Java的设计模式(4)--抽象工厂模式
提供一个创建一系列或相互依赖对象的接口,而无须指定他们具体的类。例如某些系统可能需要为用户提供一系列相关对象,但系统不希望用户直接使用new运算符实例化这些对象,而是应当由系统来控制这些对象的创建,否则用户不仅要清楚知道哪些类来创建对象,而且必须要清楚这些对象之间是如何相关的,使得用户代码和这些类型形成耦合,不利维护,一般会包括以下四种角色:
- 抽象产品(Product):一个抽象类或接口,负责定义具体产品必须实现的方法;
- 具体产品(ConcreteProduct):具体产品是一个类,如果Product是一个抽象类,那么具体产品是它的子类;如果Product是一个接口,那么具体产品是它的接口类;
- 抽象工厂(AbstractFactory):一个接口或抽象类,负责定义若干个抽象方法;
- 具体工厂(ConcreteFactory):如果抽象工厂是一个抽象类,具体工厂就是它的子类;如果是个接口就是它的实现类。具体工厂重写抽象工厂中的抽象方法,使该方法返回具体的产品实例。
抽象工厂的UML类图如下所示:
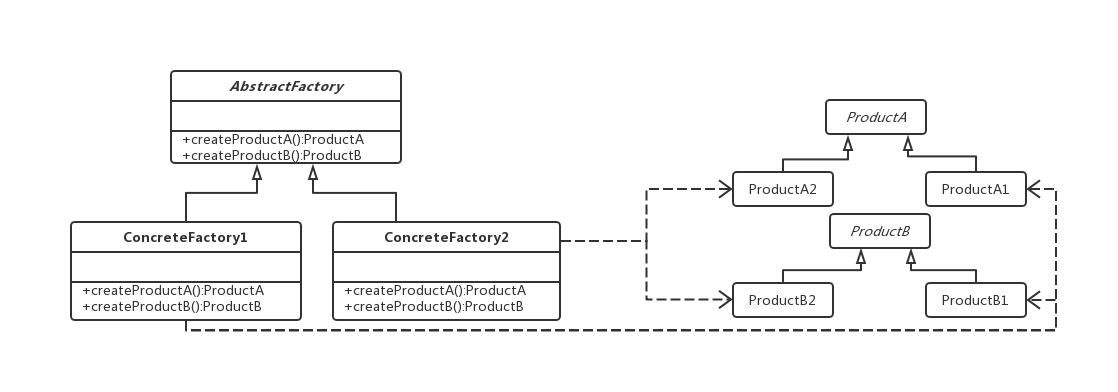
抽象工厂模式的优点:
-
- 可以为用户创建一系列相关的对象,使用户和创建这些对象的类脱藕。
- 可以方便的为用户配置一系列对象,用户使用不同的具体工厂就能得到一组相关的对象,同时也能避免用户混用不同系列中的对象。
- 可以随时增加具体工厂为用户提供一组相关的对象。
抽象工厂模式的应用场景:
-
- 系统需要为用户提供多个对象,但不希望用户直接使用new对象,希望用户和创建对象类的解耦
- 系统需要为用户提供多个相关的对象,以便用户联合使用他们,但又不希望用户来决定这些对象是如何关联的。
- 系统需要为用户提供一系列对象,但值需要用户知道这些对象有哪些方法可以用,不需要用户知道这些对象的创建过程
下面以服饰工厂生产衣服为例,为用户提供西装和牛仔裤:
1. 抽象产品,裤子和上衣
public abstract class Trousers { public abstract int getWaitstSize(); public abstract int getHeight(); public abstract String getName(); }
public abstract class UpperClothes { public abstract int getChestSize(); public abstract int getHeight(); public abstract String getName(); }
2. 具体产品
public class CowBoyTrouers extends Trousers { private int waistSize; private int height; private String name; public CowBoyTrouers(int waistSize, int height, String name) { this.waistSize = waistSize; this.height = height; this.name = name; } @Override public int getWaitstSize() { return waistSize; } @Override public int getHeight() { return height; } @Override public String getName() { return name; } }
public class WesternTrouers extends Trousers { private int waistSize; private int height; private String name; public WesternTrouers(int waistSize, int height, String name) { this.waistSize = waistSize; this.height = height; this.name = name; } @Override public int getWaitstSize() { return waistSize; } @Override public int getHeight() { return height; } @Override public String getName() { return name; } }
public class CowBoyUpperClothes extends UpperClothes { private int chextSize; private int height; private String name; public CowBoyUpperClothes(int chextSize, int height, String name) { super(); this.chextSize = chextSize; this.height = height; this.name = name; } @Override public int getHeight() { return height; } @Override public String getName() { return name; } @Override public int getChestSize() { return chextSize; } }
public class WesternUpperClothes extends UpperClothes { private int chestSize; private int height; private String name; public WesternUpperClothes(int chestSize, int height, String name) { super(); this.chestSize = chestSize; this.height = height; this.name = name; } @Override public int getChestSize() { return chestSize; } @Override public int getHeight() { return height; } @Override public String getName() { return name; } }
3. 抽象工厂
public abstract class ClotherFactory { public abstract UpperClothes createUpperClothes(int chestSize,int height); public abstract Trousers createTrousers(int waistSize,int height); }
4.具体工厂,一个负责生产西装,一个负责制作牛仔
public class BJClotherFactory extends ClotherFactory { @Override public UpperClothes createUpperClothes(int chestSize, int height) { return new WesternUpperClothes(chestSize,height,"北京牌西服上衣"); } @Override public Trousers createTrousers(int waistSize, int height) { return new WesternTrouers(waistSize, height,"北京牌西服裤子"); } }
public class SHClothesFactory extends ClotherFactory { @Override public UpperClothes createUpperClothes(int chestSize, int height) { return new CowBoyUpperClothes(chestSize, height, "上海牌牛仔上衣"); } @Override public Trousers createTrousers(int waistSize, int height) { return new CowBoyTrouers(waistSize, height, "上海牌牛仔裤子"); } }
上面这些类就是一个小框架,可以使用这个小框架编写自己的类。应用程序在使用抽象工厂模式时,只和抽象的产品、抽象工厂以及具体工厂打交道,用户只需要了解抽象产品有哪些方法即可,不需要知道有哪些具体产品。下列代码列出了一个应用程序的类。
public class Shop { private UpperClothes cloth; private Trousers trouser; public void giveSuit(ClotherFactory factory,int chestSize,int waistSize,int height){ this.cloth = factory.createUpperClothes(chestSize, height); this.trouser = factory.createTrousers(waistSize, height); showMess(); } private void showMess() { System.out.println("<套装信息>"); System.out.println(cloth.getName()+":"); System.out.print("胸围:"+cloth.getChestSize()); System.out.println(" 身高:"+cloth.getHeight()); System.out.println(trouser.getName()+":"); System.out.print("腰围:"+trouser.getWaitstSize()); System.out.println(" 身高"+trouser.getHeight()); } }
public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { Shop shop = new Shop(); ClotherFactory facory = new BJClotherFactory(); shop.giveSuit(facory, 110, 82, 170); facory = new SHClothesFactory(); shop.giveSuit(facory, 120, 88, 180); } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号