十二、linux 之 进程管理
1) 在 LINUX 中,每个执行的程序都称为一个进程。每一个进程都分配一个 ID 号(pid,进程号)。
2) 每个进程都可能以两种方式存在的。前台与后台,所谓前台进程就是用户目前的屏幕上可以进行操作的。后台进程 则是实际在操作,但由于屏幕上无法看到的进程,通常使用后台方式执行。
3) 一般系统的服务都是以后台进程的方式存在,而且都会常驻在系统中。直到关机才结束
二、显示系统执行的进程(ps)
2.1 ps指令
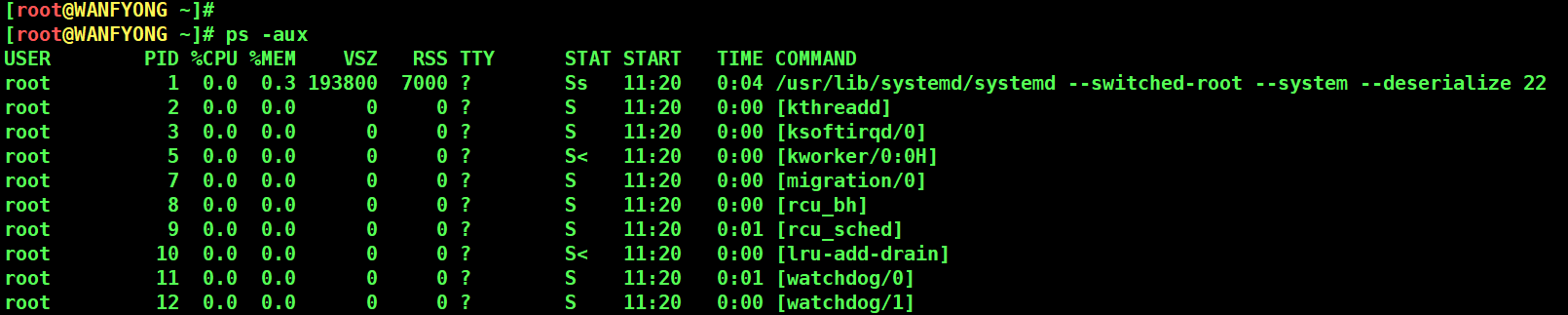
ps 命令是用来查看目前系统中,有哪些正在执行,以及它们执行的状况。可以不加任何参数.
[root@WANFYONG ~]# ps -aux USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND root 1 0.0 0.3 193800 7000 ? Ss 11:20 0:04 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --switched-root --system --deserialize 22 root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:20 0:00 [kthreadd] root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:20 0:00 [ksoftirqd/0] root 5 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 11:20 0:00 [kworker/0:0H] root 7 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:20 0:00 [migration/0] root 8 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:20 0:00 [rcu_bh] root 9 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:20 0:01 [rcu_sched] root 10 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 11:20 0:00 [lru-add-drain] root 11 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:20 0:01 [watchdog/0] root 12 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:20 0:00 [watchdog/1] root 13 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 11:20 0:00 [migration/1]
USER:用户名称
PID:进程号
%CPU:进程占用 CPU 的百分比
%MEM:进程占用物理内存的百分比
VSZ:进程占用的虚拟内存大小(单位:KB)
RSS:进程占用的物理内存大小(单位:KB)
TTY:终端名称,缩写 .
STAT:进程状态,
S-睡眠,
s-表示该进程是会话的先导进程,
N-表示进程拥有比普通优先级更低的优先级,
R- 正在运行,
D-短期等待,
Z-僵死进程,
T-被跟踪或者被停止等等
STARTED:进程的启动时间
TIME:CPU 时间,即进程使用 CPU 的总时间
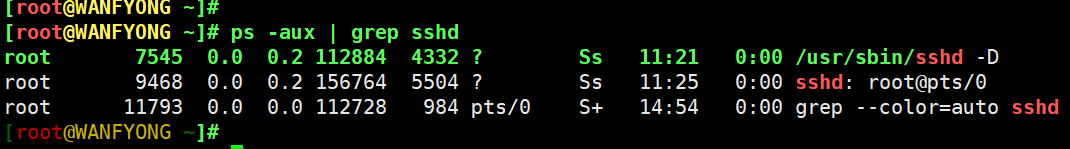
COMMAND:启动进程所用的命令和参数,如果过长会被截断显示[root@WANFYONG ~]# ps -aux | grep sshd root 7545 0.0 0.2 112884 4332 ? Ss 11:21 0:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D root 9468 0.0 0.2 156764 5504 ? Ss 11:25 0:00 sshd: root@pts/0 root 11793 0.0 0.0 112728 984 pts/0 S+ 14:54 0:00 grep --color=auto sshd [root@WANFYONG ~]#
第一个是 真正的 sshd运行的进程。
第二个是 我们登陆的 sshd 进程
第三个是 我们刚才操作 sshd 指令的进程
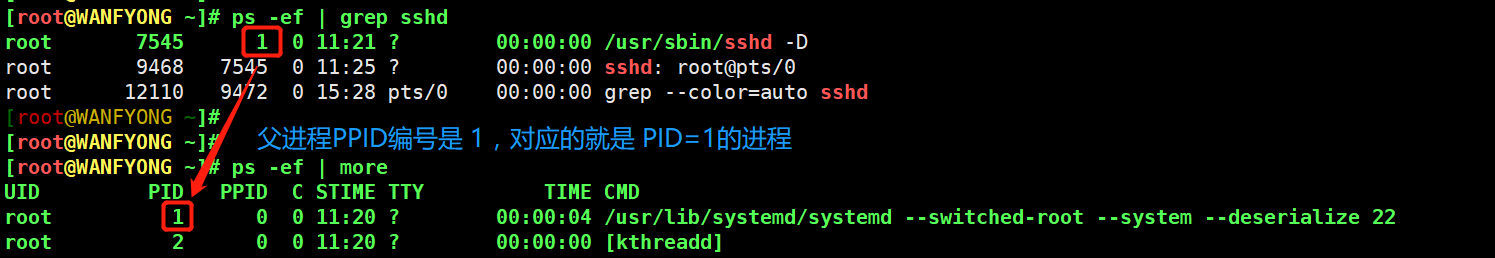
# 以全格式显示当前所有的进程,查看进程的父进程。 # 查看 sshd 的父进程信息 ps -ef 是以全格式显示当前所有的进程 # -e 显示所有进程。-f 全格式 [root@WANFYONG ~]# ps -ef | grep sshd root 7545 1 0 11:21 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D root 9468 7545 0 11:25 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/0 root 12110 9472 0 15:28 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto sshd [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# ps -ef | more UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 1 0 0 11:20 ? 00:00:04 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --switched-root --system --deserialize 22
UID:用户 ID
