Java注解处理器
注解处理器
Java 注解处理器(Annotation Processor Tool, 简称APT)是一种用于在编译时处理注解的工具。它允许你在代码编译期间读取、分析和生成代码。注解处理器通常用于生成代码、配置文件或进行其他编译时的操作。
JSR 269 是 Java 语言规范的一部分(javax.annotation.processing 包),它定义了一套用于在编译期间处理注解的标准 API。通过实现 JSR 269,我们可以编写自己的注解处理器,用于处理自定义注解。
基本使用
以下是 JSR 269 中最重要的几个接口和注解:
- javax.annotation.processing.Processor:这是插入式注解处理器的主要接口,我们需要实现它来处理注解。该接口定义了多个方法,其中最重要的是 process() 方法,用于实际处理注解。
- javax.annotation.processing.RoundEnvironment:在 process() 方法中,我们可以通过 RoundEnvironment 对象获取当前编译轮次中的所有注解和元素。
- javax.annotation.processing.SupportedAnnotationTypes:该注解用于指定我们的注解处理器支持的注解类型。我们可以使用它的 value 属性来指定一个字符串数组,每个元素表示一个注解类型的完全限定名。
- javax.annotation.processing.SupportedSourceVersion:该注解用于指定我们的注解处理器支持的源代码版本。我们可以使用它的 value 属性来指定一个 javax.lang.model.SourceVersion 枚举值。

实战案例
插件化注解处理API的使用步骤大概如下:
- 自定义一个Annotation Processor,需要继承javax.annotation.processing.AbstractProcessor,并覆写process方法。
- 自定义一个注解,注解的元注解需要指定@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)。
- 需要在声明的自定义Annotation Processor中使用javax.annotation.processing.SupportedAnnotationTypes指定在第2步创建的注解类型的名称(注意需要全类名,"包名.注解类型名称",否则会不生效)。
- 需要在声明的自定义Annotation Processor中使用javax.annotation.processing.SupportedSourceVersion指定编译版本。
- 可选操作,可以通在声明的自定义Annotation Processor中使用javax.annotation.processing.SupportedOptions指定编译参数。
下面我们仿照lombok实现一个Setter注解
自定义注解
定义一个注解@Setter,可以用在类上和方法上
package org.example;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Documented
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface Setter {
}
实现AbstractProcessor
继承AbstractProcessor,实现代码生成逻辑
Java 的注解处理器无法直接修改已存在的 Java 源文件。通常,我们会生成一个新的源文件。
package org.example;
import com.sun.source.tree.Tree;
import com.sun.tools.javac.api.JavacTrees;
import com.sun.tools.javac.code.Flags;
import com.sun.tools.javac.code.Type;
import com.sun.tools.javac.processing.JavacProcessingEnvironment;
import com.sun.tools.javac.tree.JCTree;
import com.sun.tools.javac.tree.TreeMaker;
import com.sun.tools.javac.tree.TreeTranslator;
import com.sun.tools.javac.util.Context;
import com.sun.tools.javac.util.List;
import com.sun.tools.javac.util.ListBuffer;
import com.sun.tools.javac.util.Name;
import com.sun.tools.javac.util.Names;
import javax.annotation.processing.AbstractProcessor;
import javax.annotation.processing.Messager;
import javax.annotation.processing.ProcessingEnvironment;
import javax.annotation.processing.RoundEnvironment;
import javax.annotation.processing.SupportedAnnotationTypes;
import javax.annotation.processing.SupportedSourceVersion;
import javax.lang.model.SourceVersion;
import javax.lang.model.element.Element;
import javax.lang.model.element.TypeElement;
import javax.tools.Diagnostic;
import java.util.Set;
@SupportedSourceVersion(SourceVersion.RELEASE_8)
@SupportedAnnotationTypes("org.example.Setter")
public class MyProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
private Messager messager; // 编译时期输入日志的
private JavacTrees javacTrees; // 提供了待处理的抽象语法树
private TreeMaker treeMaker; // 封装了创建AST节点的一些方法
private Names names; // 提供了创建标识符的方法
@Override
public synchronized void init(ProcessingEnvironment processingEnv) {
super.init(processingEnv);
this.messager = processingEnv.getMessager();
this.javacTrees = JavacTrees.instance(processingEnv);
