掌握 LangChain4j:深入探讨会话式 AI、RAG 和Function Calling
会话功能
快速入门
- 引入Langchian4j依赖
<dependency> <groupId>dev.langchain4j</groupId> <artifactId>langchain4j-open-ai-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.1.0-beta7</version> </dependency> - 构建OpenAiChatModel对象
// 构建OpenAiChatModel对象 OpenAiChatModel model = OpenAiChatModel.builder() .baseUrl(baseUrl) .apiKey(apiKey) .modelName("qwen-plus") .build(); - 调用chat方法与大模型交互
// 调用chat方法交互 String result = model.chat("请将下面一段英文翻译成中文:I love programming."); System.out.println(result);
打印日志信息
- 引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> <artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId> <version>1.5.18</version> </dependency> - 设置
logRequests和logResponses以打印日志信息// 构建OpenAiChatModel对象 OpenAiChatModel model = OpenAiChatModel.builder() .baseUrl(baseUrl) .apiKey(apiKey) .modelName("qwen-plus") .logRequests(true) .logResponses(true) .build();
Spring整合LangChain4j
- 构建springboot项目
- 引入起步依赖
<dependency> <groupId>dev.langchain4j</groupId> <artifactId>langchain4j</artifactId> <version>1.1.0</version> </dependency> - application.yml中配置大模型
langchain4j: open-ai: chat-model: base-url: https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1 api-key: sk-8007e602891742f59f118c678a3ab7d1 model-name: qwen-plus - 开发接口,调用大模型
@RestController
public class ChatController {
@Autowired
private OpenAiChatModel model;
@RequestMapping("/chat")
public String chat(String message) {
String result = model.chat(message);
return result;
}
}
日志相关配置
langchain4j:
open-ai:
chat-model:
base-url: https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1
api-key: sk-8007e602891742f59f118c678a3ab7d1
model-name: qwen-plus
log-request: true
log-response: true
logging:
level:
dev.langchain4j: debug
AiServices工具类
AiServices工具类封装了
- 会话记忆
- Rag知识库
- Tools工具
等,便于开发使用
AiServices的使用方式
- 引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>dev.langchain4j</groupId> <artifactId>langchain4j-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.1.0-beta7</version> </dependency> - 声明接口
public interface ConsultantService { // 用于聊天的方法 public String chat(String message); } - 使用AiServices为接口创建代理对象(下面提供了两种方式)
