MySQL数据库的基本使用
Mysql 数据库
2.1 安装mysq
-
下载解压包 解压到某个目录下
-
添加到环境变量 (将bin所在的完整路径copy到系统的path中)_
-
作为服务器 让其自启动mysql服务器
-
(mysqld --install 运行输入services(服务) 查看是是否成功)
-
删除服务 sc delete mysql 如果需要重装的话...
启动服务 net start mysql
停止服务 net stop mysql
注意 :后期打开cmd运行mysql就是客户端了 服务器后台在运行 一些指令可以在客户端输入 显示也在客户端显示
2.2 连接服务器
mysql -hip -P端口号 -u用户名 -p密码
实例:mysql -uroot -p (,密码没有设置)
mysql 5.6版本 默认是没有密码的
登录时不指定用户名和密码 默认是游客登录 是无法查询关键信息的 也不能进行操作
因为数据库本质是TCP程序 所以需要IP和端口 但是如果服务器是运行在本机上 那么可以省略IP 端口没有修改过 也是可以省略的
mysql -uroot -p密码
#修改密码
在知道原始密码的情况下可以使用mysqladmin
mysqladmin是一个用于管理数据库的程序,包括修改密码,数据备份等
修改密码:
mysqladmin -uroot -p旧密码 password 123
警告忽略即可
#破解密码:
#方式1:删除用于记录用户密码数据文件
没问题 简单粗暴 但是,这个文件里不只有你的账号信息 还有别人账号数据 还有授权相关的数据
所以你最好不要这么干!
那你在思考一下,服务器验证用户的本质是什么,是不是读取一个文件的数据来和你输入的数据进行对比,
那你可不可以这样子 我告诉我服务器说你不要去读那个授权文件,可以!
#方式2: 跳过授权表 进入系统修改授权表推荐
跳过这个操作是服务器相关的操作所以 咱的先关掉服务器重新开 在重新开的时候来告诉它
1.停止服务
2.启动服务器并添加参数
**mysqld --skip-grant-tables**
3.使用客户端登录服务器 执行修改命令 此时不需要输入密码
update mysql.user set password = password("123123") where user="root" and host="localhost"**
4.刷新权限
flush privileges
5.命令行中重启服务器验证新密码

补充
... unsigned表示为无符号 float(M,D) 浮点型 decimal(M,D) 定点型 比float更加的精准 M: 精度(总位数)D: 标度(小数位) ...
... NULL 不是假,也不是真,而是”空” NULL 的判断只能用is null,is not null NULL 影响查询速度,一般避免使值为NULL ...
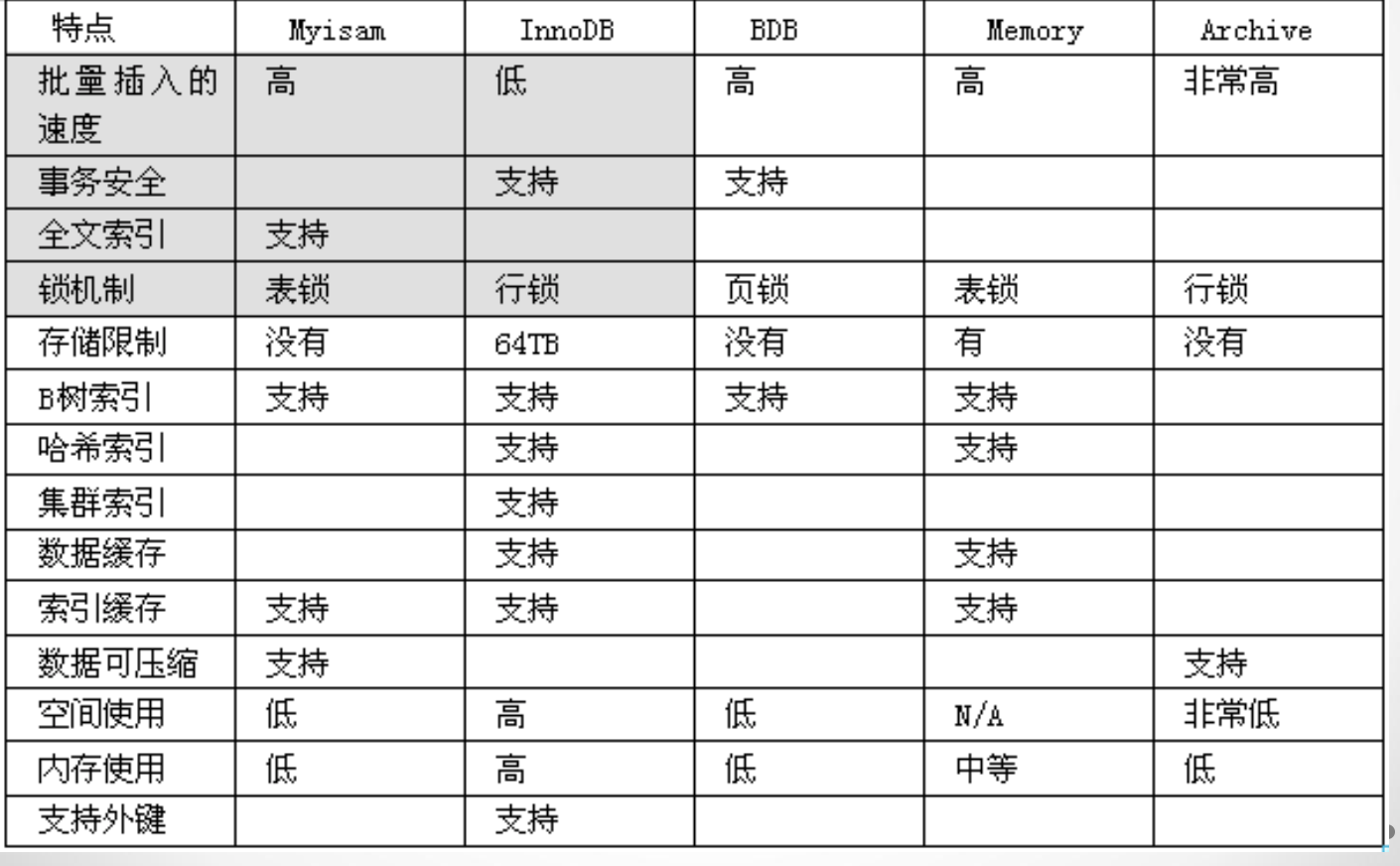
... 对不同的数据有不同的管理方式和存储方式,在mysql中称之为存储引擎 1). 文章,新闻等安全性要求不高的,选myisam 2). 订单,资金,账单,火车票等对安全性要求高的,选用innodb 3). 对于临时中转表,可以用memory型 ,速度最快 4). 中文全文索引:sphinx ...
# Innodb
1.(默认版本包含5.5)
2.支持事务
3.不支持全文索引
4.索引和数据都是在同一个文件中, .ibd
表的结构实在.frm文件中
# MyIsam
1.(默认版本5.5以下 5.3)
2.不支持事务
3.支持全文索引
4..frm: 表结构
.MYD: 表数据
.MYI: 表索引
# memory
所有的数据都保存在内存中
# 常用的全文索引: sphinx ES
数据库的基本操作
用
SQL语句: use 数据库名; 实例: use db1;
增
SQL语句: create database 数据库名 charset=utf8; 实例: create database db1; 创建了db1的库名 并指定格式为utf8
删
SQL语句: drop database 数据库名; 实例: drop database db1;
