用户授权(访问控制)
授权的方式包括 web授权和方法授权,web授权是通过 url拦截进行授权,方法授权是通过 方法拦截进行授权。他 们都会调用accessDecisionManager进行授权决策,若为web授权则拦截器为
FilterSecurityInterceptor;若为方 法授权则拦截器为MethodSecurityInterceptor。如果同时通过web授权和方法授权则先执行web授权,再执行方 法授权,最后决策通过,则允许访问资源,否则将禁止访
问。
web授权
Spring Security可以通过 http.authorizeRequests() 对web请求进行授权保护 ,Spring Security使用标准Filter建立了对web请求的拦截,最终实现对资源的授权访问。
http.authorizeRequests() //设置哪些路径可以直接访问,不需要认证 .antMatchers("/user/login","/login.html").permitAll() .anyRequest().authenticated(); //需要认证才能访问
访问控制的url匹配
在配置类中http.authorizeRequests() 主要是对url进行控制。配置顺序会影响之后授权的效果,越是具体的应该放在前面,越是笼统的应该放到后面。
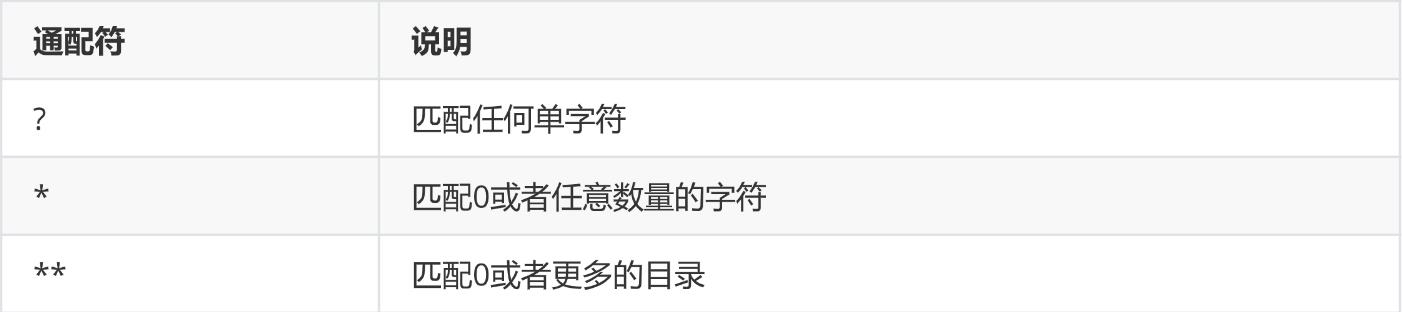
anyRequest() 表示匹配所有的请求。一般情况下此方法都会使用,设置全部内容都需要进行认证,会放在最后。 antMatchers() 方法定义如下: 参数是不定向参数,每个参数是一个 ant 表达式,用于匹配 URL规则。 ANT通配符有三种: .anyRequest().authenticated() public C antMatchers(String... antPatterns)
在实际项目中经常需要放行所有静态资源:
// 放行 js和css 目录下所有的文件 .antMatchers("/js/**","/css/**").permitAll() // 只要是.js 文件都放行 .antMatchers("/**/*.js").permitAll()
regexMatchers() 使用正则表达式进行匹配。 无论是 antMatchers() 还是 regexMatchers() 都具有两个参数的方法,其中第一个参数都是 HttpMethod ,表示请求方式,当设置了 HttpMethod 后表示只有设定的特定的请求方式才执行对应的 权限设置。 //所有以.js 结尾的文件都被放行 .regexMatchers( ".+[.]js").permitAll() .antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST,"/admin/demo").permitAll() .regexMatchers(HttpMethod.GET,".+[.]jpg").permitAll()
mvcMatchers()
适用于配置了 servletPath 的情况。 servletPath 就是所有的 URL 的统一前缀。在 SpringBoot 整合SpringMVC 的项目中可以在application.properties 中添加下面内容设置 ServletPath。 spring.mvc.servlet.path=/web
在 Spring Security 的配置类中配置 .servletPath() 是 mvcMatchers()返回值特有的方法,antMatchers()和 regexMatchers()没有这个方法。在 servletPath() 中配置了 servletPath 后, mvcMatchers()直接写 SpringMVC 中@RequestMapping()中设置的路径即可。
如果不习惯使用 mvcMatchers()也可以使用 antMatchers(),下面代码和上面代码是等效的:
.mvcMatchers("/admin/demo").servletPath("/web").permitAll() .antMatchers("/web/admin/demo").permitAll()
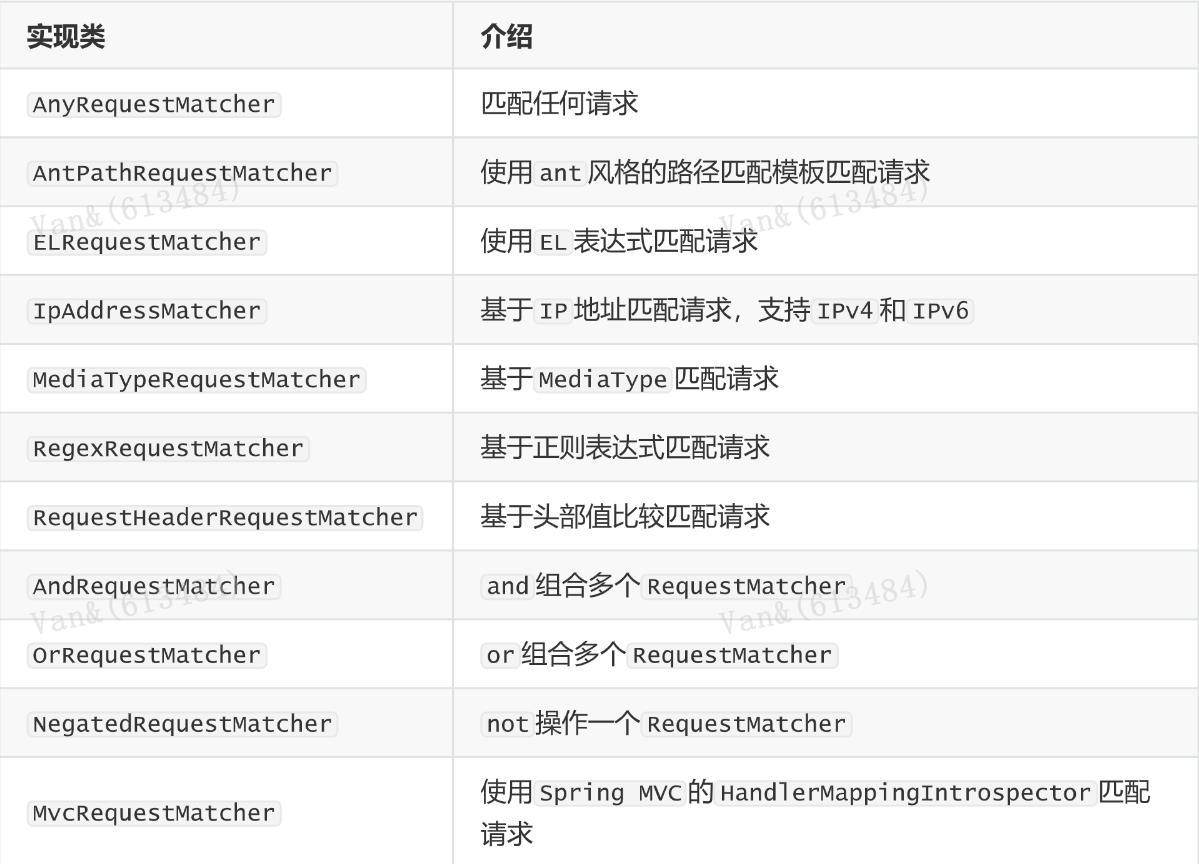
RequestMatcher接口
RequestMatcher 是 Spring Security Web 的一个概念模型接口,用于抽象建模对HttpServletRequest 请求的匹配器这一概念。 Spring Security 内置提供了一些 RequestMatcher
实现类:
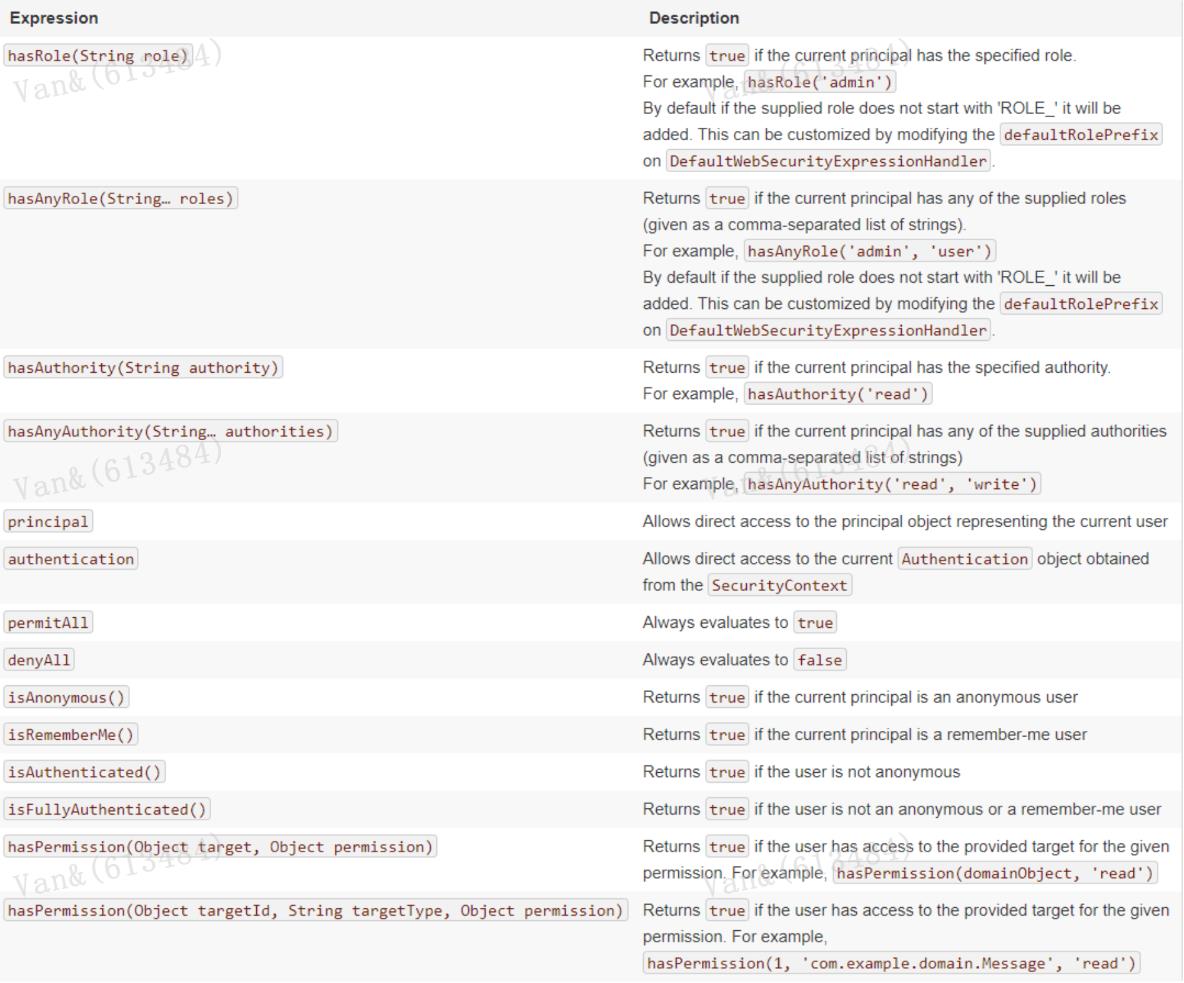
内置的访问控制 【常用】 #permitAll() 方法,所有用户可访问。 【常用】 #denyAll() 方法,所有用户不可访问。 【常用】 #authenticated() 方法,登录用户可访问。 #anonymous() 方法,无需登录,即匿名用户可访问。 #rememberMe() 方法,通过 remember me登录的用户可访问。 #fullyAuthenticated() 方法,非 remember me 登录的用户可访问。 #hasIpAddress(String ipaddressExpression) 方法,来自指定 IP 表达式的用户可访问。 【常用】 #hasRole(String role) 方法, 拥有指定角色的用户可访问,角色将被增加 “ROLE_”前缀。 【常用】 #hasAnyRole(String... roles) 方法,拥有指定任一角色的用户可访问。 【常用】 #hasAuthority(String authority) 方法,拥有指定权限( authority )的用户可访问。 【常用】 #hasAuthority(String... authorities) 方法,拥有指定任一权限( authority )的用户可访问。 【最牛】 #access(String attribute) 方法,当 Spring EL 表达式的执行结果为 true 时,可以访问。
