有向图
有向图
有向图(Directed Graph)是一种图结构,其中的边(连接节点的线)具有方向性。这意味着每条边都有一个起始节点和一个结束节点,表示从一个节点指向另一个节点。
有向图的特点
- 方向性:边的方向指示了节点之间的关系。例如,如果有一条边从节点 A 指向节点 B,表示 A 到 B 的关系,但不一定表示 B 到 A 的关系。
- 表示方式:
- 邻接矩阵:使用二维数组表示节点之间的连接关系。
- 邻接列表:使用列表或集合表示每个节点的直接邻居。
- 节点和边:
- 节点(Vertex):图中的元素,通常表示为点。
- 边(Edge):连接节点的线,表示节点之间的关系。
- 示例:
- 社交网络中的关注关系(用户 A 关注用户 B,但 B 不一定关注 A)。
- 网络流量中的路由(数据包从源节点发送到目标节点)。
实际情况中,有向图中可能有复杂的依赖关系,包括:
- 线性依赖:A→B→C
- 分支依赖:A→B, A→C
- 汇聚依赖:B→D, C→D
- 循环依赖:A→B→C→A(形成环)
实际案例
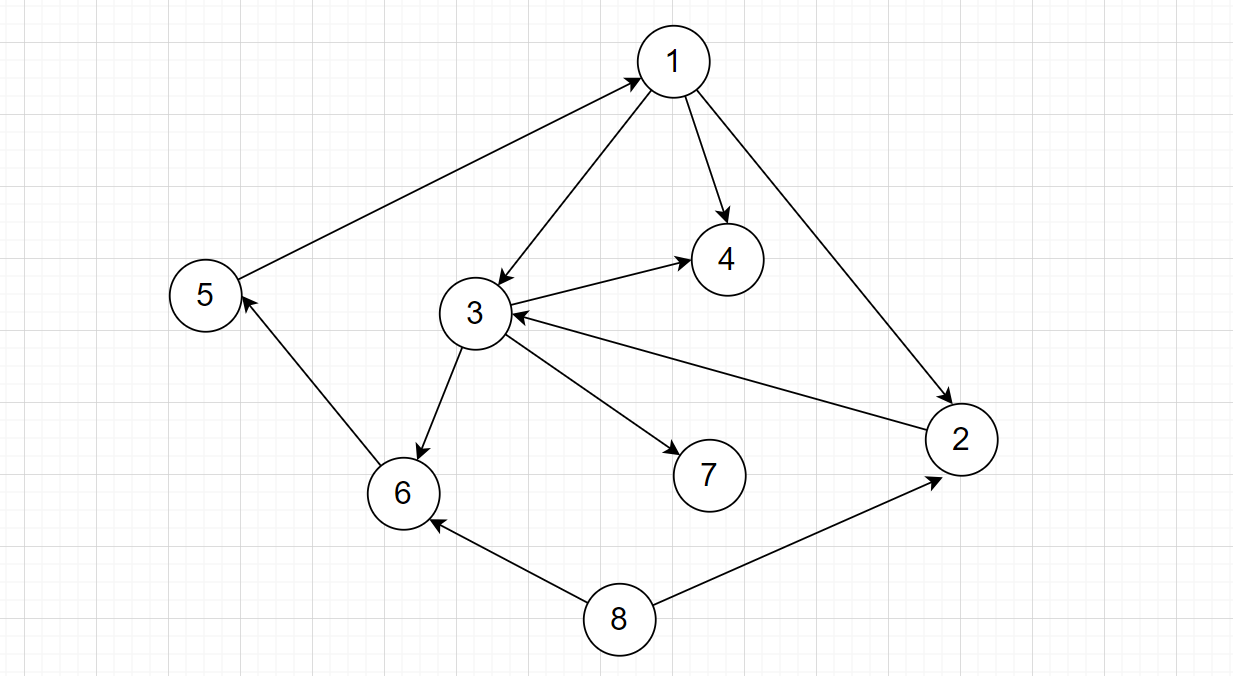
给定输入,输入的形式为一组任务依赖关系:例如 1->2表示id为1的任务依赖于id为2的任务
1->2,1->3,1->4,2->3,3->6,3->7,3->4,5->1,6->5,8->6,8->2
使用邻接表来表示:
1: [2, 3, 4]
2: [3]
3: [6, 7, 4]
5: [1]
6: [5]
8: [6, 2]
这个图长下面这个样子:
输入处理
// 表示每个依赖关系
public class Task {
Long taskId; // 任务ID
Long inputTaskId; // 依赖的任务ID
}
/**
* 处理输入
*/
public static List<Task> parseDependencies(String[] dependencyStrings) {
List<Task> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
for (String depStr : dependencyStrings) {
String[] split = depStr.split("->");
tasks.add(new Task(Long.parseLong(split[0]), Long.parseLong(split[1])));
}
return tasks;
}
/**
* 构建邻接表表示的图
*/
private static Map<Long, List<Long>> buildGraph(List<Task> tasks) {
Map<Long, List<Long>> graph = new HashMap<>();
for (Task task : tasks) {
graph.putIfAbsent(task.getTaskId(), new ArrayList<>());
if (task.getInputTaskId() != null) {
graph.get(task.getTaskId()).add(task.getInputTaskId());
}
}
return graph;
}
检测是否成环
使用深度优先搜索(DFS)检测图中是否存在环。时间复杂度:O(V+E),V是顶点数,E是边数
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "1->2,1->3,1->4,2->3,3->6,3->7,3->4,5->1,6->5,8->6,8->2";
List<Task> tasks = parseDependencies(input.split(","));
Map<Long, List<Long>> graph = buildGraph(tasks);
// 检测是否存在环
boolean hasCycle = false;
Set<Long> visited = new HashSet<>();
Set<Long> currentPath = new HashSet<>();
for (Long startNode : graph.keySet()) {
hasCycle = dfs(graph, startNode, visited, currentPath);
if (hasCycle) {
System.out.println("图中存在环!");
break;
}
}
if (!hasCycle) {
System.out.println("图中不存在环。");
}
}
/**
* 执行深度优先搜索,检测图中是否存在环。
*
* @param graph 图,表示为节点及其邻居的映射。
* @param node 当前正在访问的节点。
* @param visited 已访问节点的集合。
* @param currentPath 当前路径中的节点集合,用于检测环。
* @return 如果图中存在环,则返回 true;否则返回 false。
*/
