mybatis总结
MyBatis 框架:
MyBatis 它是一款半自动的ORM持久层框架,具有较高的SQL灵活性,内部封装了 jdbc,开发者只需要关注 sql 语句本身,而不需要处理加载驱动、创建连接、创建 statement、关闭连接,资源等繁杂的过程。MyBatis 通过xml 或注解两种方式将要执行的各种sql 语句配置起来,并通过java 对象和sql 的动态参数进行映射生成最终执行的 sql 语句,最后由 mybatis 框架执行 sql 并将结果映射为 java 对象并返回。
底层采用了:构建者模式,工厂模式,单例模式,(jdk)代理模式,组合模式,模板方法模式,适配器模式,装饰者模式,迭代器模式
搭建 Mybatis 开发环境
第一步:在pom.xml中加入依赖和插件
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.9</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/java</directory><!--所在的目录 --> <includes><!--包括目录下的.properties,.xml 文件都会扫描到 --> <include>**/*.properties</include> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> <filtering>false</filtering> </resource> </resources> <plugins> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.1</version> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
第二步:创建mybatis主配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!--properties就像EL表达式一样,就可以用${}占位符快速获取文件中配置的信息 --> <properties resource="jdbc.properties" /> <settings> <!-- 二级缓存的开启 --> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 设置缓存范围 默认(SESSION) --> <!-- 设置为SESSION时会缓存一个会话中执行的所有查询,为 STATEMENT时本地会话仅用在语句执行上, 相同 SqlSession 的不同调用将不会共享数据 --> <setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION"/> <!-- 指定 MyBatis 所用日志的具体实现,未指定时将自动查找。 --> <!-- <setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/> --> <setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J" /> <!-- 懒加载的开启 特定关联关系中可通过设置 fetchType 属性来覆盖该项的开关状态。 --> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 当开启时,任何方法的调用都会加载该对象的所有属性。 在 3.4.1 及之前的版本默认值为 true --> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> </settings> <!--配置mybatis环境 --> <environments default="mysql"> <!--id:数据源的名称 --> <environment id="mysql"> <!--配置事务类型:使用 JDBC事务(使用 Connection的提交和回滚) --> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <!--数据源 dataSource:创建数据库 Connection对象 type: POOLED 使用数据库的连接池 --> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <!--连接数据库的四个要素 --> <property name="driver" value="${driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${url}" /> <property name="username" value="${username}" /> <property name="password" value="${password}" /> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <!-- 配置mapper文件包路径的位置,SQL语句的位置 --> <package name="xyz.w9420.dao" /> </mappers> </configuration>
第三步:创建接口
package xyz.w9420.dao; import java.util.List; import xyz.w9420.entity.Student; public interface IStudentDao { Integer insertStudent(Student student); Integer insertStudentReturnKeyId(Student student); Integer updateStudent(Student student); List<Student> queryStudentAll(); Integer deleteStudent(Integer stu_id); List<Student> queryStudentAndSubjectAll(); }
第四步:创建对应的Mapper 映射文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- namespace:必须有值,自定义的唯一字符串 推荐使用:dao接口的全限定名称 --> <mapper namespace="xyz.w9420.dao.IStudentDao"> <!-- 开启二级缓存的支持 --> <cache></cache> <!-- 这个元素可以用来定义可重用的 SQL 代码片段,以便在其它语句中使用。 使用include嵌套使用SQL语句中 --> <sql id="queryStu">select * from student</sql> <!-- <select>: 查询数据, 标签中必须是select语句 id: sql语句的自定义名称,推荐使用 dao接口中方法名称, 使用名称表示要执行的 sql语句 resultType: 查询语句的返回结果数据类型,使用全限定类名 --> <!-- useCache 二级缓存的开启和关闭(默认是开启的) 可以禁用当前select语句的二级缓存,即每次select都去DB查询,默认情况是true。 针对每次查询都需要最新数据的SQL,要设置成useCache=false,禁用二级缓存。 --> <!-- flushCache 将其设置为 true 后,只要语句被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存被清空,默认值:false。 --> <select id="queryStudentAll" resultType="xyz.w9420.entity.Student" flushCache="false" useCache="true"> <include refid="queryStu"></include> </select> <!--parameterType 接口传入参数的类型 --> <!-- #{stu_id} OGNL表达式:作用是在对象和视图之间做数据的交互,可以存储对象的属性和调用对象的方法 --> <!-- 删除数据 --> <delete id="deleteStudent" parameterType="int"> delete from student where stu_id = #{stu_id}; </delete> <!-- 插入数据 --> <insert id = "insertStudent" parameterType="xyz.w9420.entity.Student"> insert into student (stu_id,stu_name,c_id) values(#{stu_id},#{stu_name},#{c_id}); </insert> <!--插入数据返回主键id --> <!-- useGeneratedKeys 表示字段为自动增长 keyColumn 数据库中的主键 keyProperty 对应实体类中的的主键字段--> <insert id="insertStudentReturnKeyId" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyColumn="stu_id" keyProperty="stu_id" parameterType="xyz.w9420.entity.Student"> insert into student (stu_id,stu_name,c_id) values(null,#{stu_name},#{c_id}); </insert> <!-- 修改数据 --> <update id="updateStudent" parameterType="xyz.w9420.entity.Student"> update student set stu_name = #{stu_name} , c_id = #{c_id} where stu_id = #{stu_id} </update> <!--主要映射数据库字段对应实体类的映射关系(能够方便的嵌套(pojo)对象 和集合) column 代表数据库的字段 property 代表对应实体类的字段 --> <resultMap type="xyz.w9420.entity.Student" id="stu_map"> <id column="stu_id" property="stu_id"/> <result column="stu_name" property="stu_name"/> <result column="c_id" property="c_id"/> <!-- 关联元素处理有一个类型的关系--> <association property="school" javaType="xyz.w9420.entity.School"> <id column="school_id" property="c_id"/> <result column="school_name" property="c_name"/> </association> <!-- 关联元素处理有集合类型的关系--> <collection property="subList" ofType="xyz.w9420.entity.Subject"> <id column="sub_id" property="id"/> <result column="sub_name" property="name"/> </collection> </resultMap> <!-- resultType 和 resultMap 之间只能同时使用一个。 --> <select id="queryStudentAndSubjectAll" resultMap="stu_map"> select s.*,ssss.c_id shcool_id ,ssss.c_name school_name,sss.id sub_id,sss.`name` sub_name from student s LEFT JOIN school ssss ON s.c_id = ssss.c_id LEFT JOIN stu_sub ss on s.stu_id = ss.stu_id LEFT JOIN subjects sss on ss.sub_id= sss.id </select> </mapper>
$与#的使用区别:
1.#符号代表底层使用的是PreparedStatement对象的预编译方式来执行sql,效率高
2.#能够避免sql注入,更安全
3.$符号代表底层使用的Statement对象来对sql的拼接,效率低
4.#有SQL注入的风险,缺乏安全性
5.$:可以替换表名和列名
缓存:
缓存就是在内存中临时数据,使用缓存可以降低数据库的压力,减少操作数据库的次数,提高了执行的效率
SqlSession对象的缓存。
当调用 SqlSession 的修改,添加,删除,commit(),close() ,clearCache(),方法时就会清空一级缓存。
当SqlSession对象消失时,mybatis的一级缓存也就消失了。
设置缓存范围:<setting name="localCacheScope" value="STATEMENT"/>
设置为SESSION时会缓存一个会话中执行的所有查询,为 STATEMENT时本地会话仅用在语句执行上,相同 SqlSession 的不同调用将不会共享数据
二级缓存: 不同sqlsession之间共享查询结果集。
SqlSessionFactory对象的缓存。
由同一个SqlSessionFactory对象创建的SqlSession共享其缓存。
当我们一级缓存消失时,我们去执行第二次的时候,我们通过日志的方式发现没有对数据的查询sql
此时的数据就是二级缓存
使用:
1、在配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml中加入以下内容(开启二级缓存总开关):cacheEnabled设置为 true
2、开启和关闭二级缓存。
在statement中设置 useCache=false 可以禁用当前select语句的二级缓存,即每次select都去DB查询,默认情况是true。
针对每次查询都需要最新数据的SQL,要设置成useCache=false,禁用二级缓存。
延迟加载:
延迟加载就是我们在真正使用数据时候才发起查询,不用的时候不查询关联的数据,延迟加载又叫按需查询(懒加载)
使用场景:一对多、多对多通常采用延迟加载
使用:需要在settings配置 <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> 特定关联关系中可通过设置 fetchType 属性来覆盖该项的开关状态。
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> 当开启时,任何方法的调用都会加载该对象的所有属性。 在 3.4.1 及之前的版本默认值为 true
动态sql:
动态SQL主要是解决查询条件不确定的情况:比方说在程序运行过程中,用户可能会不同的条件去查询,按照我们以前的
写法,可能要对这些条件都要去写相对应的SQL,这样会出现大量的sql,使我们的代码就特别冗余,体验了动态SQL
后,动态SQL可以根据某种条件动态的拼接出需要的SQL,解决了冗余问题,提高开发人员的效率。
常用的标签有if where foreach sql 等.