Context context = ((JavacProcessingEnvironment) processingEnv).getContext();
this.treeMaker = TreeMaker.instance(context);
this.names = Names.instance(context);
}
@Override
public boolean process(Set<? extends TypeElement> annotations, RoundEnvironment roundEnv) {
Set<? extends Element> elementsAnnotatedWith = roundEnv.getElementsAnnotatedWith(Setter.class);
elementsAnnotatedWith.forEach(e -> {
JCTree tree = javacTrees.getTree(e);
tree.accept(new TreeTranslator() {
@Override
public void visitClassDef(JCTree.JCClassDecl jcClassDecl) {
List<JCTree.JCVariableDecl> jcVariableDeclList = List.nil();
// 在抽象树中找出所有的变量
for (JCTree jcTree : jcClassDecl.defs) {
if (jcTree.getKind().equals(Tree.Kind.VARIABLE)) {
JCTree.JCVariableDecl jcVariableDecl = (JCTree.JCVariableDecl) jcTree;
jcVariableDeclList = jcVariableDeclList.append(jcVariableDecl);
}
}
// 对于变量进行生成方法的操作
jcVariableDeclList.forEach(jcVariableDecl -> {
messager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.NOTE, jcVariableDecl.getName() + " has been processed");
jcClassDecl.defs = jcClassDecl.defs.prepend(createSetterMethodDeclaration(jcVariableDecl));
});
super.visitClassDef(jcClassDecl);
}
});
});
return true;
}
private JCTree.JCMethodDecl createSetterMethodDeclaration(JCTree.JCVariableDecl jcVariableDecl) {
ListBuffer<JCTree.JCStatement> statements = new ListBuffer<>();
// 生成表达式 例如 this.a = a;
JCTree.JCFieldAccess lhs = treeMaker.Select(treeMaker.Ident(names.fromString("this")), jcVariableDecl.getName());
JCTree.JCIdent rhs = treeMaker.Ident(jcVariableDecl.getName());
JCTree.JCExpressionStatement aThis = treeMaker.Exec(treeMaker.Assign(lhs, rhs));
statements.append(aThis);
JCTree.JCBlock block = treeMaker.Block(0, statements.toList());
// 生成入参
JCTree.JCVariableDecl param = treeMaker.VarDef(treeMaker.Modifiers(Flags.PARAMETER), jcVariableDecl.getName(), jcVariableDecl.vartype, null);
List<JCTree.JCVariableDecl> parameters = List.of(param);
// 生成返回对象
JCTree.JCExpression methodType = treeMaker.Type(new Type.JCVoidType());
return treeMaker.MethodDef(treeMaker.Modifiers(Flags.PUBLIC), getNewMethodName(jcVariableDecl.getName()), methodType, List.nil(), parameters, List.nil(), block, null);
}
private Name getNewMethodName(Name name) {
String s = name.toString();
return names.fromString("set" + s.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + s.substring(1, name.length()));
}
}
应用程序Main.java,很简单的一个类
import org.example.Setter;
public class Main {
@Setter
static class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("Foo"); // 这里应该是飘红的状态,因为源码中并未定义setter方法
System.out.println("person.name is " + person.name);
}
}
使用注解处理器
javac编译
首先,我们使用最原始的方式来演示,目录结构如下所示
│ Main.java
└─org
└─example
MyProcessor.java
Setter.java
先编译我们的注解处理器,注解处理器相关类应该是作为单独的jar包被引入的,就像lombok一样。这里我们简单点就行
javac -d ./ ./org/example/*.java
│ Main.java
└─org
└─example
MyProcessor$1.class
MyProcessor.class
MyProcessor.java
Setter.class
Setter.java
接下来编译我们的程序,并应用我们的程序
直接使用编译参数指定,例如:javac -classpath ./ -processor org.example.MyProcessor Main.java,这里我们指定了实现了javax.annotation.processing.Processor接口的全限定类名,所以要额外指定类路径才能找到我们的MyProcessor处理器类
➜ javac -classpath ./ -processor org.example.MyProcessor Main.java
注: name has been processed
注: age has been processed
➜ tree /f
卷 Data 的文件夹 PATH 列表
卷序列号为 16F3-63DB
D:.
