0118_装饰器模式(Decorator)
装饰器模式(Decorator)
意图
动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。就增加功能来说,装饰器模式相比生成子类更为灵活。
UML 图
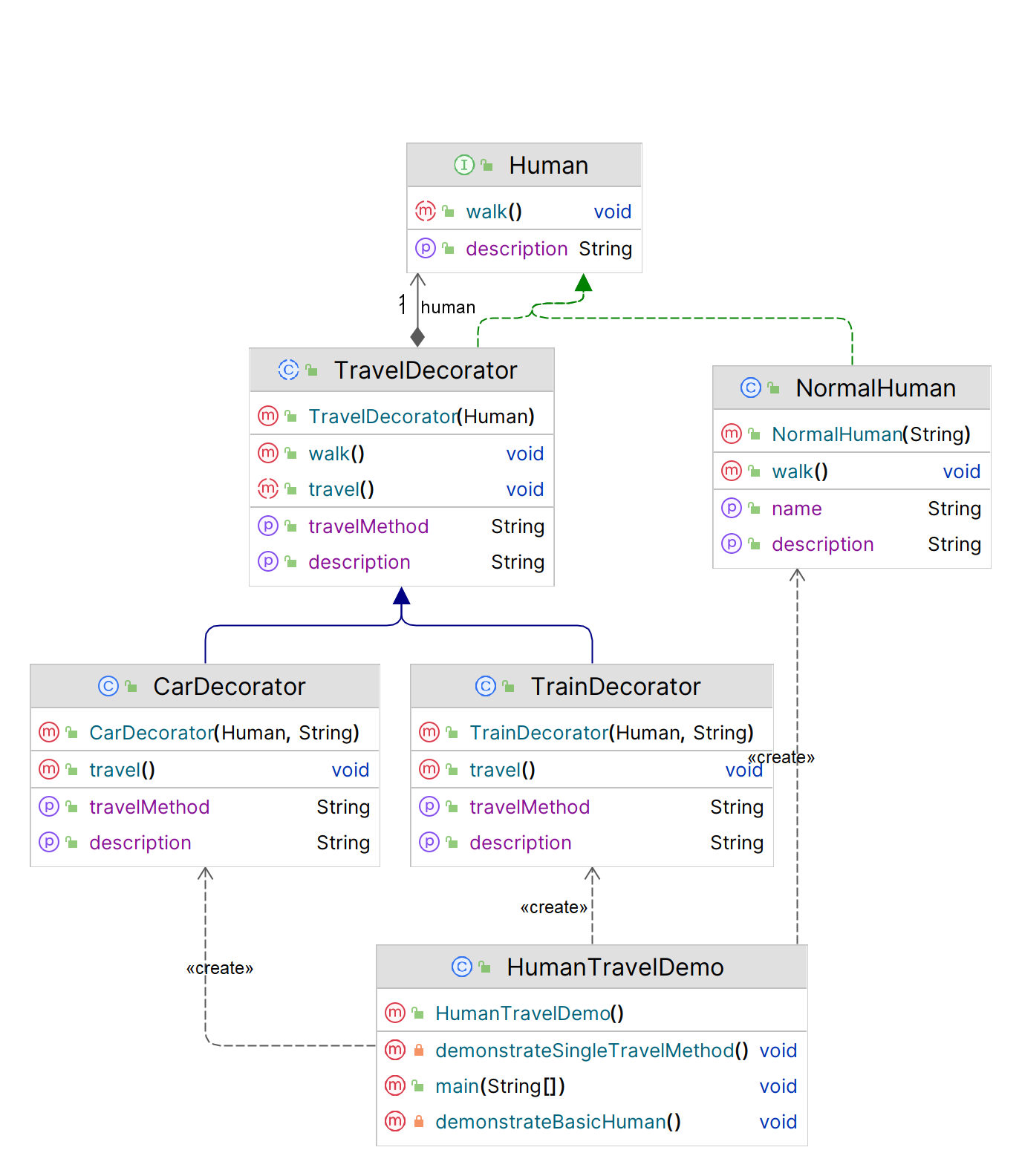
优点
- 灵活性高:比继承更灵活,可以在运行时动态地添加或撤销功能
- 避免类爆炸:通过组合而非继承来扩展功能,避免了子类数量过多的问题
- 符合开闭原则:可以在不修改现有代码的情况下添加新的装饰器
- 可以嵌套使用:多个装饰器可以嵌套使用,实现功能的组合
- 保持接口一致性:装饰器和被装饰对象实现相同的接口,对客户端透明
缺点
- 增加系统复杂性:会增加许多小类,使系统变得复杂
- 排查困难:由于装饰器可以多层嵌套,调试时可能比较困难
- 设计难度:需要正确设计装饰器的层次结构,否则可能导致系统混乱
- 顺序依赖性:装饰器的顺序可能影响最终的行为
代码示例
人类默认出行方式为走路,为了提高人类的出行速度,可以为人类动态添加坐汽车、火车等出行方式。下面为具体的实例:
1. 组件接口 (Component Interface)
// 人类接口
public interface Human {
/**
* 走路方法
*/
void walk();
/**
* 获取描述
*/
String getDescription();
}
2. 具体组件 (Concrete Component)
// 正常人类实现
public class NormalHuman implements Human {
/**
* 人类的姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 构造方法,初始化人类姓名
* @param name 姓名
*/
public NormalHuman(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 实现走路方法,输出走路信息
*/
@Override
public void walk() {
System.out.println(name + "正在走路");
}
/**
* 获取人类描述信息
* @return 返回人类姓名作为描述
*/
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return name;
}
/**
* 获取人类姓名
* @return 返回人类姓名
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
3. 装饰器抽象类 (Decorator Abstract Class)
// 出行装饰器抽象类
public abstract class TravelDecorator implements Human {
protected Human human;
public TravelDecorator(Human human) {
this.human = human;
}
@Override
public void walk() {
human.walk();
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return human.getDescription();
}
/**
* 出行方法 - 装饰器新增的方法
*/
public abstract void travel();
/**
* 获取出行方式描述
*/
public abstract String getTravelMethod();
}
4. 具体装饰器 (Concrete Decorators)
// 汽车出行装饰器
public class CarDecorator extends TravelDecorator {
private String carModel;
public CarDecorator(Human human, String carModel) {
super(human);
this.carModel = carModel;
}
@Override
public void travel() {
System.out.println(getDescription() + "正在乘坐" + carModel + "汽车出行");
}
@Override
public String getTravelMethod() {
return "汽车(" + carModel + ")";
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return human.getDescription() + "[可乘坐汽车]";
}
}
// 火车出行装饰器
public class TrainDecorator extends TravelDecorator {
private String trainType;
public TrainDecorator(Human human, String trainType) {
super(human);
this.trainType = trainType;
}
@Override
public void travel() {
System.out.println(getDescription() + "正在乘坐" + trainType + "火车出行");
}
@Override
public String getTravelMethod() {
return "火车(" + trainType + ")";
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return human.getDescription() + "[可乘坐火车]";
}
