数据挖掘实战:信用卡违约率分析
【项目目标】
这个数据集是台湾某银行 2005 年 4 月到 9 月的信用卡数据,数据集一共包括 25 个字段,现在我们的目标是要采用随机森林算法,针对这个数据集构建一个分析信用卡违约率的分类器。
【项目过程】
1.数据获取
2.数据探索、数据规范化、数据集划分
3.模型创建、模型训练、模型评估
【项目实现】
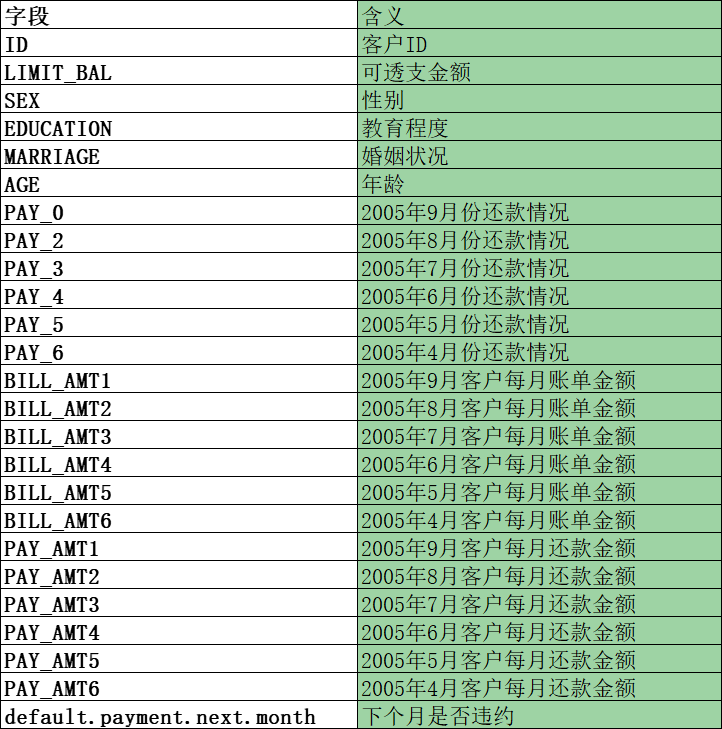
每个字段的含义如下:
1.导库
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
2.导入数据、探索数据
data = pd.read_csv("./UCI_Credit_Card.csv") data.shape
(30000, 25)
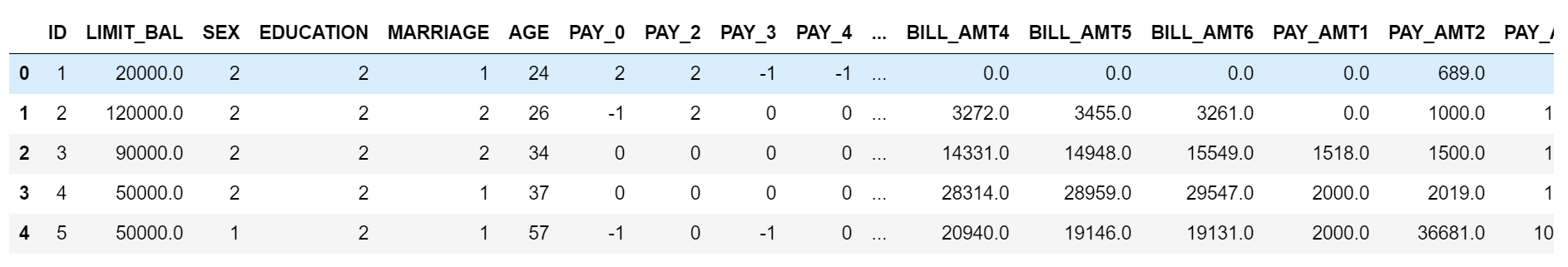
data.head()
data.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> RangeIndex: 30000 entries, 0 to 29999 Data columns (total 25 columns): # Column Non-Null Count Dtype --- ------ -------------- ----- 0 ID 30000 non-null int64 1 LIMIT_BAL 30000 non-null float64 2 SEX 30000 non-null int64 3 EDUCATION 30000 non-null int64 4 MARRIAGE 30000 non-null int64 5 AGE 30000 non-null int64 6 PAY_0 30000 non-null int64 7 PAY_2 30000 non-null int64 8 PAY_3 30000 non-null int64 9 PAY_4 30000 non-null int64 10 PAY_5 30000 non-null int64 11 PAY_6 30000 non-null int64 12 BILL_AMT1 30000 non-null float64 13 BILL_AMT2 30000 non-null float64 14 BILL_AMT3 30000 non-null float64 15 BILL_AMT4 30000 non-null float64 16 BILL_AMT5 30000 non-null float64 17 BILL_AMT6 30000 non-null float64 18 PAY_AMT1 30000 non-null float64 19 PAY_AMT2 30000 non-null float64 20 PAY_AMT3 30000 non-null float64 21 PAY_AMT4 30000 non-null float64 22 PAY_AMT5 30000 non-null float64 23 PAY_AMT6 30000 non-null float64 24 default.payment.next.month 30000 non-null int64 dtypes: float64(13), int64(12) memory usage: 5.7 MB
通过data.info()发现数据很完整,没有缺失值,不需要进行缺失值的处理
分析数据特征的类型可以发现,数据分为分类型变量和数值型变量,其中 SEX/EDUCATION/MARRIAGE 为分类型变量,其中 SEX 为无序数据,应该采用 OneHotEncoder 编码
看一下标签的分类情况