private static boolean dfs(Map<Long, List<Long>> graph, Long node,
Set<Long> visited, Set<Long> currentPath) {
// 检查当前路径是否已包含该节点
if (currentPath.contains(node)) {
return true; // 发现环,返回 true
}
// 如果节点已访问过,返回 false
if (visited.contains(node)) {
return false;
}
// 标记节点为已访问和当前路径中的节点
visited.add(node);
currentPath.add(node);
boolean hasCycle = false; // 标记是否存在环
// 遍历邻居
if (graph.containsKey(node)) {
for (Long neighbor : graph.get(node)) {
hasCycle = dfs(graph, neighbor, visited, currentPath);
if (hasCycle) {
break; // 如果发现环,停止探索
}
}
}
// 回溯
currentPath.remove(node); // 从当前路径中移除节点
return hasCycle; // 返回是否存在环
}
非递归写法:分别使用栈和不使用栈两种方式
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "1->2,1->3,1->4,2->3,3->6,3->7,3->4,5->1,6->5,8->6,8->2";
List<Task> tasks = parseDependencies(input.split(","));
Map<Long, List<Long>> graph = buildGraph(tasks);
// 检测是否存在环
boolean hasCycle = false;
Set<Long> visited = new HashSet<>();
Set<Long> currentPath = new HashSet<>();
for (Long startNode : graph.keySet()) {
if (!visited.contains(startNode)) {
hasCycle = hasCycle(graph, startNode, visited);
// 或者: hasCycle = hasCycle(graph, startNode, visited, currentPath);
if (hasCycle) {
System.out.println("图中存在环!");
break;
}
}
}
if (!hasCycle) System.out.println("图中不存在环。");
}
private static boolean hasCycle(Map<Long, List<Long>> graph, Long start, Set<Long> visited) {
Set<Long> currentPath = new HashSet<>(); // 当前路径中的节点
Stack<Long> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(start);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Long node = stack.pop();
if (currentPath.contains(node)) {
return true; // 发现环,返回 true
}
if (!visited.contains(node)) {
visited.add(node);
currentPath.add(node);
// 将邻节点压入栈
if (graph.containsKey(node)) {
for (Long neighbor : graph.get(node)) {
stack.push(neighbor);
}
}
}
// 从当前路径中移除节点
currentPath.remove(node);
}
return false; // 没有发现环
}
/**
* 迭代实现的深度优先搜索,检测图中是否存在环。
*
* @param graph 图,表示为节点及其邻居的映射。
* @param start 开始节点。
* @param visited 已访问节点的集合。
* @param currentPath 正在访问节点的集合。
* @return 如果图中存在环,则返回 true;否则返回 false。
*/
private static boolean hasCycle(Map<Long, List<Long>> graph, Long start,
Set<Long> visited, Set<Long> currentPath) {
// 使用状态来标记节点状态
Map<Long, Integer> state = new HashMap<>();