改 没有此操作 只能重写
查
show databases; 查询名下所有数据库名
数据表的基本操作
增
SQL语句: use 数据库名; 首先确定是在用哪个数据库 creata table 表名( 列名1 列类型 not null/null default 值1, 列名2 列类型 not null/null default 值2, 列名n 列类型 not null/null default 值n ) charset=utf8;
实例:
use db1; create table student( id int auto_increment primary key, # 这时设置主键的 primary key 主键 name char(32) not null default '', # 名字字符串类型 不为空,默认值为空字符串 age int not null default 0 # 设置年龄列为整形 不能为空 默认值为0 )charset=utf8; **注意最后一行是没有逗号的**
删
SQL语句 drop table 表名; 表中所有数据都会删除 实例 drop table student
改 分为改字段 新增字段
create table student( id int auto_increment primary key, # 这时设置主键的 name char(32) not null default '', # 名字字符串类型 不为空,默认值为空字符串 age int not null default 0 # 设置年龄列为整形 不能为空 默认值为0 )charset=utf8; # 这是原始数据
改字段
SQL语句 alter table 表名 change/modify 新列声明; alter table student change age stu_age int not null default 0 ; # 改单列 alter table student change age stu_age char(32), change name user char(32); # 改多列 需要用到多个change
新增字段
SQL语句: alter table 表名 add 新列声明; 实例: alter table student add gender char(32) not null default ''; # 增加单列 alter table student add gender char(32) not null default '',add class int not null default 0; # 增加多列
删除字段
SQL语句: alter table 表名 drop 列名; 实例 :alter table student drop gender; 删除单列 alter table student drop gender,drop class; 删除多列
查
SQL语句: show tables; 查看所有表 desc 表名; 查看表的结构 例如 desc student; show create table 表名; 查看表的创建过程
数据行的操作
增
insert into 表名 (列1,列2,'...列n) values (列1值,列2值,...列n值),(列1值,....列n值) ; # 一次性增加 实例:insert into student (id,name,age) values (9,'wsx',12); 增加单行 insert into 表名 (列名1, 列名2,) values(值1, 值2),(值1,值2),(值n,值n); # 增加多个值 insert into 表名 (列名1, 列名2,) select 列名1, 列名2 from 表名; # 从某个表名挑选出列名插入另一个表的列名
删
