Spark 任务划分&作业提交
1、Stage任务划分
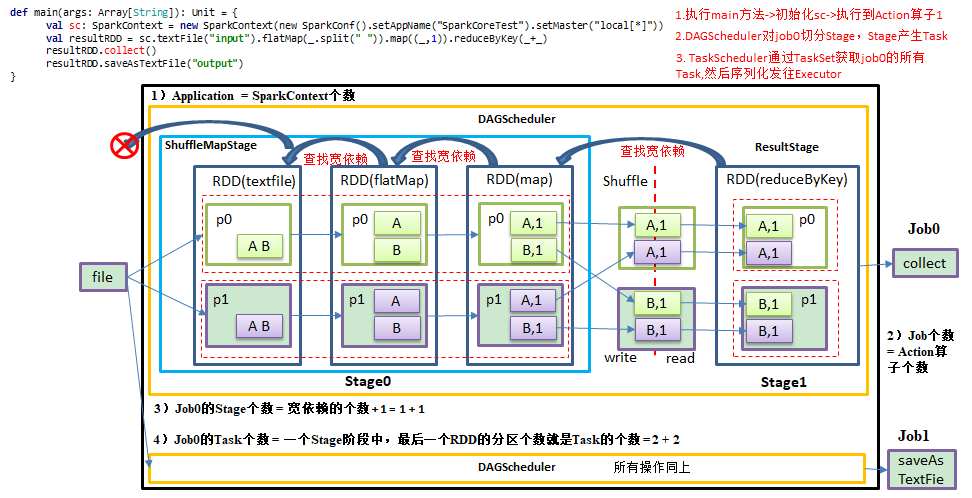
DAG有向无环图:DAG(Directed Acyclic Graph)有向无环图是由点和线组成的拓扑图形,该图形具有方向,不会闭环。原始的RDD通过一系列的转换就形成了DAG,根据RDD之间的依赖关系的不同将DAG划分成不同的Stage,对于窄依赖,partition的转换处理在Stage中完成计算。对于宽依赖,由于有Shuffle的存在,只能在parent RDD处理完成后,才能开始接下来的计算,因此宽依赖是划分Stage的依据。例如,DAG记录了RDD的转换过程和任务的阶段。
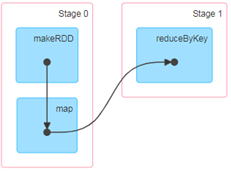
RDD任务切分中间分为:Application、Job、Stage和Task
(1)Application:初始化一个SparkContext即生成一个Application;
(2)Job:一个Action算子就会生成一个Job;
(3)Stage:Stage等于宽依赖的个数加1;
(4)Task:一个Stage阶段中,最后一个RDD的分区个数就是Task的个数。
注意:Application->Job->Stage->Task每一层都是1对n的关系。
代码实现
/**
* Job 调度
* 概念:
* 集群:Yarn || Standalone
* 应用:一个spark程序,一般创建一个SparkContex,表示创建一个应用
* 一个集群可以创建多个应用
* Job Spark 应用可以并发运行多个Job,每次触发行动操作都会提交一个Job,
* 一个Spark应用可以有多个Job
* Stage 根据job 中宽依赖的数量划分,Stage 数量 = 宽依赖数量 + 1