for (Long node : graph.keySet()) {
state.put(node, 0); // 0: 未访问, 1: 正在访问, 2: 已访问
}
// 进行迭代 DFS
state.put(start, 1); // 标记为正在访问
currentPath.add(start);
while (!currentPath.isEmpty()) {
Long node = currentPath.iterator().next(); // 获取当前路径中的第一个节点
if (graph.containsKey(node)) {
boolean hasCycle = false;
for (Long neighbor : graph.get(node)) {
if (state.get(neighbor) == 1) {
return true; // 发现环,返回 true
}
if (state.get(neighbor) == 0) {
state.put(neighbor, 1); // 标记为正在访问
currentPath.add(neighbor); // 添加到当前路径
}
}
}
// 完成对当前节点的处理
state.put(node, 2); // 标记为已访问
currentPath.remove(node); // 从当前路径中移除
}
return false; // 没有发现环
}
查找所有路径
找到所有路径的方法
-
从每个节点开始,采用深度优先搜索(DFS)。
-
记录当前路径,当到达没有出边的节点时,保存该路径。
下面是一个示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "1->2,1->3,1->4,2->3,3->6,3->7,3->4,5->1,6->5,8->6,8->2";
List<Task> tasks = parseDependencies(input.split(","));
Map<Long, List<Long>> graph = buildGraph(tasks);
// 查找所有路径
List<List<Long>> allPaths = new ArrayList<>();
for (Long startNode : graph.keySet()) {
dfs(graph, startNode, new ArrayList<>(), new HashSet<>(), allPaths);
}
// 输出所有路径
for (List<Long> path : allPaths) {
System.out.println(path);
}
}
/**
* 深度优先搜索,从给定节点查找所有路径。
*
* @param graph 图
* @param node 当前正在访问的节点
* @param path 当前构建的路径
* @param visited 已访问节点的集合,用于检测环,防止无限循环
* @param allPaths 存储所有找到的路径的列表
*/
private static void dfs(Map<Long, List<Long>> graph, Long node, List<Long> path,
Set<Long> visited, List<List<Long>> allPaths) {
// 检查是否已在当前路径中
if (visited.contains(node)) {
return; // 发现环,停止探索
}
visited.add(node);
path.add(node);
if (!graph.containsKey(node)) { // 如果没有出边,保存路径
allPaths.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
} else {
for (Long neighbor : graph.get(node)) {
dfs(graph, neighbor, path, visited, allPaths);
}
}
// 回溯
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
// 移除当前节点的访问标记,以便其他路径可以继续探索
visited.remove(node);
}
关键点说明
- 路径查找算法:使用深度优先搜索(DFS)遍历所有可能的路径
- 环处理:当检测到节点已在当前路径中时,识别为环并停止该路径的继续探索
- 起点选择:优先从没有入边的节点开始查找(如果有)
- 终止条件:当节点没有出边时,路径终止
- 通过visited集合防止无限循环
- 循环路径会被截断(不包含完整循环)
- 回溯:在回溯时,移除当前节点的访问标记,以便其他路径可以继续探索。
扩展功能
针对其他场景,可以在之前的基础上做一些改动
- 可以添加最大长度限制
- 可以过滤包含特定节点的路径
- 并行处理:不同起点的DFS可以并行执行



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号