truncate 表名; # 也是删除表中所有数据 再次添加的时候, 重新开始 速快比delete快 delete from 表名 ; 删除表中所有数据 再次添加的时候, 继续会延续上一个 ID delete from 表名 where id=12; # 删除id=12 那行 delete from 表名 where 列名条件; # 选择性删除 delete from t1 where id>10; 等等 > < = != and or 等 delete from 表名 where id = 10 and name='xxx'; and : 并且 两个条件都必须要成立 delete from 表名 where id = 10 or name='xxx'; or : 或者 只要满足一个条件成立
改
update 表名 set username='zekai'; # 把表中username下所有名字改为zekei update t3 set username='tom' where id=3; # 改 id为3 的那列 update t3 set username='owen', pwd='123' where id=3; # 改id=3的多列
数据行基本查询
SQL语句; select * from 表名; 将表中所有列全部列出来 实例: select * from student; 将student的列全部列出 select 列名,列名 from表名; 将列名从表中展现出来 select distinct 字段名 FROM 表名; # 去重 实例 :select name,age from student; # 注意 尽量不要用 * 因为会降低查询速度
数据行高阶查询
1 where条件查询
a. where 条件查询: select * from 表名 where id=10; select * from 表名 where id >10 and id<15; select * from 表名 where id > 10; != : 不等与 >= <= b. between and: 闭区间 select * from t4 where id between 9 and 12; c. in: 在某一个集合中 select * from t4 where id in (9,10,11....); select * from t4 where id in (select id from t3 where id between 2 and 4) 是可以这样使用的, 但是不建议大家使用;
2 通配符: like %
select * from 表 where name like 'ale%' - ale开头的所有(多个字符串) select * from 表 where name like 'ale_' - ale开头的所有(一个字符)
3 limit 限制取
select * from 表名 limit 索引偏移量, 取出多少条数据;
select * from t3 limit 0, 10; 第一页 # 表示第一页显示10条内容
select * from t3 limit 10, 10; 第二页
page = input('page:')
page 索引偏移量 数据量(offset)
1 0 10
2 10 10
3 20 10
4 30 10
page (page-1)*offset offset
分页核心SQL:
select * from t3 limit (page-1)*offset, offset;
4 排序 order by
降序: select * from t4 order by 列名 desc; # descending 降序 升序: select * from t4 order by 列名 asc; # ascending 升序 多列: create table t7( id int auto_increment primary key, num int not null default 0, age int not null default 0 )charset=utf8; insert into t7 (num, age) values (2, 12),(3,13),(4, 12); select * from t7 order by num desc, age asc; 如果前一列的值相等的话, 会按照后一列的值进行进一步的排序.
