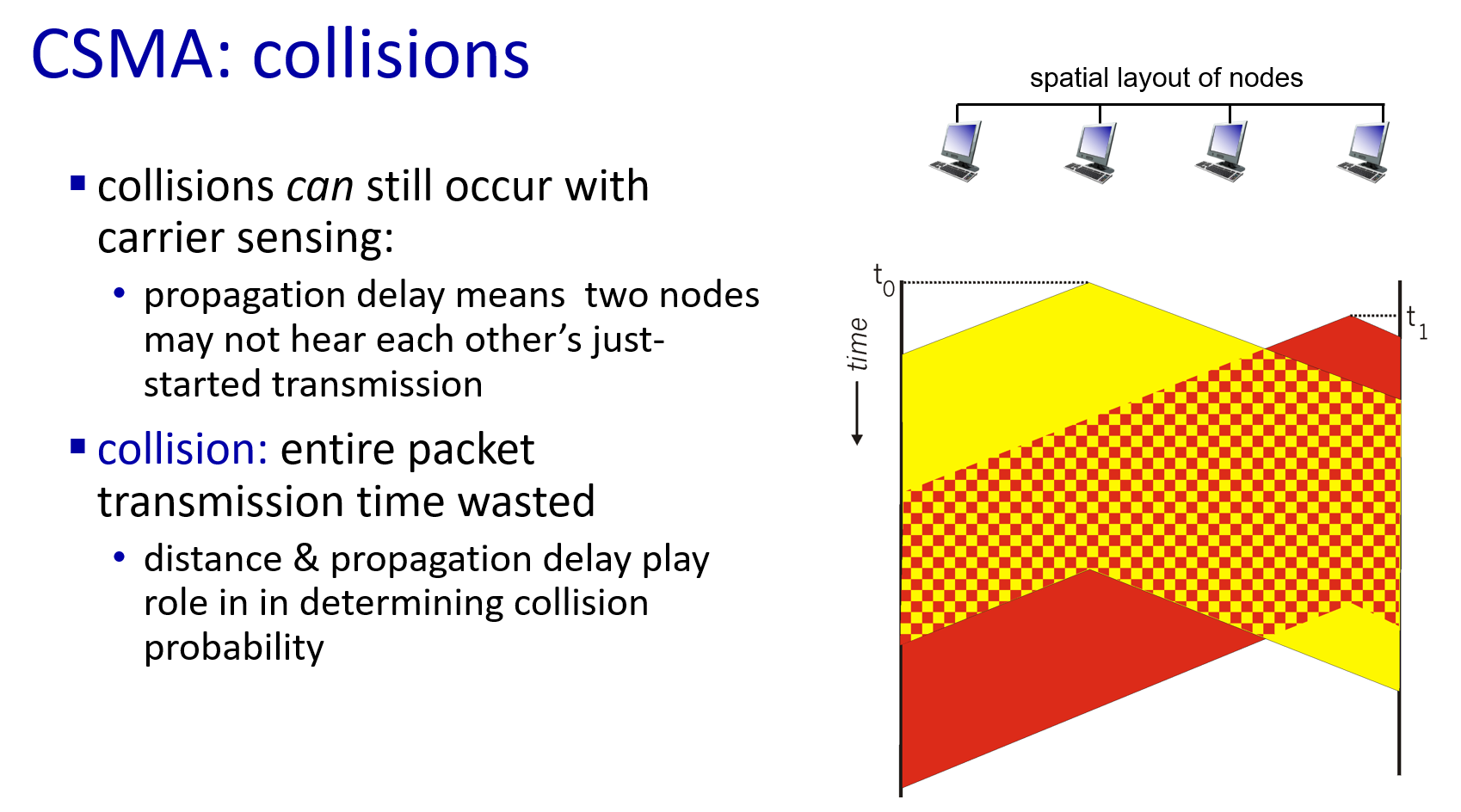

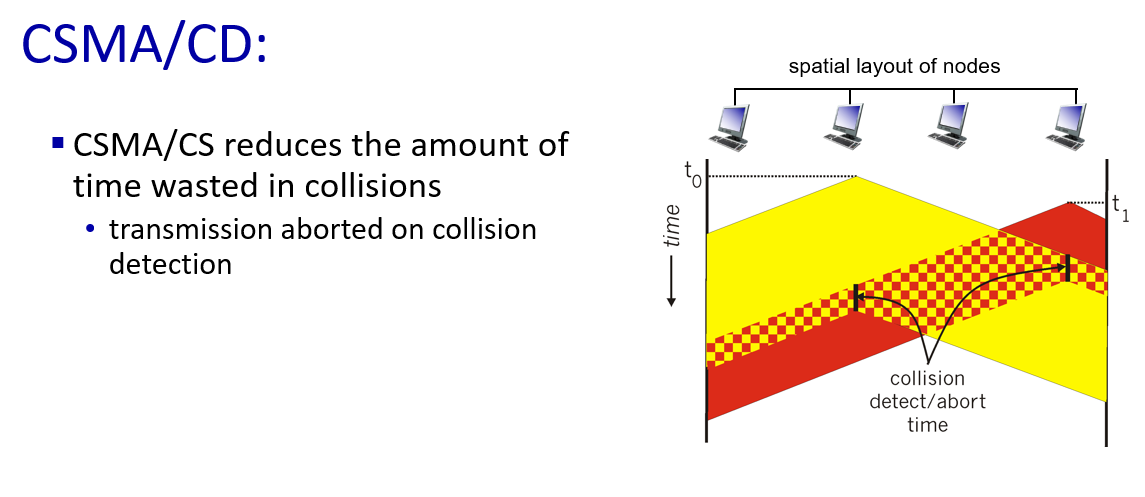

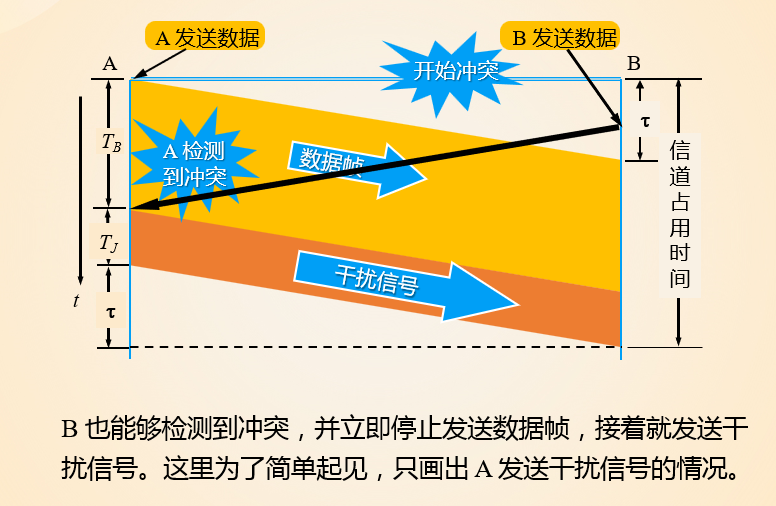

3. Taking turns

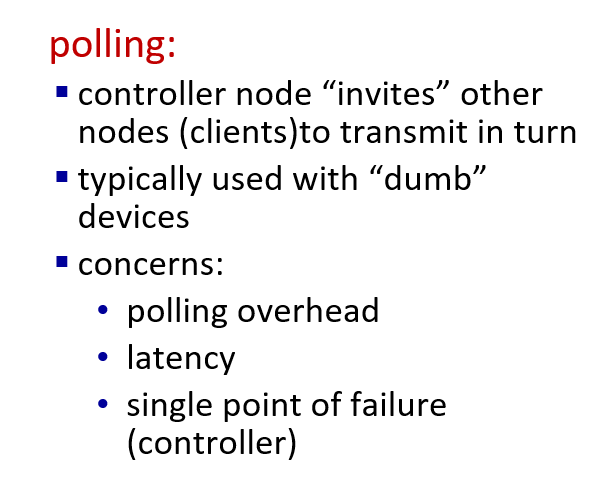
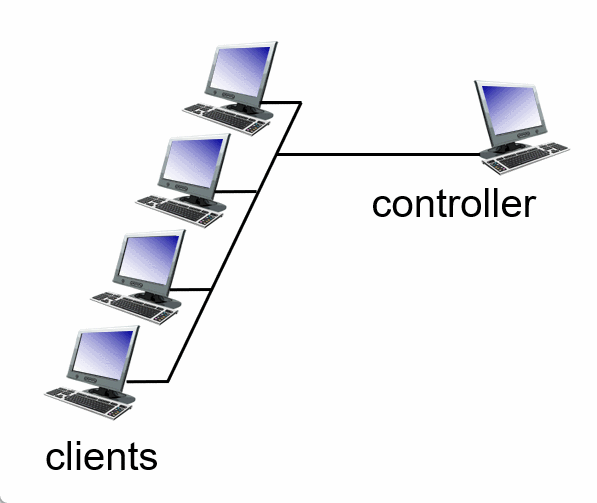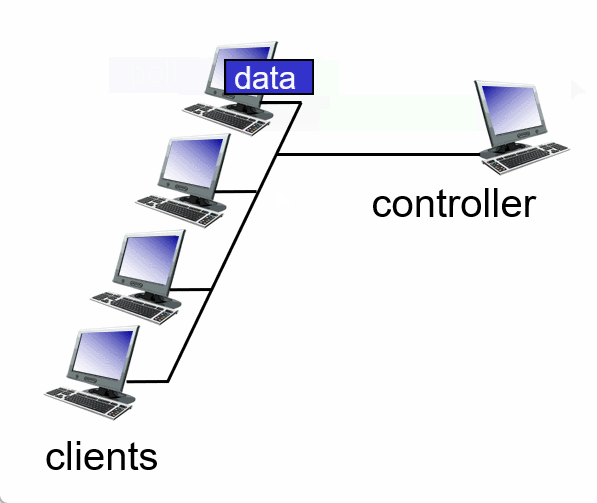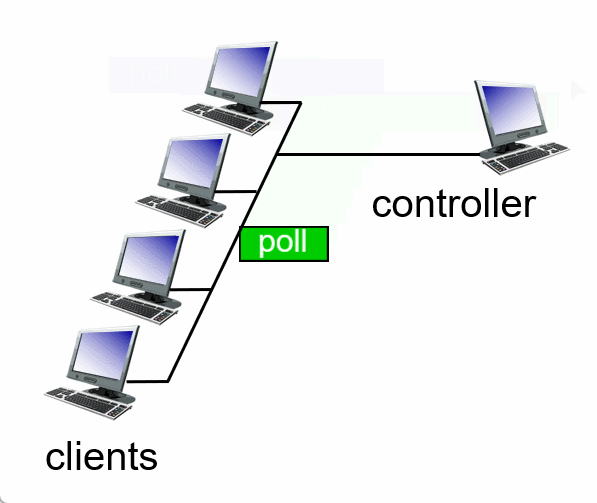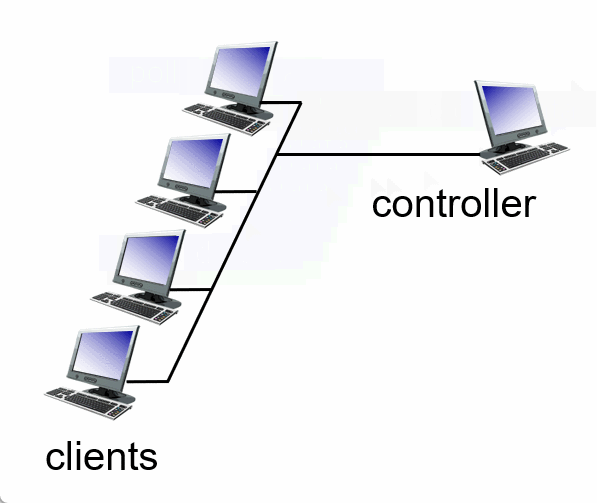

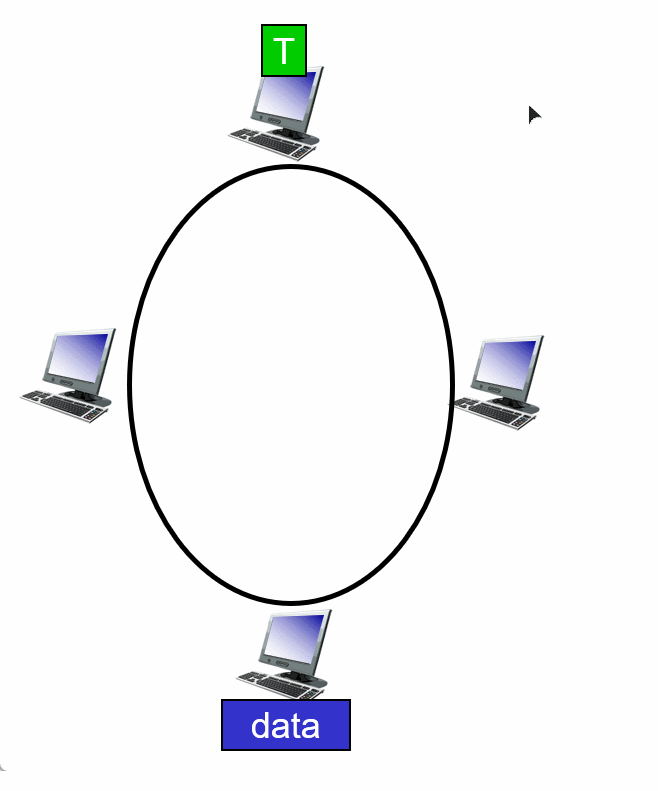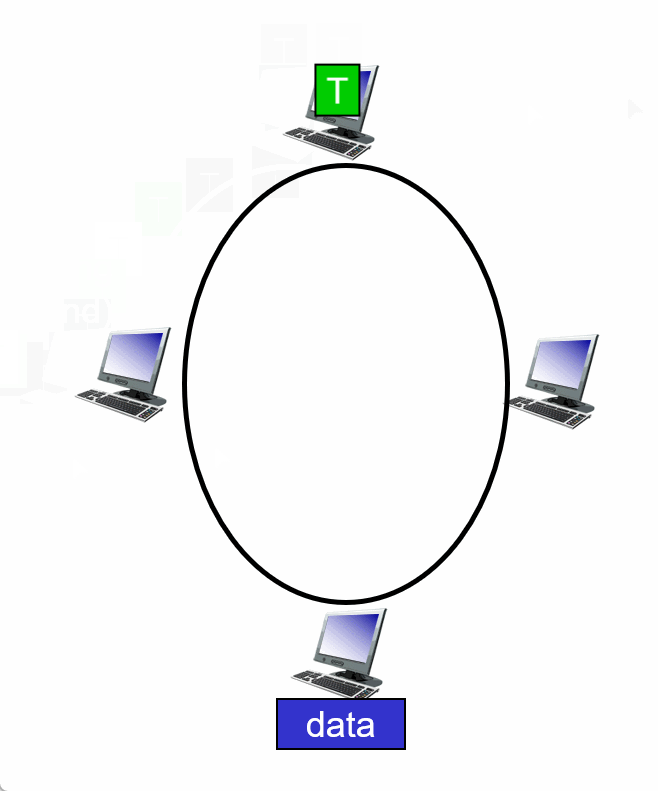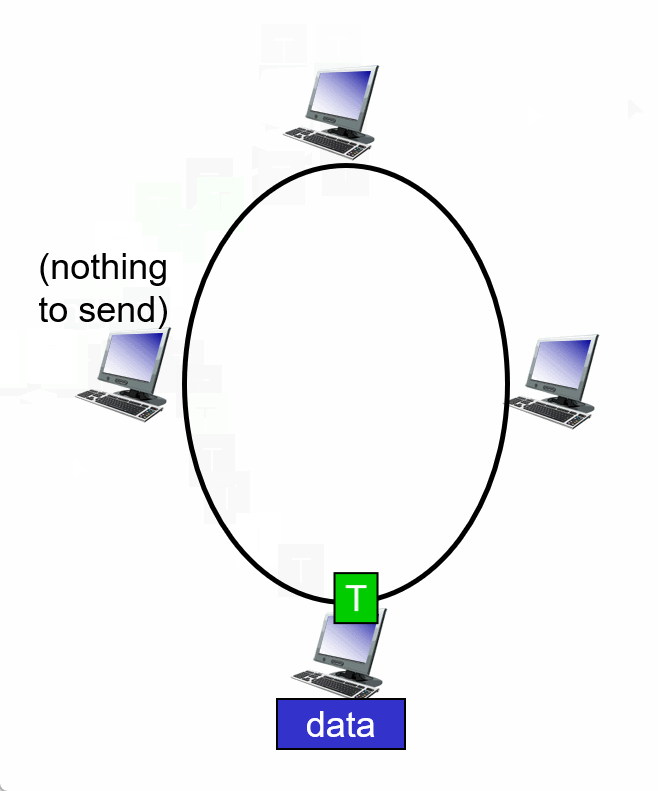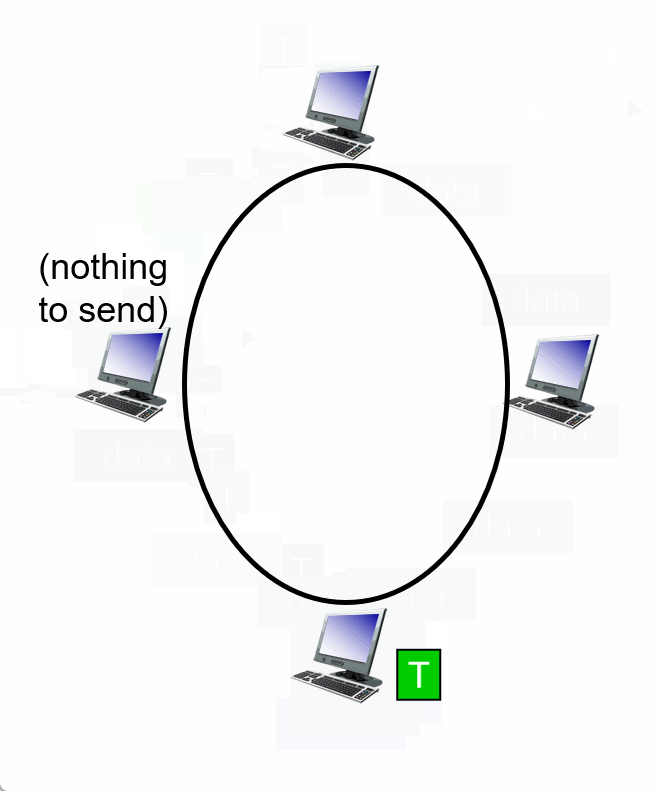
Summary
LANs
Local Area Networks
addressing, ARP
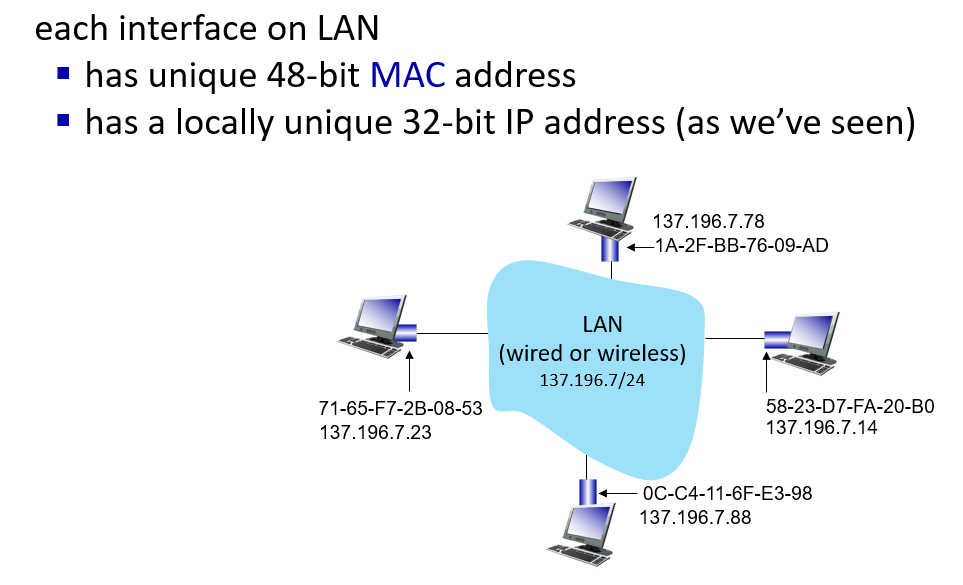
What is MAC address


ARP
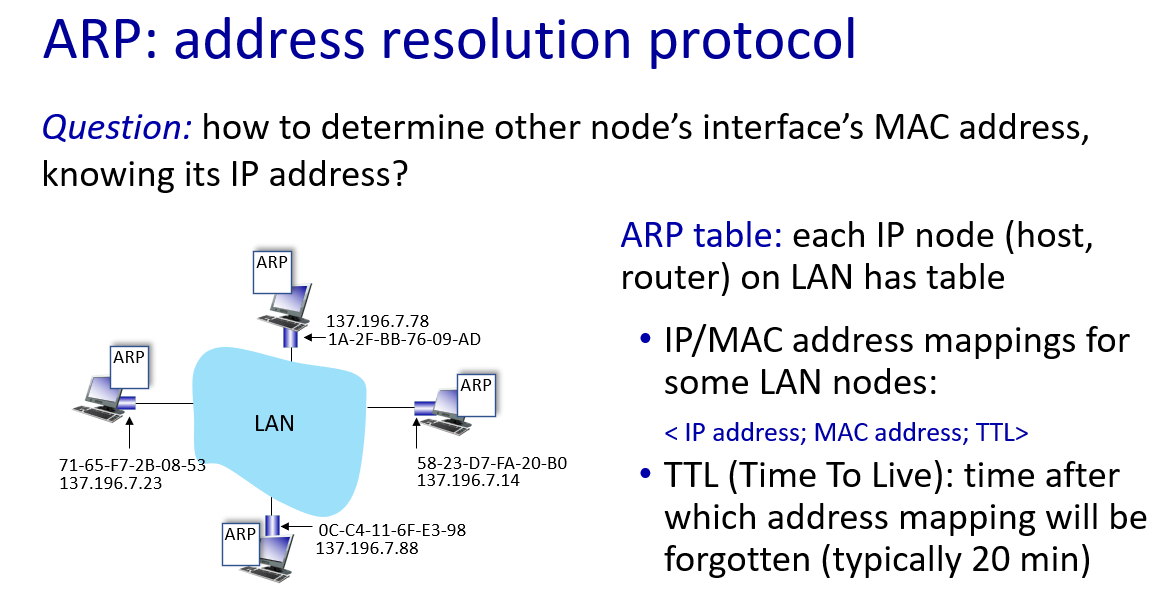
how it work
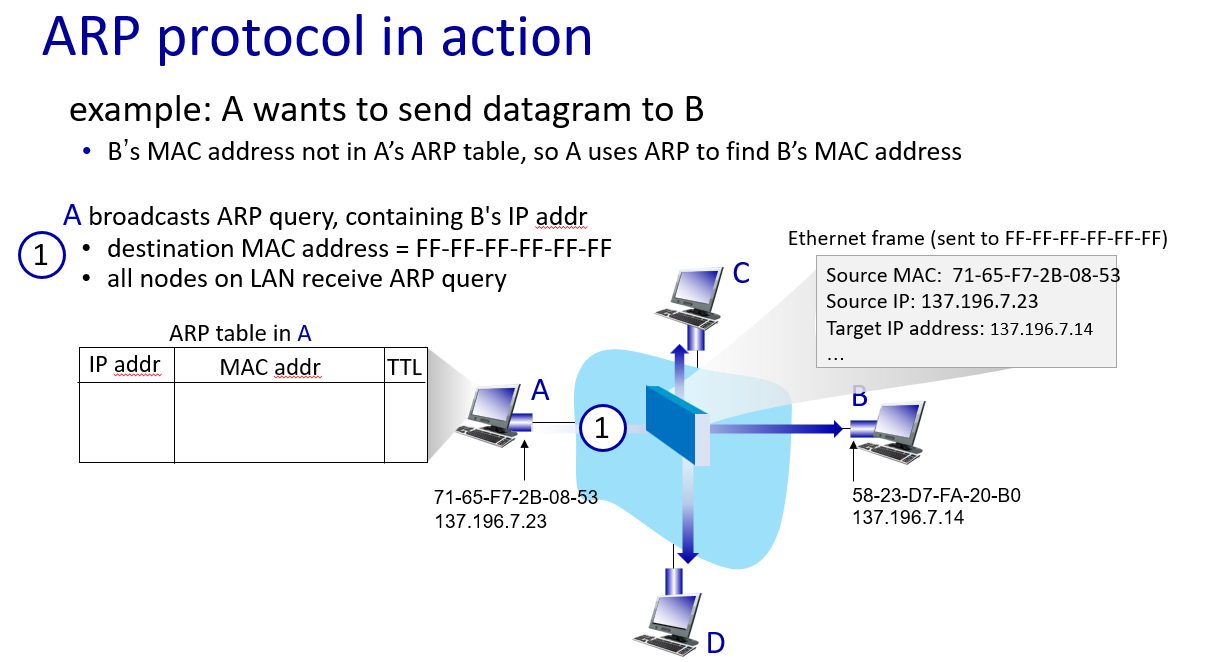
在以太网中,广播地址用于向网络中的所有设备发送数据帧。在 MAC 地址中,全为 FF 表示广播地址,而全为 00 的地址通常表示未知设备。因此,发送到全为 FF 的 MAC 地址的数据帧将被发送到网络中的所有设备。
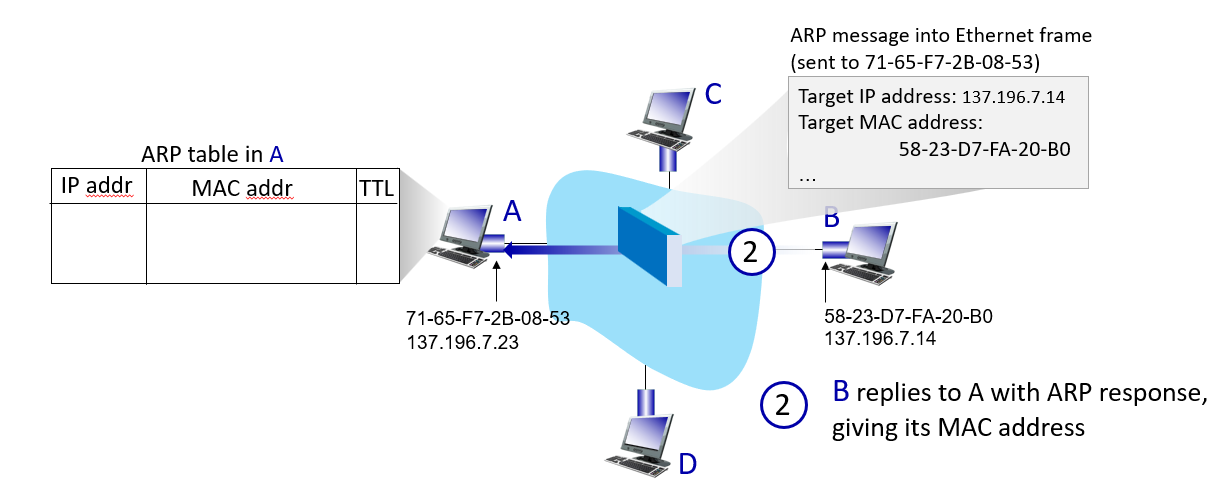
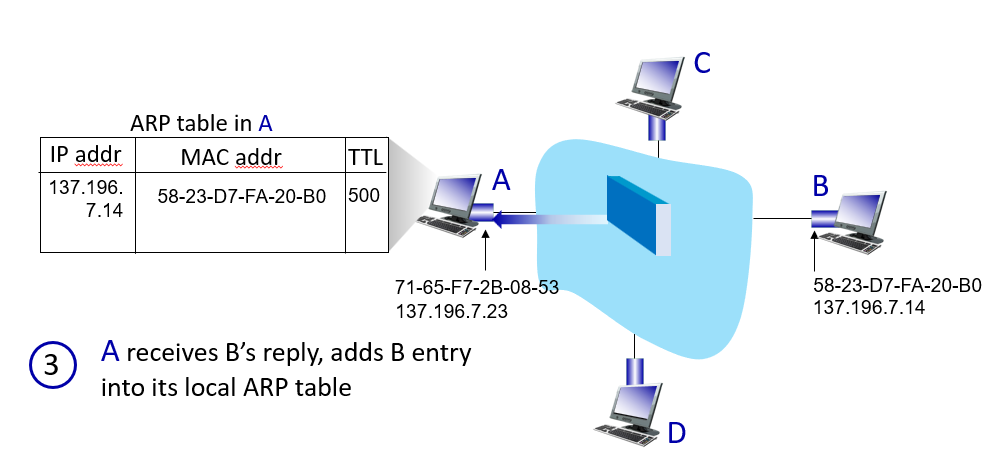
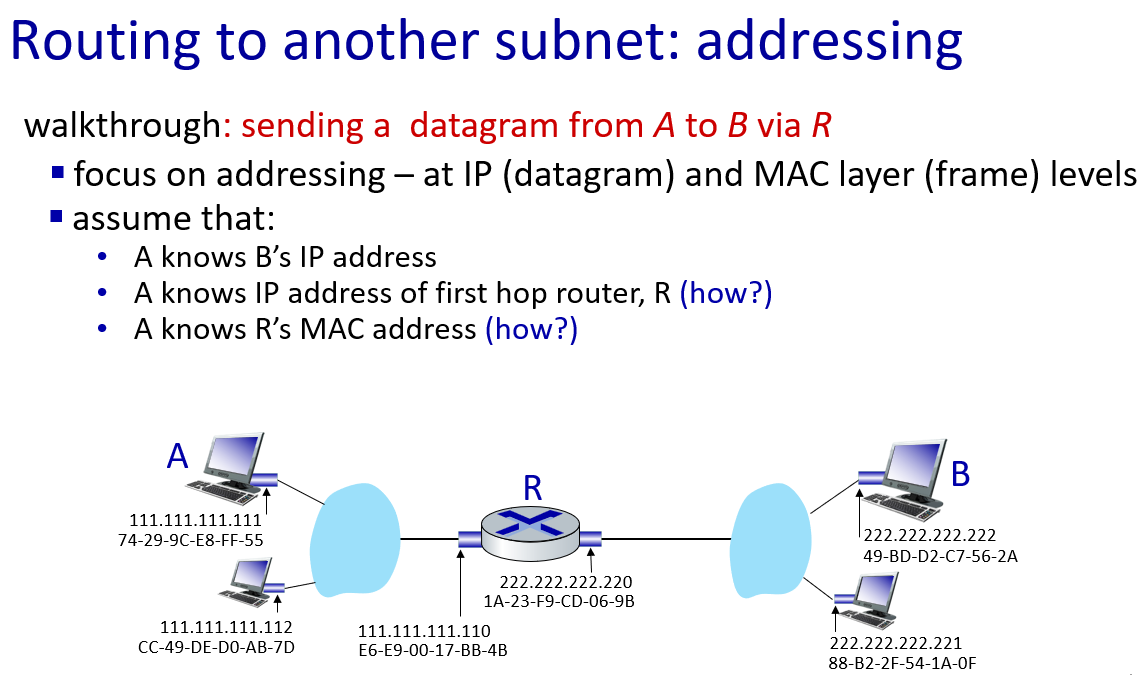
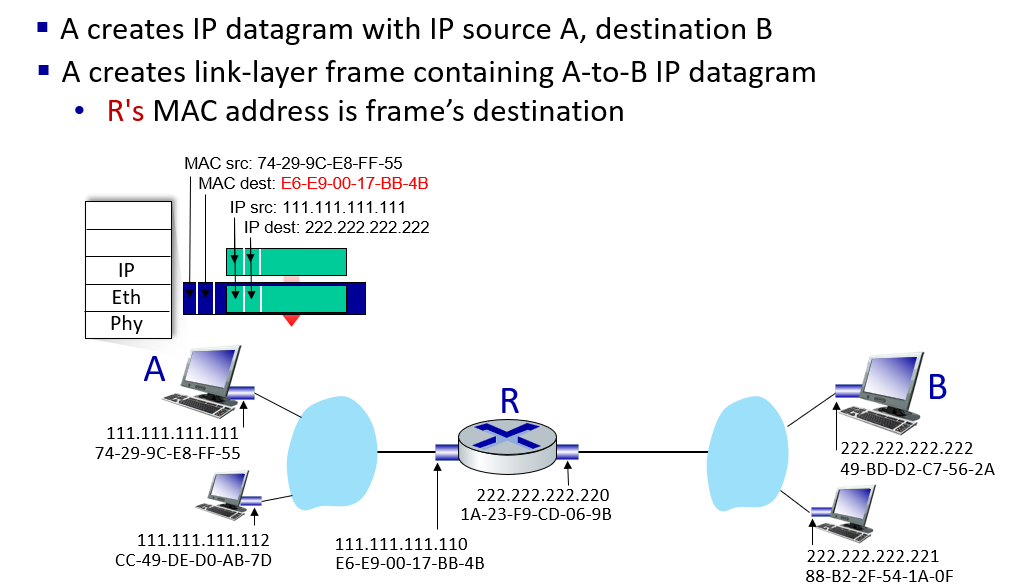
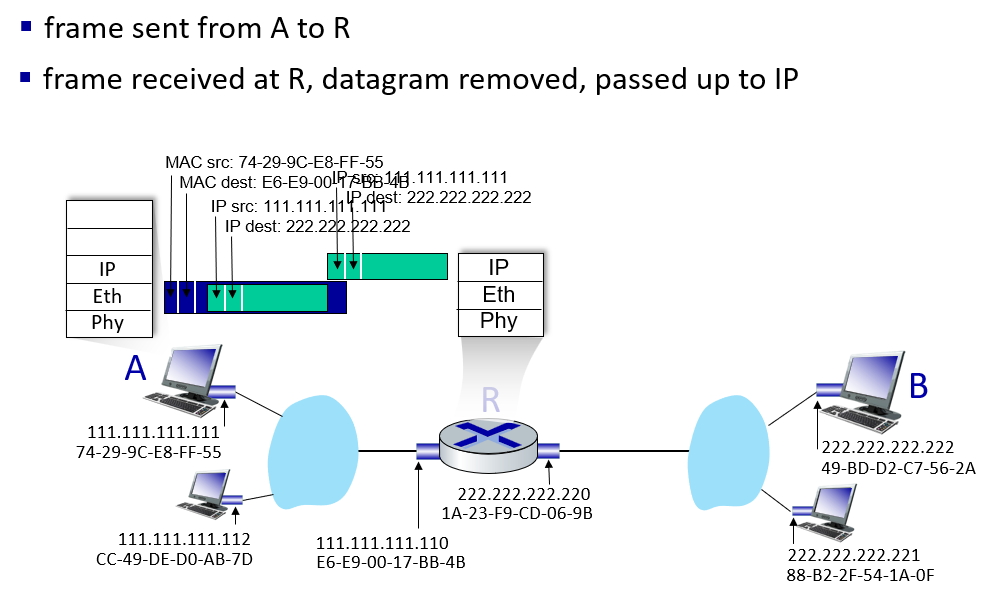
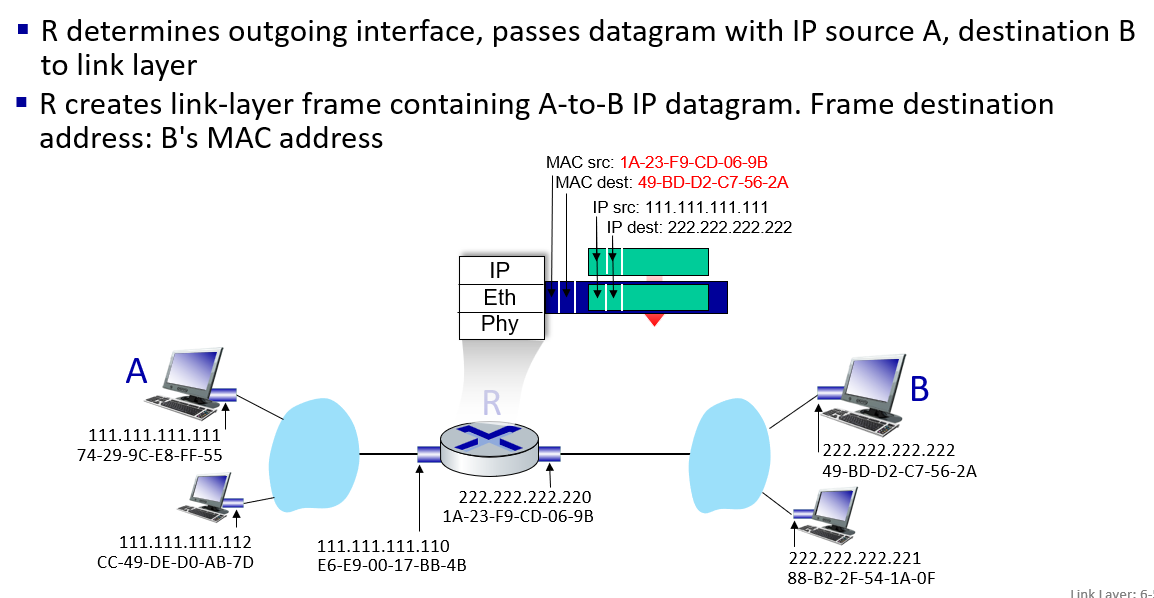
Ethernet
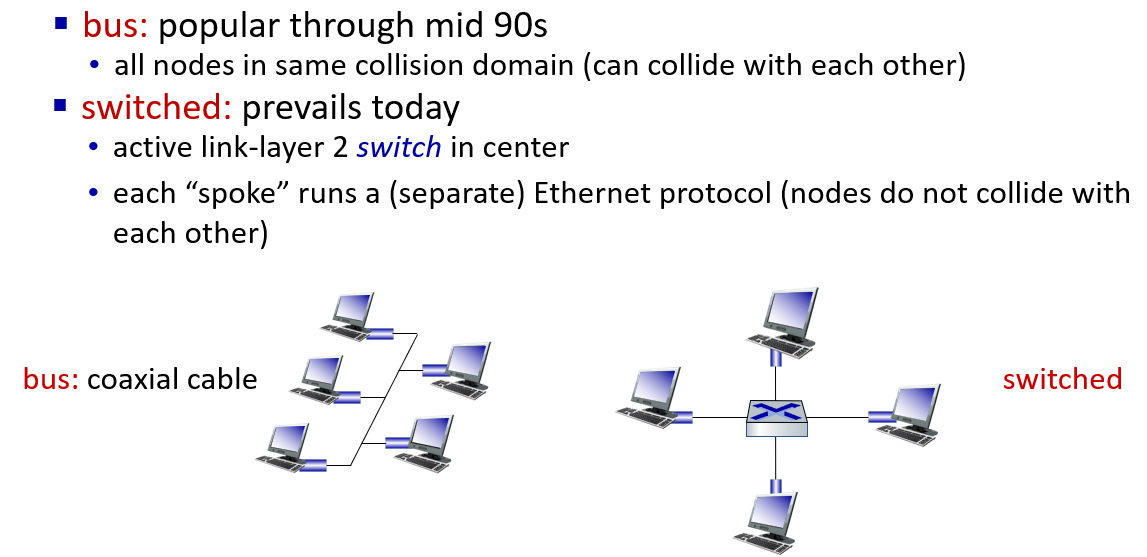
physical topology
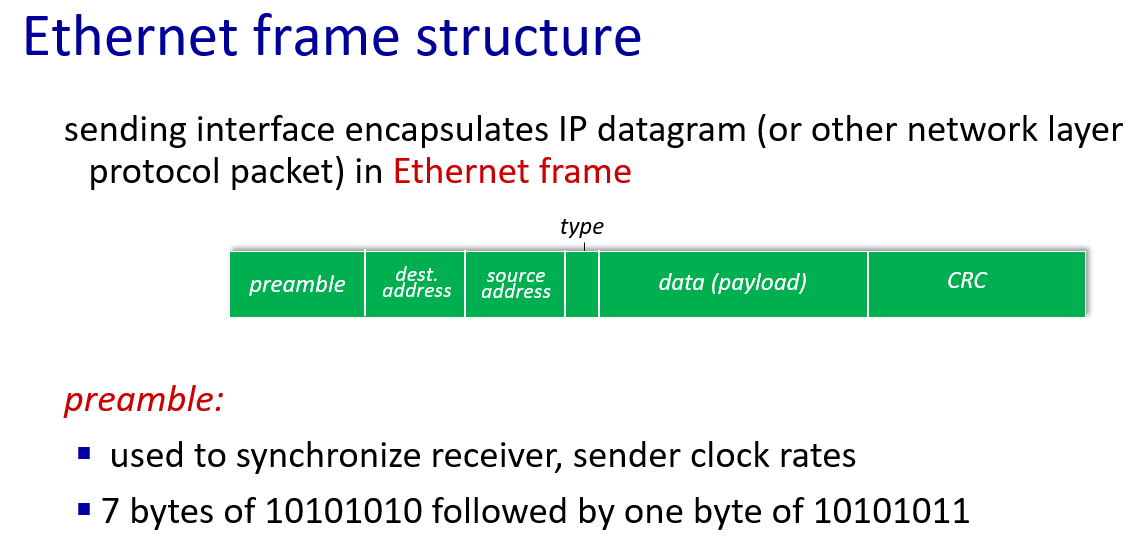
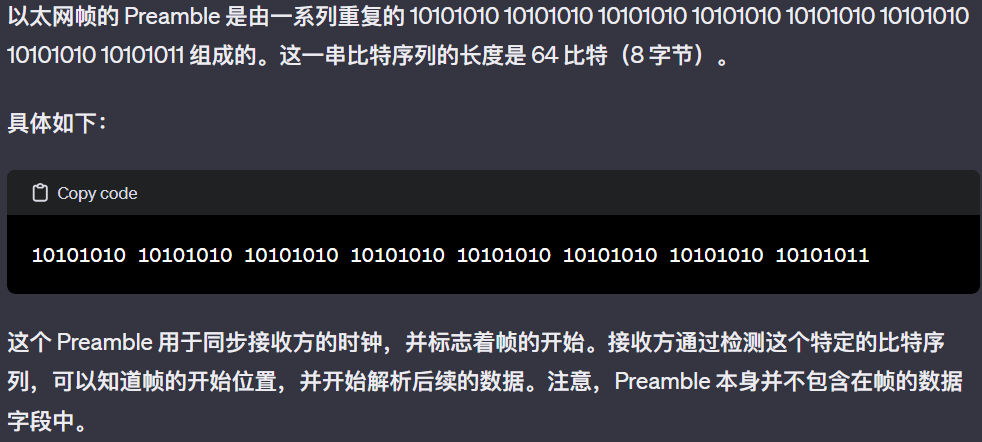