PID:进程 ID
PPID:父进程 ID
C:CPU 用于计算执行优先级的因子。数值越大,表明进程是 CPU 密集型运算,执行优先级会降低;数值越小,表 明进程是 I/O 密集型运算,执行优先级会提高
STIME:进程启动的时间
TTY:完整的终端名称
TIME:CPU 时间
CMD:启动进程所用的命令和参数
三、终止进程(kill、killall)
3.1 介绍
若是某个进程执行一半需要停止时,或是已消了很大的系统资源时,此时可以考虑停止该进程。使用 kill 命令来完 成此项任务。
kill [选项] 进程号(功能描述:通过进程号杀死/终止进程)
killall 进程名称 (功能描述:通过进程名称杀死进程,也支持通配符,这在系统因负载过大而变得很慢时很有用)选项:
-9 :表示强迫进程立即停止
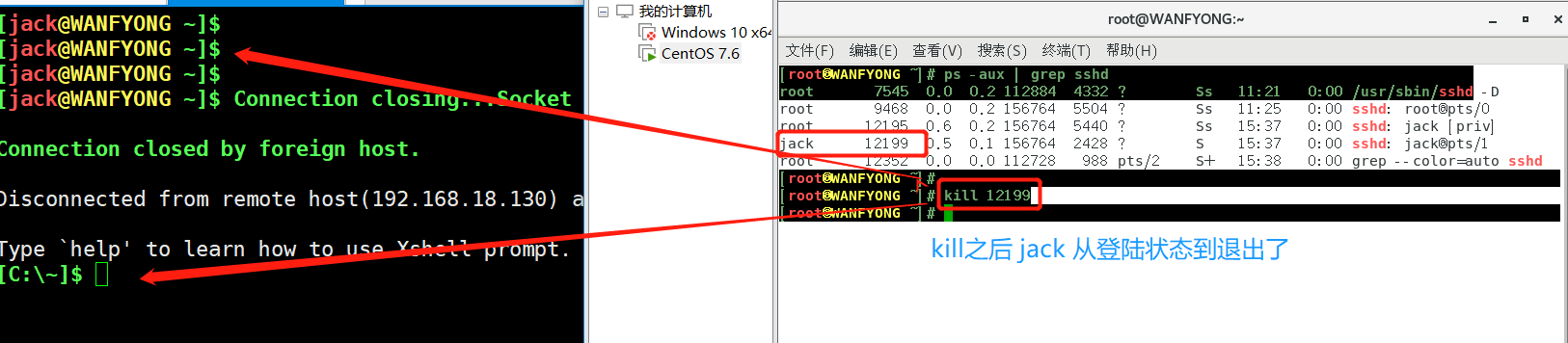
# 1. 踢掉某个非法登录用户 kill 进程号 [root@WANFYONG ~]# ps -aux | grep sshd root 7545 0.0 0.2 112884 4332 ? Ss 11:21 0:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D root 9468 0.0 0.2 156764 5504 ? Ss 11:25 0:00 sshd: root@pts/0 root 12195 1.2 0.2 156764 5448 ? Ss 15:41 0:00 sshd: jack [priv] jack 12199 0.1 0.1 156764 2436 ? S 15:41 0:00 sshd: jack@pts/1 root 12352 0.0 0.0 112728 988 pts/0 S+ 15:41 0:00 grep --color=auto sshd [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]#kill 12199
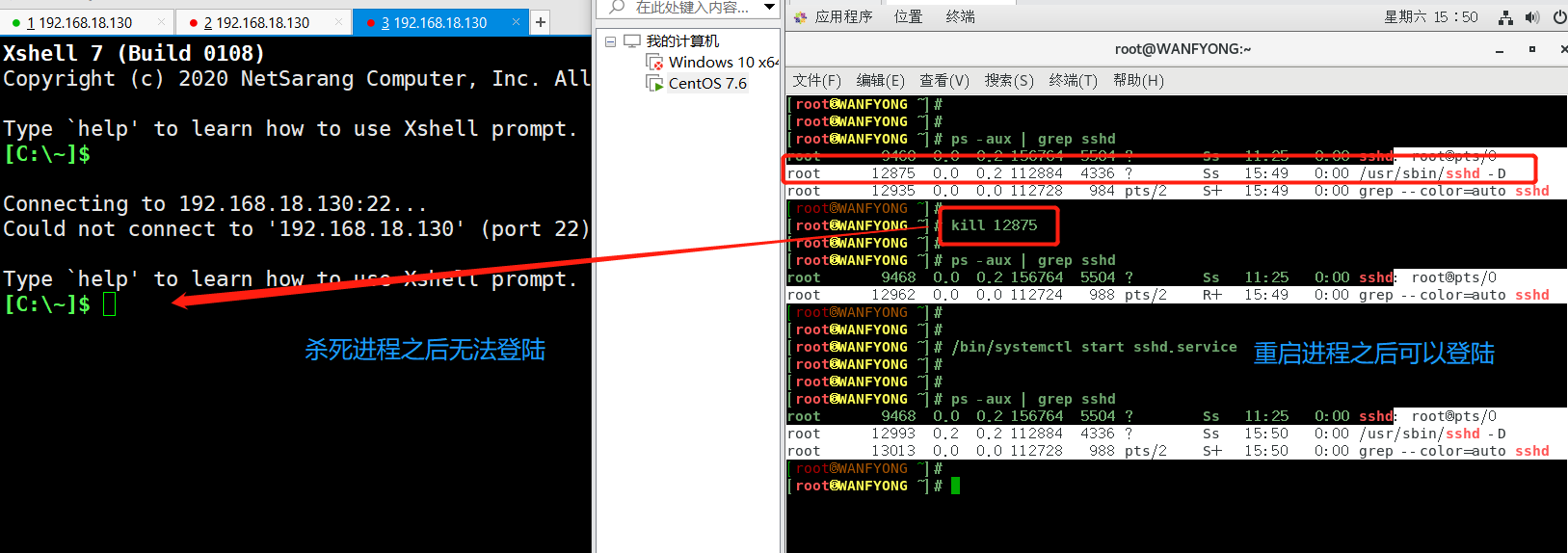
# 2. 终止远程登录服务 sshd, 在适当时候再次重启 sshd 服务 # 终止远程登录服务: kill sshd对应的进程号; # 重启sshd服务: /bin/systemctl start sshd.service [root@WANFYONG ~]# ps -aux | grep sshd root 9468 0.0 0.2 156764 5504 ? Ss 11:25 0:00 sshd: root@pts/0 root 12875 0.0 0.2 112884 4336 ? Ss 15:49 0:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D root 12935 0.0 0.0 112728 984 pts/2 S+ 15:49 0:00 grep --color=auto sshd [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# kill 12875 [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# ps -aux | grep sshd root 9468 0.0 0.2 156764 5504 ? Ss 11:25 0:00 sshd: root@pts/0 root 12962 0.0 0.0 112724 988 pts/2 R+ 15:49 0:00 grep --color=auto sshd [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# /bin/systemctl start sshd.service [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# ps -aux | grep sshd root 9468 0.0 0.2 156764 5504 ? Ss 11:25 0:00 sshd: root@pts/0 root 12993 0.2 0.2 112884 4336 ? Ss 15:50 0:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D root 13013 0.0 0.0 112728 988 pts/2 S+ 15:50 0:00 grep --color=auto sshd [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]#
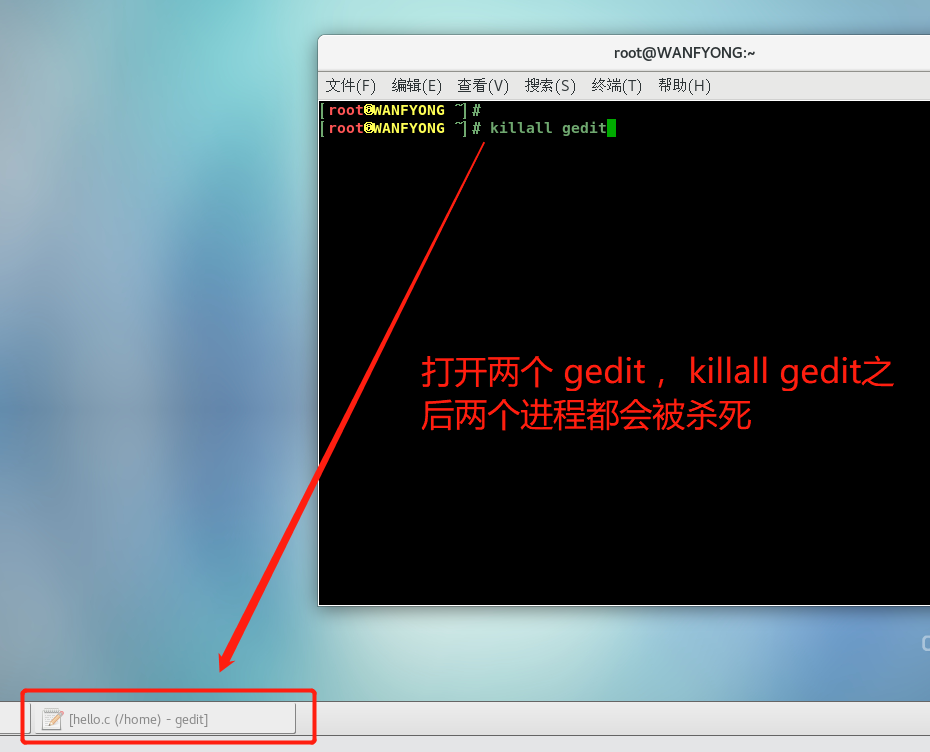