@Configuration public class CommonConfig { @Autowired private OpenAiChatModel model; @Bean public ConsultantService consultantService() { ConsultantService cs = AiServices.builder(ConsultantService.class) .chatModel(model) .build(); return cs; } }import dev.langchain4j.service.spring.AiService; import dev.langchain4j.service.spring.AiServiceWiringMode; @AiService( wiringMode = AiServiceWiringMode.EXPLICIT, chatModel = "openAiChatModel" ) public interface ConsultantService { // 用于聊天的方法 public String chat(String message); } - 在Controller中注入并使用
流式调用
- 引入依赖
<!-- 流式调用 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>dev.langchain4j</groupId> <artifactId>langchain4j-reactor</artifactId> <version>1.1.0-beta7</version> </dependency> - 配置流式模型对象
langchain4j: open-ai: chat-model: base-url: https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1 api-key: sk-8007e602891742f59f118c678a3ab7d1 model-name: qwen-plus log-request: true log-response: true streaming-chat-model: base-url: https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1 api-key: sk-8007e602891742f59f118c678a3ab7d1 model-name: qwen-plus log-request: true log-response: true- LangChain4j会自动注入chat-model、streaming-chat-model对象
- 切换接口中方法的返回值类型
@AiService( wiringMode = AiServiceWiringMode.EXPLICIT, chatModel = "openAiChatModel", streamingChatModel = "openAiStreamingChatModel" ) public interface ConsultantService { // 用于聊天的方法 @SystemMessage("You are a helpful assistant.") Flux<String> chat(String message); } - 修改controller中的代码
@RequestMapping(value = "/chat", produces = "text/html;charset=utf-8") public Flux<String> chat(String message) { Flux<String> result = consultantService.chat(message); return result; }
消息注解
@SystemMessage
系统消息
@SystemMessage("你是一名武汉大学的学生")
public Flux<String> chat(String message);
@SystemMessage(fromResource = "system.txt")
public Flux<String> chat(String message);
@UserMessage
@UserMessage("你是一名武汉大学的学生。{{it}}")
public Flux<String> chat(String message);
@SystemMessage("你是一名武汉大学的学生。{{msg}}")
public Flux<String> chat(@V("msg") String message);
- 必须使用it进行占位或者使用
@V保证同名
对比
系统信息是通过系统角色发送的,而用户消息只是进行了拼接(在用户的消息前拼接我们的信息)
会话记忆
大模型不具备记忆能力,想让大模型记住之前聊天的内容,唯一的办法就是把之前的内容和新的提示词一起发给大模型。
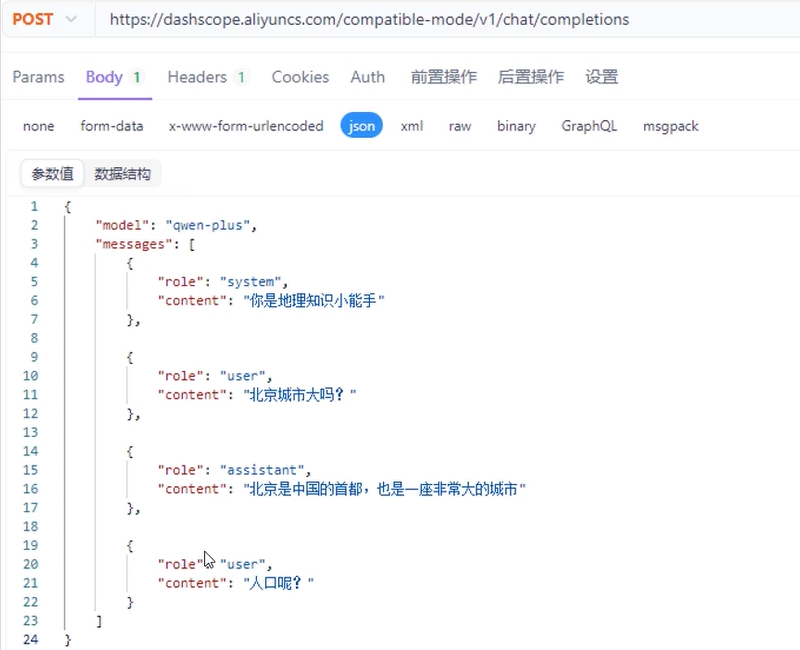
- web后端专门设置存储对象去完成消息记忆
会话记忆实现
- 定义会话记忆对象
- 配置会话记忆对象
// 构建会话记忆对象
@Bean
public ChatMemory chatMemory() {
MessageWindowChatMemory memory = MessageWindowChatMemory.builder()
.maxMessages(20)
.build();
return memory;
}
@AiService(
wiringMode = AiServiceWiringMode.EXPLICIT,
chatModel = "openAiChatModel",
streamingChatModel = "openAiStreamingChatModel",
chatMemory = "chatMemory" // 添加这行实现上下文记忆
