ConcurrentHashMap
Hashtable
1、早期java类库提供的哈希表的实现
2、线程安全:涉及到修改Hashtable的方法,使用synchronized修饰
3、串行化的方式运行,性能较差
问题:如何优化Hashtable?
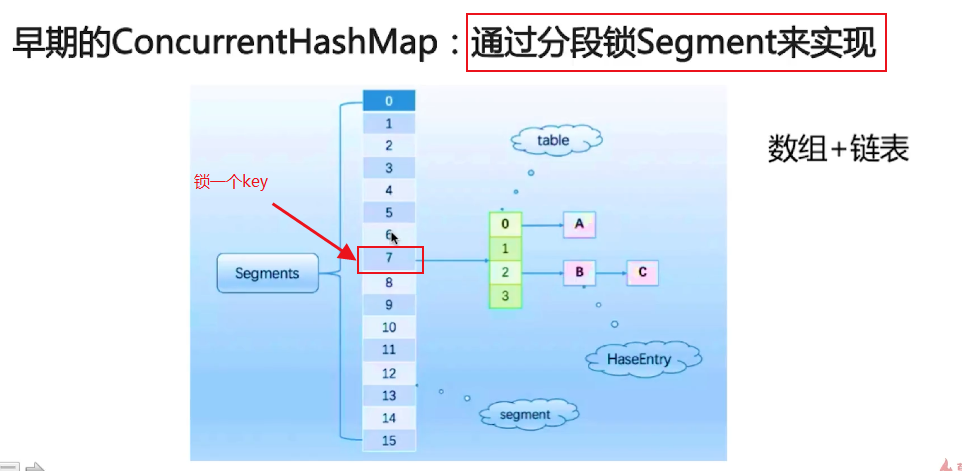
----> 1、通过锁细粒度化,将整锁拆解成多个锁进行优化

final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
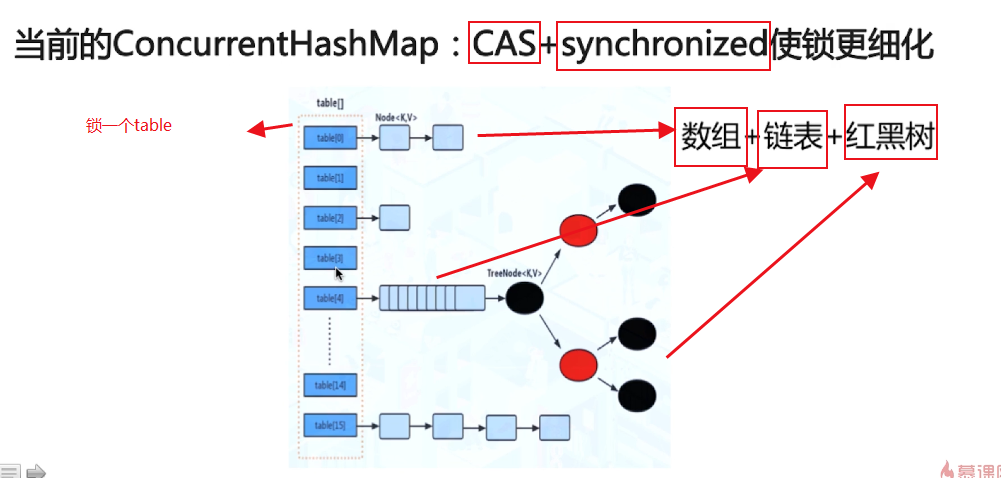
总结:
比起Segment,锁拆得更细
1、首先使用无锁操作CAS插入头节点,失败则循环重试
2、若头节点已存在,则尝试获取头节点的同步锁,再进行操作
问题:HashMap,Hashtable,conccurentHashMap的区别是什么?
---》
1、HashMap 是线程不安全的,数据结构是 数组+链表+红黑树
2、Hashtable 是线程安全的,锁住整个HashTable对象,数组+链表,在高并发的情况下,效率不高
3、conccurentHashMap ,是线程安全的,数组+链表+红黑树,用了CAS+同步锁,对hashTable的优化,将锁细粒度到table的程度来提高并发性能
4、HashMap的key\value均可为null,而其他的两个类不支持


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号