# 3. 终止多个 gedit , killall gedit [root@WANFYONG ~]# killall gedit [root@WANFYONG ~]#
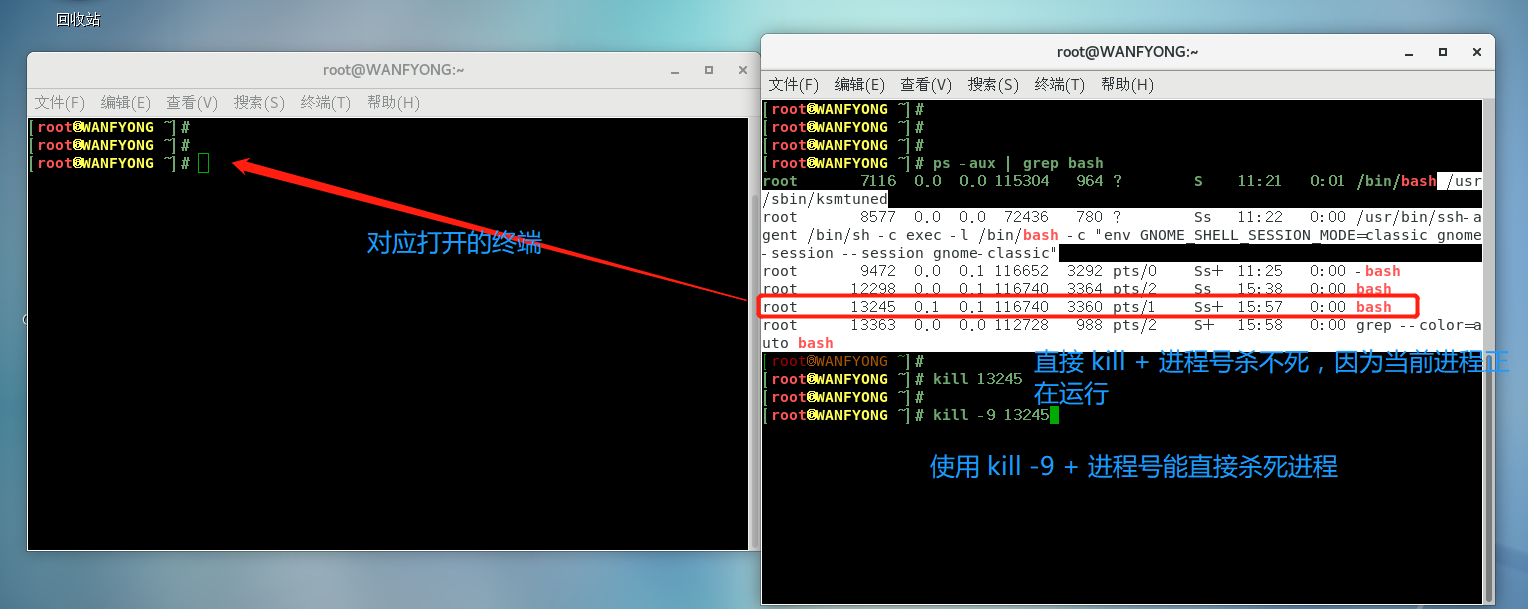
# 4. 强制杀掉一个终端, 指令 kill -9 bash对应的进程号, 此命令还可以直接杀死自己 [root@WANFYONG ~]# ps -aux | grep bash root 7116 0.0 0.0 115304 964 ? S 11:21 0:01 /bin/bash /usr/sbin/ksmtuned root 8577 0.0 0.0 72436 780 ? Ss 11:22 0:00 /usr/bin/ssh-agent /bin/sh -c exec -l /bin/bash -c "env GNOME_SHELL_SESSION_MODE=classic gnome-session --session gnome-classic" root 9472 0.0 0.1 116652 3292 pts/0 Ss+ 11:25 0:00 -bash root 12298 0.0 0.1 116740 3364 pts/2 Ss 15:38 0:00 bash root 13245 0.1 0.1 116740 3360 pts/1 Ss+ 15:57 0:00 bash root 13363 0.0 0.0 112728 988 pts/2 S+ 15:58 0:00 grep --color=auto bash [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# kill 13245 [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# kill -9 13245 [root@WANFYONG ~]#
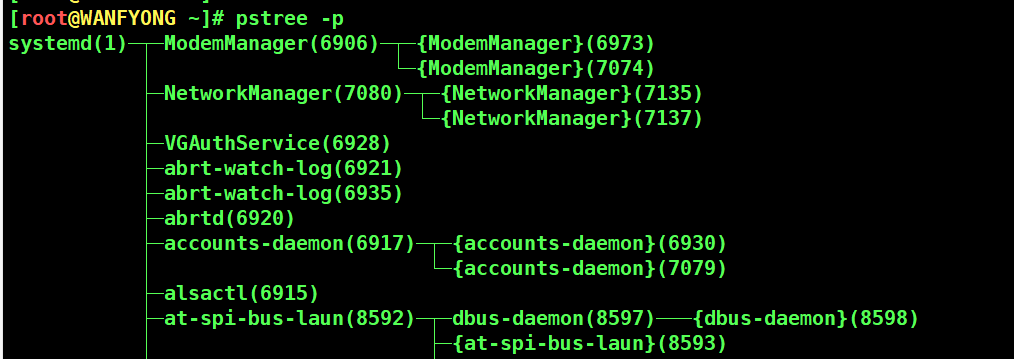
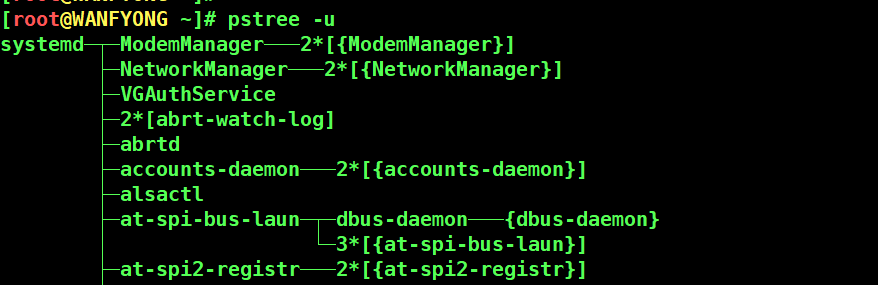
# pstree [选项] ,可以更加直观的来看进程信息 # -p :显示进程的 PID # -u :显示进程的所属用户
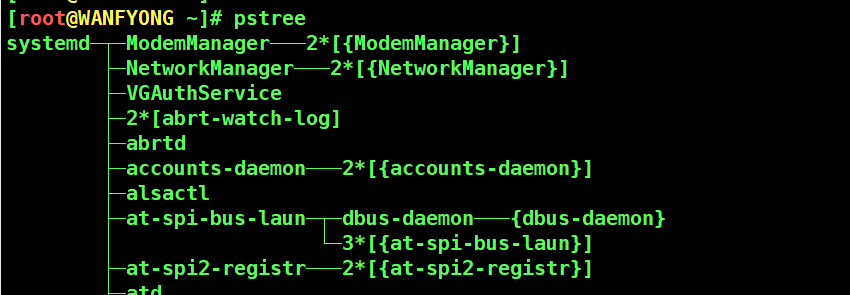
# 1. 请你树状的形式显示进程的 pid [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# pstree systemd─┬─ModemManager───2*[{ModemManager}] ├─NetworkManager───2*[{NetworkManager}] ├─VGAuthService ├─2*[abrt-watch-log] ├─abrtd ├─accounts-daemon───2*[{accounts-daemon}] ├─alsactl ├─at-spi-bus-laun─┬─dbus-daemon───{dbus-daemon} │ └─3*[{at-spi-bus-laun}] ├─at-spi2-registr───2*[{at-spi2-registr}] ... [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# pstree -p systemd(1)─┬─ModemManager(6906)─┬─{ModemManager}(6973) │ └─{ModemManager}(7074) ├─NetworkManager(7080)─┬─{NetworkManager}(7135) │ └─{NetworkManager}(7137) ├─VGAuthService(6928) ├─abrt-watch-log(6921) ├─abrt-watch-log(6935) ├─abrtd(6920) ├─accounts-daemon(6917)─┬─{accounts-daemon}(6930) │ └─{accounts-daemon}(7079) ├─alsactl(6915)
# 2. 请你树状的形式进程的用户 [root@WANFYONG ~]# pstree -u systemd─┬─ModemManager───2*[{ModemManager}] ├─NetworkManager───2*[{NetworkManager}] ├─VGAuthService ├─2*[abrt-watch-log] ├─abrtd ├─accounts-daemon───2*[{accounts-daemon}] ├─alsactl ├─at-spi-bus-laun─┬─dbus-daemon───{dbus-daemon} │ └─3*[{at-spi-bus-laun}] ├─at-spi2-registr───2*[{at-spi2-registr}]
五、服务管理(service)
5.1 介绍
服务(service) 本质就是进程,但是是运行在后台的,通常都会监听某个端口,等待其它程序的请求,比如(mysqld , sshd 防火墙等),因此我们又称为守护进程,是 Linux 中非常重要的知识点。
1) service 服务名 [start | stop | restart | reload | status]
2) 在 CentOS7.0 后 很多服务不再使用 service ,而是 systemctl
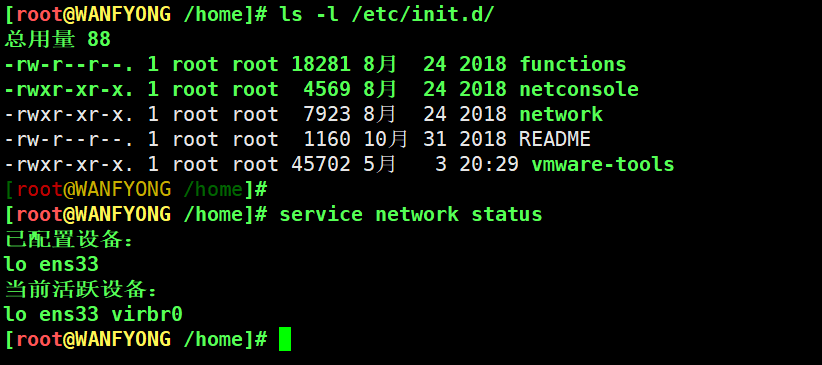
