spring boot 业务扩展
1.1 属性赋值问题
1.1.1 业务需求
说明: 如果将配置信息,通过代码的形式写死到代码中,这样的话程序的耦合性高,不便扩展.
需求: 能否为对象的属性,动态赋值.
@RestController //保证返回的数据转化为JSON public class JDBCController { private String username; //定义数据库用户名 private String password; //定义数据库密码 @RequestMapping("/getMsg") public String getMsg() { this.username = "root"; this.password = "root"; return username+"|"+password; } }
1.1.2 @Value方式赋值
1).编辑YML配置文件
# yml配置文件语法 ## 1.key: value k-v结构使用:号(空格)连接 ## 2.YML配置文件有层级关系. ## 3.YML配置文件注意缩进. ## 4.YML文件支持中文.内部编码是utf-8编码 server: port: 8090 # 设定项目发布路径 servlet: context-path: / # /代表缺省值目录 # 在配置文件中添加属性和属性值,为了防止重名发生,则添加前缀区分 jdbc: username: root password: root
2). 编辑JDBCController实现属性赋值
@RestController //保证返回的数据转化为JSON public class JDBCController { //1.需求:利用YML配置文件的信息为属性赋值 //@Value作用: 从spring容器中找到具体的key,为属性赋值. @Value("${jdbc.username}") //spel表达式 spring提供 private String username; //定义数据库用户名 @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; //定义数据库密码 @RequestMapping("/getMsg") public String getMsg() { this.username = "root"; this.password = "root"; return username+"|"+password; } @RequestMapping("/getMsgValue") public String getMsgValue() { return username+"|"+password; } }
1.1.3 批量为属性赋值
1.1.3.1 业务需求
有时某些配置可能需要很多的属性信息.如果这时利用@Value的方式赋值.则必然导致代码冗余.可读性差.
解决方案: 采用批量赋值的方式.

1.1.3.2 添加jar包文件
<!--添加属性注入-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
1.1.3.3 编辑JdbcController2
注意属性的set/get方法
@RestController @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "jdbc") //定义属性的前缀 public class JDBCController2 { //批量为属性赋值时,要求配置文件的属性与类中的属性名称必须一致. 自动的赋值. private String username; //定义数据库用户名 private String password; //定义数据库密码 //为属性赋值时,一定会调用对象的set方法. @RequestMapping("/getMsgPrefix") public String getMsgValue() { return username+"|"+password; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
1.2 指定配置文件为属性赋值
1.2.1 业务说明
YML配置文件是SpringBoot程序的核心文件.在其中添加了整合环境的重要的配置.如果有时需要业务数据进行赋值操作时.最好的方式应该采用properties的方式赋值. (通用!!!)
1.2.2 编辑pro配置文件
注意编码的格式:最好改为utf-8
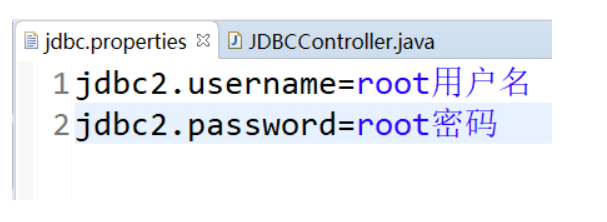
1.2.3 编辑JDBCController
说明:动态引入pro配置文件
