JAVA博客作业(二)
一、前言
(1)所涉及知识点
①字符串的使用、正则表达式的使用(4.7-1、6.7-1、6.7-2、6.7-3、6.7-4)
②聚合设计(4.7-2、5.7-5)
③继承、封装、多态(4.7-3、6.7-5、6.7-6)
④JAVA集合框架的应用(5.7-4)
⑤排序算法(5.7-2、5.7-3)
(2)题量评估:
题集4:3道 - - - - - - - - - - 较少
题集5:4道 - - - - - - - - - - 较少
题集6:6道 - - - - - - - - - - 一般
(3)难度评估
题集4:3道 - - - - - - - - - - 困难
题集5:4道 - - - - - - - - - - 较难
题集6:6道 - - - - - - - - - - 一般
二、设计与分析
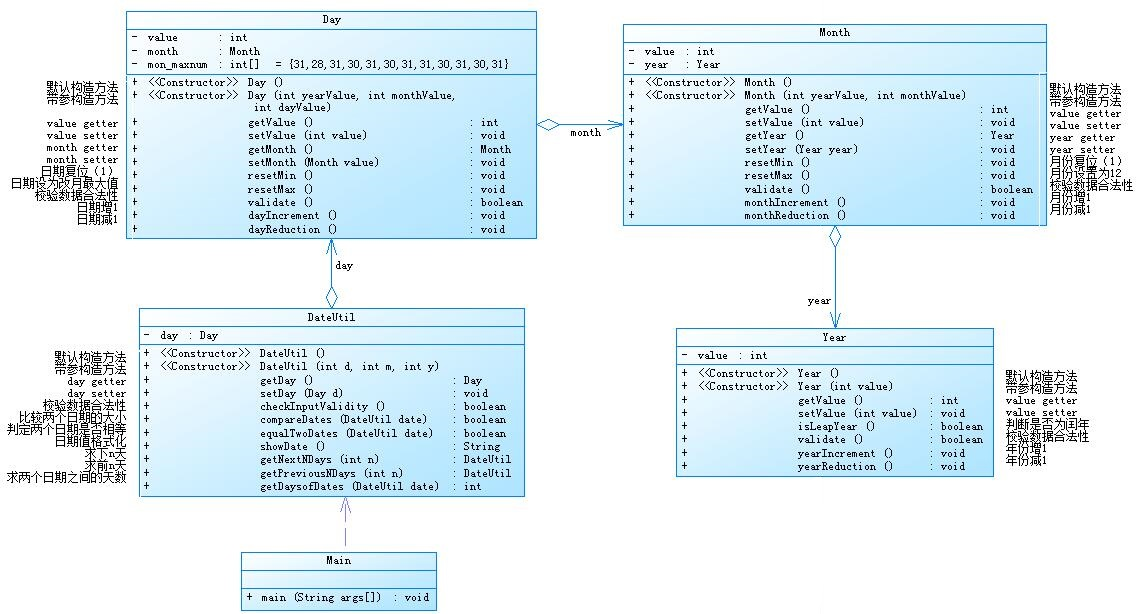
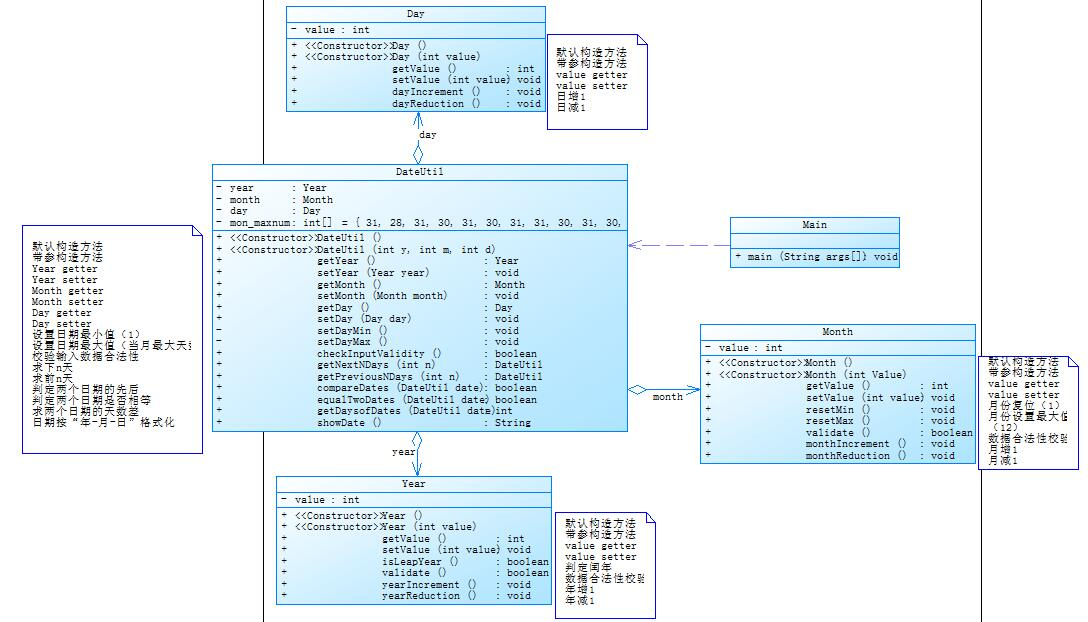
(1)日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)VS 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)
(聚合一)
1 class Dateutil{ 2 Day day; 3 int flag=0; 4 public Dateutil() { 5 6 } 7 public Dateutil(int d,int m,int y) { 8 this.day = new Day(y,m,d); 9 } 10 public void setDay(Day d) 11 { 12 this.day=d; 13 14 } 15 public Day getDay() 16 { 17 return day; 18 } 19 20 public boolean checkInputValidity() 21 { 22 if(day.validate()&&day.month.validate()&&day.month.year.validate()) 23 return true; 24 else 25 return false; 26 } 27 public boolean compareDates(Dateutil date) 28 { 29 if(day.month.year.value>date.day.month.year.value) 30 return true; 31 else if(day.month.year.value==date.day.month.year.value) 32 { 33 if(day.month.value>date.day.month.value) 34 return true; 35 else if(day.month.value==date.day.month.value) 36 { 37 if(day.value>date.day.value) 38 return true; 39 else if(day.value<date.day.value) 40 return false; 41 } 42 else 43 { 44 return false; 45 } 46 } 47 else 48 { 49 return false; 50 } 51 return false; 52 } 53 public boolean equalTwoDates(Dateutil date) 54 { 55 if(day.month.year.value==date.day.month.year.value&&day.month.value==date.day.month.value&&day.value==date.day.value) 56 return true; 57 else 58 return false; 59 } 60 public String showDate() 61 { 62 String abc=null; 63 abc=String.format("%d-%d-%d",day.month.year.value,day.month.value,day.value); 64 return abc; 65 } 66 public Dateutil getNextNDays(int n) 67 { 68 int i=0; 69 while(i!=n) 70 { 71 if(day.month.year.isLeapYear()) 72 { 73 day.mon_maxnum[1]=29; 74 } 75 else 76 { 77 day.mon_maxnum[1]=28; 78 } 79 day.dayIncrement(); 80 if(day.value==day.mon_maxnum[day.month.value-1]+1) 81 { 82 day.month.value++; 83 day.resetMin(); 84 } 85 if(day.month.value==13) 86 { 87 day.month.year.value++; 88 day.month.resetMin(); 89 } 90 i++; 91 } 92 return null; 93 } 94 public Dateutil getpreviousNDays(int n) 95 { 96 97 int i=0; 98 while(i!