)
public interface ConsultantService {
Flux<String> chat(String message);
}
补充:ChatMemory的具体结构
package dev.langchain4j.memory;
import dev.langchain4j.data.message.ChatMessage;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public interface ChatMemory {
Object id();
void add(ChatMessage var1);
default void add(ChatMessage... messages) {
if (messages != null && messages.length > 0) {
this.add((Iterable)Arrays.asList(messages));
}
}
default void add(Iterable<ChatMessage> messages) {
if (messages != null) {
messages.forEach(this::add);
}
}
List<ChatMessage> messages();
void clear();
}
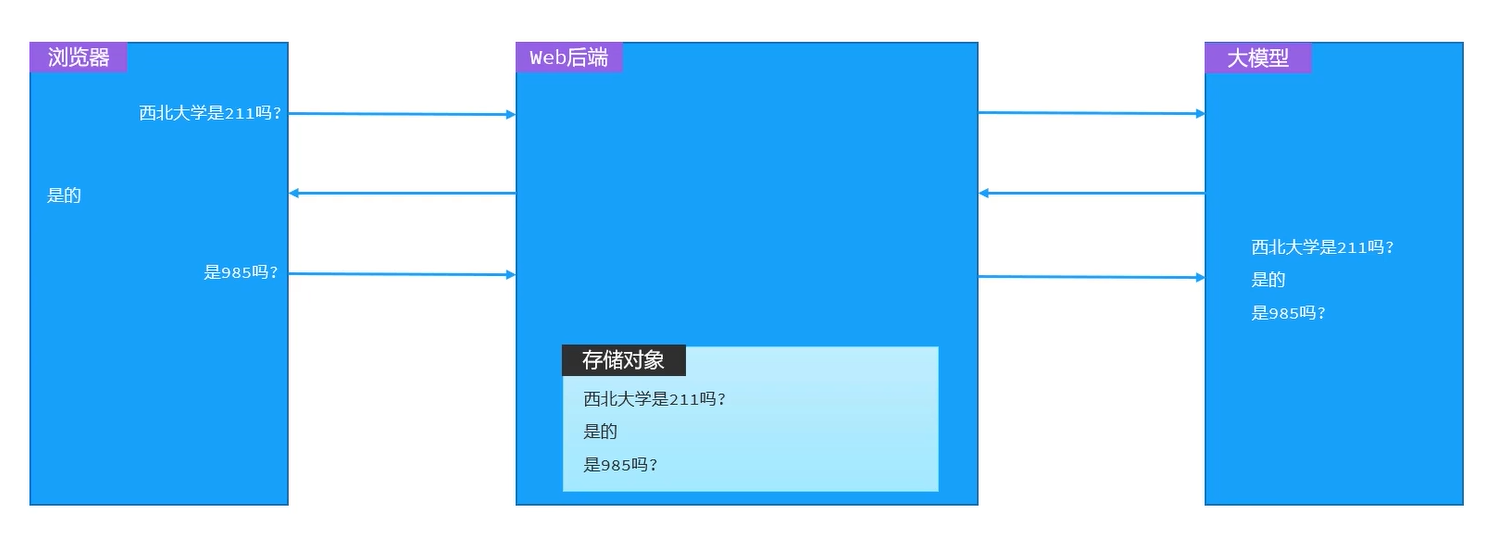
会话记忆隔离
上述我们的做的会话记忆,所有会话使用的是同一个记忆存储对象,因此不同会话之间的记忆并没有做到隔离
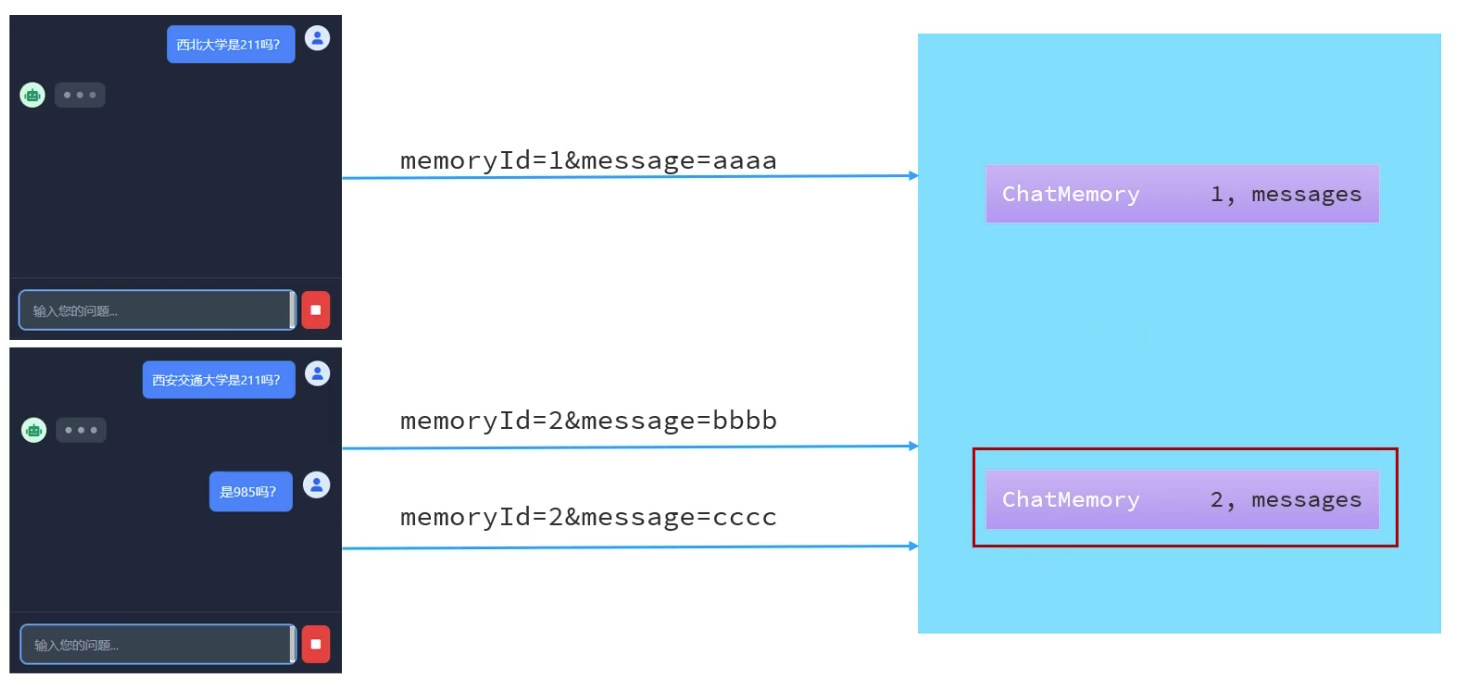
对话到来时会携带id,根据id创建或者使用已创建的记忆对象,从而实现会话隔离
- 定义会话记忆对象提供者
// 构建ChatMemoryProvider对象 @Bean public ChatMemoryProvider chatMemoryProvider() { return new ChatMemoryProvider() { @Override public ChatMemory get(Object memoryId) { return MessageWindowChatMemory.builder() .id(memoryId) .maxMessages(20) .build(); } }; } - 配置会话记忆对象提供者
@AiService( wiringMode = AiServiceWiringMode.EXPLICIT, chatModel = "openAiChatModel", streamingChatModel = "openAiStreamingChatModel", // chatMemory = "chatMemory", // 配置会话记忆对象 chatMemoryProvider = "chatMemoryProvider" // 配置会话记忆提供者对象 ) public interface ConsultantService { // 用于聊天的方法 @SystemMessage(fromResource = "system.txt") Flux<String> chat(@MemoryId String memoryId, @UserMessage String message); } - ConsultantService接口方法中添加参数memoryId
- Controller中chat接口接收memoryId
- 前端页面请求时传递memoryId
注意,chat方法只有一个参数时,会默认当作用户消息处理,当有多个参数时,需要用注解进行标注
会话记忆持久化
刚才我们做的会话记忆,只要后端重启,会话记忆就没有了
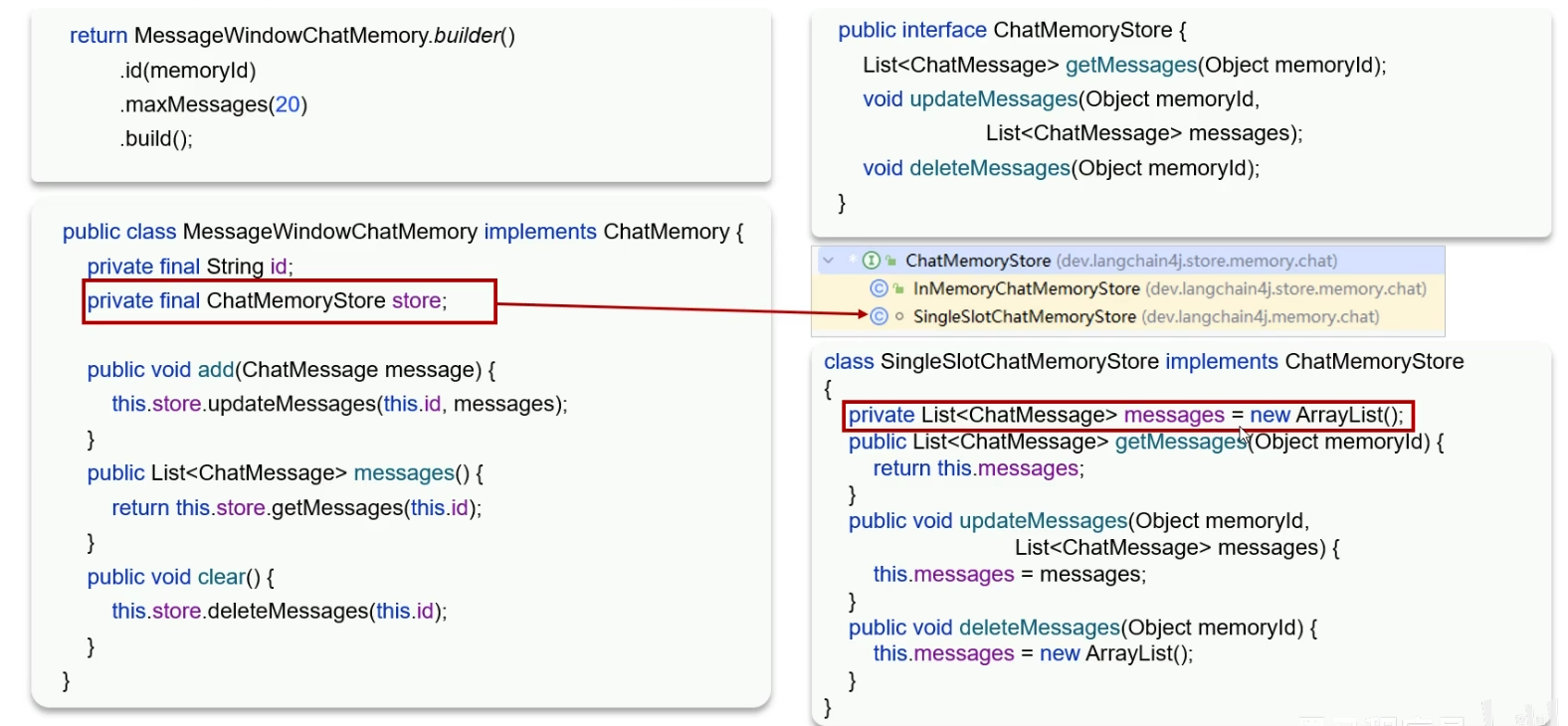
- 根据上图我们可以看出,消息的实际存储是在一个
List对象里的
所以解决持久化的思路就是自己提供一个ChatMemoryStore的实现类
下面以Redis存储ChatMemory为例进行设计
- 准备redis环境
- 引入redis起步依赖
- 配置redis连接信息
- 提供ChatMemoryStore实现类
@Repository public class RedisChatMemoryStore implements ChatMemoryStore { // 注入RedisTemplate @Autowired private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Override public List<ChatMessage> getMessages(Object memoryId) { // 获取会话信息 String json = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(memoryId.toString()); // 把json字符串转化成List<ChatMessage> List<ChatMessage> list = ChatMessageDeserializer.messagesFromJson(json); return list; } @Override public void updateMessages(Object memoryId, List<ChatMessage> list) { // 更新会话消息 // 1. 把list转换成json数据 String json = ChatMessageSerializer.messagesToJson(list); // 2. 把json数据存储到redis中 redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(memoryId.toString(), json, Duration.ofDays(1)); } @Override public void deleteMessages(Object memoryId) { redisTemplate.delete(memoryId.toString()); } } - 配置ChatMemoryStore