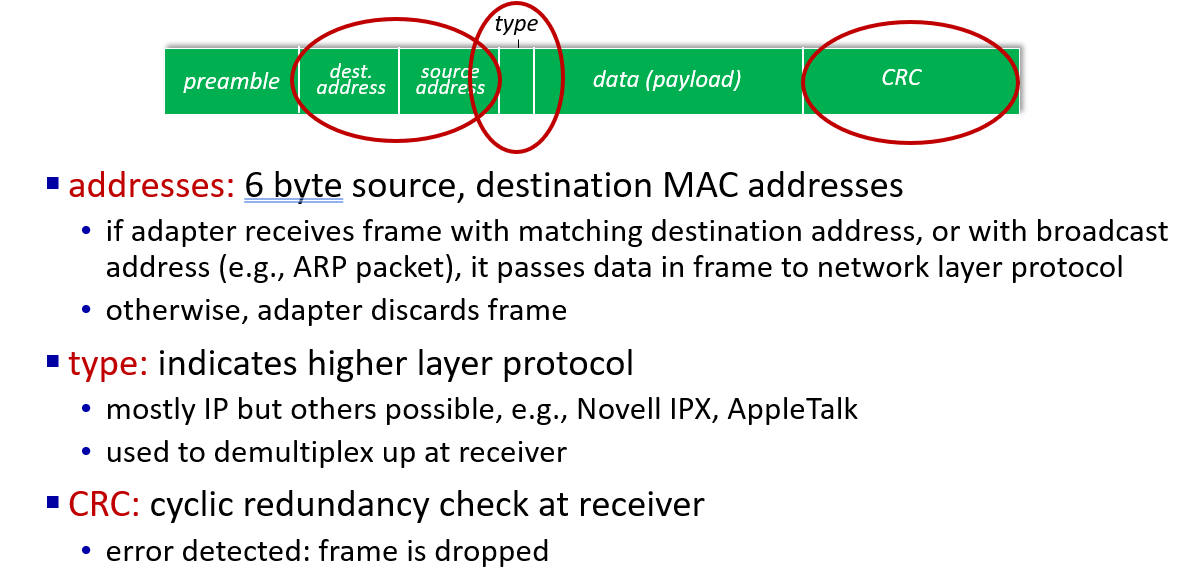
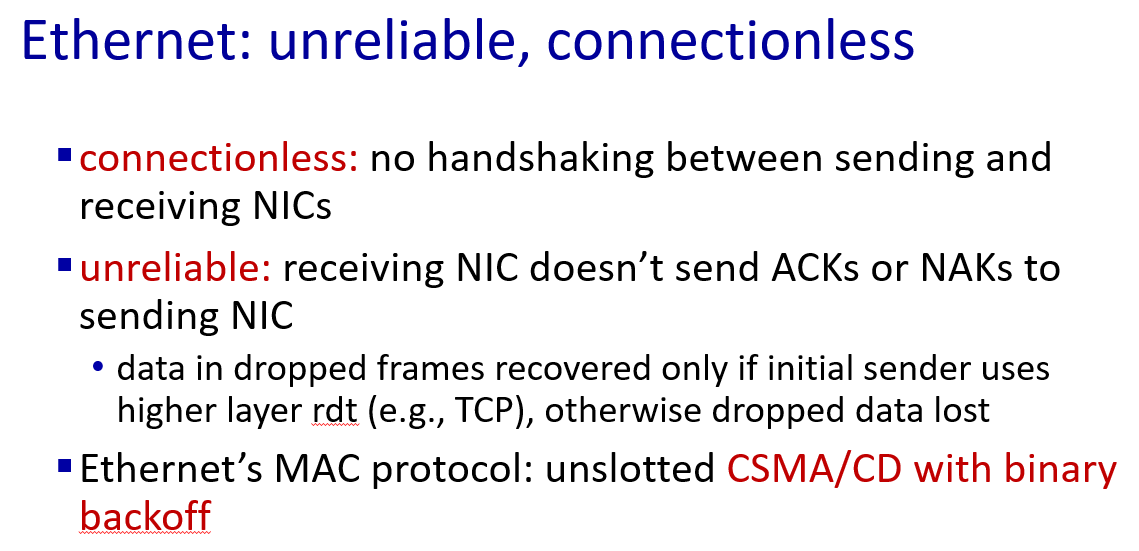
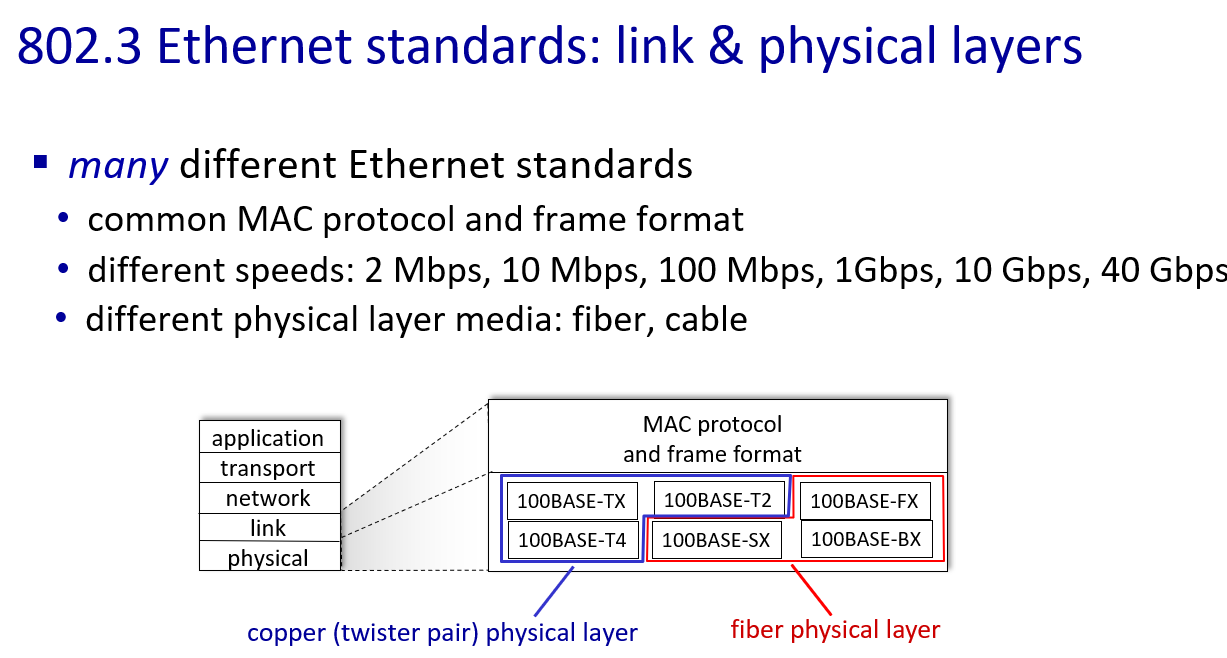
switches
只要在物理连接范围内能直接连,那么就可以直接通信,前提是,对应上“网卡编号”。当A在这个范围内发送任意信息的时候,实际上,范围内的任何主机都能收到信息。如何判断是发给自己的,就需要A在信息中包含一个网卡编号,所有收到信息的设备都会把这个编号和自己的编号进行对比,如果一样,就接收这个信息,否则丢弃。这样的网卡编号就是MAC地址
交换机,实际上就是MAC指路牌。因为,最早的时候,A发出的信息,大家都会收到,大家频繁的发信息,会造成线路传输上的浪费,为了解决这个问题,最好的办法就是“引路”。即A发出的信息,不用大家都收到,只需要B收到即可。这意味着,至少需要一个 对应的表 来控制电路的传输。这个对应的表就是MAC表,存在于交换机内部,它会把每个端口连接的机器其MAC地址记下来。最终让信息根据查MAC表来送到对应的端口即可
这里segment是网络段(LAN)的意思,交换机有选择地将数据帧发送到目标设备所在的端口

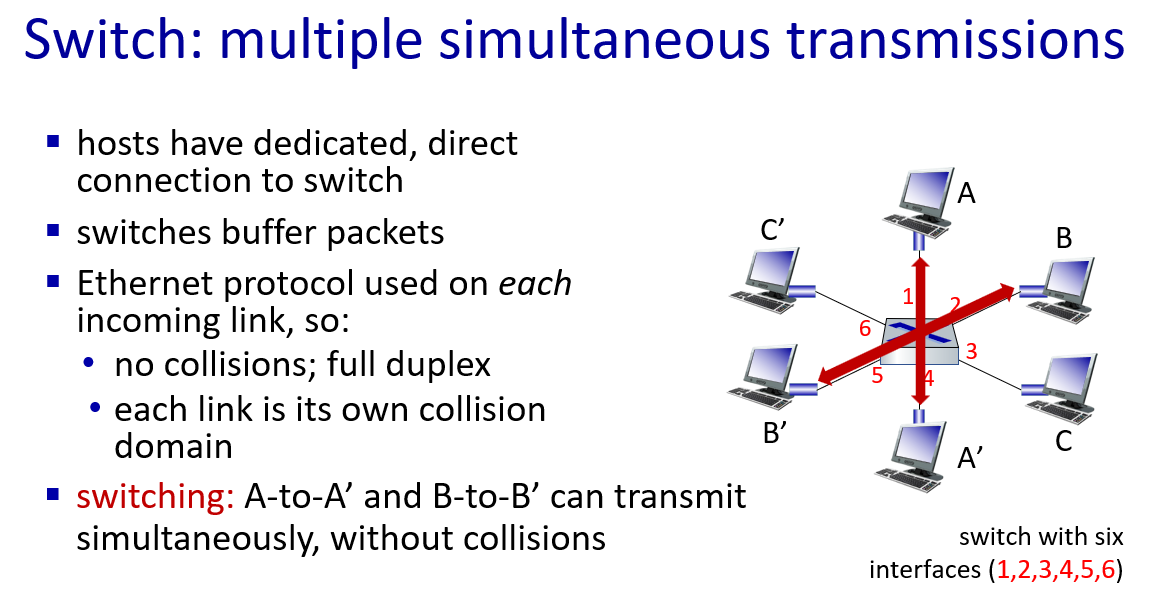
but A-to-A’ and C to A’ can not happen simultaneously

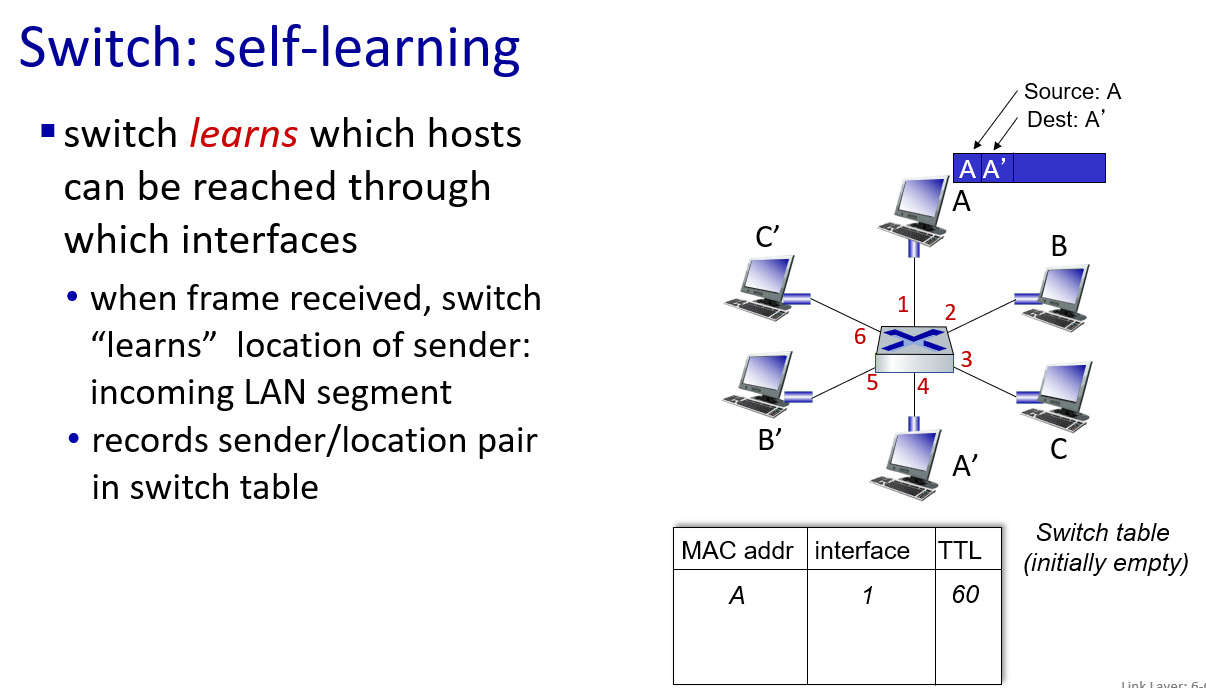
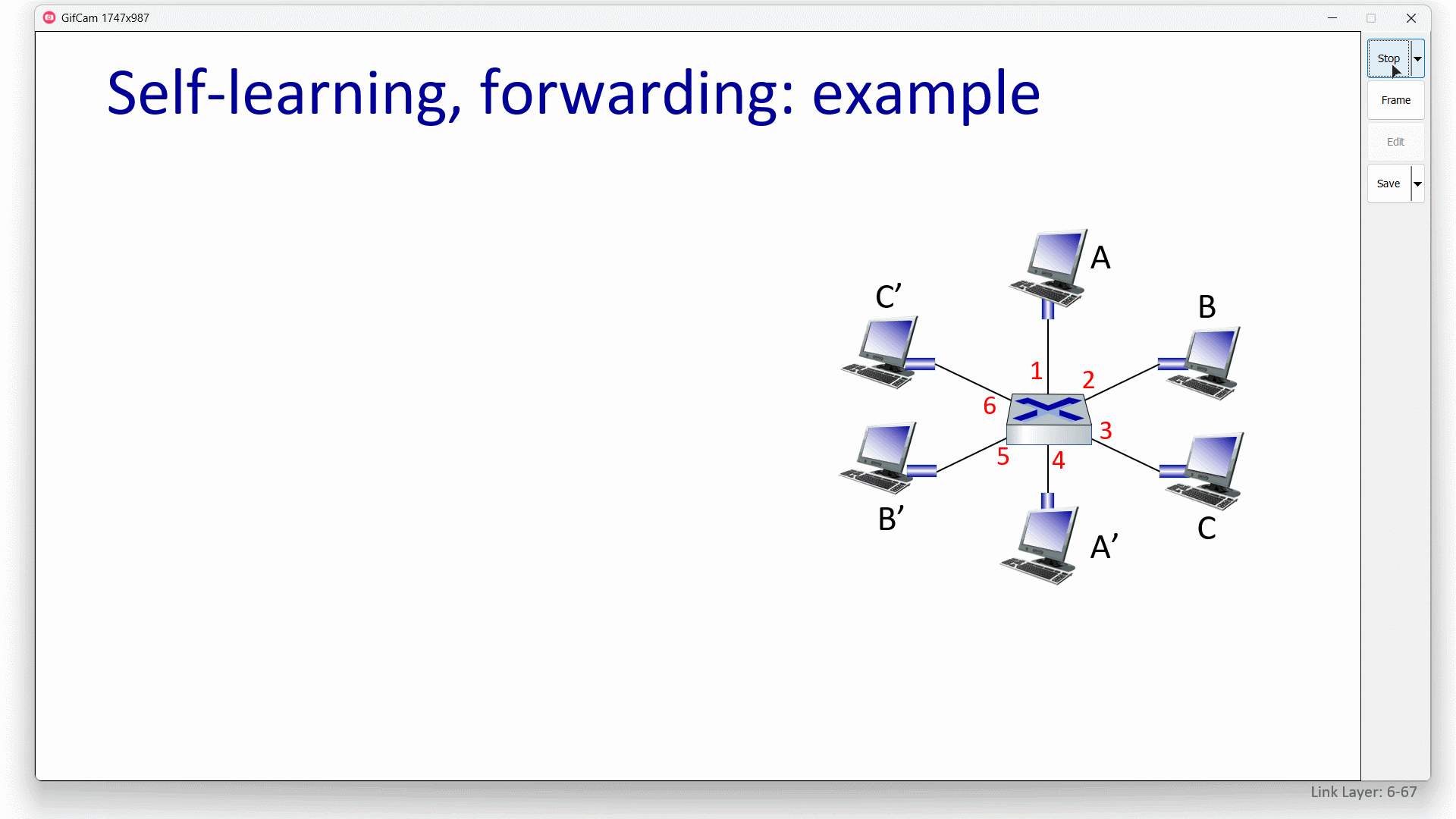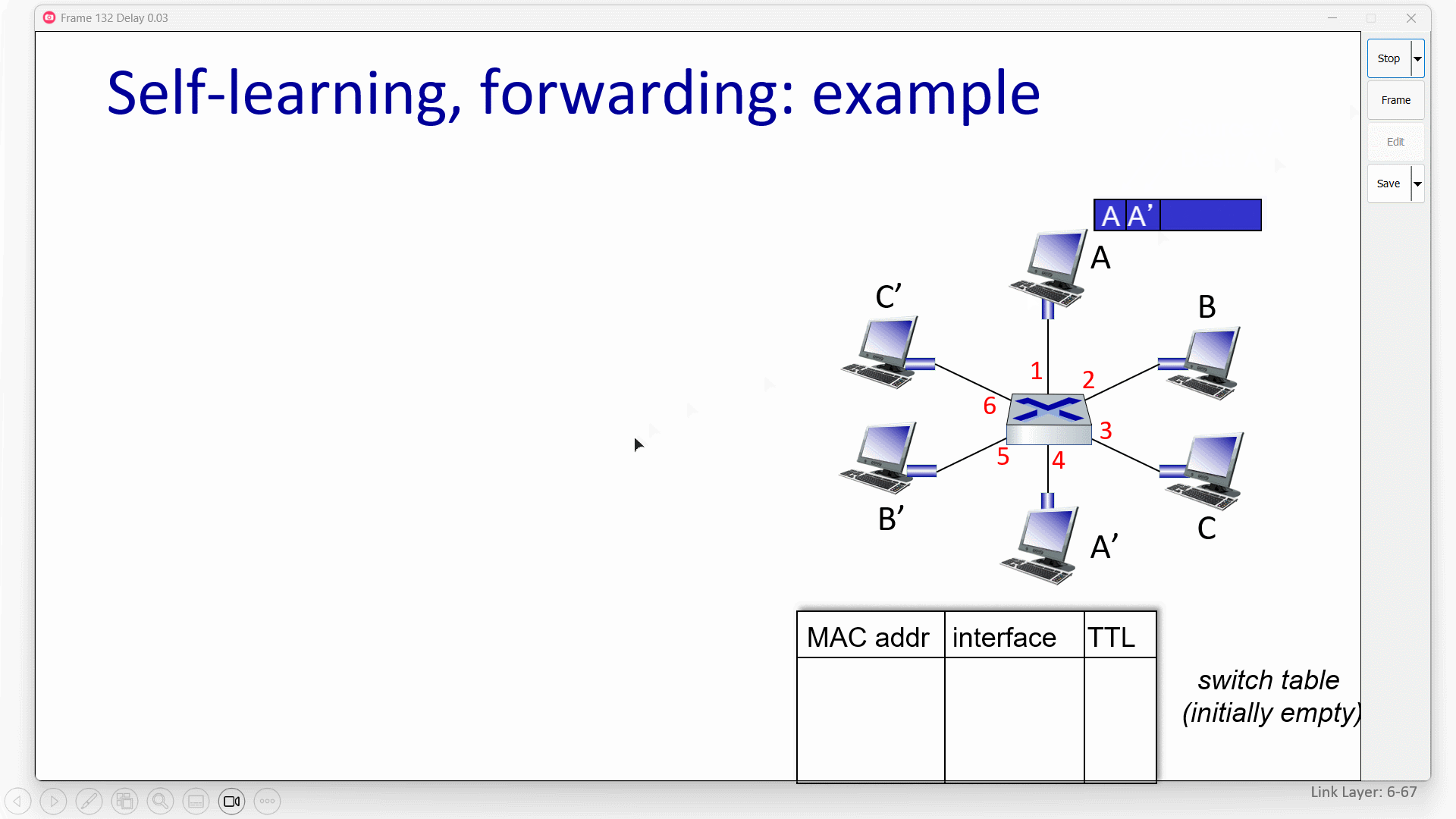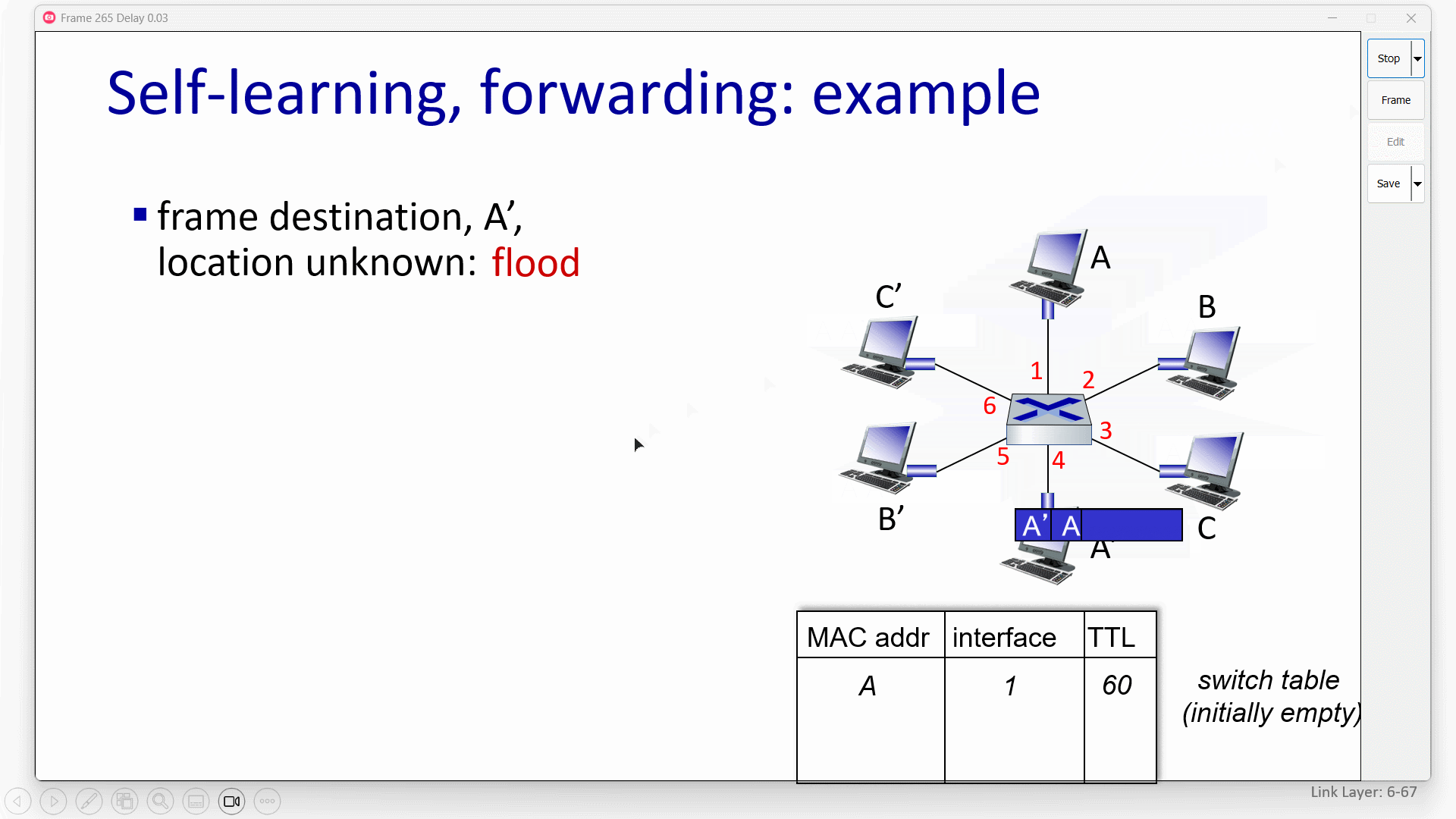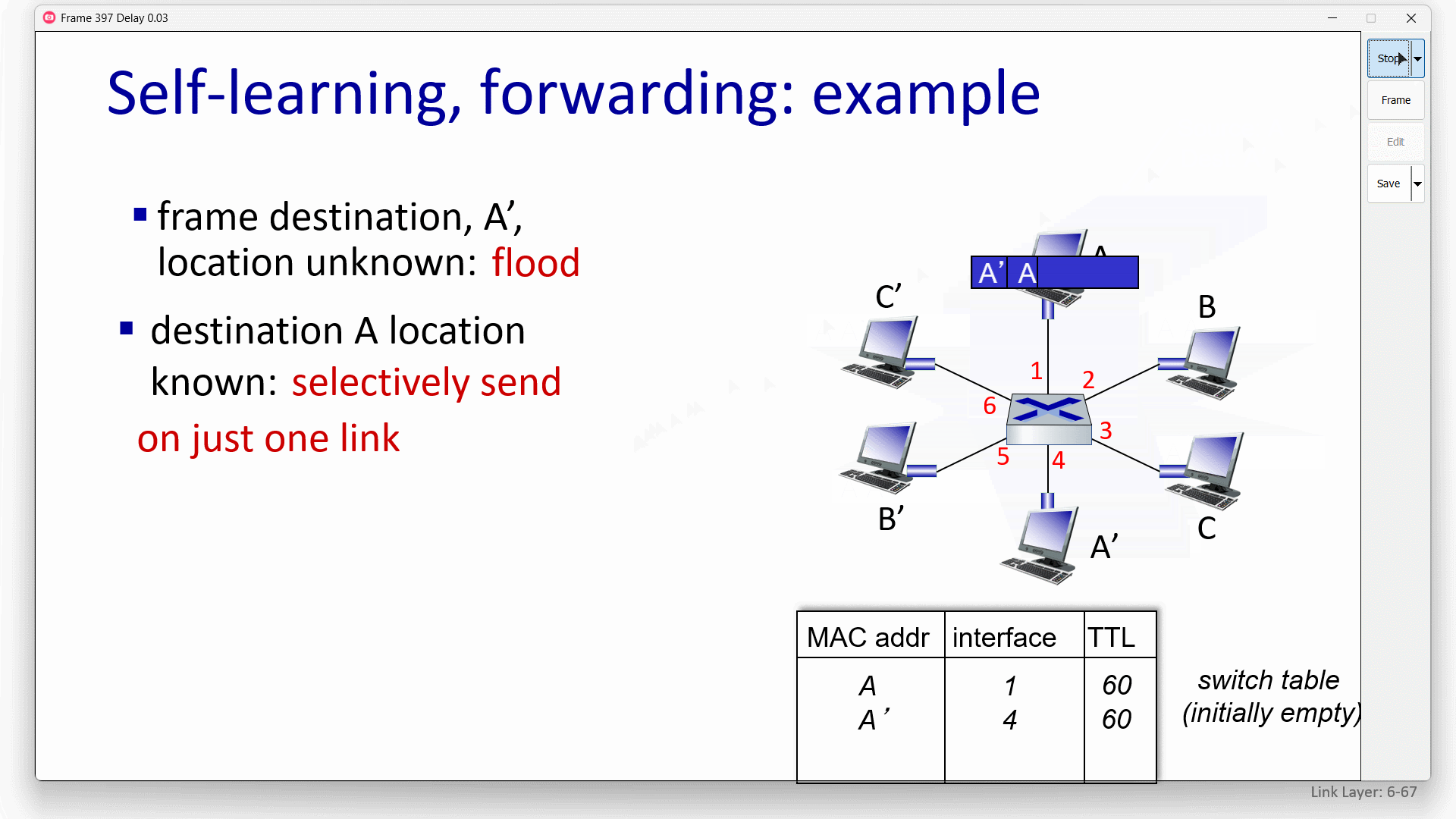