基于权限的访问控制
除了之前讲解的内置权限控制。Spring Security 中还支持很多其他权限控制。这些方法一般都用于用户 已经被认证后,判断用户是否具有特定的要求。 hasAuthority(String) 判断用户是否具有特定的权限,用户的权限是在自定义登录逻辑中创建 User 对象时指定的。权限名称大小写敏感,在配置类中通过 hasAuthority(“admin”)设置具有 admin 权限时才能访问。 否则报403错误 return new User("fox", pw,AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin,user"));//admin,user就是用户的权限
.antMatchers("/admin/demo").hasAuthority("admin")
hasAnyAuthority(String ...) 如果用户具备给定权限中某一个,就允许访问。 .antMatchers("/admin/demo").hasAnyAuthority("admin","System")
基于角色的访问控制
hasRole(String) 如果用户具备给定角色就允许访问,否则出现 403。参数取值来源于自定义登录逻辑 UserDetailsService 实现类中创建 User 对象时给 User 赋予的授权。 在给用户赋予角色时角色需要以: ROLE_开头 ,后面添加角色名称。例如:ROLE_admin 其中 admin是角 色名, ROLE_ 是固定的字符开头。
使用 hasRole()时参数也只写admin 即可,否则启动报错。 hasAnyRole(String ...) 如果用户具备给定角色的任意一个,就允许被访问 。 hasIpAddress(String) 如果请求是指定的 IP 就运行访问。 可以通过 request.getRemoteAddr() 获取 ip 地址。需要注意的是在 本机进行测试时 localhost 和 127.0.0.1 输出的 ip地址是不一样的。 自定义403处理方案 使用 Spring Security 时经常会看见 403(无权限)。Spring Security 支持自定义权限受限处理,需要 实现 AccessDeniedHandler接口 在配置类中设置访问受限后交个MyAccessDeniedHandler处理
return new User("fox", pw,AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("ROLE_admin,user"));//给用户赋予admin角色 .antMatchers("/admin/demo").hasRole("admin") // localhost --> getRemoteAddr: 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 .antMatchers("/admin/demo").hasIpAddress("127.0.0.1")
public class MyAccessDeniedHandler implements AccessDeniedHandler { @Override public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) throws IOException, ServletException { response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_FORBIDDEN); response.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf-8"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); out.write("{\"status\":\"error\",\"msg\":\"权限不足,请联系管理员!\"}"); out.flush(); out.close(); } }
http.exceptionHandling() .accessDeniedHandler(new MyAccessDeniedHandler());
基于表达式的访问控制
access(表达式) 之前学习的登录用户权限判断实际上底层实现都是调用access(表达式) https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.2.7.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#tech-intro-access-control 表达式根对象的基类是SecurityExpressionRoot,提供了一些在web和方法安全性中都可用的通用表达式。
可以通过 access() 实现和之前学习的权限控制完成相同的功能。 .antMatchers("/user/login","/login.html").access("permitAll") .antMatchers("/admin/demo").access("hasAuthority('System')")