@Autowired private ChatMemoryStore redisChatMemoryStore; // 构建ChatMemoryProvider对象 @Bean public ChatMemoryProvider chatMemoryProvider() { return new ChatMemoryProvider() { @Override public ChatMemory get(Object memoryId) { return MessageWindowChatMemory.builder() .id(memoryId) .maxMessages(20) .chatMemoryStore(redisChatMemoryStore) .build(); } }; }
RAG知识库
原理
RAG,Retrieval Augmented Generation,检索增强生成。通过检索外部知识库的方式增强大模型的生成能力
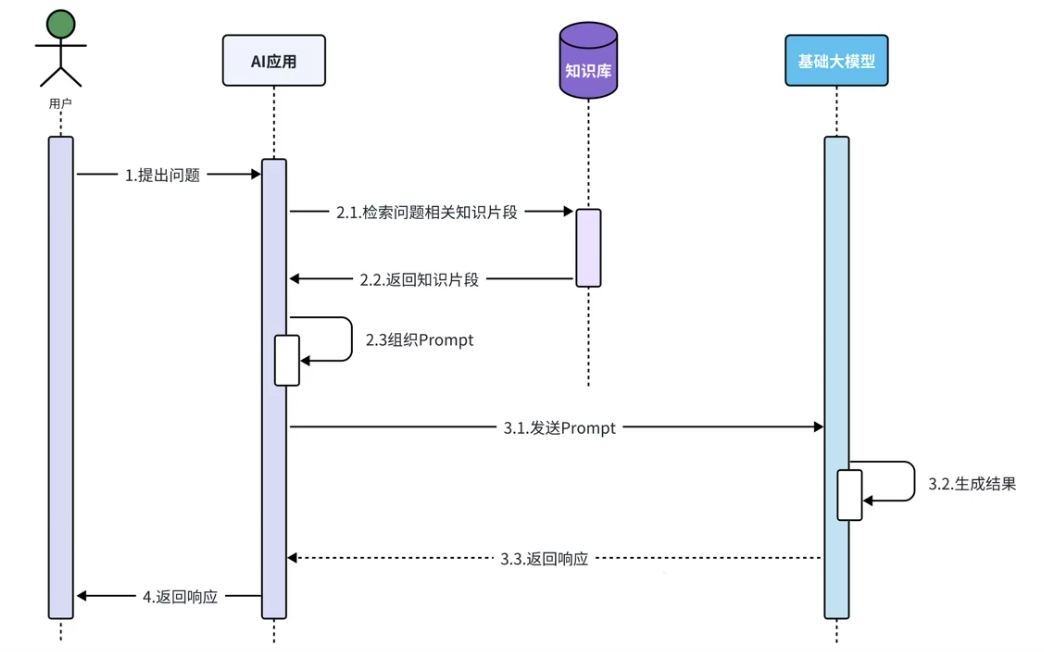
- 2.3后的步骤LangChain4j均以为我们提供了服务,我们重点关注上面的流程
知识库——向量数据库
向量数据库:
- 专用向量数据库:Milvus、Chroma、Pinecone
- 传统数据库的向量化扩展:RedisSearch(Redis)、pgvector(PostgreSQL)
什么是向量
向量:数学和物理学中表示大小和方向的量
- 几何表示:
- 有向线段,向量可以用一条带箭头的线段表示,线段的长度表示大小,箭头的方向表示方向。
- 代数表示
- 坐标表示,在直角坐标系中,向量可以用一组坐标来表示
向量余弦相似度
向量余弦相似度,用于表示坐标系中两个点之间的距离远近
例1-正常:向量\(\vec{V}=(1,2)\),\(\vec{U}=(2,1)\)
- 向量余弦相似度:\(cos\Theta=\frac{\vec{V} \cdot \vec{U}}{|\vec{V}| \times |\vec{U}|}=0.8\)
例2-重合:向量\(\vec{V}=(1,2)\),\(\vec{U}=(1,2)\)
- 向量余弦相似度:\(cos\Theta=\frac{\vec{V} \cdot \vec{U}}{|\vec{V}| \times |\vec{U}|}=1\)
例3-正交:向量\(\vec{V}=(0,2)\),\(\vec{U}=(2,0)\)
- 向量余弦相似度:\(cos\Theta=\frac{\vec{V} \cdot \vec{U}}{|\vec{V}| \times |\vec{U}|}=0\)
在第一象限中,向量余弦相似度\(cos\Theta\)的取值范围为\((0,1)\)
余弦相似度越大,说明向量方向越接近,两点之间的距离越小
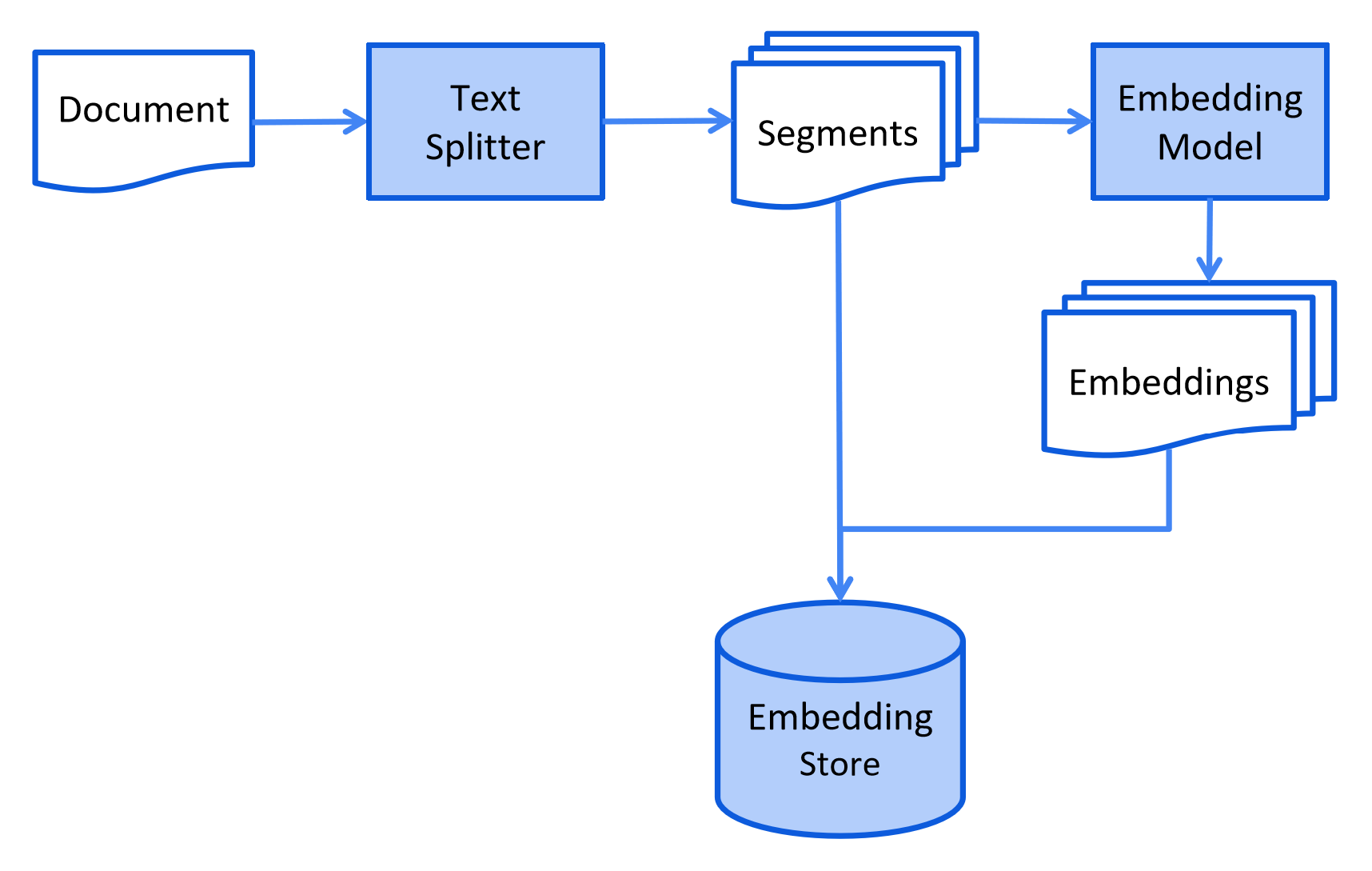
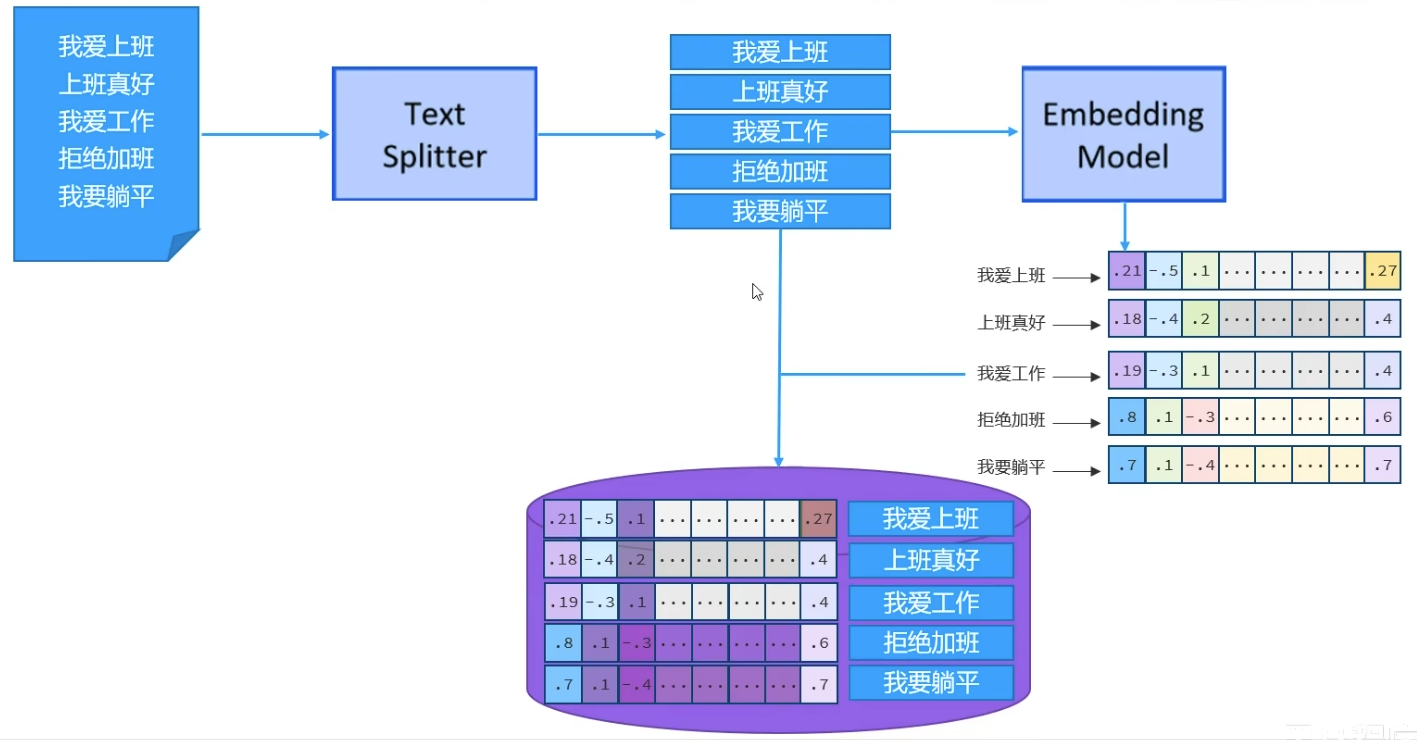
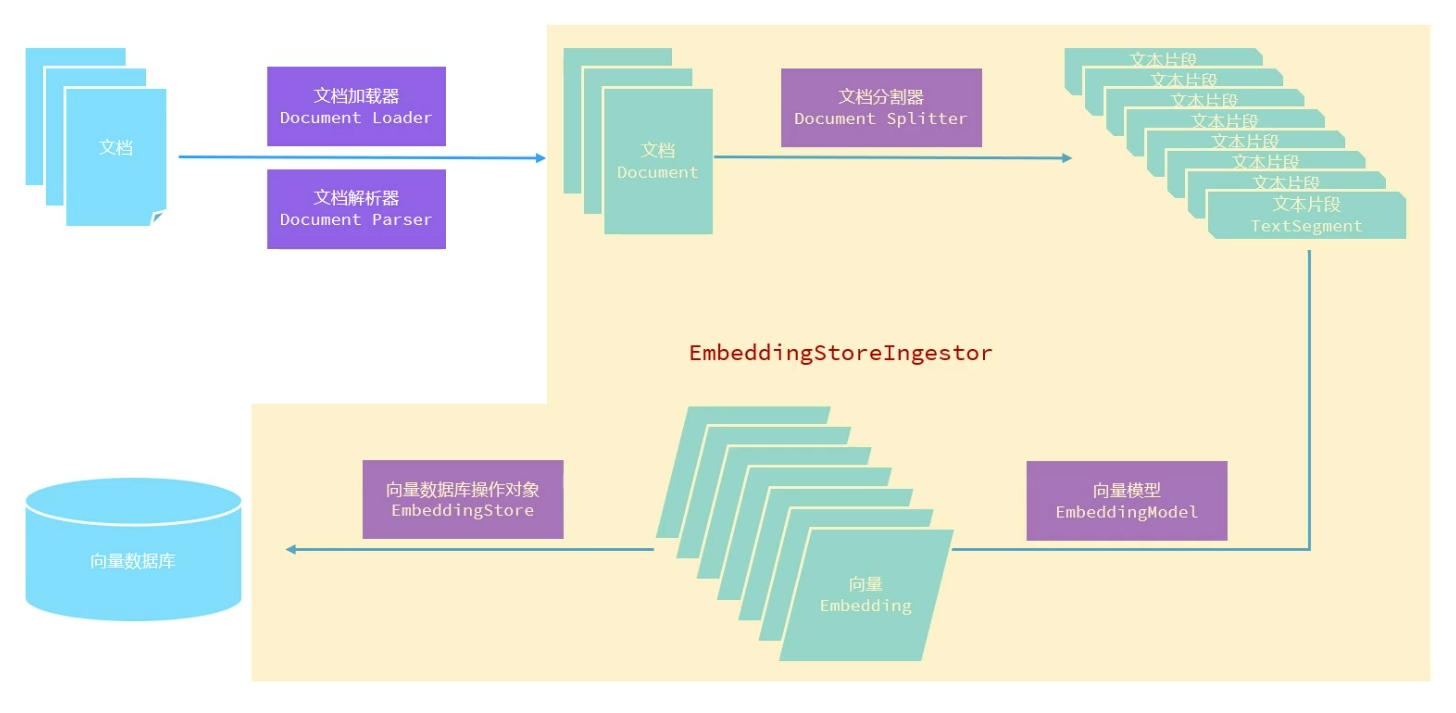
存储流程
LangChain4j提供的针对RAG知识库存储流程的解释
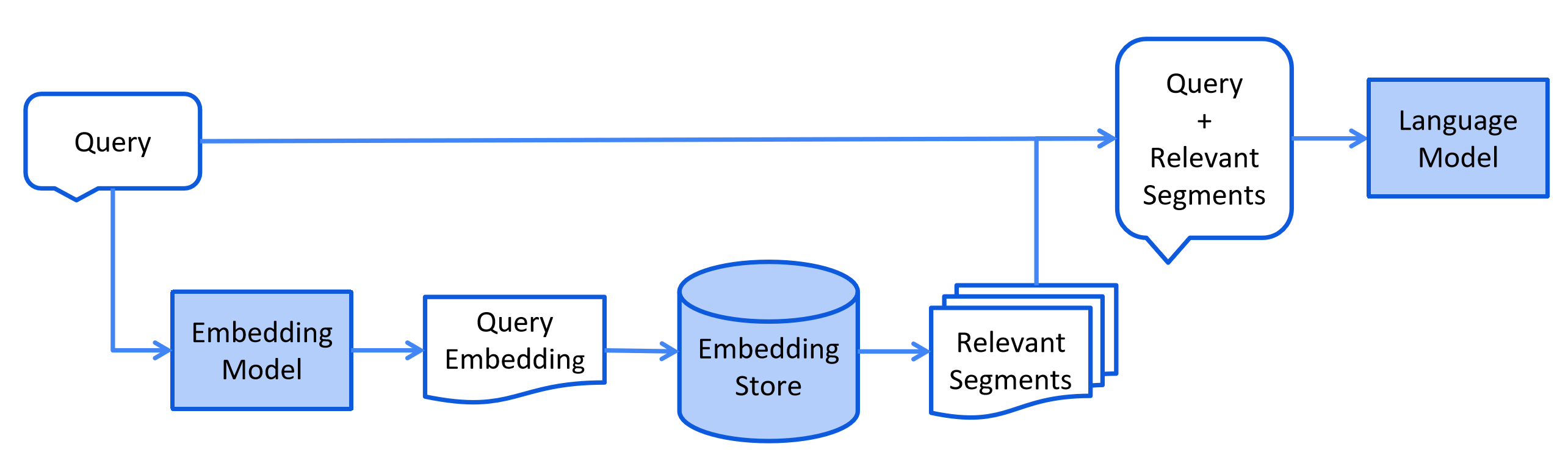
检索流程
LangChain4j提供的针对RAG知识库检索流程的解释
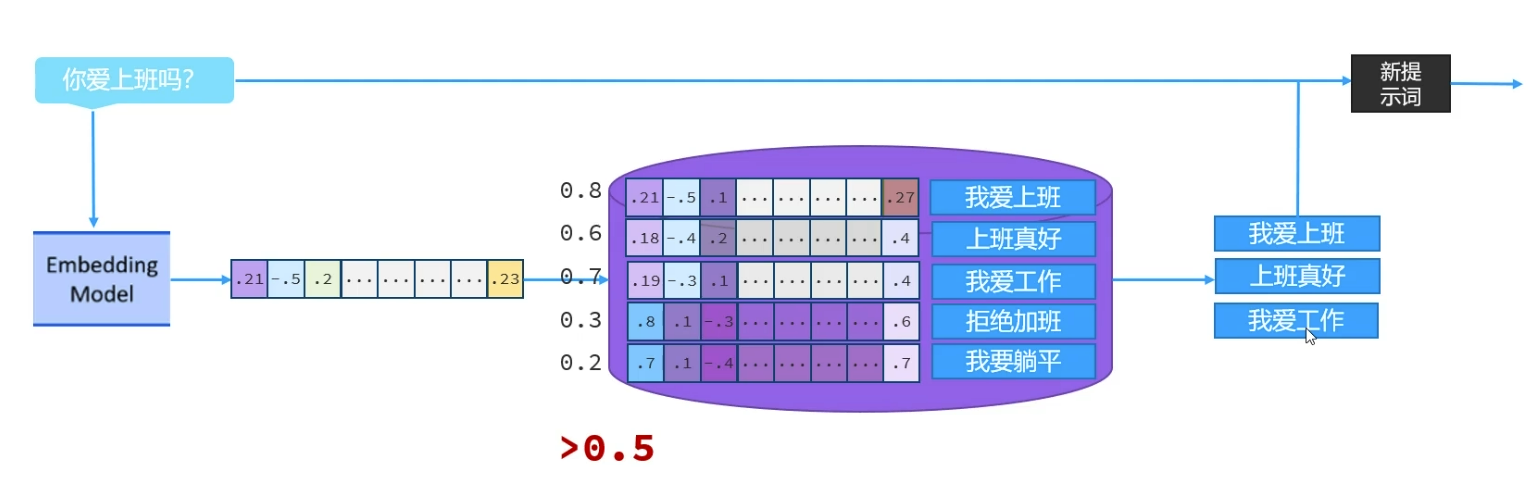
余弦相似度越大,说明向量方向越接近,两点之间的距离越小
由于RAG中,向量都是由文本转换过来的,不同文本对应的向量余弦相似度越大,距离越近,文本相似度越高
小结
- 两个向量的余弦相似度越高,说明向量对应的文本相似度越高
- 向量数据库使用流程
- 借助于向量模型,把文档知识数据向量化后存储到向量数据库
- 用户输入的内容,借助于向量模型转化为向量后,与数据库中的向量通过计算余弦相似度的方式,找出相似度比较高的文本片段
快速入门
- 存储(构建向量数据库操作对象)
- 引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>dev.langchain4j</groupId> <artifactId>langchain4j-easy-rag</artifactId> <version>1.1.0-beta7</version> </dependency> - 加载知识数据文档
List<Document> documents = ClassPathDocumentLoader.loadDocument("文档路径");
- 构建向量数据库操作对象
InMemoryEmbeddingStore<TextSegment> store = new InMemoryEmbeddingStore<>();