5 分组 group by
分组是将相同的放在一起 只显示一列 select age, 聚合函数count(num)/sum(num)/max(num)/min(num)/avg(num) from 表名 group by 列名; select age, avg(num) from t7 group by age; select age, count(num) from t7 group by age; elect age, count(num) as cnt from t7 group by age; # 显示别名 as having的二次删选: select age, count(num) as cnt from t7 group by age having cnt>1; where 和 having的区别: 1). having与where类似,可筛选数据 2). where针对表中的列发挥作用,查询数据 3). having针对查询结果中的列发挥作用,二次筛选数据, 和group by配合使用
6 去重 distinct
distinct 去重的意思 只能在查询的第一列使用 不能放在后面类使用 select distinct score.student_id,student.sname from score left join student on score.student_id=student.sid where score.course_id in(select score.course_id from score where score.student_id=1) and score.student_id!=1; # 这是对score表的student_id 这一列去重 不能放在后面进行去重
7 连表查询
select * from userinfo, department; (笛卡尔积) select * from userinfo, department where userinfo.depart_id=department.id; 左连接: select 所需查询 from 表名 left join 表名 on 左表.列名=右表.列名; select * from userinfo left join department on userinfo.depart_id=department.id; 左边的表全部显示, 右边没有用到不显示 右连接: select * from userinfo right join department on userinfo.depart_id=department.id; 右边的表全部显示, 左边没关联的用null表示 内连接: 左右两边的数据都会显示 ps: a.只需要记住左连接 left join b.可以连接多张表 通过某一个特定的条件
8 查询顺序
注意查询的顺序:where>group by > order by >顺序>限制
select name,sum(score) from 表 where id > 10 group by score having age> 12 order by age desc limit 2, 10
constraint 新建表的外键名 foreign key (新建表的列名) references 关联的表名(关联表的主键如id)
foreign key:外键的意思
references :引用的意思
primary key:主键
1 约束 2 节省空间
外键注意点
1. 不能将创建外键的语句单独拿出来 alter table userinfo add constraint fk_userinfo_depart foreign key (depart_id) references department(id); alter table userinfo drop foreign key 外键名称(fk_userinfo_depart ); 2. 外键关联的时候, 必须关联的是表的主键ID 3. 练习的时候, 将语句写在文本中, 然后考过去执行 4. 主键索引 : 加速查找 + 不能为空 + 不能重复
create table department (
id int auto_increment primary key,
depart_name varchar(32) not null default '',
num int not null default 0
)engine=Innodb charset=utf8;
create table userinfo (
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default '',
depart_id int not null default 1,
# constraint 外键名(fk_userinfo_depart) foreign key (列名(depart_id)) references 表名(department)(关联的列名(id)),
# constraint fk_userinfo_depart foreign key (depart_id) references department(id)
)engine=Innodb charset=utf8;
外键分为 一对一 一对多 多对多
外键唯一索引 unique
表
外键的变种 一对多 一对一 多对多
create table user(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name char not null default '',
phone int not null default 0
)engine=Innodb charset=utf8;
insert into user(id,name,phone) values (1,'root1',18),(2,'owen',18),(3,'Jerry' ,18);
create table host(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name char not null default '',
age int not null default 0
)engine=Innodb charset=utf8;
create table host2name(
id int auto_increment primary key,