if frame want to go to the LAN where it comes ,switch drop it.
for example: if S1 is a switch,then it need to drop frame from B to A,because they are in same LAN.
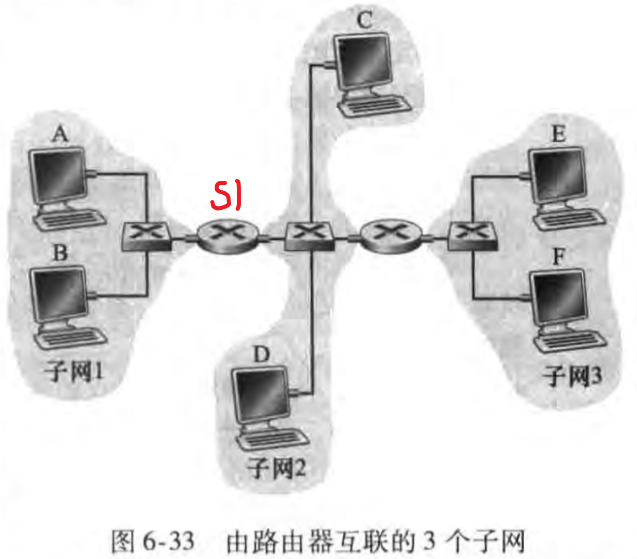
self-learning switches can be connected together
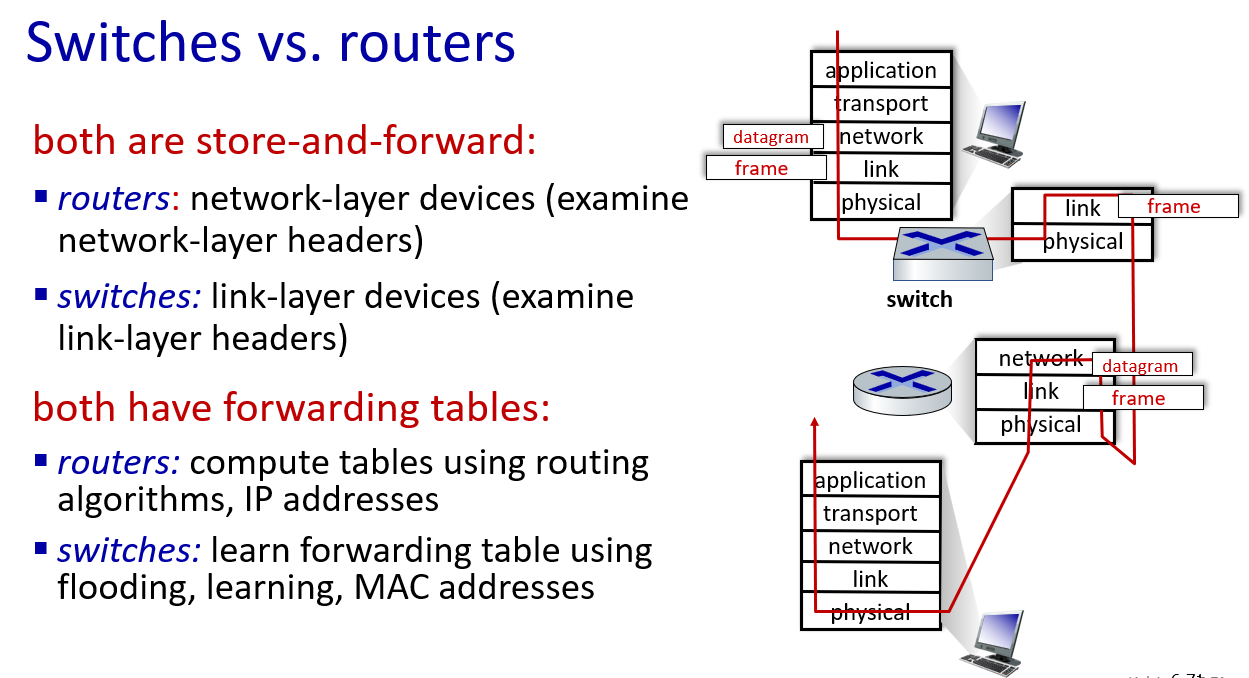
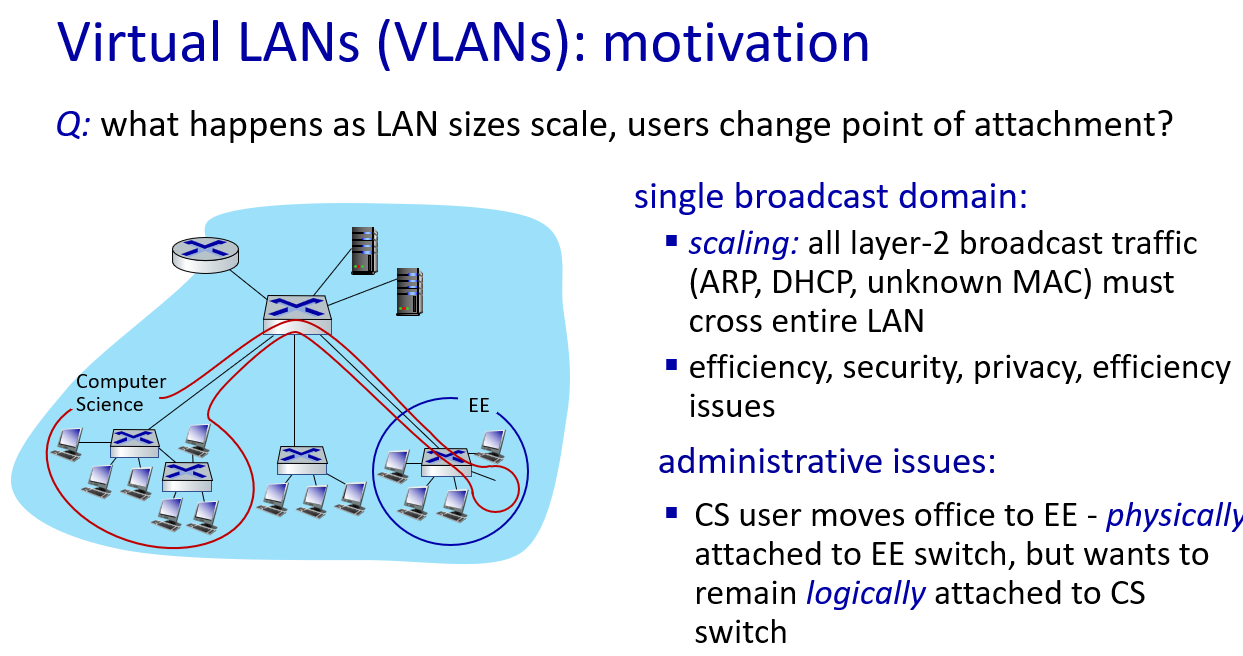
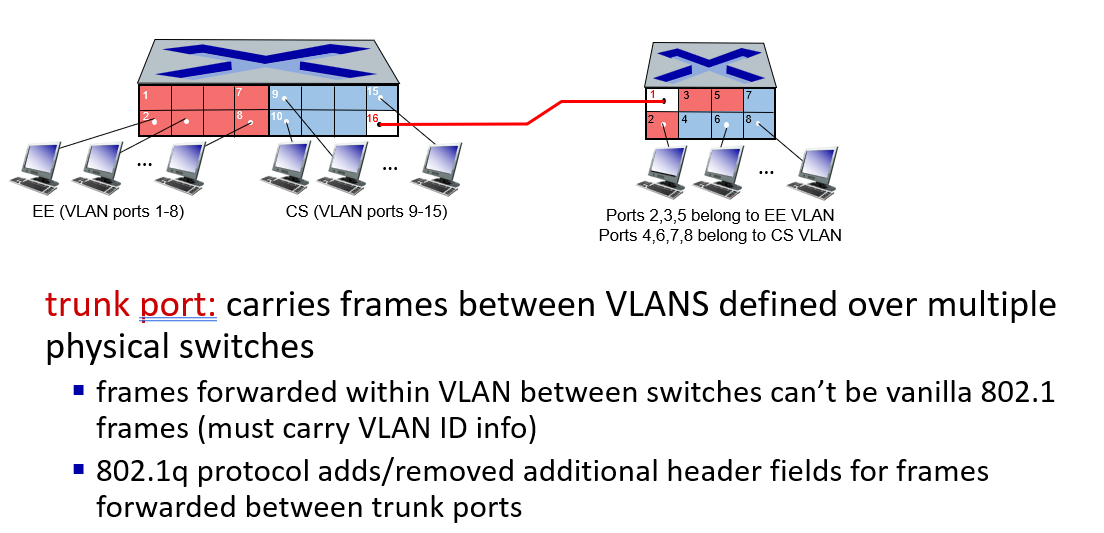
VLANs
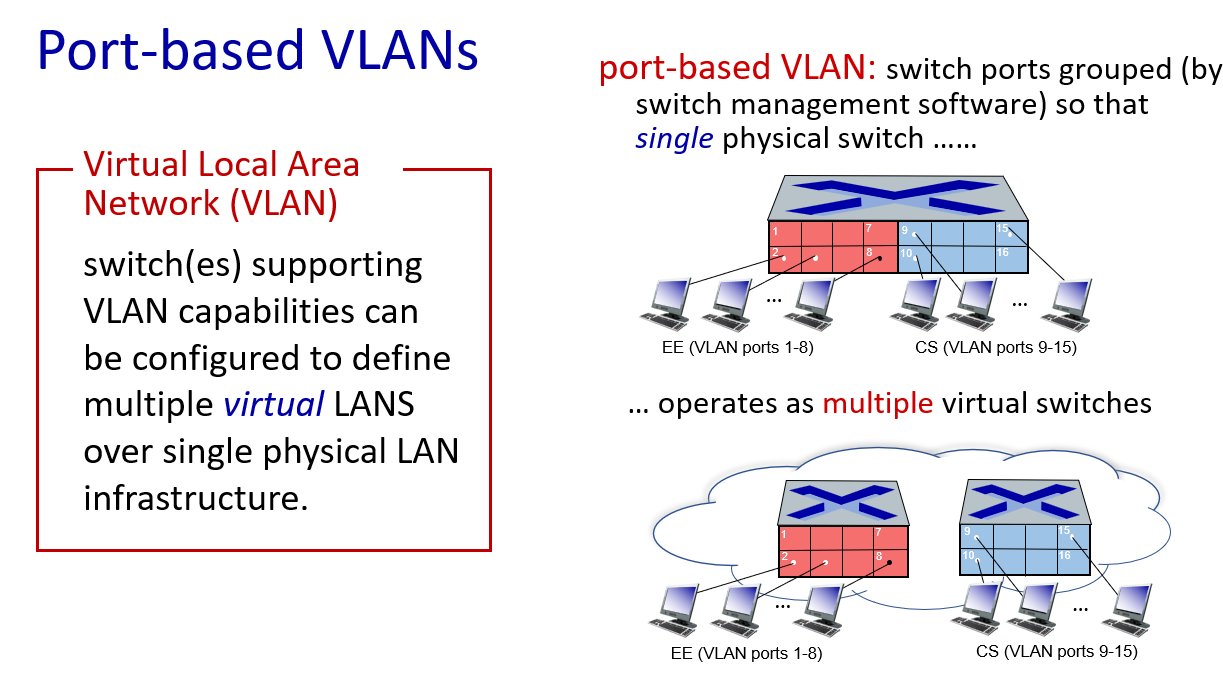
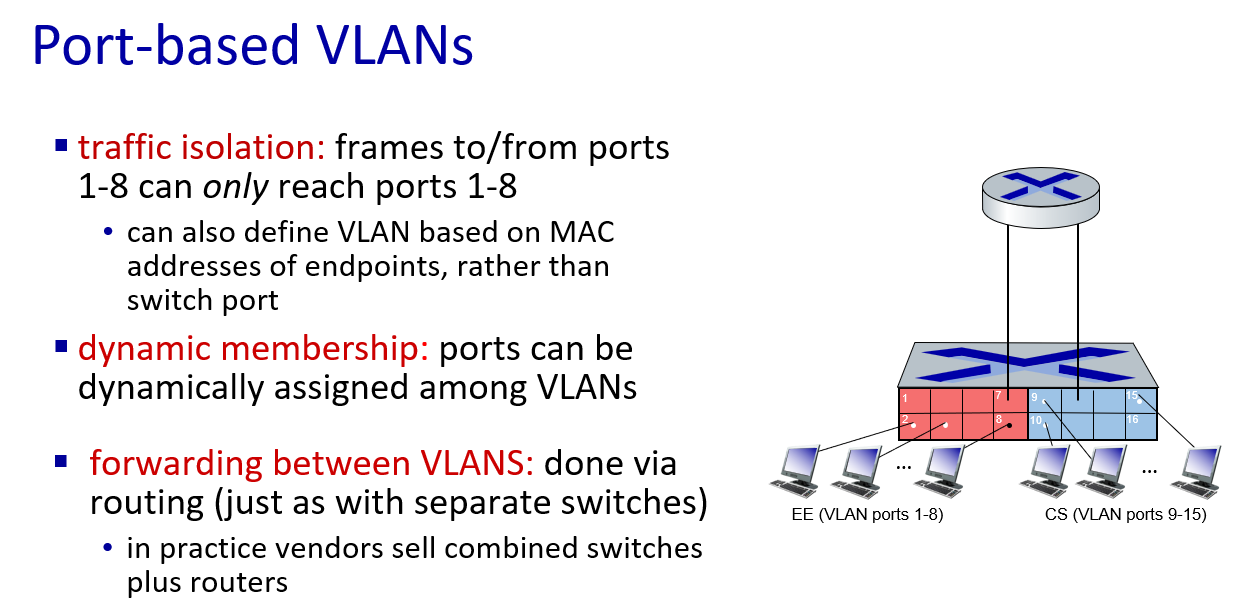
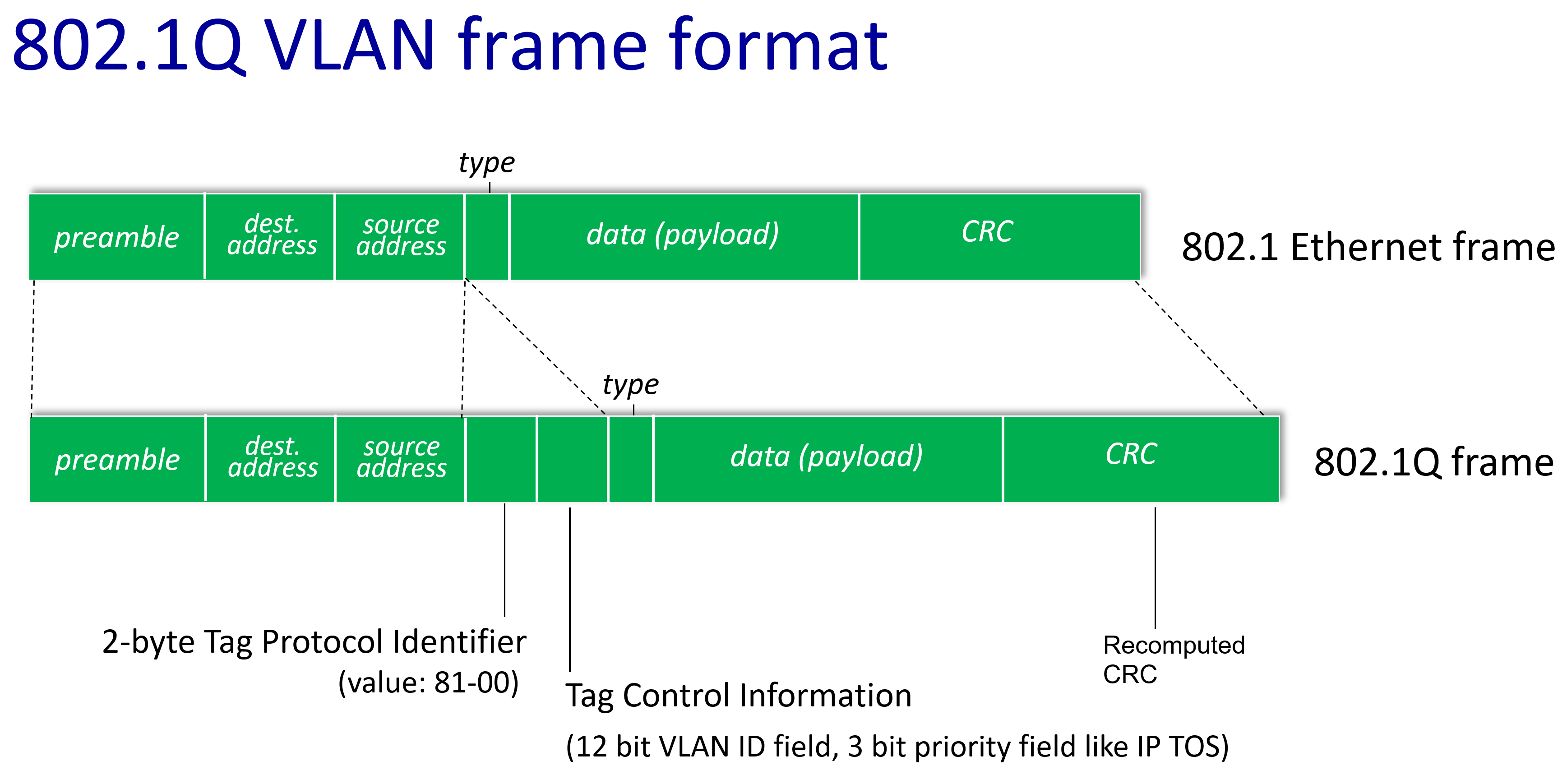
To use vlan,information need to add to 802.1 Ethernet frame.
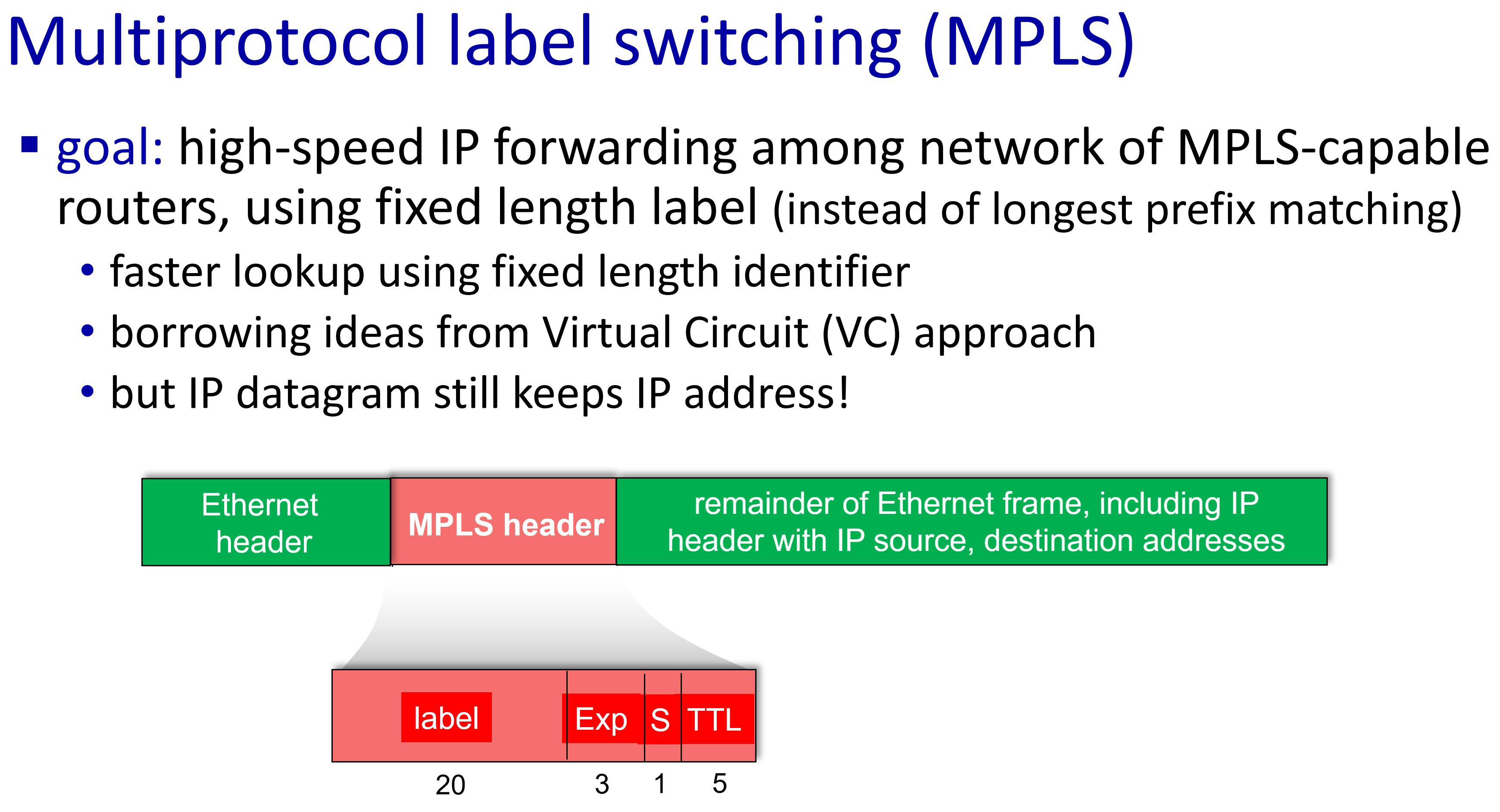
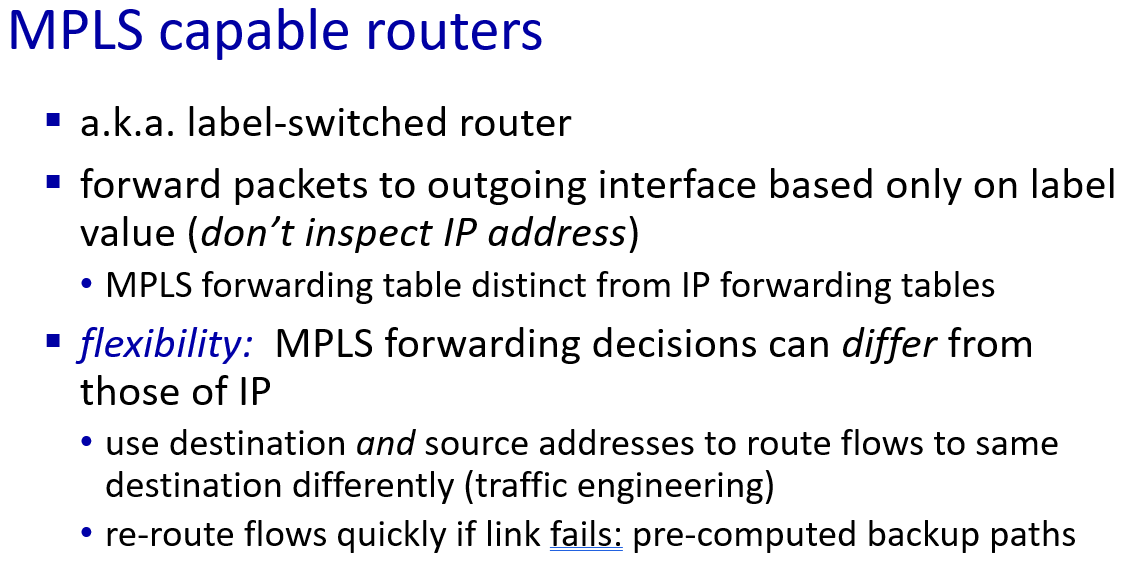
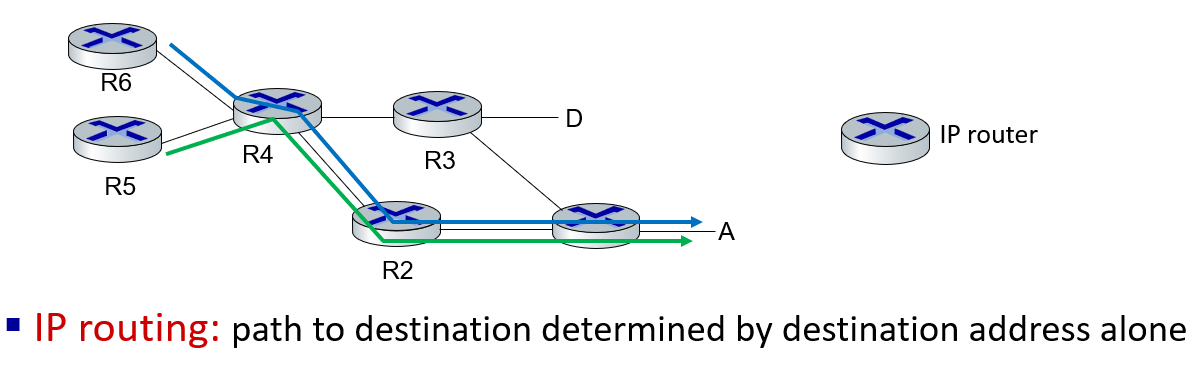
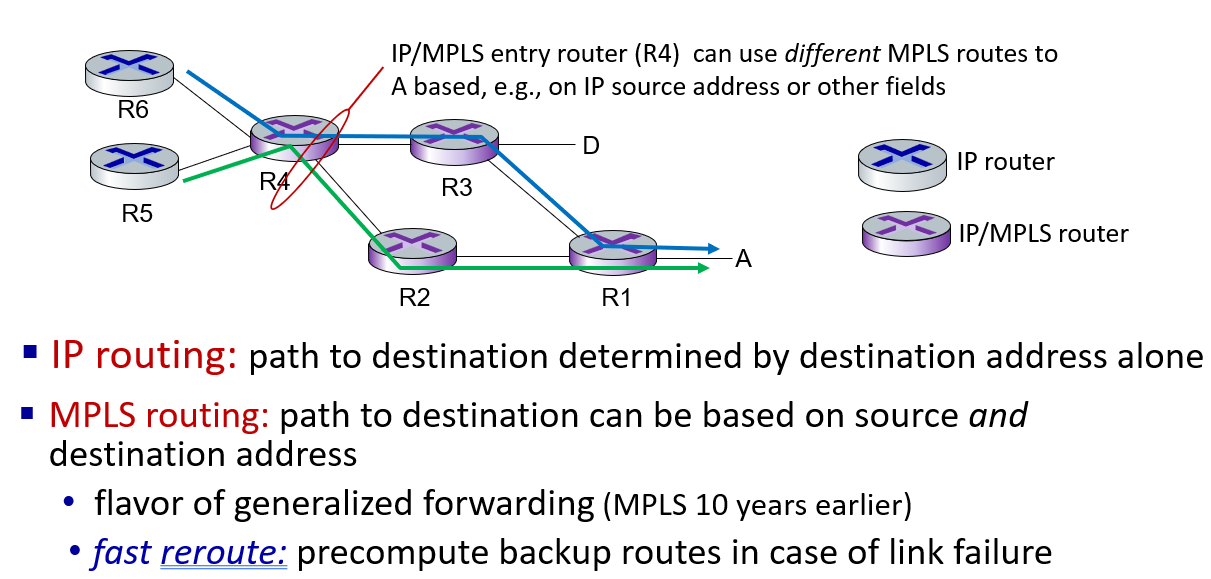
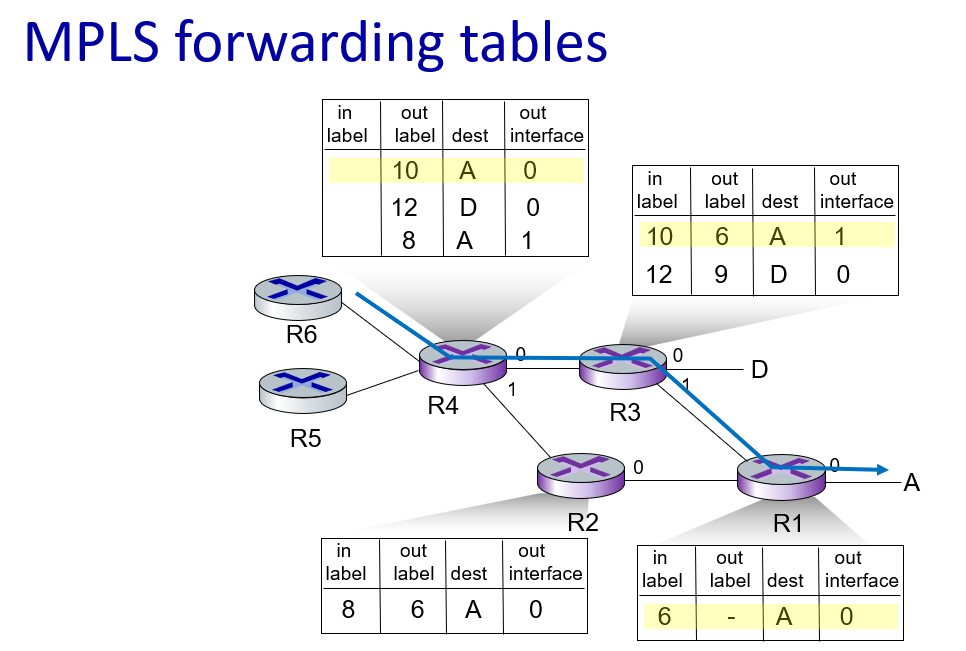
link virtualization: MPLS