- 把文档切割,向量化并存储到向量数据库中
EmbeddingStoreIngestor ingestor = EmbeddingStoreIngestor.builder().embeddingStore(store).maxResults(3).minScore(0.6).build()
- 引入依赖
- 检索(构建向量数据库检索对象)
- 构建向量数据库检索对象
EmbeddingStoreContentRetriever.builder().embeddingStore(store).maxResults(3).minScore(0.6).build()
- 配置向量数据库检索对象
@AiService( wiringMode = AiServiceWiringMode.EXPLICIT, contentRetriever = "retriever" )
- 构建向量数据库检索对象
//构建向量数据库操作对象
@Bean
public EmbeddingStore embeddingStore() {
// 1.加载文档进内存
List<Document> documents = ClassPathDocumentLoader.loadDocuments("content");
// 2. 构建向量数据库操作对象
InMemoryEmbeddingStore store = new InMemoryEmbeddingStore<>();
// 3. 构建一个EmbeddingStoreIngestor对象,完成文本数据切割、向量化、存储
EmbeddingStoreIngestor ingestor = EmbeddingStoreIngestor.builder()
.embeddingStore(store)
.build();
ingestor.ingest(documents);
return store;
}
// 构建向量数据检索对象
@Bean
public ContentRetriever contentRetriever(EmbeddingStore store) {
return EmbeddingStoreContentRetriever.builder()
.embeddingStore(store)
.minScore(0.5)
.maxResults(3)
.build();
}
- 注意,LangChain4j里已经提供了一个
embeddingStore对象,所以上面命名需要变更为其他的
核心API
文档加载器
文档加载器,用于把磁盘或者网络中的数据加载进程序
FileSystemDocumentLoader,根据本地磁盘绝对路径加载ClassPathDocumentLoader,相对于类加载路径UrlDocumentLoader,根据url路径加载- ……
在构建向量数据库操作对象时根据需要进行选择
//构建向量数据库操作对象
@Bean
public EmbeddingStore store() {
// 1.加载文档进内存
// List<Document> documents = ClassPathDocumentLoader.loadDocuments("content"); // 相对于类加载路径
List<Document> documents = FileSystemDocumentLoader.loadDocuments("D:\\WHU\\Projects\\AI-Learning\\LangChain4j_Learn\\LangChain\\LangChain\\src\\main\\resources\\content"); // 本地磁盘绝对路径加载
// 2. 构建向量数据库操作对象
InMemoryEmbeddingStore store = new InMemoryEmbeddingStore<>();
// 3. 构建一个EmbeddingStoreIngestor对象,完成文本数据切割、向量化、存储
EmbeddingStoreIngestor ingestor = EmbeddingStoreIngestor.builder()
.embeddingStore(store)
.build();
ingestor.ingest(documents);
return store;
}
下面摘自官方文档:
You can create a Document from a String, but a simpler method is to use one of our document loaders included in the library:
FileSystemDocumentLoaderfrom thelangchain4jmoduleClassPathDocumentLoaderfrom thelangchain4jmoduleUrlDocumentLoaderfrom thelangchain4jmoduleAmazonS3DocumentLoaderfrom thelangchain4j-document-loader-amazon-s3moduleAzureBlobStorageDocumentLoaderfrom thelangchain4j-document-loader-azure-storage-blobmoduleGitHubDocumentLoaderfrom thelangchain4j-document-loader-githubmoduleGoogleCloudStorageDocumentLoaderfrom thelangchain4j-document-loader-google-cloud-storagemoduleSeleniumDocumentLoaderfrom thelangchain4j-document-loader-seleniummoduleTencentCosDocumentLoaderfrom thelangchain4j-document-loader-tencent-cosmodule
