JAVA博客作业(三)
一、前言
(1)涉及知识点
①abstract抽象类的设计
②接口的使用方法
③comparable类、comparator类、ArrayList arr=new ArrayList();的使用
④加强for循环的使用
(2)题量评估
题集7:一般
题集8:一般
题集9:一般
(3)难度评估
题集7:困难
题集8:困难
题集9:一般
二、设计与分析
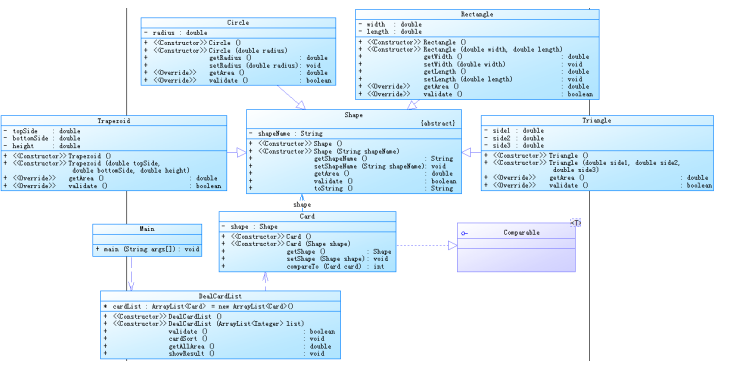
(1)7-1 图形卡片排序游戏(一)&&7-2 图形卡片分组游戏(二)
Comparable接口
Comparable接口在JDK8中的源码:
1 package java.lang; 2 import java.util.*; 3 4 package java.lang; 5 public interface Comparable<T> { 6 public int compareTo(T o); 7 }
int compareTo(T o)
比较此对象与指定对象的顺序。如果该对象小于、等于或大于指定对象,则分别返回负整数、零或正整数。
Comparator类
当元素的类型没有实现java.lang.Comparable接口而又不方便修改代码,或者实现了java.lang.Comparable接口的排序规则不适合当前的操作,那么可以考虑使用Comparator的对象来排序,强行对多个对象进行整体排序的比较。
重写compare(Object o1,Object o2)方法,比较o1和o2的大小:如果方法返回正整数,则表示o1大o2;如果返回0,表示相等;返回负整数,表示o1小于o2。
可以将 Comparator 传递给 sort 方法(如 Collections.sort 或 Arrays.sort),从而允许在排序顺序上实现精确控制。
还可以使用 Comparator 来控制某些数据结构(如有序 set或有序映射)的顺序,或者为那些没有自然顺序的对象 collection 提供排序。
ArrayList<Integer>的使用:
1.添加元素
ArrayList<Integer> list= new ArrayList<Integer>(); list.add(1); list.add(54);
2.最大最小值————— Collections.max(list),mina = Collections.min(list);
3.拷贝
ArrayList<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list2.addAll(list);
4.排序
Collections.sort(list);
5.倒序
Collections.reverse(list);
6.求的某元素首次出现位置
int i = list.indexOf(23);//list中23元素首次出现的位置
8.求和
int sum = 0; for (int i=0;i<list2.size();i++){ sum += list2.get(i); } System.out.println("list2 sum is "+sum); //利用stream求和 List<Integer> ls = new ArrayList<Integer>(); ls.add(43); ls.add(27); int sum2 = ls.stream().mapToInt(a->a).sum(); System.out.println("sum is "+sum2);
设计思路
设计图形抽象类,使其他图形可以继承共同特点,又可对不同之处进行重写:
abstract class Shape{//图形抽象类 private String type; Shape(){} Shape(String type){//构造图形 this.type = type; } public String getType() { return type; } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; } public abstract double getArea();//抽象方法——获得面积 public abstract boolean validate();//抽象方法——获得判断 @Override public String toString() {//返回结果 return this.type; } }
设计具体图形类,并继承图形类
1 class Circle extends Shape { 2 private double r; 3 private double area; 4 Circle(){} 5 Circle(double radius){ 6 this.r = radius; 7 } 8 public double getR() { 9 return r; 10 } 11 public void setR(double r) { 12 this.r = r; 13 } 14 @Override 15 public double getArea() { 16 this.area = r*r*Math.PI; 17 return area; 18 } 19 @Override 20 public boolean validate() { 21 if (r>0){ 22 return true; 23 } 24 else return false; 25 } 26 } 27 class Rectangle extends Shape {//长方形 28 private double length; 29 private double width; 30 private double area; 31 Rectangle(){} 32 Rectangle(double l,double w){ 33 this.length = l; 34 this.width = w; 35 } 36 public void setWidth(double width) { 37 this.width = width; 38 } 39 public void setLength(double length) { 40 this.length = length; 41 } 42 public double getLength() { 43 return length; 44 } 45 public double getWidth() { 46 return width; 47 } 48 49 @Override 50 public double getArea() { 51 this.area = this.length*this.width; 52 return this.area; 53 } 54 @Override 55 public boolean validate() { 56 if (length>0&&width>0){ 57 return true; 58 } 59 else return false; 60 } 61 } 62 class Triangle extends Shape {//三角形 63 private double a; 64 private double b; 65 private double c; 66 Triangle(){} 67 