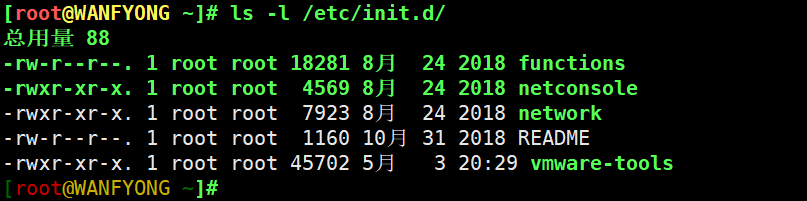
3) service 指令管理的服务在 /etc/init.d 查看
[root@WANFYONG /home]# ls -l /etc/init.d/ 总用量 88 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 18281 8月 24 2018 functions -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 4569 8月 24 2018 netconsole -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 7923 8月 24 2018 network -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1160 10月 31 2018 README -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 45702 5月 3 20:29 vmware-tools [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# service network status 已配置设备: lo ens33 当前活跃设备: lo ens33 virbr0 [root@WANFYONG /home]#
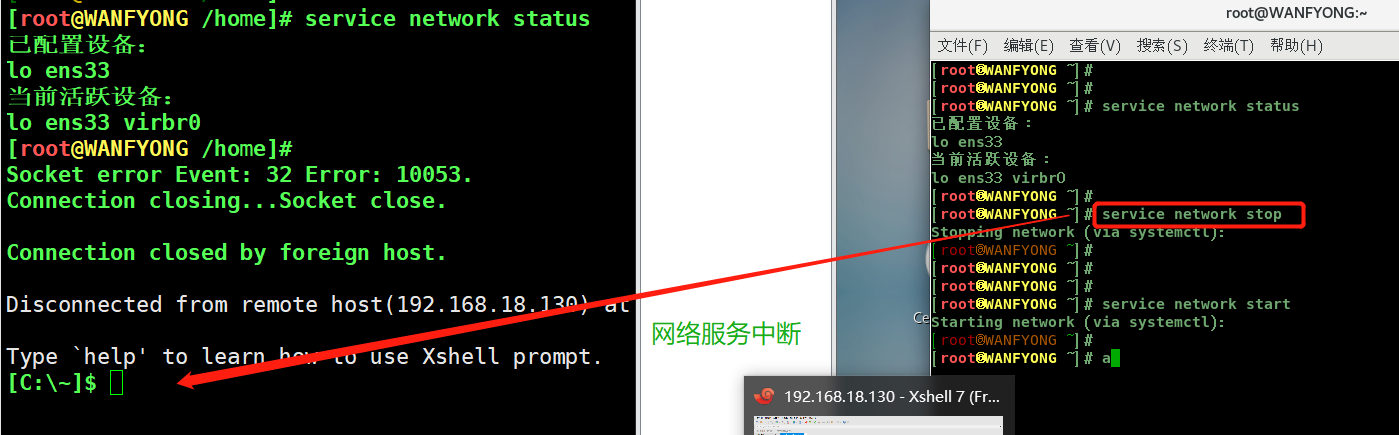
# 请使用 service 指令,查看,关闭,启动 network [注意:在虚拟系统演示,因为网络连接会关闭 [root@WANFYONG ~]# service network status 已配置设备: lo ens33 当前活跃设备: lo ens33 virbr0 [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# service network stop Stopping network (via systemctl): [ 确定 ] [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# service network start Starting network (via systemctl): [ 确定 ] [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]#
5.4 查看服务名(setup)
5.4.1 方式一
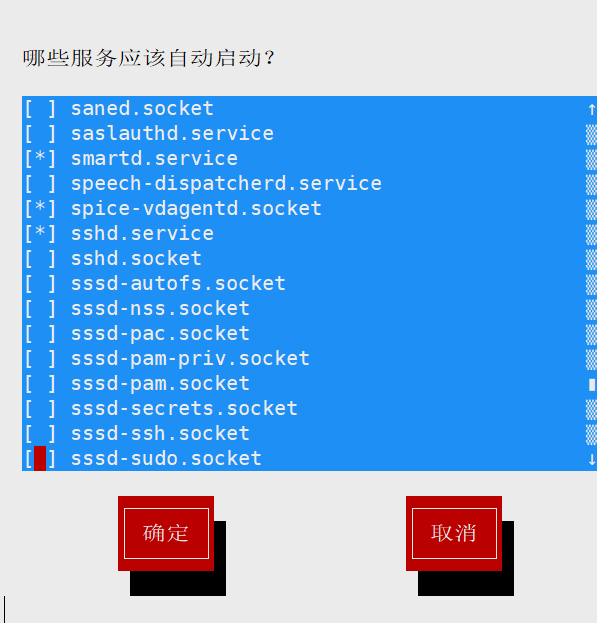
# setup --> 系统服务 # * 号 代表开机自启, 空格一下可以去掉 * 号 # 退出用 Tab 键 [root@WANFYONG ~]# setup [root@WANFYONG ~]#
# /etc/init.d 看到 service 指令管理的服务 [root@WANFYONG ~]# ls -l /etc/init.d/ 总用量 88 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 18281 8月 24 2018 functions -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 4569 8月 24 2018 netconsole -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 7923 8月 24 2018 network -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1160 10月 31 2018 README -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 45702 5月 3 20:29 vmware-tools [root@WANFYONG ~]#
Linux 系统有 7 种运行级别(runlevel):常用的是级别 3 和 5
运行级别 0:系统停机状态,系统默认运行级别不能设为 0,否则不能正常启动
运行级别 1:单用户工作状态,root 权限,用于系统维护,禁止远程登陆
运行级别 2:多用户状态(没有 NFS),不支持网络
运行级别 3:完全的多用户状态(有 NFS),无界面,登陆后进入控制台命令行模式
运行级别 4:系统未使用,保留
运行级别 5:X11 控制台,登陆后进入图形 GUI 模式
运行级别 6:系统正常关闭并重启,默认运行级别不能设为 6,否则不能正常启动
CentOS 开机流程如下:
通过 chkconfig 命令可以给服务的各个运行级别设置自 启动/关闭
chkconfig 指令管理的服务在 /etc/init.d 查看
注意: Centos7.0 后,很多服务使用 systemctl 管理
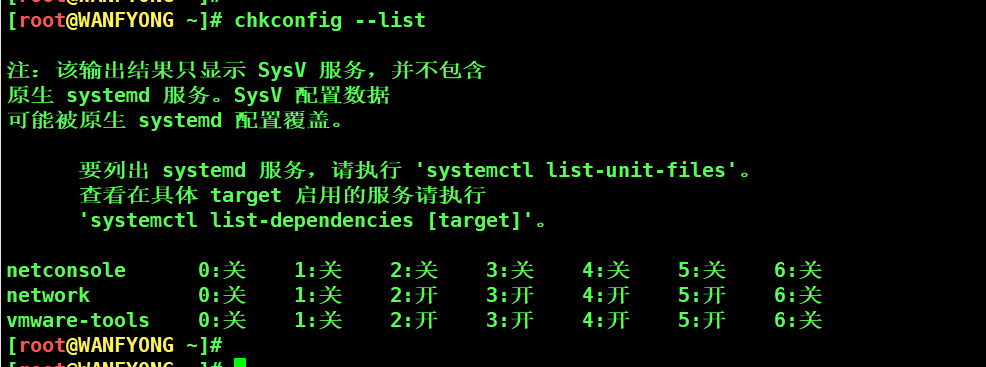