自定义方法 判断登录用户是否具有访问当前 URL 的权限。 @Component public class MySecurityExpression implements MySecurityExpressionOperations{ @Override public boolean hasPermission(HttpServletRequest request, Authentication authentication) { // 获取主体 Object obj = authentication.getPrincipal(); if (obj instanceof UserDetails){ UserDetails userDetails = (UserDetails) obj; // String name = request.getParameter("name"); //获取权限 Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = userDetails.getAuthorities(); //判断name值是否在权限中 return authorities.contains(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(name)); } return false; } 在 access 中通过bean的beanName.方法(参数)的形式进行调用: } .anyRequest().access("@mySecurityExpression.hasPermission(request,authentication )")
方法授权
基于注解的访问控制
Spring Security在方法的权限控制上支持三种类型的注解,JSR-250注解、@Secured注解和支持表达式的注解。这三种注解默认都是没有启用的,需要通过@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity来进行启用。 这些注解可以写到 Service 接口或方法上,也可以写到 Controller或 Controller 的方法上。通常情况下都是写在控制器方法上的,控制接口URL是否允许被访问。
JSR-250注解
@RolesAllowed 表示访问对应方法时所应该具有的角色。其可以标注在类上,也可以标注在方法上,当标注在类上时表示其中所有方法的执行都需要对应的角色,当标注在方法上表示执行该方法时所需要的角色,当方法和 类上都使用了@RolesAllowed进行标注,则方法上的@RolesAllowed将覆盖类上的@RolesAllowed,即方法上@RolesAllowed将对当前方法起作用。@RolesAllowed的值是由角色名称组成的数组。
@PermitAll 表示允许所有的角色进行访问,也就是说不进行权限控制。@PermitAll可以标注在方法上也可以标注在类上,当标注在方法上时则只对对应方法不进行权限控制,而标注在类上时表示对类里面所有的方法都 不进行权限控制。
(1)当@PermitAll标注在类上,而@RolesAllowed标注在方法上时则按照@RolesAllowed将覆盖@PermitAll,即需要@RolesAllowed对应的角色才能访问。 (2)当@RolesAllowed标注在类上,而@PermitAll标注在方法上时则对应的方法也是不进行权限控制的。 (3)当在类和方法上同时使用了@PermitAll和@RolesAllowed时先定义的将发生作用(这个没多大的实际意义,实际应用中不会有这样的定义)。
@DenyAll 是和PermitAll相反的,表示无论什么角色都不能访问。@DenyAll只能定义在方法上。你可能会有疑问使用@DenyAll标注的方法无论拥有什么权限都不能访问,那还定义它干啥呢?使用@DenyAll定义的方 法只是在我们的权限控制中不能访问,脱离了权限控制还是可以访问的。
开启注解 在启动类或者在配置类上添加 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(jsr250Enabled = true)
在controller方法上添加@RolesAllowed注解
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(jsr250Enabled = true) public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
修改配置类 @RolesAllowed({"ROLE_USER", "ROLE_ADMIN"}) //@PermitAll @GetMapping("/demo") public String demo() { return "spring security demo"; }
@Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.formLogin() //表单提交 .loginPage("/login.html") //自定义登录页面 .loginProcessingUrl("/user/login") //登录访问路径,必须和表单提交接口一样 .successHandler(new MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler("/main.html")) .failureHandler(new MyAuthenticationFailureHandler("/error.html")) //授权 .and().authorizeRequests() //设置哪些路径可以直接访问,不需要认证 .antMatchers("/user/login","/login.html").permitAll() .anyRequest().authenticated() //需要认证 .and().csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf防护 }
@Secured注解
@Secured是由Spring Security定义的用来支持方法权限控制的注解。它的使用也是需要启用对应的支持才会生效的。@Secured 是专门用于判断是否具有角色的,能写在方法或类上。参数要以 ROLE_开 头。
开启注解 在启动类或者在配置类上添加 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true) 在controller方法上添加@Secured 注解