user_id int not null default 0,
host_id int not null default 0,
constraint wj1 foreign key (user_id) references user(id),
constraint wj2 foreign key (host_id) references user(id),
unique(user_id) # 设置唯一索引 值不能重复
)engine=Innodb charset=utf8;
3. 一对一:
用户表:
id name age
1 zekai 23
2 eagon 34
3 lxxx 45
4 owen 83
博客表:
id url user_id (外键 + 唯一约束)
1 /linhaifeng 2
2 /zekai 1
3 /lxxx 3
4 /lxxx 4
外键 一对一
外键唯一索引 unique
建user表
create table user(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name char(32) not null default '',
age int not null default 0
)charset=utf8;
insert into user(name,age) values ('zekei',23),('egon',24),('lxxx',45),('owen',83);
建博客表
create table boke(
id int auto_increment primary key,
url varchar(32) not null default '',
user_id int not null default 0,
constraint wj1 foreign key (user_id) references user(id),
unique(user_id)
)engine=Innodb charset=utf8;
insert into boke (url,user_id) values ('/linhaifeng',2),('zekei',1),('lxxx',3),('lxxx',4);
对user_id设置了外键 另外对user_id设置了 唯一约束 表示这一行的数字不能重复 分别是2 1 3 4 假设是2234 就会报错
外键多对多 4. 多对多:
用户表:
id name phone
1 root1 1234
2 root2 1235
3 root3 1236
4 root4 1237
5 root5 1238
6 root6 1239
7 root7 1240
8 root8 1241
主机表:
id hostname
1 c1.com
2 c2.com
3 c3.com
4 c4.com
5 c5.com
为了方便查询, 用户下面有多少台主机以及某一个主机上有多少个用户, 我们需要新建第三张表:
user2host:
id userid hostid
1 1 1
2 1 2
3 1 3
4 2 4
5 2 5
6 3 2
7 3 4
创建的时候, userid 和 hostid 必须是外键, 然后联合唯一索引 unique(userid, hostid)
建zuser表
create table zuser(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name char(32) not null default '',
phone int not null default 0
)charset=utf8;
建主机表
create table host(
id int auto_increment primary key,
hostname char(32) not null default ''
)charset=utf8;
建user2host表
create table user2host (
id int auto_increment primary key,
zuser_id int not null default 0,
host_id int not null default 0,
constraint wj2 foreign key (zuser_id) references zuser(id),
constraint wj3 foreign key (host_id) references host(id),
unique(zuser_id,host_id)
)charset=utf8;
注意:外键名称 不能重复 之前wj1已经用过 这里如果再是wj1就会报错
2.9 pymysql的使用
import pymysql
# 建立连接
conn=pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='123',database='db1',charset='utf8')
# 创建游标 和指定输出字典格式
cursor=conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 写出需要执行的SQL语句
sql = "insert into t3 (name,email) values(alix,122@163.com)" #在Pymysql中不需要;结束
# sql = "insert into t3 (name,email) values(%s,%s)"
# data=[('aaa','qqq'),('bbb','222'),('ccc','333')] 多条sql语句
# 执行SQL语句
cursor.execute(sql) # 执行单条语句
# cursor.executemany(sql,data) # 执行多条语句
# 取出执行结果
res=cursor.fetchone() # 取第一行执行结果
res=cursor.fetchmany(10) # 取10执行结果
res=cursor.fetchall() # 取出所有结果
print(res)
# 在更新和删除时需要提交任务, 查询不需要这一步
conn.commit()
# 关闭资源
cursor.close() # 关闭游标
conn.close() # 关闭连接
-
案例