=n) 99 { 100 if(day.month.year.isLeapYear()) 101 { 102 day.mon_maxnum[1]=29; 103 } 104 else 105 { 106 day.mon_maxnum[1]=28; 107 } 108 day.dayReduction(); 109 if(day.value==0) 110 { 111 day.month.value--; 112 113 if(day.month.value==0) 114 { 115 day.month.year.value--; 116 day.month.resetMax(); 117 } 118 day.resetMax(); 119 } 120 i++; 121 } 122 return null; 123 } 124 public int getDaysofDates(Dateutil date) 125 { 126 int x=0,y1 = 0,y2=0,z1=0,z2=0,m=0,n=0; 127 128 if(equalTwoDates(date)) 129 { 130 return 0; 131 } 132 else 133 { 134 if(compareDates(date)) { 135 x=Math.abs(day.month.year.value-date.day.month.year.value); 136 m=x/4; 137 if (date.day.month.year.value == 1900 && !date.compareDates(new Dateutil(1900,2,28))) { 138 m--; 139 } 140 for(int i=0;i<day.month.value-1;i++) 141 { 142 y1=y1+day.mon_maxnum[i]; 143 } 144 for(int i=0;i<date.day.month.value-1;i++) 145 { 146 y2=y2+date.day.mon_maxnum[i]; 147 } 148 z1=y1+day.value; 149 z2=y2+date.day.value; 150 n=365*x+m+(z1-z2); 151 }else { 152 x=Math.abs(day.month.year.value-date.day.month.year.value); 153 m=x/4; 154 155 if (day.month.year.value == 1900 && !compareDates(new Dateutil(1900,2,28))) { 156 m--; 157 } 158 for(int i=0;i<day.month.value-1;i++) 159 { 160 y1=y1+day.mon_maxnum[i]; 161 } 162 for(int i=0;i<date.day.month.value-1;i++) 163 { 164 y2=y2+date.day.mon_maxnum[i]; 165 } 166 z1=y1+day.value; 167 z2=y2+date.day.value; 168 n=365*x+m+(z2-z1); 169 } 170 171 172 } 173 return n; 174 } 175 } 176 177 class Day 178 { 179 int value; 180 Month month; 181 int mon_maxnum[]= {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 182 public Day() { 183 184 } 185 186 public Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue) { 187 this.month=new Month(yearValue,monthValue); 188 this.value=dayValue; 189 190 191 } 192 public void setValue(int value) 193 { 194 this.value=value; 195 } 196 public int getValue() 197 { 198 return value; 199 } 200 public void setMonth(Month value) 201 { 202 this.month=value; 203 } 204 public Month getMonth() 205 { 206 return month; 207 } 208 public void resetMin() 209 { 210 value=1; 211 } 212 public void resetMax() 213 { 214 value=mon_maxnum[month.value-1]; 215 } 216 public boolean validate() 217 { 218 if(value<1||value>31) 219 return false; 220 else 221 { 222 if(month.year.isLeapYear()) 223 { 224 if((month.value==2&&value>29)||(month.value==4&&value>30)||(month.value==6&&value>30)||(month.value==9&&value>30)||(month.value==11&&value>30)) 225 return false; 226 227 } 228 else 229 { 230 if((month.value==2&&value>28)||(month.value==4&&value>30)||(month.value==6&&value>30)||(month.value==9&&value>30)||(month.value==11&&value>30)) 