【Vue2】基础知识二
脚手架文件结构
|—— node_modules
|—— public
| |—— favicon.ico: 页签图标
| |—— index.html: 主页面
|—— src
| |—— assets: 存放静态资源
| | |—— logo.png
| |—— components: 存放组件
| | |—— HelloWorld.vue
| |—— App.vue: 汇总所有文件
| |—— main.js: 入口文件
|
|—— .gitignore:git版本管理忽略的配置
|—— babel.config.js:babel的配置文件
|—— package-lock.json:包版本控制文件
|—— package.json:应用包配置文件
|—— README.md:应用描述文件
|—— vue.config.js:自定义控制脚手架配置
关于不同版本的Vue:
1.vue.js与vue.runtime.xxx.js的区别
1.vue.js是完整版的vue,包含:核心功能+模板解析器
2.vue.runtime.xxx.js 是运行版的Vue,只包含:核心功能:没有模板解析器
因为vue.runtime.xxx.js没有模板解析器,所以不能使用template配置项,需要使用
render函数接收到的createElement函数去指定具体内容。
vue.config.js配置文件
> 使用vue inspect > output.js可以查看到Vue脚手架的默认配置。
> 使用vue.config.js可以对脚手架进行个性化定制,详情见vue官网 > vue 生态cli >配置参数
ref属性
1.被用来给元素或子组件注册引用信息(id的替代者)
2.应用在html标签上获取的是真实DOM元素,应用在组件标签上是组件实例对象(vc)
3.使用方式:
打标识:<h1 ref="xxx">...</h1> 或 <School ref="xxx"></School>
获取: this.$refs.xxx
配置项props
功能:让组件接收外部传过来的值
(1)传递数据:
<Demo name="xxx"/>
(2)接收数据 (接受数据三种写法)
第一种方法(只接收):
props:['name']
第二种方法(限制类型):
props:{
name:String
}
第三种方法(限制类型、限制必要性、指定默认值):
props:{
name:{
type:String,//类型
required:true,//必要性
default:'老王'//默认值
}
}
备注:props是只读的,Vue底层会监测你对props的修改,如果进行了修改,就会发出警告,
若业务需求确实需要修改,name请复制props的内容到data中一份,然后去修改data中的数据。(data里重新return ,储存一个新变量名储存值,然后后用methods或computed计算一下)
mixin(混入) 基础模块暴露,代码复用
功能:可以把多个组件共用的配置提取成一个混入对象
使用方式:
第一步定义混合,例如:
{
data()(...),
methods:(...)
......
}
第二步使用混入,例如:
(1)全局混入:Vue.mixin(xxx)
(2)局部混入:mixins:['xxx']
插件(使用方法类似express里的中间件)
功能:用于增强Vue
本质:包含install方法的一个对象,install的第一个参数是Vue,第二个以后的参数是插件使用者传递的数据。
定义插件:对象.install = function(Vue,options){
// 全局过滤器
Vue.filter('mySlice',function (value) {})
// 定义全局指令
Vue.directive('fbind', {})
// 配置全局混入
Vue.mixin({})
// 给vue原型上添加方法(vm和vc都能用了)
Vue.prototype.$myMethod = () =>{alert('你好啊')}
Vue.prototype.$myProperty = xxx
}
使用插件:
Vue.use(plugins)
scope样式
作用:让样式在局部生效,防止冲突。
写法:<style scoped> <style lang="less">
总结TodoList案例
1.组件化编码流程:
(1). 拆分静态组件:组件要按照功能点拆分,命名不要与html元素冲突。
(2). 实现动态组件:考虑好数据的存放位置,数据是一个组件再用,还是一些组件再用;
1)一个组件在用:放在组件自身即可。
2)一些组件在用:放在他们共同的父组件上(状态提升)。
(3). 实现交互,从绑定事件开始。
2.props适用于:
(1)父组件==> 子组件 通信
(2)子组件==> 父组件 通信(要求父先给一个函数)
3.使用v-model要切记:v-model绑定的值不能是props传过来的值,因为props是只读不可修改的。
4.props传过来的若是对象类型的值,修改对象中的属性时Vue不会报错,但不推荐这样做。
webSrorage
1.存储内容大小一般支持5MB左右(不同浏览器可能还不一样)
2.浏览器通过 Window.sessionStorage 和 Window.localStorage 属性来实现本地存储机制。
3.相关API:
1.local/sessionStorage.setItem('key', 'value')
2.local/sessionStorage.getItem('key', 'value')
3.local/sessionStorage.removeItem('key')
4.local/sessionStorage.clear()
4.备注:
1.sessionStorage 存储的内容会随着浏览器窗口关闭而消失
2.LocalStorage存储的内容,需要手动清除才会消失
3.local/sessionStorage.getItem(xxx)如果对应的value获取不到,那么对应的返回值是null
4.JSONP.parse(null)的结果依然是null
组件的自定义事件★
1.一种组件间通信的方式,适用于: 子组件==>父组件
2.使用场景:A是父组件,B是子组件,B想给A传数据,name就要在A中给B绑定自定义事件(事件的回调在A中)
3.绑定自定义事件(自定义时间名称必须用小写或者用 x-x 连接):
1.第一种方式,在父组件中 <Demo @atguigu="test" /> 或 <Demo v-on:atguigu="test" />
2.第二种方式
<Demo ref="demo" />
.....
mounted(){
this.$refs.xxx.$on('atguigu', this.test)
}
3.若想让自定义事件只能触发一次,可以使用once修饰符,或$once方法。
4.触发自定义事件:this.$emit('atguigu', data)
5.解绑自定义事件:this.$off('atguigu')
6.组件上也可以绑定原生DOM事件,需要使用native修饰符。★
7.注意:通过this.$refs.xxx.$on('atguigu', options)绑定自定时事件时,回调要么配置在methods中,要么用箭头函数,否则this指向会出现问题。
全局事件总线(GlobalEventBus)
1.一种组件间通信方式,适用于任意组件间通信。
2.安装全局事件总线:
new Vue({
......
beforeCreate(){
Vue.prototype.$bus = this //安装全局事件总线,$bus就是当前应用的vm
在vm create时给vue原型对象安装一个傀儡$bus(傀儡vm实例对象)
}
.....
})
3.使用事件总线:
1).接收数据:A组件想接收数据,则在A组件中给$bus绑定自定义事件,事件的回调留在A组件自身
methods(){
demo(data){......}
}
.....
mounted(){
this.$bus.$on('事件名', this.demo) //或者直接把this.demo写成成回调函数形式
}
2).提供数据:this.$bus.$emit('事件名', data)
4.最好在beforeDestroy钩子中,用$off 去解绑当前组件所用到的事件。
消息订阅与发布(全局事件总线的封装库)(react常用)
1.一种组件间通信的方式,适用于任意组件间通信。
2.使用步骤:
1.安装pubsub: npm i pubsub-js
2.引入: import pubsub from 'pubsub-js'
3.订阅方接收数据:A组件想接收数据,则在A组件中订阅消息,订阅的回调留在A组件自身
method(){
demo(data){.....}
}
.....
mounted(){
this.pid = pubsub.subscribe('xxx', this.demo)//订阅消息
}
4.发布方提供数据:pubsub.publish('xxx', data)
5.最好在beforeDestroy钩子中,用PubSub.unsubscribe(pid) 去取消订阅
nextTick
1.语法 this.$nextTick(回调函数)
2.作用 在下一次DOM更新结束后执行其指定的回调
3.什么时候用:当改变数据后,要基于更新后的新DOM进行某些操作时,要在nextTick所指定的回调函数中执行
插槽
1.作用:让父组件向子组件指定位置插入html结构,也是一种组件间通信的方式,使用于父组件 ===> 子组件(props反向配置)
2.分类:默认插槽、具名插槽、作用域插槽
3.使用方式
1.默认插槽
父组件
<Category>
<div>html结构</div>
</Category>
子组件
<template>
<div>
<!-- 定义插槽 -->
<slot>插槽默认内容</slot>
</div>
</template>
2.具名插槽
父组件
<Category slot="center">
<div>html结构1</div>
</Category>
<Category v-slot:footer>
<div>html结构2</div>
</Category>
子组件
<template>
<div>
<!-- 定义插槽 -->
<slot name="center">插槽默认内容...</slot>
<slot name="footer">插槽默认内容...</slot>
</div>
</template>
3.作用域插槽
1.理解:数据在组件自身,但根据数据生成的结构需要的组件的使用者来决定。(games数据在Category组件中,但使用数据所遍历出来的结构由App组件决定)
2.具体编码:

<Category>
<template scope="scopeData">
<!-- 生成ul列表 -->
<ul>
<li v-for="(g, index) in scopeData.games" :key="index">{{g}}</li>
</ul>
</template>
</Category>
<Category>
<template slot-scope="scopeData">
<!-- 生成h4标题 -->
<h4 v-for="(g, index) in scopeData.games" :key="index">{{g}}</h4>
</template>
</Category>
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template>
<div>
<slot :games="games">我是默认的</slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:"Category",
props:['title'],
data() {
return {
games: ["红色警戒", "穿越火线", "劲舞团", "超级玛丽"],
};
},
}
</script>
Vuex
1.概念:在vue中实现集中式状态(数据)管理的一个Vue插件,对vue应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写),也是一种组件间通信的方式,且使用以任意组件间通信。
2.何时使用:多个组件需要共享数据时
3.搭建vuex环境
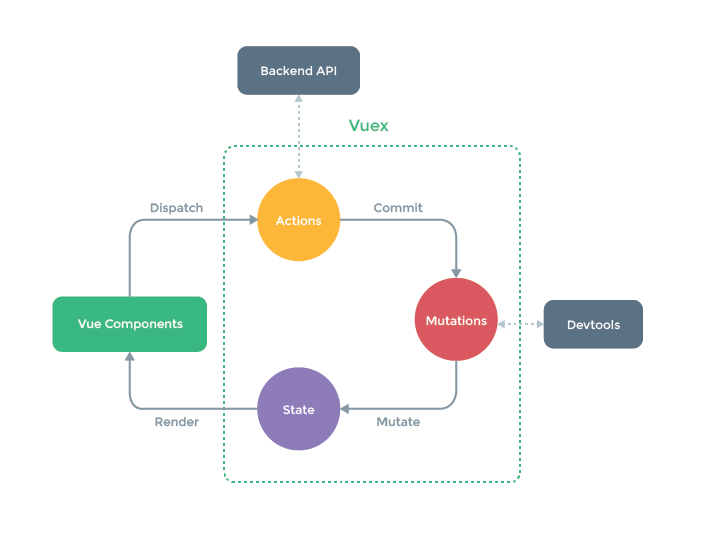
1.创建文件 src/store/index.js