写sql语句的时候, %传值的时候, 需要加引号: sql = "select * from t4 where name = '%s' and pwd = '%s'" % (username, pwd) 上面的sql语句带来的风险是: 例一: username = zekai' # select * from t4 where name = 'zekai' #' and pwd = '' 例二: username = dbsahvbdsha' or 1=1 # select * from t4 where name = 'dbsahvbdsha' or 1=1 上面出现的问题,我们称之为 SQL注入 (**********************************) 出现问题的根源是: 因为太过于相信用户的输入, 导致我们在接受用户输入的参数的时候, 并没有对他进行转义
1. 自己手工对用户输入的值进行转义
2. 使用execute()自动进行过滤
sql = "select * from t4 where name = %s and pwd = %s"
cursor.execute(sql,(username, pwd))
#$## 插入一条
cursor.execute(sql, ('lxxx', '1234'))
### 插入多条
data = [
('aaaaa', 'aaa'),
('bbbb', 'bbb'),
('ffff', '666'),
('rrrr', '888'),
]
cursor.executemany(sql, data)
try:
cursor.execute(sql, ('lxxx', '1234'))
### 删除和更新的时候, 需要事物提交
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback()
cursor.lastrowid : 最后一行的行数
简记为ACID
-
原子性(Atomicity),原子意为最小的粒子,即不能再分的事务,要么全部执行,要么全部取消(就像上面的银行例子)
-
一致性(Consistency):指事务发生前和发生后,数据的总额依然匹配
-
隔离性(Isolation):简单点说,某个事务的操作对其他事务不可见的
-
持久性(Durability):当事务完成后,其影响应该保留下来,不能撤消,只能通过“补偿性事务”来抵消之前的错误
开启事务start transaction; 或者 begin; 执行sql操作(普通sql操作) 提交/回滚(commit/rollback)
create table user(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default '',
money int not null default 1000
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
insert into user (name,money) values ('wangyong',1000),('liguo',1000);
# 正常操作
start transaction;
update user set money=1100 where name='wangyong';
updata user set money=900 where name='liguo';
# 出现异常 事务操作要么一起成功 要么一起失败
rollback;
# 最终结果, 数据未发生变化
mysql> select * from user;
+----+----------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+----------+-------+
| 1 | wangyong | 1000 |
| 2 | liguo | 1000 |
+----+----------+-------+
create table user(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default '',
money int not null default 1000
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
insert into user (name,money) values ('wangyong',1000),('liguo',1000);
# 正常操作
start transaction;
update user set money=1100 where name='wangyong';
updata user set money=900 where name='liguo';
# 出现异常 事务操作要么一起成功 要么一起失败
rollback;
# 最终结果, 数据未发生变化
mysql> select * from user;
+----+----------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+----------+-------+
| 1 | wangyong | 1000 |
| 2 | liguo | 1000 |
+----+----------+-------+
优点: 1、所有的MySql列类型(字段类型)都可以被索引,也就是可以给任意字段设置索引 2、大大加快数据的查询速度 缺点:(耗费时间,空间.降低维护速度) 1、创建索引和维护索引要耗费时间,并且随着数据量的增加所耗费的时间也会增加 2、索引也需要占空间,我们知道数据表中的数据也会有最大上线设置的,如果我们有大量的索引,索引文件可能会比数据文件更快达到上线值 3、当对表中的数据进行增加、删除、修改时,索引也需要动态的维护,降低了数据的维护速度。
使用原则: 1、对经常更新的表就避免对其进行过多的索引,对经常用于查询的字段应该创建索引, 2、数据量小的表最好不要使用索引,因为由于数据较少,可能查询全部数据花费的时间比遍历索引的时间还要短,索引就可能不会产生优化效果。 3、在一同值少的列上(字段上)不要建立索引,比如在学生表的"性别"字段上只有男,女两个不同值。相反的,在一个字段上不同值较多可以建立索引
主键索引:加速查询 + 列值唯一 + 表中只有一个(不可以有null) 普通索引:仅加速查询 唯一索引:加速查询 + 列值唯一(唯一约束) (可以有null) 组合索引:多列值组成一个索引