231 return false; 232 } 233 } 234 return true; 235 } 236 public void dayIncrement() 237 { 238 value=value+1; 239 } 240 public void dayReduction() 241 { 242 value=value-1; 243 } 244 245 } 246 class Month 247 { 248 int value; 249 Year year; 250 public Month() 251 { 252 253 } 254 public Month(int yearValue,int monthValue) 255 { 256 this.year= new Year(yearValue); 257 this.value=monthValue; 258 } 259 public void setValue(int value) 260 { 261 this.value=value; 262 } 263 public int getValue() 264 { 265 return value; 266 } 267 public void setYear(Year year) 268 { 269 this.year=year; 270 } 271 public Year getyear() 272 { 273 return year; 274 } 275 public void resetMin() 276 { 277 value=1; 278 } 279 public void resetMax() 280 { 281 value=12; 282 } 283 public boolean validate() 284 { 285 if(value<1||value>12) 286 return false; 287 else 288 return true; 289 } 290 public void monthIncrement() 291 { 292 value=value+1; 293 } 294 public void monthReduction() 295 { 296 value=value-1; 297 } 298 } 299 class Year{ 300 int value; 301 public Year() 302 {} 303 public Year(int value) 304 { 305 this.value=value; 306 } 307 public void setvalue(int value) 308 { 309 this.value=value; 310 } 311 public int getvalue() 312 { 313 return value; 314 } 315 316 public boolean isLeapYear() 317 { 318 if((value%4==0)&&(value%100!=0)||value%400==0) 319 return true; 320 return false; 321 } 322 public boolean validate() 323 { 324 325 if(value<1900||value>2050) 326 return false; 327 else 328 return true; 329 } 330 public void yearIncrement() 331 { 332 value = value+1; 333 } 334 public void yearReduction() 335 { 336 value = value-1; 337 }
(聚合二)
1 class Year { 2 private int value = 0; 3 4 public Year() { 5 6 } 7 8 public Year(int value) { 9 this.value = value; 10 } 11 12 public void setValue(int value) { 13 this.value = value; 14 } 15 16 public int getValue() { 17 return this.value; 18 } 19 20 public boolean isLeapYear() { 21 if (this.value % 400 == 0 || this.value % 4 == 0 && this.value % 100 != 0) { 22 return true; 23 } else { 24 return false; 25 } 26 } 27 28 public boolean validate() { 29 if (this.value < 1820 || this.value > 2020) { 30 return false; 31 } else { 32 return true; 33 } 34 } 35 36 public void yearIncrement() {// 年份加一 37 this.value++; 38 } 39 40 public void yearReduction() {// 年份减一 41 this.value--; 42 } 43 44 } 45 46 class Month { 47 private int value = 0; 48 49 public Month() { 50 51 } 52 53 public Month(int value) { 54 this.value = value; 55 } 56 57 public void