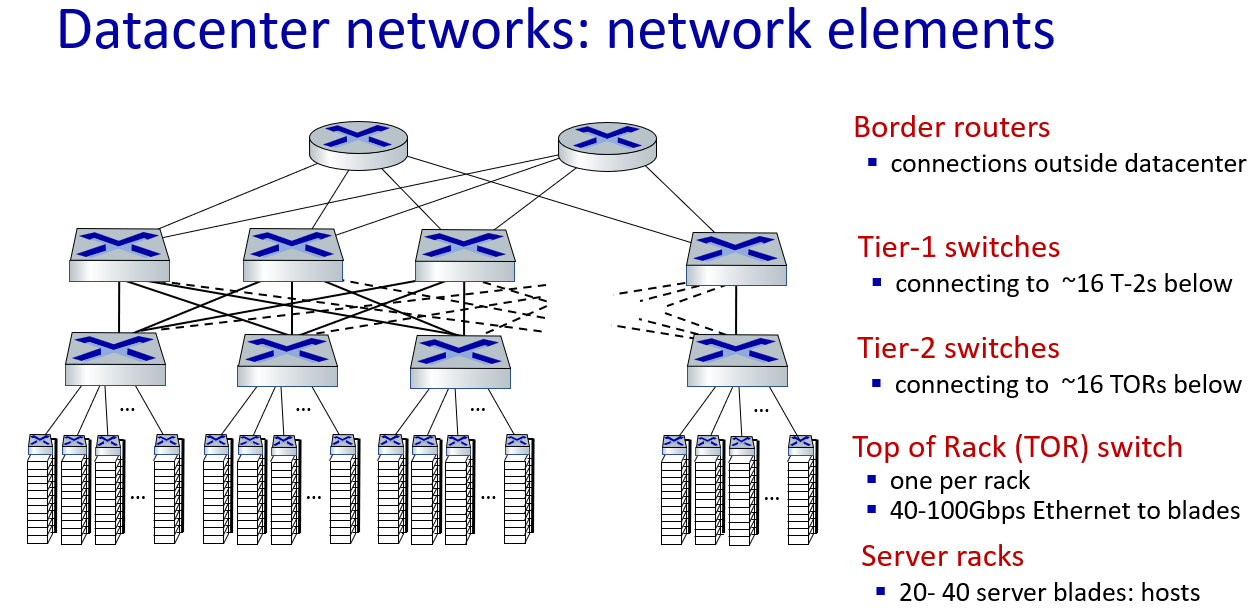
data center networking

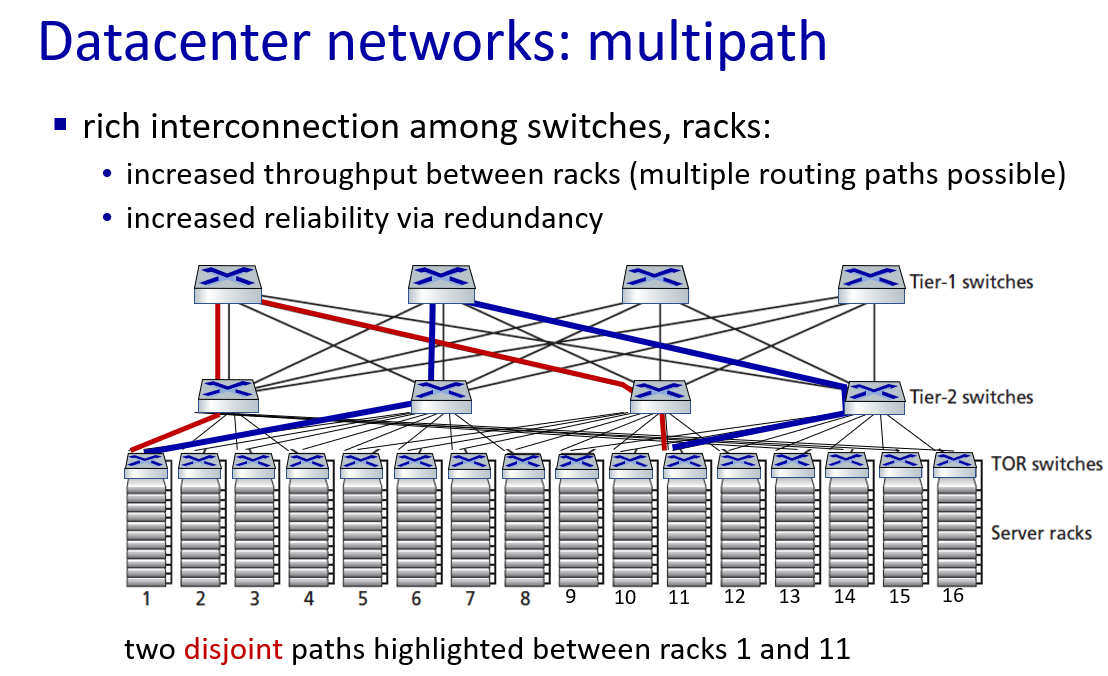
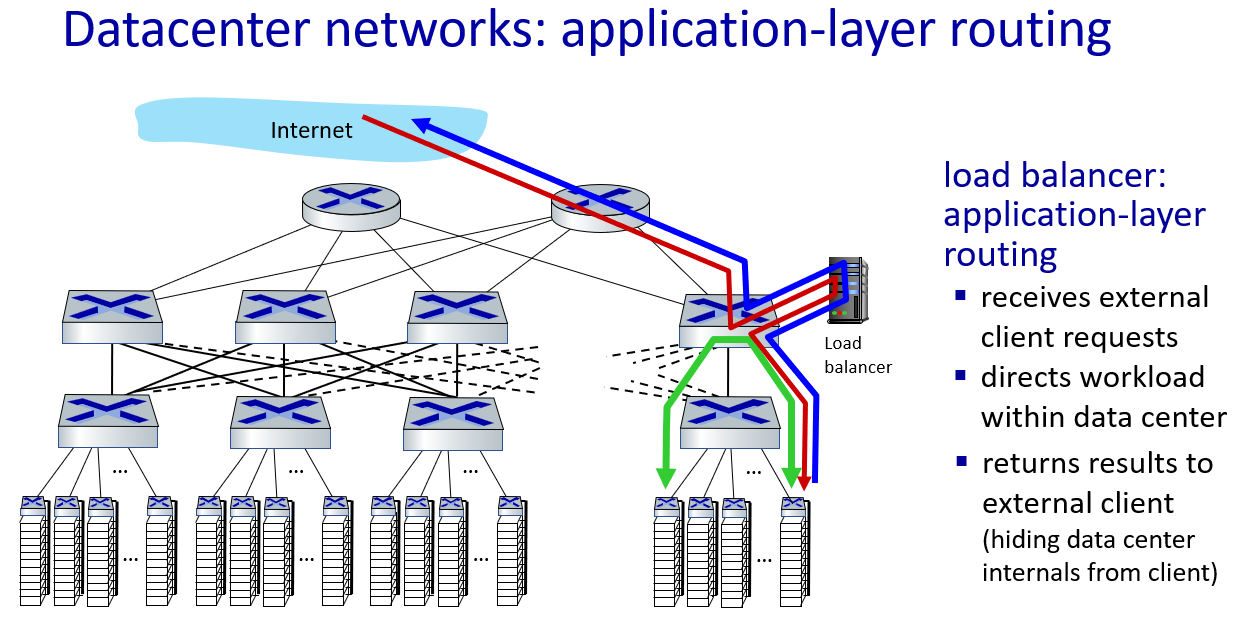
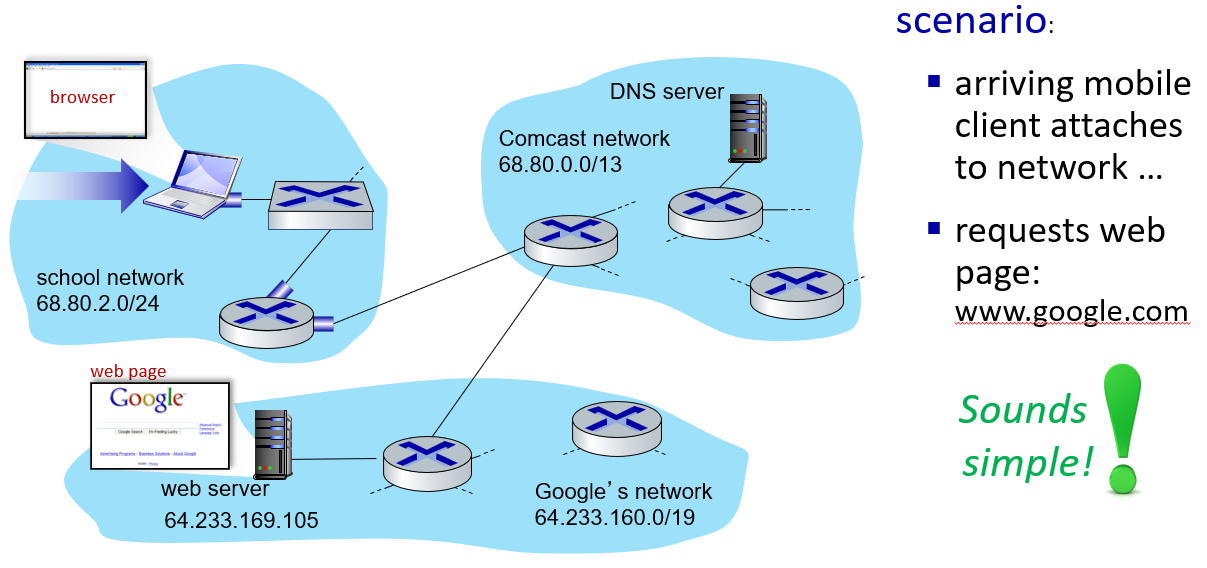
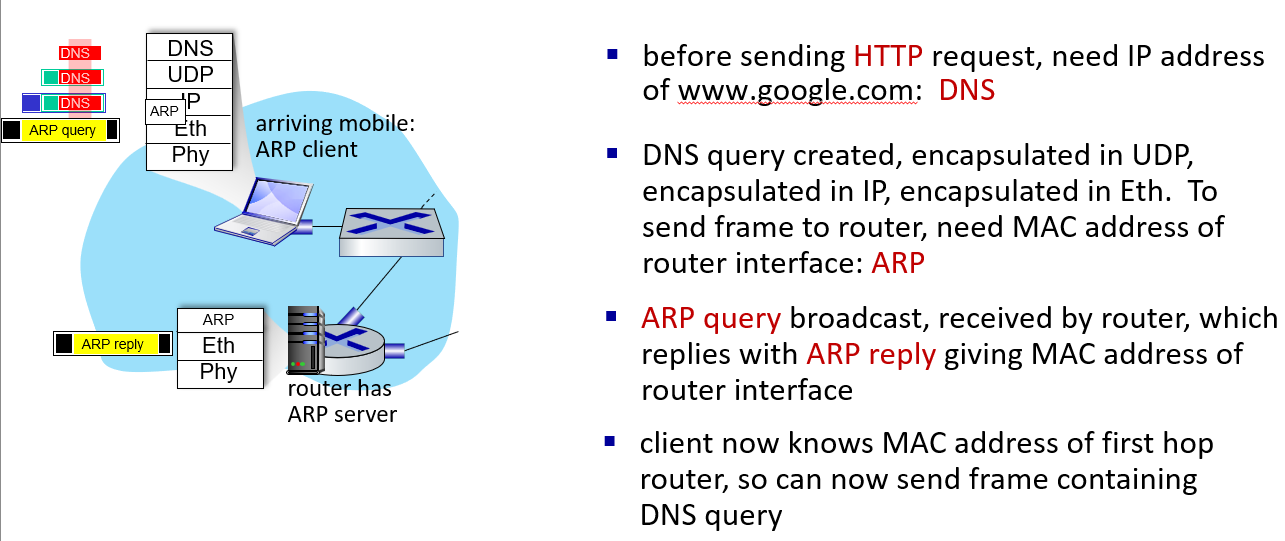
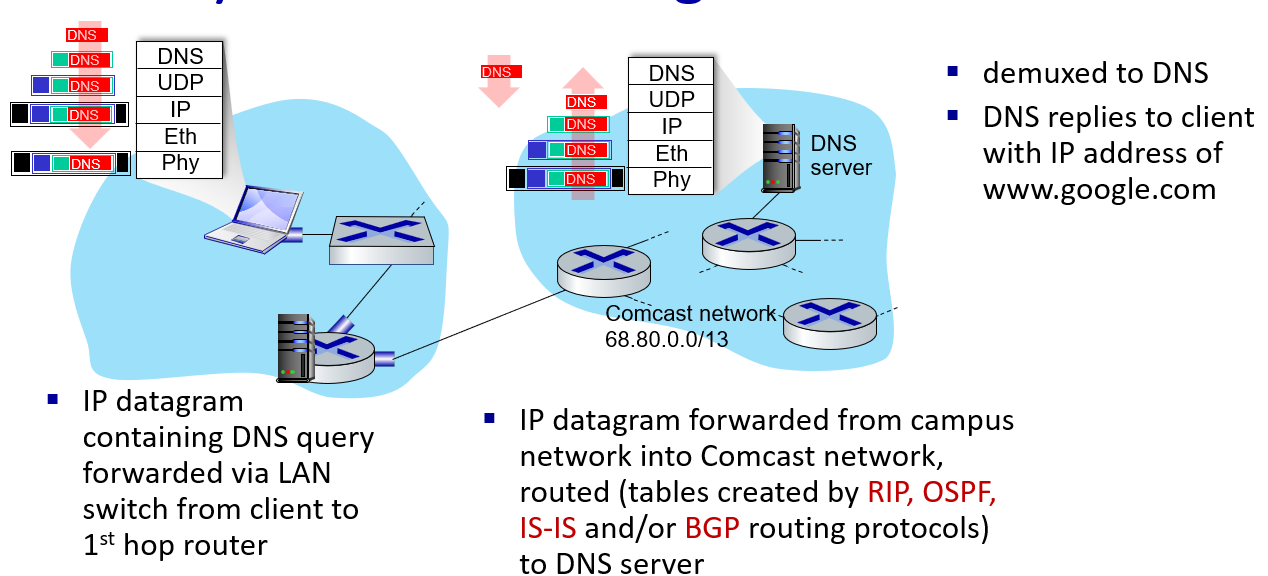
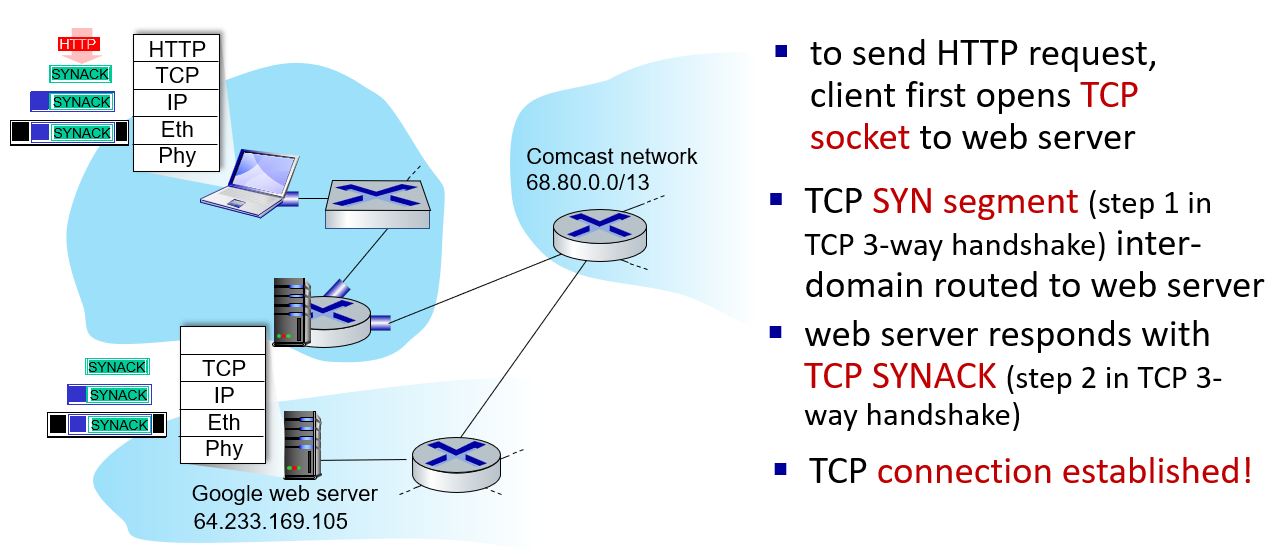
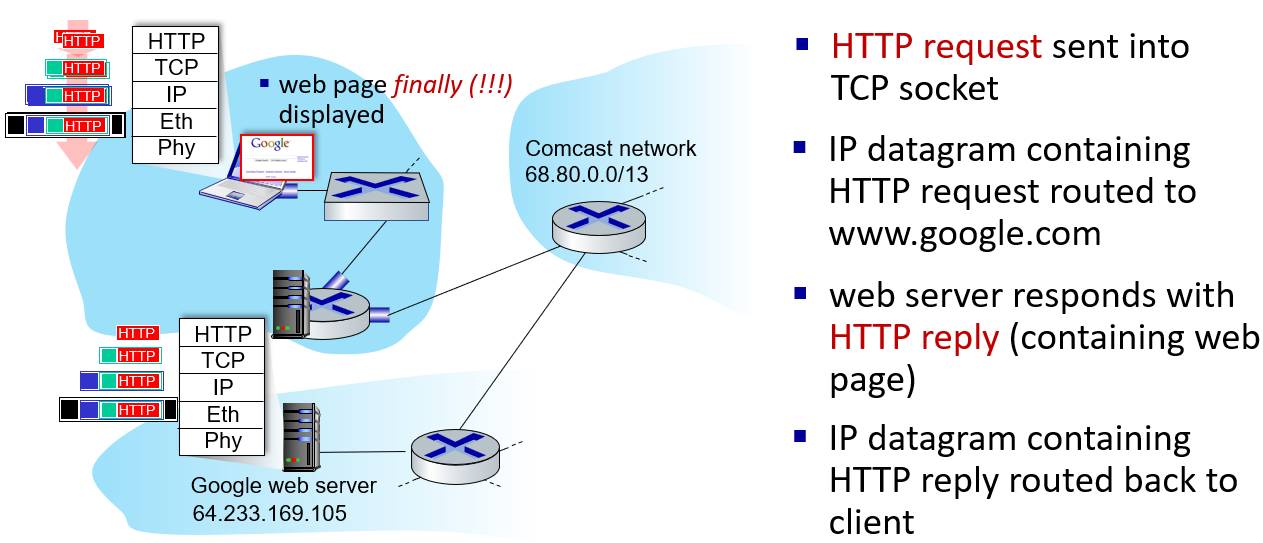
a day in the life of a web request

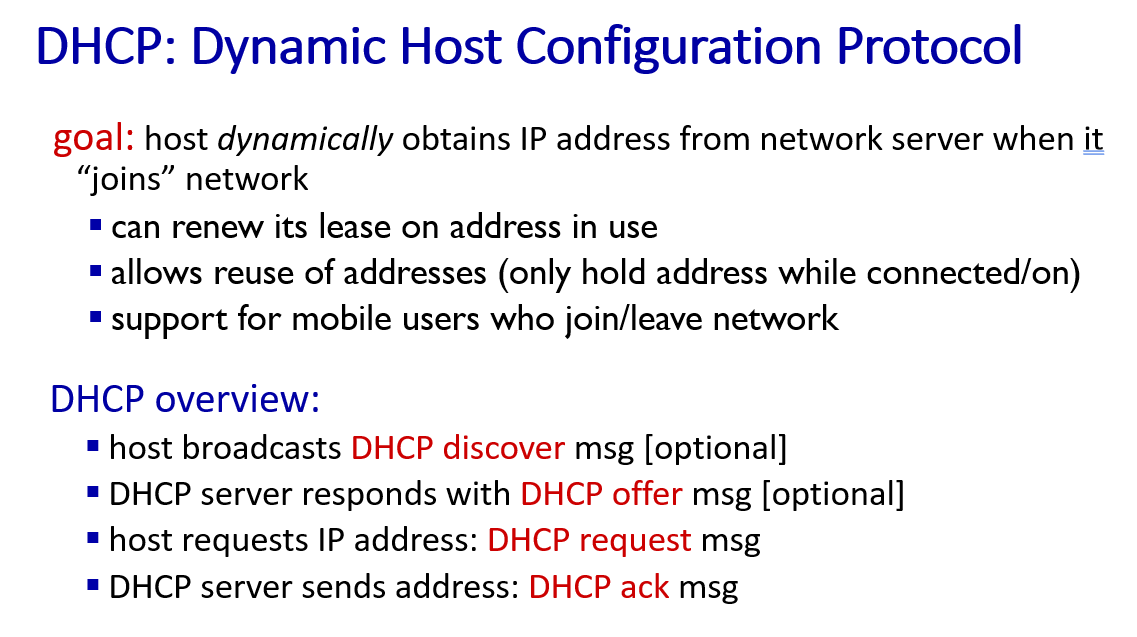
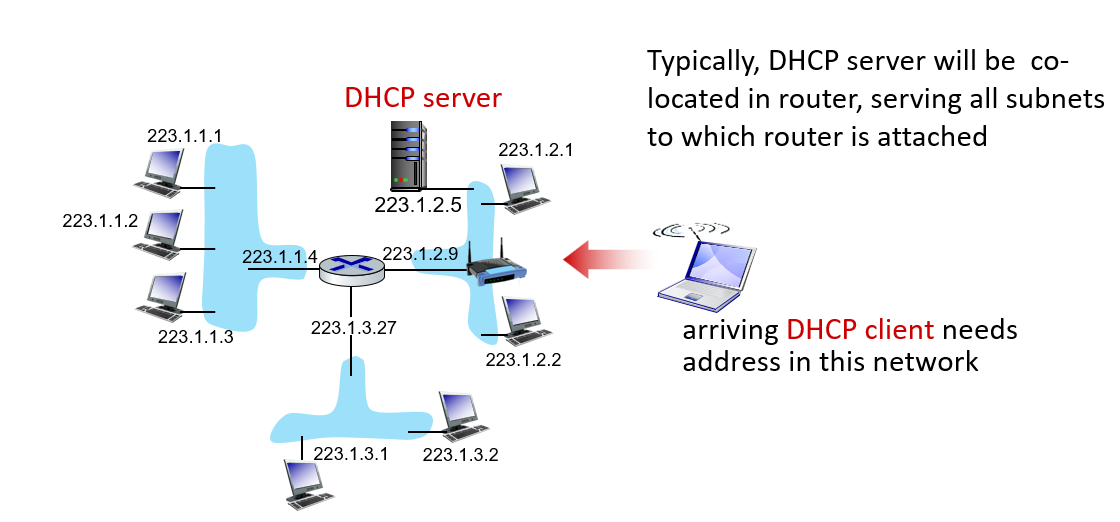
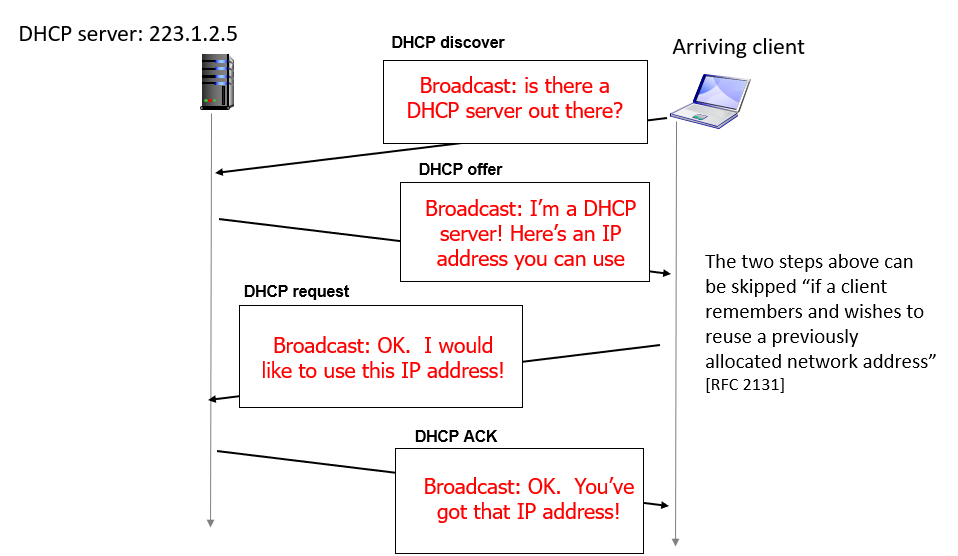
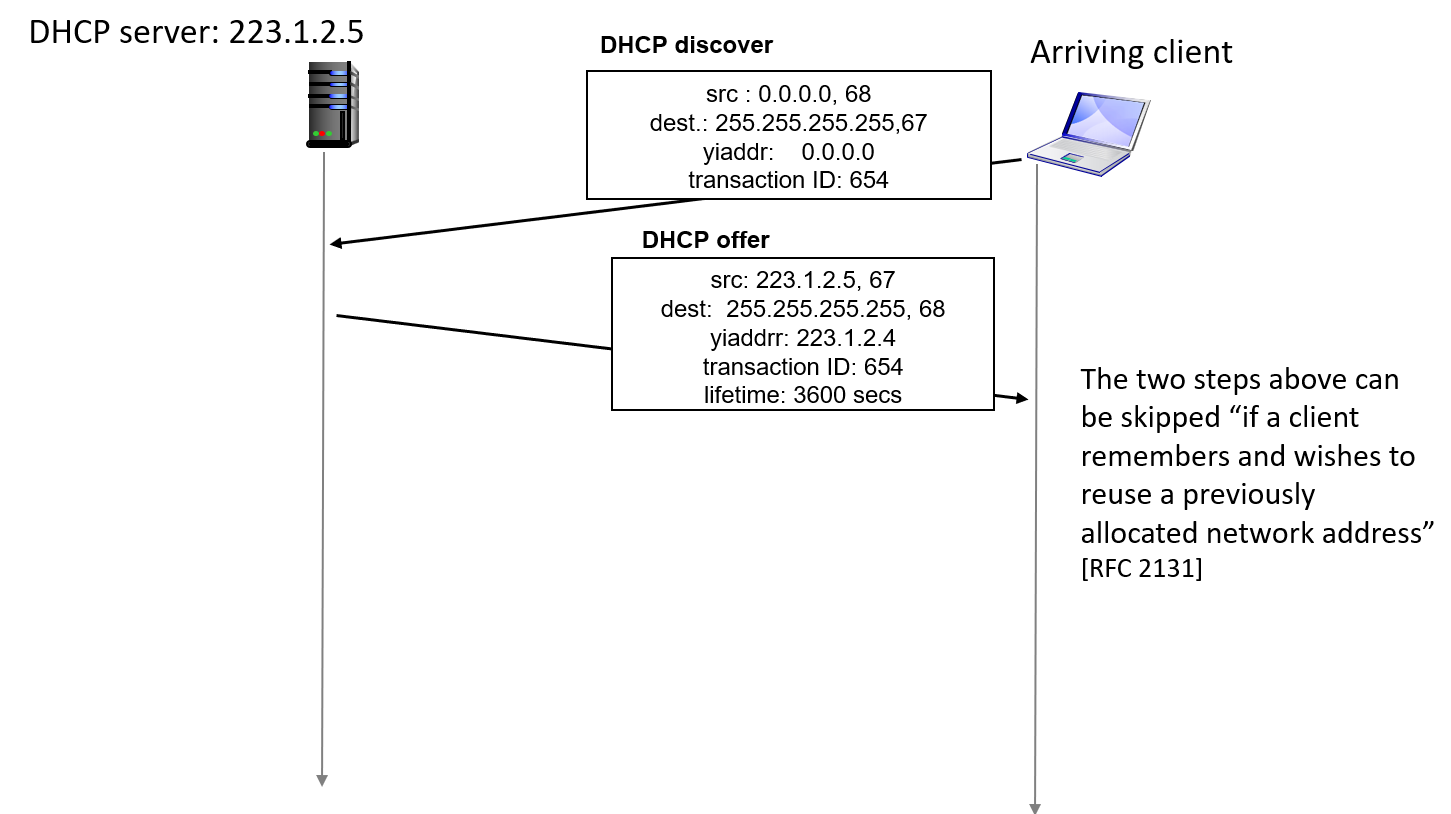
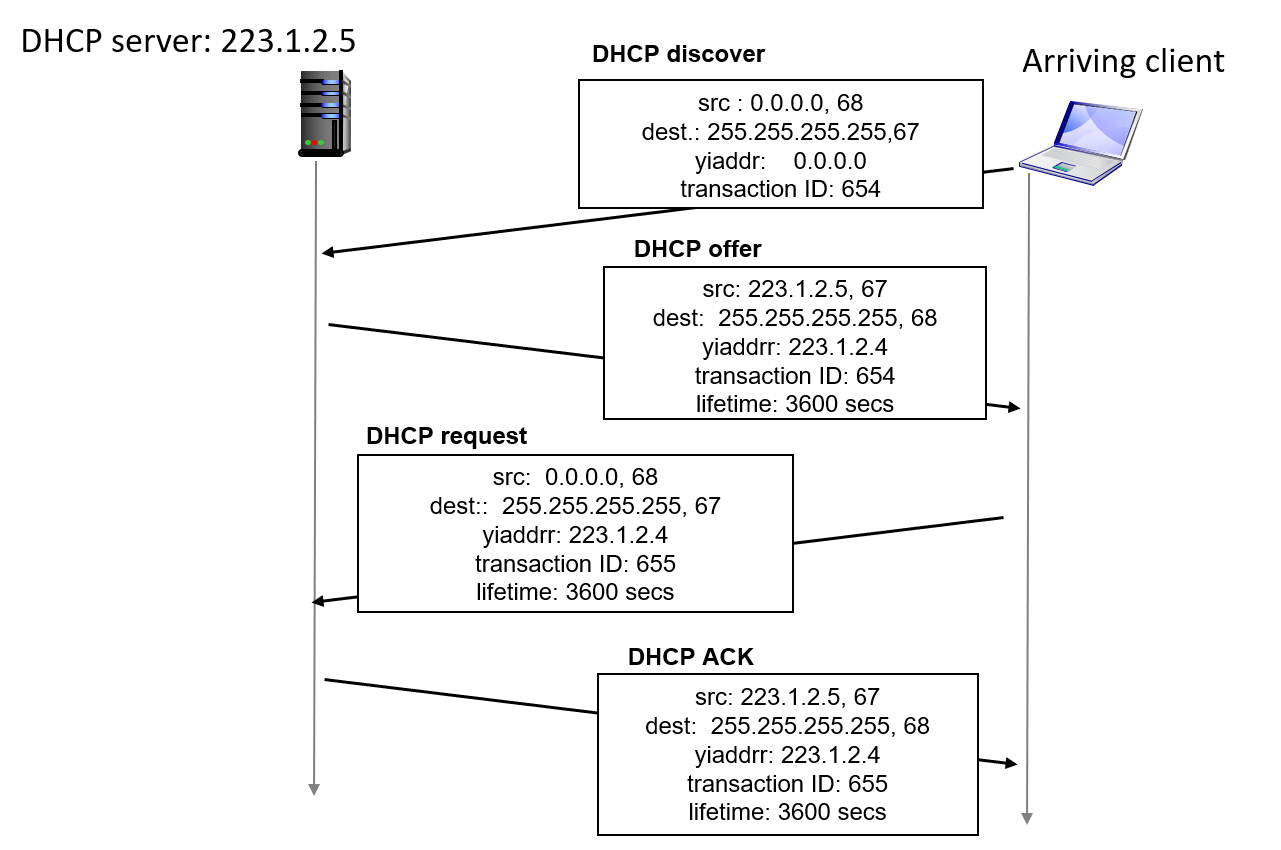
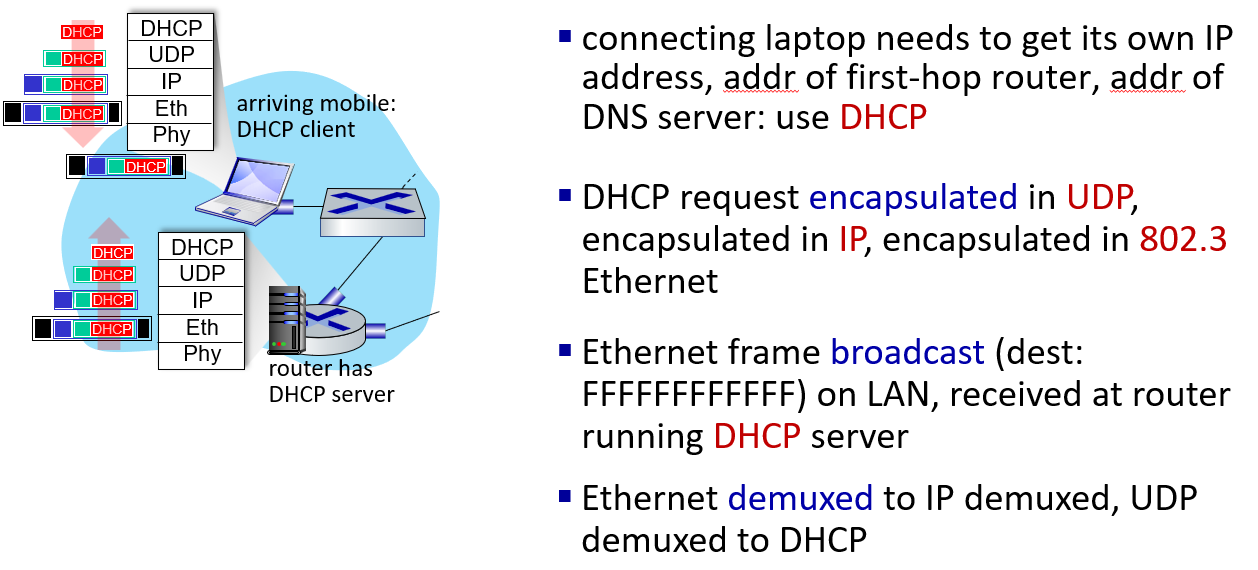
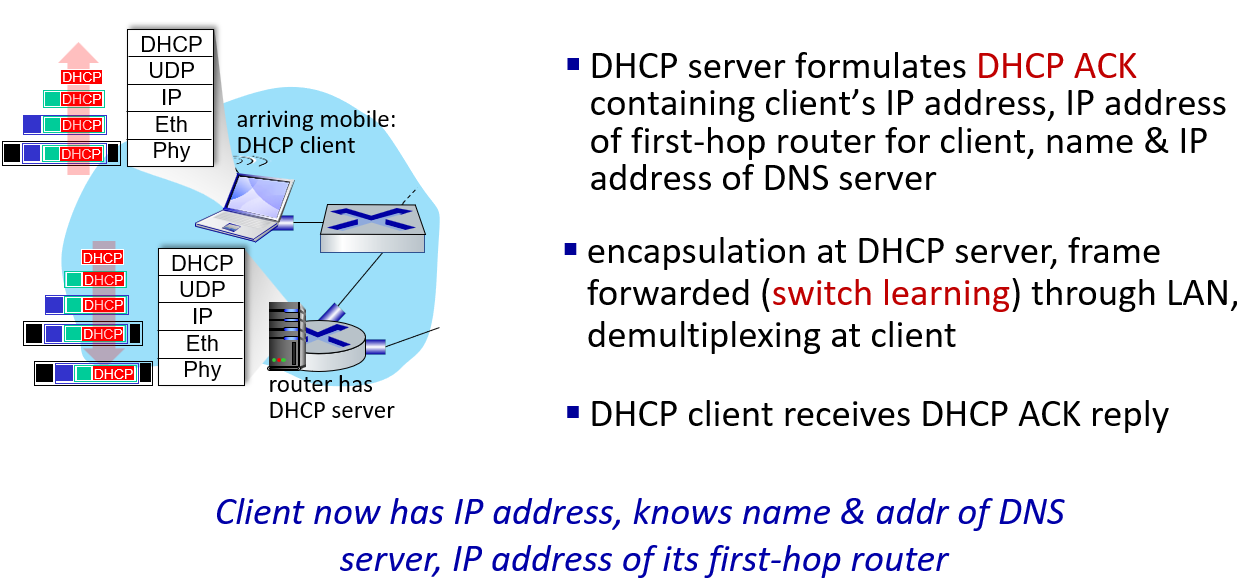
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
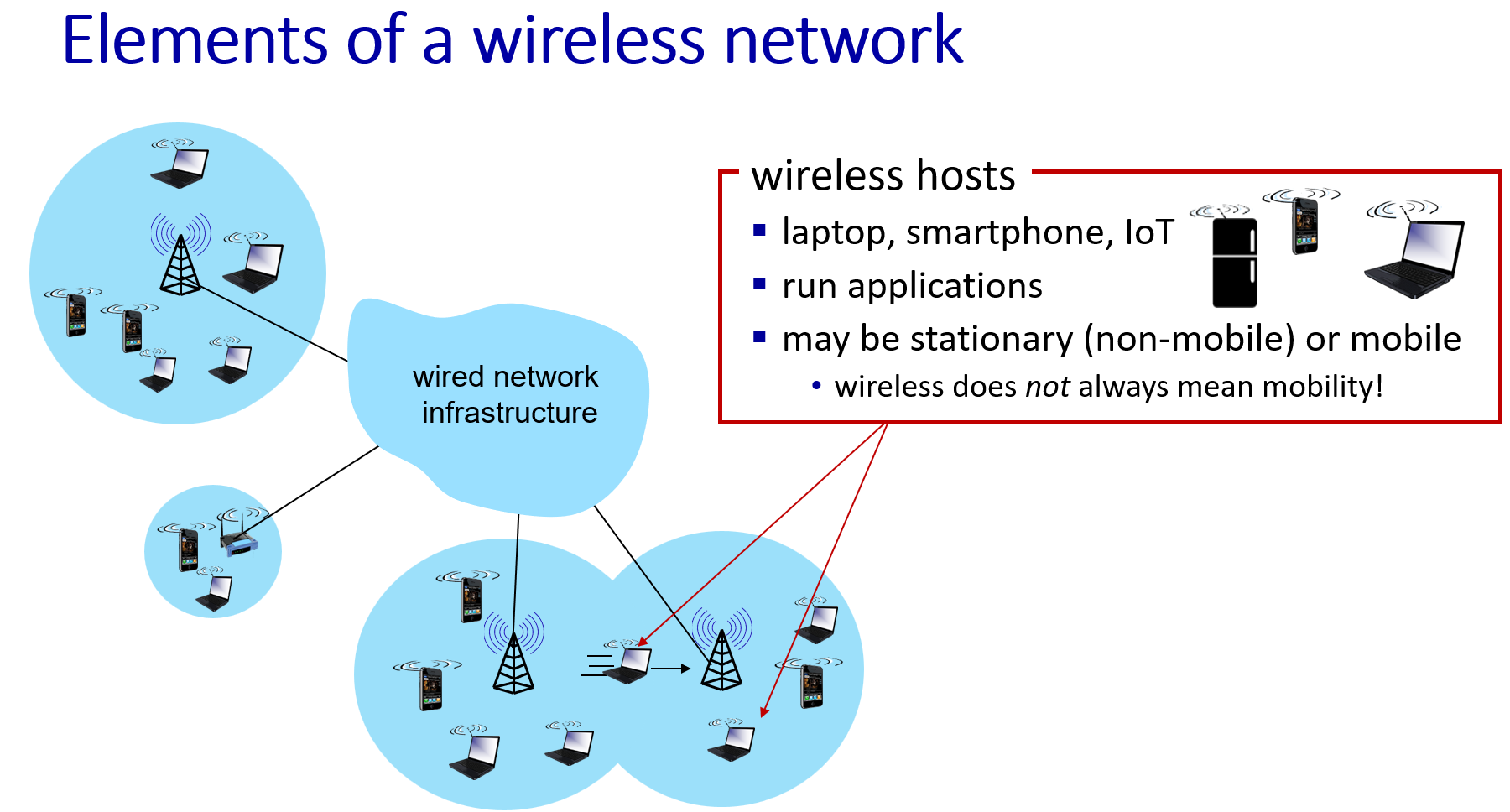
Wireless and Mobile Networks
context:more and more wireless (mobile) phone & mobile-broadband-connected devices

