mybatis源码分析——配置文件的解析
mybatis是一种半自动的orm对象关系模型框架,介于hibenate与jdbc之间,优势就是使用更加灵活,支持程序员手写sql
hibernate是自动生成的框架,不够灵活,jdbc完全手写,开发效率比较低,而mybatis在jdbc的基础上做了封装。
1:mybatis的简单使用
mysql数据库创建user表,字段name age
导入依赖maven
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.3.1</version>
</dependency>
mybatis-config.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 引入外部资源文件
resource:默认引入classpath路径下的资源文件
url:引入物理路径下的资源文件(如:d:\\jdbc.properties)
-->
<properties resource="application.properties"></properties>
<!-- 设置参数 -->
<settings>
<!-- 开启驼峰匹配:完成经典的数据库命名到java属性的映射
相当于去掉数据中的名字的下划线,和java进行匹配
-->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
<!-- 配置别名 -->
<typeAliases>
<!-- typeAlias:用来配置别名,方便映射文件使用,type:类的全限定类名,alias:别名 -->
<typeAlias type="com.example.mybatis.model.User" alias="User"/>
</typeAliases>
<!--<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.example.mybatis.plugin.MyFirstPlugin">
<property name="someProperty" value="100"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>-->
<!-- 配置环境:可以配置多个环境,default:配置某一个环境的唯一标识,表示默认使用哪个环境 -->
<environments default="development">
<!-- 配置环境,id:环境的唯一标识 -->
<environment id="development">
<!-- 事务管理器,type:使用jdbc的事务管理器 -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<!-- 数据源,type:池类型的数据源 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- 配置连接信息 -->
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 配置映射文件:用来配置sql语句和结果集类型等 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="UserMapper.xml" />
</mappers>
</configuration>
userMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//ibatis.apache.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://ibatis.apache.org/dtd/ibatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper">
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.example.mybatis.model.User">
insert into user (name,age) value(#{name},#{age})
</insert>
<select id="listUsers" resultType="com.example.mybatis.model.User">
select * from user where name = #{name}
</select>
</mapper>
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
// 解析全局配置文件mybatis-config.xml
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = builder.build(reader);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> list = userMapper.listUsers("hello105");
System.out.println(list);
}
运行结果:
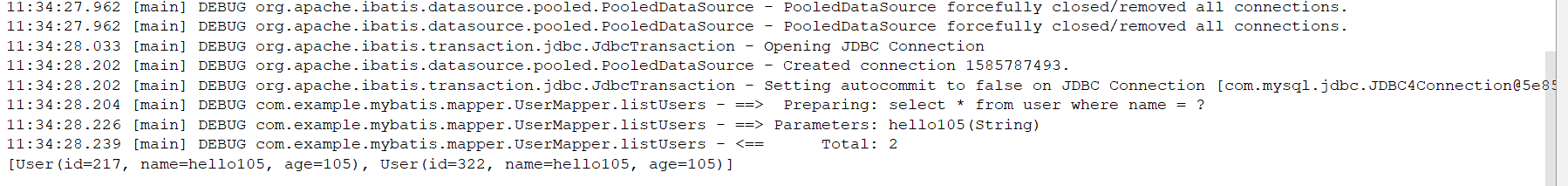
2:源码解析
将xml文件读入内存,生成Reader对象
// 将mybatis-config的配置文件读入内存,生成字符流对象
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
将字节流转换为字符流,并返回
public static Reader getResourceAsReader(String resource) throws IOException {
Reader reader;
if (charset == null) {
reader = new InputStreamReader(getResourceAsStream(resource));
} else {
reader = new InputStreamReader(getResourceAsStream(resource), charset);
}
return reader;
}
解析xml文件,生成sqlSessionFactory对象,这里是比较的一步
// 解析全局配置文件mybatis-config.xml
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = builder.build(reader);
看一下build方法
// 解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
build方法里面首先是生成一个解析器XmlConfigBuilder,然后解析parse,最后封装build,解析的主要工作毋庸置疑是放在
parse方法中完成的,下面我们来看一下解析动作
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
// 解析mybatis-config配置文件
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
首先会判断是否已经解析过,如果已经解析过,那么抛出异常,提示"每一个XMLConfigBuilder只能被解析一次"
如果之前没有被解析,那么开始解析工作,在parseConfiguration中完成,将解析后的数据封装到configuration对象中,
然后返回,现在我们来看一下parseConfiguration方法
xml中 /configuration节点作为入参传入:
// 解析mybatis-config配置文件
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
Properties settings = settingsAsPropertiess(root.evalNode("settings"));
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectionFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectionFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
// 解析环境 下的数据源信息
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
// 解析mapper.xml文件
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
这里可以对照着mybatis-config.xml文件一起看,比较直观,因为这个方法就是解析这个xml文件,然后将解析的结果封装到configuration对象中
首先是解析properties节点,解析node上的resource属性,然后把解析的结果放到defaults这个集合中,最后设置到configuration对象上
private void propertiesElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
Properties defaults = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 获取Node节点上的resource属性
String resource = context.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = context.getStringAttribute("url");
if (resource != null && url != null) {
throw new BuilderException("The properties element cannot specify both a URL and a resource based property file reference. Please specify one or the other.");
}
if (resource != null) {
// 解析resource属性,并把解析的属性放到defaults里面
defaults.putAll(Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource));
} else if (url != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url));
}
Properties vars = configuration.getVariables();
if (vars != null) {
defaults.putAll(vars);
}
parser.setVariables(defaults);
// 将defaults属性设置到configuration对象中
configuration.setVariables(defaults);
}
}
看一下解析数据源:
// 解析环境 下的数据源信息
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
if (environment == null) {
environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");
}
for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) {
String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");
if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) {
TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id)
.transactionFactory(txFactory)
.dataSource(dataSource);
configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
}
}
}
}
dataSourceElement方法将DataSource节点作为入参传入,将properties属性全部封装到 DataSourceFactory对象上,然后从数据源工厂中拿到数据源,设置到configuration对象
上
最重要的还是解析mapper.xml
// 解析mapper.xml文件
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
如果resource不为null,url为null,则进入这个方法的解析
mapperParser.parse();
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 解析sql,生成mapperStatement
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 解析命名空间,绑定代理工厂
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingChacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
下面看一下解析sql,生成mapperStatement的过程,方法
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"))
// 解析mapper.xml 里面的子元素
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
解析mapper元素中子元素,sql元素、cache元素、resultMap元素,
select|insert|update|delete等元素
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? new Jdbc3KeyGenerator() : new NoKeyGenerator();
}
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
解析select insert delete update语句,将解析后的属性传给addMappedStatement方法,
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id,
SqlSource sqlSource,
StatementType statementType,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,
Integer fetchSize,
Integer timeout,
String parameterMap,
Class<?> parameterType,
String resultMap,
Class<?> resultType,
ResultSetType resultSetType,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
boolean resultOrdered,
KeyGenerator keyGenerator,
String keyProperty,
String keyColumn,
String databaseId,
LanguageDriver lang,
String resultSets) {
if (unresolvedCacheRef) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
}
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType)
.resource(resource)
.fetchSize(fetchSize)
.timeout(timeout)
.statementType(statementType)
.keyGenerator(keyGenerator)
.keyProperty(keyProperty)
.keyColumn(keyColumn)
.databaseId(databaseId)
.lang(lang)
.resultOrdered(resultOrdered)
.resulSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id))
.resultSetType(resultSetType)
.flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect))
.cache(currentCache);
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}
将属性封装到MappedStatement对象上,然后将对象缓存到configuration中
再回过头来解析一下命名空间
// 解析命名空间,绑定代理工厂
bindMapperForNamespace();
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//ignore, bound type is not required
}
if (boundType != null) {
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag
// to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface
// look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
}
mapper.xml对应的命名空间就是mapper.java 的全路径名
<mapper namespace="com.example.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper">
判断configuration对象中是否包含这个类型,如果没有则放入configuration中
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
mapperRegistry.addMapper(type);
}
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
将类型与通过类型创建的代理工厂放入mappers缓存中。
3:重点类分析
Configuration类:
这里面最重要的类就是Configuration,它对应mybatis-config.xml文件,将xml文件解析的内容缓存到Configuration对象中
MapperRegistry注册mappper用的,将命名空间与对应的代理工厂注册到这里

