0121_组合模式(Composite)
组合模式(Composite)
意图
将对象组合成树形结构以表示"部分-整体"的层次结构。组合模式使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
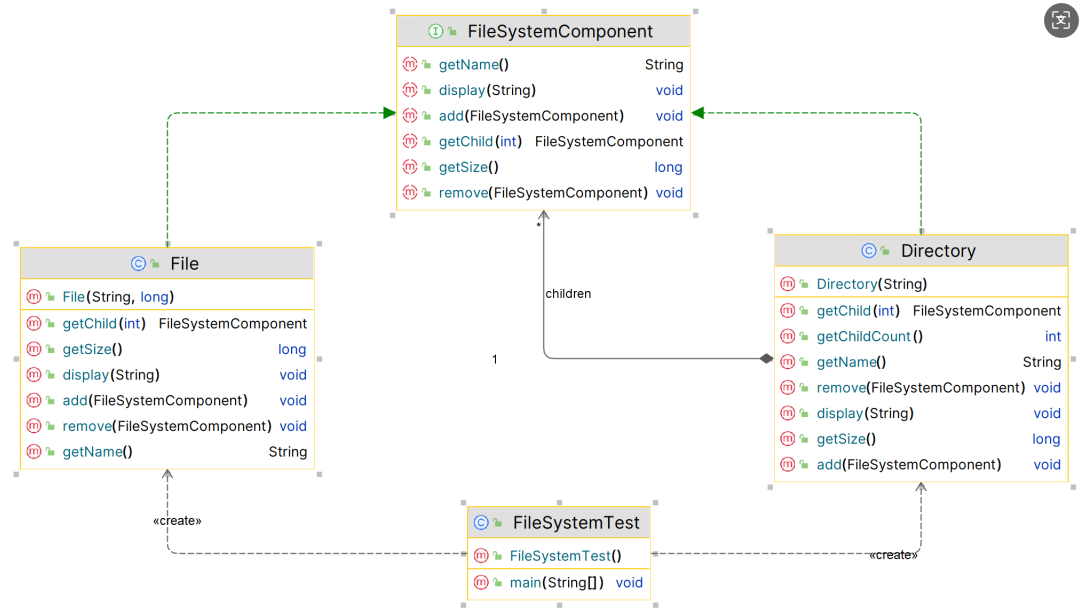
UML 图
优点
- 简化客户端代码:客户端可以一致地处理单个对象和组合对象,无需区分
- 易于扩展:可以很容易地增加新的组件类型
- 灵活的层次结构:可以构建复杂的树形结构,表示复杂的部分-整体层次
- 符合开闭原则:新增组件类型时不需要修改现有代码
- 统一处理:统一了叶子对象和容器对象的处理方式
缺点
- 设计较复杂:需要定义较多的类和接口,增加了系统的复杂性
- 类型检查困难:在运行时很难限制组合中的组件类型
- 可能违反接口隔离原则:叶子节点可能被迫实现不需要的方法
- 性能考虑:对于大型层次结构,遍历操作可能比较耗时
代码示例
以文件系统为例,文件系统包含文件和文件夹,文件夹又可以包含文件或其他文件夹:
1. 组件接口 (Component Interface)
// 文件系统组件接口
public interface FileSystemComponent {
void display(String indent);
void add(FileSystemComponent component);
void remove(FileSystemComponent component);
FileSystemComponent getChild(int index);
String getName();
long getSize();
}
2. 叶子组件 (Leaf Component)
// 文件类 - 叶子节点
public class File implements FileSystemComponent {
private String name;
private long size;
public File(String name, long size) {
this.name = name;
this.size = size;
}
@Override
public void display(String indent) {
System.out.println(indent + "📄 " + name + " (" + size + " bytes)");
}
@Override
public void add(FileSystemComponent component) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Cannot add to a file");
}
@Override
public void remove(FileSystemComponent component) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Cannot remove from a file");
}
@Override
public FileSystemComponent getChild(int index) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("File has no children");
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public long getSize() {
return size;
}
}
3. 复合组件 (Composite Component)
// 文件夹类 - 复合节点
public class Directory implements FileSystemComponent {
private String name;
private List<FileSystemComponent> children;
public Directory(String name) {
this.name = name;
this.children = new ArrayList<>();
}
@Override
public void display(String indent) {
System.out.println(indent + "📁 " + name + " (" + getSize() + " bytes)");
for (FileSystemComponent child : children) {
child.display(indent + " ");
}
}
@Override
public void add(FileSystemComponent component) {
children.add(component);
}
@Override
public void remove(FileSystemComponent component) {
children.remove(component);
}
@Override
public FileSystemComponent getChild(int index) {
return children.get(index);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public long getSize() {
long totalSize = 0;
for (FileSystemComponent child : children) {
totalSize += child.getSize();
}
return totalSize;
}
public int getChildCount() {
return children.size();
}
}
4. 客户端代码 (Client Code)
public class FileSystemTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建文件
FileSystemComponent file1 = new File("document.txt", 1024);
FileSystemComponent file2 = new File("image.jpg", 2048);
FileSystemComponent file3 = new File("video.mp4", 4096);
FileSystemComponent file4 = new File("readme.md", 512);
// 创建文件夹
Directory documents = new Directory("Documents");
Directory images = new Directory("Images");
Directory videos = new Directory("Videos");
Directory root = new Directory("Root");
// 构建层次结构
documents.add(file1);
documents.add(file4);
images.add(file2);
videos.add(file3);
root.add(documents);
root.add(images);
root.add(videos);
// 显示整个文件系统
System.out.println("文件系统结构:");
root.display("");
// 统计信息
System.out.println("\n统计信息:");
System.out.println("根目录大小: " + root.getSize() + " bytes");
System.out.println("根目录包含 " + root.getChildCount() + " 个子项");
System.out.println("文档文件夹包含 " + documents.getChildCount() + " 个文件");
}
}
在Java标准库中的应用
组合模式在Java标准库和框架中有广泛应用:
-
Swing/AWT组件
// Container可以包含其他Component,形成树形结构 JFrame frame = new JFrame(); JPanel panel = new JPanel(); JButton button = new JButton("Click me"); panel.add(button); // 面板包含按钮 frame.add(panel); // 框架包含面板 -
Java集合框架
// 虽然不完全符合组合模式,但体现了类似的思想 List<List<String>> nestedList = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> innerList = new ArrayList<>(); innerList.add("item1"); innerList.add("item2"); nestedList.add(innerList); -
XML解析
// DOM解析中的节点层次结构 Document document = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance().newDocumentBuilder().parse(file); Element rootElement = document.getDocumentElement(); NodeList children = rootElement.getChildNodes(); -
Java NIO.2文件系统
// Path和FileSystem的层次结构 Path path = Paths.get("/home/user/documents"); try (DirectoryStream<Path> stream = Files.newDirectoryStream(path)) { for (Path entry : stream) { if (Files.isDirectory(entry)) { System.out.println("目录: " + entry.getFileName()); } else { System.out.println("文件: " + entry.getFileName()); } } }
总结
组合模式通过将对象组织成树形结构,使得客户端可以统一处理单个对象和对象组合。这种模式特别适合于表示部分-整体层次结构,如文件系统、GUI组件树、组织结构等。组合模式的核心思想是通过统一的接口来隐藏单个对象和组合对象的差异,从而简化客户端的代码。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号