@RestController //保证返回的数据转化为JSON //properties与spring容器建立关系,指定pro文件之后,进行加载. 默认的加载策略,采用ISO-8859-1编码 //如果其中包含中文,则应该采用utf-8格式编码. @PropertySource(value = "classpath:/properties/jdbc.properties",encoding = "UTF-8") public class JDBCController { //1.需求:利用YML配置文件的信息为属性赋值 //@Value作用: 从spring容器中找到具体的key,为属性赋值. @Value("${jdbc2.username}") //spel表达式 spring提供 private String username; //定义数据库用户名 @Value("${jdbc2.password}") private String password; //定义数据库密码 @RequestMapping("/getMsg") public String getMsg() { this.username = "root"; this.password = "root"; return username+"|"+password; } @RequestMapping("/getMsgValue") public String getMsgValue() { return username+"|"+password; } }
1.4 关于环境部署问题
在yml配置文件中,切换配置环境,其中---为分隔符
# 设置环境的默认值 spring: profiles: active: test --- # yml配置文件语法 ## 1.key: value k-v结构使用:号(空格)连接 ## 2.YML配置文件有层级关系. ## 3.YML配置文件注意缩进. ## 4.YML文件支持中文.内部编码是utf-8编码 #为环境定义名称 spring: profiles: test server: port: 8080 # 设定项目发布路径 servlet: context-path: / # /代表缺省值目录 # 在配置文件中添加属性和属性值,为了防止重名发生,则添加前缀区分 jdbc: username: root password: root #实现配置文件的分隔 --- spring: profiles: prod server: port: 80 # 设定项目发布路径 servlet: context-path: / # /代表缺省值目录 # 在配置文件中添加属性和属性值,为了防止重名发生,则添加前缀区分 jdbc: username: com.tedu.cn password: tarena
此配置中有两个环境,一:test ,二:prod
1.5 lombok常用注解
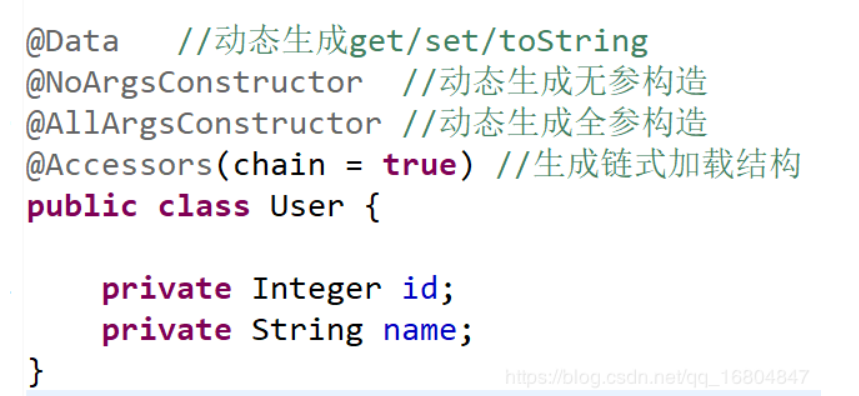
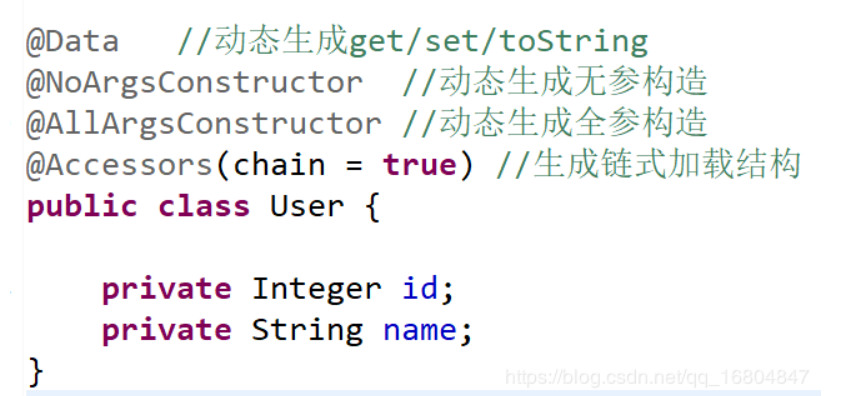
1.5.4 关于LOMBOK面试题
问题: 通过lombok可以添加set/get/toString等方法.但是需要运行环境中添加lom插件才行.如果将来程序在Linux系统中发布.问:是否需要提前安装lombok插件
A.不需要 B 需要 C 不知道/无所谓
解释: LOM插件在编译期生效. IDE工具将.java文件 编译为.class文件时,lombok插件开始工作. 为.class文件动态拼接get/set/toString等方法.所以 当程序在Linux中运行时. xxxx.jar 项目 (.class)文件. 可以直接运行.和lombok是否安装无关.
1.6 springboot整合mybatis时yml文件中的数据源配置
spring: datasource: #driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver 注释 url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jtdb?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&autoReconnect=true&allowMultiQueries=true username: root password: root
数据源配置说明:
serverTimezone=GMT%2B8 设定时区 东8区 %2B ~ +
&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8 设定编码格式
&autoReconnect=true 如果断开链接,是否重连.
&allowMultiQueries=true 是否允许批量操作.
关于配置Mybatis整合关系
mybatis: # 定义别名包 type-aliases-package: com.jt.demo.pojo # 批量导入mapper映射文件 mapper-locations: classpath:/mybatis/mappers/*.xml #开启驼峰映射 configuration: map-underscore-to-camel-case: true




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号