# chkconfig 基本语法 # 1) 查看服务 chkconfig --list [| grep xxx] # 2) chkconfig 服务名 --list # 3) chkconfig --level 5
# 1. 查看服务 chkconfig --list | grep xxx [root@WANFYONG ~]# chkconfig --list 注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含 原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据 可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。 要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。 查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行 'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。 netconsole 0:关 1:关 2:关 3:关 4:关 5:关 6:关 network 0:关 1:关 2:开 3:开 4:开 5:开 6:关 vmware-tools 0:关 1:关 2:开 3:开 4:开 5:开 6:关 [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]#
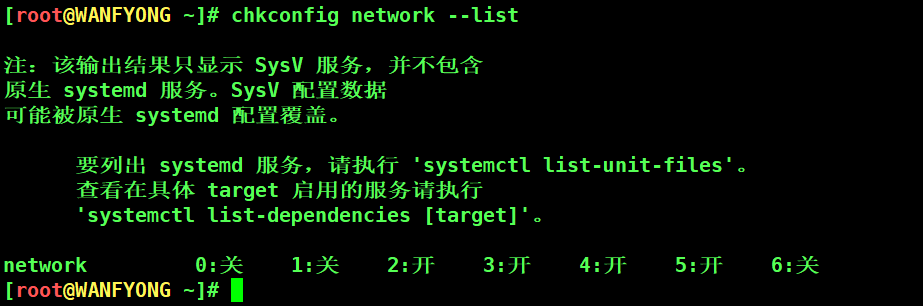
# # 2. chkconfig 服务名 --list [root@WANFYONG ~]# chkconfig network --list 注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含 原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据 可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。 要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。 查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行 'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。 network 0:关 1:关 2:开 3:开 4:开 5:开 6:关 [root@WANFYONG ~]#
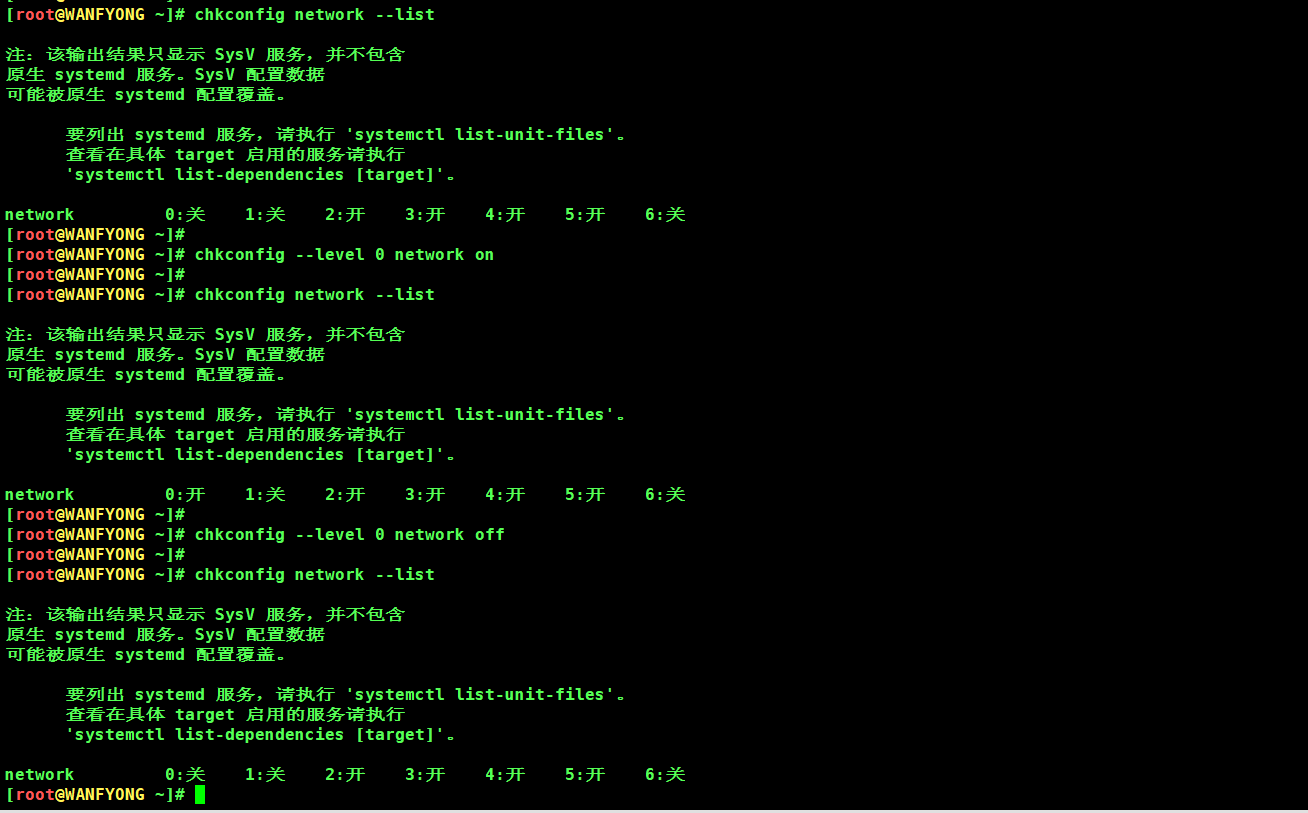
# 3. chkconfig --level 5 服务名 on/off [root@WANFYONG ~]# chkconfig network --list 注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含 原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据 可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。 要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。 查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行 'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。 network 0:关 1:关 2:开 3:开 4:开 5:开 6:关 [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# chkconfig --level 0 network on [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# chkconfig network --list 注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含 原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据 可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。 要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。 查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行 'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。 network 0:开 1:关 2:开 3:开 4:开 5:开 6:关 [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# chkconfig --level 0 network off [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# chkconfig network --list 注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含 原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据 可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。 要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。 查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行 'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。 network 0:关 1:关 2:开 3:开 4:开 5:开 6:关 [root@WANFYONG ~]#
5.7 systemctl 指令