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true) public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Secured("ROLE_ADMIN") @GetMapping("/demo") public String demo() { return " spring security demo"; }
支持表达式的注解 Spring Security中定义了四个支持使用表达式的注解,分别是@PreAuthorize、@PostAuthorize、 @PreFilter和@PostFilter。其中前两者可以用来在方法调用前或者调用后进行权限检查,后两者可以用 来对集合类型的参数或者返回值进行过滤。 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true) public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { 使用@PreAuthorize和@PostAuthorize进行访问控制 @PreAuthorize可以用来控制一个方法是否能够被调用,执行之前先判断权限,大多情况下都是使用这 个注解。 @PostAuthorize可以在方法调用完之后进行权限检查 使用@PreFilter和@PostFilter进行过滤 使用@PreFilter和@PostFilter可以对集合类型的参数或返回值进行过滤。使用@PreFilter和@PostFilter 时,Spring Security将移除使对应表达式的结果为false的元素。 //@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')") //@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_USER') or hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')") //限制只能查询Id小于10的用户 @PreAuthorize("#id<10") @RequestMapping("/findById") public User findById(long id) { User user = new User(); user.setId(id); return user; } // 限制只能查询自己的信息 @PreAuthorize("principal.username.equals(#username)") @RequestMapping("/findByName") public User findByName(String username) { User user = new User(); user.setUsername(username); return user; } //限制只能新增用户名称为abc的用户 @PreAuthorize("#user.username.equals('abc')") @RequestMapping("/add") public User add(User user) { return user; } // 在方法find()调用完成后进行权限检查,如果返回值的id是偶数则表示校验通过,否则表示校验失败,将 抛出AccessDeniedException @PostAuthorize("returnObject.id%2==0") public User find(int id) { User user = new User(); user.setId(id); return user; } @PostFilter("filterObject.id%2==0") public List<User> findAll() { List<User> userList = new ArrayList<User>(); User user; for (int i=0; i<10; i++) { user = new User(); user.setId(i); userList.add(user); } return userList; } @PreFilter(filterTarget="ids", value="filterObject%2==0") public void delete(List<Integer> ids, List<String> usernames) { }
授权原理
重写 #configure(HttpSecurity http) 方法,主要配置 URL 的权限控制调用 HttpSecurity#authorizeRequests() 方法,开始配置 URL 的权限控制。 修改 WebSecurityConfig配置类,增加 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 注解,开启对 Spring Security 注解的方法,进行权限验证。
@Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http // 配置请求地址的权限 .authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/test/echo").permitAll() // 所有用户可访问 .antMatchers("/test/admin").hasRole("ADMIN") // 需要 ADMIN 角色 .antMatchers("/test/normal").access("hasRole('ROLE_NORMAL')") // 需要 NORMAL 角色。 // 任何请求,访问的用户都需要经过认证 .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() // 设置 Form 表单登录 //自定义登录页面,可以通过 #loginPage(String loginPage) 设置 .formLogin() // .loginPage("/login") // 登录 URL 地址 .permitAll() // 所有用户可访问 .and() // 配置退出相关 .logout() // .logoutUrl("/logout") // 退出 URL 地址 .permitAll(); // 所有用户可访问 }