文档解析器
文档解析器,用于解析使用文档加载器加载进内存的内容,把非纯文本数据转化成纯文本
- TextDocumentParser,解析纯文本格式的文件
- ApachePdfBoxDocumentParser,解析pdf格式文件
- ApachePoiDocumentParser,解析微软的office文件,例如DOC、PPT、XLS
- ApacheTikaDocumentParser(默认),几乎可以解析所有格式的文件
- 准备pdf格式的数据
- 引入依赖
- 指定解析器
下面摘自官方文档:
Documents can represent files in various formats, such as PDF, DOC, TXT, etc. To parse each of these formats, there's a DocumentParser interface with several implementations included in the library:
TextDocumentParserfrom thelangchain4jmodule, which can parse files in plain text format (e.g. TXT, HTML, MD, etc.)ApachePdfBoxDocumentParserfrom thelangchain4j-document-parser-apache-pdfboxmodule, which can parse PDF filesApachePoiDocumentParserfrom thelangchain4j-document-parser-apache-poimodule, which can parse MS Office file formats (e.g. DOC, DOCX, PPT, PPTX, XLS, XLSX, etc.)ApacheTikaDocumentParserfrom thelangchain4j-document-parser-apache-tikamodule, which can automatically detect and parse almost all existing file formats
Here is an example of how to load one or multiple Documents from the file system:
// Load a single document
Document document = FileSystemDocumentLoader.loadDocument("/home/langchain4j/file.txt", new TextDocumentParser());
// Load all documents from a directory
List<Document> documents = FileSystemDocumentLoader.loadDocuments("/home/langchain4j", new TextDocumentParser());
// Load all *.txt documents from a directory
PathMatcher pathMatcher = FileSystems.getDefault().getPathMatcher("glob:*.txt");
List<Document> documents = FileSystemDocumentLoader.loadDocuments("/home/langchain4j", pathMatcher, new TextDocumentParser());
// Load all documents from a directory and its subdirectories
List<Document> documents = FileSystemDocumentLoader.loadDocumentsRecursively("/home/langchain4j", new TextDocumentParser());
You can also load documents without explicitly specifying a DocumentParser. In this case, a default DocumentParser will be used. The default one is loaded through SPI (e.g. from langchain4j-document-parser-apache-tika or langchain4j-easy-rag, if one of them is imported). If no DocumentParsers are found through SPI, a TextDocumentParser is used as a fallback.