setValue(int value) { 58 this.value = value; 59 } 60 61 public int getValue() { 62 return this.value; 63 } 64 65 public void resetMin() { 66 this.value = 1; 67 } 68 69 public void resetMax() { 70 this.value = 12; 71 } 72 73 public boolean validate() { 74 if (this.value < 1 || this.value > 12) { 75 return false; 76 } else { 77 return true; 78 } 79 } 80 81 public void monthIncrement() {// 月份加一 82 if (this.value == 12) { 83 this.value = 1; 84 } else { 85 this.value++; 86 } 87 } 88 89 public void monthReduction() {// 月份减一 90 if (this.value == 1) { 91 this.value = 12; 92 } else { 93 this.value--; 94 } 95 } 96 97 } 98 99 class Day { 100 private int value = 0; 101 102 public Day() { 103 104 } 105 106 public Day(int value) { 107 this.value = value; 108 } 109 110 public void setValue(int value) { 111 this.value = value; 112 } 113 114 public int getValue() { 115 return this.value; 116 } 117 118 public void dayIncrement() { 119 this.value++; 120 } 121 122 public void dayReduction() { 123 this.value--; 124 } 125 } 126 127 class DateUtil { 128 private Year year = new Year(); 129 private Month month = new Month(); 130 private Day day = new Day(); 131 private int[] mon_maxnum = { 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 }; 132 133 public DateUtil() { 134 135 } 136 137 public DateUtil(int year, int month, int day) { 138 this.year.setValue(year); 139 this.month.setValue(month); 140 this.day.setValue(day); 141 } 142 143 public void setYear(Year year) { 144 this.year = year; 145 } 146 147 public Year getYear() { 148 return this.year; 149 } 150 151 public void setMonth(Month month) { 152 this.month = month; 153 } 154 155 public Month getMonth() { 156 return this.month; 157 } 158 159 public void setDay(Day day) { 160 this.day = day; 161 } 162 163 public Day getDay() { 164 return this.day; 165 } 166 167 public void setDayMin() { 168 this.day.setValue(1); 169 } 170 171 public void setDayMax() { 172 if (this.year.isLeapYear() && this.month.getValue() == 2) { 173 this.day.setValue(29); 174 } else { 175 this.day.setValue(this.mon_maxnum[this.month.getValue() - 1]); 176 } 177 } 178 179 public boolean checkInputValidity() {// 校验输入数据合法性 180 int[] day = {31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; 181 boolean flag = true; 182 if (this.month.validate() && this.year.validate()) { 183 if (this.year.isLeapYear()) {// 闰年 184 if(this.day.getValue() < 1 || this.day.getValue() > day[this.month.getValue() - 1]) { 185 flag = false; 186 } 187 else { 188 flag = true; 189 } 190 } else {// 非闰年 191 if(this.day.getValue() < 1 || this.day.getValue() > this.mon_maxnum[this.month.getValue()]) { 192 flag = false; 193 } 194 else { 195 flag = true; 196 } 197 198 } 199 } 200 else { 201 flag = false; 202 } 203 return flag; 204 205 } 206 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) {// 取得year-month-day的下n天日期 207 int num = 0;// 计算天数 208 int m = 0; 209 int[] theyear = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 }; 210 if (Math.abs(this.day.getValue() + n) <= theyear[this.month.getValue()]) {// 即不满本月 211 this.day.setValue(this.day.getValue() + n); 212 } else { 213 m = theyear[this.month.getValue()] - this.day.getValue(); 214 n = n - m;// 从月末开始计算 215 num = n % 1000; 216 n = n - n % 1000; 217 this.month.monthIncrement();// 月份加一 218 do { 219 if (this.month.getValue() == 2) { 220 if (this.year.isLeapYear()) { 221 theyear[this.month.getValue()] = 29; 222 } else { 223 theyear[this.month.getValue()] = 28; 224 } 225 } 226 if (num > theyear[this.month.getValue()]) { 227 num = num - theyear[this.month.getValue()]; 228 this.month.monthIncrement();//月份加一 229 if(this.month.getValue() == 1) { 230 this.year.yearIncrement(); 231 } 232 } 233 234 } while (num > theyear[this.month.getValue()]); 235 num = num + n; 236 do { 237 if (this.month.getValue() == 2) { 238 if (this.year.isLeapYear()) { 239 theyear[this.month.getValue()] = 29; 240 } else { 241 theyear[this.month.getValue()] = 28; 242 } 243 } 244 if (num > theyear[this.month.getValue()]) { 245 num = num - theyear[this.month.getValue()]; 246 this.month.monthIncrement();//月份加一 247 if(this.month.getValue() == 1) { 248 this.year.yearIncrement(); 249 } 250 } 251 } while (num > theyear[this.month.getValue()]); 252 if (num == 0) { 253 num = 1; 254 } 255 this.day.setValue(num); 256 } 257 DateUtil obj = new DateUtil(); 258 obj.setDay(this.day); 259 obj.setMonth(this.month); 260 obj.setYear(this.year); 261 return obj; 262 } 263 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) {// 取得year-month-day的前n天日期 264 int[] theyear = { 0, 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 }; 265 if (this.day.getValue() > n) { 266 this.day.setValue(this.day.getValue() - n); 267 } else { 268 int num = 0; 269 int year = this.year.getValue(); 270 int m = this.month.getValue() - 1; 271 if (m == 0) { 272 m = 12; 273 year --; 274 this.year.setValue(year); 275 } 276 num = n - this.day.getValue(); 277 this.day.setValue(1); 278 do { 279 if (m == 2 && this.year.isLeapYear()) { 280 theyear[m] = 29; 281 } 282 if (m == 2 && !this.year.isLeapYear()) { 283 theyear[m] = 28; 284 } 285 286 if (num > theyear[m]) { 287 num = num - theyear[m]; 288 m--; 289 if (m == 0) { 290 year --; 291 this.year.setValue(year); 292 m = 12; 293 } 294 } 295 296 } while (num > theyear[m]); 297 num = theyear[m] - num; 298 this.day.setValue(num); 299 this.month.setValue(m); 300 if (m == 0) { 301 m = 12; 302 year--; 303 this.year.setValue(year); 304 } 305 this.month.setValue(m); 306 this.year.setValue(year); 307 } 308 DateUtil obj = new DateUtil(); 309 obj.setDay(this.day); 310 obj.setMonth(this.month); 311 obj.setYear(this.year); 312 return obj; 313 } 314 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) {// 比较两日期的大小 315 boolean flag = true;// 当前日期先为true否则为false 316 if (this.year.getValue() > date.year.getValue()) { 317 flag = true; 318 } 319 if (this.year.getValue() < date.year.getValue()) { 320 flag = false; 321 } 322 if (this.year.getValue() == date.year.getValue()) { 323 if (this.month.getValue() > date.month.getValue()) { 324 flag = true; 325 } 326 if (this.month.getValue() < date.month.getValue()) { 327 flag = false; 328 } 329 if (this.month.getValue() == date.month.getValue()) { 330 if (this.day.getValue() >= date.day.getValue()) { 331 flag = true; 332 } else { 333 flag = false; 334 } 335 } 336 } 337 return flag; 338 } 339 340 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {// 判断两个日期是否相等 341 if (this.year.getValue() == date.year.getValue() 342 && this.month.getValue() == date.month.getValue() 343 && this.day.getValue() == date.day.getValue()) { 344 return true; 345 } else { 346 return false; 347 } 348 } 349 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) {// 求当前日期与date之间相差的天数 350 int[] year1 = { 0, 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };// 闰年情况 351 int[] year2 = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };// 非闰年情况 352 int i = 0, num = 0, daynum = 0; 353 int num1 = 0, num2 = 0, numa = 0, numb = 0, numx = 0, numy = 0; 354 if (equalTwoDates(date)) { 355 return num = 0; 356 } else { 357 if (compareDates(date)) {// 后面日期为num1 358 num1 = this.year.getValue(); 359 numa = this.month.getValue(); 360 numx = this.day.getValue(); 361 num2 = date.year.getValue(); 362 numb = date.month.getValue(); 363 numy = date.day.getValue(); 364 } else { 365 num1 = date.year.getValue(); 366 numa = date.month.getValue(); 367 numx = date.day.getValue(); 368 num2 = this.year.getValue(); 369 numb = this.month.getValue(); 370 numy = this.day.getValue(); 371 } 372 for (i = 1; i <= numa; i++) {// 计算大的日期距该年年初的日期时长 373 this.year.setValue(num1); 374 if (this.year.isLeapYear()) { 375 if (i != numa) { 376 num = num + year1[i]; 377 } 378 if (i == numa) { 379 num = num + numx; 380 } 381 } else { 382 if (i != numa) { 383 num = num + year2[i]; 384 } 385 if (i == numa) { 386 num = num + numx; 387 } 388 } 389 } 390 for (i = num2; i < num1; i ++) { 391 this.year.setValue(i); 392 if (this.year.isLeapYear()) { 393 num = num + 366; 394 } else { 395 num = num + 365; 396 } 397 } 398 for (i = 1; i <= numb; i++) {// 计算前面的日期距年初的时间 399 this.year.setValue(num2); 400 if (this.year.isLeapYear()) { 401 if (i != numb) { 402 daynum = daynum + year1[i]; 403 } 404 if (i == numb) { 405 daynum = daynum + numy; 406 } 407 } else { 408 if (i != numb) { 409 daynum = daynum + year2[i]; 410 } 411 if (i == numb) { 412 daynum = daynum + numy; 413 } 414 } 415 } 416 num = num - daynum; 417 } 418 return num; 419 } 420 public String showDate() {// 格式化日期 421 return this.year.getValue() + "-" + this.month.getValue() + "-" 422 + this.day.getValue(); 423 } 424 425 }
比较:
聚合一仅仅是将类堆叠在一起,并未形成相互之间的声明、调用关系,在聚合二中对类进行了单独明确的声明
(2)图形继承——图形继承与多态——实现图形接口及多态性
封装:是指利用抽象数据类型将数据和基于数据的操作封装在一起,使其构成一个不可分割的独立实体,数据被保护在抽象数据类型的内部,尽可能地隐藏内部的细节,只保留一些对外接口使之与外部发生联系。
语法:private _____ ______ ;
好处:
1、良好的封装能够减少耦合。
2、类内部的结构可以自由修改。
3、可以对成员进行更精确的控制。
4、隐藏信息,实现细节。
继承: 继承是使用已存在的类的定义作为基础建立新类的技术,新类的定义可以增加新的数据或新的功能,也可以用父类的功能,但不能选择性地继承父类。
语法:extend
好处:
1、方便代码复用
2、提高效率
注意:
1、子类拥有父类非private的属性和方法。
2、子类可以拥有自己属性和方法,即子类可以对父类进行扩展。
3、子类可以用自己的方式实现父类的方法。(重写)
多态:指程序中定义的引用变量所指向的具体类型和通过该引用变量发出的方法调用在编程时并不确定,而是在程序运行期间才确定,即一个引用变量倒底会指向哪个类的实例对象,该引用变量发出的方法调用到底是哪个类中实现的方法,必须在由程序运行期间才能决定。
Java实现多态有三个必要条件:继承、重写、向上转型。
继承:在多态中必须存在有继承关系的子类和父类。
重写:子类对父类中某些方法进行重新定义,在调用这些方法时就会调用子类的方法。
向上转型:在多态中需要将子类的引用赋给父类对象,只有这样该引用才能够具备技能调用父类的方法和子类的方法。
代码中涉及的一些新的类与方法:
dateutil()——日期工具类
math.abs()——取值为非负数
题目总结:由思考如何设计一个公用的父类使各个图形可以继承——精简父类,让子类重写父类部分功能,提现子类的意义——封装留下接口,遵循开放封闭原则
(3)正则表达式技术分析&总结
符号使用:
. 匹配除换行符以外的任意字符
\w 匹配字母或数字或下划线或汉字
\s 匹配任意的空白符
\d 匹配数字
\b 匹配单词的开始或结束
^ 匹配字符串的开始(在集合字符里[^a]表示非(不匹配)的意思
$ 匹配字符串的结束
懒惰字符:
| *? | 重复任意次,但尽可能少重复 |
| +? | 重复1次或更多次,但尽可能少重复 |
| ?? | 重复0次或1次,但尽可能少重复 |
| {n,m}? | 重复n到m次,但尽可能少重复 |
| {n,}? | 重复n次以上,但尽可能少重复 |
代码中涉及的一些类
String与StringBuild类的区别:
String 类型和 StringBuffer 类型的主要性能区别其实在于 String 是不可变的对象, 因此在每次对 String 类型进行改变的时候其实都等同于生成了一个新的 String 对象,然后将指针指向新的 String 对象,这样不仅效率低下,而且大量浪费有限的内存空间,所以经常改变内容的字符串最好不要用 String 。
Pattern类:
Pattern类的作用在于编译正则表达式后创建一个匹配模式
Matcher类使用Pattern实例提供的模式信息对正则表达式进行匹配
将String转换为ParseDouble与valueOf的差别:
Double.parseDouble(java.lang.String)的参数只能是String,如果参数改为double类型提示“The method parseDouble(String) in the type Double is not applicable for the arguments (double)”错误。
Double.valueOf()的参数类型可以是浮点型或者是字符串均可。
toCharArray() 方法
将字符串转换为字符数组
Arrays.sort()方法
是对括号中的数组进行排序,时间复杂度O(n*logn),方法返回值为void。 是在原来数组的空间基础上进行升序排序,因此不需要定义一个数组接收它,即不需要返回值。
校验QQ号:
1 public static void check(String a){ 2 if(a.length()>4&&a.length()<16&&a.matches("([1-9][0-9]{4,15})")) 3 { 4 System.out.print("你输入的QQ号验证成功"); 5 } 6 else 7 System.out.print("你输入的QQ号验证失败"); 8 }
验证码校验:
public static void check(String a){ if(a.length()==4&&a.matches("[\\p{Alnum}]")) { System.out.print(a+"属于验证码"); } else System.out.print(a+"不属于验证码");
学号校验
public static void check(String a){ if(a.matches("2020(1[1-7]|61|7[1-3]|8[1-2])(0[1-9]|[1-4][0-9])")) { System.out.print("正确"); } else System.out.print("错误"); }
水文校验格式:
String time= "(((([1-9])|([1-9][0-9])|([1-9][0-9]{2})|([1-9][0-9]{3})/((([13578]|1[02])/([1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))|(([469]|11)/([1-9]|[12][0-9]|30))|(2/([1-9]|[1][0-9]|2[0-8])))))|(((([1-9][0-9])(0[48]|[2468][048]|[13579][26]))|(([48]|[2468][048]|[3579][26])00))/2/29)) ((([02468])|(1[02468])|(2[02])):00)";//时间校验
String kp="([1-9][0-9]{0,2}(\\.[0-9]{1,3})?)";
String kdkp="([1-9]\\.[0-9]{2})";//开度
大体思路:先将录入的数据整体存入StringBuild中,随后利用正则表达式识别数据分割符号“ | ”,并将数据存入字符串数组方便利用for循环对每一个类型的数据进行正确性校验,并设立flag旗帜,若存在数据错误则使flag置1,待各个位置数值检测完成则检查旗帜,没有错误再进行相关数值计算。
(4)对JAVA集合框架的应用——统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数
String.replace方法的使用:
replace方法对string进行查找和替换,并返回一个新字符串
string.replace(regexp/substr, replacement)
regexp/substr:必需。规定子字符串或要替换的模式的 RegExp 对象。
replacement:必需。一个字符串值。规定了替换文本或生成替换文本的函数。
replace() 方法执行的是查找并替换的操作。它将在 stringObject 中查找与 regexp 相匹配的子字符串,然后用给定的字符来替换这些子串。如果 regexp 具有全局标志 g,那么 replace() 方法将替换所有匹配的子串。否则,它只替换第一个匹配子串。
三、踩坑心得
1.对于正则表达式的使用不熟练,水文检测、关键词校对的题目均有参考CSDN代码
2.水文检测在测试阶段发现不能用一个if( && && && )进行全员的判断,会导致一旦前两个中判错,后面就不会执行,导致错误无法输出
3.对于关键词校对仅能看懂CSDN代码的含义,不懂得运用,无法提出修改方案。在网上的代码中有大量的类,不能明白很多类的使用原因。
四、改进建议
1.水文监测原代码没有进行类的设计,仅仅是面相过程的思想,存在全复杂度过高、不易阅读的问题。对原代码进行了修改,提出了数据校验类、数据类、校验方法类。简化不必要的声明与方法设计。
2.在数据排序作业中,仅仅是声明了三中排序算法的方法,不能提现JAVA的面向对象特点。目前估测可以建立一个数据类,其中包含三中排序算法,该类可以完成数据的存储与排序,封装的结构也方便后续对代码进行功能的增添
3.部分题目的代码设计中存在部分子类的设计很多余,子类继承之后并没有对父类进行较大的增添或是重写,这种子类以后可以不设计。
五、总结
在这一阶段的联系中,着重练习了如何使用正则表达式进行数据的校验检测,String类中各种方法的使用。但是目前存在大量问题。
1.看不懂目前题目提供的类图含义,尤其是各种关系之间的实现
2.自行设计的代码对于各种类之间的关系应该如何设计十分不明确
3.大量的类中的方法不知道含义以及使用条件
4.对于类与整体代码的设计不够简洁明了,仍然存在大量的重复代码


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号