Wireless
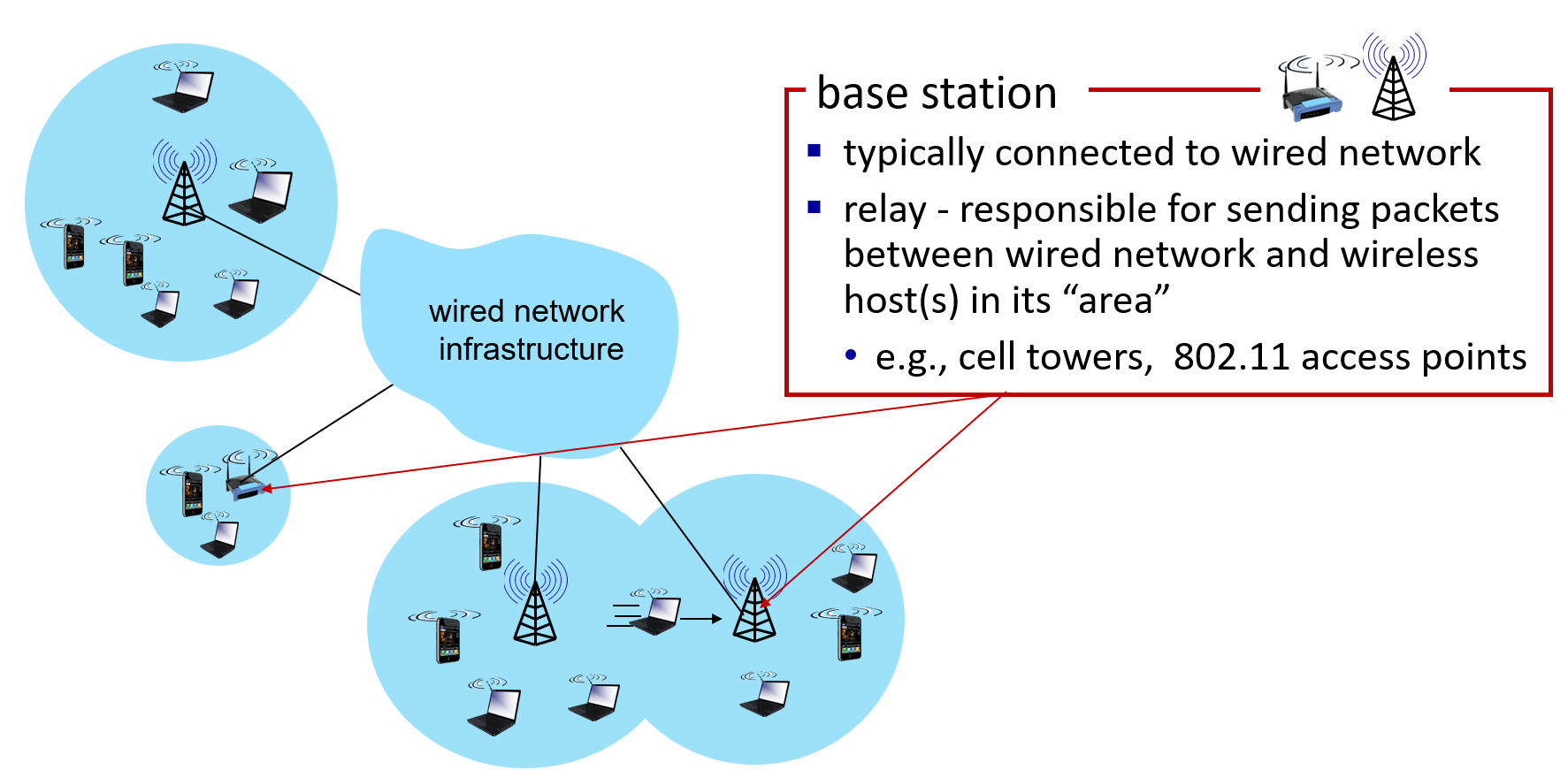
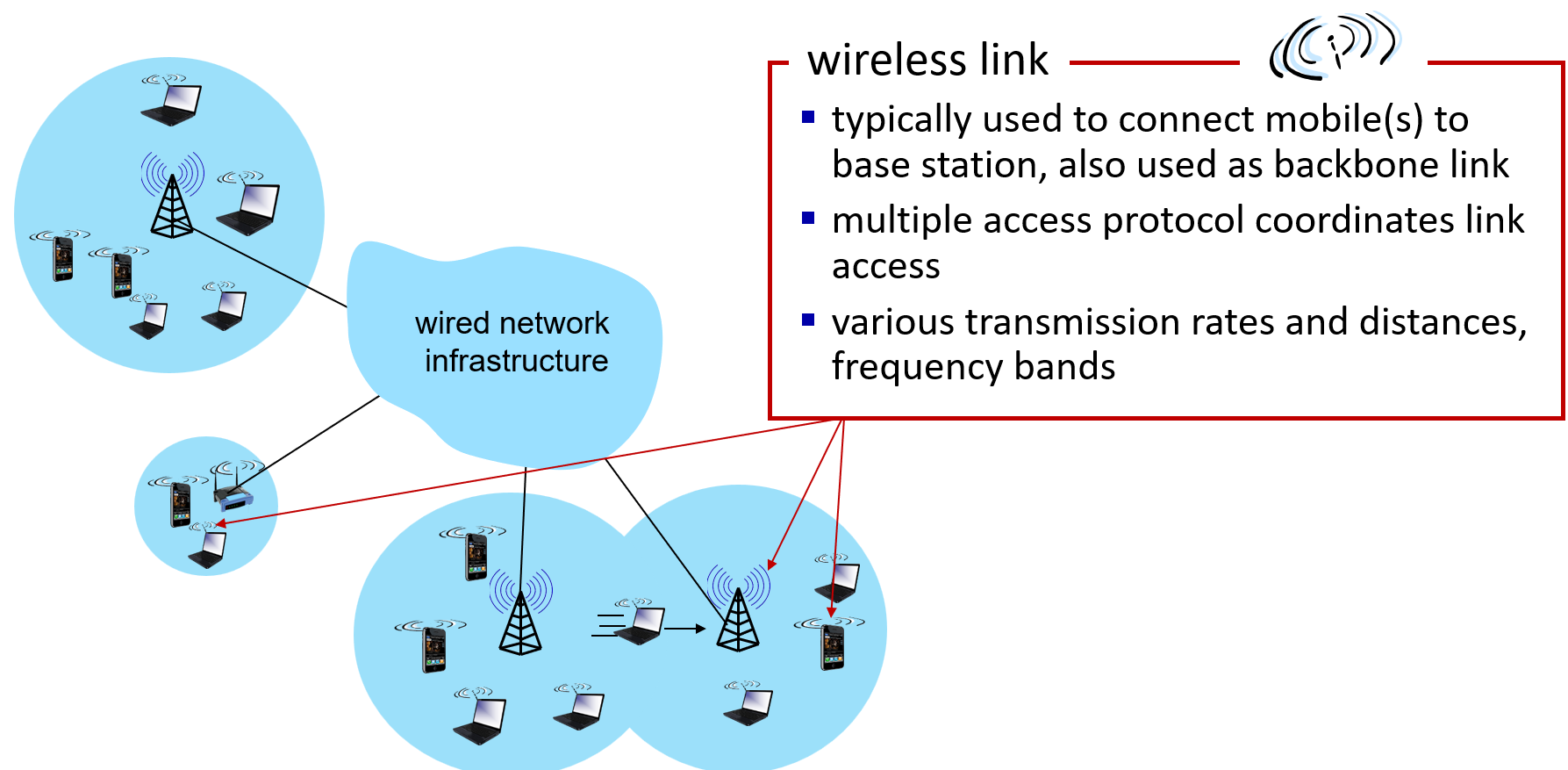
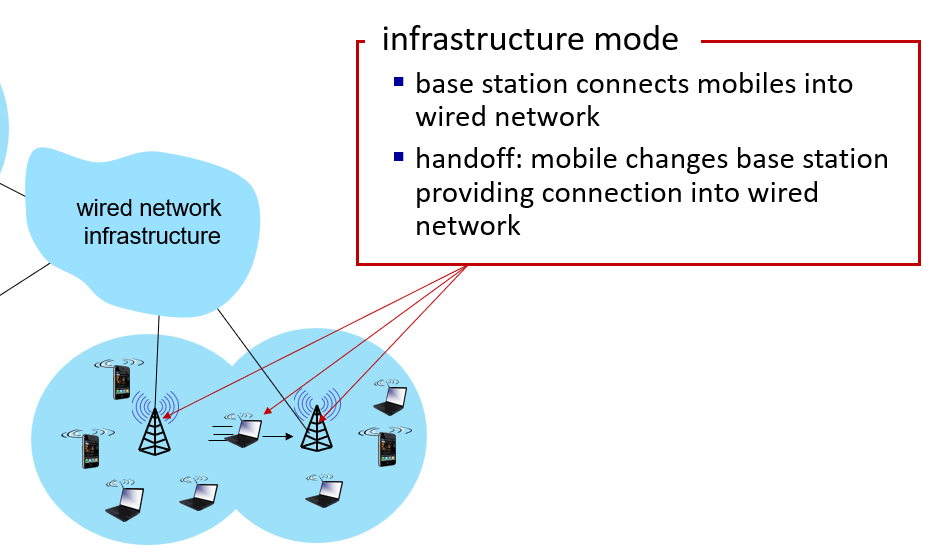
"Handoff" 在无线通信领域中指的是移动设备在切换连接基站时的过程
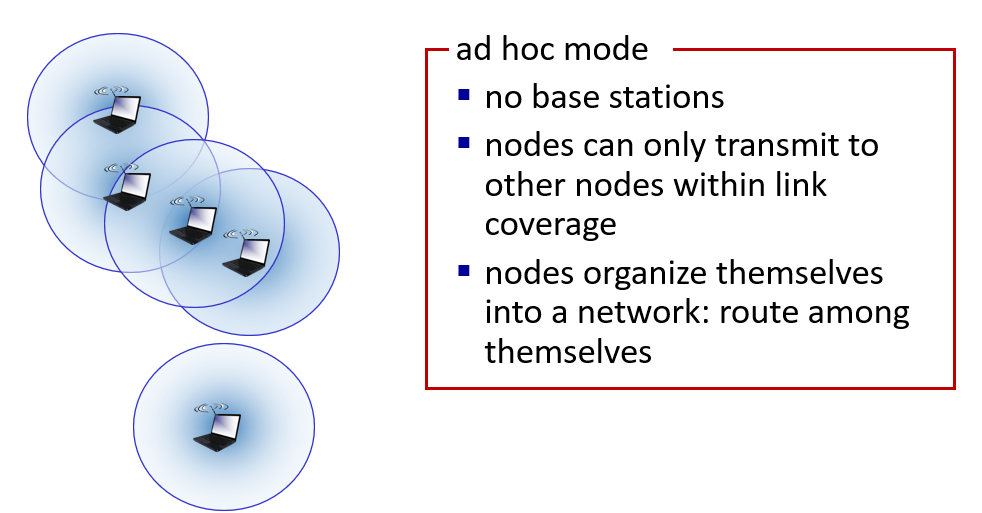
"Ad hoc mode"(自组网模式)是指无线网络中设备直接之间建立临时连接,而不需要经过中央的无线接入点(AP)或基站
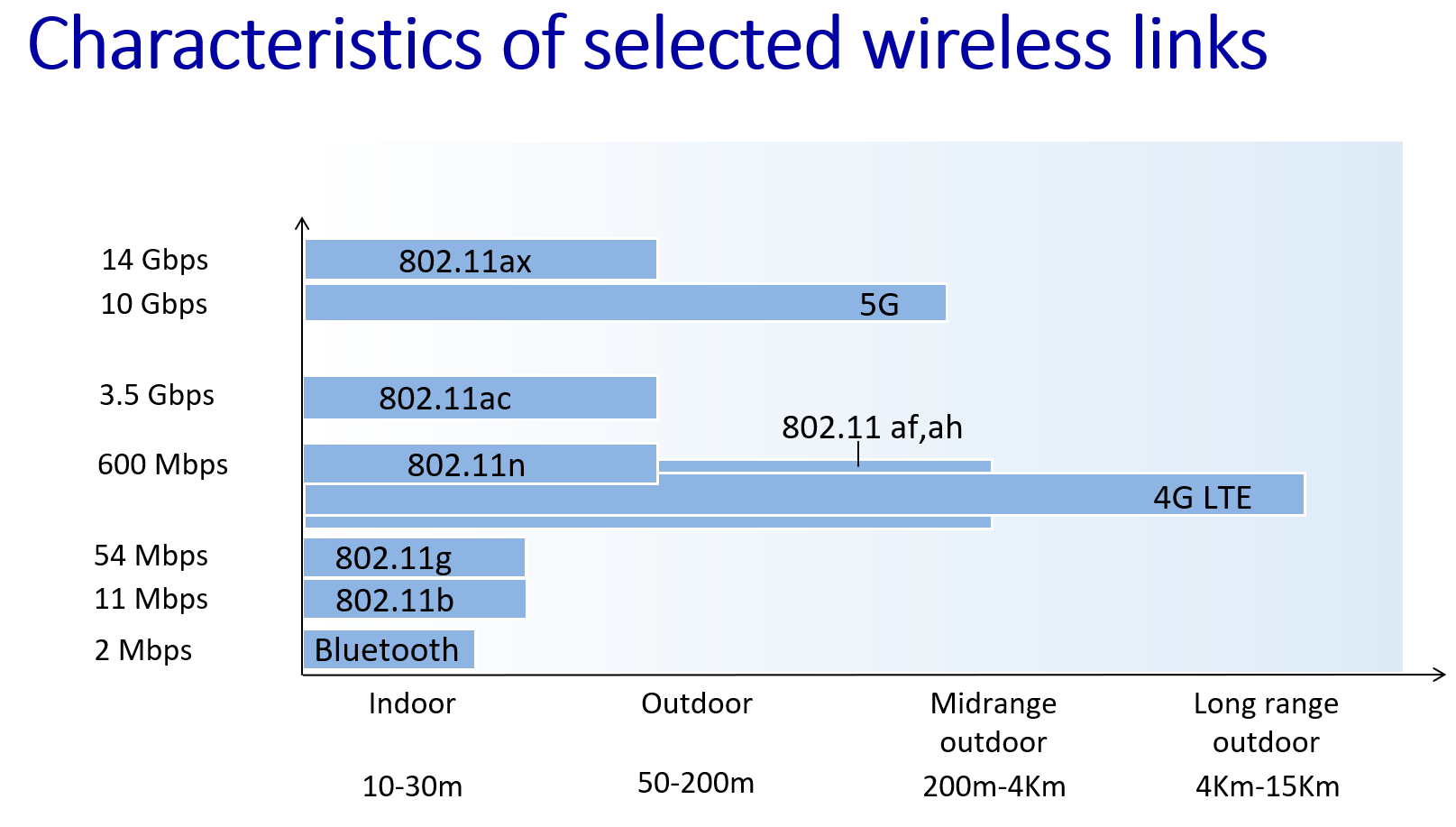
new characteristics
-
3 characteristics

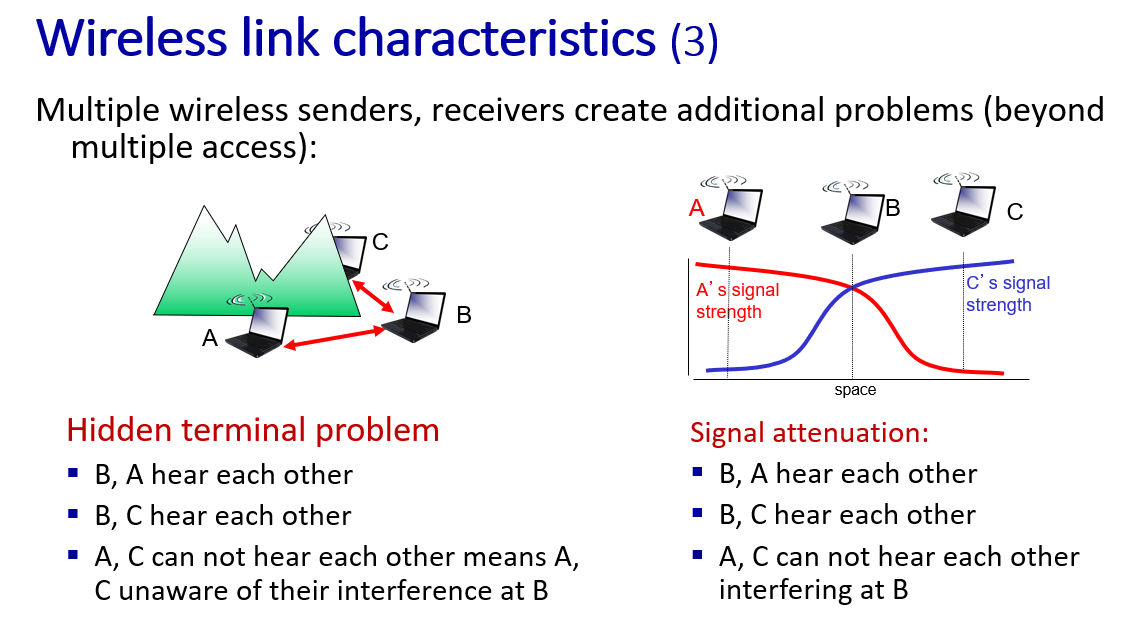
CDMA
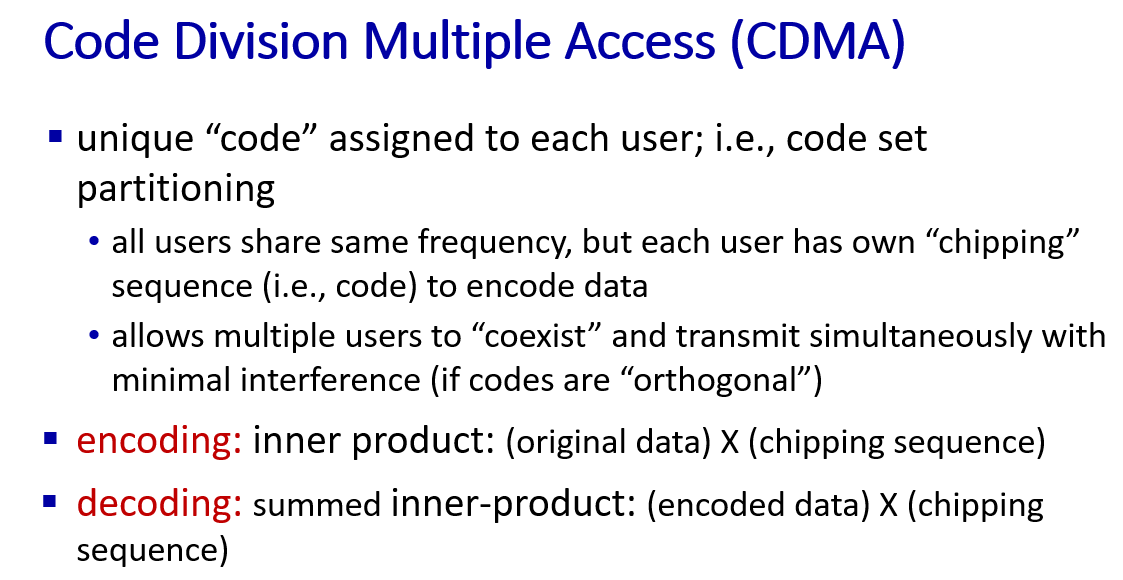
orthogonal 正交的


-
正交码片序列的数量取决于序列的长度和它们的正交性质。在理论上,如果有一个长度为N 的二进制码片序列,且这些序列是两两正交的,那么最多可以有\(2^N\)个正交码片序列。
d represent data , one bit
code represent unique code of each device, m bit
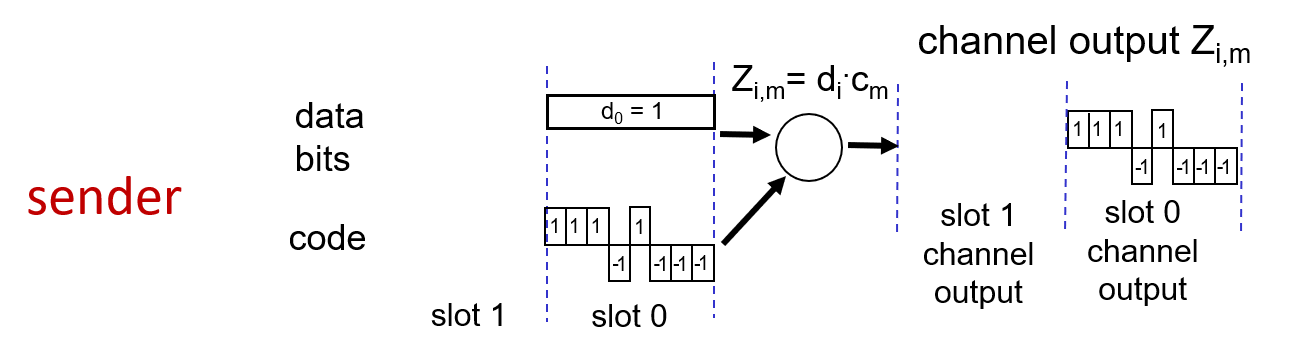
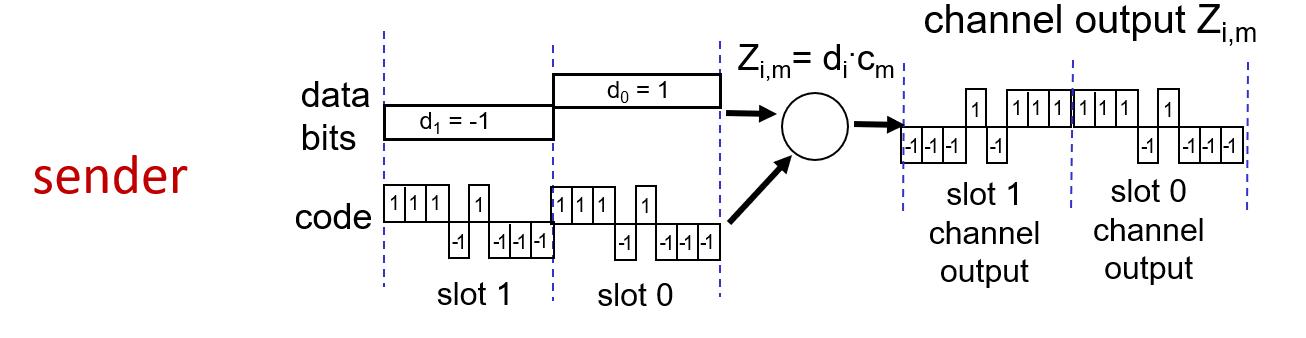
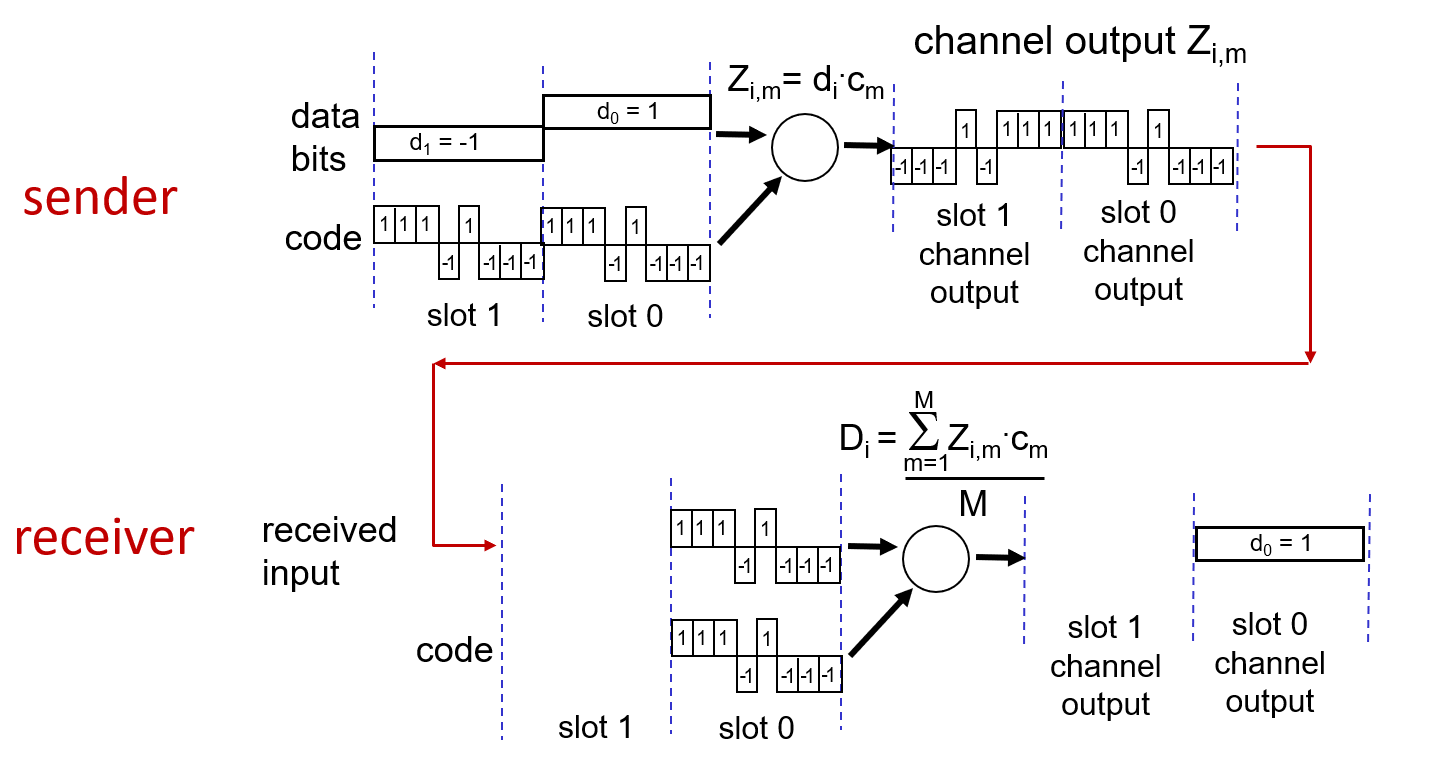
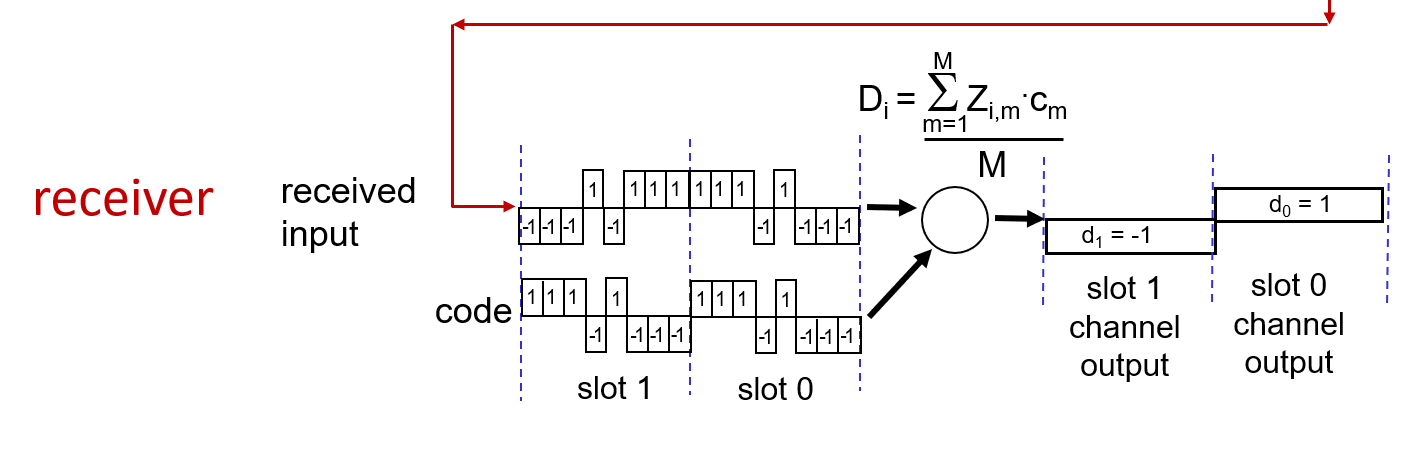
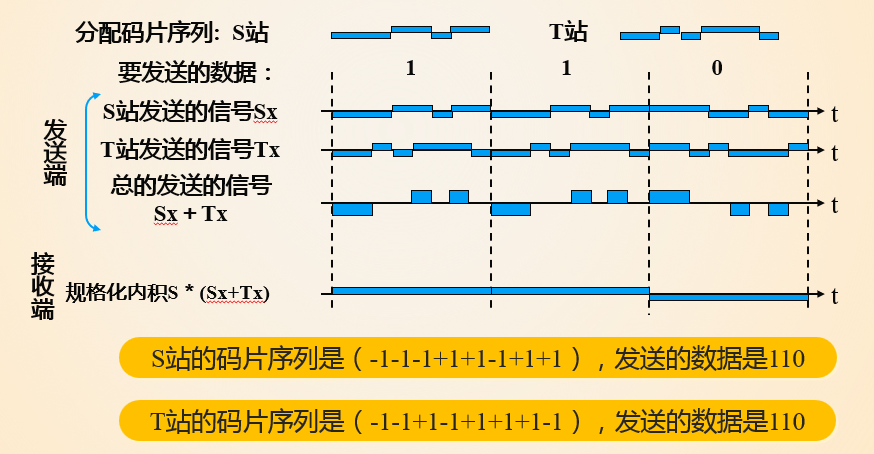
receiver check the channel output with the origin code.
in this scenario different device use different slot,this is not useful yet
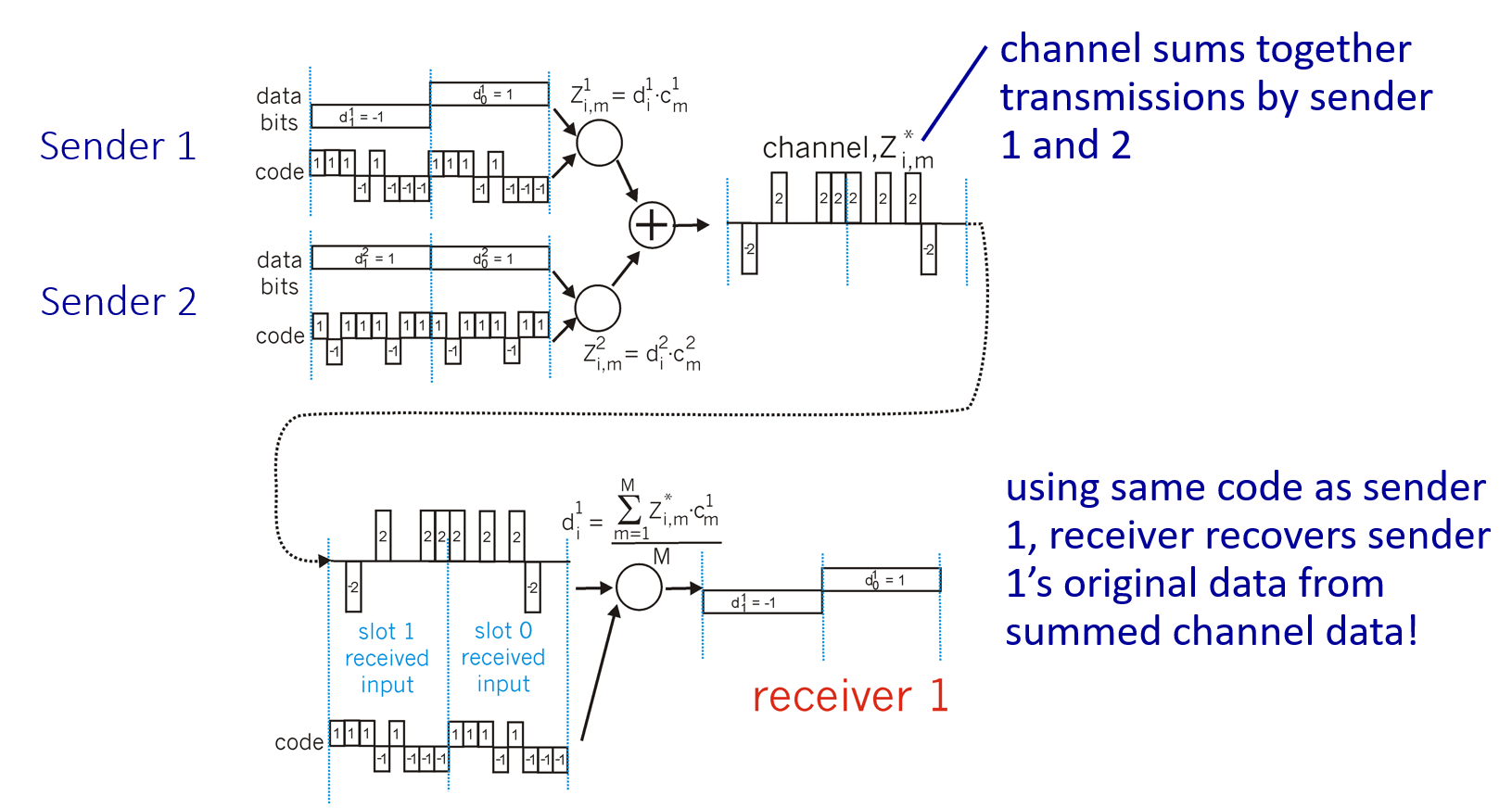
use the slot together,that is useful
WiFi: 802.11 wireless LANs
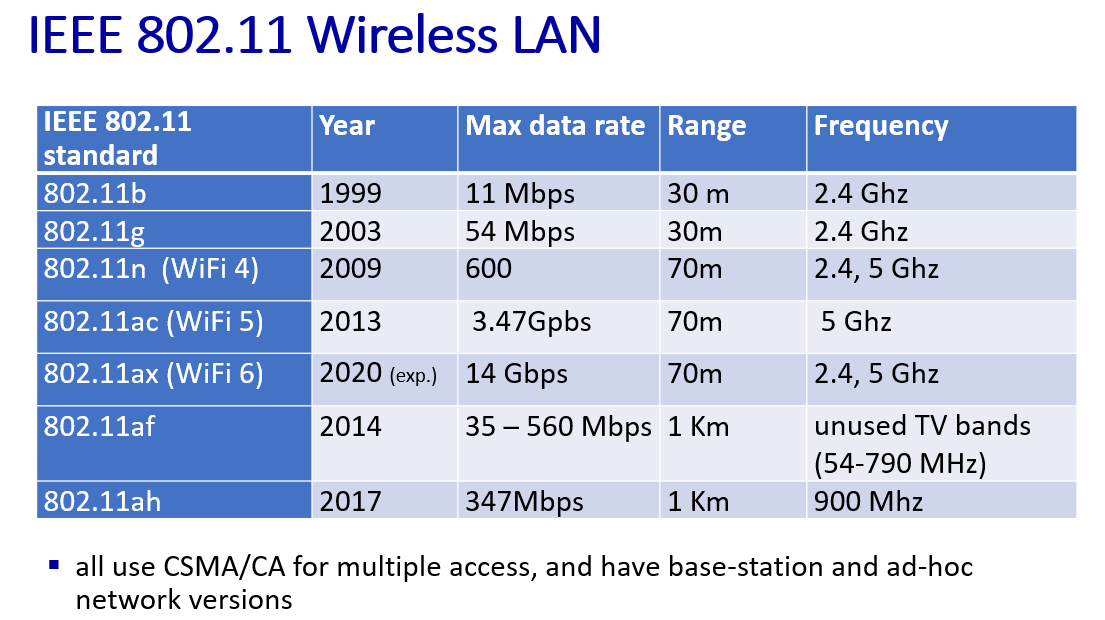