<!-- !该文件用于创建Vuex中最为核心的store --> <!-- !引入vue --> import Vue from 'vue' <!-- !引入Vuex --> import Vuex from 'vuex' <!-- !使用vuex插件 --> Vue.use(Vuex) <!-- !准备actions,用于响应组件中的动作 --> const actions ={} <!-- !准备mutations,用于操作数据(state) --> const mutations ={} <!-- !准备state,用于存储数据 --> const state ={} <!-- !创建并暴露store --> export default new Vuex.Store({ actions, mutations, state })
2.main.js中创建vm时传入store配置项

import Vue from "vue"; import App from './App.vue'; Vue.config.productionTip = false; <!-- !引入store --> import store from './store/index' new Vue({ el:"#app", render:(h)=> h(App), store, beforeCreate() { Vue.prototype.$bus = this }, })
3.基本使用,配置actions、配置mutations、操作文件store.js

1. <!-- !该文件用于创建Vuex中最为核心的store --> <!-- !引入vue --> import Vue from 'vue' <!-- !引入Vuex --> import Vuex from 'vuex' <!-- !使用vuex插件 --> Vue.use(Vuex) <!-- !准备actions,用于响应组件中的动作 --> const actions ={ jia(context, value) { console.log('actions中的jia被调用'); context.commit('JIA', value) } } <!-- !准备mutations,用于操作数据(state) --> const mutations ={ JIA(state, value){ console.log('mutations中的JIA被调用'); state.sum += value } } <!-- !准备state,用于存储数据 --> const state ={ sum:0 //当前的和 } <!-- !创建并暴露store --> export default new Vuex.Store({ actions, mutations, state }) <!-- !模板里不用写this,js脚本里写应该加this --> 2.组件中读取vuex中的数据:$store.state.sum 3.组件中修改vuex中的数据:$store.dispatch('actions中的方法名', 数据) 或直接 $store.commite('mutations中的方法名', 数据) 若没有网络请求或其他业务逻辑,组件中也可以越过actions,即不写dispatch,直接编写commit
4.getters的使用
1.概念:当state中的数据需要经过加工再使用时,可以使用getters加工
2.在store.js中追加getters配置
3.组件中读取数据,$store.getters.bigSum