@Configuration @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true) public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @RestController @RequestMapping("/demo") public class DemoController { @PermitAll @GetMapping("/echo") public String demo() { return "示例返回"; } @GetMapping("/home") public String home() { return "我是首页"; } @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')") @GetMapping("/admin") public String admin() { return "我是管理员"; } @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_NORMAL')") @GetMapping("/normal") public String normal() { return "我是普通用户"; } }
授权流程
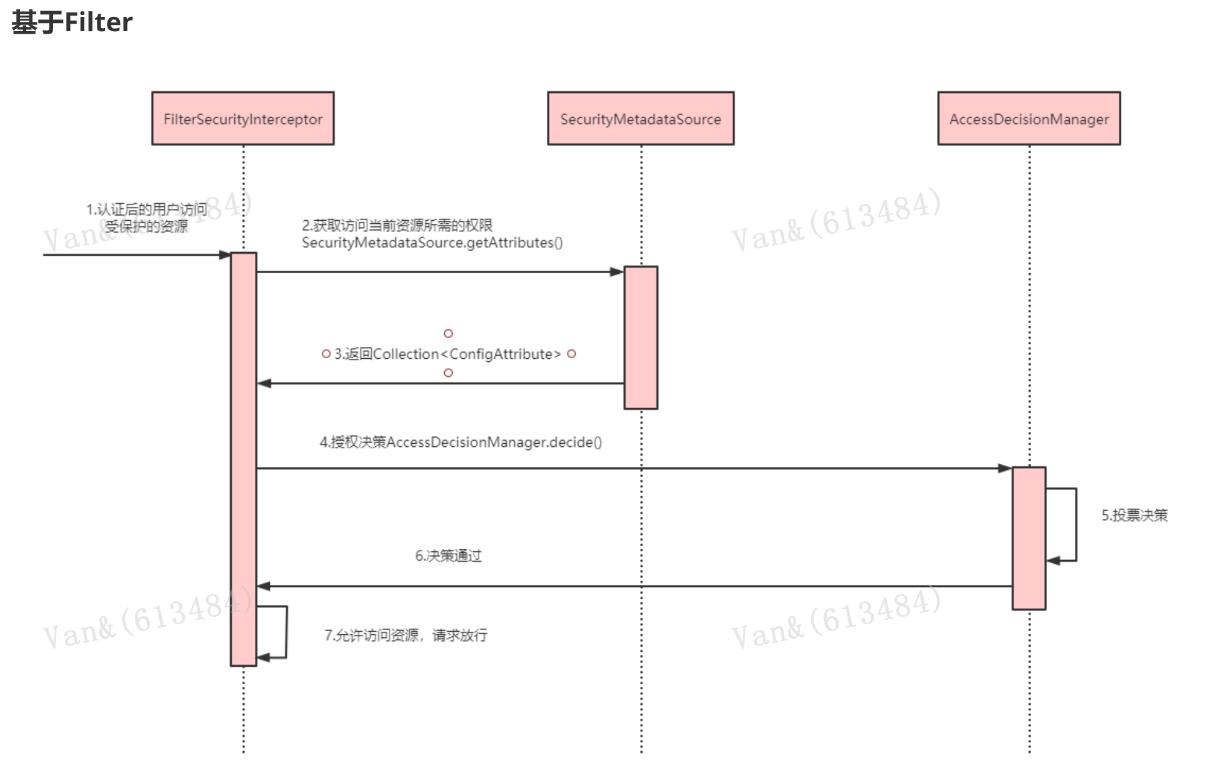
1. 拦截请求,已认证用户访问受保护的web资源将被SecurityFilterChain中的FilterSecurityInterceptor 的子 类拦截。 2. 获取资源访问策略,FilterSecurityInterceptor会从 SecurityMetadataSource 的子类DefaultFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource 获取要访问当前资源所需要的权限Collection 。 SecurityMetadataSource其实就是读取访问策略的抽象,而读取的内容,其实就是我们配置的访问规则 3. 最后,FilterSecurityInterceptor会调用 AccessDecisionManager 进行授权决策,若决策通过,则允许访问资 源,否则将禁止访问。
基于AOP
//MethodSecurityInterceptor#invoke public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(mi); Object result; try { result = mi.proceed(); } finally { super.finallyInvocation(token); } return super.afterInvocation(token, result); }
相关接口
AccessDecisionManager AccessDecisionManager采用投票的方式来确定是否能够访问受保护资源。 AccessDecisionManager 中包含的一系列AccessDecisionVoter将会被用来对Authentication是否有权访问受保护对象进行投票, AccessDecisionManager根据投票结果,做出最终决策 。 public interface AccessDecisionManager { // ~ Methods // ================================================================================ ======================== /** * 用来鉴定当前用户是否有访问对应受保护资源的权限 * authentication:要访问资源的访问者的身份 * o bject:要访问的受保护资源,web请求对应FilterInvocation * configAttributes:是受保护资源的访问策略,通过SecurityMetadataSource获取 * / void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException, InsufficientAuthenticationException; boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute); boolean supports(Class<?> clazz); }
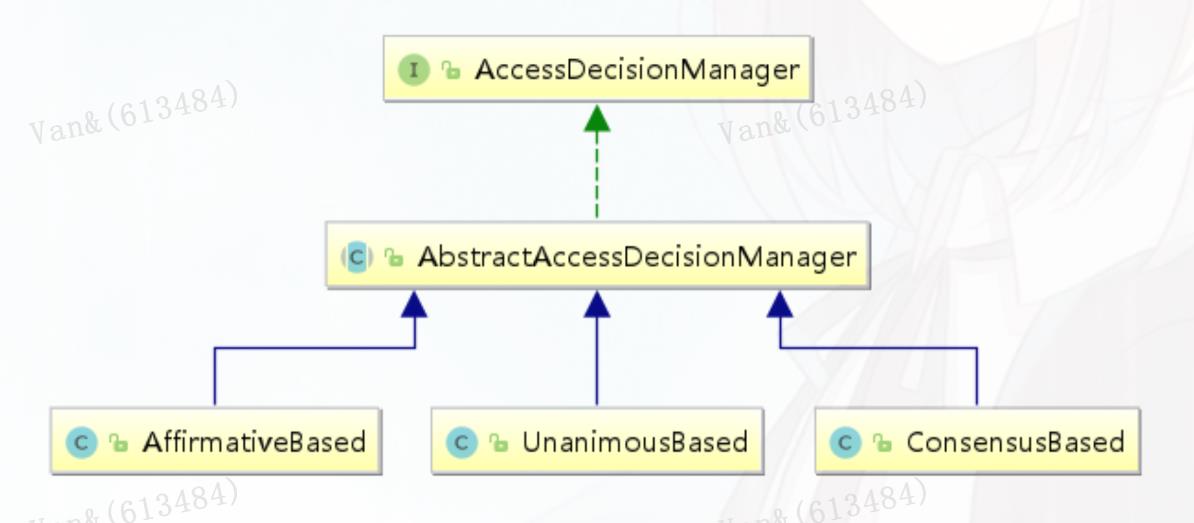
AffirmativeBased AffirmativeBased的逻辑是:
(1)只要有AccessDecisionVoter的投票为ACCESS_GRANTED则同意用户进行访问;
(2)如果全部弃权也表示通过;
(3)如果没有一个人投赞成票,但是有人投反对票,则将抛出AccessDeniedException。
Spring security默认使用的是AffirmativeBased。
ConsensusBased ConsensusBased的逻辑是:
(1)如果赞成票多于反对票则表示通过。
(2)反过来,如果反对票多于赞成票则将抛出AccessDeniedException。
(3)如果赞成票与反对票相同且不等于0,并且属性allowIfEqualGrantedDeniedDecisions的值为true,则表 示通过,否则将抛出异常AccessDeniedException。参数allowIfEqualGrantedDeniedDecisions的值默认为true。 (4)如果所 有的AccessDecisionVoter都弃权了,则将视参数allowIfAllAbstainDecisions的值而定,如果该值 为true则表示通过,否则将抛出异常AccessDeniedException。参数allowIfAllAbstainDecisions的值默认 为false。