注解开发
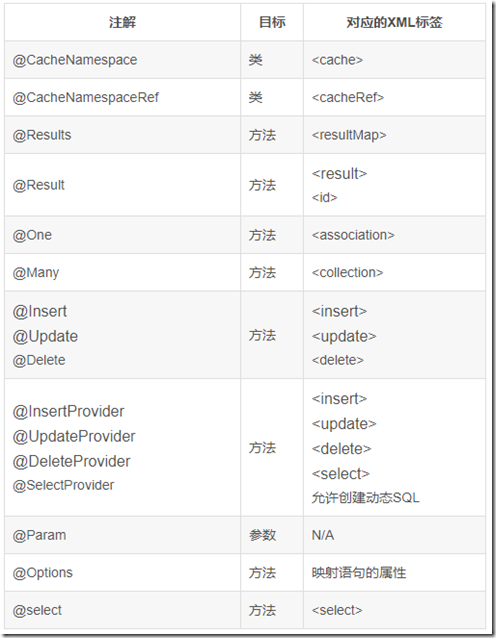
常用的注解:
代码演示:
package xyz.w9420.dao; import java.util.List; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Many; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.One; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Options; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Result; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.ResultMap; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Results; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.SelectProvider; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.FetchType; import xyz.w9420.entity.User; import xyz.w9420.entity.User01; import xyz.w9420.provider.UserProvider; /** * @author 作者 E-mail:1543350583@qq.com * @version */ @CacheNamespace public interface IUserDao { /** * 查询User对应的所有角色和银行卡 * * @return */ @Select("select * from user") @Results(id = "userMap", value = { @Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"), @Result(column = "username", property = "username"), @Result(column = "sex", property = "sex"), @Result(column = "birthday", property = "birthday"), @Result(column = "address", property = "address"), @Result(column = "id", property = "account", one = @One(select = "xyz.w9420.dao.IAccountDao.queryAccount", fetchType = FetchType.EAGER)), @Result(column = "id", property = "roleList", many = @Many(select = "xyz.w9420.dao.IRoleDao.queryRole", fetchType = FetchType.DEFAULT)) }) List<User> queryUserAll(); @Select("select * from user") @ResultMap("userMap") List<User> queryUsers(); @Insert("insert into user (username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})") @Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyColumn = "id", keyProperty = "id") Integer insertUserReturnKeyId(User user); @Select("<script>select * from user <where><if test='_parameter != null'>and id = #{_parameter}</if></where></script>") User queryUserById(Integer id); @Insert("insert into user (id,username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{id},#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})") Integer insertUser(User user); @Delete("delete from user where id = #{id}") Integer deleteUser(Integer id); @Update("update user set username = #{username},birthday = #{birthday},sex = #{sex},address = #{address} where id = #{id}") Integer updateUser(User user); @SelectProvider(type = UserProvider.class, method = "queryUserByName") List<User01> queryUserByName(String name); }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号