Java 实践:生产者与消费者
实践项目:生产者与消费者【经典多线程问题】
问题引出:
生产者和消费者指的是两个不同的线程类对象,操作同一个空间资源的情况。
需求引出:
—— 生产者负责生产数据,消费者负责取走数据
—— 生产者生产完一组数据之后,消费者就要取走一组数据
设置三个类:数据类、生产类、消费类;生产和消费类是线程类,同时操作同一个数据类;生产类负责每次向数据类中写入一组数据;消费类负责每次从数据类中取出一组数据。
1 package hello; 2 3 class Info { // 数据类 4 private String title ; 5 private String content; 6 public void setTitle(String title) { 7 this.title = title ; 8 } 9 public String getTitle() { 10 return title ; 11 } 12 public String getContent() { 13 return content ; 14 } 15 public void setContent(String content) { 16 this.content = content ; 17 } 18 19 } 20 21 class Producer implements Runnable { // 生成者类(线程) 22 private Info info ; 23 public Producer(Info info) { 24 this.info = info ; 25 } 26 @Override 27 public void run() { 28 for (int x = 0 ; x < 100 ; x ++ ) { 29 try { 30 Thread.sleep(200); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 if ( x % 2 == 0 ) { 35 this.info.setTitle("张三"); 36 this.info.setContent("男"); 37 } else { 38 this.info.setTitle("王五"); 39 this.info.setContent("男"); 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 45 class Consumer implements Runnable { 46 private Info info ; 47 public Consumer(Info info) { 48 this.info = info ; 49 } 50 @Override 51 public void run() { 52 for (int x = 0 ; x < 100 ; x ++) { 53 try { 54 Thread.sleep(100); 55 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 56 e.printStackTrace(); 57 } 58 System.out.println(this.info.getTitle() + "——" + this.info.getContent()); 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 63 public class TestDemo { 64 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 65 Info info = new Info() ; 66 new Thread(new Producer(info)).start(); 67 new Thread(new Consumer(info)).start(); 68 } 69 }
上例程序执行后,会发现“错位的现象”;出现类似数据为取走,就存入新的数据的错误。【不同步且异步现象导致】
1 package hello; 2 3 class Info { // 数据类 4 private String title ; 5 private String content; 6 public synchronized void set(String title , String content) { 7 this.title = title ; 8 try { 9 Thread.sleep(100); 10 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 11 e.printStackTrace(); 12 } 13 14 this.content = content ; 15 } 16 public synchronized void get() { 17 try { 18 Thread.sleep(100); 19 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } 22 System.out.println(this.title + "——" + this.content); 23 } 24 25 } 26 27 class Producer implements Runnable { // 生成者类(线程) 28 private Info info ; 29 public Producer(Info info) { 30 this.info = info ; 31 } 32 @Override 33 public void run() { 34 for (int x = 0 ; x < 100 ; x ++ ) { 35 if ( x % 2 == 0 ) { 36 this.info.set("张三", "男"); 37 } else { 38 this.info.set("李悦", "女"); 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 44 class Consumer implements Runnable { 45 private Info info ; 46 public Consumer(Info info) { 47 this.info = info ; 48 } 49 @Override 50 public void run() { 51 for (int x = 0 ; x < 100 ; x ++) { 52 this.info.get(); 53 } 54 } 55 } 56 57 public class TestDemo { 58 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 59 Info info = new Info() ; 60 new Thread(new Producer(info)).start(); 61 new Thread(new Consumer(info)).start(); 62 } 63 }
通过“同步方法”,解决了数据不同步的问题,但是于此而来的问题就是:数据的重复操作。
针对上两例程序,我们通过Object类的支持,来解决数据重复操作的问题:
如果像上例的设计,需要在程序中加入一个等待机制;当数据未取则等待数据取出后在存入,当数据未存等待数据存入后取出。而Object类中提供有专门的“等待”。
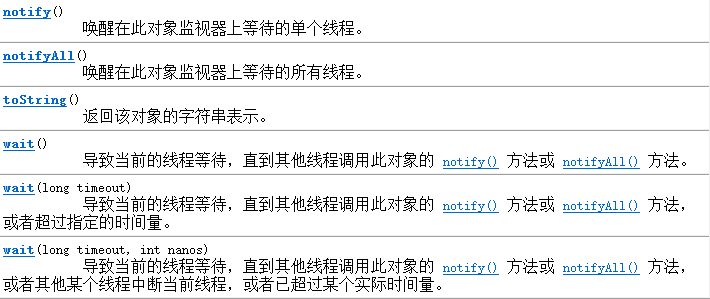
等待: public final void wait() throws InterruptedException
唤醒第一个等待线程: public final void notify() ;
唤醒全部的等待进入: public final void notifyAll(); //优先级高越有可能先唤醒
通过Object的线程等待和唤醒功能完善程序:
1 package hello; 2 3 class Info { // 数据类 4 private String title ; 5 private String content; 6 private boolean flag = true ; 7 // true:表示可以生产,不可以取走 8 // false:表示不可以生产,可以取走 9 public synchronized void set(String title , String content) { 10 if (this.flag == false) { // 发现不可以生产,则等待线程 11 try { 12 super.wait(); // 通过super调用自己的超类(父类)Object类中的wait()方法等待线程 13 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 } 17 this.title = title ; 18 try { 19 Thread.sleep(100); 20 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } 23 this.content = content ; 24 this.flag = false ;// 修改标记 25 super.notify(); //唤醒其他等待线程 26 } 27 public synchronized void get() { 28 if (this.flag == true) { 29 try { 30 super.wait(); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 } 35 try { 36 Thread.sleep(100); 37 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } 40 System.out.println(this.title + "——" + this.content); 41 this.flag = true ; //修改标记 42 super.notify(); // 唤醒其他线程 43 } 44 45 } 46 47 class Producer implements Runnable { // 生成者类(线程) 48 private Info info ; 49 public Producer(Info info) { 50 this.info = info ; 51 } 52 @Override 53 public void run() { 54 for (int x = 0 ; x < 100 ; x ++ ) { 55 if ( x % 2 == 0 ) { 56 this.info.set("张三", "男"); 57 } else { 58 this.info.set("李悦", "女"); 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 } 63 64 class Consumer implements Runnable { 65 private Info info ; 66 public Consumer(Info info) { 67 this.info = info ; 68 } 69 @Override 70 public void run() { 71 for (int x = 0 ; x < 100 ; x ++) { 72 this.info.get(); 73 } 74 } 75 } 76 77 public class TestDemo { 78 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 79 Info info = new Info() ; 80 new Thread(new Producer(info)).start(); 81 new Thread(new Consumer(info)).start(); 82 } 83 }
我们依靠Object类中的等待唤醒机制完成了代码的要求。
------------------------




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号