UnanimousBased
UnanimousBased的逻辑与另外两种实现有点不一样,另外两种会一次性把受保护对象的配置属性全部传递 给AccessDecisionVoter进行投票,而UnanimousBased会一次只传递一个ConfigAttribute给 AccessDecisionVoter进行投票。这也就意味着如果我们的AccessDecisionVoter的逻辑是只要传递进来的 ConfigAttribute中有一个能够匹配则投赞成票,但是放到UnanimousBased中其投票结果就不一定 是赞成了。
UnanimousBased的逻辑具体来说是这样的:
(1)如果受保护对象配置的某一个ConfigAttribute被任意的AccessDecisionVoter反对了,则将抛出 AccessDeniedException。
(2)如果没有反对票,但是有赞成票,则表示通过。
(3)如果全部弃权了,则将视参数allowIfAllAbstainDecisions的值而定,true则通过,false则抛出 AccessDeniedException。
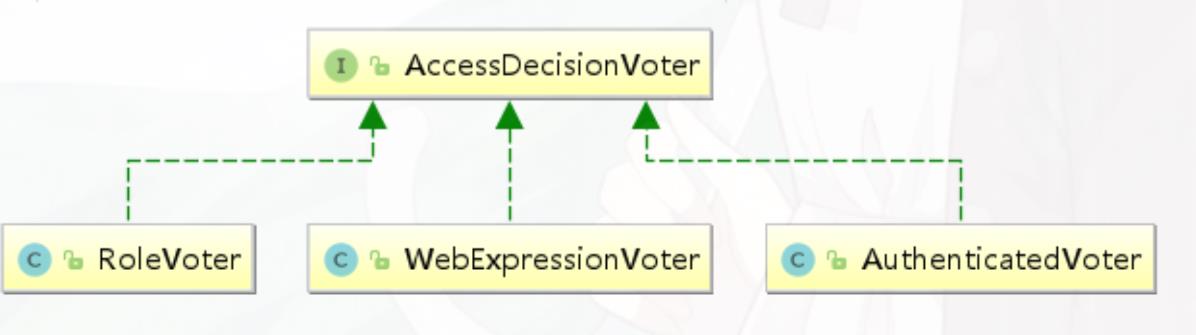
AccessDecisionVoter
public interface AccessDecisionVoter<S> { int ACCESS_GRANTED = 1; //同意 int ACCESS_ABSTAIN = 0; //弃权 int ACCESS_DENIED = -1; //拒绝 boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute); boolean supports(Class<?> clazz); // 返回结果是AccessDecisionVoter中定义的三个常量之一 int vote(Authentication authentication, S object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes); }
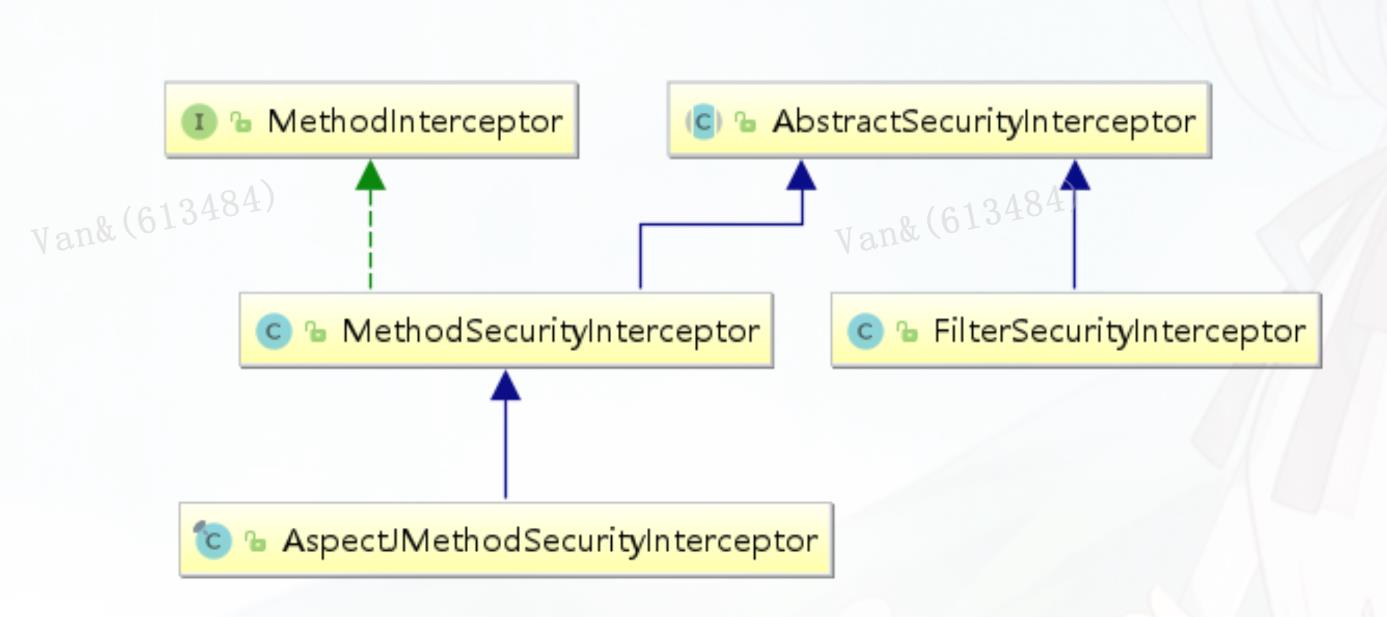
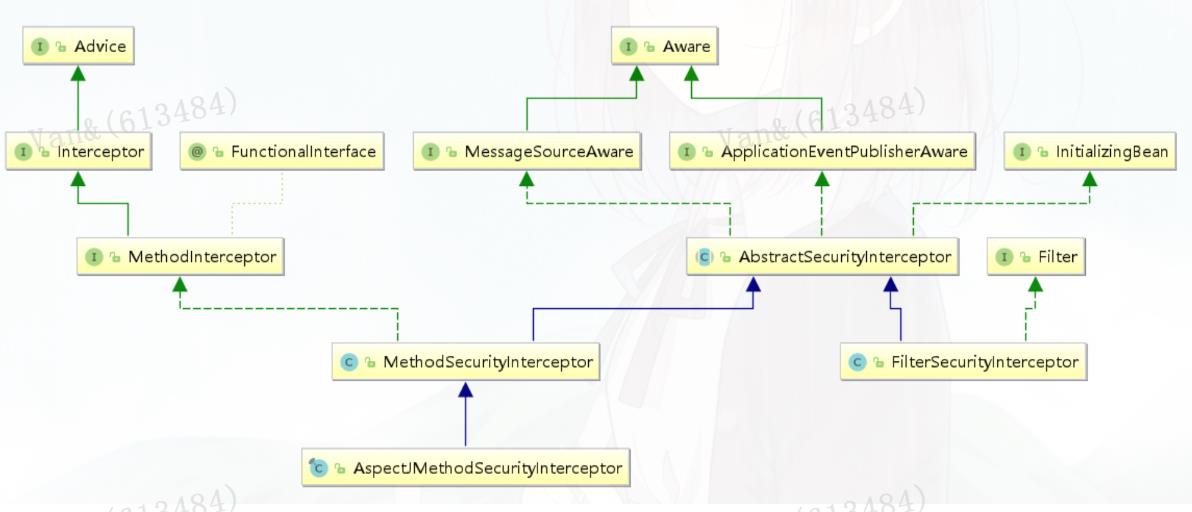
MethodSecurityInterceptor Spring Security提供了两类AbstractSecurityInterceptor,基于AOP Alliance的MethodSecurityInterceptor,和基于Aspectj继承自MethodSecurityInterceptor的 AspectJMethodSecurityInterceptor
//MethodSecurityInterceptor#invoke public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(mi); Object result; try { result = mi.proceed(); } finally { super.finallyInvocation(token); } return super.afterInvocation(token, result); }
Spring Security实现原理
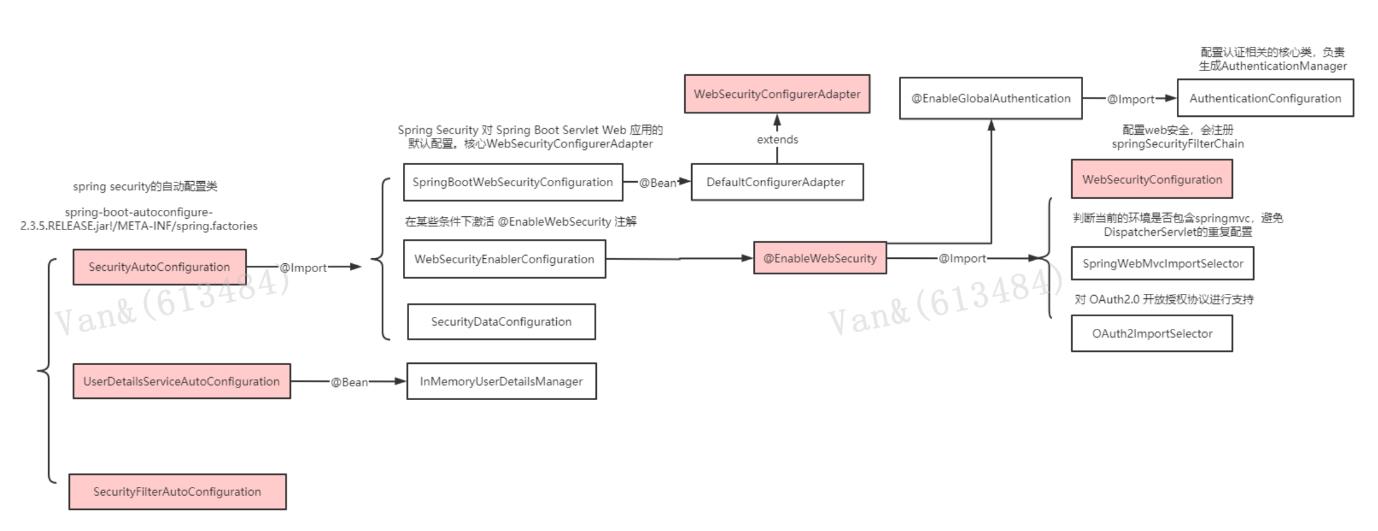
3.1 核心配置 @EnableWebSecurity
https://www.processon.com/view/link/5fa53783637689653d8af2f7
@Retention(value = java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(value = { java.lang.annotation.ElementType.TYPE }) @Documented @Import({ WebSecurityConfiguration.class, SpringWebMvcImportSelector.class, OAuth2ImportSelector.class }) @EnableGlobalAuthentication @Configuration public @interface EnableWebSecurity { /** * Controls debugging support for Spring Security. Default is false. * @return if true, enables debug support with Spring Security * / boolean debug() default false; }
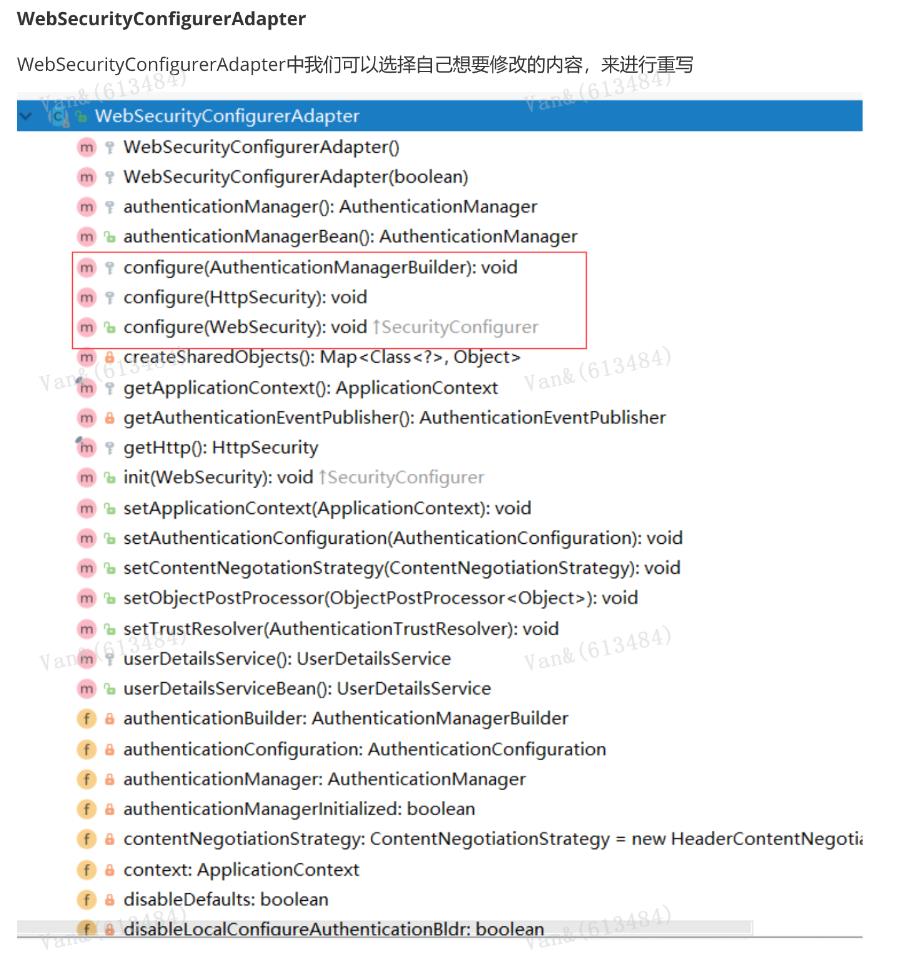
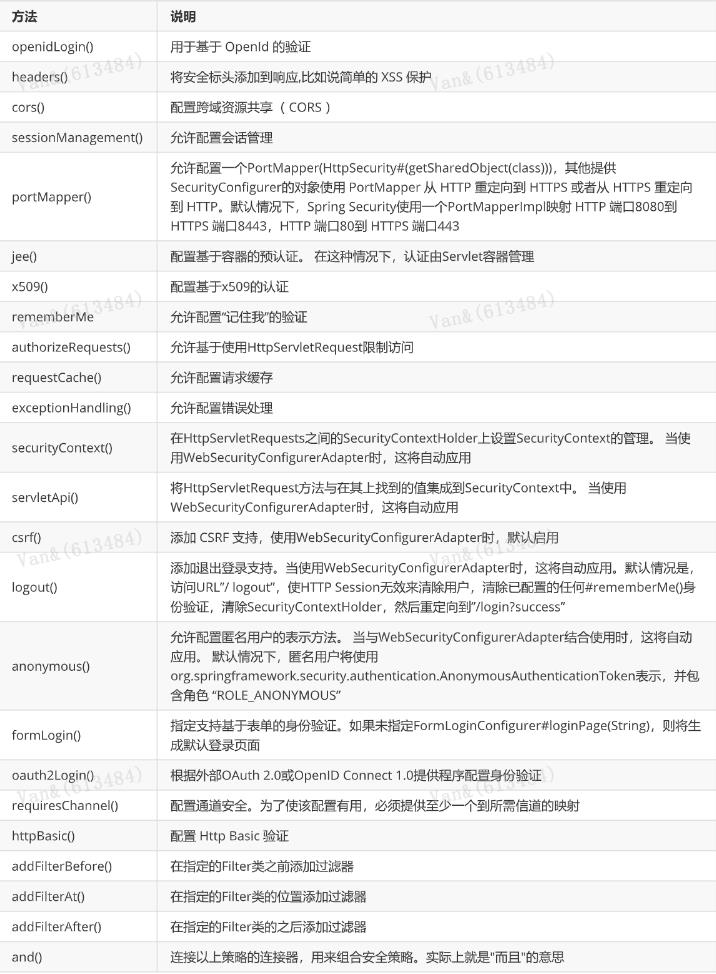
