Soil Erosion
Introduction
Soil erosion is a phenomenon in which water and soil are lost at the same time due to the influence of natural or man-made factors; rainwater that cannot be absorbed locally, flows downhill and washes away the soil.
The main causes are large ground slope, inappropriate land use, destruction of ground vegetation, irrational farming techniques, loose soil, deforestation, overgrazing and so on.
The harm of soil erosion is mainly manifested in: soil tillage layer is eroded, destruction, so that the land fertility is increasingly depleted; silt rivers, channels, reservoirs, reduce the effectiveness of water conservancy projects, and even lead to drought and flooding, seriously affecting industrial and agricultural production; soil erosion of mountainous areas of agricultural production and downstream of the river to bring a serious threat.
In 2021, China added 62,000 square kilometers of new erosion control area throughout the year .
In 2022, China added 63,000 square kilometers of new soil erosion control area throughout the year.

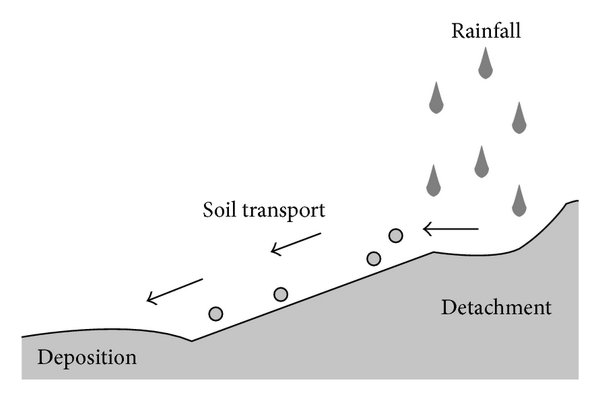
Causes
1. Natural factors.
There are four main aspects: climate, rainfall, ground material composition and vegetation.
① Topography: gully development, steep slopes; the steeper the slope of the ground, the faster the flow rate of surface runoff, the stronger the erosive power of soil scouring. The longer the slope, the more surface runoff is pooled, and the stronger the scouring force.
Rainfall. Generate soil erosion of rainfall, generally more intense rainstorms, rainfall intensity exceeds the intensity of soil infiltration will produce surface (hyperinfiltration) runoff, resulting in erosion of the surface of the scouring.
③ Ground material composition.
④ Vegetation. Forest and grass vegetation of a certain degree of closure has the effect of protecting the soil from erosion. The higher the degree of depression, the stronger the soil and water conservation.
2. Human factors.
Man's unreasonable use of land, the destruction of ground vegetation and stable terrain, resulting in serious soil erosion.
① destruction of vegetation.
② unreasonable farming system.
③Mining.
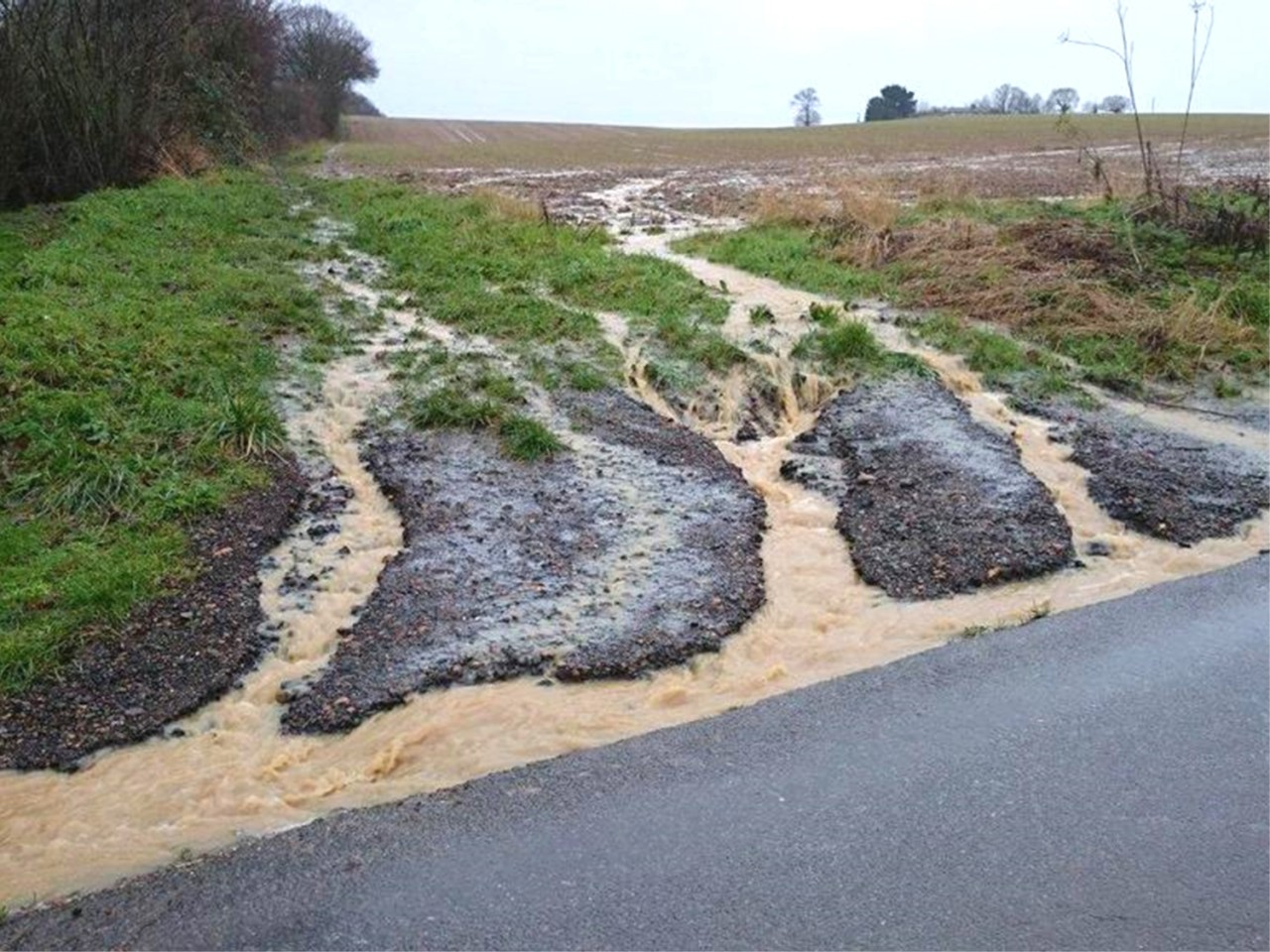