<!-- !准备getters,用于将state中的数据进行加工 --> const getters ={ bigSum(state){ return state.sum*10 } } <!-- !创建并暴露store --> export default new Vuex.Store({ actions, mutations, state, getters })
6.四个map方法的使用

1.mapState:用于帮助我们映射state中的数据为计算属性 <!-- !借助mapMutations生成对应的方法,方法中会调用commit去联系mutations(数组写法) --> computed:{ ...mapMutations(['JIA', 'JIAN']), } <!-- !借助mapMutations生成对应的方法,方法中会调用commit去联系mutations(对象写法) --> computed:{ ...mapMutations({increase:'JIA', decrease:'JIAN'}), } 2.mapGetters方法:用于帮助我们映射getters中的数据为计算属性 <!-- !借助mapStae生成计算属性,从state中读取数据。(对象写法) --> computed:{ ...mapGetters({bigSum:'bigsum'}) } <!-- !借助mapState生成计算属性,从state中读取数据。(数组写法) --> computed:{ ...mapGetters(['bigSum']) } 3.mapActions方法:用于帮助我们生成与actions对话的方法,即:包含$store.dispatch(xxx)的函数 <!-- !借助mapMutations生成对应的方法,方法中会调用diapatch去联系actions(数组写法) --> methods:{ ...mapActions(['jiaOdd', 'jiaWait']), } <!-- !借助mapMutations生成对应的方法,方法中会调用diapatch去联系actions(对象写法) --> methods:{ ...mapActions({increaseOdd:'jiaOdd', increaseWait:'jiaWait'}) }
7.模块化+命名空间
1.目的:让代码更好维护,让多种数据分类更加明确。
2.修改store.js(inde.js)

<!-- !求和相关的配置 --> const countAbout = { <!-- *开启命名空间,以区分不同组件 --> namespaced:true, state: { x:1 }, actions: { ... }, mutations: { ... }, getters: { bigSum(state) { return state.sum * 10 } } } <!-- !人员管理相关的配置 --> const personAbout = { <!-- *开启命名空间,以区分不同组件 --> namespaced:true, state: { x:1 }, actions: { ... }, mutations: { ... }, } <!-- !创建并(暴露)store --> const store = new Vuex.Store({ modules:{ countAbout:countOptions, personAbout:personOptions } })
3.开启命名空间后,组件中读取state数据(这里直接去案例里看具体写法)Count.vue里用了map方式,Person.vue用了纯自己写的
方式一、自己直接读取
return this.$store.state.personAbout.personList
方式二、借助mapState读取
...mapState('countAbout', ['sum', 'school', 'subject']),
4.开启命名空间后,组件中读取getters数据
方式一、组件直接读取
return this.$store.getters['personAbout/firstPersonName']
方式二、借助mapGetters读取
...mapGetters('countAbout', ['bigSum'])
5.开启命名空间后,组件中调用dispatch数据
方式一、组件直接读取
this.$store.dispatch('personAbout/addPersonWang', personObj)
方式二、借助mapGetters读取
...mapActions('countAbout', {increaseOdd:'jiaOdd', increaseWait:'jiaWait'})
6.开启命名空间后,组件中调用commit
方式一、组件直接读取
this.$store.commit('personAbout/ADD_PERSON', personObj)
方式二、借助mapGetters读取
...mapMutations('countAbout', {increase:'JIA', decrease:'JIAN'}),
路由
1.理解:一个路由(route)就是一组映射关系(key - value),多个路由需要路由器(router进行管理)
2.前端路由:key是路径,value是组件。
一、基本使用
1.安装vue-router,命令:npm i vue-router
2.应用插件:Vue.use(VueRouter)
3.编写router配置项

<!-- !该文件专门用于创建整个应用的路由器 --> import VueRouter from "vue-router"; <!-- !引入路由组件 --> import About from '../components/About' import Home from '../components/Home' <!-- !创建并暴露一个路由器,去管理一组一组的路由规则 --> export default new VueRouter({ routes:[ { path:'/about', component:About }, { path:'/home', component:Home }, ] })
4.实现切换(active-class可配置高亮样式)
<router-link active-class="active" to="/about">About</router-link>
5.指定展示位置
<router-view></router-view>
二、几个注意点
1.路由组件通常存放在pages文件夹,一般组件通常存放在components文件夹。
2.通过切换,‘隐藏’了的路由组件,默认是被销毁掉的,需要的时候再去挂载
3.每个组件都有组件的$route睡醒,里面存储着组件的路由消息。
4.整个应用只有一个router,可以通过组件的$router属性获取到
三、多级路由(嵌套路由)
1.配置路由规则,使用children配置项

