AgentScope深入分析-LLM&MCP
能力之源:模型、MCP 与工具系统核心解析
请关注公众号【碳硅化合物AI】
摘要
智能体需要与外部世界交互,这离不开模型、工具和 MCP(Model Context Protocol)的支持。AgentScope 通过统一的接口设计,让智能体能够无缝使用不同的模型提供商、执行各种工具函数,以及集成 MCP 服务。本文将深入分析 ChatModelBase 的模型无关设计、Toolkit 的工具管理机制,以及 MCP 协议的集成方式。通过阅读本文,你会理解框架如何实现"一次编程,适配所有模型",工具如何被注册和执行,以及 MCP 如何扩展智能体的能力边界。
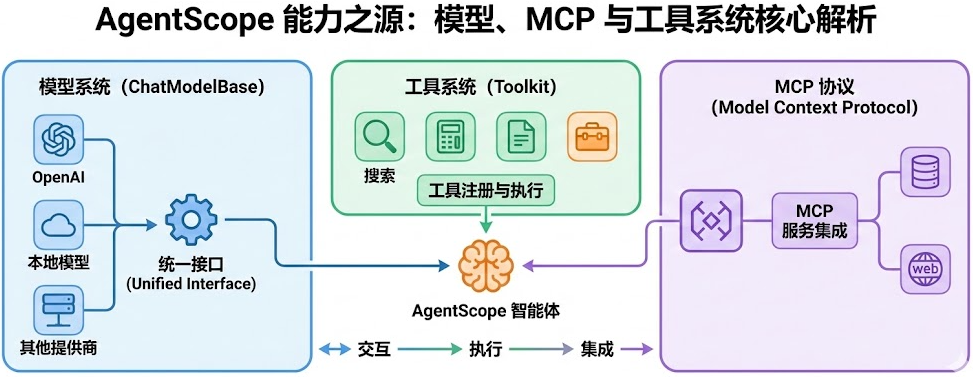
入口类与类关系
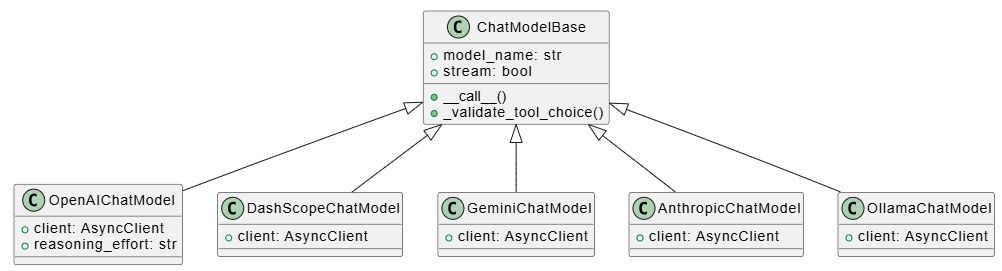
模型系统的类层次
AgentScope 通过 ChatModelBase 抽象接口实现了模型无关设计:
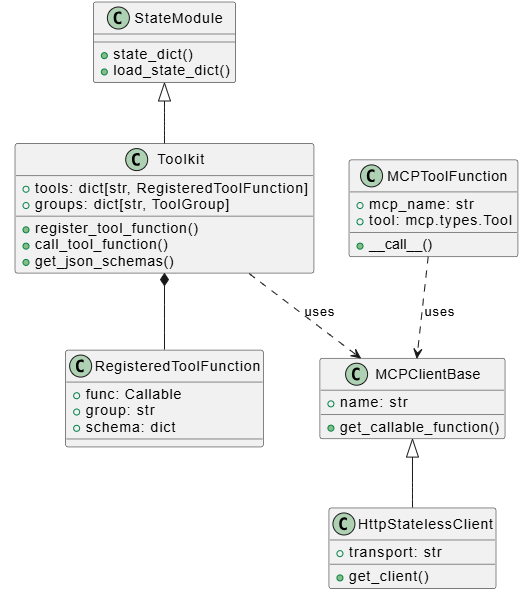
工具系统的类层次
工具系统由 Toolkit 统一管理:
关键代码:ChatModelBase 接口
让我们看看模型基类是如何定义的:
class ChatModelBase:
"""Base class for chat models."""
model_name: str
"""The model name"""
stream: bool
"""Is the model output streaming or not"""
def __init__(
self,
model_name: str,
stream: bool,
) -> None:
"""Initialize the chat model base class."""
self.model_name = model_name
self.stream = stream
@abstractmethod
async def __call__(
self,
*args: Any,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> ChatResponse | AsyncGenerator[ChatResponse, None]:
pass
def _validate_tool_choice(
self,
tool_choice: str,
tools: list[dict] | None,
) -> None:
"""Validate tool_choice parameter."""