Consequences
Severe soil erosion has resulted in a reduction in the area of cultivated land, a decline in soil fertility, a decrease in crop yields, and a prominent contradiction between people and land. In order to survive, local farmers have had to reclaim large quantities of sloping land, planting a wide variety of crops for a meager income, forming a vicious circle of "the poorer the more they reclaim, the more they reclaim the poorer they get", which has worsened the ecological environment, constrained economic development and exacerbated poverty. In the national "87" poverty alleviation program, there are 126 poor counties in the Loess Plateau region, accounting for 21.3% of the total number of poor counties in the country, with a poverty-stricken population of 23 million people, accounting for 28.8% of the national poverty-stricken population. After years of poverty alleviation, there are still nearly 10 million poor people, which is one of the regions in China where the poor population is concentrated. Severe soil erosion has also caused the region to suffer from transportation inconvenience and difficulties in drinking water for people and animals, seriously restricting the sustainable development of the regional economy and society.
Soil erosion is very harmful, mainly in the following aspects:
1.Decrease or even loss of land productivity
2.siltation of rivers, lakes, reservoirs
3.pollution of water quality affects the ecological balance
Solutions
Comprehensive governance
Principle: Adjust the land-use structure and combine governance with development.
1. Compressing agricultural land, focusing on the construction of Sichuan land, loess land, dam land, and gently sloping terraces, fully tapping water resources, adopting modern agricultural technology measures, improving land productivity, and gradually building basic farmland with drought and flood-proofing, and high and stable yields (basic premise).
2. Expand the area of forest and grass plantation;
3.Improve the vegetation of natural pasture, overloaded and overgrazing places should appropriately compress the number of livestock, improve the quality of livestock, and implement rotational sealing and rotational grazing;
4.Reclaiming and backfilling.
Practice: Comprehensive management of small watersheds
Focus: maintain soil and water, develop and utilize soil and water resources, and establish an organic and efficient agricultural, forestry and animal husbandry production system.
Approach: preserve loess, protect slopes and fix ditches.
Mode: engineering measures (building dams and reservoirs, leveling land, building basic farmland, pumping and diverting water for irrigation).
Biological measures
Agricultural technical measures (deep ploughing and soil reformation, scientific fertilizer application, selection and breeding of good seeds, mulching, crop rotation and replanting).



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号