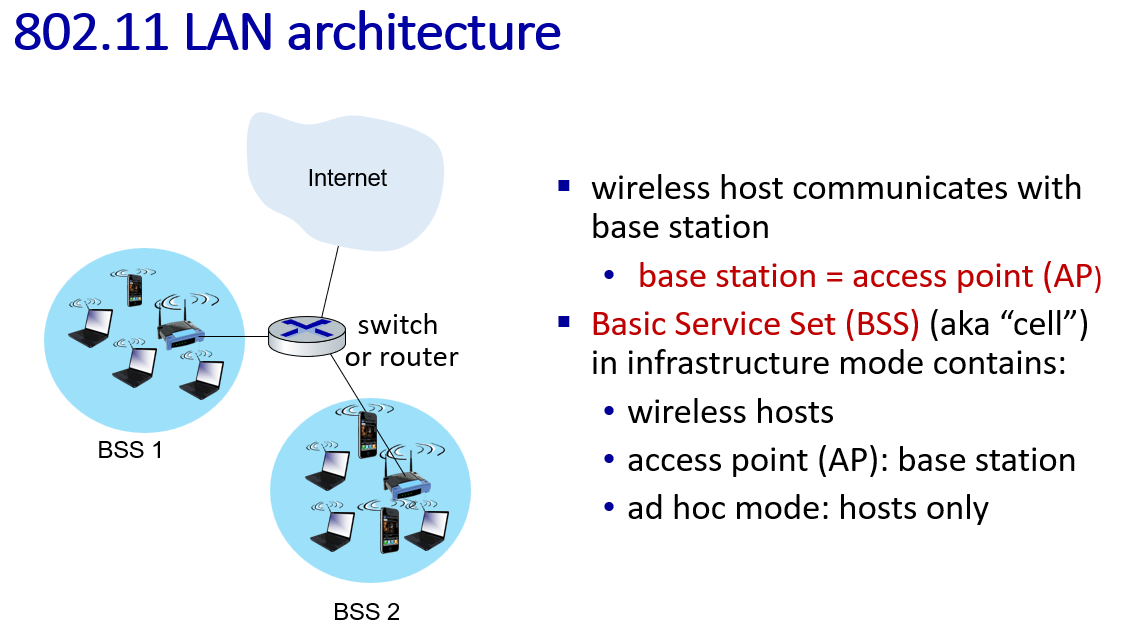

Spectrum division

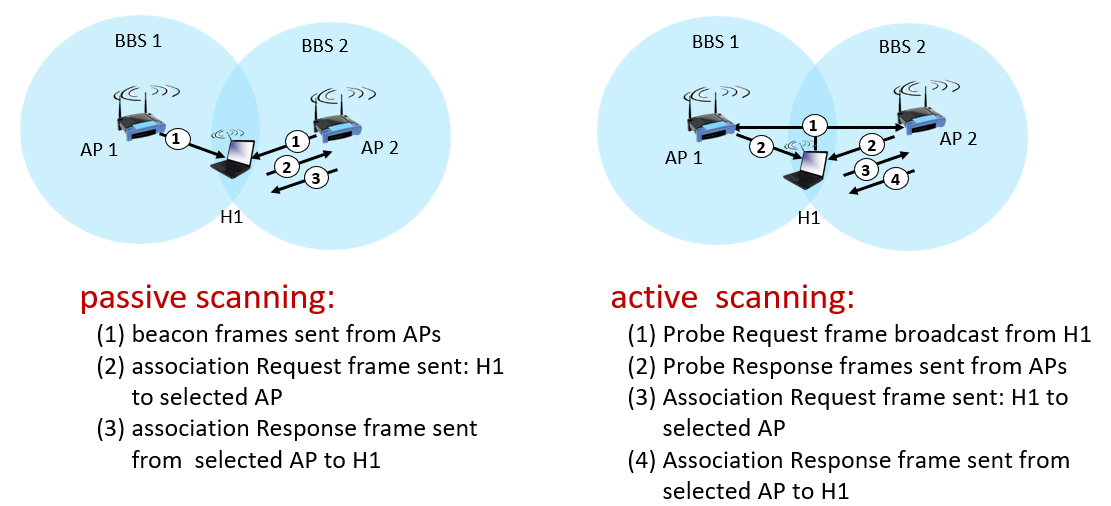
beacon frame or probe request
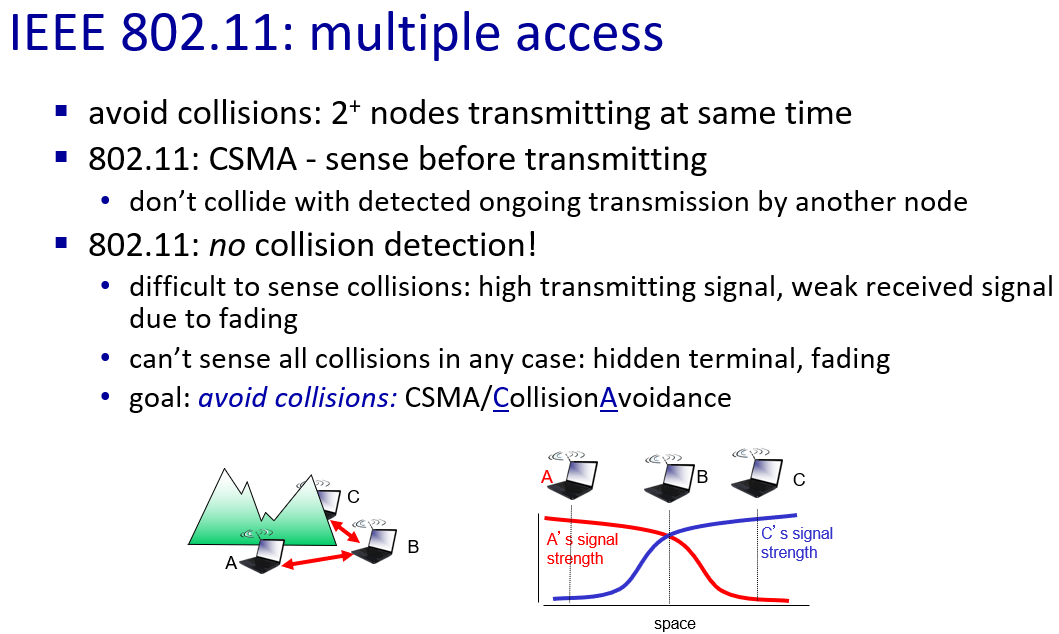
- 检测碰撞的能力要求站点具有同时发送和接收的能力
- 接收信号的强度可能远远小于发送信号的强度,从而被淹没,无法检测到
- 即使站点具备同时发送和监听的能力,也会由于隐蔽终端和衰减的问题,也会无法检测到所有的碰撞
- hidden terminal: A、C之间存在障碍物,它们不知道彼此的干扰
- fading:A,C 因为它们信号强度的衰减不能互相“听见”
CDMA和CSMA/CA的区别

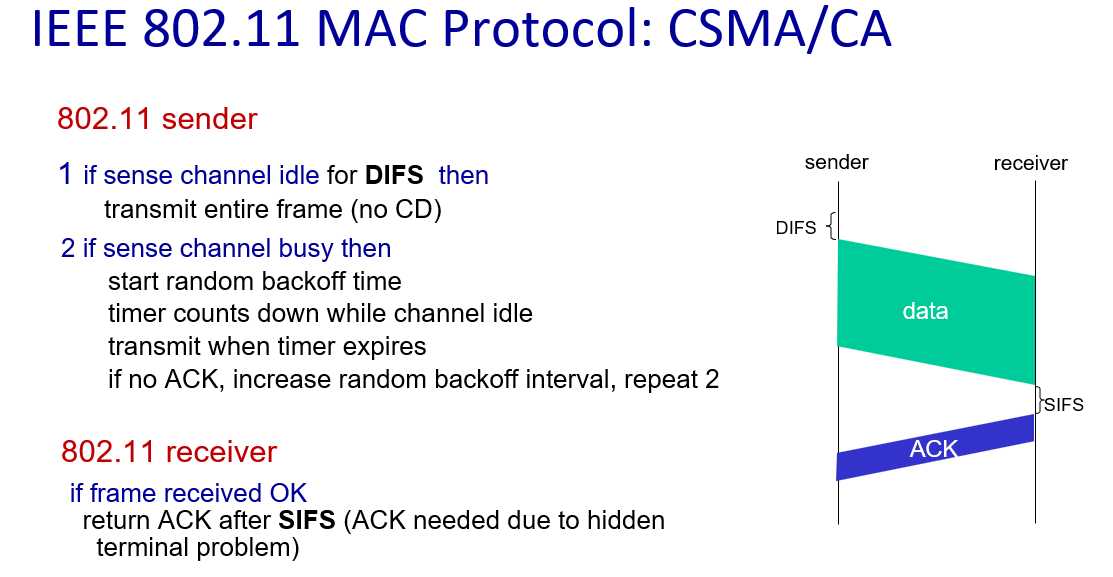
DIFS,全称为 Distributed Inter-Frame Space(分布式帧间隙),是Wi-Fi网络中用于协调设备之间竞争传输权的时间间隔。DIFS是通过在信道上引入一个短暂的间隔来确保在设备开始传输数据之前,其他设备有足够的时间检测信道是否空闲,以减少碰撞的可能性
随机退避计时器在通道保持空闲的同时开始倒计时
在传输后,设备等待接收设备的确认(ACK)
如果在指定的时间内没有收到确认,表示可能发生了碰撞或传输问题
在这种情况下,设备增加随机退避间隔,引入额外的随机性,以避免重复的碰撞
SIFS,全称为 Short Inter-Frame Space(短帧间隙),是Wi-Fi网络中一种较短的时间间隔,用于在特定情况下优先级较高的帧之间进行传输
在无线网络中,隐藏终端问题指的是一个设备可能无法侦测被阻挡的设备的存在,从而认为信道是空闲的,导致数据传输发生冲突,ACK用来确保数据正确传输

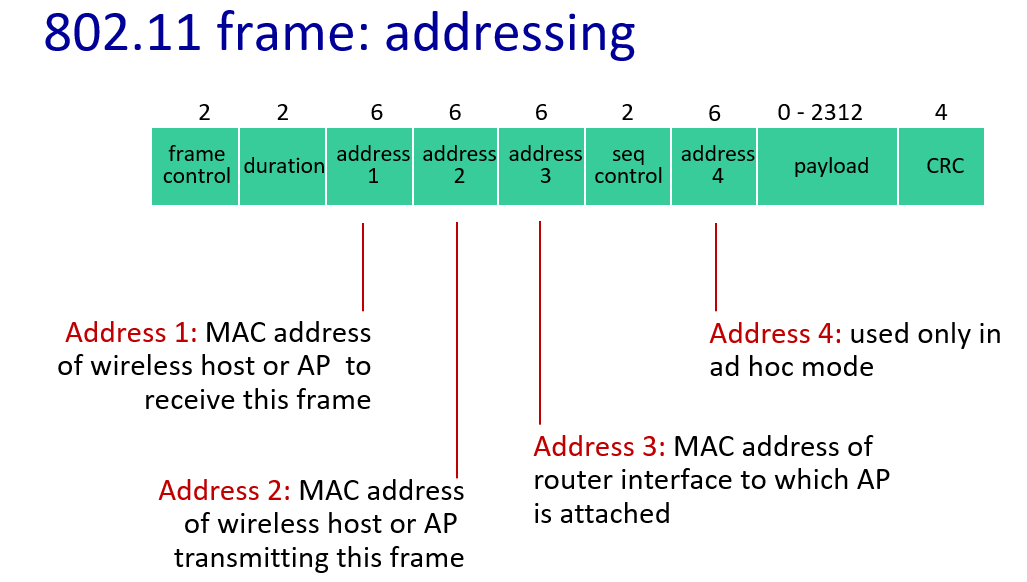
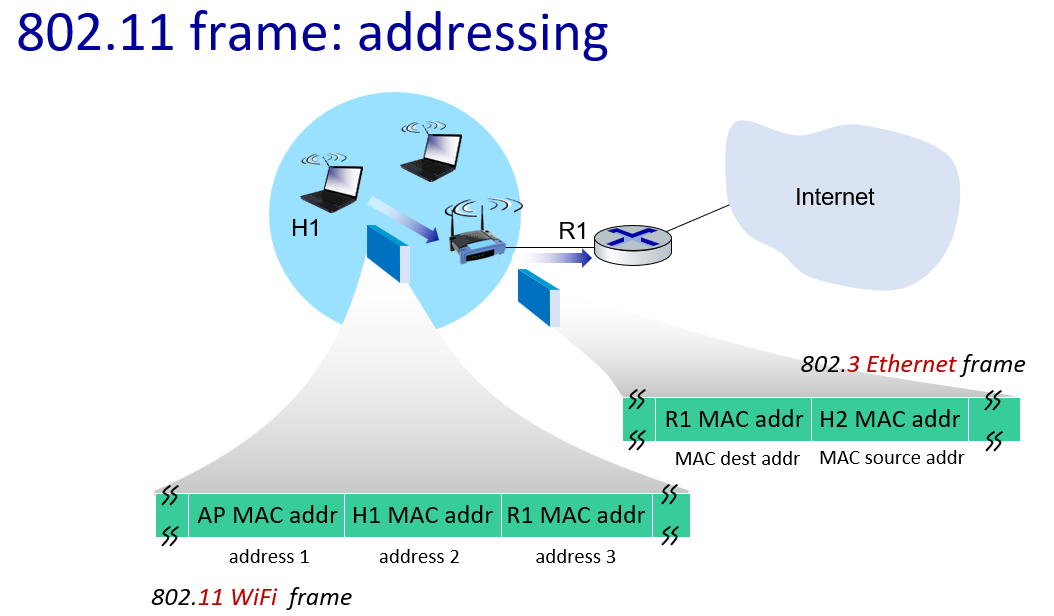
addressing
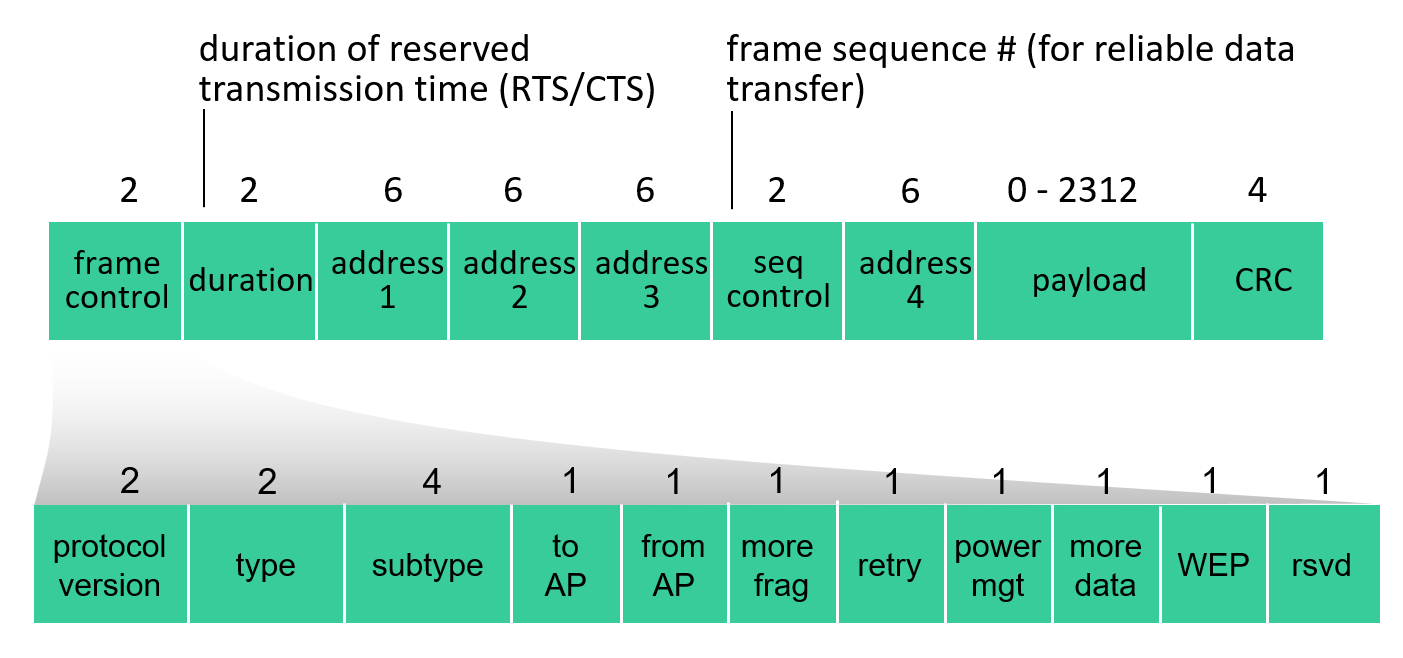
type->帧类型(RTS,CTS , ACK ,数据)
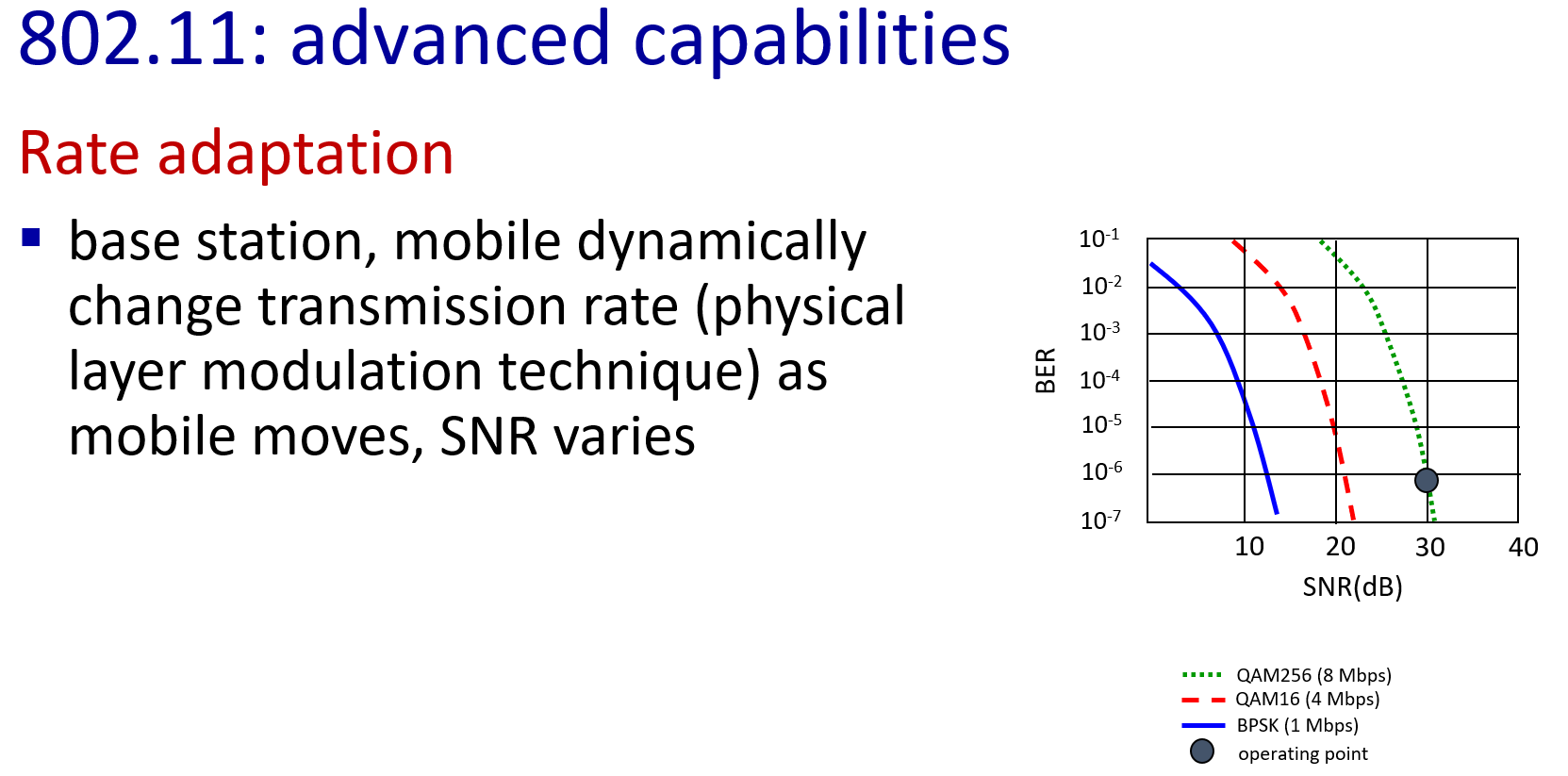
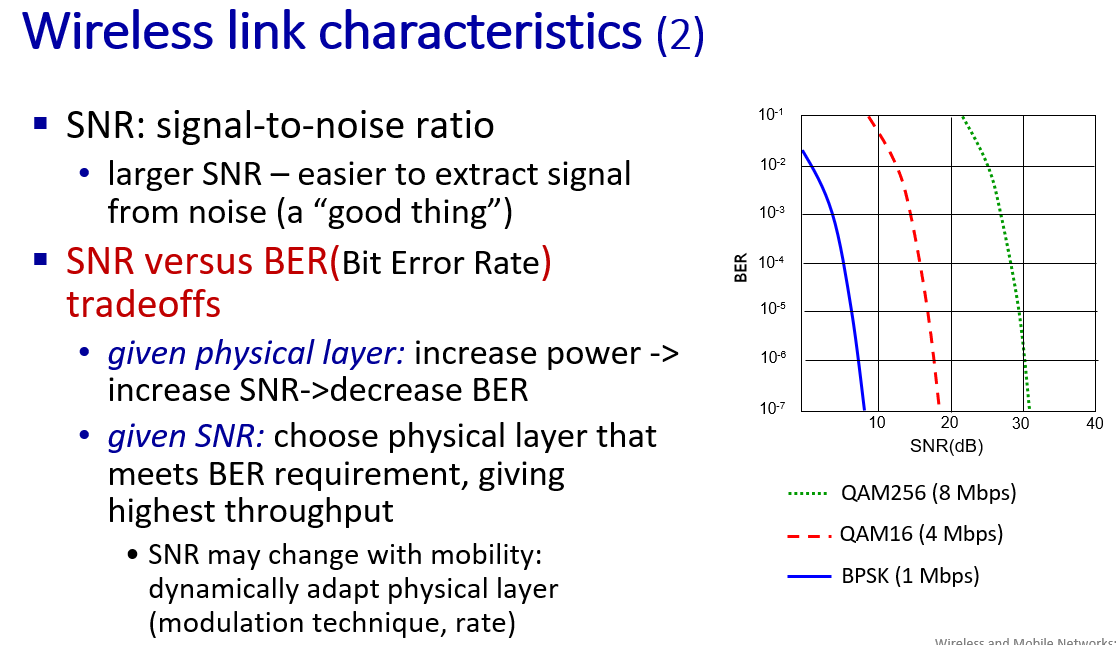
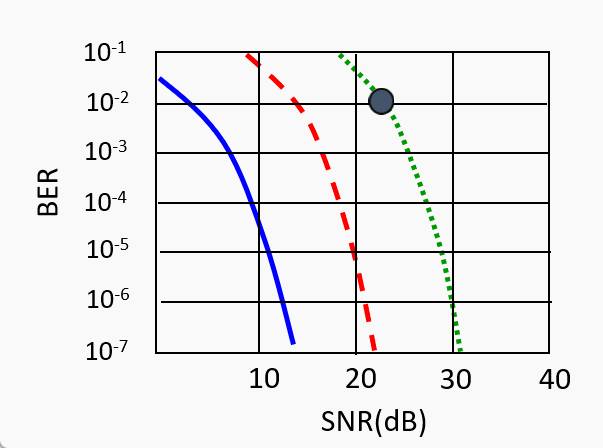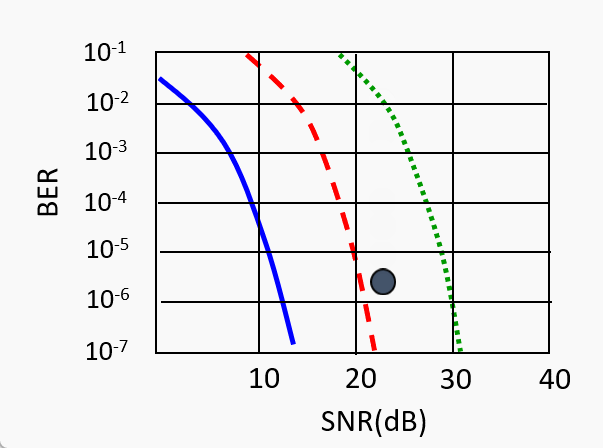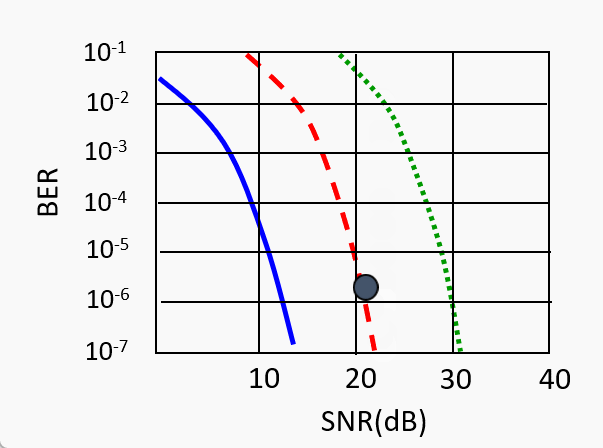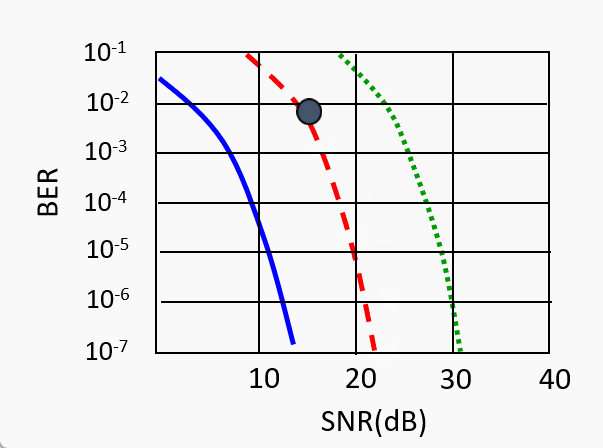
SNR decreases, BER increase as node moves away from base station
When BER becomes too high, switch to lower transmission rate but with lower BER

