SpringBoot学习笔记三
Spring Boot 启动原理
任何一个 Spring Boot 项目都会有一个启动类,其中有一个 @SpringBootApplication 注解。
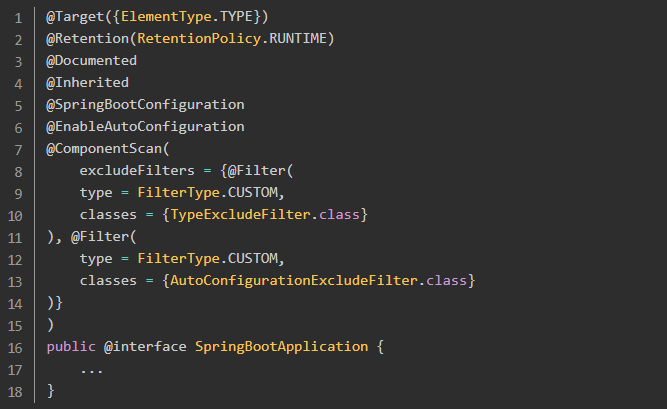
其中,比较关键的注解:
- @SpringBootConfiguration:标记当前类为配置类
- @EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置
- @ComponentScan:扫描主类所在的同级包以及下级包里的Bean
在进入核心注解 @EnableAutoConfiguration 的源码中。
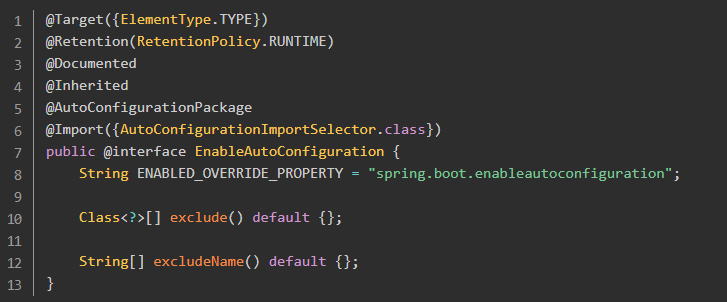
其中的关键部分是 @Import 注解导入的配置功能,AutoConfigurationImportSelector 使用 getCandidateConfigurations 方法得到待配置的class的类名集合。
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames 方法会扫描 META-INF/spring.factories 文件。
查看 spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.1.3.RELEASE.jar 中的 spring.factories 。
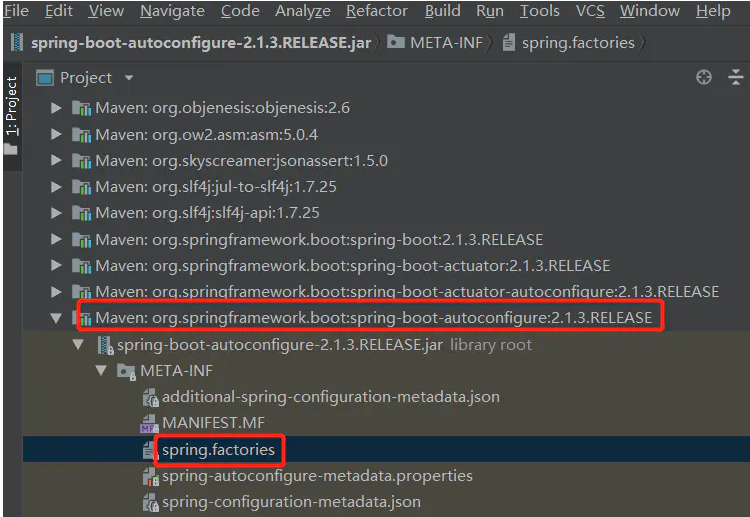
可以看到其中的自动配置。
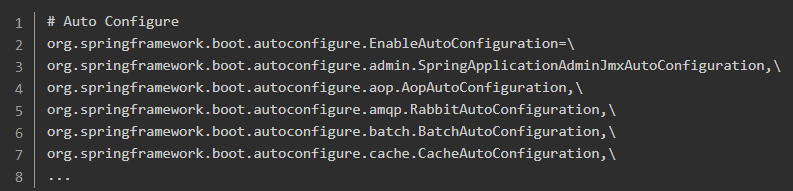
核心注解
打开任意的 AutoConfiguration 文件(spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.1.3.RELEASE.jar 中),可以看到很多的条件注解,这些注解包含在 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition 包中,如下所示:
- @ConditionalOnBean:当容器里有指定Bean的条件下
- @ConditionalOnClass:当类路径下有指定的类的条件下
- @ConditionalOnExpression:基于SpEL表达式作为判断条件
- @ConditionalOnJava:基于JVM版本作为判断条件
- @ConditionalOnJndi:在JNDI存在的条件下查找指定的位置
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean:当容器里没有指定Bean的情况下
- @ConditionalOnMissingClass:当容器里没有指定类的情况下
- @ConditionalOnWebApplication:当前项目时Web项目的条件下
- @ConditionalOnNotWebApplication:当前项目不是Web项目的条件下
- @ConditionalOnProperty:指定的属性是否有指定的值
- @ConditionalOnResource:类路径是否有指定的值
- @ConditionalOnOnSingleCandidate:当指定Bean在容器中只有一个,或者有多个但是指定首选的Bean
- @ConditionalOnWebApplication: 当前项目是在 Web 项目的条件下。
这些注解都组合了@Conditional注解,只是使用了不同的条件。
实例分析
下面通过一个简单的 Spring Boot 内置的自动配置: http的编码配置来讲解一下配置流程。
在常规项目中配置 Http 编码的时候是在 web.xml 中配置一个 filter 。
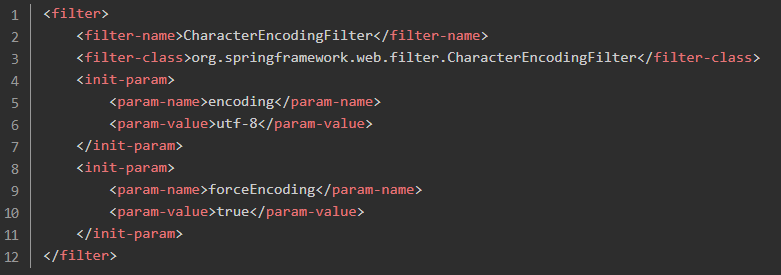
自动配置需要满足两个条件:
- 能配置 CharacterEncodingFilter 这个 Bean;
- 能配置 encoding 和 forceEncoding 两个参数。
配置参数的时候使用了在SpringBoot基础章节中讲述的类型安全配置,Spring Boot 也是基于这一点实现的。双击shift全局搜索 HttpProperties(这里需要注意,不是老版本中的 HttpEncodingProperties)。
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.http"
) // 配置前缀
public class HttpProperties {
private boolean logRequestDetails;
private final HttpProperties.Encoding encoding = new HttpProperties.Encoding();
public HttpProperties() {
}
public boolean isLogRequestDetails() {
return this.logRequestDetails;
}
public void setLogRequestDetails(boolean logRequestDetails) {
this.logRequestDetails = logRequestDetails;
}
public HttpProperties.Encoding getEncoding() {
return this.encoding;
}
public static class Encoding {
public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET;
private Charset charset;
private Boolean force;
private Boolean forceRequest;
private Boolean forceResponse;
private Map<Locale, Charset> mapping;
public Encoding() {
this.charset = DEFAULT_CHARSET;
}
public Charset getCharset() {
return this.charset;
}
public void setCharset(Charset charset) {
this.charset = charset;
}
public boolean isForce() {
return Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.force);
}
public void setForce(boolean force) {
this.force = force;
}
public boolean isForceRequest() {
return Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.forceRequest);
}
public void setForceRequest(boolean forceRequest) {
this.forceRequest = forceRequest;
}
public boolean isForceResponse() {
return Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.forceResponse);
}
public void setForceResponse(boolean forceResponse) {
this.forceResponse = forceResponse;
}
public Map<Locale, Charset> getMapping() {
return this.mapping;
}
public 