<!-- !创建并暴露一个路由器 --> export default new VueRouter({ routes:[ { path:'/about', component:About }, { path:'/home', component:Home, children:[ //通过childrend配置子级路由 { path:'news', //二级路由不能加路径/ component:News, }, { path:'message', //二级路由不能加路径/ component:Message, }, ] }, ] })
2.跳转(要写完整路径)
<router-link to="/home/message">Message</router-link>
四、路由的query参数
1.传递参数

<!-- !跳转路由并携带query参数,to的字符串写法 -->
<router-link :to="`/home/message/detail?id=${m.id}&title=${m.title}`">{{m.title}}</router-link>
<!-- !跳转路由并携带query参数,to的对象写法 -->
<router-link :to="{
path:'/home/message/detail',
query:{
id:m.id,
title:m.title
}
}">
{{m.title}}</router-link>
2.接收参数
$route.query.id
$route.query.title
五、命名路由
1.作用:可以简化路由的跳转
2.如何使用
1.给路由命名:

{ path:'/demo', component:Demo, children:[ { path:'test', //二级路由不能加路径/ component:Test, children:[ { name:'hello', path:'welcome', //二级路由不能加路径/ component:Hello, } ] }, ] },
2.简化跳转

<!-- !简化前,需要写完整路径 -->
<router-link to="/demo/test/welcome">跳转</router-link>
<!-- !简化后,直接通过名字跳转 -->
<router-link :to="{name:'hello'}">跳转</router-link>
<!-- !简化写法配合传递参数 -->
<router-link :to="{
name:'hello',
<!-- //path:'/home/message/detail', -->
query:{
id:m.id,
title:m.title
}
}">
跳转</router-link>
六、路由的params参数
1.配置路由,声明并接收params参数

{ path:'/demo', component:Demo, children:[ { path:'test', //二级路由不能加路径/ component:Test, children:[ { name:'hello', path:'/demo/:id/:title', //使用占位符声明并接收params参数 component:Hello, } ] }, ] },
2.传递参数
路由使用params参数时,若使用to的对象写法,则不能使用path配置项(/aa/bb),必须使用name配置

<!-- !跳转并携带params参数,to的字符串写法 --> <router-link to="/demo/test/welcome/666/你好">跳转</router-link> <!-- !跳转并携带params参数,to 的对象写法 --> <router-link :to="{ name:'hello', //路由使用params参数时,若使用to的对象写法,则不能使用path配置项(/aa/bb),必须使用name配置 query:{ id:m.id, title:m.title } }"> 跳转</router-link>
3.接收参数
$route.params.id
$route.params.title
七、路由的props配置
作用:让路由组件更方便的收到参数

{ path:'message', component:Message, children:[ { name:'xiangqing', path:'detail', //二级路由不能加路径 component:Detail, <!-- !props的第一种写法,值为对象,该对象中的所有key-value都会以props的形式传给Detail组件 --> props:{a:1,b:'hello'} <!-- !props的第二种写法,值为对象,若布尔值为真,就会把路由组件收到的所有params参数,以props的形式传给Detail组件 --> props:true <!-- !props的第三种写法,值为函数,此写法最强大,此处可以解构赋值并连续解构赋值 --> props({$route}){ return { id:$route.query.id, title:$route.query.title } } } ] },
八、<router-link>的replace属性
1.作用:控制路由器跳转时操作浏览器历史记录的模式
2.浏览器的历史记录有两种写入方式:分别为push和replace,push是追加历史记录,replace是替换当前的记录,路由跳转时候默认为push
3.如何开启replace模式<router-link replace ...>News</router-link>
九、编程时路由导航
1.作用:不借助<router-link>实现路由跳转,让路由跳转更加灵活
2.具体编码

<!-- !$router的两个API --> this.$router.push({ name:'xiangqing', //使用params参数不允许使用path配置项 query:{ id:m.id, title:m.title } }) this.$router.replace({ name:'xiangqing', //使用params参数不允许使用path配置项 query:{ id:m.id, title:m.title } }) <!-- !$router的另外三个API --> 前进 back(){ this.$router.back() }, 后退 forward(){ this.$router.forward() }, 可前进也可后退 test(){ this.$router.go(+3) }
洗尽铅华始见金,褪去浮华归本真



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号