hashlib模块
# hash 对不可变的数据(int str bool tuple)进行哈希算法.
# 将数据 str tuple 转化成等长度的一串数字。
print(hash('fdsaf')) #-6093672036167375890 print(hash('alex')) #-6445252693057063416 print(hash('wusir')) #7049968618054091070 print(hash(1)) #1
# hashlib 模块
# 加密模块,摘要算法。 # 它里面包含的加密算法非常多:MD5 sha。 ''' alex|alex3714_nb 太白|hao123_nb '''
import hashlib ret = hashlib.md5() # 产生一个hashlib的md5的一个对象 ret.update('alex'.encode('utf-8')) #这个对象里面的update对alex加密 print(ret.hexdigest()) #消化 16进制 这样就出来了加密的结果 ##534b44a19bf18d20b71ecc4eb77c572f
用途:
# 1,对密码进行加密。
# 2,文件的校验
MD5加密:
# 1,对密码进行加密。(md5)
# a,普通加密 # 写一个空的register文件 import hashlib def encryption(password): #给password加密 ret = hashlib.md5() ret.update(password.encode('utf-8')) return ret.hexdigest() def register(): username = input('>>>') password = input('>>>') password = encryption(password) #把password传进去,得出来是密文的,赋值给左右的password变量名 with open('register', encoding='utf-8', mode='a') as f1: #写到register文件里面 f1.write('{}|{}\n'.format(username, password)) register() # 那怎么校验呢? # 输入密码,你也MD5,数据库取出来一匹配,一样,那就证明密码是一致的。
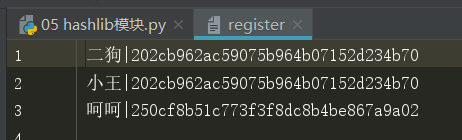
# b, 加固定盐。 ''' dsaflsak@123213OHJ123 #简单密码普遍存在: 123456 111111 666666 .... ''' import hashlib ret = hashlib.md5('老男孩教育'.encode('utf-8')) ret.update('alex3714'.encode('utf-8')) print(ret.hexdigest()) #40a2a6182104b181fc32fac0eae2137f
# c 动态加盐。 import hashlib username = 'alex' #这个是输入的,这是写死的 password = 'alex3714' ret = hashlib.md5(username[::2].encode('utf-8')) ret.update('alex3714'.encode('utf-8')) print(ret.hexdigest()) #738a8a4e045770793f3ae23ec895d957
一般加固定盐就行了,金融公司可以会用动态加盐。也可能会用sha算法。
SHA加密
# import hashlib # ret = hashlib.sha1() #sha1 # ret.update('alex'.encode('utf-8')) # print(ret.hexdigest())
# import hashlib # ret = hashlib.sha512() #sha512 # ret.update('fdsklafdsjafklsdajflksdfjsadf'.encode('utf-8')) # print(ret.hexdigest())
# 固定盐动态盐与上面一致。
# 2,文件的校验。
# 比较文件校验1和文件校验2文件是否一致。
# 小文件 直接f1.read import hashlib def file_hashlib(file): ret = hashlib.md5() with open(file, mode='rb') as f1: ret.update(f1.read()) return ret.hexdigest() print(file_hashlib('文件校验1')) print(file_hashlib('文件校验2'))
# 大文件:使用for循环 #推荐 import hashlib def file_hashlib(file): ret = hashlib.md5() with open(file, mode='rb') as f1: for i in f1: ret.update(i) return ret.hexdigest() print(file_hashlib('文件校验1')) print(file_hashlib('文件校验2'))
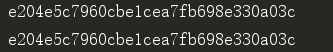
对字符串的叠加update,文件校验
import hashlib s1 = '狗哥,好黑呀,现场怼呀' ret = hashlib.md5() ret.update(s1.encode('utf-8')) print(ret.hexdigest()) # 7bc77d0bc1281428e5c63e628fa40c49 ret = hashlib.md5() ret.update('狗哥'.encode('utf-8')) ret.update(',好黑呀'.encode('utf-8')) ret.update(',现场'.encode('utf-8')) ret.update('怼'.encode('utf-8')) ret.update('呀'.encode('utf-8')) print(ret.hexdigest()) # 7bc77d0bc1281428e5c63e628fa40c49
作者:wangkaiok —— 小菜鸟111
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/wangkaiok/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,但未经作者同意禁止转载,转载必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号