* Task:每个Stage 由多个 task 组成,每个stage 的最后一个RDD的分区的数量就是当前stage的 task 数量
*/
object Spark02_Task {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//创建 配置对象
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("wordcount").setMaster("local[2]")
//配置上下文对象
var sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf)
val rdd: RDD[String] = sc.makeRDD(List("hello spark", "flink", "hello", "word hello"))
//rdd 血缘关系
println(rdd.toDebugString)
println(rdd.dependencies)
println("**************************************")
val flatMap: RDD[String] = rdd.flatMap(_.split(" "))
println(flatMap.toDebugString)
println(flatMap.dependencies)
println("**************************************")
val map: RDD[(String, Int)] = flatMap.map((_, 1))
println(map.toDebugString)
println(map.dependencies)
println("**************************************")
val resRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = map.reduceByKey(_ + _)
/*println(resRDD.toDebugString)
println(resRDD.dependencies)*/
resRDD.collect().foreach(println)
resRDD.saveAsTextFile("E:\\workspace_idea\\spark0520\\output")
Thread.sleep(900000000 )
//关闭
sc.stop()
}
}
job 数量
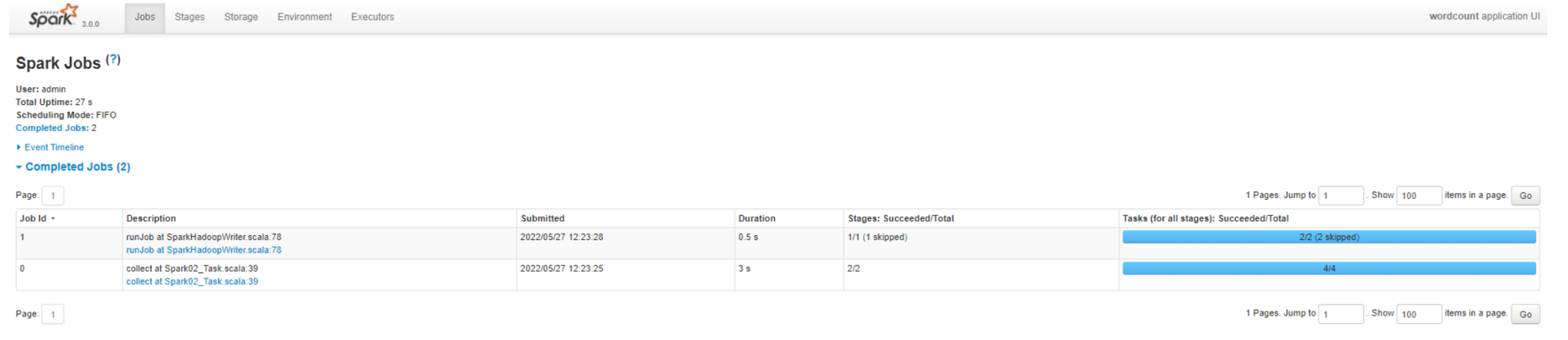
Stage 数量
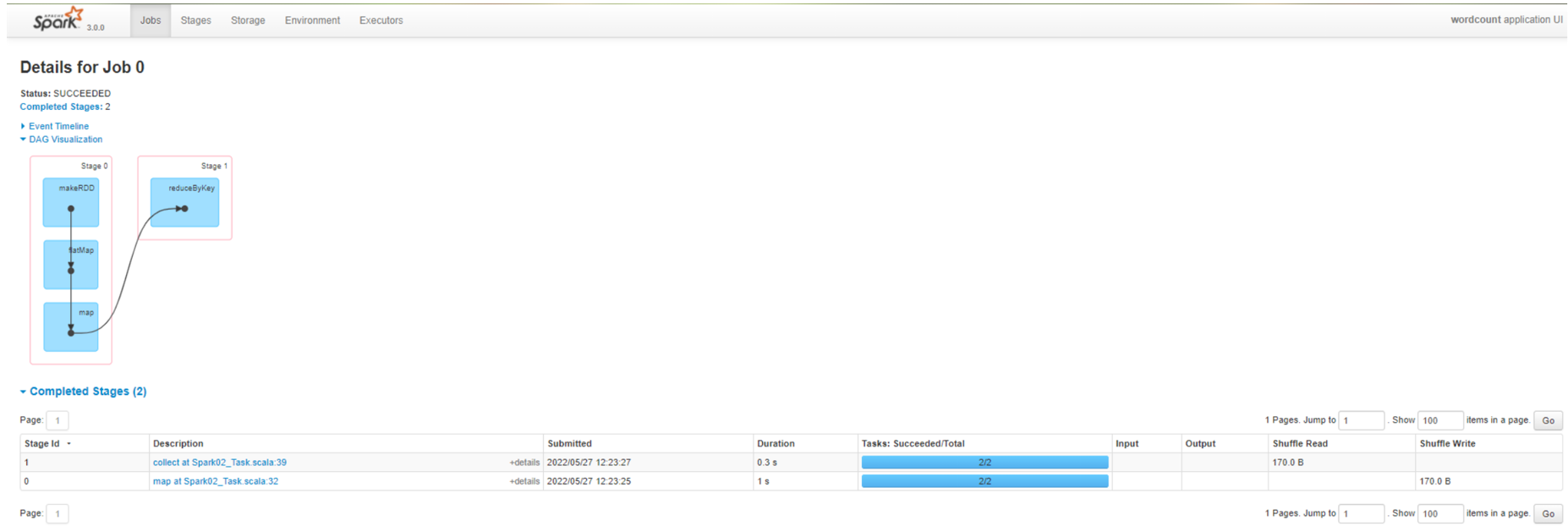
查看Job0的Stage。由于只有1个Shuffle阶段,所以Stage个数为2
查看Job1的Stage。由于只有1个Shuffle阶段,所以Stage个数为2。
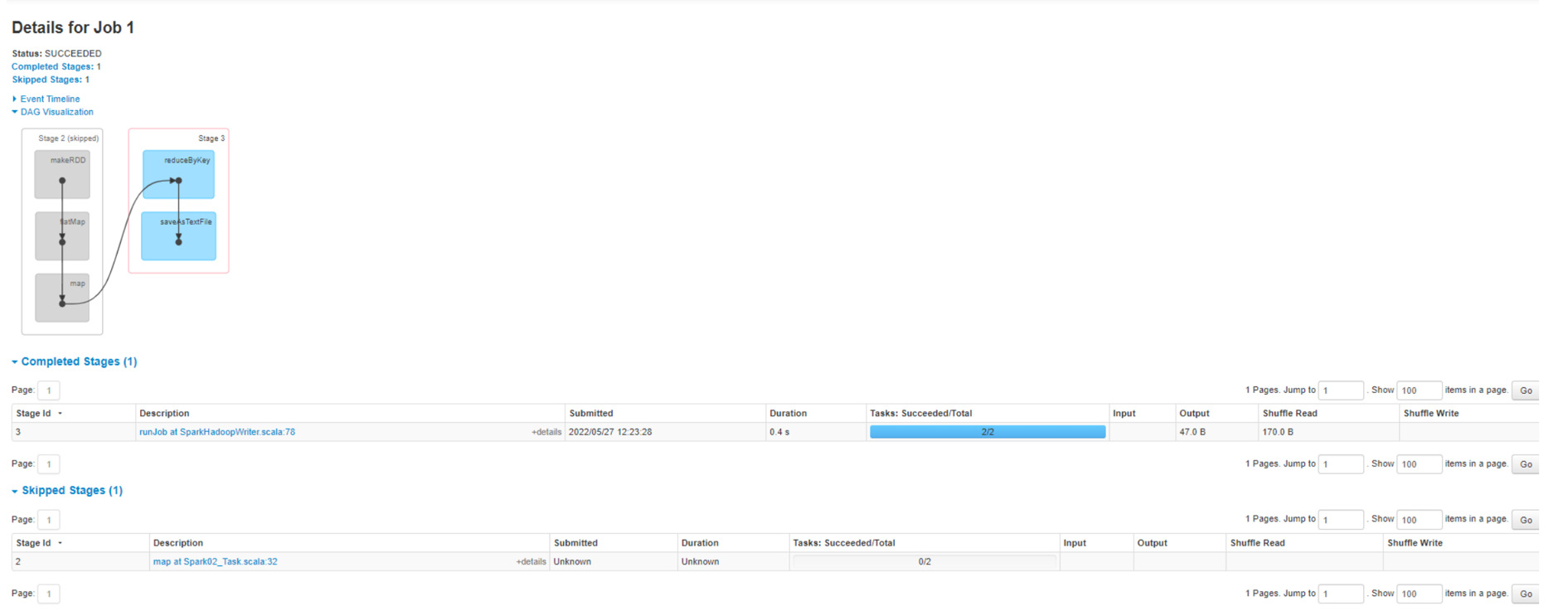
Task 数量:查看Job0的Stage0的Task个数

查看Job0的Stage1的Task个数

注意:如果存在shuffle过程,系统会自动进行缓存,UI界面显示skipped的部分
2、作业提交源码
1、以collect()为例来跟踪作业提交流程,按住 ctrl 点击 collect()
resRDD.collect().foreach(println)
2、此时进入 RDD 抽象类的 collect() 方法,可以看到,这里调用了sc的runJob方法,点击 runJob
/**
* Return an array that contains all of the elements in this RDD.