HttpSecurity 安全过滤器链配置 @Configuration public class CustomWebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/resources/**", "/signup", "/about").permitAll() .antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") .antMatchers("/db/**").access("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')") .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() .formLogin() .usernameParameter("username") .passwordParameter("password") authorizeRequests()配置路径拦截,表明路径访问所对应的权限,角色,认证信息。 formLogin()对应表单认证相关的配置 logout()对应了注销相关的配置 httpBasic()可以配置basic登录 所有的http相关配置可以通过查看HttpSecurity的主要方法获取。 .failureForwardUrl("/login?error") .loginPage("/login") .permitAll() .and() .logout() .logoutUrl("/logout") .logoutSuccessUrl("/index") .permitAll() .and() .httpBasic() .disable(); } }
WebSecurity 核心过滤器配置 WebSecurity 基于Servlet Filter 用来配置 springSecurityFilterChain,而springSecurityFilterChain 又 被委托给了 Spring Security 核心过滤器DelegatingFilterProxy 。我们一般不会过多来自定义 WebSecurity , 使用较多的使其ignoring() 方法用来忽略 Spring Security 对静态资源的控制。 AuthenticationManagerBuilder 认证管理器配置 全局配置, 使用@Autowired注入的AuthenticationManagerBuilder是全局的身份认证器,作用域可以 跨越多个WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter。 public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception { web .ignoring() .antMatchers("/resources/**"); } @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth .inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("admin").password("admin").roles("USER"); } @Autowired public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth .inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("admin").password("admin").roles("USER"); }
FilterChain
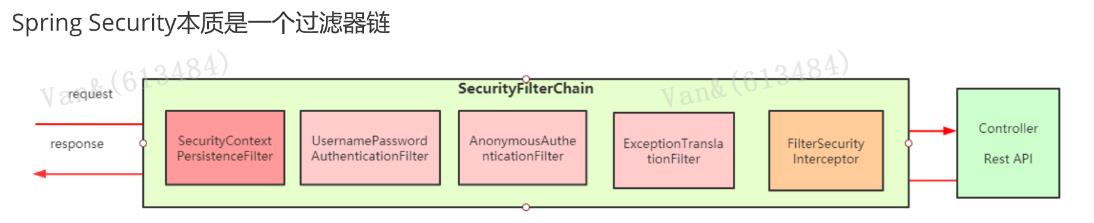
认证的调用栈
SecurityFilterChain SecurityContextPersistenceFilter 两个主要职责:请求来临时,创建 SecurityContext 安全上下文信息,请求结束时清空 SecurityContextHolder。过滤器负责核心的处理流程,存储安全上下文和读取安全上下文的工作完全委 托给了HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository去处理 public interface SecurityFilterChain { boolean matches(HttpServletRequest request); List<Filter> getFilters(); } //SecurityContextPersistenceFilter#doFilter HttpRequestResponseHolder holder = new HttpRequestResponseHolder(request, response); //从Session中获取安全上下文信息,不存在创建一个新的SecurityContext SecurityContext contextBeforeChainExecution = repo.loadContext(holder); try { //请求开始时,设置安全上下文信息 SecurityContextHolder.setContext(contextBeforeChainExecution); chain.doFilter(holder.getRequest(), holder.getResponse()); } finally { //请求结束后,清空安全上下文信息 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 表单提交了username和password,被封装成token进行一系列的认证,便是主要通过这个过滤器完成 的,在表单认证的方法中,这是最最关键的过滤器。 SecurityContext contextAfterChainExecution = SecurityContextHolder . getContext(); // AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter Authentication authResult; try { // 调用UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter的attemptAuthentication方法 authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response); if (authResult == null) { // return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed // authentication //子类未完成认证,立刻返回 return; } sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response); } catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) { logger.error( " An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.", failed); unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed); return; } catch (AuthenticationException failed) { // Authentication failed unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed); return; } // Authentication success if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) { chain.doFilter(request, response); } successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult); // UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter#attemptAuthentication public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException { if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) { throw new AuthenticationServiceException( " Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod()); } ExceptionTranslationFilter ExceptionTranslationFilter异常转换过滤器位于整个springSecurityFilterChain的后方,用来转换整个 链路中出现的异常。此过滤器本身不处理异常,而是将认证过程中出现的异常交给内部维护的一些类去 处理,一般处理两大类异常:AccessDeniedException访问异常和AuthenticationException认证异常。 FilterSecurityInterceptor FilterSecurityInterceptor从SecurityContextHolder中获取Authentication对象,然后比对用户拥有的 权限和资源所需的权限。这是一个方法级的权限过滤器, 基本位于过滤链的最底部 。这个过滤器决定了 访问特定路径应该具备的权限,访问的用户的角色,权限是什么?访问的路径需要什么样的角色和权 限?这些判断和处理都是由该类进行的。 HeaderWriterFilter: 用来给http响应添加一些Header,比如X-Frame-Options, X-XSS- Protection*,X-Content-Type-Options. CsrfFilter:在spring4中被默认开启的一个过滤器,用于防止csrf攻击(跨站点请求伪造(Cross- site request forgery)) LogoutFilter :处理注销的过滤器 RequestCacheAwareFilter: 内部维护了一个RequestCache,用于缓存request请求 SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter :对ServletRequest进行了一次包装,使得request 具有更加丰富的API SessionManagementFilter: 和session相关的过滤器,内部维护了一个 SessionAuthenticationStrategy,两者组合使用,常用来防止会话固定攻击保护( session- fixation protection attack ),以及限制同一用户开启多个会话的数量 AnonymousAuthenticationFilter 匿名身份过滤器,spring security为了兼容未登录的访问,也走了一套认证流程,只不过是一个匿 名的身份。 String username = obtainUsername(request); String password = obtainPassword(request); if (username == null) { username = "" ; } if (password == null) { password = ""; } username = username.trim(); //将认证信息封装成token, 当前认证状态是false UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken( username, password); // Allow subclasses to set the "details" property setDetails(request, authRequest); // 通过AuthenticationManager去认证,并返回认证信息 return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest); } 3.3 主线源码分析 https://www.processon.com/view/link/5fa3ae25e401fd45d10296e1



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号