5.7.1 systemctl管理指令
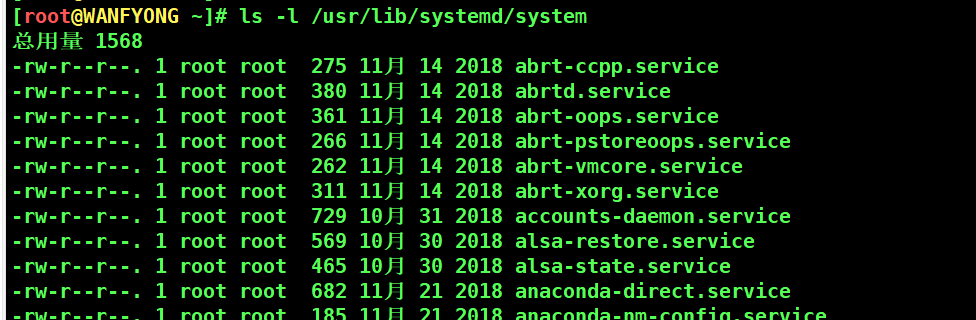
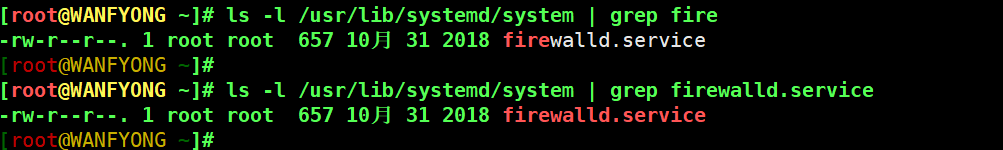
# 基本语法: systemctl [start | stop | restart | status] 服务名 # systemctl 指令管理的服务在 /usr/lib/systemd/system 查看[root@WANFYONG ~]# ls -l /usr/lib/systemd/system 总用量 1568 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 275 11月 14 2018 abrt-ccpp.service -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 380 11月 14 2018 abrtd.service -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 361 11月 14 2018 abrt-oops.service -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 266 11月 14 2018 abrt-pstoreoops.service -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 262 11月 14 2018 abrt-vmcore.service -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 311 11月 14 2018 abrt-xorg.service -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 729 10月 31 2018 accounts-daemon.service -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 569 10月 30 2018 alsa-restore.service -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 465 10月 30 2018 alsa-state.service -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 682 11月 21 2018 anaconda-direct.service [root@WANFYONG ~]# ls -l /usr/lib/systemd/system | grep fire -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 657 10月 31 2018 firewalld.service [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# ls -l /usr/lib/systemd/system | grep firewalld.service -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 657 10月 31 2018 firewalld.service [root@WANFYONG ~]#
# systemctl list-unit-files [ | grep 服务名] (查看服务开机启动状态, grep 可以进行过滤) # systemctl enable/disable 服务名 (设置服务开机启动) ,在运行级别 3和5同时起作用,永久生效 # systemctl is-enabled 服务名 (查询某个服务是否是自启动的)
# 1. systemctl list-unit-files [ | grep 服务名] (查看服务开机启动状态, grep 可以进行过滤) [root@WANFYONG ~]# systemctl list-unit-files | grep firewalld firewalld.service disabled [root@WANFYONG ~]#
# 2. systemctl enable 服务名 (设置服务开机启动) ,在运行级别 3和5同时起作用 [root@WANFYONG ~]# systemctl list-unit-files | grep firewalld firewalld.service disabled [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# systemctl enable firewalld Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service. Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/firewalld.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service. [root@WANFYONG ~]# reboot [root@WANFYONG ~]# systemctl list-unit-files | grep firewalld firewalld.service enabled [root@WANFYONG ~]#
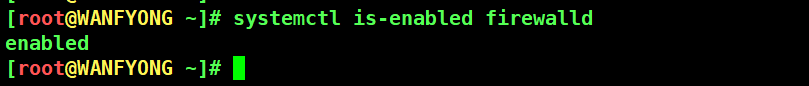