# 验证工具选择参数的有效性
# ...
这个接口非常简洁,只定义了核心方法。所有模型提供商都实现这个接口,这样智能体就可以无缝切换不同的模型。
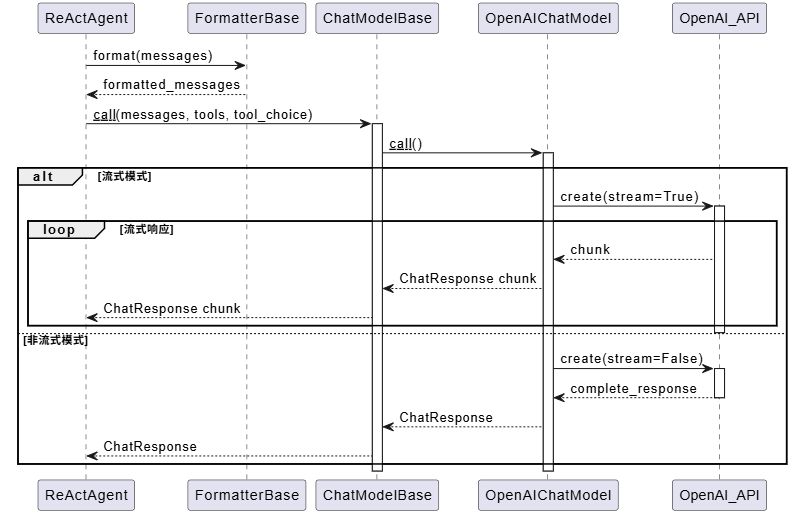
关键流程分析
模型调用流程
模型调用的流程相对直接,但支持流式和非流式两种模式:
工具执行流程
工具执行是 ReAct 模式中的关键环节:
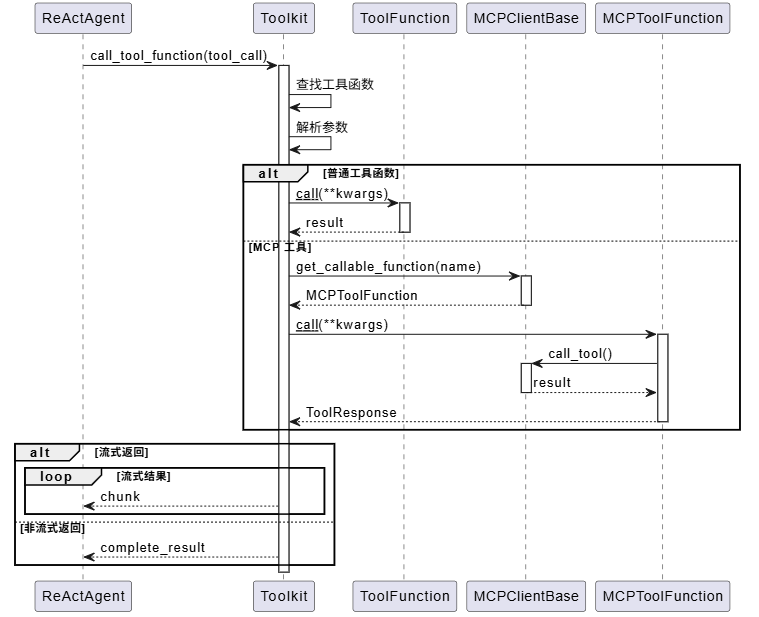
MCP 工具调用流程
MCP 协议的集成让 AgentScope 可以使用外部服务:
关键技术点
1. 模型无关设计的实现
这是 AgentScope 的一个核心设计理念。通过 ChatModelBase 抽象接口,所有模型提供商都实现相同的接口:
@abstractmethod
async def __call__(
self,
*args: Any,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> ChatResponse | AsyncGenerator[ChatResponse, None]:
pass
这样,当你写代码时:
# 可以轻松切换模型
model = DashScopeChatModel(...) # 或 OpenAIChatModel、GeminiChatModel 等
agent = ReActAgent(model=model, ...)