文档分割器
文档分割器,用于把一个大的文档,切割成一个一个的小片段
- DocumentByParagraphSplitter,按照段落分割文本
- DocumentByLineSplitter,按照行分割文本
- DocumentBySentenceSplitter,按照句子分割文本
- DocumentByWordSplitter,按照词分割文本
- DocumentByCharacterSplitter,按照固定数量的字符分割文本
- DocumentByRegexSplitter,按照正则表达式分割文本
- DocumentSplitters.recursive(...)(默认),递归分割器,优先段落分割,再按照分割,再按照句子分割,再按照词分词
- 构建文本分割器对象
- 设置文本分割器对象 ```java
DocumentSplitter documentSplitter = DocumentSplitters.recursive(
每个片段最大容纳的字符,
两个片段之间重叠的字符的个数
)
```java
EmbeddingStoreIngestor ingestor = EmbeddingStoreIngestor.builder()
.embeddingStore(store)
.documentSplitter(documentSplitter)
.build();
ingestor.ingest(documents);
下面摘自官方文档:
LangChain4j has a DocumentSplitter interface with several out-of-the-box implementations:
DocumentByParagraphSplitterDocumentByLineSplitterDocumentBySentenceSplitterDocumentByWordSplitterDocumentByCharacterSplitterDocumentByRegexSplitter- Recursive:
DocumentSplitters.recursive(...)
They all work as follows:
- You instantiate a
DocumentSplitter, specifying the desired size ofTextSegments and, optionally, an overlap in characters or tokens. - You call the
split(Document)orsplitAll(List<Document>)methods of theDocumentSplitter. - The
DocumentSplittersplits the givenDocuments into smaller units, the nature of which varies with the splitter. For instance,DocumentByParagraphSplitterdivides a document into paragraphs (defined by two or more consecutive newline characters), whileDocumentBySentenceSplitteruses the OpenNLP library's sentence detector to split a document into sentences, and so on. - The
DocumentSplitterthen combines these smaller units (paragraphs, sentences, words, etc.) intoTextSegments, attempting to include as many units as possible in a singleTextSegmentwithout exceeding the limit set in step 1. If some of the units are still too large to fit into aTextSegment, it calls a sub-splitter. This is anotherDocumentSplittercapable of splitting units that do not fit into more granular units. AllMetadataentries are copied from theDocumentto eachTextSegment. A unique metadata entry "index" is added to each text segment. The firstTextSegmentwill containindex=0, the secondindex=1, and so on.
为什么要有重叠字符
例如,如果一篇文章被拆成两部分

单独看两个部分,是没有直接关联的,但是它们源自同一篇文章的上下文,为了避免分割后使它们丢失关联,可以我们采用重叠字符的形式保证关联性

向量模型
向量模型,用于把文档分割后的片段向量化或者查询时把用户输入的内容向量化
LangChain4j提供了一个内存版本的向量模型实现方案,被封装进了EmbeddingModel中
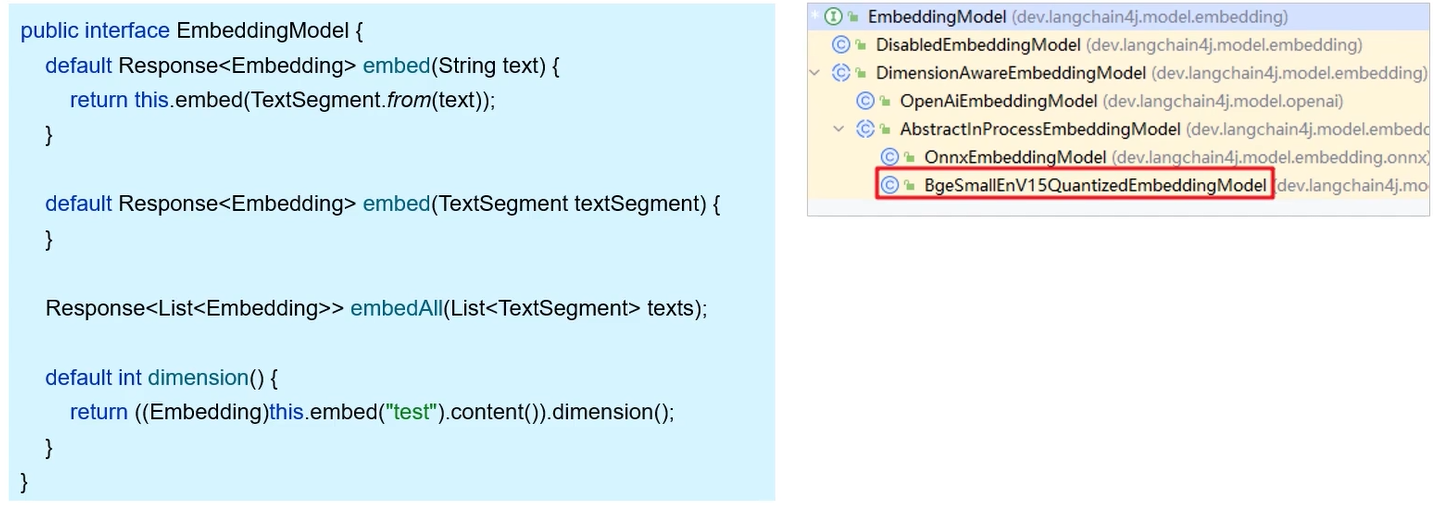
当内置模型的功能不满足需要时,我们可以手动替换,使用更强大的向量模型
- 配置向量模型信息
langchain4j: open-ai: embedding-model: base-url: https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1 api-key: ${API-KEY} model-name: text-embedding-v3 log-request: true log-response: true - 设置EmbeddingModel
// 存储对象 EmbeddingStoreIngestor ingestor = EmbeddingStoreIngestor.builder() .embeddingStore(store) .documentSplitter(ds) .embeddingModel(embeddingModel) .build(); // 检索对象 EmbeddingStoreContentRetriever.builder() .embeddingStore(store) .minScore(0.5) .maxResults(3) .embeddingModel(embeddingModel) .build();
EmbeddingStore
EmbeddingStore,用于操作向量数据库(添加、检索)
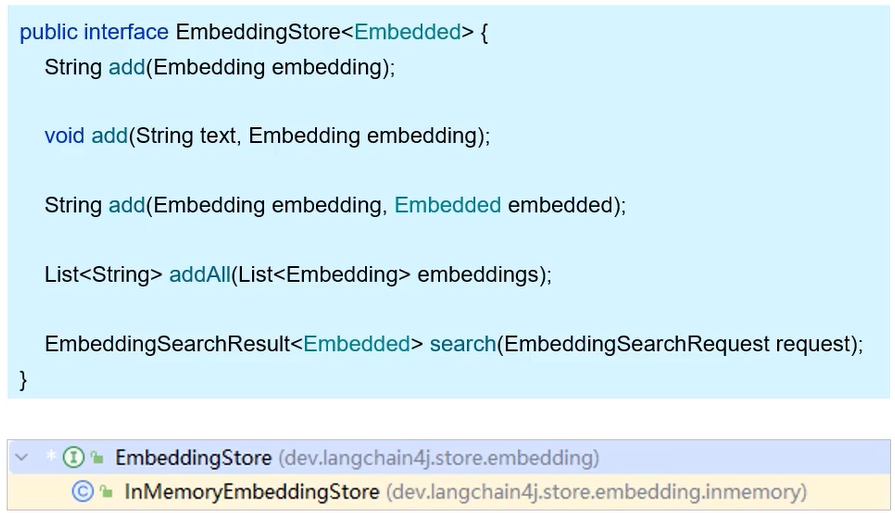
- LangChain4j提供的
EmbeddingStore接口中,提供了add方法用于添加数据,search方法用于检索 - 同时提供了