# 3. systemctl is-enabled 服务名 (查询某个服务是否是自启动的) [root@WANFYONG ~]# systemctl is-enabled firewalld enabled [root@WANFYONG ~]#
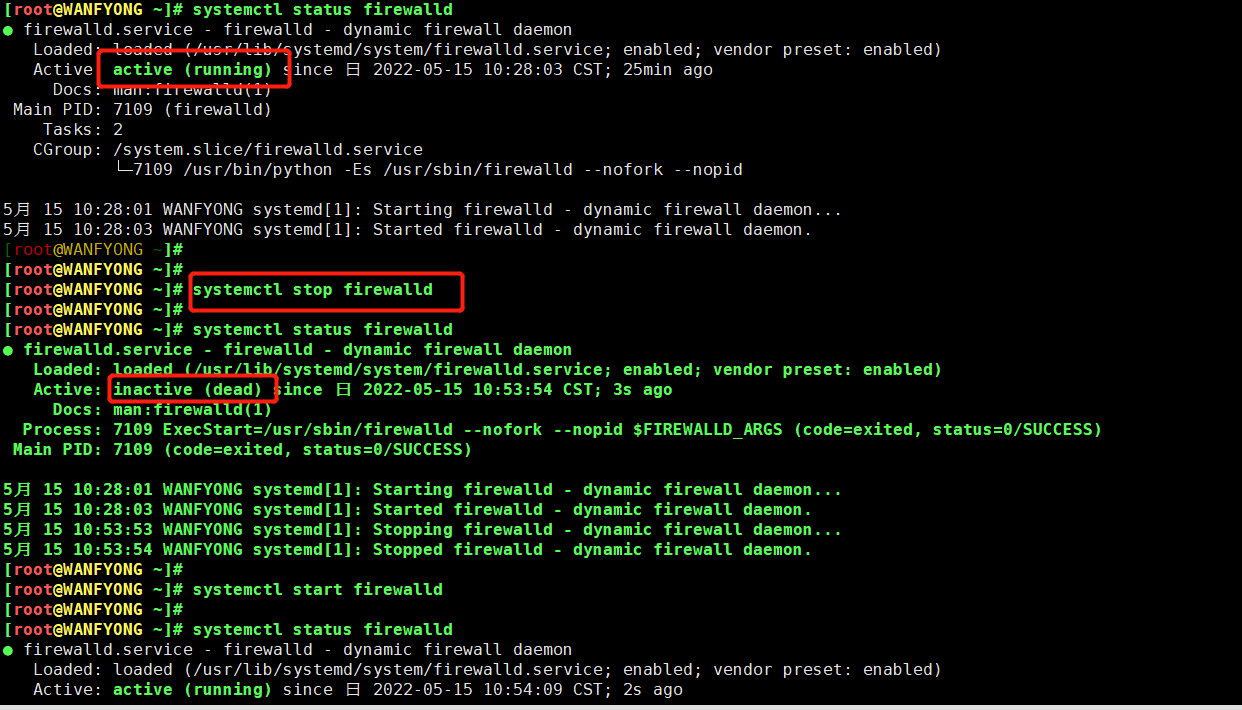
# 查看当前防火墙的状况,关闭防火墙和重启防火墙。 # systemctl status firewalld # systemctl stop firewalld 临时生效 # systemctl start firewalld 临时生效 [root@WANFYONG ~]# systemctl status firewalld ● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since 日 2022-05-15 10:28:03 CST; 25min ago Docs: man:firewalld(1) Main PID: 7109 (firewalld) Tasks: 2 CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service └─7109 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid 5月 15 10:28:01 WANFYONG systemd[1]: Starting firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon... 5月 15 10:28:03 WANFYONG systemd[1]: Started firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon. [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# systemctl stop firewalld [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# systemctl status firewalld ● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: inactive (dead) since 日 2022-05-15 10:53:54 CST; 3s ago Docs: man:firewalld(1) Process: 7109 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid $FIREWALLD_ARGS (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 7109 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) 5月 15 10:28:01 WANFYONG systemd[1]: Starting firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon... 5月 15 10:28:03 WANFYONG systemd[1]: Started firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon. 5月 15 10:53:53 WANFYONG systemd[1]: Stopping firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon... 5月 15 10:53:54 WANFYONG systemd[1]: Stopped firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon. [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# systemctl start firewalld
# 关闭或者启用防火墙后,立即生效。 # 这种方式只是临时生效,当重启系统后,还是回归以前对服务的设置。 # 如果希望设置某个服务自启动或关闭永久生效,要使用 systemctl [enable|disable] 服务名
5.7.5 打开或关闭指定端口
5.7.5.1 防火墙在端口中的作用
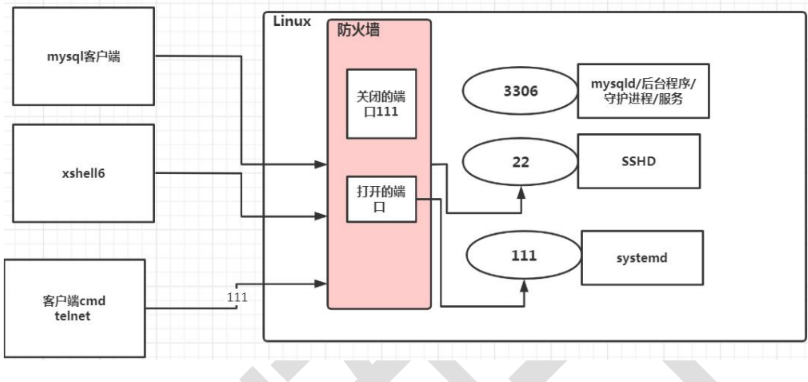
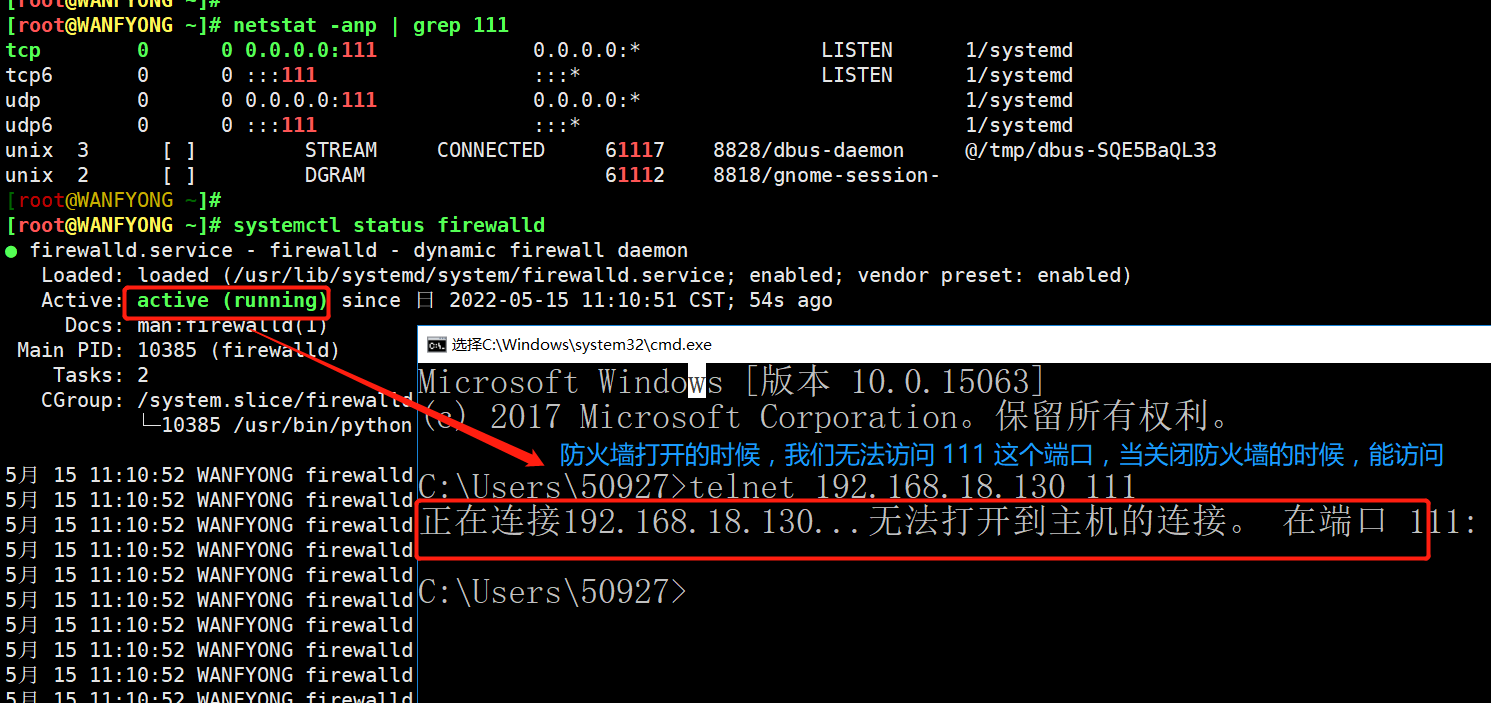
在真正的生产环境,往往需要将防火墙打开,但问题来了,如果我们把防火墙打开,那么外部请求数据包就不能跟服务器监听端口通讯。这时,需要打开指定的端口。比如 80、22、8080 等,这个又怎么做呢?
