CompletableFuture 使用
Future的局限性,它没法直接对多个任务进行链式、组合等处理,而CompletableFuture是对Future的扩展和增强。CompletableFuture实现了Future接口,并在此基础上进行了丰富的扩展,增加了异步回调、流式处理、多个Future组合处理的能力,完美弥补了Future的局限性,同时CompletableFuture实现了对任务编排的能力。借助这项能力,可以轻松地组织不同任务的运行顺序、规则以及方式。 而在以往,虽然通过CountDownLatch等工具类也可以实现任务的编排,但需要复杂的逻辑处理,不仅耗费精力且难以维护。
使用CompletableFuture场景
执行比较耗时的操作时,尤其是那些依赖一个或多个远程服务的操作,使用异步任务可以改善程序的性能,加快程序的响应速度
使用CompletableFuture类,它提供了异常管理的机制,让你有机会抛出、管理异步任务执行种发生的异常
如果这些异步任务之间相互独立,或者他们之间的的某一些的结果是另一些的输入,你可以讲这些异步任务构造或合并成一个
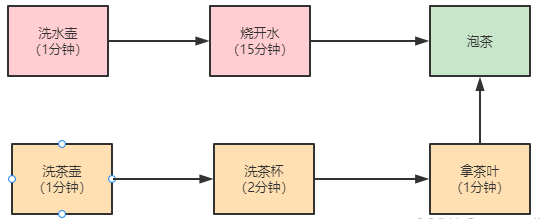
@Test public void FutureTest() throws Exception { // 创建任务T2的FutureTask FutureTask<String> ft2 = new FutureTask<>(new T2Task()); // 创建任务T1的FutureTask FutureTask<String> ft1 = new FutureTask<>(new T1Task(ft2)); // 线程T1执行任务ft1 Thread T1 = new Thread(ft1); T1.start(); // 线程T2执行任务ft2 Thread T2 = new Thread(ft2); T2.start(); // 等待线程T1执行结果 System.out.println(ft1.get()); } // T1Task需要执行的任务: // 洗水壶、烧开水、泡茶 class T1Task implements Callable<String> { FutureTask<String> ft2; // T1任务需要T2任务的FutureTask T1Task(FutureTask<String> ft2) { this.ft2 = ft2; } @Override public String call() throws Exception { System.out.println("T1:洗水壶..."); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); System.out.println("T1:洗水壶 完成..."); System.out.println("T1:烧开水..."); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(15); System.out.println("T1:烧开水 完成..."); // 获取T2线程的茶叶 String tf = ft2.get(); System.out.println("T1:泡茶..." + tf); return "上茶:" + tf; } } // T2Task需要执行的任务: // 洗茶壶、洗茶杯、拿茶叶 class T2Task implements Callable<String> { @Override public String call() throws Exception { System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶..."); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶 完成..."); System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯..."); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯 完成..."); System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶..."); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶 拿好 龙井..."); return "龙井"; } }
CompletableFuture
@Test public void CompletableFutureTest() { //任务1:洗水壶->烧开水 CompletableFuture<Void> f1 = CompletableFuture .runAsync(() -> { try { System.out.println("T1:洗水壶..."); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); System.out.println("T1:洗水壶 完成..."); System.out.println("T1:烧开水..."); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(15); System.out.println("T1:烧开水 完成..."); } catch (Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } }); //任务2:洗茶壶->洗茶杯->拿茶叶 CompletableFuture<String> f2 = CompletableFuture .supplyAsync(() -> { try { System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶..."); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶 完成..."); System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯..."); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯 完成..."); System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶..."); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶 拿好 龙井..."); return "龙井"; } catch (Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); return ""; } }); //任务3:任务1和任务2完成后执行:泡茶 CompletableFuture<String> f3 = f1.thenCombine(f2, (p, tf) -> { System.out.println("T1:泡茶..." + tf); return "上茶:" + tf; }); //等待任务3执行结果 //join()和get()方法都是用来获取CompletableFuture异步之后的返回值。 // join()方法抛出的是uncheck异常(即未经检查的异常),不会强制开发者抛出。 // get()方法抛出的是经过检查的异常,ExecutionException, InterruptedException 需要用户手动处理(抛出或者 try catch) System.out.println(f3.join()); // }
依赖关系
thenApply():把前面任务的执行结果,交给后面的Function
thenCompose():用来连接两个有依赖关系的任务,结果由第二个任务返回
and集合关系
thenCombine():合并任务,有返回值
thenAccepetBoth():两个任务执行完成后,将结果交给thenAccepetBoth处理,无返回值
runAfterBoth():两个任务都执行完成后,执行下一步操作(Runnable类型任务)
or聚合关系
applyToEither():两个任务哪个执行的快,就使用哪一个结果,有返回值
acceptEither():两个任务哪个执行的快,就消费哪一个结果,无返回值
runAfterEither():任意一个任务执行完成,进行下一步操作(Runnable类型任务)
并行执行
allOf():当所有给定的 CompletableFuture 完成时,返回一个新的 CompletableFuture
anyOf():当任何一个给定的CompletablFuture完成时,返回一个新的CompletableFuture
结果处理
whenComplete:当任务完成时,将使用结果(或 null)和此阶段的异常(或 null如果没有)执行给定操作
exceptionally:返回一个新的CompletableFuture,当前面的CompletableFuture完成时,它也完成,当它异常完成时,给定函数的异常触发这个CompletableFuture的完成
通常的线程池接口类ExecutorService,其中execute方法的返回值是void,即无法获取异步任务的执行状态,3个重载的submit方法的返回值是Future,可以据此获取任务执行的状态和结果,示例如下:
@Test public void FutureSubmitTest() throws Exception { // 创建异步执行任务: ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); Future<Double> cf = executorService.submit(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } if(false){ throw new RuntimeException("test"); }else{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return 1.2; } }); System.out.println("main thread start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); //等待子任务执行完成,如果已完成则直接返回结果 //如果执行任务异常,则get方法会把之前捕获的异常重新抛出 System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get()); System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }
supplyAsync / runAsync
supplyAsync表示创建带返回值的异步任务的,相当于ExecutorService submit(Callable<T> task) 方法,runAsync表示创建无返回值的异步任务,相当于ExecutorService submit(Runnable task)方法,这两方法的效果跟submit是一样的,测试用例如下:
/** * 表示创建带返回值的异步任务的,相当于ExecutorService submit(Callable<T> task) 方法 * @throws Exception */ @Test public void supplyAsyncTest() throws Exception { // 创建异步执行任务,有返回值 CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } if(false){ throw new RuntimeException("test"); }else{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return 1.2; } }); System.out.println("main thread start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); //等待子任务执行完成 System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get()); System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); } /** * 创建无返回值的异步任务,相当于ExecutorService submit(Runnable task)方法 * @throws Exception */ @Test public void runAsyncTest() throws Exception { // 创建异步执行任务,无返回值 CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } if(false){ throw new RuntimeException("test"); }else{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); } }); System.out.println("main thread start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); //等待子任务执行完成 System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get()); System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }
这两方法各有一个重载版本,可以指定执行异步任务的Executor实现,如果不指定,默认使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),如果机器是单核的,则默认使用ThreadPerTaskExecutor,该类是一个内部类,每次执行execute都会创建一个新线程。测试用例如下:
@Test public void supplyAsyncForkJoinPoolTest() throws Exception { ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(); // 创建异步执行任务: CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " start,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } if (false) { throw new RuntimeException("test"); } else { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " exit,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); return 1.2; } }, pool); System.out.println("main thread start,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); //等待子任务执行完成 System.out.println("run result->" + cf.get()); System.out.println("main thread exit,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); } @Test public void runAsyncExecutorTest() throws Exception { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); // 创建异步执行任务: CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " start,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } if (false) { throw new RuntimeException("test"); } else { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " exit,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); } }, executorService); System.out.println("main thread start,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); //等待子任务执行完成 System.out.println("run result->" + cf.get()); System.out.println("main thread exit,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); }
thenApply / thenApplyAsync
thenApply 表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作,即回调方法,会将该任务的执行结果即方法返回值作为入参传递到回调方法中
@Test public void thenApplyTest() throws Exception { ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(); // 创建异步执行任务: CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " start job1,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " exit job1,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); return 1.2; }, pool); //cf关联的异步任务的返回值作为方法入参,传入到thenApply的方法中 //thenApply这里实际创建了一个新的CompletableFuture实例 CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = cf.thenApply((result) -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " start job2,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " exit job2,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); return "test:" + result; }); System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); //等待子任务执行完成 System.out.println("run result->" + cf.get()); System.out.println("main thread start cf2.get(),time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); System.out.println("run result->" + cf2.get()); System.out.println("main thread exit,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis()); }
thenAccept / thenRun
thenAccept 同 thenApply 接收上一个任务的返回值作为参数,但是无返回值;thenRun 的方法没有入参,也买有返回值
@Test public void thenAcceptTest() throws Exception { ForkJoinPool pool=new ForkJoinPool(); // 创建异步执行任务: CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return 1.2; },pool); //cf关联的异步任务的返回值作为方法入参,传入到thenApply的方法中 CompletableFuture cf2=cf.thenApply((result)->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return "test:"+result; }).thenAccept((result)-> { //接收上一个任务的执行结果作为入参,但是没有返回值 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(result); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }).thenRun(()->{ //无入参,也没有返回值 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println("thenRun do something"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }); System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); //等待子任务执行完成 System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get()); System.out.println("main thread start cf2.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); //cf2 等待最后一个thenRun执行完成 System.out.println("run result->"+cf2.get()); System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }
exceptionally
exceptionally方法指定某个任务执行异常时执行的回调方法,会将抛出异常作为参数传递到回调方法中,如果该任务正常执行则会exceptionally方法返回的CompletionStage的result就是该任务正常执行的结果
@Test public void exceptionally() throws Exception { ForkJoinPool pool=new ForkJoinPool(); // 创建异步执行任务: CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } if(true){ throw new RuntimeException("test"); }else{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return 1.2; } },pool); //cf执行异常时,将抛出的异常作为入参传递给回调方法 CompletableFuture<Double> cf2= cf.exceptionally((param)->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println("error stack trace->"); param.printStackTrace(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return -1.1; }); //cf正常执行时执行的逻辑,如果执行异常则不调用此逻辑 CompletableFuture cf3=cf.thenAccept((param)->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println("param->"+param); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }); System.out.println("main thread start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); //等待子任务执行完成,此处无论是job2和job3都可以实现job2退出,主线程才退出,如果是cf,则主线程不会等待job2执行完成自动退出了 //cf2.get时,没有异常,但是依然有返回值,就是cf的返回值 System.out.println("run result->"+cf2.get()); System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }
whenComplete
whenComplete是当某个任务执行完成后执行的回调方法,会将执行结果或者执行期间抛出的异常传递给回调方法,如果是正常执行则异常为null,回调方法对应的CompletableFuture的result和该任务一致,如果该任务正常执行,则get方法返回执行结果,如果是执行异常,则get方法抛出异常
@Test public void whenComplete() throws Exception { // 创建异步执行任务: CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } if(false){ throw new RuntimeException("test"); }else{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return 1.2; } }); //cf执行完成后会将执行结果和执行过程中抛出的异常传入回调方法,如果是正常执行的则传入的异常为null CompletableFuture<Double> cf2=cf.whenComplete((a,b)->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } if(b!=null){ System.out.println("error stack trace->"); b.printStackTrace(); }else{ System.out.println("run succ,result->"+a); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }); //等待子任务执行完成 System.out.println("main thread start wait,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); //如果cf是正常执行的,cf2.get的结果就是cf执行的结果 //如果cf是执行异常,则cf2.get会抛出异常 System.out.println("run result->"+cf2.get()); System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }
handle
跟whenComplete基本一致,区别在于handle的回调方法有返回值,且handle方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是回调方法的执行结果或者回调方法执行期间抛出的异常,与原始CompletableFuture的result无关了
@Test public void handle() throws Exception { // 创建异步执行任务: CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } if(true){ throw new RuntimeException("test"); }else{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return 1.2; } }); //cf执行完成后会将执行结果和执行过程中抛出的异常传入回调方法,如果是正常执行的则传入的异常为null CompletableFuture<String> cf2=cf.handle((a,b)->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } if(b!=null){ System.out.println("error stack trace->"); b.printStackTrace(); }else{ System.out.println("run succ,result->"+a); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); if(b!=null){ return "run error"; }else{ return "run succ"; } }); //等待子任务执行完成 System.out.println("main thread start wait,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); //get的结果是cf2的返回值,跟cf没关系了 System.out.println("run result->"+cf2.get()); System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }
thenCombine / thenAcceptBoth / runAfterBoth
这三个方法都是将两个CompletableFuture组合起来,只有这两个都正常执行完了才会执行某个任务,区别在于,thenCombine会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参传递到指定方法中,且该方法有返回值;thenAcceptBoth同样将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,但是无返回值;runAfterBoth没有入参,也没有返回值。注意两个任务中只要有一个执行异常,则将该异常信息作为指定任务的执行结果。
@Test public void thenCombine() throws Exception { // 创建异步执行任务: CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return 1.2; }); CompletableFuture<Double> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(1500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return 3.2; }); //cf和cf2的异步任务都执行完成后,会将其执行结果作为方法入参传递给cf3,且有返回值 CompletableFuture<Double> cf3=cf.thenCombine(cf2,(a,b)->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); System.out.println("job3 param a->"+a+",b->"+b); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return a+b; }); //cf和cf2的异步任务都执行完成后,会将其执行结果作为方法入参传递给cf3,无返回值 CompletableFuture cf4=cf.thenAcceptBoth(cf2,(a,b)->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); System.out.println("job4 param a->"+a+",b->"+b); try { Thread.sleep(1500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }); //cf4和cf3都执行完成后,执行cf5,无入参,无返回值 CompletableFuture cf5=cf4.runAfterBoth(cf3,()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job5,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println("cf5 do something"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job5,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }); System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); //等待子任务执行完成 System.out.println("cf run result->"+cf.get()); System.out.println("main thread start cf5.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); System.out.println("cf5 run result->"+cf5.get()); System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }
applyToEither / acceptEither / runAfterEither
这三个方法都是将两个CompletableFuture组合起来,只要其中一个执行完了就会执行某个任务(job3 的参数为先执行结果),其区别在于
applyToEither会将已经执行完成的任务的执行结果作为方法入参,并有返回值;
acceptEither同样将已经执行完成的任务的执行结果作为方法入参,但是没有返回值;
runAfterEither没有方法入参,也没有返回值。注意两个任务中只要有一个执行异常,则将该异常信息作为指定任务的执行结果
@Test public void applyToEither() throws Exception { // 创建异步执行任务: CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return 1.2; }); CompletableFuture<Double> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(1500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return 3.2; }); //cf和cf2的异步任务都执行完成后,会将其执行结果作为方法入参传递给cf3,且有返回值 CompletableFuture<Double> cf3=cf.applyToEither(cf2,(result)->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); System.out.println("job3 param result->"+result); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return result; }); //cf和cf2的异步任务都执行完成后,会将其执行结果作为方法入参传递给cf3,无返回值 CompletableFuture cf4=cf.acceptEither(cf2,(result)->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); System.out.println("job4 param result->"+result); try { Thread.sleep(1500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }); //cf4和cf3都执行完成后,执行cf5,无入参,无返回值 CompletableFuture cf5=cf4.runAfterEither(cf3,()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job5,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println("cf5 do something"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job5,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }); System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); //等待子任务执行完成 System.out.println("cf run result->"+cf.get()); System.out.println("main thread start cf5.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); System.out.println("cf5 run result->"+cf5.get()); System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }
thenCompose
thenCompose方法会在某个任务执行完成后,将该任务的执行结果作为方法入参然后执行指定的方法,该方法会返回一个新的CompletableFuture实例,如果该CompletableFuture实例的result不为null,则返回一个基于该result的新的CompletableFuture实例;如果该CompletableFuture实例为null,则,然后执行这个新任务
@Test public void thenCompose() throws Exception { // 创建异步执行任务: CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return 1.2; }); CompletableFuture<String> cf2= cf.thenCompose((param)->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return "job3 test"; }); }); System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); //等待子任务执行完成 System.out.println("cf run result->"+cf.get()); System.out.println("main thread start cf2.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); System.out.println("cf2 run result->"+cf2.get()); System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }
allOf / anyOf
allOf返回的CompletableFuture是多个任务都执行完成后才会执行,只有有一个任务执行异常,则返回的CompletableFuture执行get方法时会抛出异常,如果都是正常执行,则get返回null。
@Test public void test11() throws Exception { // 创建异步执行任务: CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return 1.2; }); CompletableFuture<Double> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(1500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return 3.2; }); CompletableFuture<Double> cf3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(1300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } // throw new RuntimeException("test"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); return 2.2; }); //allof等待所有任务执行完成才执行cf4,如果有一个任务异常终止,则cf4.get时会抛出异常,都是正常执行,cf4.get返回null //anyOf是只有一个任务执行完成,无论是正常执行或者执行异常,都会执行cf4,cf4.get的结果就是已执行完成的任务的执行结果 CompletableFuture cf4=CompletableFuture.allOf(cf,cf2,cf3).whenComplete((a,b)->{ if(b!=null){ System.out.println("error stack trace->"); b.printStackTrace(); }else{ System.out.println("run succ,result->"+a); } }); System.out.println("main thread start cf4.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); //等待子任务执行完成 System.out.println("cf4 run result->"+cf4.get()); System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis()); }
https://blog.csdn.net/sermonlizhi/article/details/123356877
https://blog.csdn.net/sermonlizhi/article/details/123356877
本文来自博客园,作者:VipSoft 转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/vipsoft/p/16539793.html

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号