# 第一种:
create table test(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default ''
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
# 第二种:
create table test(
id int not null default 0,
name varchar(32) not null default ''
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
alter table test change id id int auto_increment primary key
# 第一种
create table test(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default '',
index ix_name (name)
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
# 第二种
create table test(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default ''
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
create index ix_name on test (name);
2. 创建索引
create index index_name on table_name(column_name);
3. 删除索引
drop index_name on table_name;
4. 查看索引
show index from table_name;
1. 创建表 + 索引
# 第一种
create table test(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default '',
unique ix_name (name)
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
# 第二种 create unique index 索引名称 on 表名(name);
create table test(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null default ''
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
create unique index ix_name on test (name);
2. 创建索引
create unique index 索引名 on 表名(列名);
3. 删除索引
drop unique index 索引名 on 表名;
联合索引
组合索引是将n个列组合成一个索引
其应用场景为:频繁的同时使用n列来进行查询,如:where n1 = ‘alex’ and n2 = 666;
1. 创建表 + 索引
create table test(
id int auto_increment primary key,
age int not null default 0,
name varchar(32) not null default ''
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
create unique index ix_name_age on test (age, name);
create table in3(
nid int not null auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(32) not null,
email varchar(64) not null,
extra text
)
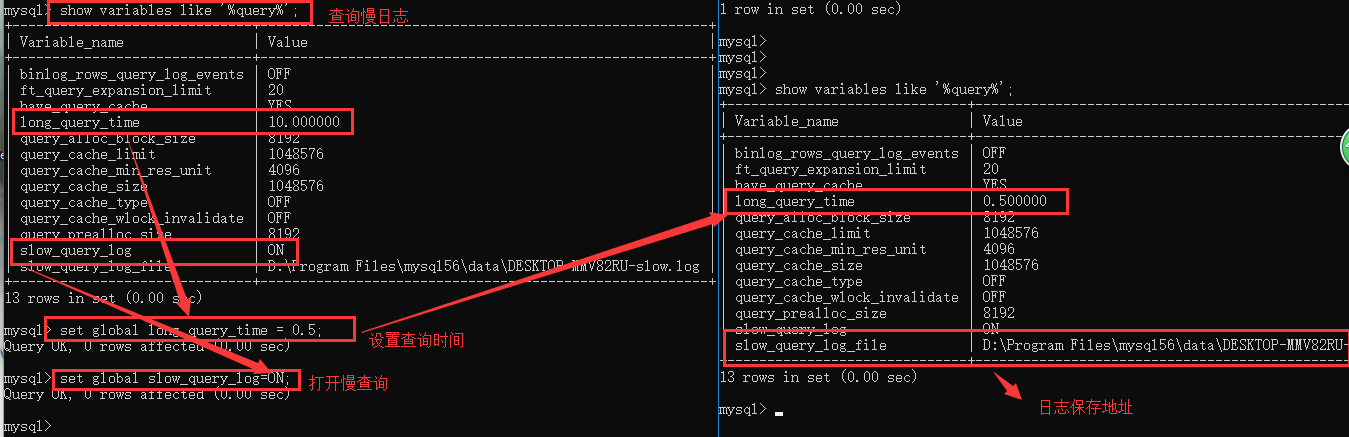
日志文件: 记录了执行速度特别慢的SQL语句
可以通过慢日志来检查查询的时间的等 然后呢针对性的做数据库优化
slow_query_log = OFF 是否开启慢日志记录 long_query_time = 2 时间限制,超过此时间,则记录 slow_query_log_file = /usr/slow.log 日志文件
1. show variables like '%query%'; 2. set global long_query_time = 1; 设置慢查询的时间 3. set global slow_query_log = ON 4. set global slow_query_log_file = E:\program\mysql-5.6.44-winx64\data\oldboy-slow.log
SQL审计 (记录sql的操作语句) show variables like '%general%';

创建用户
create user '用户名'@'IP地址' identified by '密码';
creaee user 'zekai'@'192.168.1.123' identified by '123qwe';
creaee user 'zekai'@'192.168.1.%' identified by '123qwe';
create user 'zekai'@'%' identified by '123qwe';
#
删除用户
drop user '用户名'@'IP地址';
修改用户
rename user '用户名'@'IP地址' to '新用户名'@'IP地址';
修改密码
set password for '用户名'@'IP地址' = Password('新密码')
授权:
grant 权限 on 数据库.表 to '用户'@'IP地址' -- 授权
grant select on db1.* to 'zekai'@'%';
grant select on *.* to 'zekai'@'%';
grant select, insert, delete on db1.* to 'zekai'@'%';
记住:
flush privileges; # 刷新生效



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号