# 1. 打开端口: firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=端口号/协议 # 2. 关闭端口: firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-port=端口号/协议 # 3. 重新载入,才能生效 : firewall-cmd --reload # 4. 查询端口是否开放: firewall-cmd --query-port=端口/协议
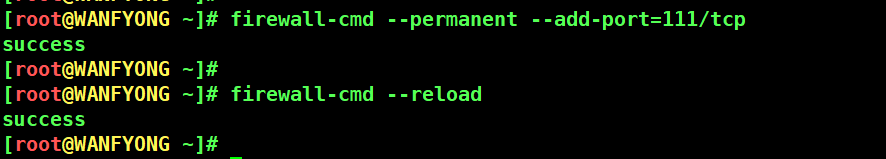
# 1. 打开端口 111, 需要重新载入防火墙 [root@WANFYONG ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=111/tcp success [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success [root@WANFYONG ~]#
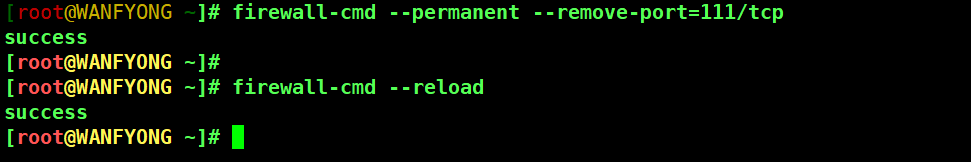
# 2. 关闭端口 111, 需要重新载入防火墙 [root@WANFYONG ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-port=111/tcp success [root@WANFYONG ~]# [root@WANFYONG ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success [root@WANFYONG ~]#
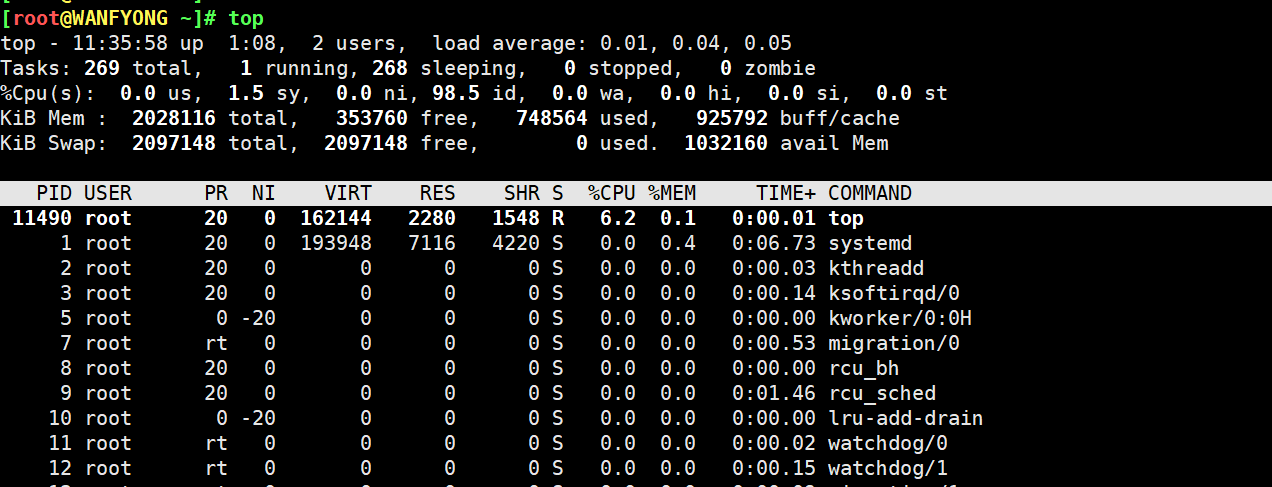
top 与 ps 命令很相似。它们都用来显示正在执行的进程。Top 与 ps 最大的不同之处,在于 top 在执行一段时间可以 更新正在运行的的进程。
top [选项]
输入 top 之后,再输入下面操作 字符 即可。
P 以cpu使用率排序,默认就这个
M 以内存使用率排序
N 以pid排序
u 监听具体用户
k 终止指定进程
q 退出top
# 1. 监视特定用户, 比如我们监控 root 用户 top:输入此命令,按回车键,查看执行的进程。 u:然后输入 "u" 回车,再输入用户名 root,即可
# 2:终止指定的进程, 比如我们要结束 root 登录 top:输入此命令,按回车键,查看执行的进程。 k:然后输入 "k" 回车,再输入要结束的进程 ID 号
# 指定系统状态更新的时间(每隔 10 秒自动更新), 默认是 3 秒 top -d 10
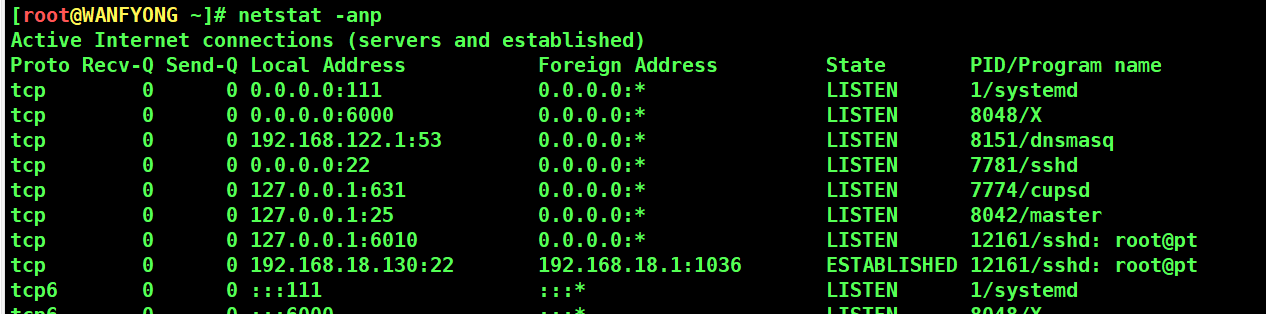
# netstat [选项] # -an 按一定顺序排列输出 # -p 显示哪个进程在调用[root@WANFYONG ~]# netstat -anp Active Internet connections (servers and established) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1/systemd tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:6000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 8048/X tcp 0 0 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 8151/dnsmasq tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7781/sshd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7774/cupsd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 8042/master tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6010 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 12161/sshd: root@pt tcp 0 0 192.168.18.130:22 192.168.18.1:1036 ESTABLISHED 12161/sshd: root@pt
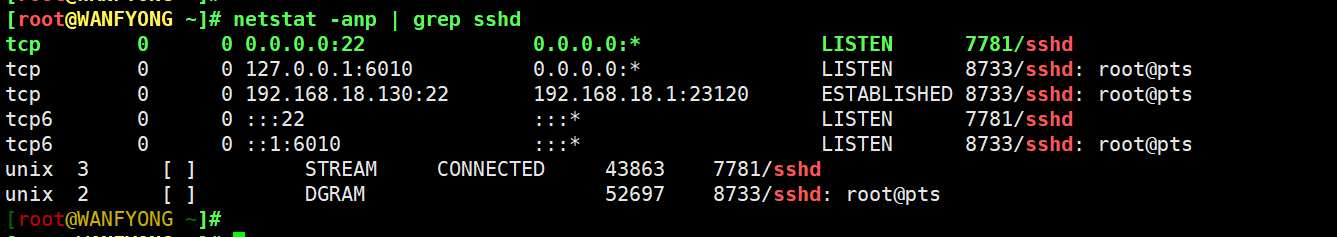
# 查看服务名为 sshd 的服务的信息。 [root@WANFYONG ~]# netstat -anp | grep sshd tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7781/sshd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6010 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 8733/sshd: root@pts tcp 0 0 192.168.18.130:22 192.168.18.1:23120 ESTABLISHED 8733/sshd: root@pts tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 7781/sshd tcp6 0 0 ::1:6010 :::* LISTEN 8733/sshd: root@pts unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 43863 7781/sshd unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 52697 8733/sshd: root@pts [root@WANFYONG ~]#









 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号