Cellular networks: 4G and 5G
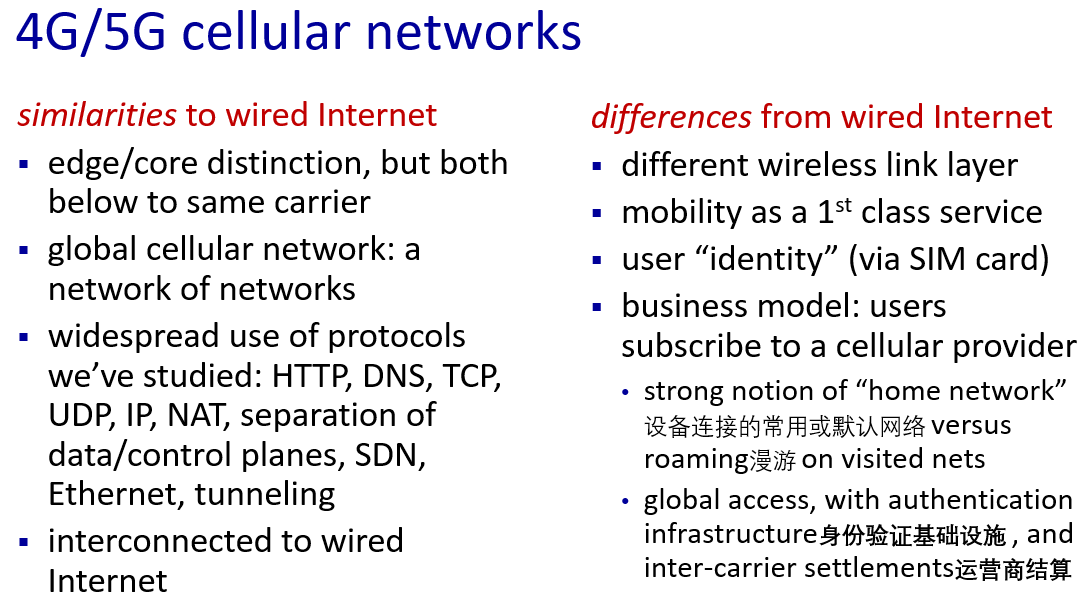
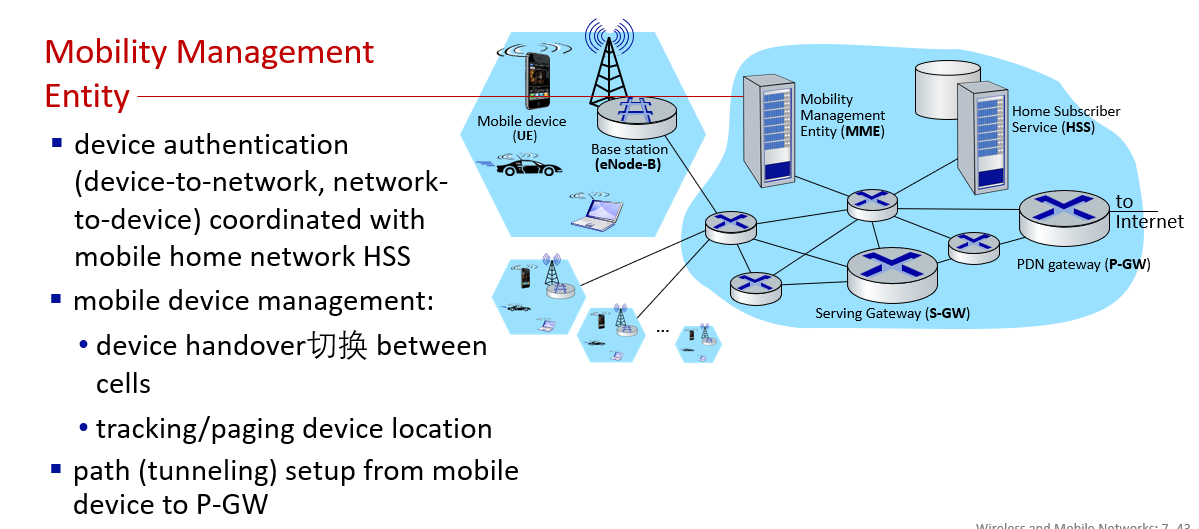
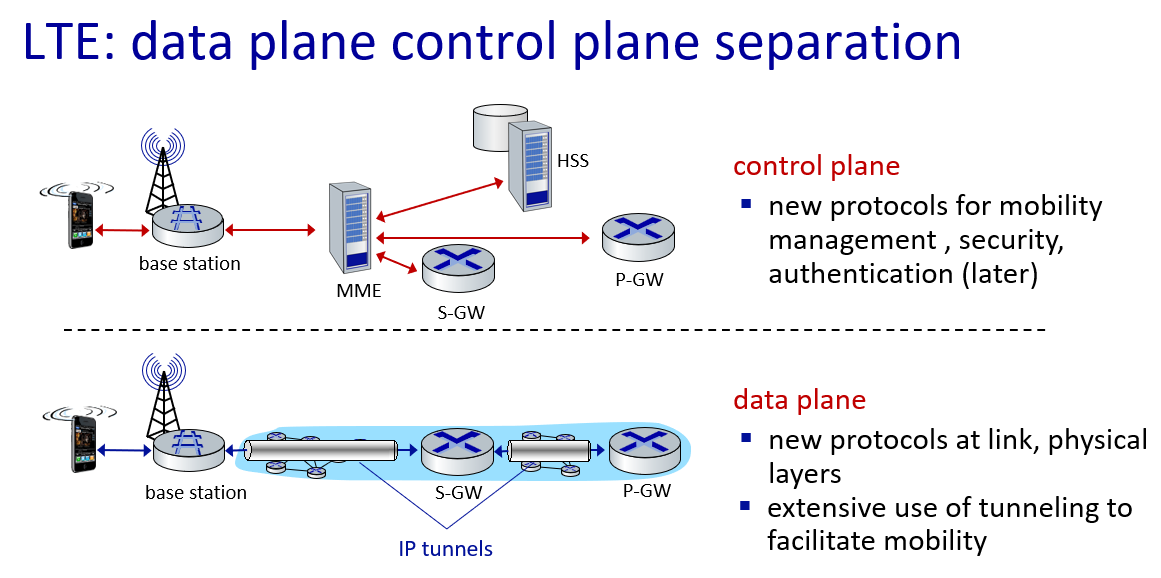
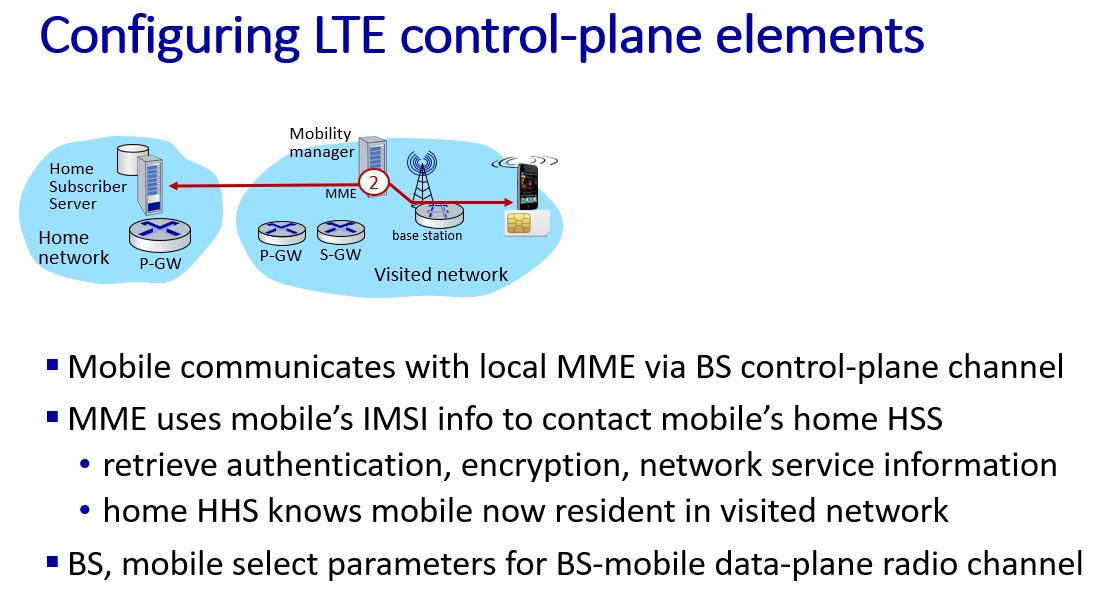
Element of 4G LTE architecture
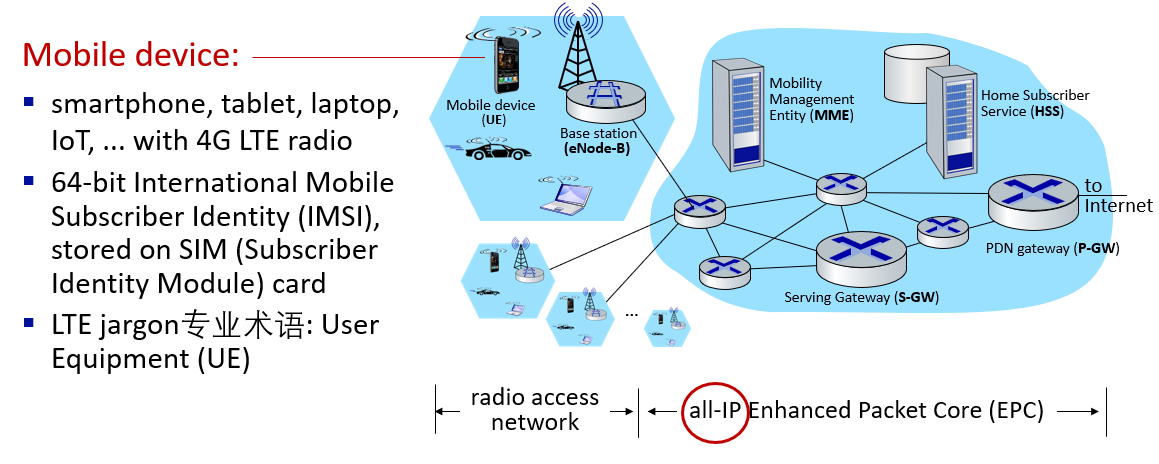
"All-IP Enhanced Packet Core (EPC)" 意味着LTE网络的核心部分(EPC)完全采用互联网协议(IP),这有助于实现更高效、灵活和统一的移动通信环境
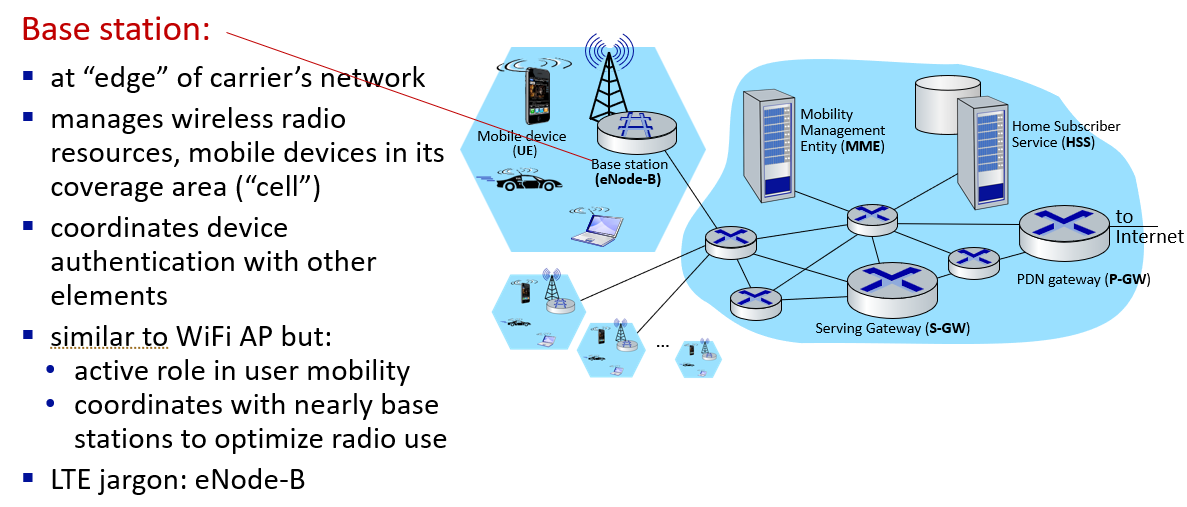
eNodeB(Evolved Node B)是LTE网络中负责与用户设备通信的基站,它是LTE中基站技术(Node B)的演进,为更高速、更先进的移动通信提供支持
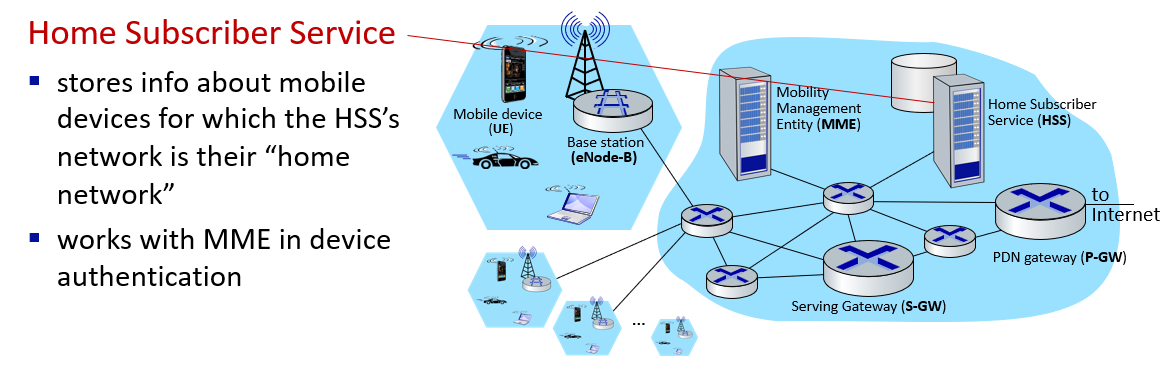
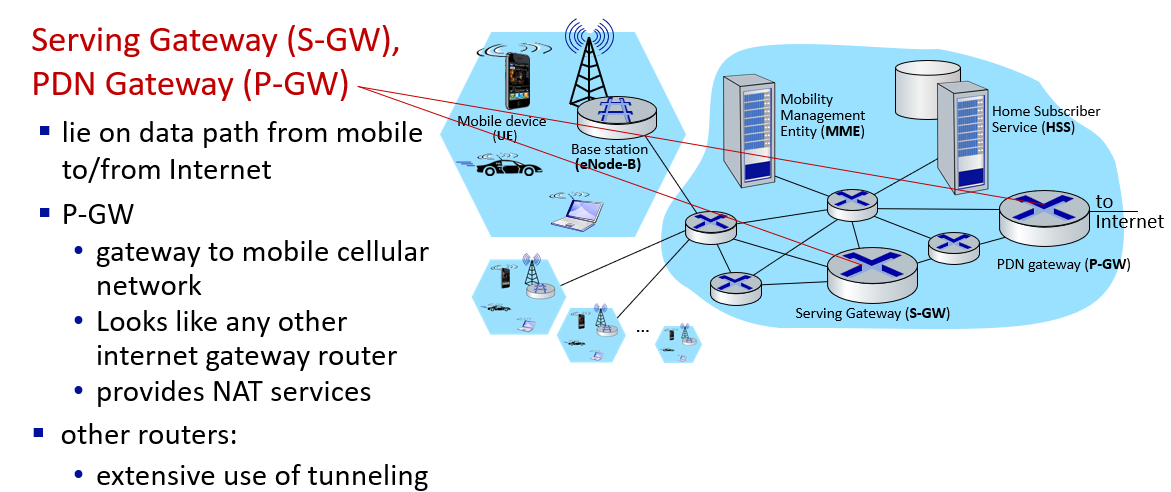
PDN Gateway(Packet Data Network Gateway)是LTE网络的一个关键组件,负责连接LTE网络与外部数据网络,如互联网。它充当用户设备(UE)和外部数据网络之间的接口,处理数据传输、路由、地址分配、QoS(服务质量)管理等功能
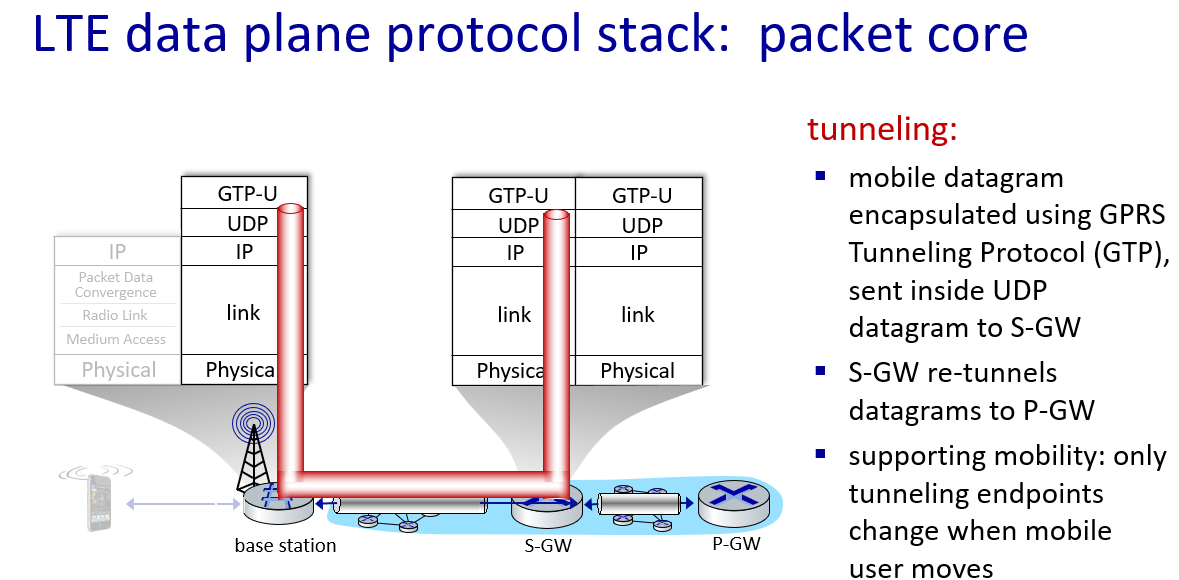
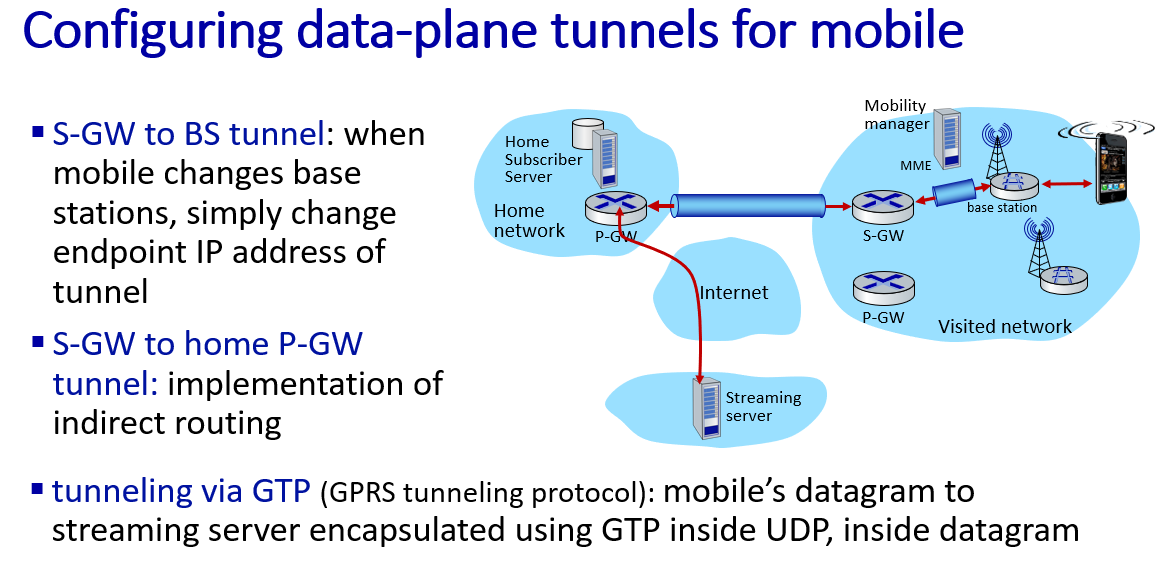
GPRS 是 "General Packet Radio Service" 的缩写,翻译为“通用分组无线服务”
GTP 主要用于在移动通信网络中的不同网络元素之间建立隧道,以便有效地传输用户数据和控制信息
GTP 分为两个主要部分:
GTP-C(Control Plane): 用于传输控制信息,例如切换信令、用户位置更新等
GTP-U(User Plane): 用于传输用户数据,例如互联网流量、多媒体内容等
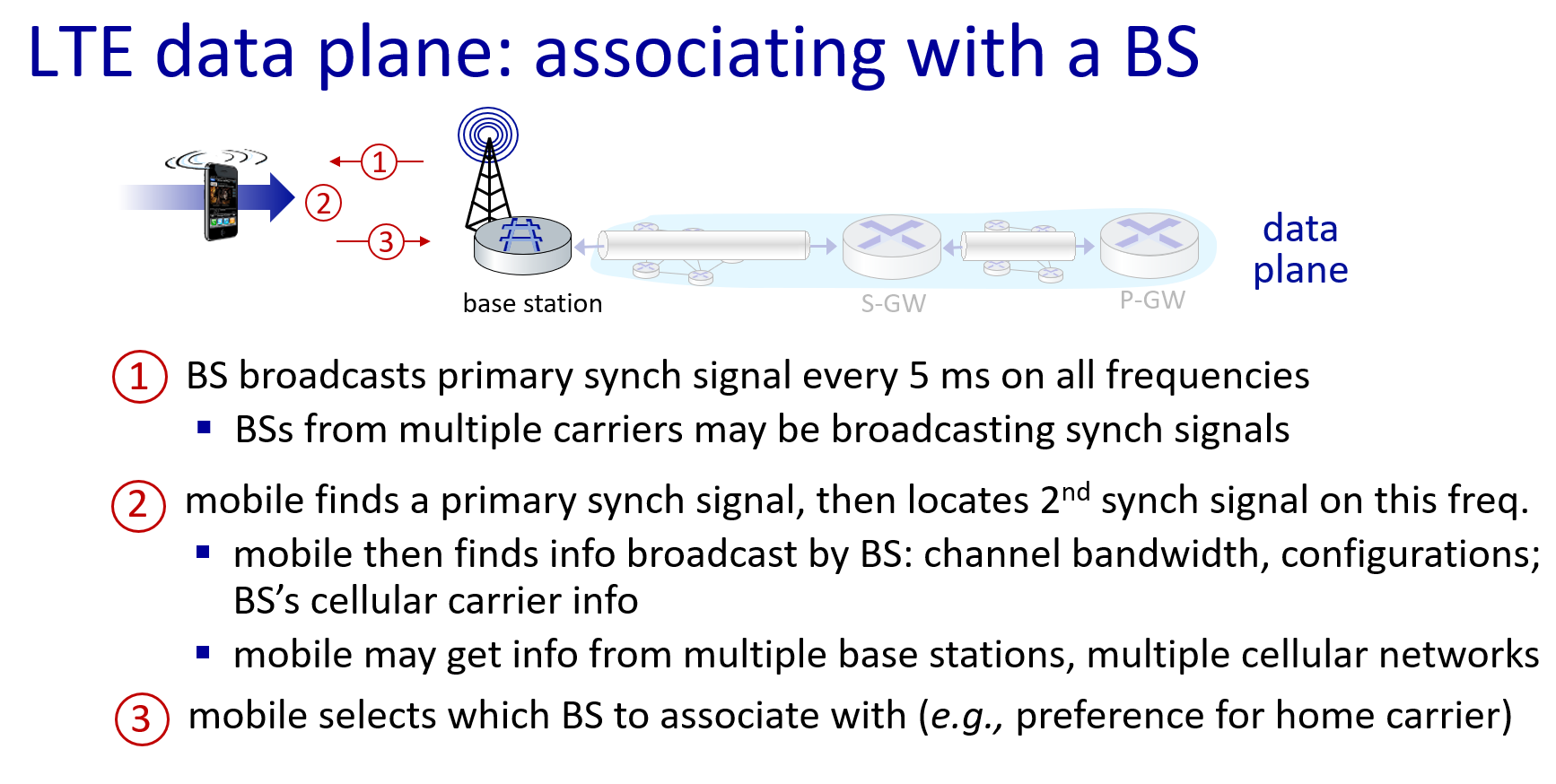

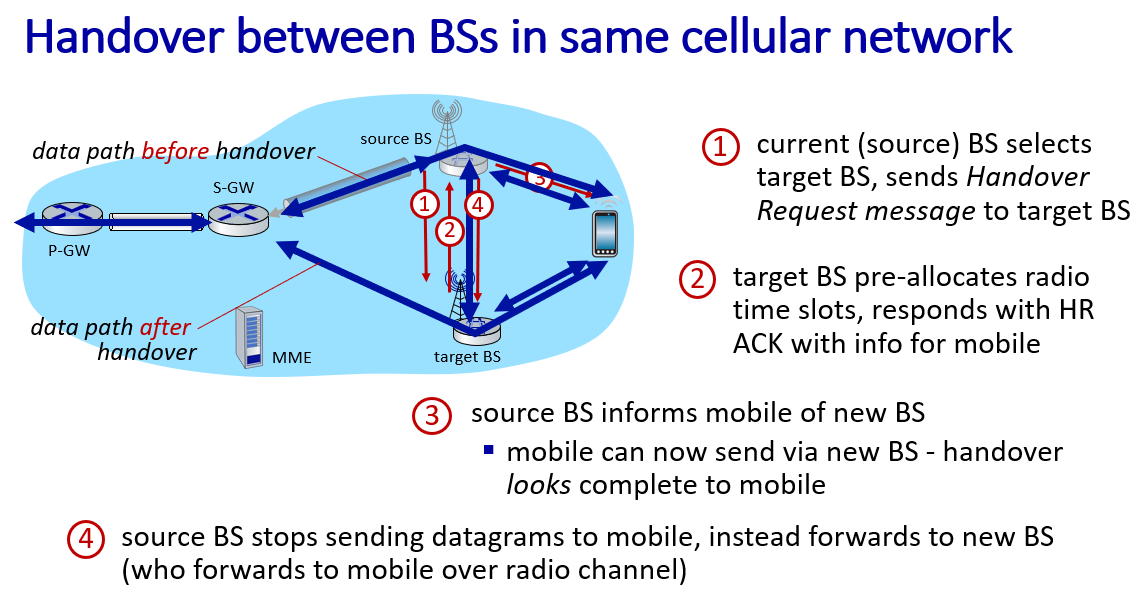
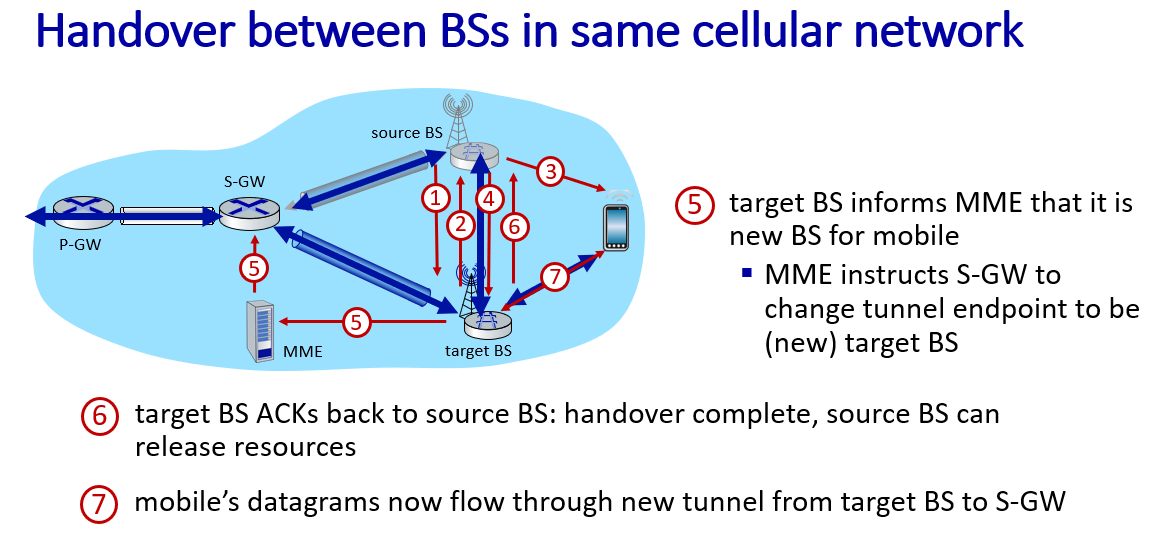
Mobility
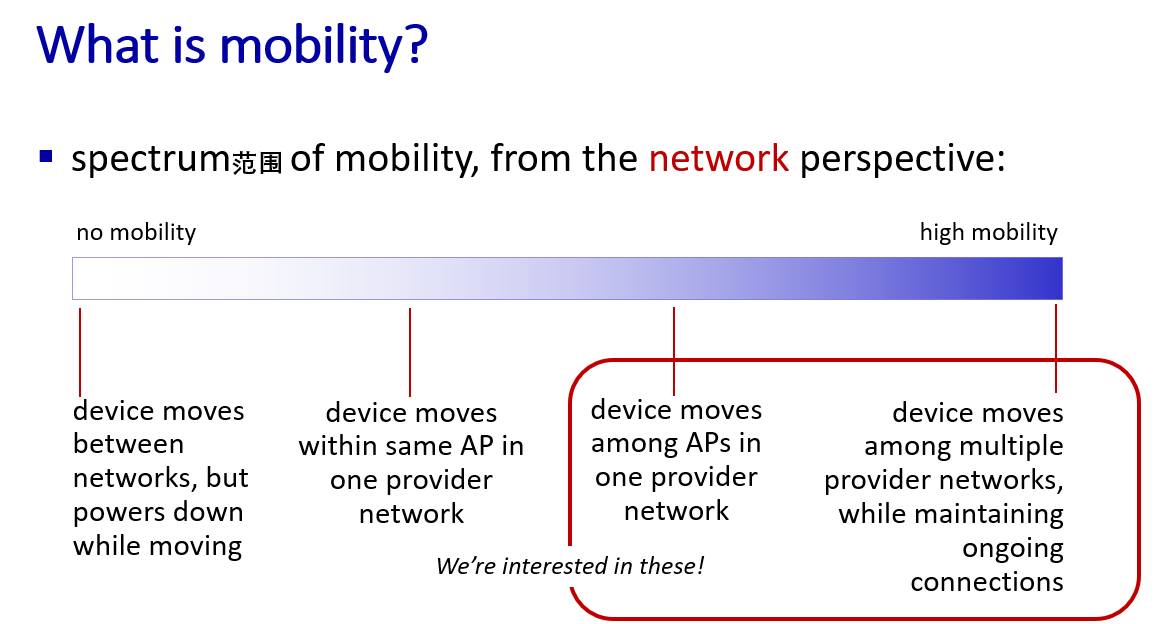
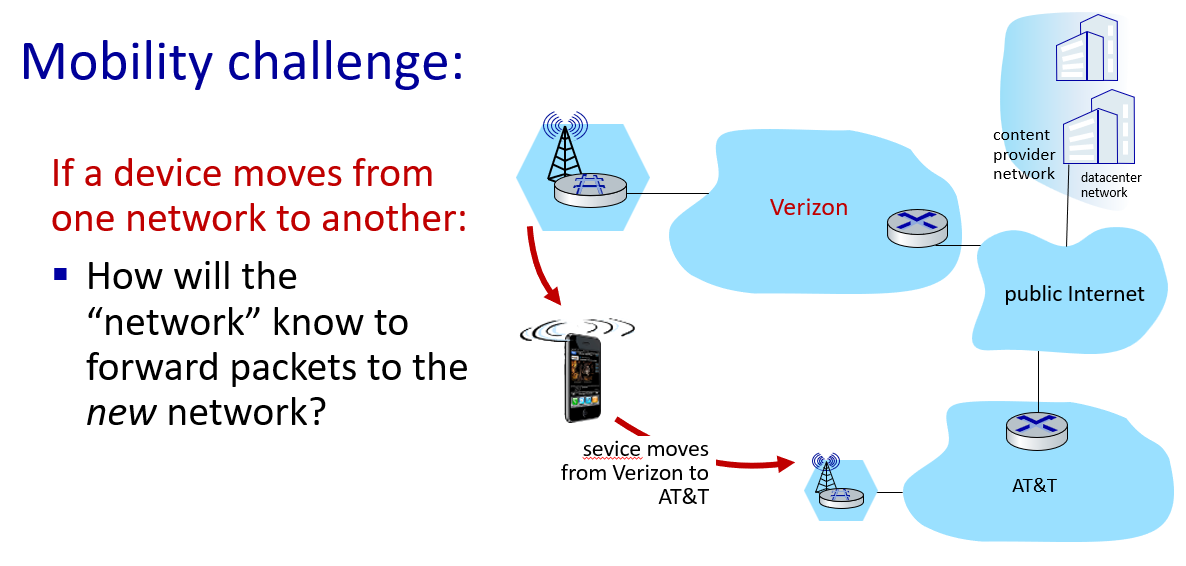
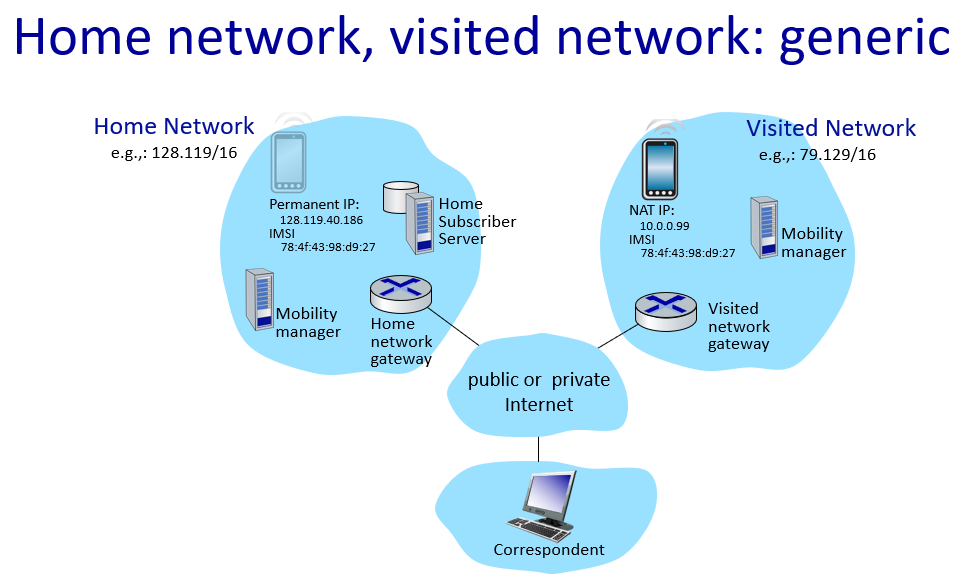
Mobility management: principles


通信者(correspondent)
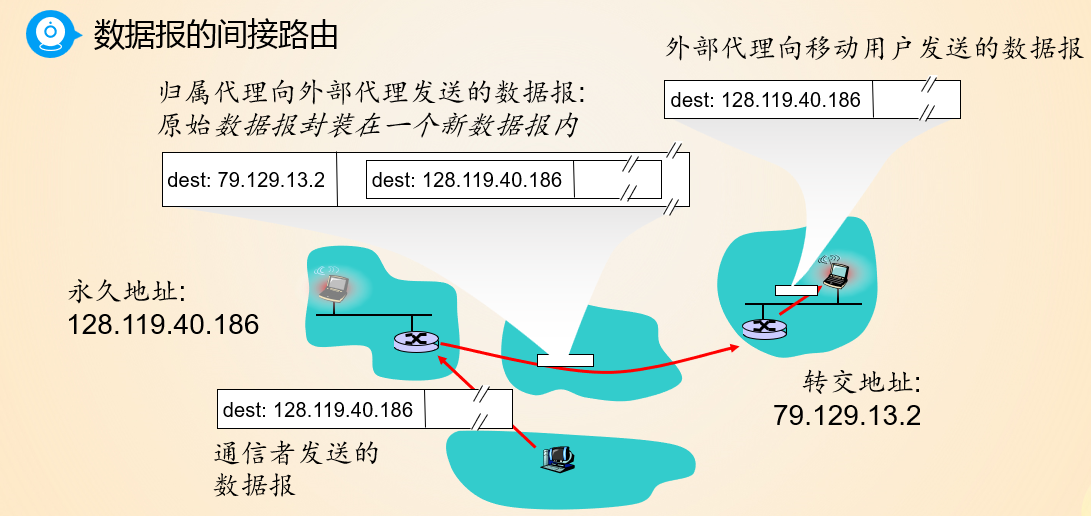
indirect routing->call his/her parent
direct routing->facebook
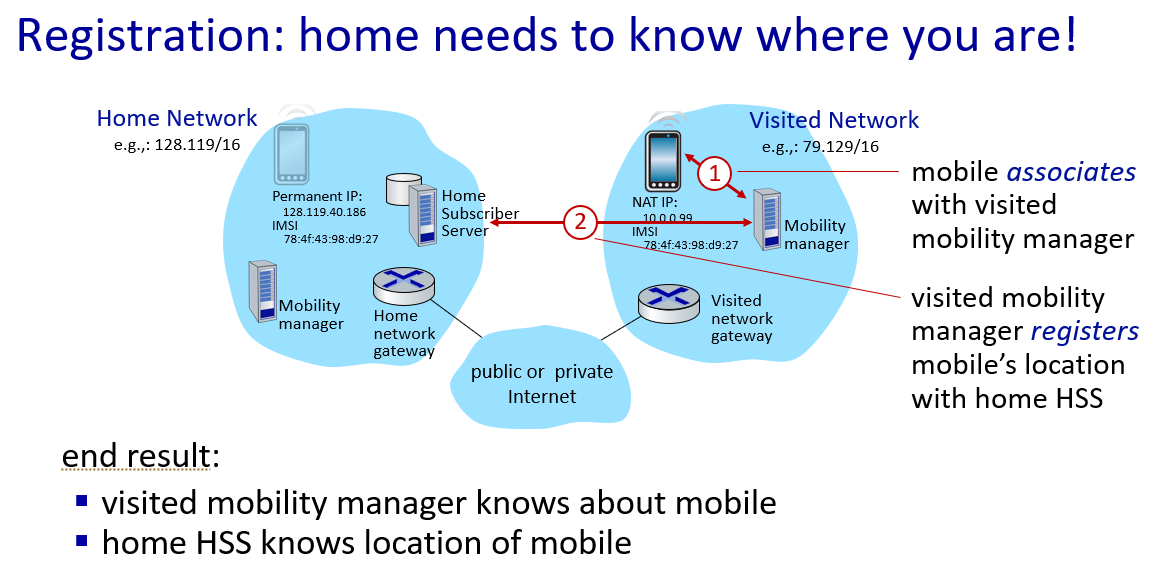
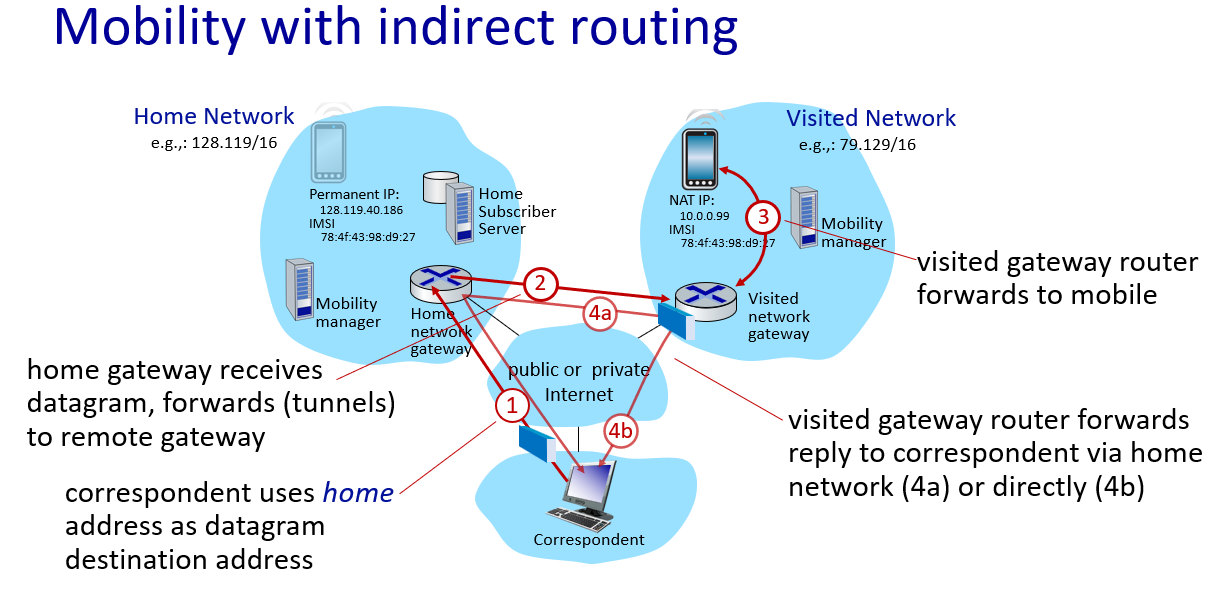
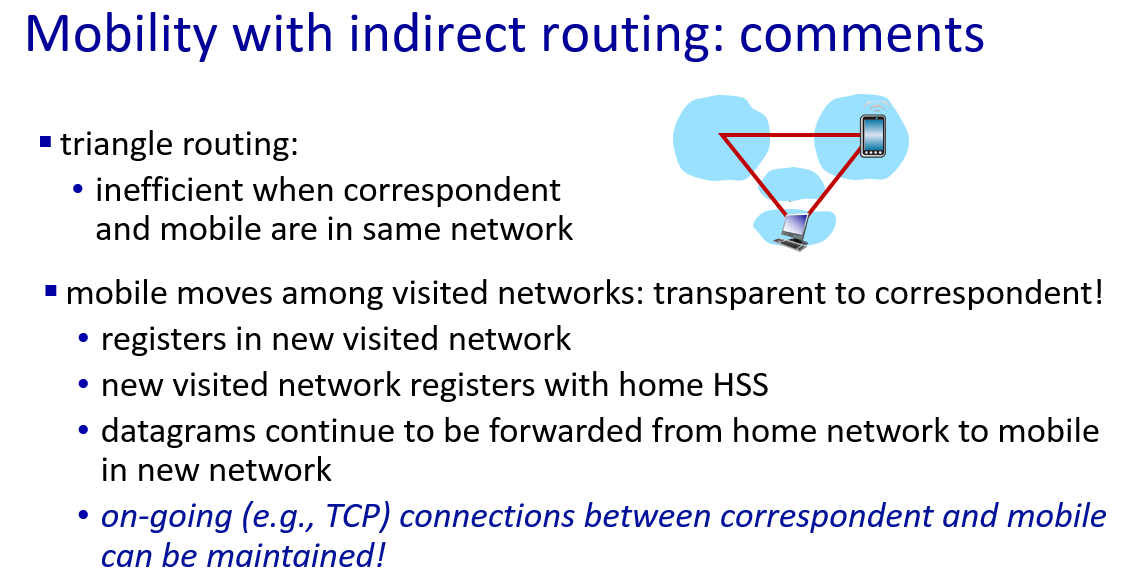
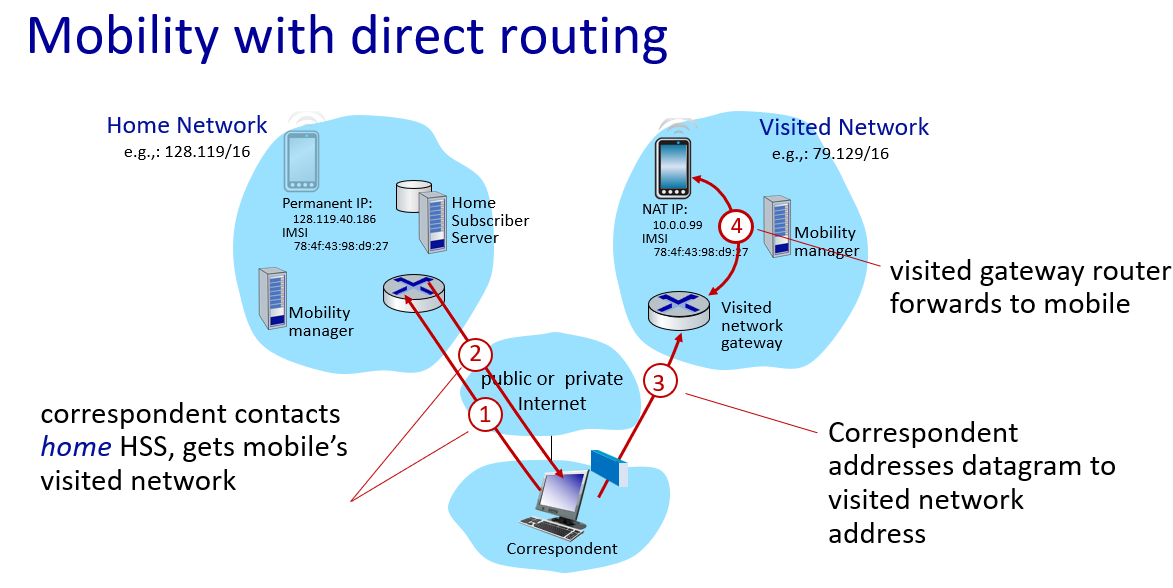