│ Main$Person.class
│ Main.class
│ Main.java
│
└─org
└─example
MyProcessor$1.class
MyProcessor.class
MyProcessor.java
Setter.class
Setter.java
# 编译成功,运行我们的程序,可以看到注解处理器生效了
➜ java Main
person.name is Foo
javac支持以下注解处理器相关参数
-proc:{none,only}
Control whether annotation processing and/or compilation is done.
-processor <class1>[,<class2>,<class3>...]
Names of the annotation processors to run; bypasses default discovery process
-processorpath <path> Specify where to find annotation processors
-parameters Generate metadata for reflection on method parameters
SPI服务注册
另一种方式是通过SPI服务注册指定,在META-INF/services/javax.annotation.processing.Processor文件中添加
org.example.MyProcessor
这种方式就要求将注解处理器打成jar包了,同时还要放到类路径下
D:.
│ Main$Person.class
│ Main.class
│ Main.java
│
├─META-INF
│ └─services
│ javax.annotation.processing.Processor
│
└─org
└─example
MyProcessor$1.class
MyProcessor.class
MyProcessor.java
Setter.class
Setter.java
打包:jar cvf mylombok.jar -C .
已添加清单
正在添加: Main$Person.class(输入 = 543) (输出 = 323)(压缩了 40%)
正在添加: Main.class(输入 = 754) (输出 = 460)(压缩了 38%)
正在添加: Main.java(输入 = 345) (输出 = 187)(压缩了 45%)
正在忽略条目META-INF/
正在添加: META-INF/services/(输入 = 0) (输出 = 0)(存储了 0%)
正在添加: META-INF/services/javax.annotation.processing.Processor(输入 = 23) (输出 = 25)(压缩了 -8%)
正在添加: org/(输入 = 0) (输出 = 0)(存储了 0%)
正在添加: org/example/(输入 = 0) (输出 = 0)(存储了 0%)
正在添加: org/example/MyProcessor$1.class(输入 = 3275) (输出 = 1392)(压缩了 57%)
正在添加: org/example/MyProcessor.class(输入 = 6997) (输出 = 2399)(压缩了 65%)
