左值与右值
Lvalue:可以出现在 operator= 左边的
Rvalue:只能出现在operator= 右边的
int a = 1; int a = b; a = b; a = a + b; a + b = a; // error,a + b 是右值 string s1 = "hello"; string s2 = "world"; s1 + s2 = s1; // ok string() = "world" // ok
注意,虽然 string 等许多容器的临时对象可以被赋值,但编译器见到临时对象会认为它是右值!
int foo() { return 3; } ... int x = foo(); // ok int y = &foo(); // error foo() = 3; // error
简单地说,能取到地址的(在内存中,而不是在寄存器中)就是右值,其余都是左值。
Rvalue Reference 右值引用
当赋值操作的右边是右值(rvalue),左边的对象不需要特意分配内存去存放这个拷贝(copy),而可以搬移(move)右边对象的资源。
用于解决不必要的拷贝和实现完美转发(perfect forwarding)。
Move Semantics 移动语义
move 相当于 浅拷贝 + 打断原指针,原来的对象无法再使用。
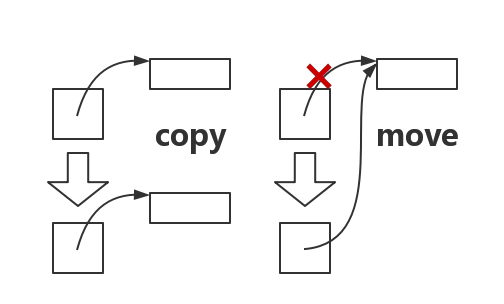
STL 许多地方使用到了右值引用和 move 语义,如 vector 中的 insert() 函数
iterator insert(const_iterator pos, const value_type& x); iterator insert(const_iterator pos, const value_type&& x) // 接受右值引用 { return emplace(pos, std::move(x)); } // 将左值变量放到std::move()中,就取得了它的右值引用
Perfect Forwading 完美转发
一个 Unperfect Forwarding 不完美转发的例子
1 void process(int& i) { 2 cout << "process(int&): " << i << endl; 3 } 4 5 void process(int&& i) { 6 cout << "process(int&&): " << i << endl; 7 } 8 9 void forward(int&& i) { 10 cout << "forward(int&&): " << i << ", "; 11 process(i); 12 } 13 14 int main() { 15 int a = 0; 16 process(a); // process(int&): 0 17 process(1); // process(int&&): 1 18 process(move(a)); // process(int&&): 0 19 forward(2); // forward(int&&): 2, process(int&): 2 20 // Rvalue经由forward()传给另一个函数却变为Lvalue 21 // 原因是传递过程中它变成了named object 22 forward(move(a)); // forward(int&&): 0, process(int&): 0 23 // forward(a); // error, cannot bind 'int' lvalue to 'int&&' 24 return 0; 25 }
这时需要使用 std::forward<T>(),保留参数的左/右值特性。
void forward(int&& i) { cout << "forward(int&&): " << i << ", "; process(std::forward<int>(i)); } int main() { int a = 0; forward(2); // forward(int&&): 2, process(int&&): 2 forward(move(a)); // forward(int&&): 0, process(int&&): 0 return 0; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号