SMU2025寒假训练周报1
经过一周的训练感觉暴力搜索在很多方面很受用,但是自己容易理不清,还需加强
一.pta天梯赛1
1. 用扑克牌计算24点
原题链接:7-11 用扑克牌计算24点 - 2025寒假天梯赛训练1
只需用两个括号就可以涵盖所有情况
即
((a op b) op c) op d
(a op (b op c)) op d
a op ((b op c) op d)
a op (b op (c op d))
(a op b) op (c op d)
穷举这五种情况即可
查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define PII pair<int,int>
char op[5]= {'#','+','-','*','/',};
double cal(double x,double y,int op)
{
switch(op)
{
case 1:
return x+y;
case 2:
return x-y;
case 3:
return x*y;
case 4:
return x/y;
}
}
double cal_m1(double i,double j,double k,double t,int op1,int op2,int op3)
{
double r1,r2,r3;
r1 = cal(i,j,op1);
r2 = cal(r1,k,op2);
r3 = cal(r2,t,op3);
return r3;
}
double cal_m2(double i,double j,double k,double t,int op1,int op2,int op3)
{
double r1,r2,r3 ;
r1 = cal(i,j,op1);
r2 = cal(k,t,op3);
r3 = cal(r1,r2,op2);
return r3;
}
double cal_m3(double i,double j,double k,double t,int op1,int op2,int op3)
{
double r1,r2,r3;
r1 = cal(j,k,op2);
r2 = cal(i,r1,op1);
r3 = cal(r2,t,op3);
return r3;
}
double cal_m4(double i,double j,double k,double t,int op1,int op2,int op3)
{
double r1,r2,r3 ;
r1 = cal(k,t,op3);
r2 = cal(j,r1,op2);
r3 = cal(i,r2,op1);
return r3;
}
double cal_m5(double i,double j,double k,double t,int op1,int op2,int op3)
{
double r1,r2,r3;
r1 = cal(j,k,op2);
r2 = cal(r1,t,op3);
r3 = cal(i,r2,op1);
return r3;
}
int get_24(int i,int j,int k,int t)
{
for(int op1 = 1; op1 <= 4; op1++)
{
for(int op2 = 1; op2 <= 4; op2++)
{
for(int op3 = 1; op3 <= 4; op3++)
{
if(cal_m1(i,j,k,t,op1,op2,op3) == 24)
{
printf("((%d%c%d)%c%d)%c%d\n",i,op[op1],j,op[op2],k,op[op3],t);
return 1;
}
if(cal_m2(i,j,k,t,op1,op2,op3) == 24)
{
printf("(%d%c%d)%c(%d%c%d)\n",i,op[op1],j,op[op2],k,op[op3],t);
return 1;
}
if(cal_m3(i,j,k,t,op1,op2,op3) == 24)
{
printf("(%d%c(%d%c%d))%c%d\n",i,op[op1],j,op[op2],k,op[op3],t);
return 1;
}
if(cal_m4(i,j,k,t,op1,op2,op3) == 24)
{
printf("%d%c(%d%c(%d%c%d))\n",i,op[op1],j,op[op2],k,op[op3],t);
return 1;
}
if(cal_m5(i,j,k,t,op1,op2,op3) == 24)
{
printf("%d%c((%d%c%d)%c%d)\n",i,op[op1],j,op[op2],k,op[op3],t);
return 1;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int a[4];
int t1, t2, t3, t4;
int flag;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
if(j==i)
continue;
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
if(i==k||j==k)
continue;
for(int t = 0; t < 4; t++)
{
if(t==i||t==j||t==k)
continue;
t1 = a[i], t2= a[j], t3= a[k], t4= a[t];
flag = get_24(t1,t2,t3,t4);
if(flag ==1)
break;
}
if(flag == 1)
break;
}
if(flag == 1)
break;
}
if(flag == 1)
break;
}
if(flag == 0)
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}2.玩转二叉树
原题链接:7-12 玩转二叉树 - 2025寒假天梯赛训练1
模拟手算过程更简单,直接归并按前序根左右,中序左根右来递归,并且递归过程中记录每一个根结点,由于层序遍历的性质,左右孩子分别为2*x,2*x+1,所以递归是左右孩子反过来就可以实现左右孩子反转
查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> qian,zhong,l(100000,-1);
void ceng(int root,int start,int end,int x)
{
if(start>end)return;
int i;
for(i=start;i<=end;i++)
{
if(zhong[i]==qian[root])break;
}
l[x]=qian[root];
ceng(root+1,start,i-1,2*x+1);
ceng(root+i-start+1,i+1,end,2*x);
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
zhong.resize(n+1);
qian.resize(n+1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>zhong[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>qian[i];
ceng(1,1,n,1);
int f=0;
for(int i=1;;i++){
if(f==n) break;
if(l[i]!=-1){
if(i==1) cout<<l[i];
else cout<<" "<<l[i];
f++;
}
}
return 0;
}3.六度空间
原题链接:7-13 六度空间 - 2025寒假天梯赛训练1(补题)
这个题直接暴搜也可以骗27分,正解是最短路算法,每个点统计到其他点的距离并统计比例,dijkstra和spfa都能过
查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
int a[1010][1010];
signed main(){
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<=n;j++)
{
if(i==j)a[i][j]=0;
else a[i][j]=400000;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y;
cin>>x>>y;
a[x][y]=1;
a[y][x]=1;
}
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]>a[i][k]+a[k][j])