正在添加: org/example/MyProcessor.java(输入 = 4624) (输出 = 1362)(压缩了 70%)
正在添加: org/example/Setter.class(输入 = 428) (输出 = 258)(压缩了 39%)
正在添加: org/example/Setter.java(输入 = 361) (输出 = 171)(压缩了 52%)
# Powershell
Get-ChildItem -File -Exclude *.java, *.jar |
ForEach-Object { $_.FullName -replace '\\', '/' } |
ForEach-Object { & jar rf myproject.jar $_ }
编译程序:javac -classpath ./mylombok.jar Main.java
➜ javac -classpath ./mylombok.jar Main.java
注: name has been processed
注: age has been processed
运行程序:java Main,和前面一样的效果
Idea编译配置
如果使用Idea来进行编译,则需要在Idea里进行配置:Build, Execution, Deployment > Compiler > Annotation Processor
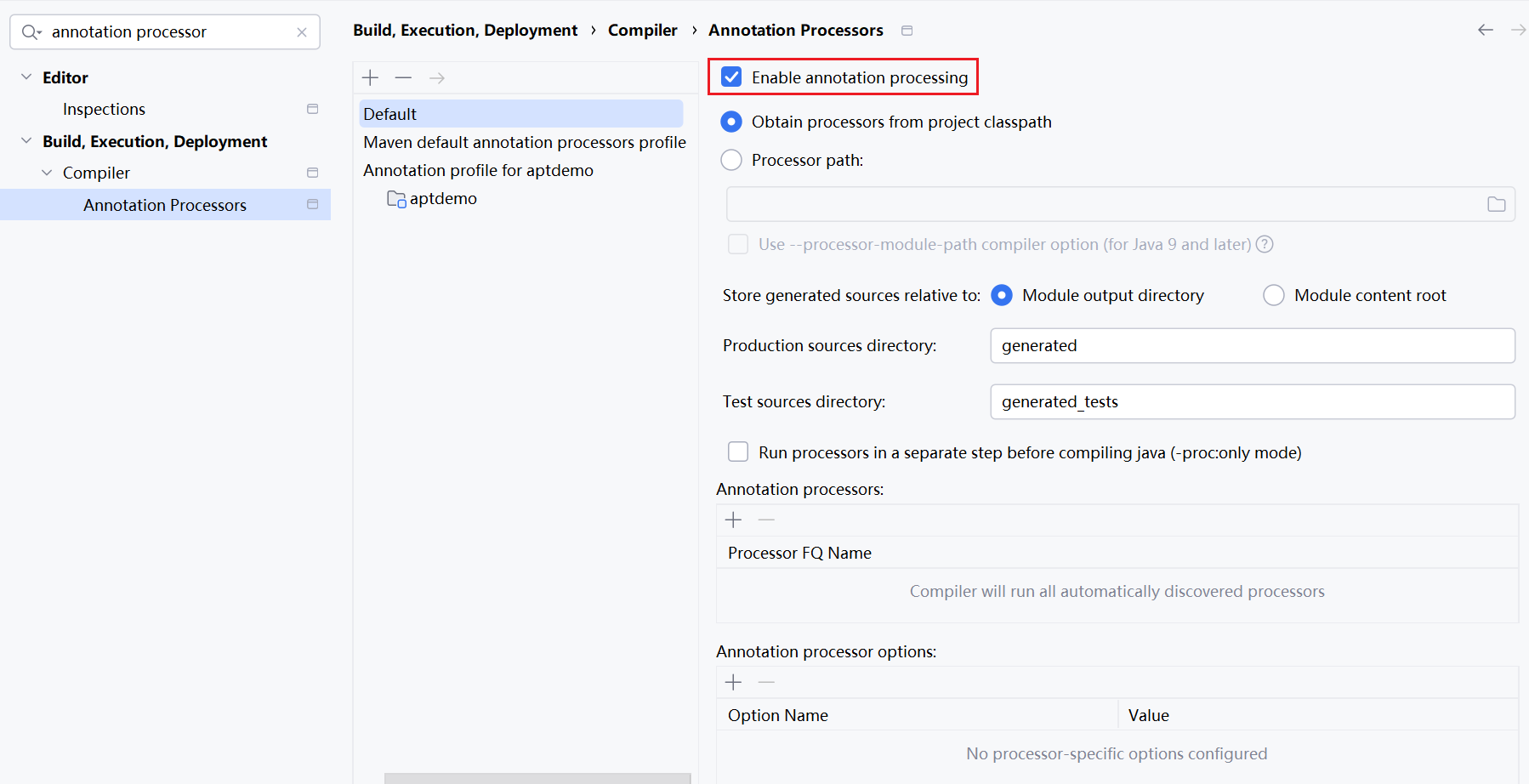
添加Annotation processors的全限定类名
Maven编译配置
通过maven编译进行触发,则需要先将jar包放到仓库中,然后在maven-compiler-plugin插件中配置相应的注解处理器坐标
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.7.0</version>
<configuration>
<annotationProcessorPaths>
<path>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.20</version>
</path>
</annotationProcessorPaths>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
参考资料
- JSR 269
https://download.oracle.com/otndocs/jcp/pluggable_annotation_processing-1_8-mrel2-spec/ - JEP117 Remove the Annotation-Processing Tool (apt): https://openjdk.org/jeps/117
- https://matthiasngeo.medium.com/the-problem-with-annotation-processors-802548a3bfdb
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/11385628/how-to-write-a-java-annotation-processor



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号