*
* @note This method should only be used if the resulting array is expected to be small, as
* all the data is loaded into the driver's memory.
*/
def collect(): Array[T] = withScope {
val results = sc.runJob(this, (iter: Iterator[T]) => iter.toArray)
Array.concat(results: _*)
}
3、此时进入里了 SparkContex的runJob方法,只是这里有调用了一个 runJob 方法,再次点击runJob
/**
* Run a job on all partitions in an RDD and return the results in an array.
*
* @param rdd target RDD to run tasks on
* @param func a function to run on each partition of the RDD
* @return in-memory collection with a result of the job (each collection element will contain
* a result from one partition)
*/
def runJob[T, U: ClassTag](rdd: RDD[T], func: Iterator[T] => U): Array[U] = {
runJob(rdd, func, 0 until rdd.partitions.length)
}
4、这里调用了SparkContext 的 runJob 方法。此时点击 这里的 runJob 方法
/**
* Run a function on a given set of partitions in an RDD and return the results as an array.
*
* @param rdd target RDD to run tasks on
* @param func a function to run on each partition of the RDD
* @param partitions set of partitions to run on; some jobs may not want to compute on all
* partitions of the target RDD, e.g. for operations like `first()`
* @return in-memory collection with a result of the job (each collection element will contain
* a result from one partition)
*/
def runJob[T, U: ClassTag](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: Iterator[T] => U,
partitions: Seq[Int]): Array[U] = {
val cleanedFunc = clean(func)
runJob(rdd, (ctx: TaskContext, it: Iterator[T]) => cleanedFunc(it), partitions)
}
5、又是一个 runJob在,继续点击
/**
* Run a function on a given set of partitions in an RDD and return the results as an array.
* The function that is run against each partition additionally takes `TaskContext` argument.
*
* @param rdd target RDD to run tasks on
* @param func a function to run on each partition of the RDD
* @param partitions set of partitions to run on; some jobs may not want to compute on all
* partitions of the target RDD, e.g. for operations like `first()`
* @return in-memory collection with a result of the job (each collection element will contain
* a result from one partition)
*/
def runJob[T, U: ClassTag](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U,
partitions: Seq[Int]): Array[U] = {
val results = new Array[U](partitions.size)
runJob[T, U](rdd, func, partitions, (index, res) => results(index) = res)
results
}
6、发现还是调用了SparkContext内部的一个 runJob,不过此时可以大概看出一点端倪,最后是调用了dagScheduler 的一个 runJob 方法,下面看下 dagScheduler 内部的 runJob 长什么样
/**
* Run a function on a given set of partitions in an RDD and pass the results to the given
* handler function. This is the main entry point for all actions in Spark.