缓存解析的Statement语句,key为sqlId的全路径名称,value为封装这个sql属性信息的对象

XMLConfigBuilder类: 用来解析mybatis-config.xml文件
XMLMapperBuilder类:用来解析Mapper.xml文件
总结:
1:类加载器读取mybatis-config.xml文件为字节流InputStream,然后将InputStream转换为字符流Reader
2:sqlSessionFactoryBuilder将解析Reader的工作委托给XMLConfigBuilder类处理
3:XMLConfigBuilder类又将解析mapper.xml的工作委托给XMLMapperBuilder类处理
4:XMLMapperBuilder类解析mapper.xml,sql、insert、update、select等元素,将解析后的数据封装到MapperStatement对象中,然后注册到MapperRegistry中
MapperRegistry是Configuration的属性,解析命名空间,将命名空间与Class对应的MapperProxyFactory映射缓存到mapperStatementMaps缓存中,以被后面使用,所以
所有的解析工作完成后,Configuration对象包含所有的mybatis-config.xml数据
SqlSessionFactory 用维护了Configuration对象
对应关系:
硬盘 内存对象
mybatis-config.xml Configuration
mapper.xml sql属性 mappedStatements
mapper.xml 命名空间 mapperRegistry
这一节的mybatis文件的解析就到这里了,下一节看mybatis的数据绑定


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号