a[i][j]=a[i][k]+a[k][j];
}
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int sum=0;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(a[j][i]<=6)sum++;
}
cout<<i<<":"<<" ";
printf("%0.2lf",sum*1.0/n*100);
cout<<"%"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}二.codeforce个人
1.D. Minimum Euler Cycle
这个题开始暴力写的并没有想到规律,但他是有向完全图的欧拉回路,其实只需要多列几种情况就很清晰了。
例如n=5时,121314152324253435451,规律就是如此
查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define PII pair<int,int>
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int T; scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--) {
ll n, l, r; scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &n, &l, &r);
ll p = 1;
for(p = 1; p <= n - 1; p++) {
if(p * (n * 2 - p - 1ll) > l) break;
}
p -= 2;
ll st = (p * ((n * 2) - p - 1));
p = p + 1;
for(ll i = p; i < n; i++) {
for(ll j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
st++;
if(st >= l && st <= r) printf("%lld ", i);
st++;
if(st >= l && st <= r) printf("%lld ", j);
if(st > r) break;
}
}
if(st < r) printf("1");
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}三.牛客训练营1
1.井然有序之窗
原题链接:H-井然有序之窗_2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营1
这个题以前做过类似的,当时秒了,但是现在很遗憾,其实就是把每个区间从小到大从前到后铺开在全集上,然后从最小的数开始遍历赋值,用过的的就排除掉,这样能最优化结果
查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define PII pair<int,int>
vector<int>c(1000000,-1);
int sign[1000000];
struct node{
int m,l,r;
}a[1000000];
bool cmp(node x,node y)
{
if(x.r==y.r)return x.l<y.l;
return x.r<y.r;
}
signed main() {
int n;
cin >> n;set<int>s;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
s.insert(i);
cin>>a[i].l>>a[i].r;
a[i].m=i;
}
sort(a+1,a+1+n,cmp);
int kk=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
auto x=s.lower_bound(a[i].l);
if(*x>a[i].r||*x<a[i].l)
{
kk=1;
break;
}
c[a[i].m]=*x;
s.erase(*x);
}
if(kk)cout<<-1;
else
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cout<<c[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}2.数值膨胀之美
原题链接:M-数值膨胀之美_2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营1
赛时过了但是因为数据太弱才过,其实有逻辑不通的地方。正解就是将最小值翻倍。如果想要扩大区间,我们则选择“包含最小值和次小值”的最小区间,以此类推,逐渐扩大自己区间并更新最小极差
查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
pair<int,int>a[202020];
int b[202020];
signed main(){
int n,i;
cin>>n;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>a[i].first,a[i].second=i;
b[i]=a[i].first;
}
a[n].first=2e9;
sort(a,a+n);
int l=a[0].second,r=a[0].second;
int ma=max(a[0].first*2,a[n-1].first);
int res=ma-min(a[0].first*2,a[1].first);
for(i=1;i<n;i++){
while(a[i].second<l){
l--;
ma=max(ma,b[l]*2);
}
while(a[i].second>r){
r++;
ma=max(ma,b[r]*2);
}
res=min(res,ma-min(a[0].first*2,a[i+1].first));
}
cout<<res;
}四.牛客训练营2
1.一起画很大的圆
原题链接:H-一起画很大的圆!_2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营2
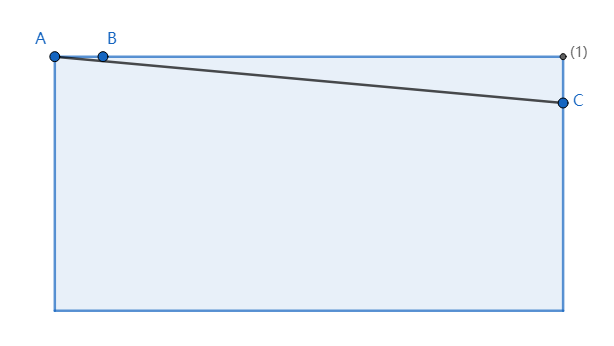
如图,最大化圆应该我们应当使得斜边尽可能的大,同时斜边所对的角尽可能的接近 0度 或 180度,,这里注意b应该在长边上。
查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define PII pair<int,int>
vector<int>v[30];
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int a,b,c,d;
cin>>a>>b>>c>>d;
if(d-c>b-a)
{
cout<<a<<" "<<c+1<<endl;
cout<<a<<" "<<c<<endl;
cout<<a+1<<" "<<d<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<a<<" "<<d-1<<endl;
cout<<b-1<<" "<<d<<endl;
cout<<b<<" "<<d<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}2.字符串外串
字符串和x-y呈现正相关,只需在字符串里填充x-y的字母就可以,如果x=y或者x-y>26则没有合适的字福串填入就不成立。
例如16 4那么就可以循环填入12种不同的字母abcdefghijklabcdef即可
查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define PII pair<int,int>
vector<int>v[30];
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int x,y;
cin>>x>>y;
if(x==y||x-y>26)cout<<"NO"<<endl;
else
{
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
int k=x-y;
for(int i=1;i<=x;i++)
{
cout<<(char)('a'+i%k);
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号