*
* @param rdd target RDD to run tasks on
* @param func a function to run on each partition of the RDD
* @param partitions set of partitions to run on; some jobs may not want to compute on all
* partitions of the target RDD, e.g. for operations like `first()`
* @param resultHandler callback to pass each result to
*/
def runJob[T, U: ClassTag](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U,
partitions: Seq[Int],
resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit): Unit = {
if (stopped.get()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("SparkContext has been shutdown")
}
val callSite = getCallSite
val cleanedFunc = clean(func)
logInfo("Starting job: " + callSite.shortForm)
if (conf.getBoolean("spark.logLineage", false)) {
logInfo("RDD's recursive dependencies:\n" + rdd.toDebugString)
}
dagScheduler.runJob(rdd, cleanedFunc, partitions, callSite, resultHandler, localProperties.get)
progressBar.foreach(_.finishAll())
rdd.doCheckpoint()
}
7、下面是 DAGScheduler 调用的方法,此处重点可以关注下,作业提交 submitJob,val waiter = submitJob(rdd, func, partitions, callSite, resultHandler, properties)
/**
* Run an action job on the given RDD and pass all the results to the resultHandler function as
* they arrive.
*
* @param rdd target RDD to run tasks on
* @param func a function to run on each partition of the RDD
* @param partitions set of partitions to run on; some jobs may not want to compute on all
* partitions of the target RDD, e.g. for operations like first()
* @param callSite where in the user program this job was called
* @param resultHandler callback to pass each result to
* @param properties scheduler properties to attach to this job, e.g. fair scheduler pool name
*
* @note Throws `Exception` when the job fails
*/
def runJob[T, U](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U,
partitions: Seq[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit,
properties: Properties): Unit = {
val start = System.nanoTime
val waiter = submitJob(rdd, func, partitions, callSite, resultHandler, properties)
ThreadUtils.awaitReady(waiter.completionFuture, Duration.Inf)
waiter.completionFuture.value.get match {
case scala.util.Success(_) =>
logInfo("Job %d finished: %s, took %f s".format
(waiter.jobId, callSite.shortForm, (System.nanoTime - start) / 1e9))
case scala.util.Failure(exception) =>
logInfo("Job %d failed: %s, took %f s".format
(waiter.jobId, callSite.shortForm, (System.nanoTime - start) / 1e9))
// SPARK-8644: Include user stack trace in exceptions coming from DAGScheduler.
val callerStackTrace = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace.tail
exception.setStackTrace(exception.getStackTrace ++ callerStackTrace)
throw exception
}
}
8、作业提交逻辑:关注下 eventProcessLoop.post(JobSubmitted
def submitJob[T, U](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U,
partitions: Seq[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit,
properties: Properties): JobWaiter[U] = {
// Check to make sure we are not launching a task on a partition that does not exist.
val maxPartitions = rdd.partitions.length
partitions.find(p => p >= maxPartitions || p < 0).foreach { p =>
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Attempting to access a non-existent partition: " + p + ". " +
"Total number of partitions: " + maxPartitions)
}
val jobId = nextJobId.getAndIncrement()
if (partitions.isEmpty) {
val clonedProperties = Utils.cloneProperties(properties)
if (sc.getLocalProperty(SparkContext.SPARK_JOB_DESCRIPTION) == null) {
clonedProperties.setProperty(SparkContext.SPARK_JOB_DESCRIPTION, callSite.shortForm)
}
val time = clock.getTimeMillis()
listenerBus.post(
SparkListenerJobStart(jobId, time, Seq.empty, clonedProperties))
listenerBus.post(
SparkListenerJobEnd(jobId, time, JobSucceeded))
// Return immediately if the job is running 0 tasks
return new JobWaiter[U](this, jobId, 0, resultHandler)
}
assert(partitions.nonEmpty)
val func2 = func.asInstanceOf[(TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _]
val waiter = new JobWaiter[U](this, jobId, partitions.size, resultHandler)
eventProcessLoop.post(JobSubmitted(
jobId, rdd, func2, partitions.toArray, callSite, waiter,
Utils.cloneProperties(properties)))
waiter
}
9、提交作业到队列 eventQueue.put(event),查看 eventQueue 逻辑
/**
* Put the event into the event queue. The event thread will process it later.
*/
def post(event: E): Unit = {
if (!stopped.get) {
if (eventThread.isAlive) {
eventQueue.put(event)
} else {
onError(new IllegalStateException(s"$name has already been stopped accidentally."))