if mobile changes visited network,handled like this
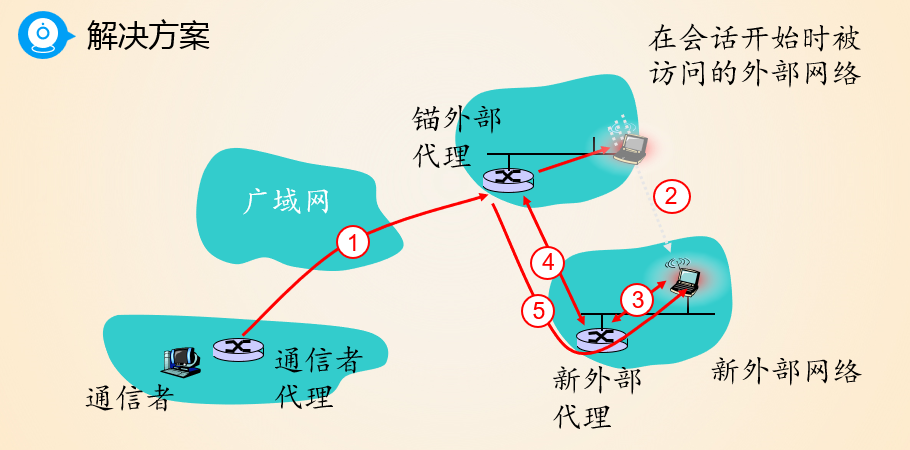
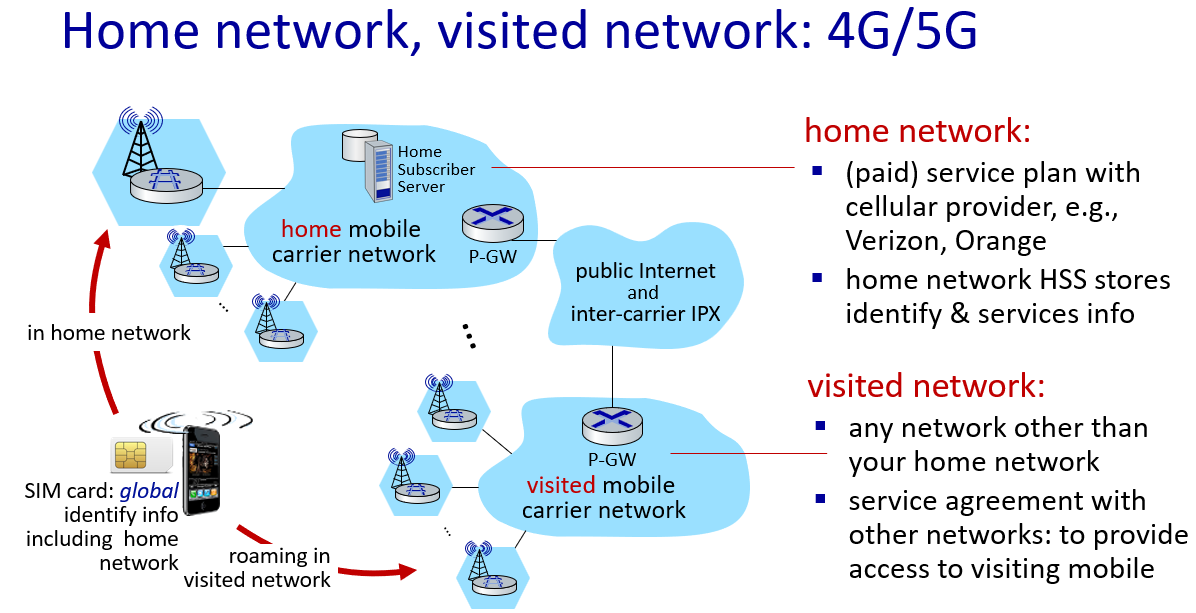
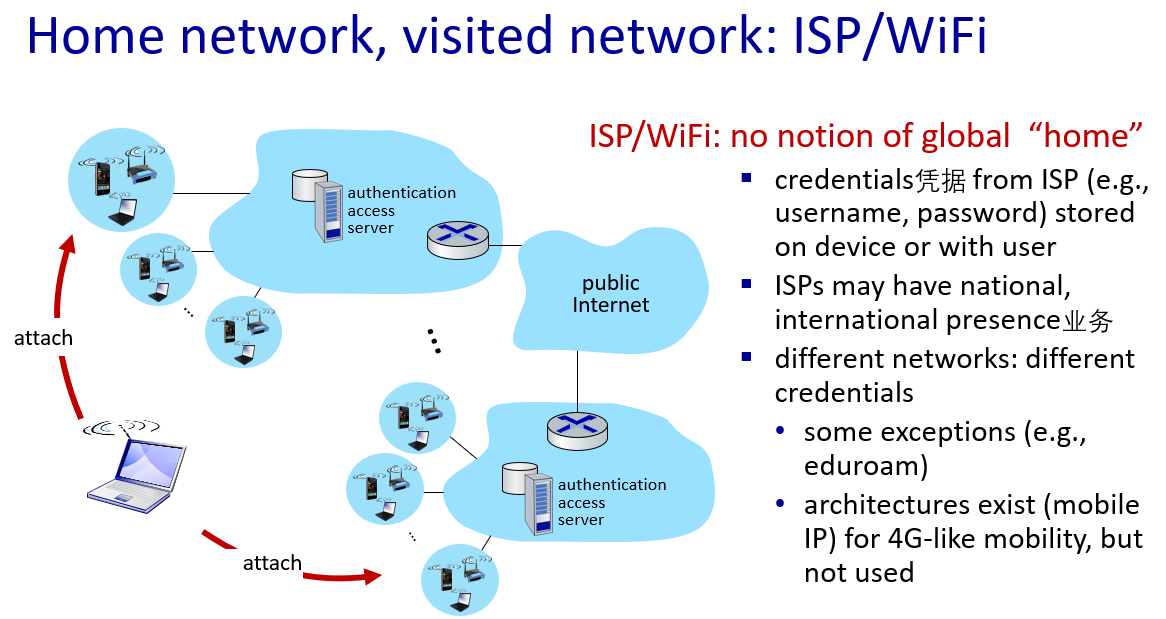
Mobility management: practice
- 4G/5G networks
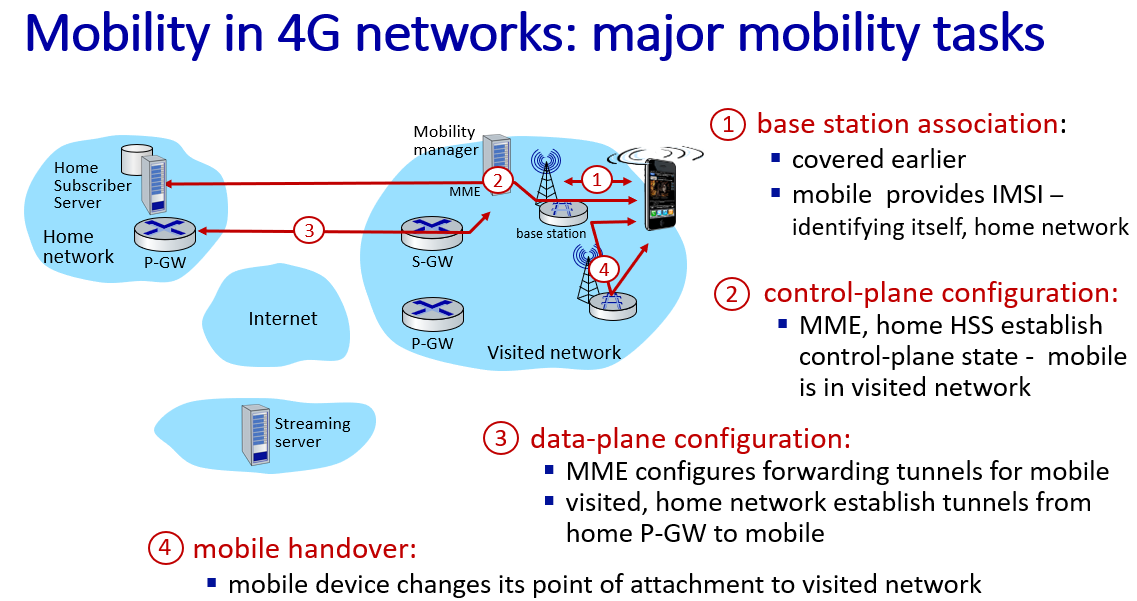
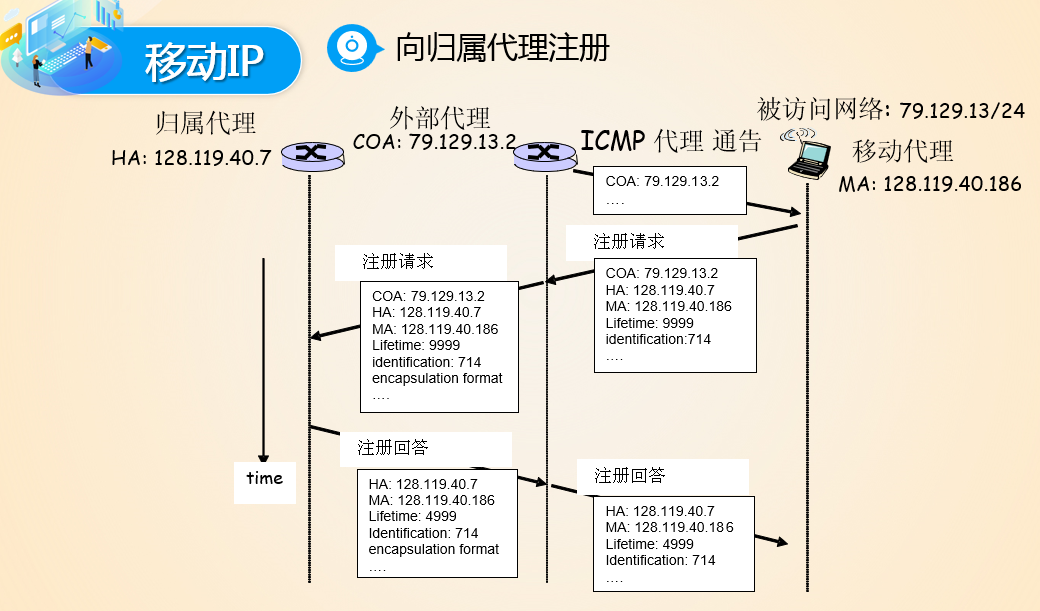
- Mobile IP


通信者只知道移动设备的永久IP,通过归属代理和外部代理,实现了移动IP
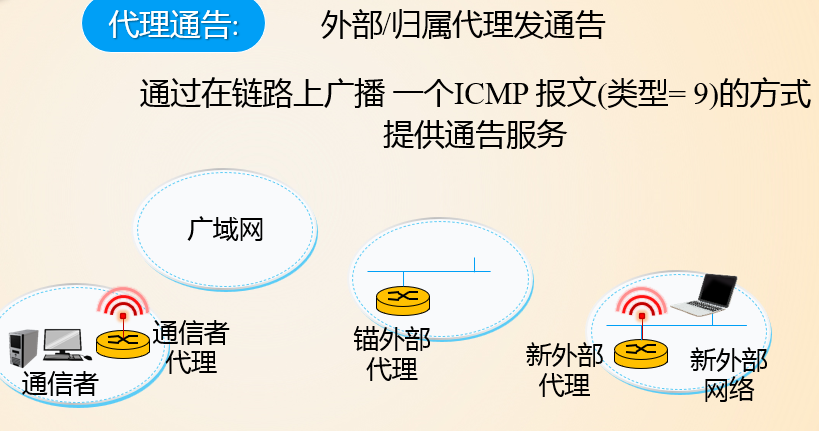
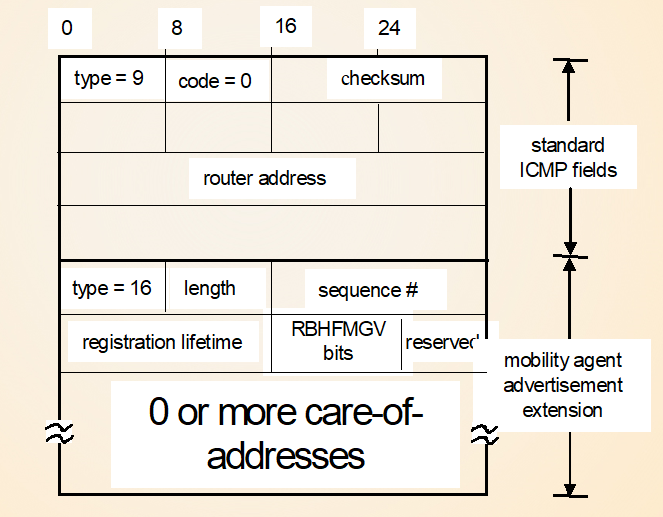
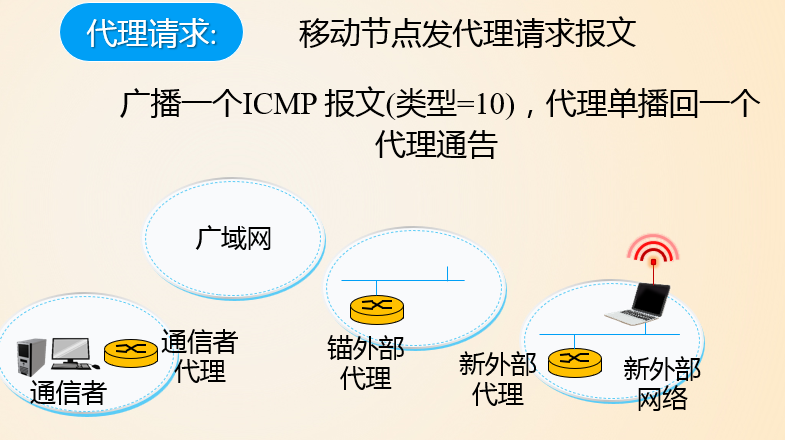
代理发现
Mobility: impact on higher-layer protocols

Review Question
1.1“主机”和“端系统”之间有什么不同?列举几种不同类型的端系统。Web服务器是一种端系统吗?
(1)没有区别。根据书本内容,“主机”和“终端系统”是可以互用的。
(2)终端系统包括PC、工作站、网络服务器、邮件服务器、PDA、连接网络的游戏控制台等等。
(3)由(2)可知,网络服务器是终端系统。
1.8 能够运行以太网的一些物理媒体是什么?
大部分情况为双绞线,也可以使用光纤
1.10 描述今天最为流行的无线因特网接入技术。对它们进行比较和对照
现在最流行的无线网技术有两种:
(1)WiFi。用于无线局域网,无线用戶从辐射范围为几十米的基站(例如无线接入点) 传输/接收数据包。基站连接无线网络,并为无线用戶提供无线网服务。
(2)3G和4G大范围无线网。此系统通过电信服务商提供的基站,由蜂窝电话通过同一个无线设备传输数据。可以提供基站几十千米范围内的无线网络。
1.13 假定在发送主机和接收主机间只有一台分组交换机。发送主机和交换机间以及交换机和接收主机间的传输速率分别是\(R_1\)和\(R_2\)。假设该交换机使用存储转发分组交换方式,发送一个长度\(L\)的分组的端到端总时延是什么?(忽略排队时延、传播时延和处理时延。)
t0时发送端主机开始传输数据, t1= L/R1时发送端完成传输并且交换机收到完整的数据包(没有传播延时)。因为交换机在t1时已收到完整包,那么 t1时交换机开始传输数据包至接收主机。 t2=t1+ L/R2时交换机完成输出并且接收主机收到完整包(没有传播延时)。因此,端到端总延时是L/R1+ L/R2
1.18 —个长度为1000字节的分组经距离为2500km的链路传播,传播速率为\(2.5*l0^8\)m/s并且传输速率为2Mbps,它需要用多长时间?更为一般地,一个长度为L的分组经距离为d的链路传播,传播速率为s并且传输速率为Rbps,它需要用多长时间?该时延与传输速率相关吗?
第一问为传播时延,为10 msec.更为一般的传播时延为d/s.和传输速率无关.
1.19 假定主机A要向主机B发送一个大文件。从主机A到主机B的路径上有3段链路,其速率分别为R1 = 500kbps, R2 = 2Mbps, R3 = 1 Mbps
a. 假定该网络中没有其他流量,该文件传送的吞吐量是多少?
b. 假定该文件为4MB。用吞吐量除以文件长度,将该文件传输到主机B大致需要多长时间?
c. 重复(a)和(b),只是这时R2减小到100kbps.
a) 500kps 大文件转发,吞吐量由瓶颈路径的速率决定
b) 64s
c) 100kps;320秒
1.20 假定端系统A要向端系统B发送一个大文件。在一个非常高的层次上,描述端系统怎样从该文件生成分组。当这些分组之一到达某分组交换机时,该交换机使用分组中的什么信息来决定将该分组转发到哪一条链路上?因特网中的分组交换为什么可以与驱车从一个城市到另一个城市并沿途询问方向相类比?
终端系统A将大文件拆分为块。A通过添加文件头信息至每一个块来从文件生成多个数据包。数据包的头信息包含目标(终端系统B)IP地址。数据包交换机通过包中的目标IP地址来决定发送链路。考虑到包目标地址,包选择哪条路走和包选择哪条输出链路走的方法相似。包从源IP地址到目的IP地址和从驱车从一个城市到另一个城市类似,每经过一个路由器,路由器参照转发表给出包要走的链路和沿途询问方向类比.
1.23 因特网协议栈中的5个层次有哪些?在这些层次中,每层的主要任务是什么?
网络协议的自顶向下的五层是:应用层、传输层、网络层、链路层和物理层,每个层次有不同的功能和任务。
物理层(Physical Layer):
主要任务是定义物理连接的标准,包括电缆、光纤、无线电等。它处理位的传输,也就是在物理媒介上传输比特流。
数据链路层(Data Link Layer):
主要任务是提供可靠的点对点通信,通过物理层传输的比特流划分为数据帧,实现帧的同步、流量控制和错误检测。此层还包括子层MAC(介质访问控制),它处理多路访问和数据帧的地址。
网络层(Network Layer):
主要任务是在源和目的地之间选择最佳路径,以确保数据包的传递。它负责寻址、路由和分包,使得数据能够在不同网络之间传输。
传输层(Transport Layer):
主要任务是为端到端的通信提供可靠的数据传输。它通过使用端口号来区分不同的应用程序,提供流量控制、差错恢复和顺序控制,以确保数据在通信双方之间的可靠传输。
应用层(Application Layer):
主要任务是为用户提供网络服务和应用。这一层包含了各种协议,如HTTP、FTP、SMTP等,支持用户进行各种网络活动,如文件传输、电子邮件和远程登录。
1.25 路由器处理因特网协议栈中的哪些层次?链路层交换机处理的是哪些层次?主机处理的是哪些层次?
路由器处理网络、链路、物理层(第1到3层)。(实际上现代路由器有时担任防火墙、缓存组件和处理传输层)链路层交换机处理链路层和网络层(第1到2层)。主机处理所有的五层。
2.2 网络体系结构与应用程序体系结构之间有什么区别?
网络架构是指将通信过程组织成多个层次(例如,五层网络架构)。另一方面,应用程序体系结构是由应用程序开发人员设计的,它决定了应用程序的广泛结构(例如,C-S或P2P)。
2.5 运行在一台主机上的一个进程,使用什么信息来标识运行在另一台主机上的进程?
目标主机的IP地址和目标进程中套接字的端口号。
2.10 握手协议的作用是什么?
如果两个通信实体在相互发送数据之前先交换控制包,则协议使用握手。SMTP在应用层使用握手,而HTTP不使用握手。
2.11 为什么HTTP、SMTP及POP3都运行在TCP,而不是UDP上?
与这些协议相关联的应用程序要求以正确的顺序接收所有应用程序数据,并且不存在间隔。TCP提供此服务,而UDP不提供此服务。
2.16 假定Alice使用一个基于Web的电子邮件账户(例如Hotmail或Gmail)向Bob发报文,而Bob使用POP3从他的邮件服务器访问自己的邮件。讨论该报文是如何从Alice主机到Bob主机的。要列出在两台主机间移动该报文时所使用的各种应用层协议.
该消息首先通过HTTP从Alice的主机发送到她的邮件服务器。然后,Alice的邮件服务器通过SMTP向Bob的邮件服务器发送消息。然后Bob通过POP3将消息从他的邮件服务器传输到他的主机。
2.20 仔细检查收到的电子邮件,查找由使用.edu电子邮件地址的用户发送的报文首部。从其首部,能够确定发送该报文的主机的IP地址吗?对于由Gmail账号发送的报文做相同的事。
您应该能够使用.edu电子邮件地址查看发送方的IP地址。但是,如果用戶使用Gmail帐戶,您将无法看到发件人的IP地址。
2.21 在BitTorrent中,假定Alice向Bob提供一个30秒间隔的文件块吞吐量。Bob将必须进行回报,在相同的间隔中向Alice提供文件块吗?为什么?
Bob也没有必要为Alice提供块(chunks)。Alice必须是Bob的前4位邻居,Bob才能向她发送块;即使Alice在30秒的间隔内向Bob提供块,也可能不会发生这种情况。
2.23 覆盖网络是什么?它包括路由器吗?在覆盖网络中边是什么?
P2P文件共享系统中的覆盖网络由参与文件共享系统的节点和节点之间的逻辑链接组成。覆盖网络不包括路由器。如果A和B之间有一个半永久的TCP连接,则从节点A到节点B有一个逻辑链路(图论术语中的“边缘”)。
3.1 假定网络层提供了下列服务。在源主机中的网络层接受最大长度1200字节和来自运输层的目的主机地址的报文段。网络层则保证将该报文段交付给位于目的主机的运输层。假定在冃的主机上能够运行许多网络应用进程
a. 设计可能最简单的运输层协议,该协议将使应用程序数据到达位于目的主机的所希望的进程。假设在目的主机中的操作系统已经为每个运行的应用进程分配了一个4字节的端口号。
b. 修改这个协议,使它向目的进程提供一个的“返回地址”。
c. 在你的协议中,该运输层在计算机网络的核心中“必须做任何事”吗?
a)将此协议称为简单传输协议(STP,Simple Transport Protocol)。在发送方,STP从发送进程接受不超过1196字节的数据块、目标主机地址和目标端口号。STP在每个块中添加一个4字节的头,并将目标进程的端口号放在这个标头中。然后,STP将目标主机地址和结果段提供给网络层。网络层将段传送到目标主机上的STP。STP然后检查段中的端口号,从段中提取数据,并将数据传递给由端口号标识的进程。
b)段现在有两个头字段:源端口字段和目标端口字段。在发送方,STP接受不超过1192字节的数据块、目标主机地址、源端口号和目标端口号。STP创建一个段,其中包含应用程序数据、源端口号和目标端口号。然后,它将段和目标主机地址提供给网络层。在接收到段后,接收主机上的STP给出应用程序的应用程序数据和源端口号。
c)不,传输层不需要在核心中做任何事情;传输层“存活”在最终系统中。
3.4 描述应用程序开发者为什么可能选择在UDP上运行应用程序而不是在TCP上运行的原因。
应用程序开发人员可能不希望其应用程序使用TCP的拥塞控制,这会在拥塞时限制应用程序的发送速率。通常,IP电话和IP视频会议应用程序的设计者选择在UDP上运行他们的应用程序,因为他们希望避免TCP的拥塞控制。另外,有些应用程序不需要TCP提供的可靠数据传输。
3.8 假定在主机C端口 80上运行的一个Web服务器。假定这个Web服务器使用持续连接,并且正在接收来自两台不同主机A和B的请求。被发送的所有请求都通过位于主机C的相同套接字吗?如果它们通过不同的套接字传递,这两个套接字都具有端口 80吗?讨论和解释之:
对于每个持久连接,Web服务器创建一个单独的“连接套接字”。每个连接套接字被标识为具有四个元组:(源IP地址、源端口号、目标IP地址、目标端口号)。当主机C接收和IP数据报,它检查数据报/段中的这四个字段确定TCP段的有效负载应该通过哪个套接字。因此,来自A和B的请求通过不同的套接字。
这两个套接字的标识符用于目标端口的参数都为80;但是,这些套接字的标识符中源IP地址为不同值。
3.12 在配套网站上使用Go-Back-N (回退/V步)Java小程序。
a. 让源发送5个分组,在这5个分组的任何一个到达目的地之前暂停该动画。然后毁掉第一个分组并继续该动画。试描述发生的情况。
b. 重复该实验,只是现在让第一个分组到达目的地并毁掉第一个确认。再次描述发生的情况。
c. 最后,尝试发送6个分组。发生了什么情况?
a)丢包造成一段时间后,所有五个包都被重传。
b)由于Go-Back-N使用累积数据,ACK的丢失没有触发任何重传。
c)发送方无法发送第六个分组,因为发送窗口大小固定为5。
3.13 重复复习题R12,但是现在使用Selective Repeat (选择重传)Java小程序。选择重传和回退 N步有什么不同?
a)当分组丢失时,接收的4个分组被缓冲接收器。完成后超时,发送方重新发送丢失的数据包,接收
方传送缓冲的数据包,数据包以正确的顺序应用。
b)发送方重发第一个分组,接收器收到后发送了重复ACK。
c)因为发送窗口大小已固定为5,发件人无法发送第六个数据包
当一个数据包丢失时,GO-Back-N重新传输所有数据包,而选择性重复仅重新传输丢失的数据包。在确认丢失的情况下,选择性重复发送一个重复的确认,而返回N使用累积确认,因此不需要重复的确认。
3.14 .是非判断题:
a. 主机A经过一条TCP连接向主机B发送一个大文件。假设主机B没有数据发往主机A。因为主机B不能随数据捎带确认,所以主机B将不向主机A发送确认。
b. 在连接的整个过程中,TCP的rwnd的长度决不会变化。
c. 假设主机A通过一条TCP连接向主机B发送一个大文件。主机A发送但未被确认的字节数不会
超过接收缓存的大小。
d.假设主机A通过一条TCP连接向主机B发送一个大文件。如果对于这条连接的一个报文段的序号为m则对于后继报文段的序号将必然是m + 1。
e. TCP报文段在它的首部中有一个rwnd字段。
f-假定在一条TCP连接中最后的SampleRTT等于1秒,那么对于该连接的Timeout Interval的当前值必定大于等于1秒。
g.假设主机A通过一条TCP连接向主机B发送一个序号为38的4个字节的报文段。在这个相同的报文段中,确认号必定是42。
F F T F T F F
3.15 假设主机A通过一条TCP连接向主机B发送两个紧接着的TCP报文段。第一个报文段的序号为90,第二个报文段序号为110。
a.第一个报文段中有多少数据?
b.假设第一个报文段丢失而第二个报文段到达主机B。那么在主机B发往主机A的确认报文中,确认号应该是多少?
a) 20 bytes
b) ack number = 90
3.17 假设两条TCP连接存在于一个带宽为R bps的瓶颈链路上。它们都要发送一个很大的文件(以相同方向经过瓶颈链路),并且两者是同时开始发送文件。那么TCP将为每条连接分配什么样的传输速率?
R/2
4.3 我们对网络层执行的转发功能和路由选择功能进行区别。路由选择和转发的主要区别是什么?
路由和转发之间的主要区别在于:转发是路由器将分组从其输入接口传送到其输出接口的本地动作,转发发生在非常短的时标(通常为几纳秒),并且因此通常以硬件实现。路由是指网络范围确定数据包从源接收到目的地的端到端路径的过程。路由发生在更⻓时间的时标上(通常是秒),且通常用软件实现。
4.22 IP地址223. 1.3.27的32比特二进制等价形式是什么?
11011111 00000001 00000011 00011100
4.25 假设某应用每20ms生成一个40字节的数据块,每块封装在一个TCP报文段中,TCP报文段再封装在一个IP数据报中。每个数据报的开销有多大?应用数据所占百分比是多少?
TCP头部大小: 20字节(固定部分) + 可能的选项字段大小。IP头部大小: 20字节(IPv4,不包括选项字段)或者40字节(IPv6,不包括扩展头部)。每个数据报的开销为80字节。应用数据占据每个数据报的50%。
PS:
UDP(用户数据报协议)头部的大小是8个字节。UDP头部包含以下字段:
源端口(Source Port): 2字节
目标端口(Destination Port): 2字节
长度(Length): 2字节,包括头部和数据
检验和(Checksum): 2字节
5.4 比较和对照链路状态和距离矢量这两种路由选择算法。
链路状态算法:使用完整的、全局的网络知识来计算源和目的地之间的最小成本路径。
距离向量路由:最小成本路径的计算是以迭代的、分布式的方式进行的。节点只知道它应该向其转发数据包的邻居,以便沿着成本最低的路径到达给定的目的地,以及该路径从自身到目的地的成本。
5.8 是非判断题:当一台OSPF路由器发送它的链路状态信息时,它仅向那些直接相邻的节点发送。解释理由。
假的。
使用OSPF,路由器将其链路状态信息广播到它所属的自治系统中的所有其他路由器,而不仅仅是它的邻近路由器。这是因为使用OSPF,每个路由器都需要构造一个完整的AS拓扑图,然后本地运行Dijkstra的最短路径算法来确定它对所有其他节点的最小代价路径。
6.2 如果在因特网中的所有链路都提供可靠的交付服务,TCP可靠传输服务将是多余的吗?为什么?
虽然每个链路保证通过链路发送的IP数据报将在链路的另一端无错误地被接收,但不能保证IP数据报将以适当的顺序到达最终目的地。使用IP,同一TCP连接中的数据报可以在网络中采取不同的路由,从而导致出现故障。仍然需要TCP以正确的顺序向应用程序的接收端提供字节流。此外,IP可能由于路由循环或设备故障而丢失数据包。
6.4 假设两个节点同时经一个速率为R的广播信道开始传输一个长度为L的分组。用\(d_{prop}\)叫表示这两个节点之间的传播时延。如果\(d_{prop}\)< L/R、会出现碰撞吗?为什么?
当一个节点正在发送时,它将开始从另一个节点接收一个分组,这将发生冲突。
6.6 在CSMA/CD中,在第5次碰撞后,节点选择K =4的概率有多大?结果K=4在10Mbps以太网上对应于多少秒的时延?
在第5次碰撞之后,适配器从{0,1,2,...,31}中选择。它选择4的概率是1/32。等待512/10Mbps*4=204.8微秒。
6.10 假设节点A、B和C (通过它们的适配器)都连接到同一个广播局域网上.如果A向B发送数千个IP数据报,每个封装帧都有B的MAC地址,C的适配器会处理这些帧吗?如果会C的适配器将会把这些帧中的IP数据报传递给C的网络层吗?如果A用MAC广播地址来发送这些帧,你的回答将有怎样的变化呢?
C的适配器将处理这些帧,但是适配器不会将数据报传递到协议栈中。如果使用MAC广播地址,则C的适配器将处理帧并将数据报传递到协议栈。
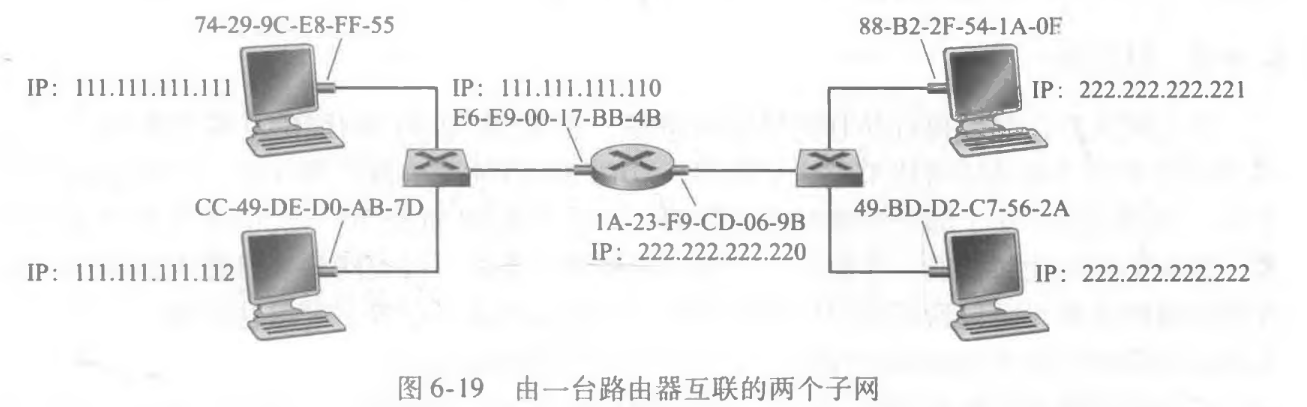
6.12 对于图6-19中的网络,路由器有两个ARP模块,每个都有自己的ARP表。同样的MAC地址可能在两张表中都出现吗?
不可能。每个LAN都有自己的一组不同的适配器,每个适配器都有一个唯一的MAC地址
7.1 一个无线网络运行在“基础设施模式”下是什么含义?如果某网络没有运行在基础设施模式下,那么它运行在什么模式下?这种运行模式与基础设施模式之间有什么不同?
在基础设施模式的操作,每一个无线主机都通过一个基站(接入点)连接到更大的网络。如果不是在基础模式操作,网络以ad-hoc模式操作。在ad-hoc模式下,无线主机没有可连接的基础设施。在缺少基础设施的情况下,设备直接与彼此通信,建立网络,同时主机必须自己提供如路由器、地址分配、DNS类似名称翻译和更多的服务。
7.2 在7.1节的分类法中,所确定的四种无线网络类型各是什么?你已经使用的是这些无线网络类型中的哪一种?
a)单跳,基于基础设施 你在教室、咖啡屋或图书馆中所使用的802. 11网络,以及4GLTE数据网络都属于这种类型
b)单跳,无基础设施 诸如键盘、扬声器和戴在头上的耳机等小型无线设备
c)多跳,基于基础设施 某些无线传感网络和所谓无线网状网
d)多跳,无基础设施
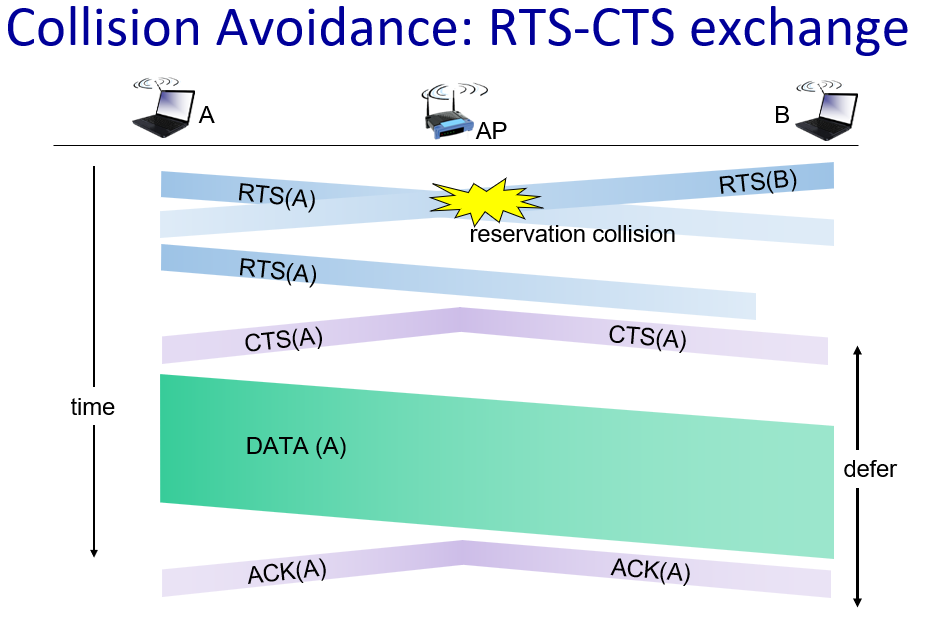
7.6 是非判断:802. 11站在传输一个数据帧前,必须首先发送一个RTS帧并收到一个对应的CTS帧。
假.在802.11协议中,使用RTS/CTS(请求发送/清除发送)过程是一种可选的机制,而不是必须的。在某些情况下,使用RTS/CTS可能会引入额外的开销,尤其是在短数据帧的情况下。因此,802.11协议允许在不使用RTS/CTS的情况下直接发送数据帧。
7.7 为什么802. 11中使用了确认,而有线以太网中却未使用?
无线信道具有不确定性和可变性,包括信号衰减、多径效应、干扰等。这使得在无线网络中更容易发生数据包的丢失。无线网络中可能存在隐藏终端问题,其中两个站点可能无法感知对方的存在,因此可能在相同时间内发送数据而导致碰撞。802.11引入了帧确认机制,以允许发送方知道数据帧是否成功被接收。确认机制有助于处理无线信道的不确定性,提高数据传输的可靠性。
7.11 7. 3. 4节讨论了 802. 11移动性,其中无线站点从一个BSS到同一子网中的另一个BSS.当AP是通过交换机互连时,为了让交换机能适当地转发帧,一个AP可能需要发送一个带有哄骗的MAC地址的帧,为什么?
最初,交换机在其转发表中有一个条目,该条目将无线站与较早的AP相关联。当无线站与新AP相关联时,新AP创建具有无线站点MAC地址的帧并广播该帧。该帧由交换机接收。这迫使交换机更新其转发表,以便通过新的AP发送发送到无线站的帧。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号