每日总结3.10
Python While 循环语句
Python 编程中 while 语句用于循环执行程序,即在某条件下,循环执行某段程序,以处理需要重复处理的相同任务。其基本形式为:
while 判断条件(condition):
执行语句(statements)……
执行语句可以是单个语句或语句块。判断条件可以是任何表达式,任何非零、或非空(null)的值均为true。
当判断条件假 false 时,循环结束。
执行流程图如下:
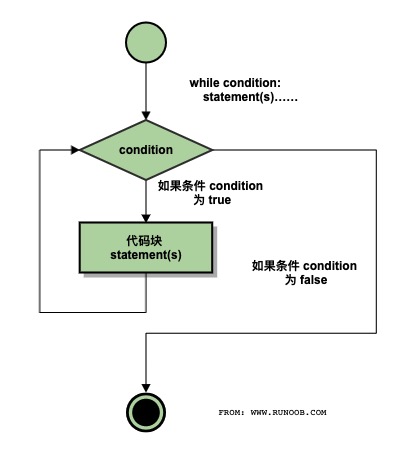
Gif 演示 Python while 语句执行过程

复杂一点:

实例
运行实例 »
以上代码执行输出结果:
The count is: 0
The count is: 1
The count is: 2
The count is: 3
The count is: 4
The count is: 5
The count is: 6
The count is: 7
The count is: 8
Good bye!
while 语句时还有另外两个重要的命令 continue,break 来跳过循环,continue 用于跳过该次循环,break 则是用于退出循环,此外"判断条件"还可以是个常值,表示循环必定成立,具体用法如下:
无限循环
如果条件判断语句永远为 true,循环将会无限的执行下去,如下实例:
实例
以上实例输出结果:
Enter a number :20
You entered: 20
Enter a number :29
You entered: 29
Enter a number :3
You entered: 3
Enter a number between :Traceback (most recent call last):
File "test.py", line 5, in <module>
num = raw_input("Enter a number :")
KeyboardInterrupt
注意:以上的无限循环你可以使用 CTRL+C 来中断循环。
循环使用 else 语句
在 python 中,while … else 在循环条件为 false 时执行 else 语句块:
实例
以上实例输出结果为:
0 is less than 5
1 is less than 5
2 is less than 5
3 is less than 5
4 is less than 5
5 is not less than 5
简单语句组
类似 if 语句的语法,如果你的 while 循环体中只有一条语句,你可以将该语句与while写在同一行中, 如下所示:
实例
注意:以上的无限循环你可以使用 CTRL+C 来中断循环。
Python for 循环语句
Python for循环可以遍历任何序列的项目,如一个列表或者一个字符串。
语法:
for循环的语法格式如下:
for iterating_var in sequence:
statements(s)
流程图:
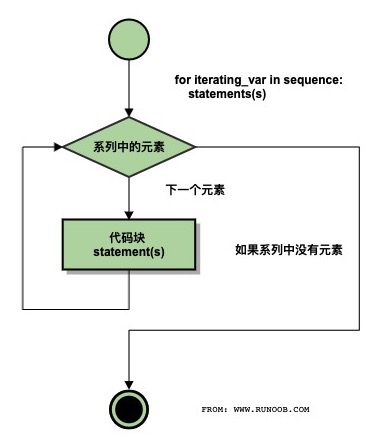
实例:
实例
尝试一下 »
以上实例输出结果:
当前字母 : P
当前字母 : y
当前字母 : t
当前字母 : h
当前字母 : o
当前字母 : n
当前水果 : banana
当前水果 : apple
当前水果 : mango
Good bye!
通过序列索引迭代
另外一种执行循环的遍历方式是通过索引,如下实例:
实例
以上实例输出结果:
当前水果 : banana
当前水果 : apple
当前水果 : mango
Good bye!
以上实例我们使用了内置函数 len() 和 range(),函数 len() 返回列表的长度,即元素的个数。 range返回一个序列的数。
循环使用 else 语句
在 python 中,for … else 表示这样的意思,for 中的语句和普通的没有区别,else 中的语句会在循环正常执行完(即 for 不是通过 break 跳出而中断的)的情况下执行,while … else 也是一样。
实例
尝试一下 »
以上实例输出结果:
10 等于 2 * 5
11 是一个质数
12 等于 2 * 6
13 是一个质数
14 等于 2 * 7
15 等于 3 * 5
16 等于 2 * 8
17 是一个质数
18 等于 2 * 9
19 是一个质数



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号