智能体的其他代码完全不需要改变。这种设计让框架具有极强的灵活性。
2. 异步调用和流式处理
AgentScope 1.0 完全拥抱异步编程。模型调用、工具执行都支持异步和流式:
# 流式调用模型
async for chunk in model(messages):
# 处理每个 chunk
print(chunk.content)
# 流式执行工具
async for chunk in toolkit.call_tool_function(tool_call):
# 处理工具执行结果
print(chunk.content)
这种设计让框架能够:
- 实时显示生成内容(流式输出)
- 高效处理并发请求
- 支持长时间运行的工具
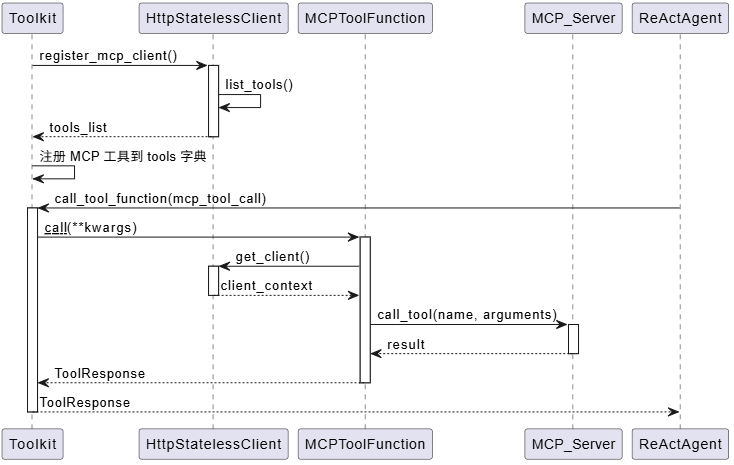
3. MCP 协议的集成
MCP(Model Context Protocol)是一个标准协议,让智能体能够使用外部服务。AgentScope 通过 MCPClientBase 抽象接口支持 MCP:
async def get_callable_function(
self,
func_name: str,
wrap_tool_result: bool = True,
) -> Callable:
"""Get a tool function by its name."""
if self._tools is None:
await self.list_tools()
target_tool = None
for tool in self._tools:
if tool.name == func_name:
target_tool = tool
break
if target_tool is None:
raise ValueError(f"Tool '{func_name}' not found in the MCP server")
return MCPToolFunction(
mcp_name=self.name,
tool=target_tool,
wrap_tool_result=wrap_tool_result,
client_gen=self.get_client,
)
这个设计非常巧妙:
- 无状态客户端:每次工具调用都创建新的会话,避免状态污染
- 统一接口:MCP 工具和普通工具使用相同的接口
- 细粒度控制:可以获取单个工具函数,也可以批量注册
4. 工具的执行和结果处理
Toolkit 的工具执行机制支持多种场景:
async def call_tool_function(
self,
tool_call: ToolUseBlock,
) -> AsyncGenerator[ToolResponse, None]:
"""Execute the tool function by the ToolUseBlock."""
# 检查工具是否存在
if tool_call["name"] not in self.tools:
return _object_wrapper(
ToolResponse(content=[TextBlock(...)]),
None,
)
# 获取工具函数
tool_func = self.tools[tool_call["name"]]
# 检查工具组是否激活
if (
tool_func.group != "basic"
and not self.groups[tool_func.group].active
):
return _object_wrapper(
ToolResponse(content=[TextBlock(...)]),
None,
)
# 准备参数并执行
# ...
工具执行支持:
- 同步/异步工具:自动包装同步工具为异步
- 流式/非流式返回:统一返回
AsyncGenerator[ToolResponse, None] - 错误处理:自动捕获异常并返回错误信息
- 工具分组:支持按组激活/停用工具
总结
模型、MCP 和工具系统是 AgentScope 框架中让智能体具备"能力"的三个核心系统:
- 模型系统:通过统一的接口实现模型无关,让智能体可以无缝切换不同的模型提供商
- 工具系统:通过 Toolkit 统一管理工具,支持分组、流式执行、错误处理等高级特性
- MCP 系统:通过标准协议集成外部服务,扩展智能体的能力边界
这三个系统的设计都体现了 AgentScope 的核心理念:模块化、透明、可扩展。在下一篇文章中,我们会分析 Pipeline 和消息系统的实现,这些组件负责多智能体的协调和通信。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号