}
}
}
9、底层调用了 doOnReceive(event) 方法,但是这里是一个抽象类,查看其实现类,ctrl+H
private[scheduler] class DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop(dagScheduler: DAGScheduler)
extends EventLoop[DAGSchedulerEvent]("dag-scheduler-event-loop") with Logging {
private[this] val timer = dagScheduler.metricsSource.messageProcessingTimer
/**
* The main event loop of the DAG scheduler.
*/
override def onReceive(event: DAGSchedulerEvent): Unit = {
val timerContext = timer.time()
try {
doOnReceive(event)
} finally {
timerContext.stop()
}
}
复制 doOnReceive ,去实现类里查看实现逻辑
10、实现方法调用了 doOnReceive
/**
* The main event loop of the DAG scheduler.
*/
override def onReceive(event: DAGSchedulerEvent): Unit = {
val timerContext = timer.time()
try {
doOnReceive(event)
} finally {
timerContext.stop()
}
}
11、查看 doOnReceive 逻辑
private def doOnReceive(event: DAGSchedulerEvent): Unit = event match {
case JobSubmitted(jobId, rdd, func, partitions, callSite, listener, properties) =>
dagScheduler.handleJobSubmitted(jobId, rdd, func, partitions, callSite, listener, properties)
12、handleJobSubmitted 在内部创建了 ActiveJob,至此完成落叶提交流程
private[scheduler] def handleJobSubmitted(jobId: Int,
finalRDD: RDD[_],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _,
partitions: Array[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
listener: JobListener,
properties: Properties): Unit = {
var finalStage: ResultStage = null
try {
// New stage creation may throw an exception if, for example, jobs are run on a
// HadoopRDD whose underlying HDFS files have been deleted.
finalStage = createResultStage(finalRDD, func, partitions, jobId, callSite)
} catch {
case e: BarrierJobSlotsNumberCheckFailed =>
// If jobId doesn't exist in the map, Scala coverts its value null to 0: Int automatically.
val numCheckFailures = barrierJobIdToNumTasksCheckFailures.compute(jobId,
(_: Int, value: Int) => value + 1)
logWarning(s"Barrier stage in job $jobId requires ${e.requiredConcurrentTasks} slots, " +
s"but only ${e.maxConcurrentTasks} are available. " +
s"Will retry up to ${maxFailureNumTasksCheck - numCheckFailures + 1} more times")
if (numCheckFailures <= maxFailureNumTasksCheck) {
messageScheduler.schedule(
new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = eventProcessLoop.post(JobSubmitted(jobId, finalRDD, func,
partitions, callSite, listener, properties))
},
timeIntervalNumTasksCheck,
TimeUnit.SECONDS
)
return
} else {
// Job failed, clear internal data.
barrierJobIdToNumTasksCheckFailures.remove(jobId)
listener.jobFailed(e)
return
}
case e: Exception =>
logWarning("Creating new stage failed due to exception - job: " + jobId, e)
listener.jobFailed(e)
return
}
// Job submitted, clear internal data.
barrierJobIdToNumTasksCheckFailures.remove(jobId)
val job = new ActiveJob(jobId, finalStage, callSite, listener, properties)
clearCacheLocs()
logInfo("Got job %s (%s) with %d output partitions".format(
job.jobId, callSite.shortForm, partitions.length))
logInfo("Final stage: " + finalStage + " (" + finalStage.name + ")")
logInfo("Parents of final stage: " + finalStage.parents)
logInfo("Missing parents: " + getMissingParentStages(finalStage))
val jobSubmissionTime = clock.getTimeMillis()
jobIdToActiveJob(jobId) = job
activeJobs += job
finalStage.setActiveJob(job)
val stageIds = jobIdToStageIds(jobId).toArray
val stageInfos = stageIds.flatMap(id => stageIdToStage.get(id).map(_.latestInfo))
listenerBus.post(
SparkListenerJobStart(job.jobId, jobSubmissionTime, stageInfos, properties))
submitStage(finalStage)
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号