}
5. 客户端代码 (Client Code)
public class HumanTravelDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("=== 人类出行方式装饰器模式演示 ===\n");
// 演示基础人类能力
demonstrateBasicHuman();
// 演示单种出行方式的装饰
demonstrateSingleTravelMethod();
}
/**
* 演示基础人类能力
* 展示未经过任何装饰的普通人类
*/
private static void demonstrateBasicHuman() {
System.out.println("1. 基础人类能力:");
Human person = new NormalHuman("张三");
person.walk(); // 基础走路能力
System.out.println("描述: " + person.getDescription());
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 演示单种出行方式
* 展示通过装饰器为人类添加单一出行方式的能力
*/
private static void demonstrateSingleTravelMethod() {
System.out.println("2. 单种出行方式:");
Human person = new NormalHuman("李四");
// 添加汽车出行能力
TravelDecorator carPerson = new CarDecorator(person, "宝马X5");
carPerson.walk(); // 仍然可以走路
carPerson.travel(); // 新增的出行能力
System.out.println("出行方式: " + carPerson.getTravelMethod());
System.out.println("描述: " + carPerson.getDescription());
System.out.println();
// 添加火车出行能力
TravelDecorator trainPerson = new TrainDecorator(person, "高铁");
trainPerson.walk(); // 仍然可以走路
trainPerson.travel(); // 新增的出行能力
System.out.println("出行方式: " + trainPerson.getTravelMethod());
System.out.println("描述: " + trainPerson.getDescription());
System.out.println();
}
}
在Java标准库中的应用
装饰器模式在Java标准库中有很多应用:
-
Java IO流体系
// 基础组件 FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("file.txt"); // 装饰器:添加缓冲功能 BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream); // 装饰器:添加数据读取功能 DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(bufferedInputStream); -
Java集合框架
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); // 装饰器:添加同步功能 List<String> synchronizedList = Collections.synchronizedList(list); // 装饰器:添加不可修改功能 List<String> unmodifiableList = Collections.unmodifiableList(list); -
Java Servlet
// HttpServletResponseWrapper是装饰器模式的典型应用 public class CompressionResponseWrapper extends HttpServletResponseWrapper { private GZIPOutputStream gzipOutputStream; public CompressionResponseWrapper(HttpServletResponse response) { super(response); } @Override public ServletOutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException { if (gzipOutputStream == null) { gzipOutputStream = new GZIPOutputStream(response.getOutputStream()); } return new FilterServletOutputStream(gzipOutputStream); } }
总结
装饰器模式通过组合而非继承的方式,动态地为对象添加额外的职责。它提供了一种灵活的替代方案来扩展对象的功能,避免了使用继承导致的类爆炸问题。装饰器模式保持了接口的一致性,对客户端透明,同时支持功能的组合和嵌套使用。
该模式特别适用于以下场景:
- 需要在不影响其他对象的情况下,动态、透明地添加职责
- 需要撤销的功能
- 通过继承扩展功能不切实际(如需要大量子类)
在Java标准库中,IO流体系是装饰器模式的经典实现,通过层层装饰可以为基本的IO功能添加缓冲、数据转换等附加功能。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号