Triangle(double l1,double l2,double l3){ 68 this.a = l1; 69 this.b = l2; 70 this.c = l3; 71 } 72 @Override 73 public double getArea() { 74 double p = 0.5*(a+b+c); 75 double area = p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c); 76 return Math.pow(area,0.5); 77 } 78 79 @Override 80 public boolean validate() { 81 if (a>0&&b>0&&c>0&&(a+b>c&&a+c>b&&b+c>a)){ 82 return true; 83 }else { 84 return false; 85 } 86 } 87 } 88 class Trapezoid extends Shape {//梯形 89 double h; 90 double hl; 91 double dl; 92 Trapezoid(){} 93 Trapezoid(double hl,double dl,double h){ 94 this.hl = hl; 95 this.dl = dl; 96 this.h = h; 97 } 98 @Override 99 public double getArea() { 100 double area = (hl+dl)*h*0.5; 101 return area; 102 } 103 @Override 104 public boolean validate() { 105 if (hl>0&&dl>0&&h>0){ 106 return true; 107 }else 108 return false; 109 } 110 }
创建一个新的类,继承comparable类,用来进行图形的比较:
1 class C implements Comparable<C>{//创建接口(implement) 继承comparable类,重写比较方法 2 private Shape shape; 3 public C(){} 4 public C(Shape shape){ 5 this.shape = shape; 6 } 7 public void setShape(Shape shape) { 8 this.shape = shape; 9 } 10 11 public Shape getShape() { 12 return shape; 13 } 14 15 @Override 16 public int compareTo(C card) { 17 return -(int)(shape.getArea()-card.getShape().getArea()); 18 } 19 }
设计一个类专门负责对输入制的处理,通过调用这个类的创建方法来判断应该创建什么类型的卡片,完成对象的建造,并在这个类中设计相应的值得判断、整体排序、整体面积输出等游戏功能
class DealCardList{ ArrayList<C> cardList =new ArrayList<>(); DealCardList(){} DealCardList(ArrayList<Integer> list){ for(Integer card:list){//便利list数组,将其存入card中 switch (card){//将图形存入cardlist case 1://圆形 double r = work7_1.Game.input.nextDouble(); C card1 = new C(new Circle(r)); card1.getShape().setType("Circle"); cardList.add(card1); break; case 2://矩形 double h = work7_1.Game.input.nextDouble(); double w = work7_1.Game.input.nextDouble(); C card2 = new C(new Rectangle(h,w)); card2.getShape().setType("Rectangle"); cardList.add(card2); break; case 3://三角形 double a = work7_1.Game.input.nextDouble(); double b = work7_1.Game.input.nextDouble(); double c = work7_1.Game.input.nextDouble(); C card3 = new C(new Triangle(a,b,c)); card3.getShape().setType("Triangle"); cardList.add(card3); break; case 4://梯形 double hl = work7_1.Game.input.nextDouble(); double dl = work7_1.Game.input.nextDouble(); double l = work7_1.Game.input.nextDouble(); C card4 = new C(new Trapezoid(hl,dl,l)); card4.getShape().setType("Trapezoid"); cardList.add(card4); break; } } } public boolean validate(){//有效性 for(C card:cardList){ if (!card.getShape().validate()){ return false; } } return true; } public void cardSort(){//做排序 TreeSet<C> cards = new TreeSet<>(cardList); for (C card : cards) { System.out.print(card.getShape()+":"); System.out.printf("%.2f ",card.getShape().getArea()); } } public double getAllArea(){ double sum = 0; for (C card : cardList){ sum+=card.getShape().getArea(); } return sum; } public void showResult(){ System.out.println("The original list:");//大家的面积 for (C card : cardList){ System.out.print(card.getShape()+":"); System.out.printf("%.2f ",card.getShape().getArea()); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("The sorted list:");//排序后的面积 cardSort(); System.out.println(); System.out.printf("Sum of area:%.2f",getAllArea());//要用printf才能使用%.2f } }