data["default.payment.next.month"].value_counts()
0 23364 1 6636 Name: default.payment.next.month, dtype: int64
df = pd.DataFrame({'default.payment.next.month': next_month.index,'values': next_month.values})
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.figure()
plt.bar(["0","1"],df["values"],)
plt.title('信用卡违约率客户\n (违约:1,守约:0)')
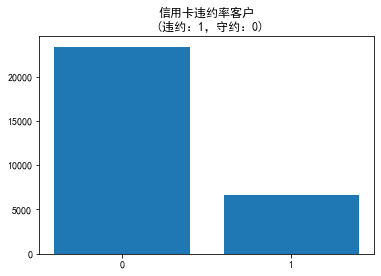
可以看到,不存在严重的样本不均衡问题
接下来对 SEX 进行独热编码
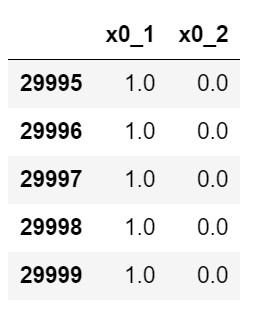
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder ohe = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False) ohe.fit(data["SEX"].values.reshape(-1, 1)) SEX_df = pd.DataFrame(ohe.transform(data["SEX"].values.reshape(-1, 1)), columns=ohe.get_feature_names()) SEX_df.tail()
删除无用字段 SEX ID
data.drop(["SEX","ID"], inplace=True, axis=1)
# 分类型变量 data_cv = pd.concat([data.iloc[:,[1,2]],SEX_df],axis=1) data_cv
# 数值型变量 data_mv = pd.concat([data["LIMIT_BAL"],data.iloc[:,3:22]],axis=1) data_mv
# 数值型变量归一化 ss = StandardScaler() data_mv_std = ss.fit_transform(data_mv) data_mv_std_df = pd.DataFrame(data_mv_std) data_mv_std_df
# 划分特征与标签 features = pd.concat([data_mv_std_df,data_cv],axis=1) target = data.iloc[:,-1]
使用GridSearchCV对随机森林分类器进行超参数选择
rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_jobs=-1,max_features= 'sqrt' ,n_estimators=50, oob_score = True) param_grid = { 'n_estimators': [50,200], 'max_features': ['auto', 'sqrt', 'log2'] } CV_rfc = GridSearchCV(estimator=rfc, param_grid=param_grid, cv= 5) CV_rfc.fit(features, target) CV_rfc.best_params_
{'max_features': 'log2', 'n_estimators': 200}
CV_rfc.best_score_
0.8164




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号