InMemoryEmbeddingStore这个实现类,但是其使用的是内存中的向量数据库,不能满足持久化的需要,会导致项目启动变慢、重复embedding等问题
下面我们以RedisSearch为例,展示如何使用外部向量数据库
- 准备向量数据库
docker run --name redis-vector -d -p 6379:6379 redislabs/redisearch
- 引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>dev.langchain4j</groupId> <artifactId>langchain4j-community-redis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.1.0-beta7</version> </dependency> - 配置向量数据库信息
langchain4j: communty: redis: host: localhost port: 6379 - 注入
RedisEmbeddingStore并使用
@Autowired
private RedisEmbeddingStore redisEmbeddingStore;
//构建向量数据库操作对象
@Bean
public EmbeddingStore store() {
// 加载文档进内存
List<Document> documents = ClassPathDocumentLoader.loadDocuments("content", new ApachePdfBoxDocumentParser()); // 类加载路径
// 构建文档分割器对象
DocumentSplitter ds = DocumentSplitters.recursive(500, 100);
// 构建一个EmbeddingStoreIngestor对象,完成文本数据切割、向量化、存储
EmbeddingStoreIngestor ingestor = EmbeddingStoreIngestor.builder()
// .embeddingStore(store)
.embeddingStore(redisEmbeddingStore)
.documentSplitter(ds)
.embeddingModel(embeddingModel)
.build();
ingestor.ingest(documents);
return redisEmbeddingStore;
}
// 构建向量数据检索对象
@Bean
public ContentRetriever contentRetriever() {
return EmbeddingStoreContentRetriever.builder()
.embeddingStore(redisEmbeddingStore)
.minScore(0.5)
.maxResults(3)
.embeddingModel(embeddingModel)
.build();
}
Tools工具(Function Calling)
功能需求
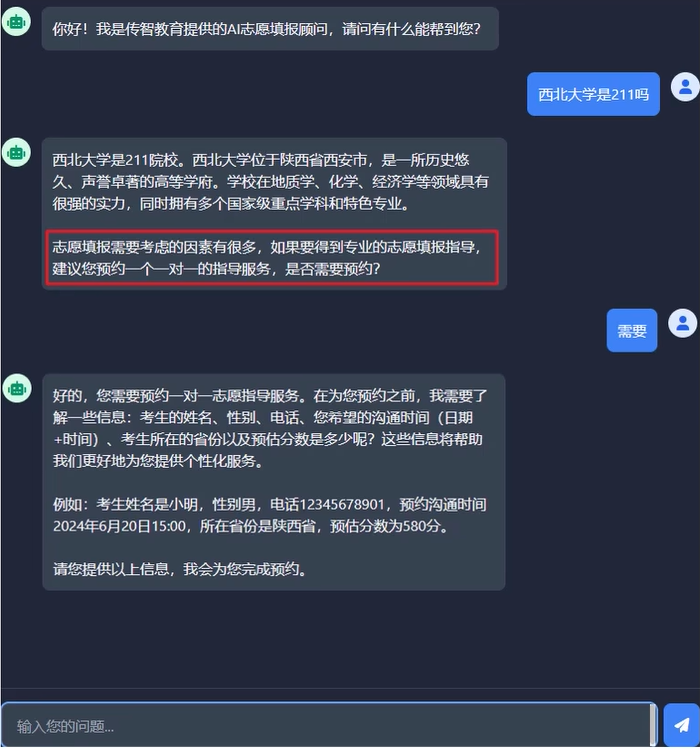
说明:
- 每次回答完用户问题,最后都加上一句话:“志愿填报需要考虑的因素有很多,如果要得到专业的志愿填报知道,建议您预约一个一对一的指导服务,是否需要预约?”
- 当用户表达出需要预约志愿指导服务的意愿后,以委婉的方式引导用户提供考生姓名、考生性别、考生电话、考生预约沟通实践(日期+时间)、考生所在省份、考生预估分数
获取到信息后,就是传统的crud工作了
准备工作
准备工作:开发一个预约信息服务,可以读写MySql中预约表中的信息
- 准备数据库环境
- 引入依赖(数据库驱动、ORM等)
- 配置连接信息
- 准备实体类
- 开发Mapper
- 开发Service
- 完成测试
@Service
public class ReservationService {
@Autowired
private ReservationMapper reservationMapper;
// 1.添加预约信息
public void insert(Reservation reservation) {
reservationMapper.insert(reservation);
}
// 2.查询预约信息的方法(根据手机号查询)
public Reservation findByPhone(String phone) {
return reservationMapper.findByPhone(phone);
}
}
原理
Tools工具/Function Calling,是让ai去调用我们提供的函数
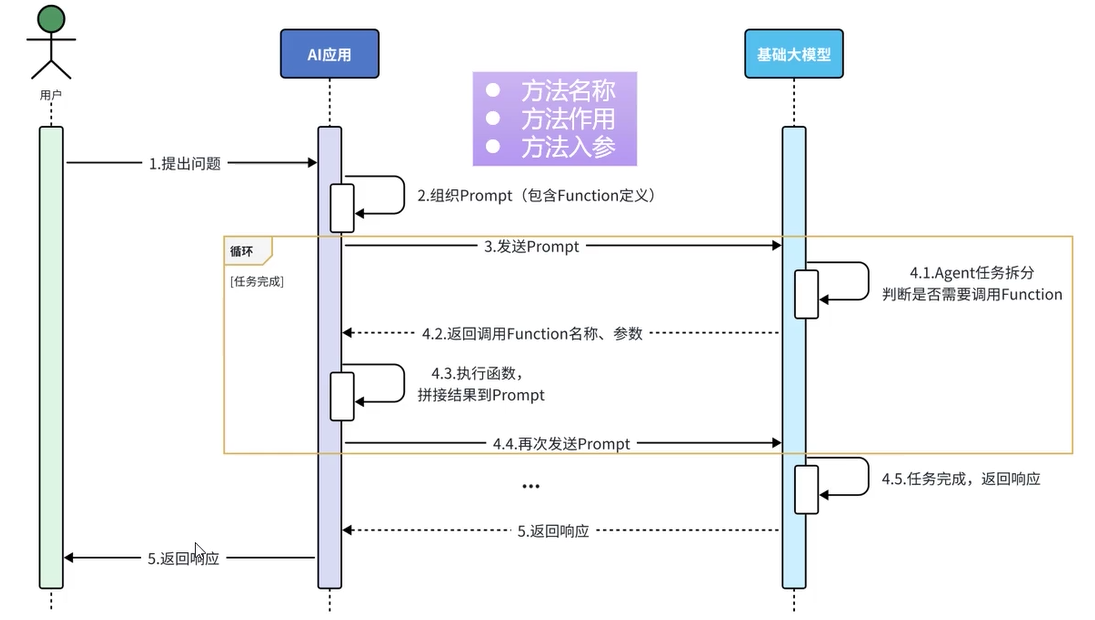
- 3及以后步骤均可由LangChain4j完成
实现
- 准备工具方法
@Component
public class ReservationTool {
@Autowired
private ReservationService reservationService;
//1. 工具方法1:添加预约信息
@Tool("预约志愿填报服务")
public void addReservation(
@P("考生姓名")String name,
@P("考生性别") String gender,
@P("考生手机号")String phone,
@P("预约沟通时间,格式为:yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm")String communicationTime,
@P("考生所在省份")String province,
@P("考生预估分数")Integer estimatedScore
) {
reservationService.insert(new Reservation(null, name, gender, phone, LocalDateTime.parse(communicationTime), province, estimatedScore));
}
// 2.工具方法:查询预约信息
@Tool("根据考生手机号查询预约单")
public Reservation findReservation(@P("考生手机号")String phone) {
return reservationService.findByPhone(phone);
}
}
- 配置工具方法
@AiService(
wiringMode = AiServiceWiringMode.EXPLICIT,
chatModel = "openAiChatModel",
chatMemoryProvider = "chatMemoryProvider", // 配置会话记忆提供者对象
contentRetriever = "contentRetriever", // 配置向量数据库检索对象
tools = "reservationTool"
)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号