在主函数中首先创建ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();用于输入数据的存放,然后进行输入的数据校验,第一次校验合格后在进行下一步卡片的创建。在卡片创建时再对输入的各个参数进行校验,当一切校验完成后再进行相应数值的计算并输出
(2)7-3 ATM机类结构设计(一)&&7-1 ATM机类结构设计(二)
设计思路
设计银行(Bank类),带有银行姓名,ATM列表
设计用户类(Account类),带有用户、账户、密码、金额数。用于虚拟构建一个用户
设计存款机(ATM类)完成对ATM机功能的实现,可进行卡号校验、金额校验、操作校验、余额查询等功能的实现
1 class Bank{ 2 String bankname; 3 ArrayList<String> AList; 4 public Bank(){ 5 } 6 public Bank(String name,ArrayList<String> ATM){ 7 this.bankname = name; 8 this.AList = ATM; 9 } 10 public void setAList(ArrayList<String> AList) { 11 this.AList = AList; 12 } 13 14 public void setBankname(String bankname) { 15 this.bankname = bankname; 16 } 17 18 public String getBankname() { 19 return bankname; 20 } 21 22 public ArrayList<String> getAList() { 23 return AList; 24 } 25 26 } 27 class Account{ 28 private String Uname;//用户 29 private String account;//账户 30 private String password;//账户密码 31 private double money; 32 ArrayList<String> cardList = new ArrayList<>(); 33 public Account(){ 34 } 35 public Account(String name,String account,String password,double money,ArrayList<String> cardList){ 36 this.account = account; 37 this.Uname = name; 38 this.password = password; 39 this.cardList = cardList; 40 this.money = money; 41 } 42 43 public ArrayList<String> getCardList() { 44 return cardList; 45 } 46 47 public double getMoney() { 48 return money; 49 } 50 51 public void setMoney(double money) { 52 this.money = money; 53 } 54 55 public String getAccount() { 56 return account; 57 } 58 59 public String getUname() { 60 return Uname; 61 } 62 63 public String getPassword() { 64 return password; 65 } 66 } 67 class ATM{ 68 69 ArrayList<Account> accountList; 70 ArrayList<Bank> atmList; 71 String card; 72 String password; 73 String Ano; 74 double money; 75 boolean check = false; 76 int location = 0; 77 int Blocation = 0; 78 public ATM(ArrayList<Account> accountList,ArrayList<Bank> ATMList,String card,String password,String no,double money){//更改内容构造向ATM存入数据 79 this.Ano = no; 80 this.accountList = accountList; 81 this.money = money; 82 this.card = card; 83 this.password = password; 84 this.atmList = ATMList; 85 } 86 public ATM(ArrayList<Account> accountList,String card){//查看金额构造 87 this.accountList = accountList; 88 this.card = card; 89 } 90 91 public void setAno(String ano) { 92 Ano = ano; 93 } 94 95 public String getAno() { 96 return Ano; 97 } 98 public void CheckATMno(){//ATM编号校验 99 int i; 100 int j; 101 int flag = 0; 102 for(i = 0;i<atmList.size();i++){ 103 for (j=0;j<atmList.get(i).getAList().size();j++){ 104 if (Ano.equals(atmList.get(i).getAList().get(j))){ 105 flag = 1; 106 Blocation = i; 107 break; 108 } 109 } 110 if (flag == 1){ 111 break; 112 } 113 } 114 if (flag==0){//没找到 115 System.out.println("Sorry,the ATM's id is wrong."); 116 check = false; 117 } 118 } 119 public void CheckUser(){//用户校验(卡号存在性) 120 int i; 121 int j; 122 for (i=0;i<accountList.size();i++){//账号是否存在 123 for (j = 0;j<accountList.get(i).getCardList().size();j++) { 124 if (card.equals(accountList.get(i).getCardList().get(j))) { 125 check = true; 126 this.location = i; 127 break; 128 } 129 } 130 if (check == true){ 131 break; 132 } 133 }if(check == false) {//没找到卡号 134 System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist."); 135 } 136 } 137 public void CheckKey() {//密码校验 138 if (check == true) { 139 if (!password.equals(accountList.get(location).getPassword())) {//密码错误 140 System.out.println("Sorry,your password is wrong."); 141 check = false; 142 } 143 } 144 } 145 public boolean CheckMoney(){//金额校验 146 if (money>0&&(accountList.get(location).getMoney()-money)<0){ 147 System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); 148 return false; 149 }else return true; 150 } 151 public void UserChange(){//用户操作 152 double exMoney = accountList.get(location).getMoney()-money; 153 accountList.get(location).setMoney(exMoney); 154 } 155 public void moneyCheck(){//金额查询 156 System.out.printf("¥%.2f\n",accountList.get(location).getMoney()); 157 } 158 public void CheckCrossBank(){//跨行校验,05、06号机器——中国工商 159 160 } 161 public void menu(){ 162 if(money<0) { 163 System.out.printf(accountList.get(location).getUname() + "在" + atmList.get(Blocation).getBankname() + "的" + Ano + "号ATM机上存款¥%.2f\n",Math.abs(money)); 164 }else { 165 System.out.printf(accountList.get(location).getUname() + "在" + atmList.get(Blocation).getBankname() + "的" + Ano + "号ATM机上取款¥%.2f\n",money); 166 } 167 System.out.printf("当前余额为¥%.2f\n",accountList.get(location).getMoney()); 168 } 169 }
主函数部分:
首先要进行数据的存储。运用ArrayList<String>a= new ArrayList<>()的功能,完成如ATM机号列表、卡号账户列表的创建。再使用ArrayList<类>= new ArrayList<>(),将其中的类替换为银行类/用户类,即可再创建出相应的类列表,作为数据库,方便后期的查找校验。

功能部分,首先对输入进行判断,再调用ATM相关校验函数完成用户相应操作
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); String uinput; uinput = scanner.nextLine(); while (!uinput.equals("#")){ String[] user=uinput.split("\\s+"); if (user.length==1){//只查看存款 ATM atm1 = new ATM(Account,user[0]); atm1.CheckUser(); atm1.moneyCheck(); }else if (user.length!=1){// ATM atm2 = new ATM(Account,ATMList,user[0],user[1],user[2],Double.parseDouble(user[3])); atm2.CheckUser();//检验账户存在问题 atm2.CheckKey();//检验密码 atm2.CheckATMno();//校验ATM编号是否存在 if (atm2.check == true) {//卡号存在、密码正确、ATM编号正确——进行存取操作 if (atm2.CheckMoney()==true){//钱数充足 atm2.UserChange(); atm2.menu(); } } } uinput = scanner.nextLine(); }
第二次ATM实验在原有基础上进行改动,相对简单不少,基于原有的类形式仅增加了税率属性设置,更改了菜单的样式。在本次作业中修补了原先无法实现跨行检测的bug。
增添功能:
①透支操作
public boolean TzChange(){//透支操作 double tMoney = Math.abs(money-accountList.get(location).getMoney()); double sxMoney = 0; if (tMoney<50000) {//可以透支 if (accountList.get(location).getMoney()<=0){//没有余额 sxMoney=money*tCharge; }else {//有余额 sxMoney=tMoney*tCharge; } accountList.get(location).setMoney(-(tMoney+sxMoney+cCharge)); return true; }else {//违规透支 return false; } }
②税率设置
public Bank(String name,ArrayList<String> ATM,double charge){ this.bankname = name; this.AList = ATM; this.charge = charge;//新增税率设置 }
三、踩坑心得
①起初不了解ArrayList<>类、加强for循环的使用环境与方法的很多功能,在实际项目中使用后发现是真的好用
②类的设计不够好,部分功能没有进行准确的封装,比如在写ATM管理的题目时,基本对原先的功能如金额校验等进行了重写。
四、改进建议
①ATM机的题还应该再次对ATM类进行修改,,目前的功能实现都是由主函数直接调用ATM中的功能。应该争取将主函数中的判断部分都交由ATM实行,仅在主函数中仅构造出一个ATM就可以完成全部工作。
五、总结
这三次作业的题量整体是不多的,难得主要是对所有学过的知识的综合运用,很多时候编程都存在着拿不准应该使用什么结构,运用什么类更合适的问题,大部分的作业还需要去借鉴CSDN上的思路才完成。个人独立编写程序的能力还有很大的提升空间。在试验时也发现自己对于虚拟类的使用以及各种继承、重写、接口的使用方法都不是很了解,还需要在这些方面进行提升,


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号